Application of Continuous Wavelet Transform and Convolutional Neural Network in Decoding Motor Imagery Brain-Computer Interface
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Motor Imagery EEG Datasets
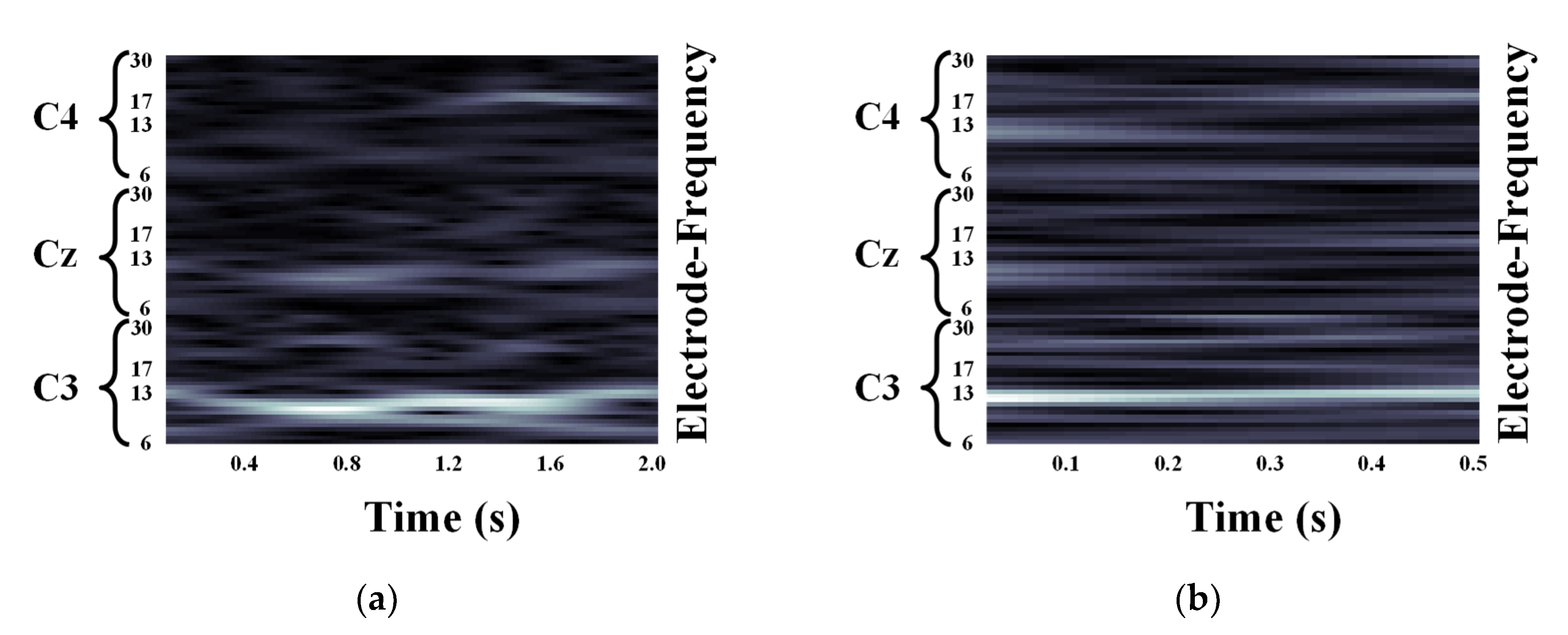
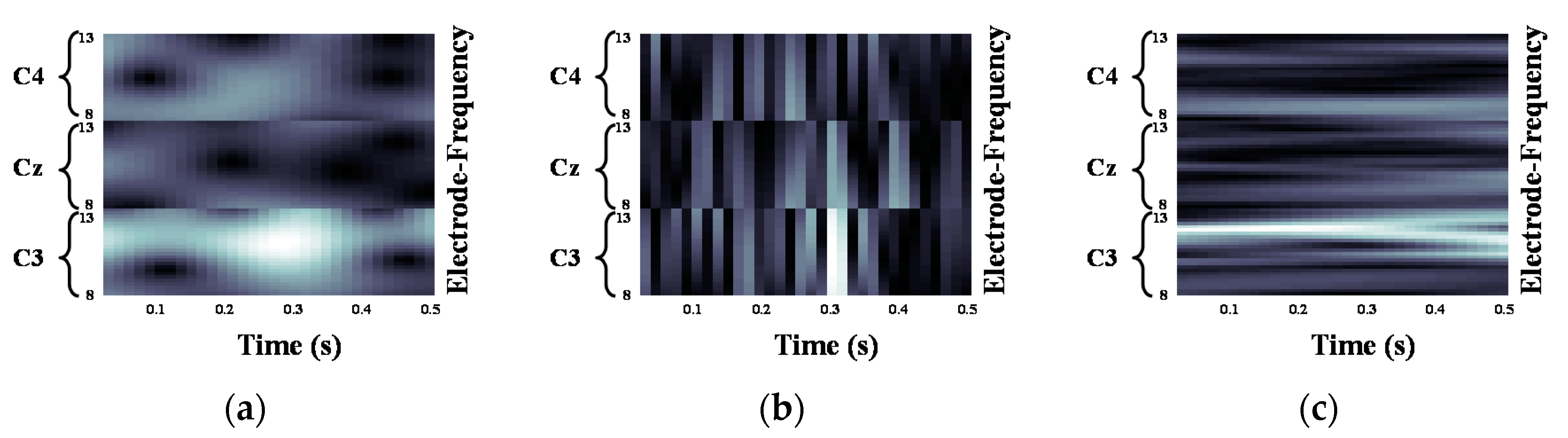
2.2. Motor Imagery EEG Image Form Using Continuous Wavelet Transform
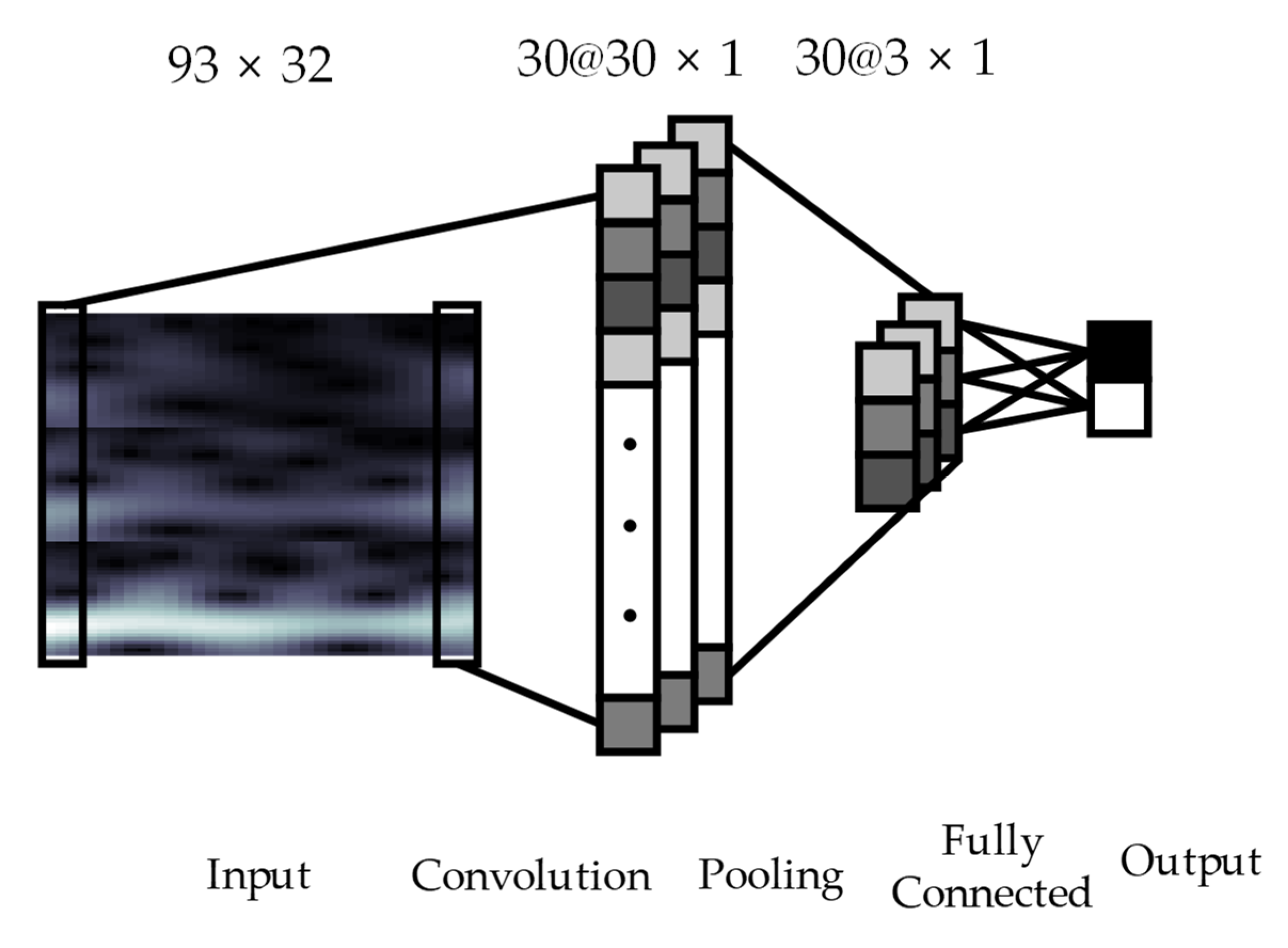
2.3. Convolutional Neural Networks Architecture
3. Results
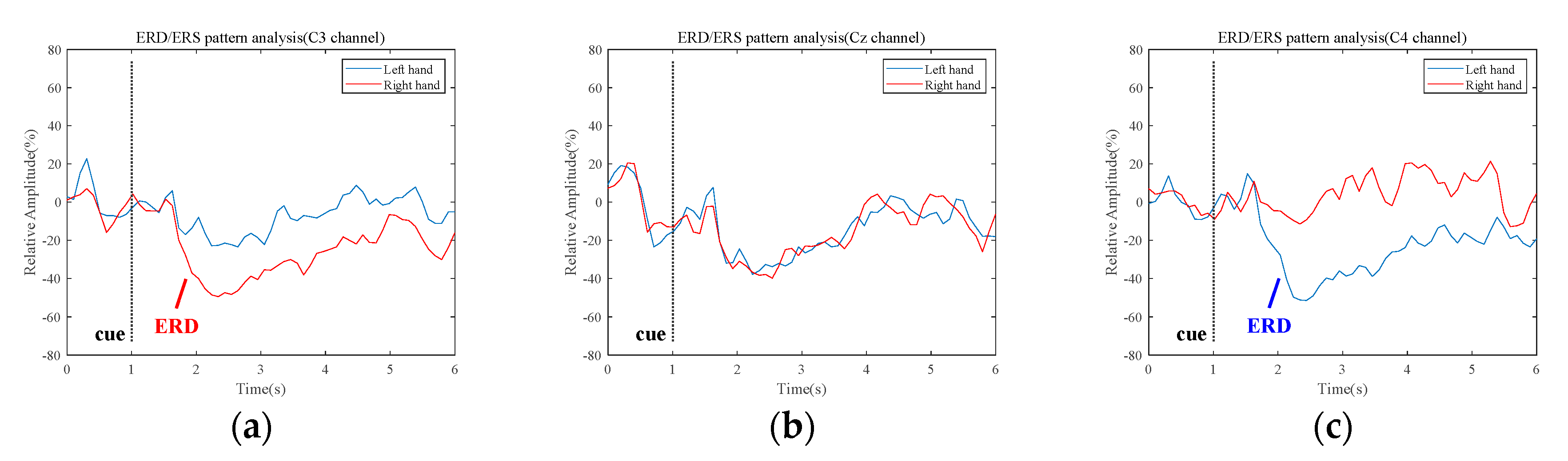
3.1. Quantification of the Event-Related Desynchronization/Event-Related Synchronization Pattern
3.2. Classification Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Hong, B. Visual and Auditory Brain–Computer Interfaces. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 1436–1447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Neuper, C.; Flotzinger, D.; Pregenzer, M. EEG-based discrimination between imagination of right and left hand movement. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1997, 103, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, L.; Lotte, F.; Lécuyer, A. Two Brains, One Game: Design and Evaluation of a Multiuser BCI Video Game Based on Motor Imagery. IEEE Trans. Comput. Intell. AI Games 2013, 5, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Yin, E.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Hu, D. Self-Paced Operation of a Wheelchair Based on a Hybrid Brain-Computer Interface Combining Motor Imagery and P300 Potential. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 2516–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankertz, B.; Sannelli, C.; Halder, S.; Hammer, E.M.; Kübler, A.; Müller, K.-R.; Curio, G.; Dickhaus, T. Neurophysiological predictor of SMR-based BCI performance. Neuroimage 2010, 51, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmyna, N.; Lindgren, J.T.; Lécuyer, A. Attending to Visual Stimuli versus Performing Visual Imagery as a Control Strategy for EEG-based Brain-Computer Interfaces. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpaw, J.R.; Birbaumer, N.; Heetderks, W.J.; McFarland, D.J.; Peckham, P.H.; Schalk, G.; Donchin, E.; Quatrano, L.A.; Robinson, C.J.; Vaughan, T.M. Brain-computer interface technology: A review of the first international meeting. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 2000, 8, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas-Alonso, L.F.; Gomez-Gil, J. Brain Computer Interfaces, a Review. Sensors 2012, 12, 1211–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Zheng, D.; Na, R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S. EEG Classification of Motor Imagery Using a Novel Deep Learning Framework. Sensors 2019, 19, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramoser, H.; Muller-Gerking, J.; Pfurtscheller, G. Optimal spatial filtering of single trial EEG during imagined hand movement. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 2000, 8, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Clemente, R.; Olias, J.; Thiyam, D.B.; Cichocki, A.; Cruces, S. Information Theoretic Approaches for Motor-Imagery BCI Systems: Review and Experimental Comparison. Entropy 2018, 20, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, K.K.; Chin, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.; Guan, C. Filter Bank Common Spatial Pattern (FBCSP). In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Hong Kong, China, 1–8 June 2008; pp. 2390–2397. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Lee, D.; Lee, S. Filter Bank Regularized Common Spatial Pattern Ensemble for Small Sample Motor Imagery Classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolliffe, I. Principal component analysis. In International Encyclopedia of Statistical Science; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 1094–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Comon, P. Independent component analysis, A new concept? Signal Process. 1994, 36, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-Y.; Sun, Y.-N. EEG-based motor imagery analysis using weighted wavelet transform features. J. Neurosci. Methods 2009, 176, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotte, F.; Bougrain, L.; Cichocki, A.; Clerc, M.; Congedo, M.; Rakotomamonjy, A.; Yger, F. A review of classification algorithms for EEG-based brain–computer interfaces: A 10 year update. