Abstract
Online sources of information are a matter of special interest in tourism research. In particular, they are key elements in the formation of destination image. The purpose of this paper is to examine the relationship between online sources of information and destination image and to analyze the mediating role of motivation to co-create in that relationship. A research model was developed, and hypotheses were tested on data collected from 394 usable responses about the World Heritage city of Cuenca (Spain). The results show that online commercial sources have a direct positive impact on the conative, affective and cognitive dimensions of the tourist image, in this order. Additionally, this study supports the view that motivation to co-create mediates the relationship between online information sources and destination image. Finally, motivation to co-create was also found to have a positive and direct impact, in this order, on conative, cognitive and affective image. The main value of our research is that it underlines the essential influence of motivation to co-create in the relationship between online information sources and destination image. This study also provides a critical review of the existing literature by positing a conceptual theoretical framework that links three types of online sources of information (social media sources, online commercial sources and online non-commercial sources) and destination image.
1. Introduction
Tourists have traditionally relied on travel agencies, tour operators, brochures, travel guides, friends and family when planning a trip [1,2]. However, the proliferation and the development of online sources of information has drastically changed this paradigm. In addition to providing consumers with access to book and purchase a wide range of tourism products and services [3], online information sources have significantly transformed the way consumers gather information, make decisions and give their opinions about purchases [4,5].
In the tourism industry, this means that many tourists use online information sources to carry out activities such as choosing a destination or booking a table in a restaurant or a hotel room [6,7]. Moreover, the expansion of these online environments has allowed nearly anyone to publish information about a destination, and for travelers to check and share this information in real time. As a result, people’s decisions to visit and recommend a place are increasingly shaped by comments, ideas, photographs and videos that others upload to these sources [8].
In order to leverage these developments, companies use online information sources to develop direct relationships with travelers in the different phases of their journey. This process—known as value co-creation or the co-creation experience [9,10]—is a matter of special interest in the literature [11,12,13] and for the broader tourism sector. Specifically, co-creation has been posited as a necessary condition for competitiveness, due to the significant changes in tourism behavior [14] and a paradigm shift in how the tourism industry creates and offers experiences [15]. As a result of the use of these sources, the way a destination image is created has now changed, requiring a reinterpretation of who participates in the image-formation process, and how [16]. Thus, although Destination Marketing Organizations (DMOs) still play a significant role in the image process, this work is shared by other agents, including tourists. As a result of this sharing process, the image of a destination is now co-created [16].
Despite the growing number of articles about destination marketing [17], few have analyzed value co-creation in the tourism sector and its implications for companies [16,17,18]. On the one hand, many studies have analyzed the impact of the Internet and the mainstream media on destination image [2,19], and, on the other hand, the academic literature also recognizes online information sources as an important tool for enacting co-creation activities [20,21,22,23,24]. There is less research, however, on how co-creation generates value in the tourist experience [16] and the mechanisms underlying the relationship between online information sources and destination image. In this sense, few studies have analyzed how and why tourists engage in co-creation activities by using different types of online sources of information [25], while others have shown that the images perceived by tourists do not usually coincide with the images projected by providers and DMOs [26]. Few are the studies that treat online information sources as useful platforms for companies to strengthen the participation of users in the construction of the image [27]. Furthermore, it is crucial to know which sources are more important for individuals when making decisions about their travel plans [26].
Therefore, in order to cover this research gap, this article proposes to broaden the relationship between online information sources and destination image by incorporating the motivation to co-create as a mediating variable in the relationship that has not been examined in prior research. Examining why consumers engage in co-creation activities can guide companies to develop effective communication strategies with consumers in a way that creates superior value for themselves and for the company or destination itself [28]. Specifically, the study of motivation to co-create lacks sufficient understanding in the context of the destination image. Companies and promoters in charge of promoting a tourist destination typically use images that are not consistent with reality and provide little information about the destination [29]. In this sense, motivating consumers to share their experiences and perceptions about the destination can lead to a clearer and more coherent image being transmitted to other users, encouraging other travelers to visit the place. Most researchers have thus far been more concerned with understanding the effect of destination image on tourist behavior than with determining what influences the image [30]. Motivation is considered a key concept to understand consumer behavior in tourism and in the process of choosing a destination [31], and, in turn, the image of the destination is strongly related to motivation [32].
