Removal of Chromium(VI) from Contaminated Water Using Untreated Moringa Leaves as Biosorbent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
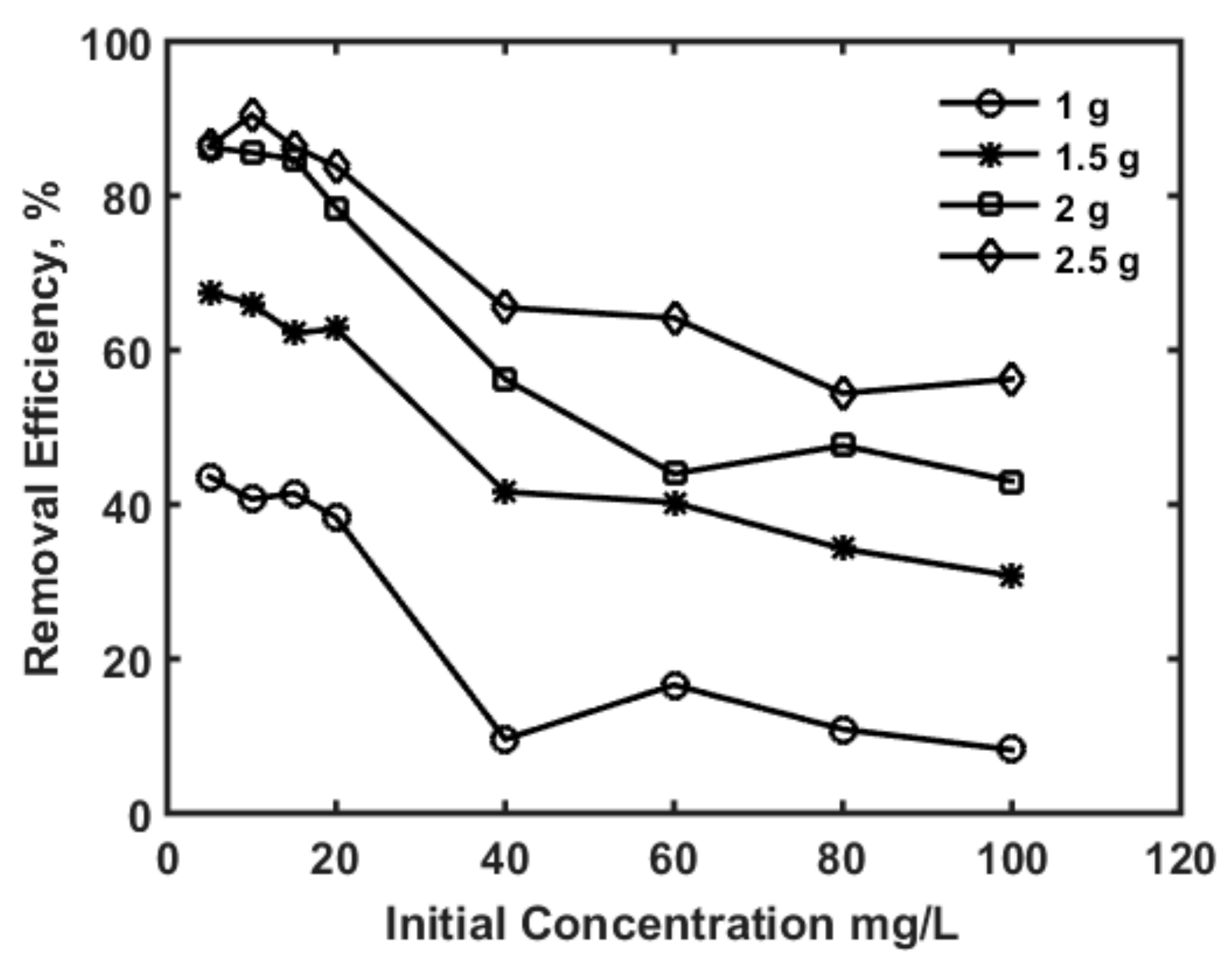
3.1. Adsorption Isotherms and Kinetics Modelling
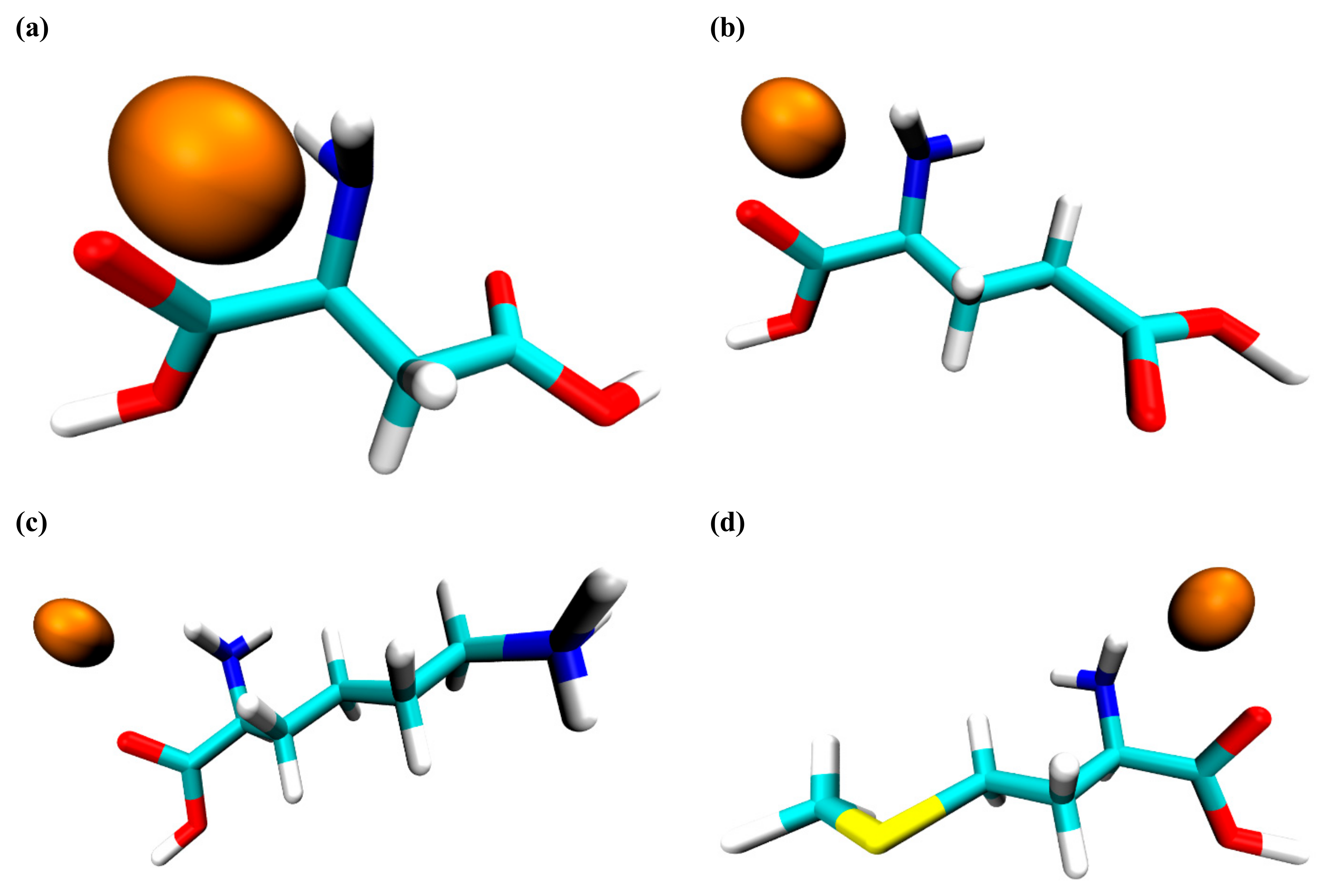
3.2. Docking Simulation Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, K.; Renu, N.; Agarwal, M. Methodologies for Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewater: An Overview. Interdi. Engironm. Rev. 2017, 18, 124–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Li, X. Bioreduction of Chromium (VI) By Bacillus Sp. Isolated from Soils of Iron Mineral Area. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2009, 45, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shen, H.; Pan, S.; Hu, M. Synthesis, Characterization and Properties of Ethylenediamine-Functionalized Fe3O4 Magnetic Polymers for Removal of Cr (VI) In Wastewater. J. Hazard Mater. 2010, 182, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinuthia, G.K.; Ngure, V.; Beti, D.; Lugalia, R.; Wangila, A.; Kamau, L. Levels of heavy metals in wastewater and soil samples from open drainage channels in Nairobi, Kenya: Community health implication. Sci Rep. 2020, 10, 8434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golbaz, S.; Jafari, A.; Rafiee, M.; Kalantary, R. Separate and Simultaneous Removal of Phenol, Chromium, and Cyanide from Aqueous Solution by Coagulation/Precipitation: Mechanisms and Theory. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 253, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittert, I.; de Lima Brandão, H.; Pina, F.; da Silva, E.; de Souza, S.; de Souza, A.; Botelho, C.; Boaventura, R.; Vilar, V. Integrated Reduction/Oxidation Reactions And Sorption Processes For Cr(VI) Removal From Aqueous Solutions Using Laminaria Digitata Macro-Algae. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 237, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gładysz-Płaska, A.; Majdan, M.; Pikus, S.; Sternik, D. Simultaneous Adsorption of Chromium (VI) and Phenol on Natural Red Clay Modified By HDTMA. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 179, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaco, S.; Fernandes, S.; Quina, M.; Ferreira, L. Removal of Chromium from Electroplating Industry Effluents by Ion Exchange Resins. J. Hazard Mater. 2007, 144, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Xu, X.; Papelis, C.; Cath, T.; Xu, P. Sorption of Metals and Metalloids from Reverse Osmosis Concentrate on Drinking Water Treatment Solids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 134, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, S.; El-Naas, M. Characterization of the Removal of Chromium (VI) from Groundwater by Electrocoagulation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2775–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yue, Q.; Mao, Y.; Gao, B.; Gao, Y.; Huang, L. Enhanced Adsorption of Chromium onto Activated Carbon by Microwave-Assisted H3PO4 Mixed with Fe/Al/Mn Activation. J. Hazard Mater. 2014, 265, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pehlivan, E.; Cetin, S. Sorption of Cr (VI) Ions on Two Lewatit-Anion Exchange Resins and Their Quantitative Determination Using UV–Visible Spectrophotometer. J. Hazard Mater. 2009, 163, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Gu, Z.; Gang, D.; Liu, C.; Ilton, E.; Deng, B. Cr (VI) Removal from Aqueous Solution by Activated Carbon Coated with Quaternized Poly(4-Vinylpyridine). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4748–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankararamakrishnan, N.; Jaiswal, M.; Verma, N. Composite Nanofloral Clusters of Carbon Nanotubes and Activated Alumina: An Efficient Sorbent For Heavy Metal Removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 235, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Dai, R.; Lan, Y. Rapid Reduction of Cr(VI) Coupling with Efficient Removal of Total Chromium in the Coexistence of Zn(0) and Silica Gel. J. Hazard Mater. 2012, 243, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, N.; El-Wakeel, S.; Abd El-Latif, R. Biosorption and Desorption Studies on Chromium(VI) by Novel Biosorbents of Raw Rutin And Rutin Resin. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.; Mudhoo, A.; Lofrano, G.; Chattopadhyaya, M. Biomass-Derived Biosorbents for Metal Ions Sequestration: Adsorbent Modification and Activation Methods and Adsorbent Regeneration. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liao, M.; Zeng, H.; Xu, S.; Liu, X.; Du, J.; Zhu, P.; Huang, Q. Temperature Effect On Chromium(VI) Removal By Mg/Al Mixed Metal Oxides As Adsorbents. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 102, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaumik, M.; Leswifi, T.; Maity, A.; Srinivasu, V.; Onyango, M. Removal of Fluoride from Aqueous Solution by Polypyrrole/Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanocomposite. J. Hazard Mater. 2011, 186, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogeshwaran, V.; Priya, A.K. Removal of Hexavalent Chromium by Adsorption Using Natural Wastes-A Review. Adv. Recycl. Waste Manag. 2017, 2, 1000141. [Google Scholar]