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 031005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Nam, Y.; Choi, S. Composite common spatial pattern for subject-to-subject transfer. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2009, 16, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazli, S.; Popescu, F.; Danóczy, M.; Blankertz, B.; Müller, K.-R.; Grozea, C. Subject-independent mental state classification in single trials. Neural Netw. 2009, 22, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Ahn, M.; Kim, K.; Jun, S.C. Increasing session-to-session transfer in a brain–computer interface with on-site background noise acquisition. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 066009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Li, T.; Ren, X.; Miao, H. A Deep Learning Scheme for Motor Imagery Classification based on Restricted Boltzmann Machines. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, P.; Steinkraus, D.; Platt, J.C. Best Practices for Convolutional Neural Networks Applied to Visual Document Analysis. In Seventh International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 958–963. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; LeCun, Y. Scaling Learning Algorithms towards AI. In Large-Scale Kernel Machines; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 1–41. ISBN 1002620262. [Google Scholar]
- Tabar, Y.R.; Halici, U. A novel deep learning approach for classification of EEG motor imagery signals. J. Neural Eng. 2017, 14, 016003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BCI Competitions. Available online: http://www.bbci.de/competition/ (accessed on 25 January 2019).
- Leeb, R.; Lee, F.; Keinrath, C.; Scherer, R.; Bischof, H.; Pfurtscheller, G. Brain–Computer Communication: Motivation, Aim, and Impact of Exploring a Virtual Apartment. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2007, 15, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeb, R.; Brunner, C.; Mueller-Put, G.; Schloegl, A.; Pfurtscheller, G. BCI Competition 2008-Graz Data Set b; Graz University of Technology: Graz, Austria, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bashar, S.K.; Bhuiyan, M.I.H. Classification of motor imagery movements using multivariate empirical mode decomposition and short time Fourier transform based hybrid method. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2016, 19, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.J.; Castejón, C.; García-Prada, J.C. Review of Recent Advances in the Application of the Wavelet Transform to Diagnose Cracked Rotors. Algorithms 2016, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, F.; Patrick, F.; Paulo, G.; Olivier, L. Time-Frequency Toolbox; CNRS France-Rice University: Paris, France, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Meignen, S.; Oberlin, T.; McLaughlin, S. A New Algorithm for Multicomponent Signals Analysis Based on SynchroSqueezing: With an Application to Signal Sampling and Denoising. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 60, 5787–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, R.H.; Paez, J.; Bordeianu, C.C. A Survey of Computational Physics: Introductory Computational Science; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Lopes da Silva, F.H. Event-related EEG/MEG synchronization and desynchronization: Basic principles. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1999, 110, 1842–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Sun, S.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, S. A Brain-Machine Interface Based on ERD/ERS for an Upper-Limb Exoskeleton Control. Sensors 2016, 16, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.; Nam, C.S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Whang, M.C. Event-related (De)synchronization (ERD/ERS) during motor imagery tasks: Implications for brain–computer interfaces. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2011, 41, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dataset | Subjects | Channels | Trials | Sampling Frequency (Hz) | MI Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCI competition Ⅳ dataset 2b | 9 | C3, Cz, C4 | 400 | 250 | 2 (left/right hands) |
| BCI competition Ⅱ dataset Ⅲ | 1 | C3, Cz, C4 | 280 | 128 |
| Subjects | Accuracy (%) and Standard Deviation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STFT [25] | CWT | ||||||
| Morlet | Mexican Hat | Bump | |||||
| mu + beta | mu + beta | mu | mu + beta | mu | mu + beta | mu | |