These main aims of this study were as follows: (1) We aimed to identify the influence of online information sources on destination image. We established a theoretical classification of online information sources (into social media sources, online commercial sources and online non-commercial sources) and considered three dimensions of destination image (cognitive, affective and conative). Online information sources refer to how important the source is for the individual to search for tourist information, and thus we intended to better understand “which” source has the strongest impact on destination image. (2) We aimed to determine the mediating role of motivation to co-create in the relationship between online information sources and destination image. Thus, the greater the importance of the source for the individual, the more motivated he/she will be to co-create. (3) We aimed to study the relationship between online information sources and motivation to co-create. Lastly, (4) we aimed to examine the effect of motivation to co-create on destination image.
This paper is organized as follows. Firstly, the conceptual framework of this paper, including the hypotheses proposed, is presented. Secondly, the article describes the research design and methodologies. Thirdly, based on the data collected in a survey about the Spanish World Heritage City of Cuenca, this paper presents the results of our analysis. We then discuss the main findings and conclusions. Finally, the article highlights research directions, limitations of the study and the most significant managerial and research implications of the results.
2. Conceptual Framework
2.1. Destination Image
Due to the dynamic and competitive environment of the tourism industry [33], destinations must create and promote a brand image that allows them to improve their positioning and emphasize their uniqueness [34]. The destination-image concept is framed within the destination branding strategy, considered a fundamental factor in the selection of a tourist destination [35]. At present, due to the current dynamic and competitive environment of the tourism industry, the image constitutes a key management tool [33], as it impacts the decision-making of tourists, the preferences for a destination and the level of satisfaction and future intention of behavior [36]. In other words, tourists who have a favorable image of a destination are more likely to visit or recommend it to others [37].
Since the term “destination image” was coined by Reference [38], it has been widely defined and studied by numerous researchers in the academic literature. However, to clarify its meaning, it should be differentiated from another of the key components that make up the destination brand, such as the identity of the destination, since both concepts have been widely debated in the academic literature in terms of their differences and similarities [39]. Thus, while destination identity refers to an infinite variety of tangible and intangible elements that characterize the place and make it characteristic or unique; destination image refers to the mental representation that an individual has about the knowledge (beliefs), feelings and global impression of a destination [40], that is, what tourists perceive and internalize [41].
According to Reference [42], identity refers to the essence of the place, what makes it possible to distinguish the destination from other similar destinations, while the image is the perception that individuals have of that place [43], or as Urry calls it, “the tourist gaze” [44]. Likewise, although the elements of the identity of the destination are conceived from the supply side and involve business owners, DMOs and tourism managers [44], the image is analyzed from the perspective of consumers or tourists [45,46]. In this way, the elements and values that make up identity are transmitted through the image [47], so that an easily recognizable identity can reflect an image of a superior place [48].
In recent years, the image that tourists perceive of a place has radically changed due to the proliferation of online information sources [49]. Destination image is considered a multidimensional phenomenon [50], and thanks to the use of these tools, anyone can publish information about the destination that other users can consult, actively influencing the creation of the image based on their personal experiences and visual and textual contributions [8]. Their influence is so great that online information sources are considered agents of destination-image formation [49,50,51].
2.2. Online Information Sources as Formation Agents of the Destination Image
Online information sources are currently considered one of the best opportunities for destinations to become known, as they connect destinations directly with visitors and are one of the main sources of information for tourists [52]. Before traveling, tourists learn a lot about their destination by using a wide range of online platforms. Thus, it is crucial for destinations to identify what type of source is more important for users to develop effective tourism marketing strategies [53].
