Unavoidable Destroyed Exergy in Crude Oil Pipelines due to Wax Precipitation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Definition of Unavoidable Destroyed Exergy
3. Determination of Unavoidable Destroyed Exergy for Waxy Crude Oil
3.1. Crude Oil Critical Transition Temperature
3.2. Determination of the Specific Heat Capacity of Waxy Crude Oil
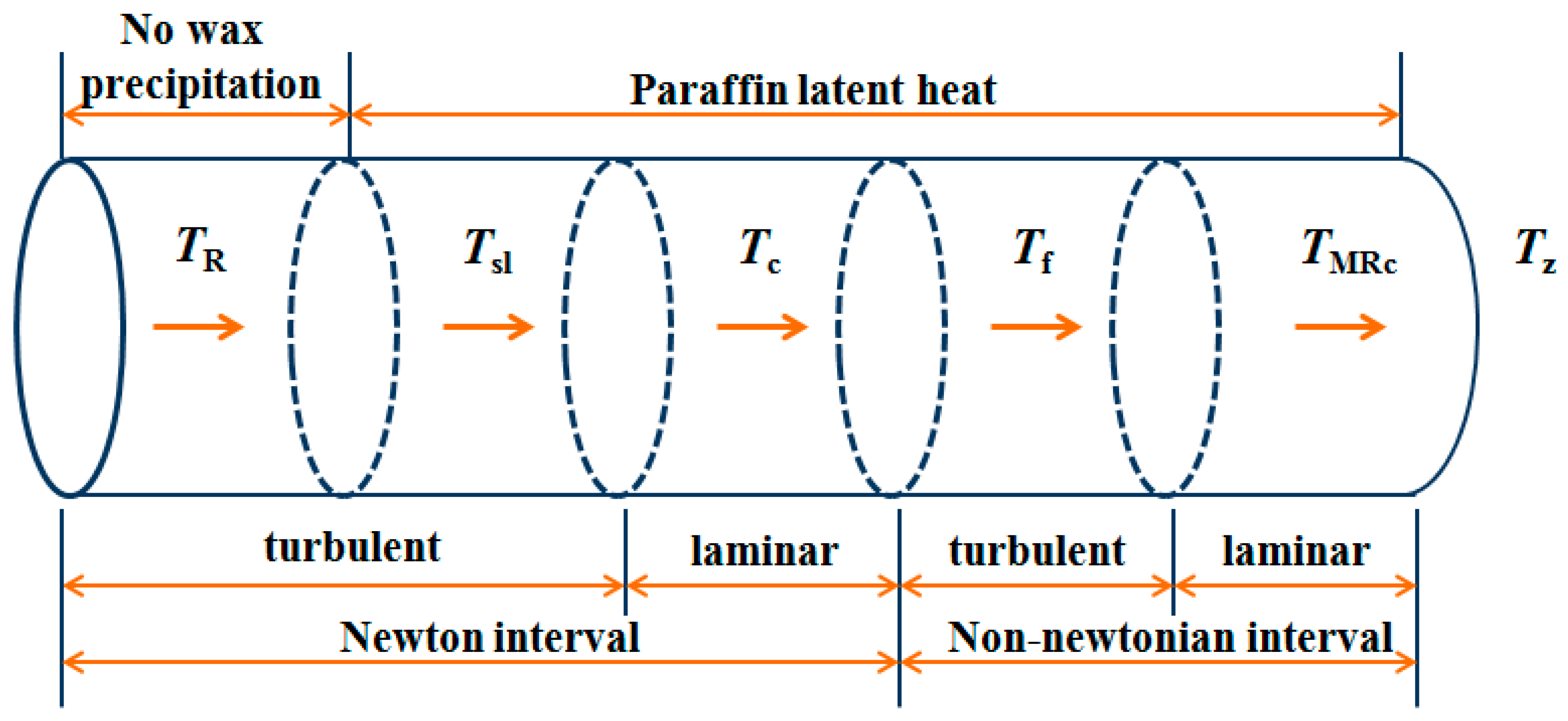
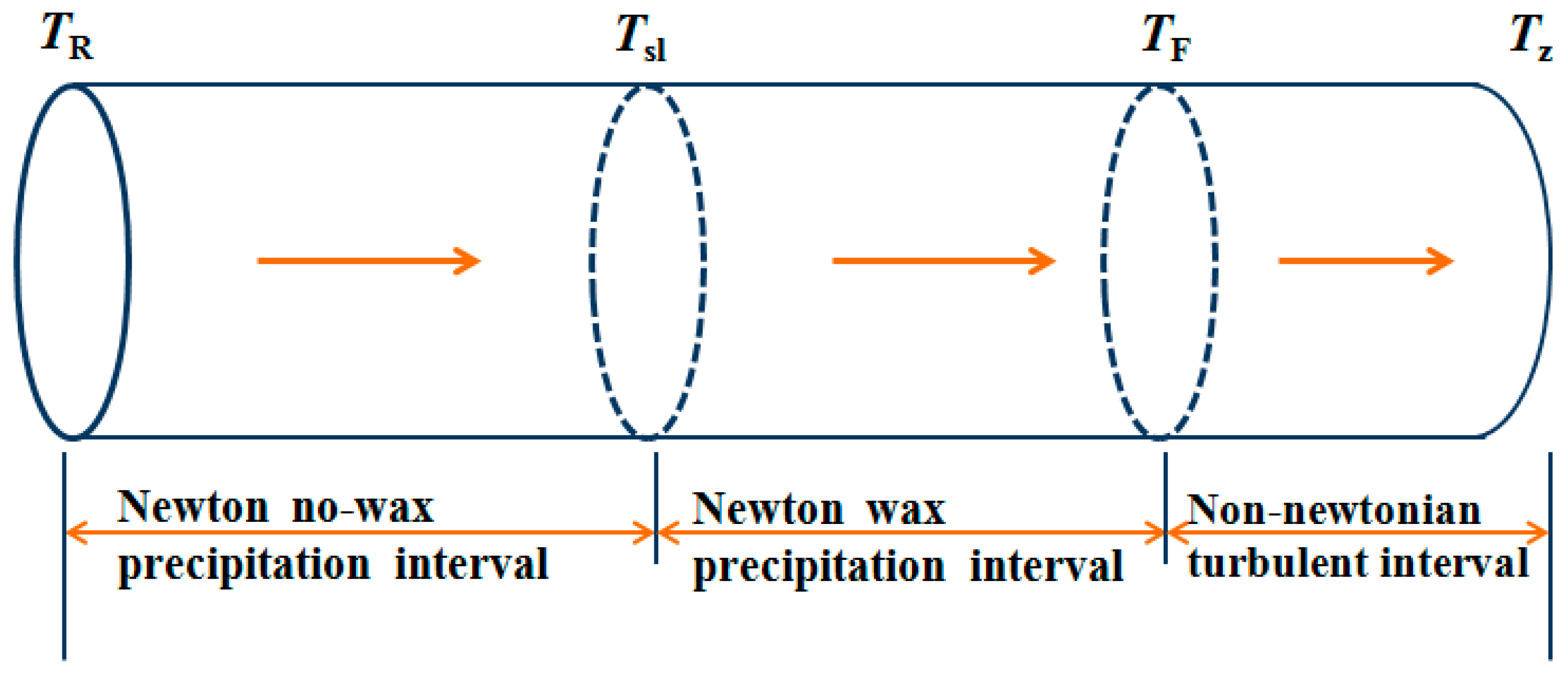
3.3. Temperature Range of Pipeline Transportation
3.4. Calculation of Unavoidable Destroyed Exergy
3.4.1. Unavoidable Thermal Destroyed Exergy
3.4.2. Unavoidable Pressure Destroyed Exergy
3.5. The Calculation Process of Unavoidable Destroyed Exergy
4. Calculation Example
4.1. Basic Data
4.1.1. Critical Transition Temperature
4.1.2. Pipeline Transmission Temperature Intervals
4.1.3. Theoretical Outstation Temperature
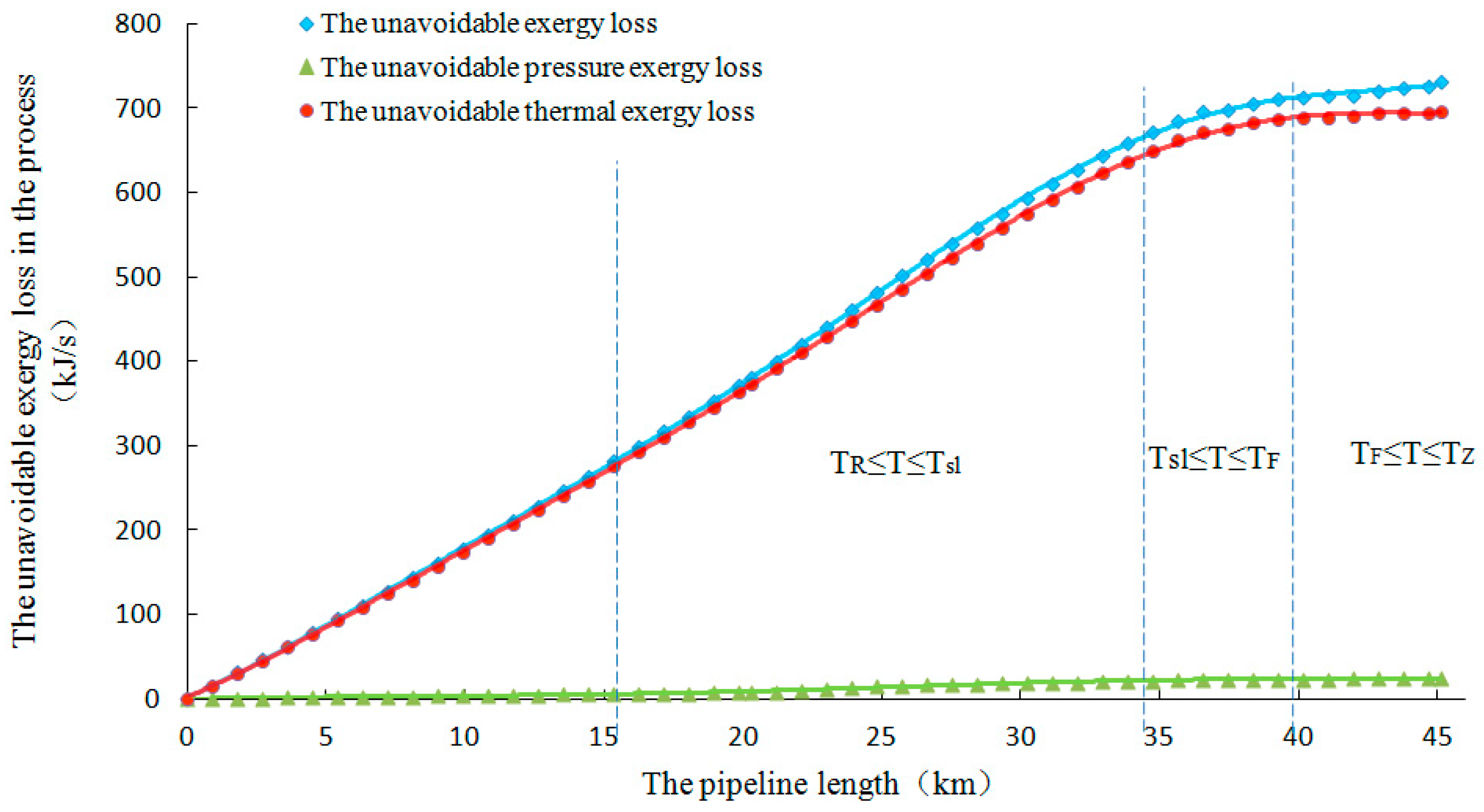
4.2. Calculation Results and Analysis of Unavoidable Destroyed Exergy
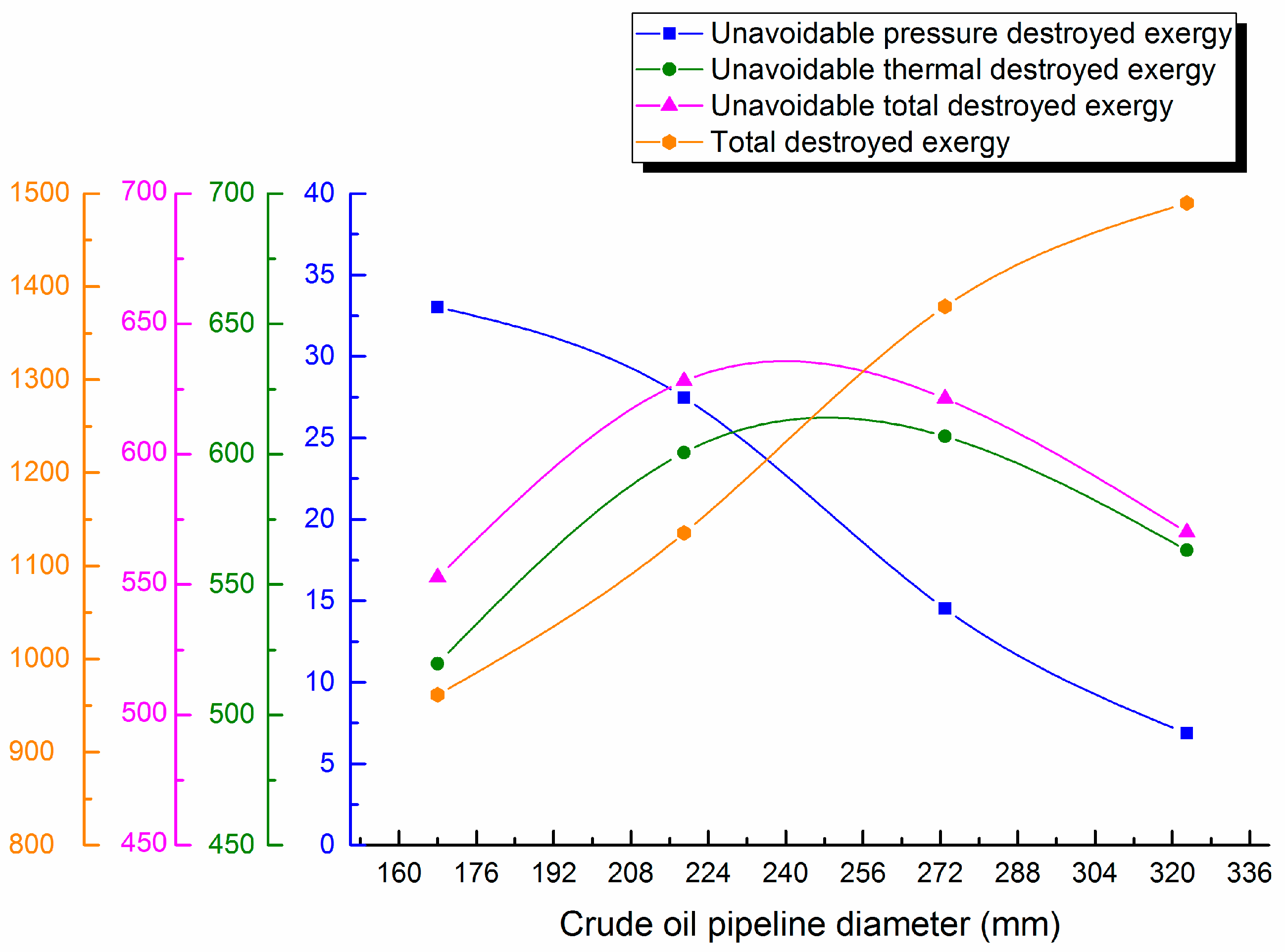
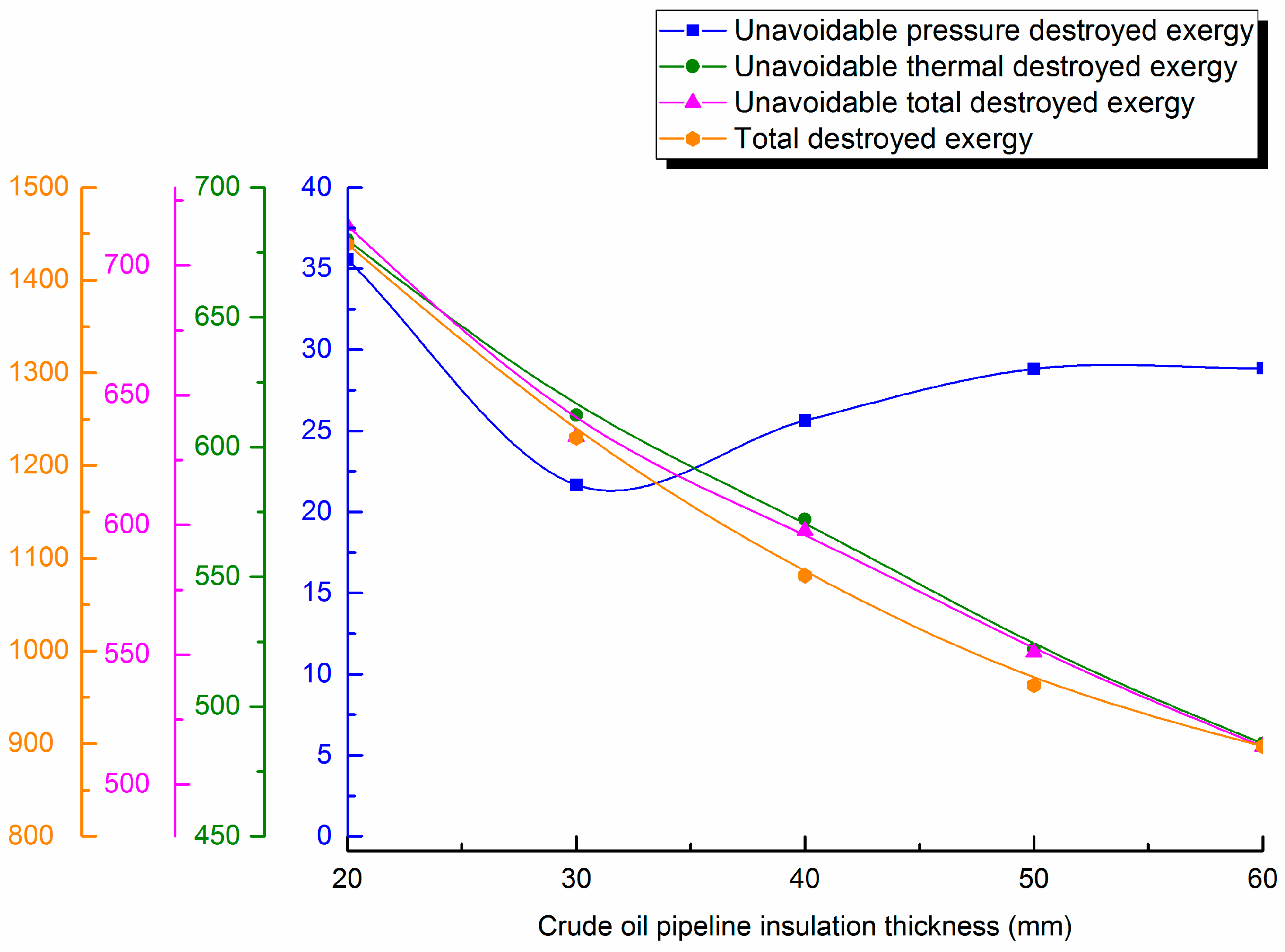
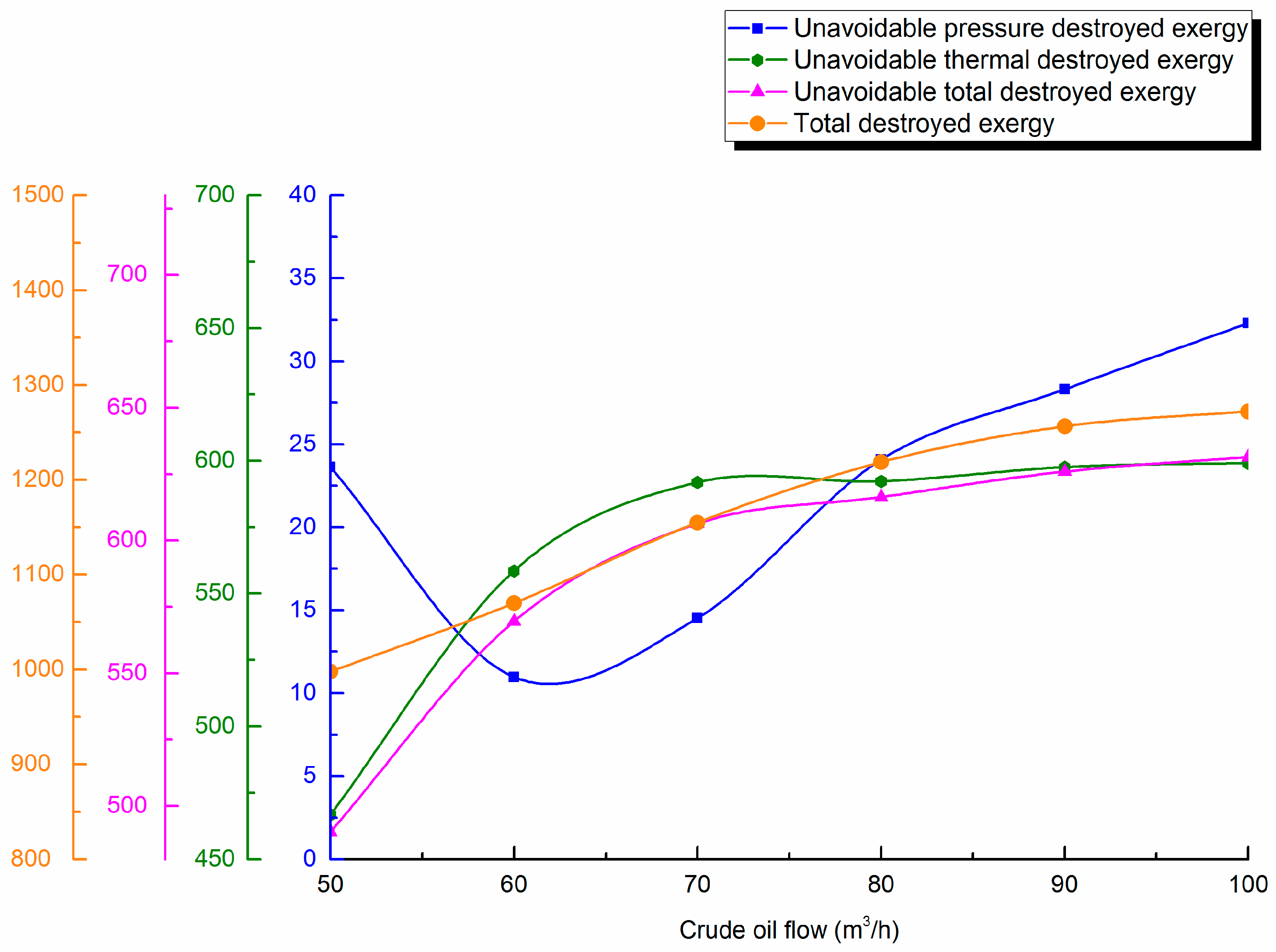
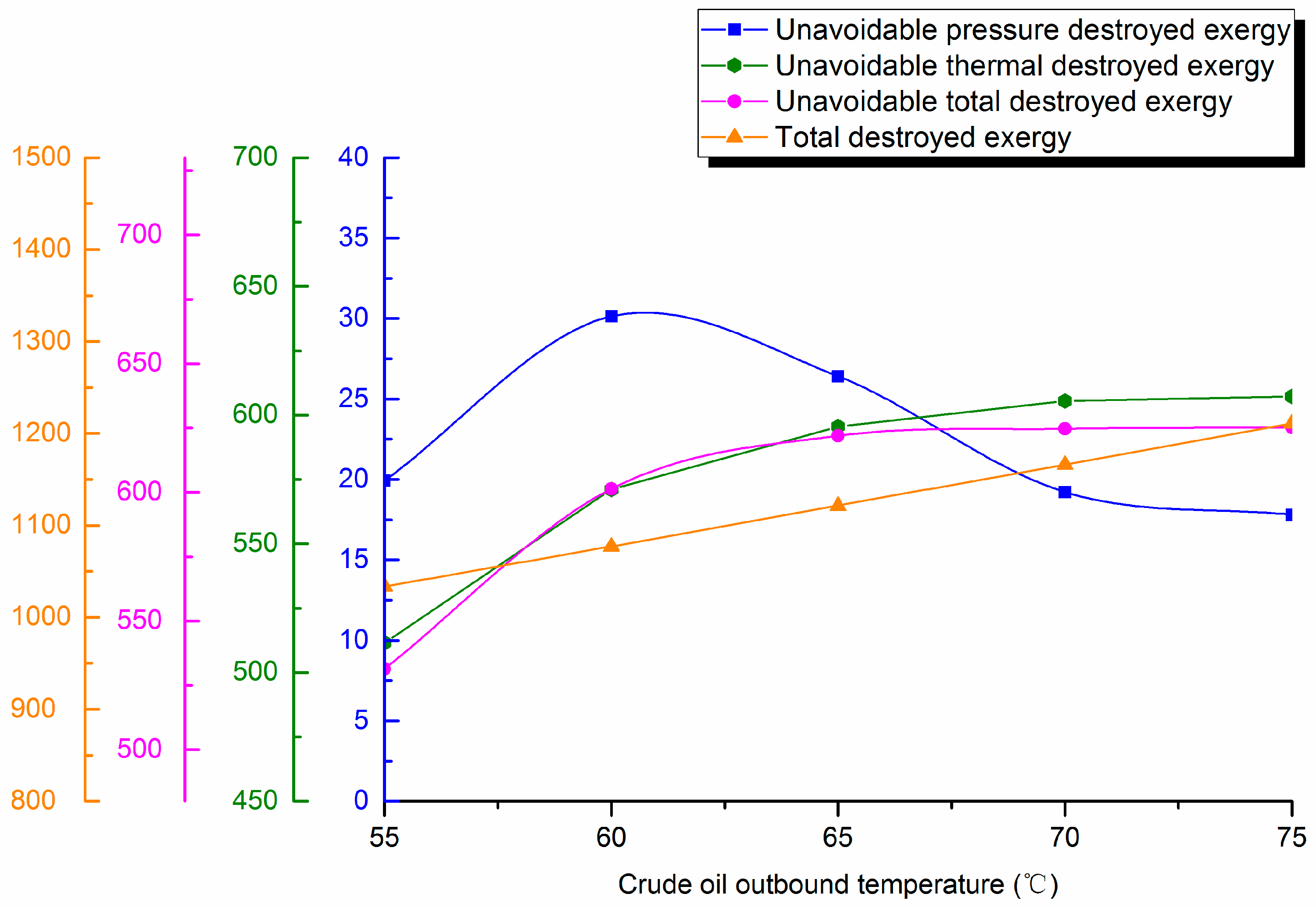
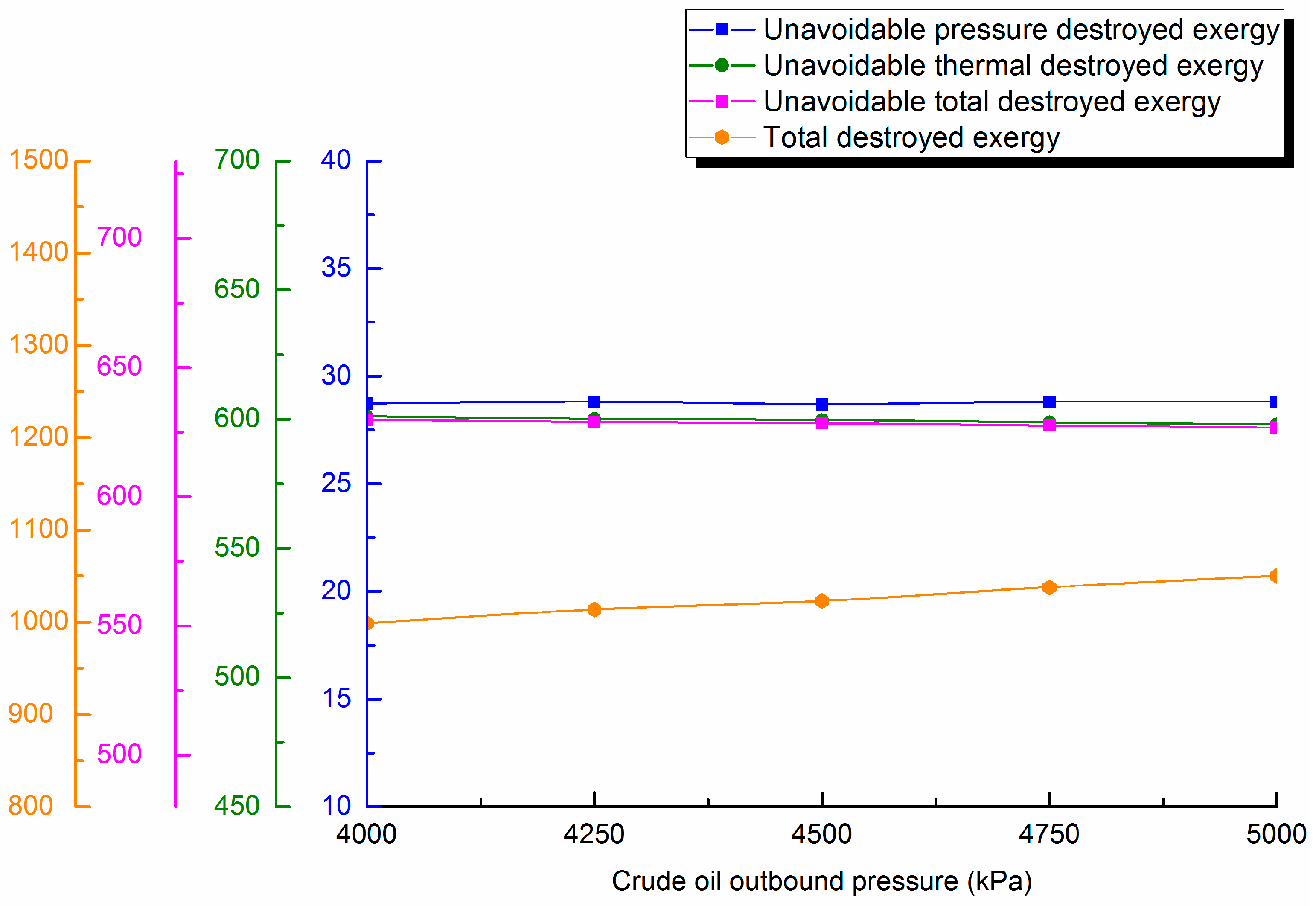
4.3. Influence of Design Parameters on Unavoidable Destroyed Exergy Loss
4.3.1. Change with Pipeline Diameter
4.3.2. Change with Insulation Layer Thickness
4.3.3. Change with Buried Depth
4.4. Influence of Operational Parameters on Unavoidable Destroyed Exergy
4.4.1. Throughput