| 1 | 74.5 ± 4.6 | 85.6 ± 1.3 | 84.7 ± 1.6 | 81.8 ± 1.3 | 81.7 ± 1.6 | 83.2 ± 1.4 | 82.4 ± 1.1 |
| 2 | 64.3 ± 2.0 | 72.8 ± 1.4 | 72.7 ± 2.0 | 70.6 ± 2.1 | 71.9 ± 2.0 | 73.8 ± 2.1 | 72.5 ± 2.0 |
| 3 | 71.8 ± 1.6 | 78.0 ± 1.9 | 79.5 ± 2.1 | 76.4 ± 1.8 | 74.7 ± 2.1 | 71.5 ± 2.1 | 73.6 ± 1.8 |
| 4 | 94.5 ± 0.2 | 95.4 ± 1.0 | 96.4 ± 0.5 | 96.0 ± 0.4 | 95.0 ± 0.9 | 96.2 ± 0.8 | 97.4 ± 0.5 |
| 5 | 79.5 ± 2.5 | 82.6 ± 1.7 | 79.6 ± 2.1 | 78.7 ± 1.9 | 75.6 ± 2.0 | 81.0 ± 1.0 | 73.1 ± 1.7 |
| 6 | 75.0 ± 2.4 | 79.8 ± 2.1 | 77.9 ± 1.6 | 75.5 ± 2.2 | 76.9 ± 1.5 | 80.6 ± 1.8 | 81.0 ± 1.3 |
| 7 | 70.5 ± 2.3 | 82.9 ± 1.2 | 81.0 ± 1.6 | 82.1 ± 1.2 | 81.4 ± 1.8 | 78.9 ± 2.0 | 81.7 ± 1.9 |
| 8 | 71.8 ± 4.1 | 85.0 ± 1.9 | 85.7 ± 1.7 | 84.7 ± 1.4 | 83.5 ± 1.4 | 83.5 ± 1.5 | 83.1 ± 1.6 |
| 9 | 71.0 ± 1.1 | 85.3 ± 1.9 | 84.9 ± 1.4 | 84.6 ± 1.2 | 85.1 ± 1.7 | 86.6 ± 1.4 | 84.0 ± 2.2 |
| Mean | 74.8 ± 2.3 | 83.0 ± 1.6 | 82.5 ± 1.6 | 81.2 ± 1.5 | 80.6 ± 1.7 | 81.7 ± 1.6 | 81.0 ± 1.6 |
| Frequency Band | Accuracy (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| STFT [25] | Morlet | Mexican Hat | Bump | |
| Mu + beta | 89.3 | 89.3 | 90.0 | 92.9 |
| mu | N/A | 91.4 | 89.2 | 91.4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.K.; Choi, Y.-S. Application of Continuous Wavelet Transform and Convolutional Neural Network in Decoding Motor Imagery Brain-Computer Interface. Entropy 2019, 21, 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21121199
Lee HK, Choi Y-S. Application of Continuous Wavelet Transform and Convolutional Neural Network in Decoding Motor Imagery Brain-Computer Interface. Entropy. 2019; 21(12):1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21121199
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hyeon Kyu, and Young-Seok Choi. 2019. "Application of Continuous Wavelet Transform and Convolutional Neural Network in Decoding Motor Imagery Brain-Computer Interface" Entropy 21, no. 12: 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21121199
APA StyleLee, H. K., & Choi, Y.-S. (2019). Application of Continuous Wavelet Transform and Convolutional Neural Network in Decoding Motor Imagery Brain-Computer Interface. Entropy, 21(12), 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21121199






