Abstract
To explore the existence of self-organization during friction, this paper considers the motion of all atoms in a systems consisting of an Atomic Force Microscope metal tip sliding on a metal slab. The tip and the slab are set in relative motion with constant velocity. The vibrations of individual atoms with respect to that relative motion are obtained explicitly using Molecular Dynamics with Embedded Atom Method potentials. First, we obtain signatures of Self Organized Criticality in that the stick-slip jump force probability densities are power laws with exponents in the range (0.5, 1.5) for aluminum and copper. Second, we characterize the dynamical attractor by the entropy content of the overall atomic jittering. We find that in all cases, friction minimizes the entropy and thus makes a strong case for self-organization.
PACS Codes:
68.35.Af
1. Introduction
Friction at the atomic scale has been rekindled as an active area of research for 20 years. Although it is well established that the laws of friction at the nanoscale differ from the well known ones for macroscopic bodies set forth centuries ago by Coulomb and Amontons [1], general principles for nanofriction do not exist to date. Prominent models to remedy this situation were proposed in the mid-20th century by Tabor and Bowden on the basis of microasperities [2]. On the one hand, this lack of an overarching approach has led to interesting novel phenomena, such as superlubricity, self-healing and stick-slip phenomena in atomic friction. On the other hand, and taking into consideration the accrued empirical information collected in the last 50 years, relevant proposals to set friction on a sound theoretical framework have been put forward recently on the basis of general thermodynamics principles by Nosonovsky [3]. These are very exciting times to study the foundations of friction due to the recent widespread access to unrelated but germane tools: the science of complexity [4], atomic force microscopy and related technologies [5,6,7,8], accessible computer power [9], and the development of large interatomic potential databases [10,11].
In particular dry friction stick-slip motion has attracted particular attention as it serves as a model for fundamental macroscopic phenomena such as earthquakes [12,13,14,15], as well as it serves as a conceptual connector, at the microscopic level, between friction and self organized criticality (SOC) [16,17]. Also entropy has been proposed as a unifiying concept to understand friction and wear under different conditions [18].
Thus, it is pertinent to study well controlled systems to clarify the connection between friction and stick-slip, and of friction and entropy. An ideal scenario for a controlled situation consists on the production of reproducible atomic dynamics during friction. This is possible via full solution of the equations of motion of the many particle system, for well controlled external parameters such as ambient temperature and velocity. Here we present such results based on Molecular Dynamics computer simulations that model explicit stick-slip motion in dry friction between a metal sample and an Atomic Force Microscope metalic tip. This Molecular Dynamics is implemented using the code and visualization tools developed by LAMMPS at Sandia National Laboratories [19]. We begin by showing empirical evidence of the presence of signatures of Self Organized Criticality in the form of power laws. Then we interpret the dynamic attractor as a fluctuating state involving atoms in the neighborhood of the contact that reduce the entropy of the system. This article is a sequel of previous experimental and theoretical studies of atomic stick-slip in nanofriction, in search for the possible existance of SOC and its corresponding attractor [20,21,22,23].
The paper is organized as follows: in Section 2, Methods, we explain the the Molecular Dynamics approach for the tip-sample metal systems of interest. In that section we also present the method to measure power law exponents of the stick-slip avalanches, and the computation of the entropy of the whole system. Section 3 shows the main results of this article. Section 4 presents the conclusions.
2. Methods
This section is divided into three subsections where we describe respectively, the Molecular Dynamics setup, the probability distribution of stick-slip avalanches, and the entropy content of the tip-sample system.
2.1. Molecular Dynamics
As explained in the introduction, we obtain the motion of individual atoms in the system via the program LAMMPS [19]. The atomistic model entails a copper (aluminum) tip and a copper (aluminum) flat slab (Figure 1). The tip is made in the shape of a truncated cone, with top radius of 2.0 nm (2.3 nm) and bottom radius of 1.3 nm (1.4 nm). The slab is 1.88 nm (2.10 nm) thick in the z direction, and 4.86 nm (5.45 nm) in the x and y directions, with periodic boundary conditions in x and y. The uppermost three atomic planes of the tip are constrained to move in tandem, as a single rigid body, while the lowest three atomic planes of the slab (made up of nine planes) are fixed. Temperature is considered via the introduction of fictitious tiny particles with the appropriate Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution of velocities, the Langevin thermostat [24,25,26,27]. Pressure is controlled via simulated forces on the top layer as described in [28,29]. To simulate nominal constant velocity of the tip with respect to the slab, the top three atomic planes of the tip are moved rigidly at constant velocity while all the other atoms in the system (except the fixed layer in the slab as explained above) move according to Newton’s second law under Embedded Atom Method potentials [30], and under the NPT (constant number of particles, pressure and temperature). Speed and temperature used are reported in the caption of Figure 1. In particular the temperature of 1K was chosen because we are interested in the atomic motion induced by friction alone. Higher temperatures would induce vibrational modes, that although present in many real situations, they would mask the friction-only effects that we are trying to understand here. Newton’s second law for each particle is implemented as described in the foundational LAMMPS Molecular Dynamics article [31].