4.4.2. Outstation Temperature
4.4.3. Outstation Pressure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Re | Reynolds number (−) |
| dynamic viscosity coefficient (N·s/m2) | |
| D | inner diameter of oil pipeline (m) |
| crude oil flow velocity (m/s) | |
| oil flow viscosity (m2/s) | |
| density (kJ/m) | |
| T | the crude oil temperature (°C) |
| P | pressure (Pa) |
| c | crude oil specific heat capacity (kJ/(kg·°C) |
| A | consistency coefficient fitting constant parameter (−) |
| B | consistency coefficient fitting constant paramete (−) |
| a | fitting constant of specific heat capacity curve (−) |
| m | fitting constant of specific heat capacity curve (−) |
| K | pipeline total heat transfer coefficient (W/(m2 °C) |
| S | pipe section area (m2) |
| h | friction loss (m) |
| Q | pipe volume flow (m3/s) |
| L | pipeline length (km) |
| G | oil mass flow (kg/s) |
| i | hydraulic gradient (−) |
| crude oil consistency coefficient (Pa·s) | |
| crude oil rheological constant parameter (−) | |
| Subscripts | |
| x | exergy (kJ) |
| U | unavoidable (−) |
| A | avoidable (−) |
| min | theoretical minimums (−) |
| c | Newtonian flow critical point (−) |
| MRc | non-Newtonian flow critical point (−) |
| sl | wax appearance point (−) |
| F | abnormal point (−) |
| 0 | ambient (−) |
| R | initial point (−) |
| L | terminal point in different temperature ranges (−) |
| Z | end point |
| Rl | theoretical terminal point |