- AL-Othman, Z.; Ali, R.; Naushad, M. Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Aqueous Medium by Activated Carbon Prepared From Peanut Shell: Adsorption Kinetics, Equilibrium and Thermodynamic Studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 184, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALOthman, Z.; Naushad, M.; Ali, R. Kinetic, Equilibrium Isotherm and Thermodynamic Studies of Cr(VI) Adsorption Onto Low-Cost Adsorbent Developed from Peanut Shell Activated with Phosphoric Acid. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R 2013, 20, 3351–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Ke-hong, L.; Qi, L.; Ju, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H. Superfine grinding affects physicochemical, thermal and structural properties of Moringa Oleifera leaf powders. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 151, 112472. [Google Scholar]
- Cuellar-Nuñez, M.L.; Luzardo-Ocampo, I.; Campos-Vega, R.; Gallegos-Corona, M.A.; González de Mejía, E.; Loarca-Piña, G. Physicochemical and nutraceutical properties of moringa (Moringa oleifera) leaves and their effects in an in vivo AOM/DSS-induced colorectal carcinogenesis model. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, G.; Priyadarsini, K.; Satav, J.; Banavalikar, M.; Sohoni, D.; Biyani, M.; Mohan, H. Comparative Antioxidant Activity Of Individual Herbal Components Used In Ayurvedic Medicine. Phytochemistry 2003, 63, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naznin, A.; Mamunur, R.; Amran, M. Comparison of Leaves Extract with Atenolol on Serum Triglyceride, Serum Cholesterol, Blood Glucose, Heart Weight, Body Weight in Adrenaline Induced Rats. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 15, 253–258. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, D.; Ramana, D.; Seshaiah, K.; Reddy, A. Biosorption Of Ni(II) from Aqueous Phase by Moringa Oleifera Bark, a Low Cost Biosorbent. Desalination 2011, 268, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, V.; Coelho, N. Selective Extraction And Preconcentration Of Chromium Using Moringa Oleifera Husks As Biosorbent And Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2013, 109, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obuseng, V.; Nareetsile, F.; Kwaambwa, H. A Study Of The Removal Of Heavy Metals From Aqueous Solutions By Moringa Oleifera Seeds And Amine-Based Ligand 1,4-Bis[N,N-Bis(2-Picoyl)Amino]Butane. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 730, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, D.; Harinath, Y.; Seshaiah, K.; Reddy, A. Biosorption Of Pb(II) From Aqueous Solutions Using Chemically Modified Moringa Oleifera Tree Leaves. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aja, P.; Nwachukwu, N.; Ibiam, U.; Igwenyi, I.; Offor, C.; Orji, U. Chemical Constituents of Moringa Oleifera Leaves and Seeds From Abakaliki, Nigeria. Am. J. Phytomedicine Clin. Ther. 2014, 3, 310–321. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Balomajumder, C. Removal of Cr(VI) and Phenol Using Water Hyacinth from Single and Binary Solution in the Artificial Photosynthesis Chamber. J. Water Process. Eng. 2015, 7, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venditti, F.; Cuomo, F.; Ceglie, A.; Ambrosone, L.; Lopez, F. Effects of Sulfate Ions and Slightly Acidic Ph Conditions on Cr(VI) Adsorption onto Silica Gelatin Composite. J. Hazard Mater. 