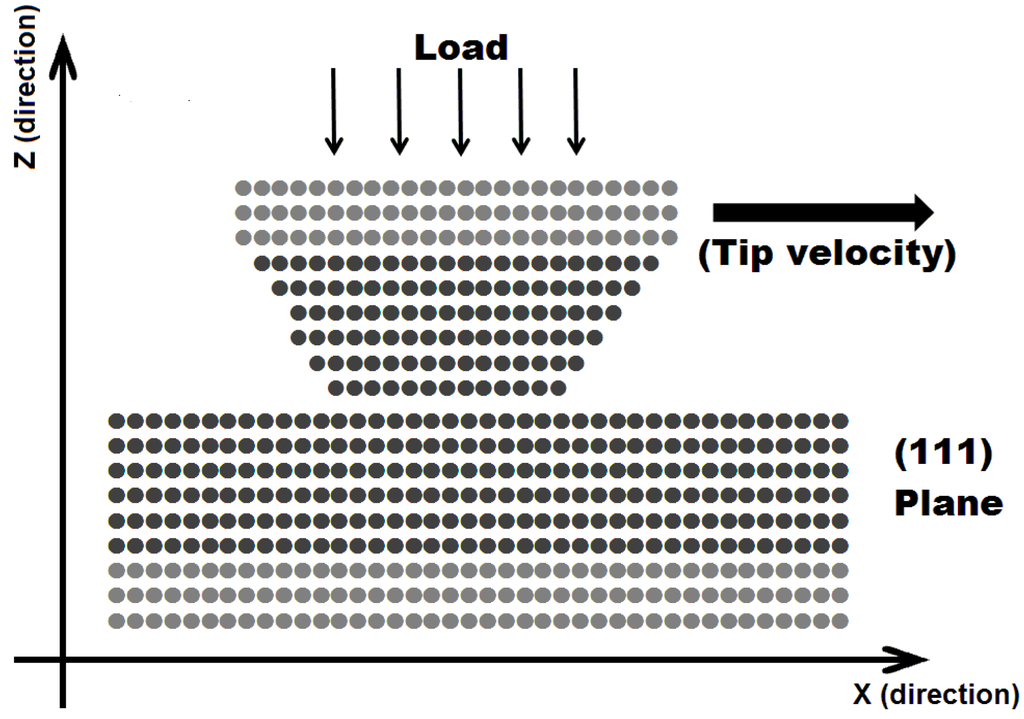
Figure 1.
Two-dimensional cartoon of the actual three-dimensional atomic system. The speed of the tip was consistently 1m/s, and the temperature 1K. Data was collected during 1.6 ns with a time resolution of 4 fs. The light gray atoms behave as follows. The lowest three atomic planes (in the slab) were kept fixed. The upper three atomic planes (in the tip) were rigidly moved at constant velocity. The dark gray atoms are externally unrestricted. They move according to the Molecular Dynamic algorithm. For each time step, we collect the instantaneous friction force. The program is run for tips of orientations varying in 1° angular increments to simulate the rearrangement of the apex atoms during sliding.
2.2. Stick-Slip Statistics
Using MD as described in Section 2.1, we monitor the instantaneous frictional force as the top layers of the tip are pulled at a constant velocity. A typical friction-vs-displacement curve is shown in Figure 2, where one sees the avalanche behavior characteristic of SOC in dry friction.
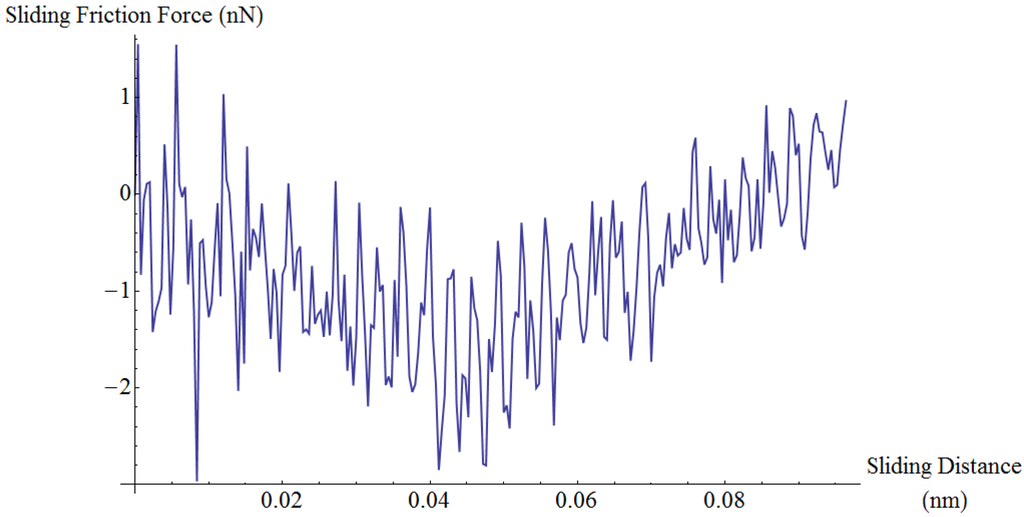
Figure 2.
Representative friction force versus time trace. In this case, the result corresponds to a copper tip and a copper sample at T = 1 K, with load 1 nN, tip speed 1 m/s and time resolution 4 fs.