| Zl | theoretical end point |
References
- Hou, L.; Qi, S.M.; Li, J. Thoughts on energy conservation and consumption reduction of crude oil pipeline transportation system. J. Oil-Gasfield Surf. Eng. 2008, 27, 62–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.C.; Zhang, Y.G.; Fan, A.F. Improvement of gas consumption evaluation method for crude oil gathering and transportation system. J. Oil-Gasfield Surf. Eng. 2001, 20, 24–25. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, L.L.; Liu, B.; Wu, C.C.; Xing, X.K.; Chou, J. Application of energy consumption indicators based on hydraulic horsepower in the analysis of energy consumption of oil and gas pipeline. J. Oil Gas Storage Transp. 2012, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probert, S.D.; Chu, C.Y. Internally insulated hot-oil pipelines. J. Appl. Energy 1983, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.V.; Voldsund, M.; Breuhaus, P. Energy efficiency measures for offshore oil and gas platforms. J. Energy 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, M.; Sciubba, E. Extended Exergy Accounting as a general method for assessing the primary resource consumption of social and industrial systems. J. Int. J. Exergy 2007, 4, 421–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciubba, E. Why Emergy- and Exergy Analysis are non-commensurable methods for the assessment of energy conversion systems. J. Int. J. Exergy 2009, 6, 523–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Dai, J.; Sciubba, E. Ecological accounting for China based on extended exergy. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 37, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia, U.; Sciubba, E. From Lotka to the entropy generation approach. J. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2013, 392, 3634–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M. Description and Analysis of Thermodynamics Exergy Flow in Oil Pipeline Transportation System. Master’s Thesis, North East Petroleum University, Daqing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z. Establishment and Application of Multi-level Exergy Transfer Evaluation System for Energy Consumption in Crude Oil Pipeline. Master’s Thesis, North East Petroleum University, Daqing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.S. Thermodynamic Analysis Method of Energy System; Jiaotong University Press: Xi’an, China, 2005; ISBN 7-5605-1944-X. [Google Scholar]
- Tsatsaronis, G.; Park, M.H. On avoidable and unavoidable exergy destructions and investment costs in thermal systems. J. Energy Convers. Manag. 2002, 43, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.T. A Research on the Flow Characteristics of Waxy Crude Oil Pipeline. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y.; Liu, D.J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, F.; Gao, Z. Effect of wax deposit area in waxy hot oil pipeline on whole running conditions. J. Oil Gas Storage Transp. 2014, 33, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.W.; Han, X.C.; Yan, D.F. Design Specification for Oil Pipeline Process, GB 50253-2003; Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.Y. Design and Management of Oil Pipeline; Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2010; ISBN 978-7-5021-7886-4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.X. Rheology of Crude Oil; China University of Petroleum Press: Beijing, China, 2012; ISBN 978-7-5636-2157-6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.H. Design and Management of Oil Pipeline; China University of Petroleum Press: Beijing, China, 2013; ISBN 978-7-5636-2241-2. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q.L.; Zheng, A.B.; Pan, C.L.; Sun, W.; Liu, Y. Studies on Energy Consumption of Crude Oil Pipeline Transportation Process Based on the Unavoidable Exergy Loss Rate. J. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.L.; Gan, Y.F.; Su, W.K.; Liu, Y.; Sun, W.; Xu, Y. Research on Exergy Flow Composition and Exergy Loss Mechanisms for Waxy Crude Oil Pipeline Transport Processes. Energies 2017, 10, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.L.; Zheng, A.B.; Song, S.; Wu, H.; Lv, L.L.; Liu, Y. Studies on the Exergy Transfer Law for the Irreversible Process in the Waxy Crude Oil Pipeline Transportation. Entropy 2018, 20, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Lou, Y.H. Code for Design of Oil-Gas Gathering and Transportation Systems of Oilfield, GB 50350-2015; Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]