Every day, millions of photographs, comments and videos are uploaded to different online sources, being an expression and image of each individual [54]. They allow tourists to interact with the destination and also perceive a certain image of it before their visit. The relationship between online information sources and destination image has been examined in recent studies [16,55]. Due to the proliferation and development of online information sources, the Internet is home to a wealth of information, and so consumers are now more active in the search for tourist content. As a result, more than receiving information, consumers use online sources as a “supplier of information” ([51], p. 77). Consequently, image has become more complex than ever and is becoming more unmanageable [51].
Before the arrival of these platforms, consumers received tourist information only through marketing campaigns carried out by companies and public and private organizations, which tried to convey a positive image of the destination. The information was therefore unidirectional, from the company to the consumer [51]. The development of online sources of information has changed this paradigm in such a way that the credibility of these agents faces a key challenge, since the direction of the information has changed significantly [51], becoming multidirectional and interactive ([56], p. 16).
Currently, one of the main ways of evaluating the image of a destination is through the way in which tourists represent the destination on social networks [57] through published images [58], videos or recommendations, among others [57]. This trend can have important effects on the perceptions or emotions of users towards destinations in their cognitive, affective or behavioral dimensions [27]. While the cognitive image refers to the beliefs and knowledge that a tourist holds about the physical and abstract attributes of a destination, the affective image refers to the emotions or sense of attachment that the tourist feels towards a place [40]. Finally, the conative image reflects the behavioral intention to visit a place [59,60]; in other words, the conative is the action component that determines whether a trip is to be made [61].
Thus, users can have an anticipated cognitive image of what they expect to see or do in a certain destination through the information they have collected on the different online platforms [62], for example, how to get to the restaurant according to the location information shown in the social media profile [63]. The user can also create an affective image of the destination by receiving information from the comments, images and reviews of other travelers about the destination (excellent, WOW, amazing and impressive) [64]. Finally, and based on their cognitive and affective perception, the user takes the action of visiting the destination or not and making positive comments (e-WOM) (conative image), [63] for example, “A destination worth seeing, I will definitely return” [64].
In the field of tourism, many studies have examined how online information sources influence destination image [2,19,63,65,66,67]. However, most of these studies focus on the post-visit image and also consider online information sources as a single construct [68] or individually (TripAdvisor [64], blogs [69], Facebook [70], Twitter [16] and destination webpage) [41]. Consequently, previous researchers have underlined the need to analyze additional sources in the online environment in order to measure the amount of information used to plan a trip, such as social networks and consumer-generated content [53]. The topic of the image-formation process in online information sources has been the subject of little study, especially empirical research [63].
In this line, and according to Reference [21], there is no formal classification of the different online sources of information. In general, most research has focused more on how these sources affect the travel planning process [71] and less on its role in creating the destination’s image. In the present paper, and based on the previous literature, we consider three categories of online sources of information: (1) social media sources (SMS), (2) online commercial sources (OCS) and (3) online non-commercial sources (ONCS). This classification, which is detailed below, is an important contribution to the literature of tourism marketing and opens a new avenue of research in this field. In this sense, it is necessary to indicate that a person may use only one type of online information source, or more than one. The greater the importance of the source for the individual, the more motivated the individual will be to co-create. Therefore, the influence on the perceived image of the destination will also be different.
First, we aligned social media sources with generic social networks and tourism blogs. Traditionally, friends, family and trusted others (word-of-mouth) [72,73] serve as key agents in the formation of images [74]. The major difference is that this word-of-mouth is now electronic (hereafter referred to as eWOM), even though both essentially involve the exchange of information among consumers [75]. User-generated content, both before and after the trip, is an important source of information as it allows us to observe how tourists have perceived the destination and how they have lived their experience [41]. In addition, and before traveling, user-generated content can influence the decision-making process if it is perceived to be credible, which, in turn, depends on the user’s previous knowledge, previous traveling experience and the type of platform [16]. Blogs and social networks allow consumers to interact with other users, resolve doubts, and share ideas, opinions and new content.