In this case, the avalanches are in the form of stick-slip events of different sizes. We analyze the probability distribution of such events (jumps) by looking at the histograms of jumps. We will see in the Results section, that these probability distributions follow power laws with fractional exponents in all cases, necessary signatures of SOC. Specifically, we test whether:
where P(J) is the probability density of the jump size J. If indeed such a power law exists, the parameter α is expected to be positive, indicating the decreasing probability of finding increasingly larger events. As explained in [32], Equation (1) describes the probability of J in a range [Jmin, Jmax]. There must be a lower bound Jmin, to avoid divergences of Equation (1), and also because there is a resolution limit in any experiment. The upper bound Jmax is related with the necessarily finite size of the sample, which makes large events very rare and thus renders impossible any statistical analysis in that region. Thus, as is the case with many other power laws in Nature, we must search for indications of Equation (1) in a finite central range of J.
P(J) ~ J−α
2.3. Tip-Sample Entropy
If SOC is indeed happening, as suggested by the power law probability distributions of the stick-slip jumps, one is immediately prompted to enquire into the nature of the attractor. In other words, in this non-equilibrium system, how this steady state is approached, and what microscopic intuition can be developed. To this end, we monitor the jittering of the atoms during sliding, and ask whether there is a global trend. Specifically, at each instant of time, we calculate the vertical displacement of each atom with respect to a fixed position, in the reference frame moving at the constant velocity equal to the externally applied sliding velocity. Then, at each time step, we compute the entropy content of the whole system. This is done by first constructing the histogram of vertical positions zi(t), where i labels each atom in the system, and this is done at each instant of time. From zi(t), we produce a histogram of heights from which we obtain the probability πi(t) of getting zi at time t. Finally, the entropy is computed thus:
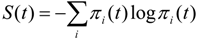
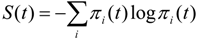
Since the system is small, of nanometer dimensions, this entropy measure should provide a spatially localized characterization of the attractor.
3. Results
We show first the probability of jumps histograms for a copper tip on a copper substrate, and for an aluminum tip on an aluminum substrate for various normal loads.
3.1. Probability of Jumps
From the MD friction force traces (such as in Figure 2), we extract the force sudden changes and compute their probability distributions. As explained in the previous section and is typical of power law behavior, we find in all cases a range [Jmin, Jmax] within which the jumps J are well characterized by power law probability densities. In Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5 we show these results for an aluminum tip sliding on an aluminum substrate, subjected to normal loads of 1.0, 1.5 and 2.0 nN. The corresponding exponents are (the α in Equation (1)) are 1.40, 0.99, 1.00 respectively. Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8 show similar results, this time for copper. The loads are also 1.0, 1.5 and 2.0 nN, while the corresponding exponents are 0.64, 1.16 and 0.74. This lack of correlation between the exponents and load and material (Table 1) has been noticed and reported in the past [20,21]. Yet, the results are consistent with the existence of power laws in all cases studied which suggests Self Organized Criticality, and begets the question: what is the attractor? That will be addressed in the next subsection.

Figure 3.
Histogram in log-log scale of friction force jumps. The probability in the vertical axes is not normalized. Aluminum on aluminum at an external normal load of 1nN. The exponent of the power law, extracted from the blue region of the data is – 1.40.

Table 1.
Power exponents of the stick-slip jump force probability distribution with fractional values in the range (0.5, 1.5).
| Load | Material | |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Copper | |
| 1.0 nN | 1.40 | 0.64 |
| 1.5 nN | 0.99 | 1.16 |
| 2.0 nN | 1.00 | 0.74 |
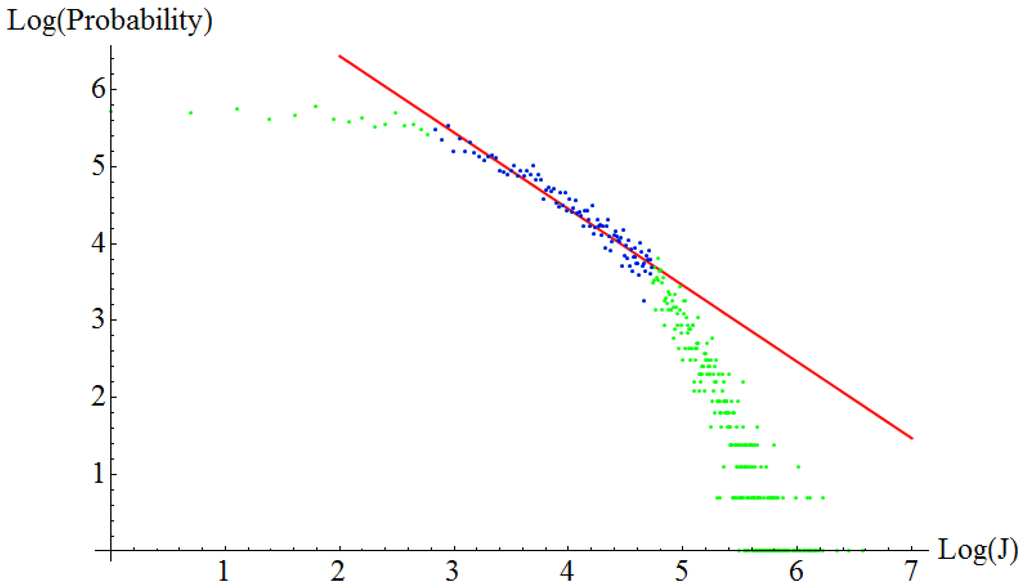
Figure 4.
Histogram in log-log scale of friction force jumps. Aluminum on aluminum at an external normal load of 1.5 nN. The exponent of the power law, extracted from the blue region of the data is – 0.99.