| Parameter | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shengli crude oil | 0.4840 | 1.9255 | 0.03465 | 0.01164 |
| Daqing crude oil | 0.9085 | 1.7585 | 0.01732 | 0.01567 |
| Puyang crude oil | 0.6753 | 1.7258 | 0.0264 | 0.01217 |
| Renqiu crude oil | 0.1970 | 1.8880 | 0.0476 | 0.02117 |
| Item | Data | Item | Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pipeline length | 45121 m | Pipeline diameter | Φ219 × 5.6 mm |
| Buried depth | 1600 mm | Wax Appearance point | 47.7 °C |
| Outstation temperature | 65 °C | Anomalous point | 36.2 °C |
| Outstation pressure | 4.5 MPa | Condensation point | 25 °C |
| Pipeline throughput | 70 m3/h | Density (30 °C) | 860 kg/m3 |
| Ambient temperature | −4.4 °C | Density (50 °C) | 830 kg/m3 |
| Soil thermal conductivity | 1.4 W/(m·°C) | Viscosity (30 °C) | 70 mPa·s |
| Pipe thermal conductivity | 45.24 W/(m·°C) | Viscosity (50 °C) | 9.41 mPa·s |
| Pipeline Transmission Temperature Region | Newton Turbulent Non-Wax Precipitation | Newton Turbulent Wax Precipitation | Non-Newton Turbulence | Whole Process of Crude Oil Pipeline Transportation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The unavoidable pressure destroyed exergy (kJ/s) | 7.749 | 15.828 | 0.042 | 23.621 |