2010, 173, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, B.; Gill, R.; Bailey, D.; Kabay, N.; Arda, M. Sorption of Cr(VI) From Aqueous Solution by Amberlite XAD-7 Resin Impregnated with Aliquat 336. React. Funct. Poly. 2004, 60, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ege, S. Organic Chemistry: Structure and ReactiVity, 4th ed.; Houghton Mifflin Co.: Boston, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, R.; Bilehal, D.; Nandibewoor, S. Oxidation of Isoniazid by Quinolinium Dichromate in an Aqueous Acid Medium and Kinetic Determination of Isoniazid in Pure and Pharmaceutical Formulations. Anal. Sci. 2004, 20, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Al-Abadleh, H.; Mifflin, A.; Bertin, P.; Nguyen, S.; Geiger, F. Control of Carboxylic Acid and Ester Groups on Chromium (VI) Binding to Functionalized Silica/Water Interfaces Studied by Second Harmonic Generation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 9691–9702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmuir, I. The Constitution and Fundamental Properties of Solids and Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Über Die Adsorption in Lösungen. Z. Für. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redlich, O.; Peterson, D. A Useful Adsorption Isotherm. J. Phys Chem. 1959, 63, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.; Chakravorti, R. Pore And Solid Diffusion Models For Fixed-Bed Adsorbers. AIChE J. 1974, 20, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur Theorie Der Sogenannten Adsorption Gelöster Stoffe. K. Sven. Vetensk. Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y. Second-Order Kinetic Model for the Sorption of Cadmium onto Tree Fern: A Comparison of Linear and Non-Linear Methods. Water Res. 2006, 40, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A. Autodock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with A New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual Molecular Dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RCSB PDB. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Morris, G.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.; Belew, R.; Goodsell, D.; Olson, A. Autodock4 And Autodocktools4: Automated Docking with Selective Receptor Flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Gu, J. Reduction of Hexavalent Chromium by Ascorbic Acid In Aqueous Solutions. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
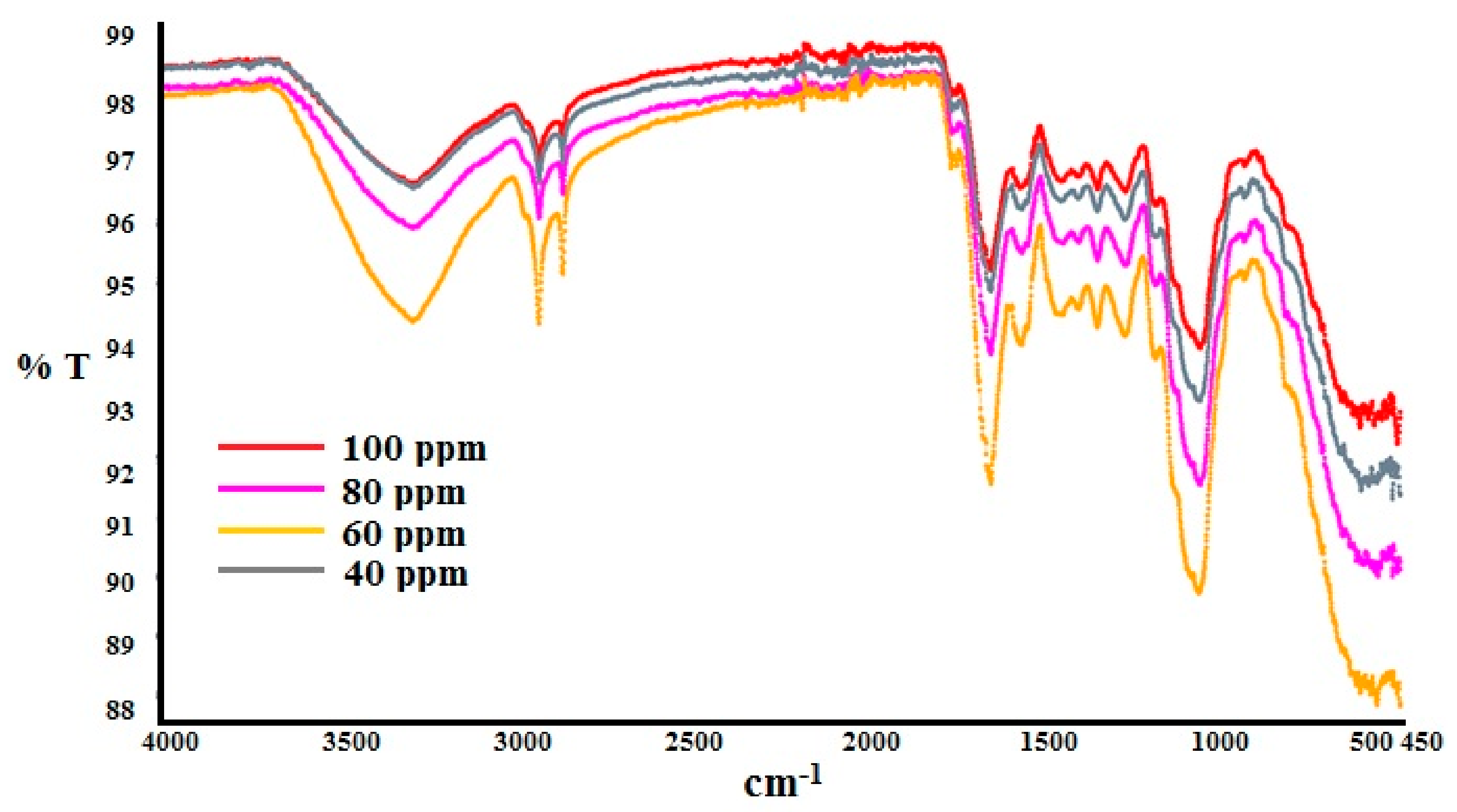
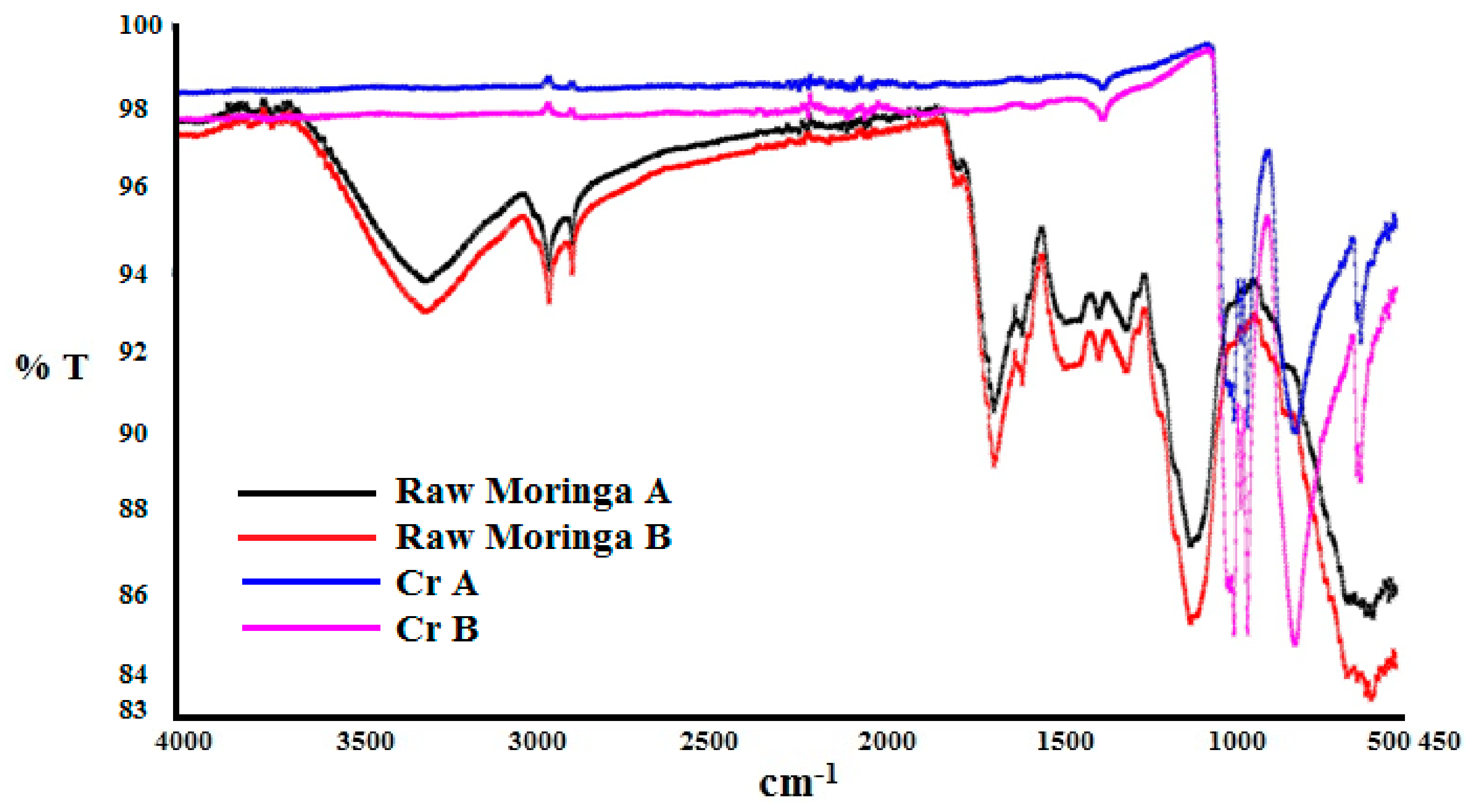
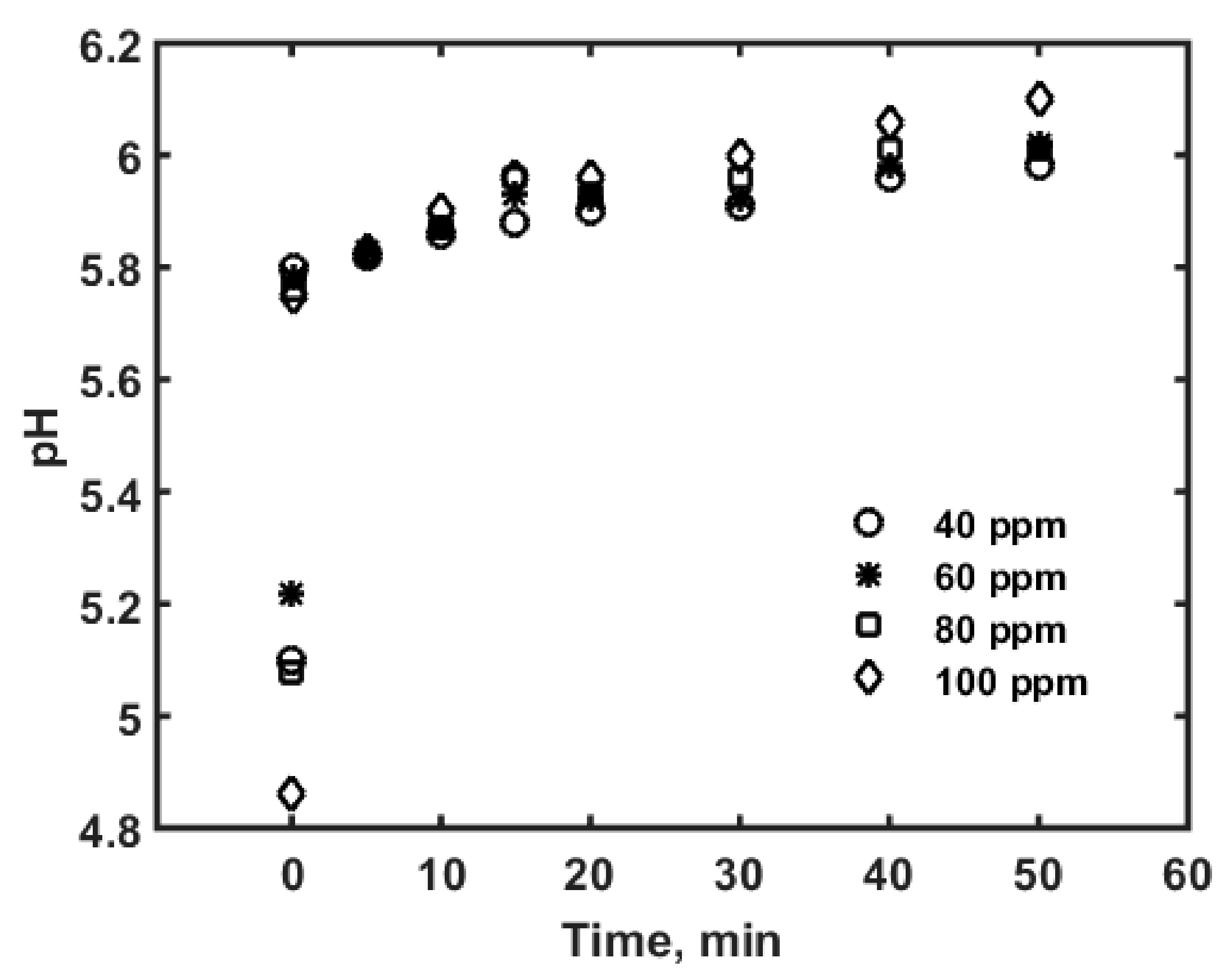
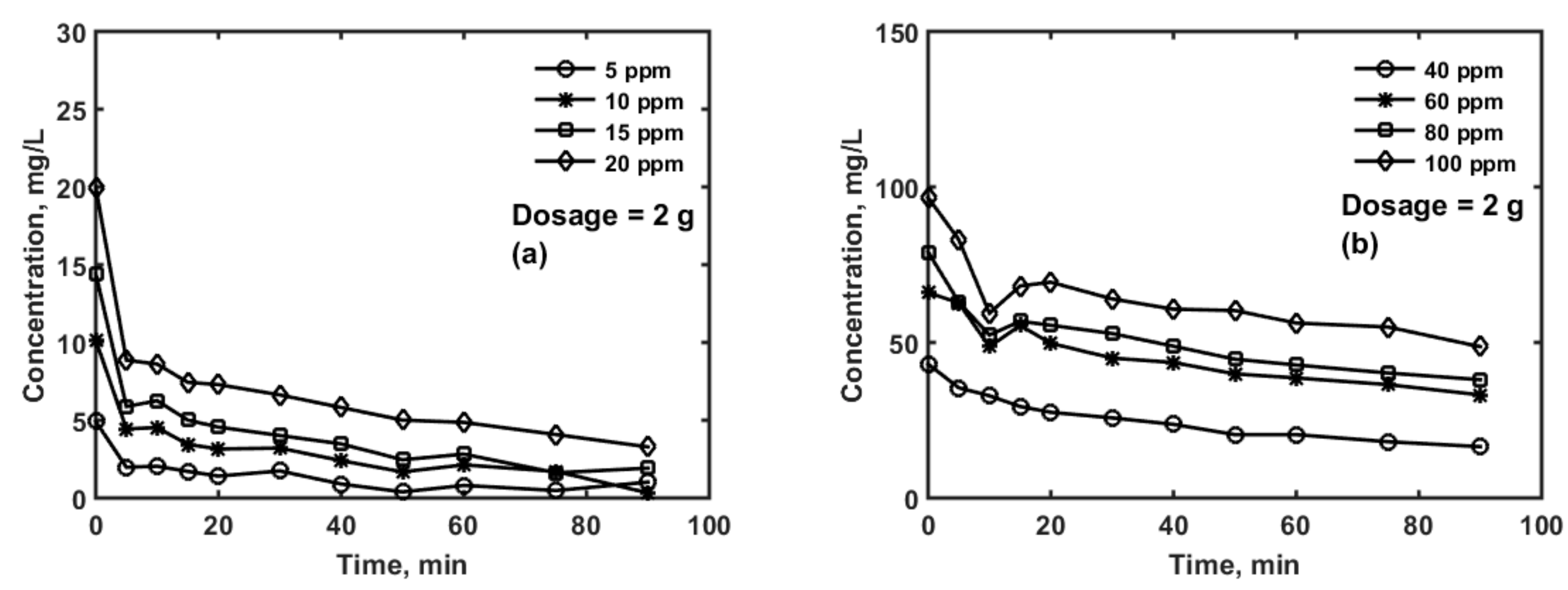
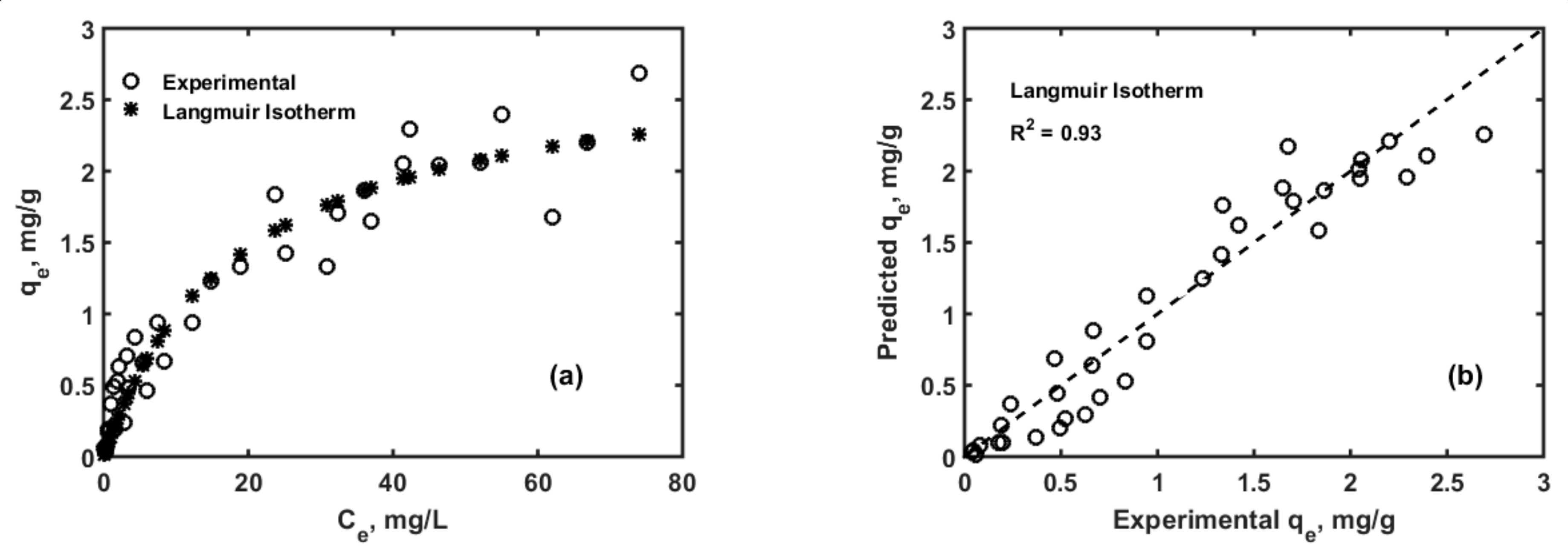
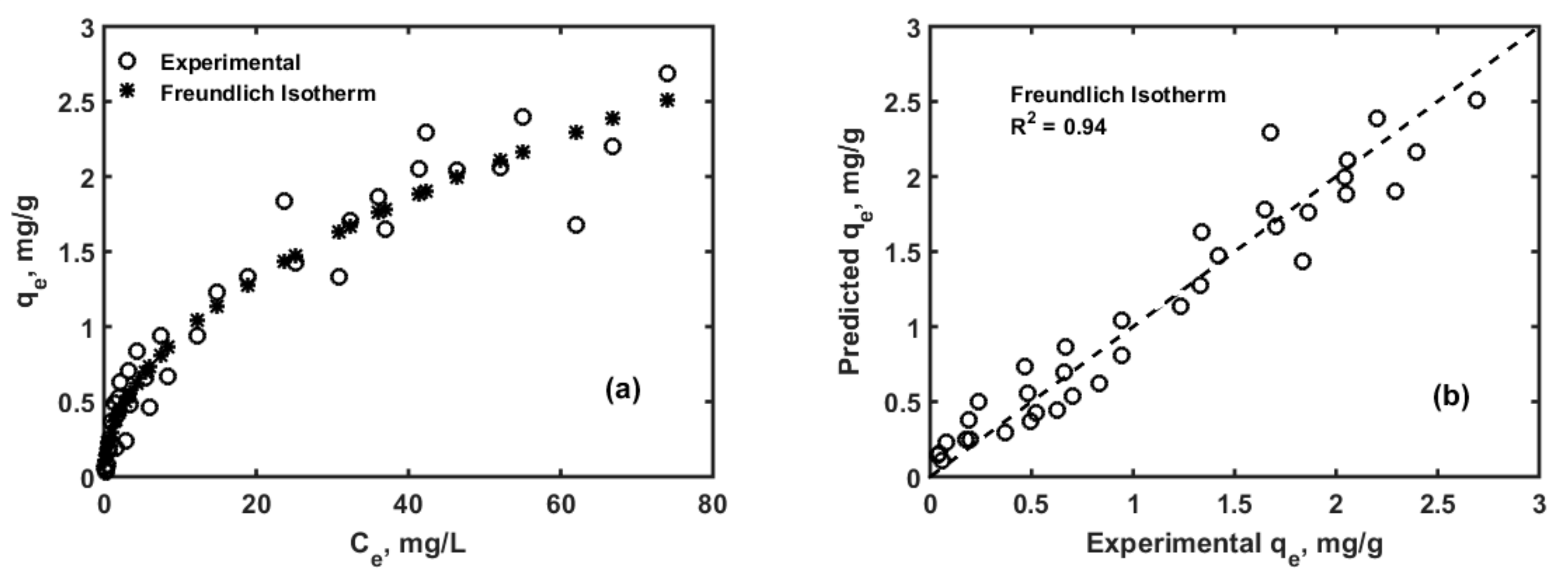
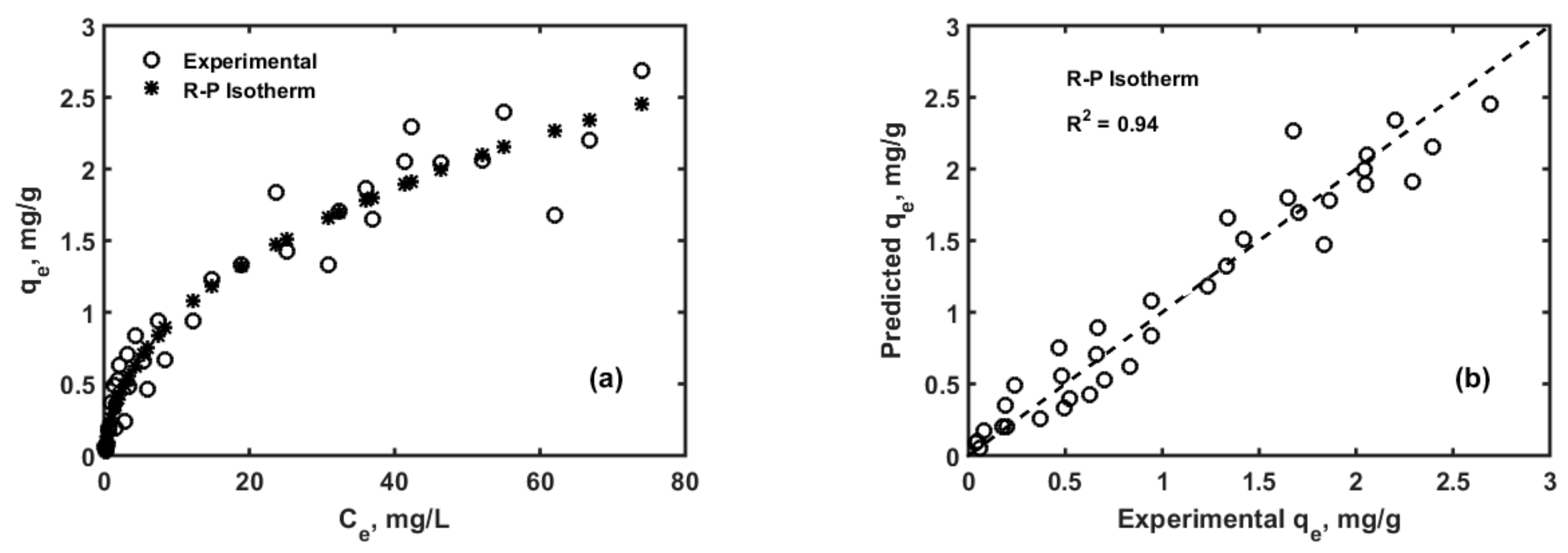
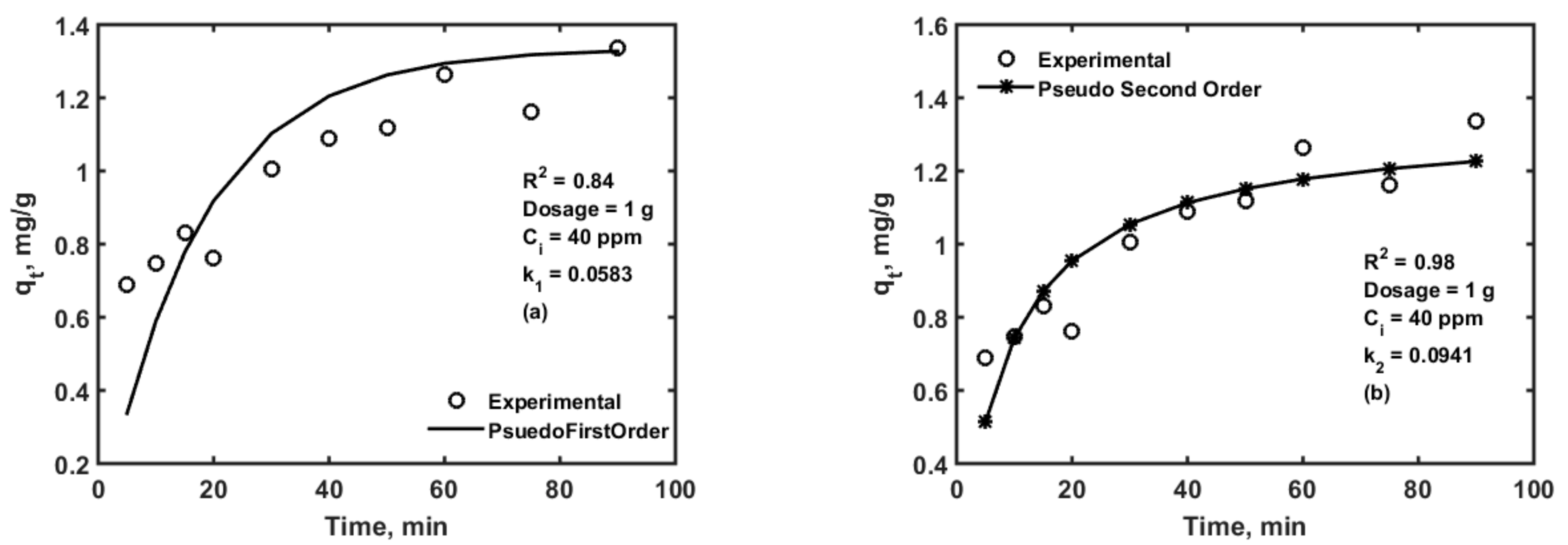
| Parameter | Values | 99% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|
| kL | 0.0535 | 0.0316 | 0.0753 |
| qm | 2.8293 | 2.4015 | 3.2570 |
| kF | 0.3029 | 0.2271 | 0.3787 |
| n | 2.0368 | 1.7546 | 2.3190 |
| kRP | 0.5907 | 0.0000 | 1.8929 |
| αRP | 1.2840 | 0.0000 | 5.3536 |
| β | 0.5981 | 0.3780 | 0.8181 |
| Component | Docking Score or Affinity (kcal/mol) | No. of Highest Score Docked Sites and Its Corresponding Site Group | Docked Structure  |
|---|---|---|---|
| Valine | −0.5 | 1 site, carboxyl group | 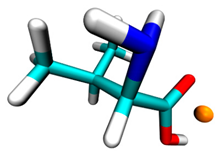 |
| Tyrosine | −0.5 | 1 site, carboxyl group | 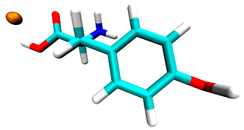 |