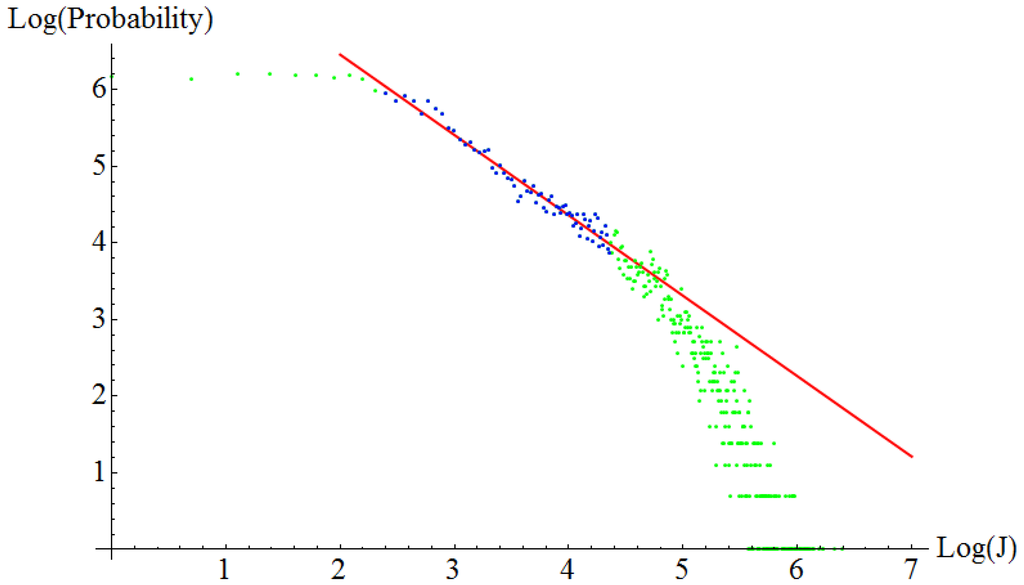
Figure 5.
Histogram in log-log scale of friction force jumps. Aluminum on aluminum at an external normal load of 2.0 nN. The exponent of the power law, extracted from the blue region of the data is – 1.00.
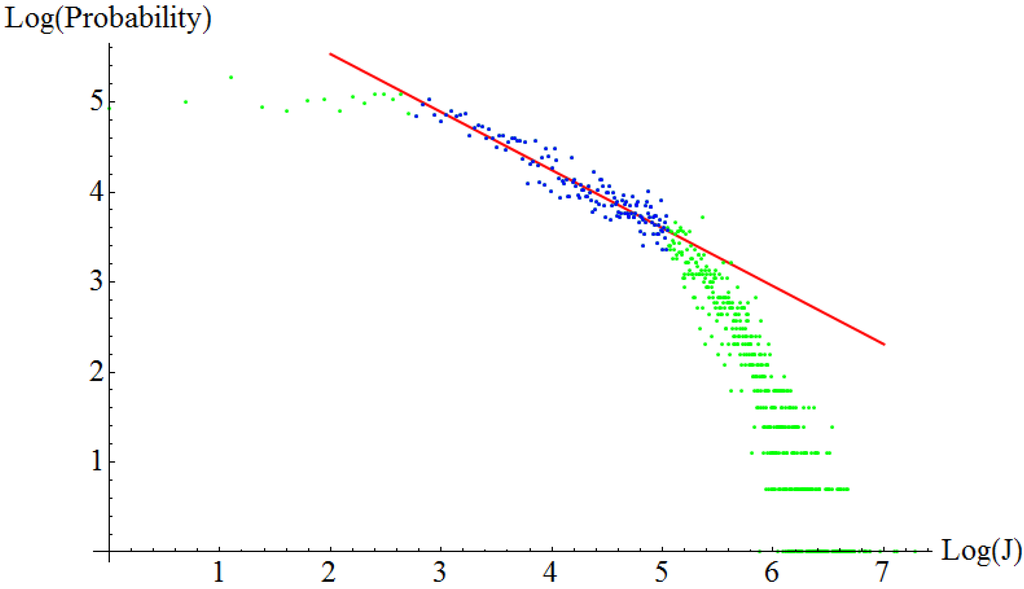
Figure 6.
Histogram in log-log scale of friction force jumps. Copper on copper at an external normal load of 1.0 nN. The exponent of the power law, extracted from the blue region of the data is – 0.64.