| The unavoidable thermal destroyed exergy (kJ/s) | 373.379 | 315.716 | 30.217 | 719.313 |
| The unavoidable destroyed exergy (kJ/s) | 381.128 | 331.544 | 30.259 | 742.934 |
| The ratio between unavoidable pressure destroyed exergy and pressure destroyed exergy (%) | 9.409 | 22.202 | 0.328 | 14.178 |
| The ratio between unavoidable thermal destroyed exergy and thermal destroyed exergy (%) | 58.429 | 61.883 | 34.786 | 58.193 |
| Pipeline Diameters | 168 mm | 219 mm | 273 mm | 323 mm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interval length of pipe transmission (km) | Newton no-wax precipitation | 37.450 | 28.877 | 24.816 | 21.685 |
| Newton wax precipitation | 7.671 | 16.244 | 20.305 | 21.631 | |
| non-Newton turbulence | / | / | / | 1.805 | |
| End point temperature (°C) | Newton no-wax precipitation | 43.83 | 47.81 | 47.64 | 47.86 |
| Newton wax precipitation | 40.47 | 40.26 | 37.39 | 36.61 | |
| non-Newton turbulence | / | / | / | 35.85 | |
| Theoretical outstation temperature (°C) | 41.32 | 43.44 | 43.64 | 42.57 | |
| Throughput | 50 m3/h | 60 m3/h | 70 m3/h | 80 m3/h | 90 m3/h | 100 m3/h | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pipeline interval length (km) | Newton no-wax precipitation | 14.438 | 17.597 | 20.304 | 23.914 | 27.975 | 29.779 |
| Newton wax precipitation | 14.438 | 16.243 | 18.951 | 21.207 | 17.146 | 15.342 | |
| Non-Newton turbulence wax precipitation | 8.573 | 11.281 | 5.866 | / | / | / | |