| Proline | −0.5 | 1 site, carboxyl group | 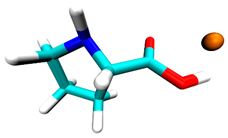 |
| Methionine | −0.5 | 1 site, carboxyl group | 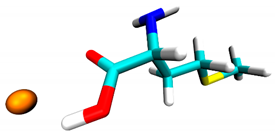 |
| Lysine | −0.5 | 1 site, carboxyl group | 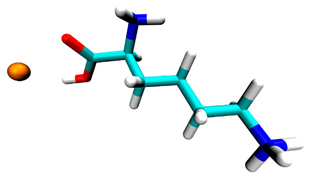 |
| Glutamic acid | −0.5 | 2 sites, carboxyl group | 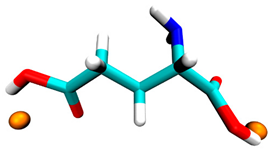 |
| Aspartic acid | −0.5 | 2 sites, carboxyl group | 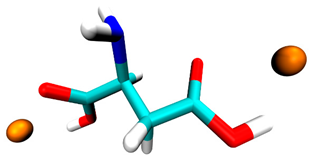 |
| Ascorbic acid | −0.6 | 4 sites, hydroxyl group | 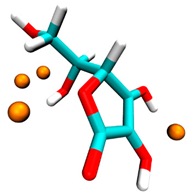 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madhuranthakam, C.M.R.; Thomas, A.; Akhter, Z.; Fernandes, S.Q.; Elkamel, A. Removal of Chromium(VI) from Contaminated Water Using Untreated Moringa Leaves as Biosorbent. Pollutants 2021, 1, 51-64. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants1010005
Madhuranthakam CMR, Thomas A, Akhter Z, Fernandes SQ, Elkamel A. Removal of Chromium(VI) from Contaminated Water Using Untreated Moringa Leaves as Biosorbent. Pollutants. 2021; 1(1):51-64. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants1010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadhuranthakam, Chandra Mouli R., Archana Thomas, Zhainab Akhter, Shannon Q. Fernandes, and Ali Elkamel. 2021. "Removal of Chromium(VI) from Contaminated Water Using Untreated Moringa Leaves as Biosorbent" Pollutants 1, no. 1: 51-64. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants1010005
APA StyleMadhuranthakam, C. M. R., Thomas, A., Akhter, Z., Fernandes, S. Q., & Elkamel, A. (2021). Removal of Chromium(VI) from Contaminated Water Using Untreated Moringa Leaves as Biosorbent. Pollutants, 1(1), 51-64. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants1010005