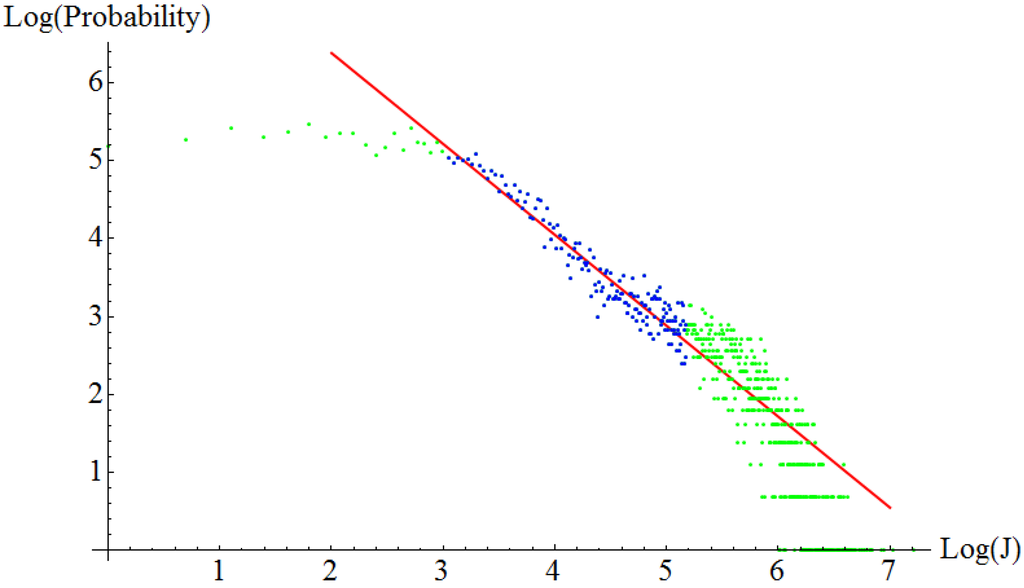
Figure 7.
Histogram in log-log scale of friction force jumps. Copper on copper at an external normal load of 1.5nN. The exponent of the power law, extracted from the blue region of the data is – 1.16.
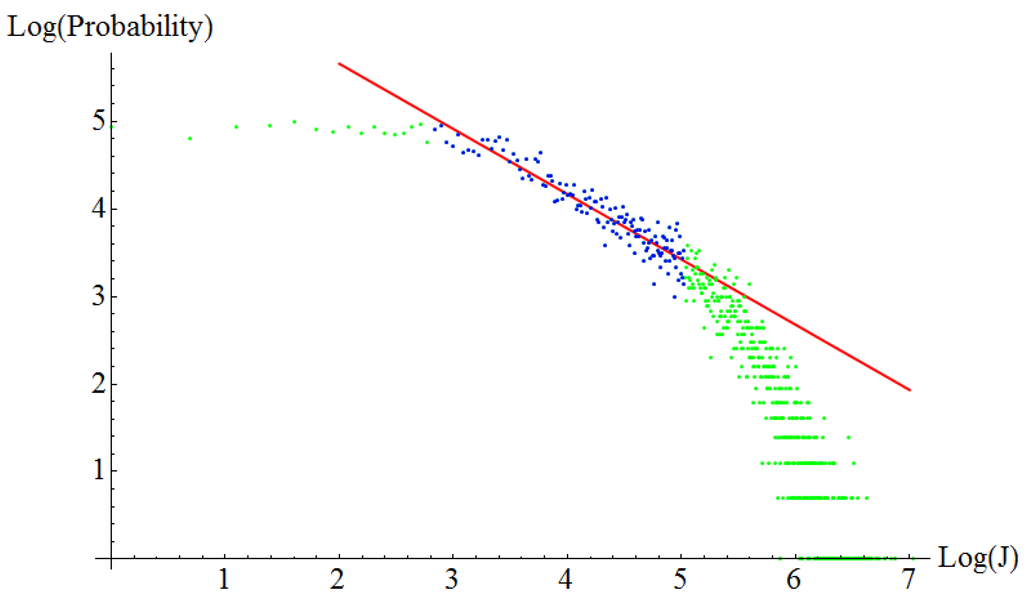
Figure 8.
Histogram in log-log scale of friction force jumps. Copper on copper at an external normal load of 2.0nN. The exponent of the power law, extracted from the blue region of the data is – 0.74.
3.2. Entropy of Jittering
With the indication of Self Organized Criticality in Section 3.2, we search for the attractor. Since this is a system in constant motion far from equilibrium, the attractor cannot be a fixed point in phase space. Instead, we conceptually think of this attractor as a global motion of the atoms of the system, as if dancing in concert. Specifically, we monitor the jittering of all atoms measured with respect to their initial positions in the moving reference frame. At each time step, we consider the collection of the vertical displacement of all the atoms. Thereafter, we compute the entropy (Equation (2)) of that collection, and observe its evolution with time. For all the six cases considered (aluminum and copper under different normal loads) the qualitative behavior is the same: the entropy decreases as a function of time (Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14). This is a direct observation of self-organization as smaller entropies indicate. In addition, the large time small entropy proves to be a proper label for the attractor.
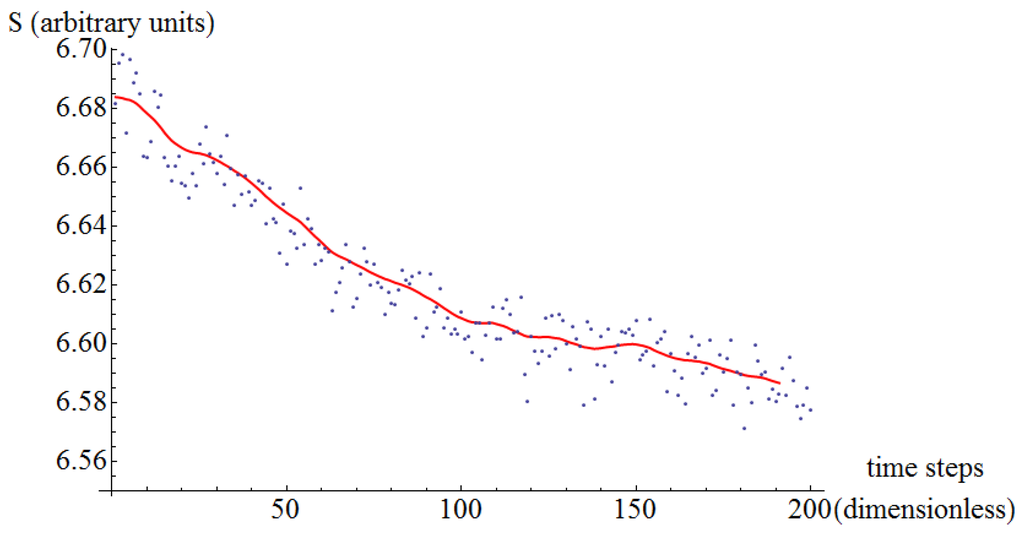
Figure 9.