| Non-Newton laminar wax precipitation | 7.671 | / | / | / | / | / | |
| Total heat transfer coefficient (W/m2 °C) | Newton no-wax precipitation | 0.469 | 0.472 | 0.470 | 0.476 | 0.471 | 0.471 |
| Newton wax precipitation | 0.447 | 0.460 | 0.468 | 0.467 | 0.469 | 0.470 | |
| Non-Newton turbulence wax precipitation | 0.416 | 0.42652 | 0.461 | / | / | / | |
| Non-Newton laminar wax precipitation | 0.356 | / | / | / | / | / | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Q.; Yang, J.; Zheng, A.; Yang, L.; Gan, Y.; Liu, Y. Unavoidable Destroyed Exergy in Crude Oil Pipelines due to Wax Precipitation. Entropy 2019, 21, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21010058
Cheng Q, Yang J, Zheng A, Yang L, Gan Y, Liu Y. Unavoidable Destroyed Exergy in Crude Oil Pipelines due to Wax Precipitation. Entropy. 2019; 21(1):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21010058
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Qinglin, JinWei Yang, Anbo Zheng, Lu Yang, Yifan Gan, and Yang Liu. 2019. "Unavoidable Destroyed Exergy in Crude Oil Pipelines due to Wax Precipitation" Entropy 21, no. 1: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21010058
APA StyleCheng, Q., Yang, J., Zheng, A., Yang, L., Gan, Y., & Liu, Y. (2019). Unavoidable Destroyed Exergy in Crude Oil Pipelines due to Wax Precipitation. Entropy, 21(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21010058





