Sending-or-Not-Sending Twin-Field Quantum Key Distribution with Light Source Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
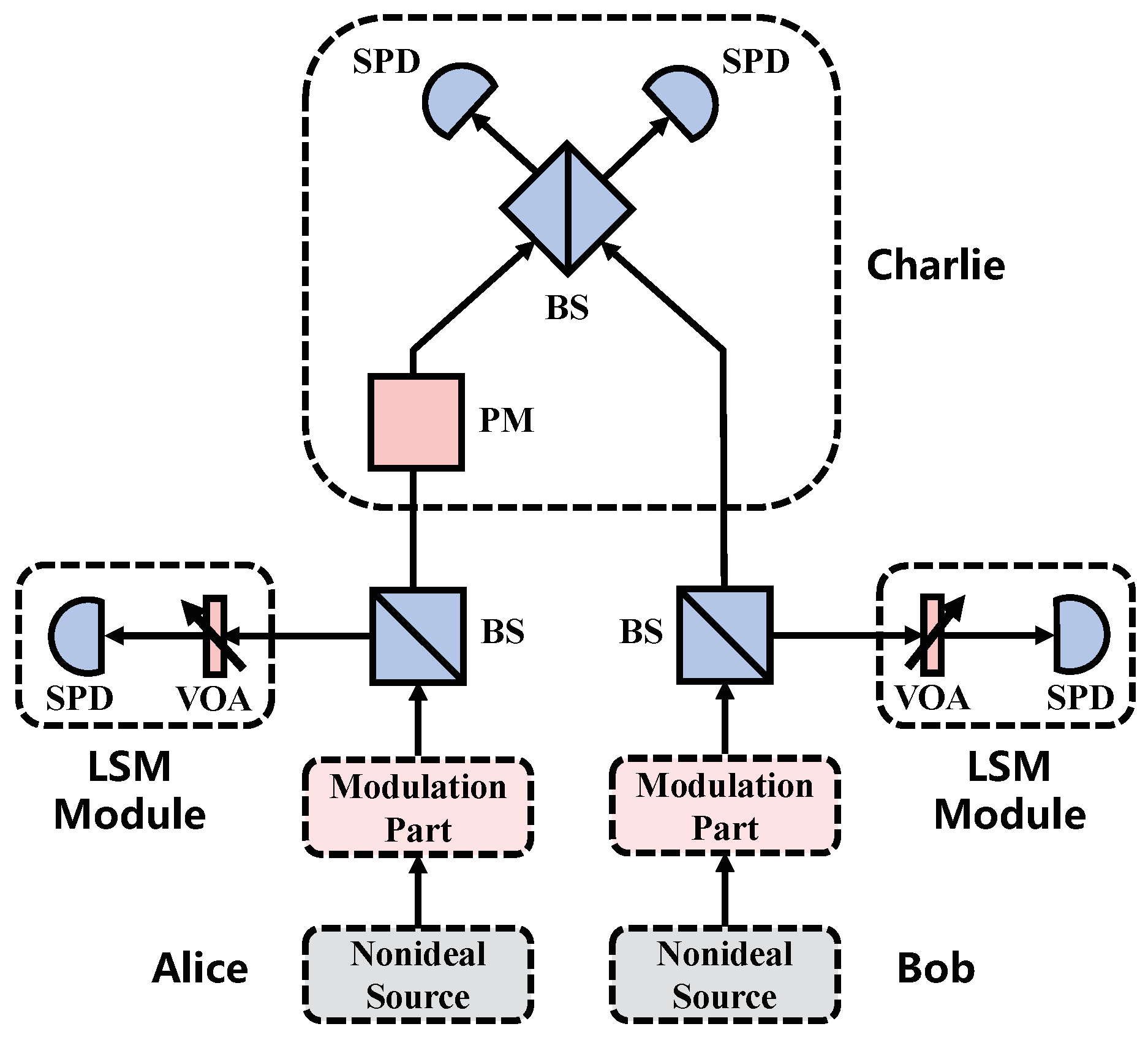
2. SNS Protocol with LSM
2.1. Security Analysis under UPC
Secret Key Rate
2.2. Parameters Estimation with LSM
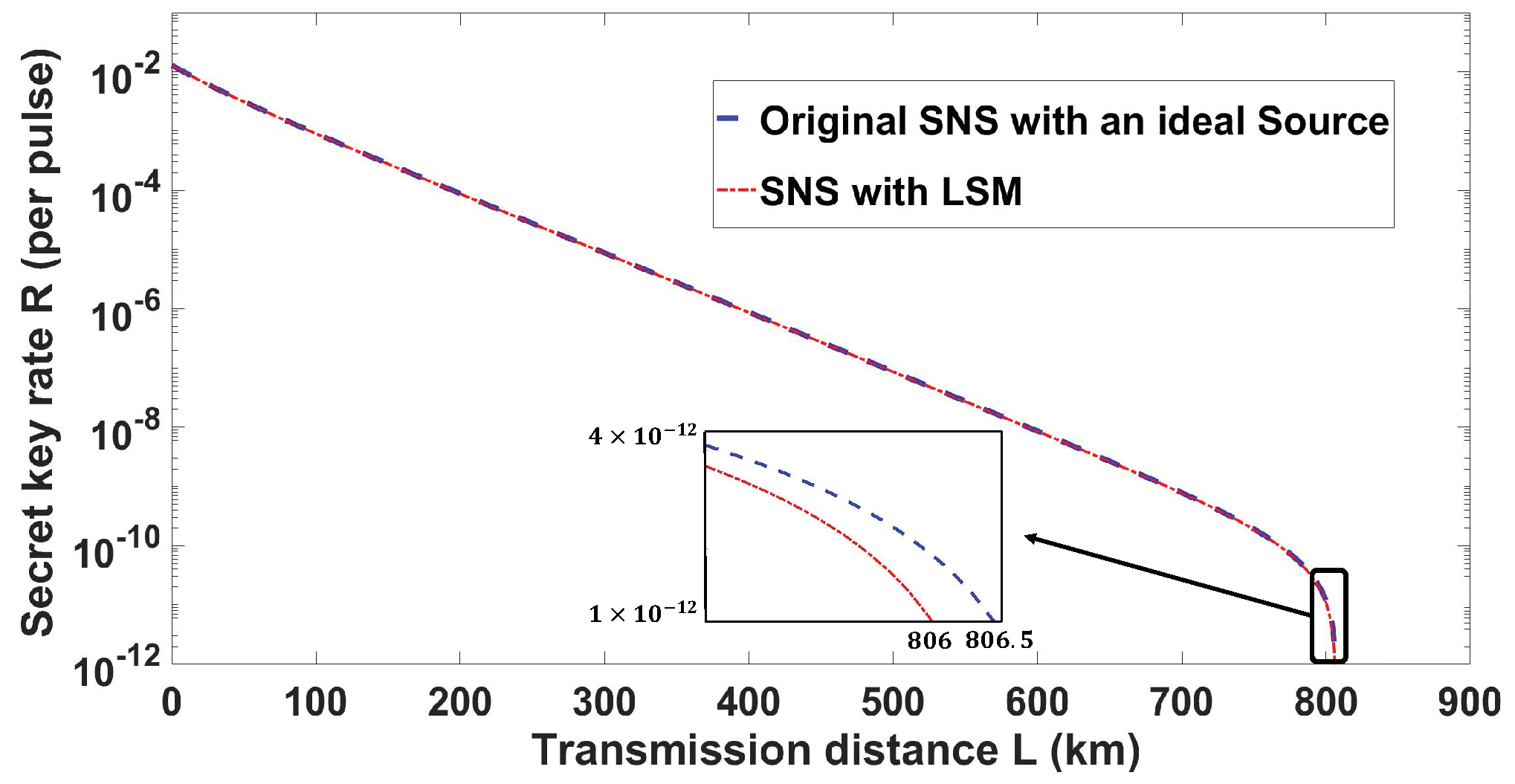
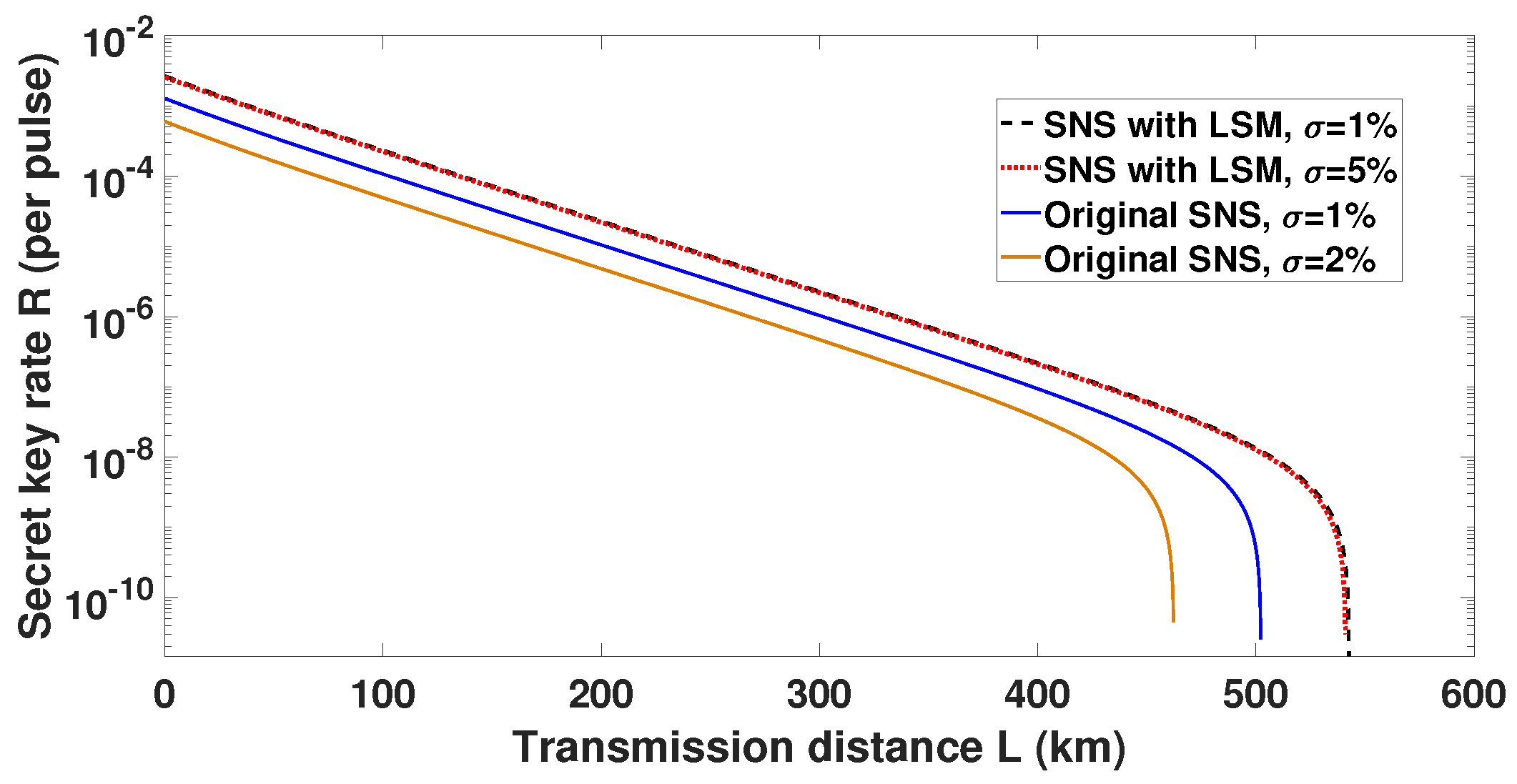
3. Performance with Numerical Simulation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Convex Form of under UPC
References
- Bennett, C.H.; Brassard, G. Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2014, 560, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekert, A.K. Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 67, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisin, N.; Ribordy, G.; Tittel, W.; Zbinden, H. Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 145–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarani, V.; Bechmann-Pasquinucci, H.; Cerf, N.J.; Dušek, M.; Lütkenhaus, N.; Peev, M. The security of practical quantum key distribution. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 1301–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.-K.; Curty, M.; Tamaki, K. Secure quantum key distribution. Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirandola, S.; Vitali, D.; Tombesi, P.; Lloyd, S. Macroscopic entanglement by entanglement swapping. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 150403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunstein, S.L.; Pirandola, S. Side-channel-free quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 130502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.-K.; Curty, M.; Qi, B. Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 130503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Curty, M.; Qi, B.; Lo, H.-K. Practical aspects of measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. New J. Phys. 2013, 15, 113007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-H.; Yu, Z.-W.; Wang, X.-B. Tightened estimation can improve the key rate of measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution by more than 100%. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 89, 052325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-H.; Yu, Z.-W.; Wang, X.-B. Making the decoy-state measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution practically useful. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 93, 042324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Razavi, M. Alternative schemes for measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 86, 062319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenok, A.; Slater, J.A.; Chan, P.; Lucio-Martinez, I.; Tittel, W. Real-World Two-Photon Interference and Proof-of-Principle Quantum Key Distribution Immune to Detector Attacks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 130501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Yin, H.-L.; Chen, T.-Y.; Chen, Z.-B. Long-Distance Measurement-Device-Independent Multiparty Quantum Communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 090501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.-L.; Chen, T.-Y.; Yu, Z.-W.; Liu, H.; You, L.-X.; Zhou, Y.-H.; Chen, S.J.; Mao, Y.Q.; Huang, M.Q.; Zhang, W.J.; et al. Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution Over a 404 km Optical Fiber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 190501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Xu, F.; Peng, X.; Guo, H. Continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 89, 052301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-C.; Li, Z.; Yu, S.; Gu, W.; Peng, X.; Guo, H. Continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution using squeezed states. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 90, 052325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirandola, S.; Ottaviani, C.; Spedalieri, G.; Weedbrook, C.; Braunstein, S.L.; Lloyd, S.; Gehring, T.; Jacobsen, C.S.; Andersen, U.L. High-rate measurement-device-independent quantum cryptography. Nat. Photonics 2015, 9, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Wei, S.; Su, Q.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, H. High speed continuous variable source-independent quantum random number generation. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 025013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, W.-Y. Quantum key distribution with high loss: Toward global secure communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 057901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucamarini, M.; Yuan, Z.L.; Dynes, J.F.; Shields, A.J. Overcoming the rate-distance limit of quantum key distribution without quantum repeaters. Nature 2018, 557, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-B.; Yu, Z.-W.; Hu, X.-L. Twin-field quantum key distribution with large misalignment error. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 98, 062323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zeng, P.; Zhou, H. Phase-Matching Quantum Key Distribution. Phys. Rev. X 2018, 8, 031043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, K.; Lo, H.-K.; Wang, W.Y.; Lucamarini, M. Information theoretic security of quantum key distribution overcoming the repeaterless secret key capacity bound. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.05511. [Google Scholar]
- Curty, M.; Azuma, K.; Lo, H.-K. Simple security proof of twin-field type quantum key distribution protocol. NPJ Quantum Inform. 2019, 5, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasselli, F.; Curty, M. Practical decoy-state method for twin-field quantum key distribution. New J. Phys. 2019, 21, 073001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.-W.; Hu, X.-L.; Jiang, C.; Hu, H.; Wang, X.-B. Sending-or-not-sending twin-field quantum key distribution in practice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minder, M.; Pittaluga, M.; Roberts, G.L.; Lucamarini, M.; Dynes, J.F.; Yuan, Z.L.; Shields, A.J. Experimental quantum key distribution beyond the repeaterless secret key capacity. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; He, D.-Y.; Yin, Z.-Q.; Lu, F.-Y.; Cui, C.-H.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, G.-C.; Han, Z.-F. Beating the Fundamental Rate-Distance Limit in a Proof-of-Principle Quantum Key Distribution System. Phys. Rev. X 2019, 9, 021046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-B.; Hu, X.-L.; Yu, Z.-W. Effective Eavesdropping to Twin-Field Quantum Key Distribution. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.02272. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.-B. Decoy-state quantum key distribution with large random errors of light intensity. Phys. Rev. A 2007, 75, 052301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisin, N.; Fasel, S.; Kraus, B.; Zbinden, H.; Ribordy, G. Trojan-horse attacks on quantum-key-distribution systems. Phys. Rev. A 2006, 73, 022320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qi, B.; Lo, H.-K. Quantum key distribution with an unknown and untrusted source. Phys. Rev. A 2008, 77, 052327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Jiang, H.; Xu, B.; Ma, X.; Guo, H. Experimental quantum-key distribution with an untrusted source. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 2077–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Xu, B.; Guo, H. Passive-scheme analysis for solving the untrusted source problem in quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 042320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Peng, X.; Guo, H. Passive scheme with a photon-number-resolving detector for monitoring the untrusted source in a plug-and-play quantum-key-distribution system. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 82, 042301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Peng, X.; Guo, H. Light Source Monitoring in Quantum Key Distribution With Single-Photon Detector at Room Temperature. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2018, 54, 9300110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, Z.; Xu, B.; Guo, H. Monitoring an untrusted light source with single-photon detectors in measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 99, 052302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-B.; Peng, C.-Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Pan, J.-W. General theory of decoy-state quantum cryptography with source errors. Phys. Rev. A 2008, 77, 042311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qi, B.; Lo, H.-K.; Qian, L. Security analysis of an untrusted source for quantum key distribution: passive approach. New J. Phys. 2010, 12, 023024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, W.; Han, Z.; Guo, G. Experimental demonstration of counteracting imperfect sources in a practical one-way quantum-key-distribution system. Phys. Rev. A 2009, 80, 062309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| f | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| f | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, B.; Guo, H. Sending-or-Not-Sending Twin-Field Quantum Key Distribution with Light Source Monitoring. Entropy 2020, 22, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22010036
Qiao Y, Chen Z, Zhang Y, Xu B, Guo H. Sending-or-Not-Sending Twin-Field Quantum Key Distribution with Light Source Monitoring. Entropy. 2020; 22(1):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22010036
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Yucheng, Ziyang Chen, Yichen Zhang, Bingjie Xu, and Hong Guo. 2020. "Sending-or-Not-Sending Twin-Field Quantum Key Distribution with Light Source Monitoring" Entropy 22, no. 1: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22010036
APA StyleQiao, Y., Chen, Z., Zhang, Y., Xu, B., & Guo, H. (2020). Sending-or-Not-Sending Twin-Field Quantum Key Distribution with Light Source Monitoring. Entropy, 22(1), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22010036