Entropy of jittering as a function of time. Aluminum on aluminum at an external normal load of 1 nN. The scattered points are the actual values measured, while the continuum line is a moving average to aid the eye see the trend.
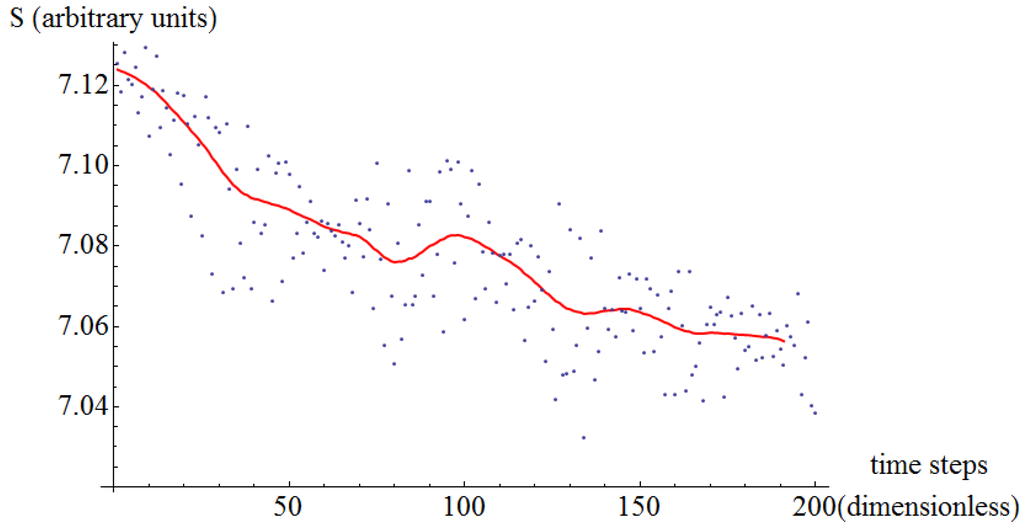
Figure 10.
Entropy of jittering as a function of time. Aluminum on aluminum at an external normal load of 1.5 nN.
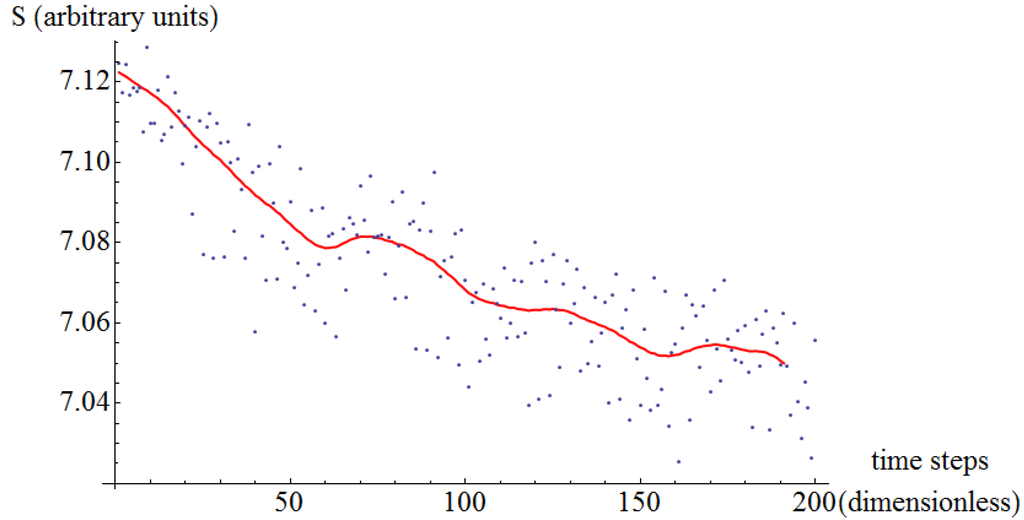
Figure 11.
Entropy of jittering as a function of time. Aluminum on aluminum at an external normal load of 2 nN.