Second, we aligned online commercial sources with the official website of the city and province, reservation websites with user ratings and tourist providers’ websites. Similar to conventional commercial sources (i.e., brochures, advertisements and travel posters) [65], these resources have a singular objective: promoting the destination and its image [76] to a specific audience. Thus, the images that derive from these media are primarily the “by-product” of marketing agencies, not a consequence of consumers themselves [73].
Third, we aligned online non-commercial sources with maps, and pictures and media websites. Similar to traditional non-commercial sources of information (e.g., travel guides, reports, documentaries, etc.) [8], the goal of these media is to foster general knowledge about the destination [77], and they usually adjust better to the real preferences of the tourist [26]. Importantly, these media are not directly controlled by the destination’s authorities: they could contribute to these sites themselves, but they largely have no control over what appears in the news or how regular users interpret content about a destination [59].
Given the above, we hypothesized a positive relationship between the importance of the platform for the individual as a tourist information source and the destination image. More specifically, we developed three hypotheses—one for each category of online information source:
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
The importance of social media sources (SMSs) for the individual positively and significantly influences destination image.
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
The importance of online commercial sources (OCSs) for the individual positively and significantly influences destination image.
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
The importance of online non-commercial sources (ONCSs) for the individual positively and significantly influences destination image.
2.3. The Mediating Role of Motivation to Co-Create
The development of online information sources has generated an open line of communication between companies and consumers, both of whom can make positive contributions to new products and services. In general, consumers tend to feel comfortable with online sources, thus accepting companies that occupy the same digital space—although some consumers relate more easily to online companies than others [67]. In general, online information sources constitute interactive environments for businesses and consumers to generate content and co-create value. In addition, they provide more dynamic connections and more meaningful relationships between both actors [22].
Some studies in the relevant literature have observed how co-creation affects a company’s image. For example, Reference [78] suggested that the image of the company is related to consumer value and affects its results. Ref. [79] examined brand co-creation as the process in which different stakeholders co-create the identity and brand image of a company, both directly and indirectly, through cooperation, communication and interaction between the different actors in the network. Ref. [80] found that brand image is projected and developed by users through social networks and has greater credibility than the image promoted by creative companies. In addition, the study by Reference [24] proposed a conceptual framework between co-creation, brand image and performance in the market.
Despite these previous works, it seems that research on the co-creation of a tourist destination’s image is a relatively neglected area in the tourism literature [81]. As discussed, online information sources are important mechanisms that can influence the image of the destination. However, the previous literature does not specify whether this relationship is direct or can be mediated or moderated by one or more other factors, with researchers paying little attention to the study of possible factors that may currently act as intermediaries in the relationship between online information sources and the image of the destination.
There are, however, some interesting studies in this research line. For example, Reference [82] took Portugal as a reference to analyze the destination image projected on social networks through the comments and the information that tourists share as co-creators of opinion. Ref. [80] investigated the effects of co-creation on the image that Fuerteventura projects on Twitter. Ref. [63] analyzed the effect of the quality of the information of a social network on a tourist destination, while Reference [50] analyzed how perceived interactivity on the destination’s webpage influences the user’s intention to interact with the webpage and other consumers.
Reference [40] showed that, in addition to other stimulating factors, the image of the destination is formed by the characteristics of the tourists themselves and personal factors, such as motivation. In the tourism industry, authors have suggested how consumers interact with travel companies on different online platforms for a variety of reasons [8,83], such as seeking information to inspire their trip, or gathering useful information and insights for future travel. In addition, Reference [83] highlighted how recognition and consumers’ rewards, while not among the main motivations for consumer co-creation, also constitute other ways in which tourists seek to participate in co-creation processes. In fact, certain initiatives, such as status within the company or rewards for reviews, were perceived as motivation to co-create. Considering that the relevant literature has detected a significant influence of co-creation on destination image, it might also be expected that tourists’ motivation to participate in co-creation activities on online information sources exert a positive and significant influence on destination image. Hence, in line with the theoretical grounding, Hypothesis 4 proposes that the motivation to co-create the tourism experience influences the cognitive, affective and conative image:
Hypothesis 4 (H4).