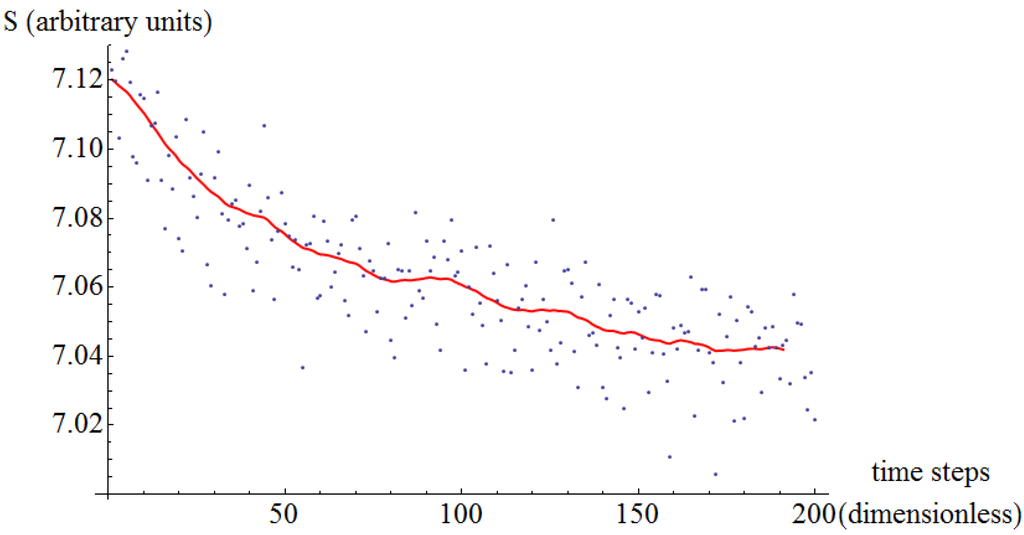
Figure 12.
Entropy of jittering as a function of time. Copper on copper at an external normal load of 1 nN.
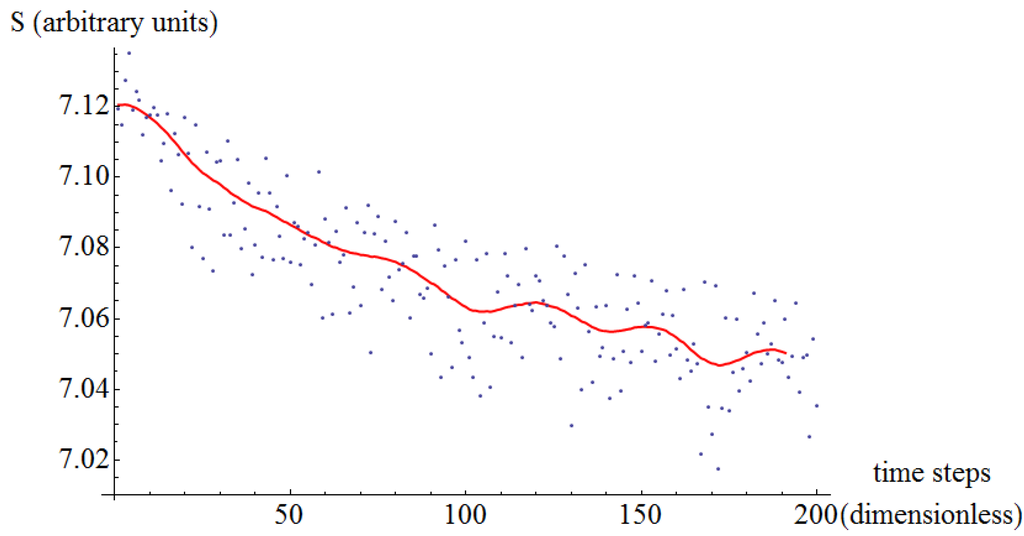
Figure 13.
Entropy of jittering as a function of time. Copper on copper at an external normal load of 1.5 nN.
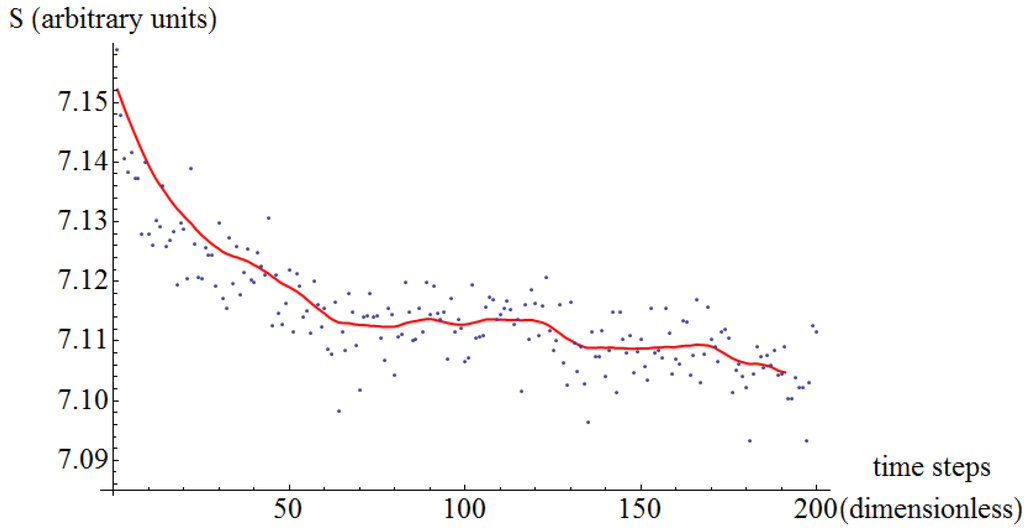
Figure 14.
Entropy of jittering as a function of time. Copper on copper at an external normal load of 2 nN.
4. Conclusions
We have performed Molecular Dynamics computer experiments on atomic clusters to obtain the individual motion of all atoms during stick-slip dry friction motion. We considered aluminum and copper systems under various normal loads and found in all cases power law statistics which strongly suggests Self Organized Criticality. We backed up this suspicion by directly analyzing the jittering of all atoms in the system. This jittering was quantified by measuring its entropy content. In all cases studied, we found that the entropy decreases with time, which directly shows that friction tends to self organize the system. Also, the asymptotic value of the entropy at large times can be used as a label to characterize the attractor in steady state. Molecular Dynamics allows us to monitor the motion of each individual atom, in particular in the attractor state. Although this can be computed, our brain cannot comprehend such vast number of varying coordinates. However, it is as if, in steady state the atoms form a chorus that sings their entropy value, a concept simple to grasp.
Acknowledgments
Work supported by the Jay and Jeanie Schottenstein Program of Yeshiva University and by the Gamson Fund.
Author Contributions
F.Z. conceived and designed the numerical experiments; P.C. performed the numerical experiments; F.Z. wrote the paper; P.C. read and commented on the paper and prepared the figures; P.C. and F.Z. analyzed the data. Both authors have read and approved the final published manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Baumberger, T. Dry Friction Dynamics at Low Velocities. In Physics of Sliding Friction; NATO ASI Series; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 311, pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden, F.P.; Tabor, D. The Friction and Lubrication of Solids; Oxford University: New York, NY, USA, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Nosonovsky, M.; Mortazavi, V. Friction-Induced Vibrations and Self-Organization; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Trabesinger, A. Complexity. Nat. Phys. 2012, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpick, R.W.; Salmeron, M. Scratching the Surface: Fundamental Investigations of Tribology with Atomic Force Microscopy. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 1163–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykara, M.Z.; Schwarz, U.D. Noncontact atomic force microscopy II. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.; Krim, J. Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM) Applications to Tribology. In Encyclopedia of Tribology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 2727–2733. [Google Scholar]
- Israelachvili, J. Intermolecular and Surface Forces, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb, S.; Sterling, T. Exascale Computing. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2013, 15, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Plimpton, S.J.; Thompson, A.P. Computational Aspects of Many-body Potentials. MRS Bull. 2012, 37, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, C.A.; Tavazza, F.; Trautt, Z.T.; Buarque de Macedo, R.A. Considerations for choosing and using force fields and interatomic potentials in materials science and engineering. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2013, 17, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, J.N.; Langer, J.S. Properties of earthquakes generated by fault dynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1989, 62, 2632–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, J.M.; Langer, J.S.; Shaw, B.E. Dynamics of earthquake faults. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1994, 66, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burridge, R.; Knopoff, L. Model and theoretical seismicity. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1967, 57, 3411–3471. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, J.N.; Langer, J.S.; Shaw, B.E.; Tang, C. Intrinsic properties of a Burridge-Knopoff model of an earthquake fault. Phys. Rev. A 1991, 44, 884–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.S.; Gershman, I.S.; Yamamoto, K.; Biksa, A.; Veldhuis, S.C.; Beake, B.D.; Kovalev, A.I. Self-Organization during Friction in Complex Surface Engineered Tribosystems. Entropy 2010, 12, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, E. Turing Systems, Entropy, and Kinetic Models for Self-Healing Surfaces. Entropy 2010, 12, 554–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosonovsky, M. Entropy in Tribology: in the Search for Applications. Entropy 2010, 12, 1345–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LAMMPS Molecular Dynamics Simulator. Available online: http://lammps.sandia.gov/ (accessed on 28 May 2014).
- Zypman, F.; Ferrante, J.; Jansen, M.; Scanlon, K.; Abel, P. Evidence of self-organized criticality in dry sliding friction. J. Phys. Cond. Matt. Lett. 2003, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, M.; Ferrante, J.; Schilowitz, A.; Yablon, D.; Zypman, F. Self-organized criticality in nanotribology. In MRS Proceedings; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; Volume 782. [Google Scholar]
- Buldyrev, J.; Ferrante, F.; Zypman, F. Dry friction avalanches: Experiment and theory. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 74, 066110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleurquin, P.; Fort, H.; Kornbluth, M.; Sandler, R.; Segall, M.; Zypman, F. Negentropy generation and fractality in dry friction of polished surfaces. Entropy 2010, 12, 480–489. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, T.; Stoll, E. Molecular-dynamics study of a three-dimensional one-component model for distortive phase transitions. Phys. Rev. B 1978, 17, 1302–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, C.C. Qualitative dynamics of generalized Langevin equations and the theory of chemical reaction rates. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 116, 2516–2528. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Quantum Thermal Transport from Classical Molecular Dynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 160601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantorovich, L. Generalized Langevin equation for solids I. Rigorous derivation and main properties. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 094304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyna, G.J.; Tobias, D.J.; Klein, M.L. Constant pressure molecular dynamics algorithms. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 101, 4177–4189. [Google Scholar]
- Feller, S.E.; Zhang, Y.; Pastor, R.W.; Brooks, B.R. Constant pressure molecular dynamics simulation: The Langevin piston method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 4613–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daw, M.S.; Baskes, M. Embedded-atom method: Derivation and application to impurities, surfaces, and other defects in metals. Phys. Rev. B 1984, 29, 6443–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plimpton, S.J. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauset, A.; Shalizi, C.R.; Newman, M.E.J. Data Analysis, Statistics and Probability. SIAM Rev. 2009, 51, 661–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).