Motivation to co-create the tourist experience positively and significantly influences destination image.
Several authors point out that more research is needed on the relationship between online information sources and co-creation [22,84,85]. There have also been an increasing number of calls for further research on the significance of online platforms in the configuration of image [82]. Online sources of information are considered an important agent of image formation and, at the same time, a key platform for tourism co-creation. This paper considers co-creation as a tool that encourages tourists and users to share comments, ideas, videos and photographs on different information platforms. Furthermore, the present study considers that this co-created content influences the online image projected by a particular destination, which will influence the decision of other users to visit and recommend the place. Specifically, this research aims to measure the motivation for co-creation, that is, what motives lead users to participate in creative co-creation tasks, sharing their opinions on the destination online. Companies may not create a co-creation experience that really motivates the participants to collaborate in the co-creation process, and therefore they run the risk of causing little interest in the innovation process [10]. Hence, knowing and identifying the motivational factors is crucial to maximize the attractiveness of the activity in the innovative users [86] and, consequently, contribute effectively to the creation and projection of the destination image of online form.
Due to the high degree of interrelation between motivation to co-create and destination image, it is assumed that the motivation to co-create in tourism will have a mediating effect between online information sources and the destination image. Thus, we posit the following:
Hypothesis 5 (H5).
The effect of SMS on destination image is positively mediated by the motivation to co-create the tourism experience.
Hypothesis 6 (H6).
The effect of OCS on destination image is positively mediated by the motivation to co-create the tourism experience.
Hypothesis 7 (H7).
The effect of ONCS on destination image is positively mediated by the motivation to co-create the tourism experience.
Figure 1, below, shows our proposed conceptual model.
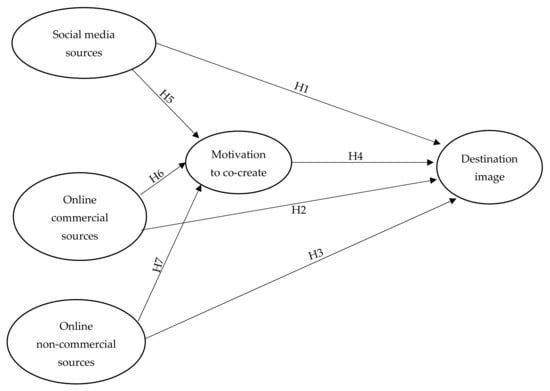
Figure 1.
Proposed research model.
3. Methods
3.1. Sample and Procedure
We developed an online questionnaire to test our proposed hypotheses. Data collection was conducted between 26 June and 31 July 2019. We sought out respondents of at least 18 years of age who used online information sources to find tourist information about the city of Cuenca. This destination is a small city of around 55,000 inhabitants located in inland Spain, in the northeast of the Castilla-La Mancha region.
Several reasons led us to choose Cuenca as a tourist destination for this study. First, it has a rich cultural, natural and historical heritage that led to its designation as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1996. Although the province of Cuenca is very large, only the city itself is considered a World Heritage site. As the UNESCO Committee indicated, “Cuenca is considered an example of the medieval fortress town that has preserved its original townscape remarkably intact” (https://whc.unesco.org/, accessed on 15 June 2021). Having this international recognition represents an important boost for Cuenca in terms of tourism, which, however, must be seized and further enhanced to project an image of a differentiated tourist destination of authenticity and uniqueness.
Second, tourism is one of the most important industries for Cuenca, meaning that any knowledge on how to enhance its destination image is especially important. This industry accounts for around 16% of employment in the city, with more than 2200 businesses (e.g., hoteliers, transport and tourist guides, etc.) dedicated to this sector [87], overall representing the non-negligible rate of 12% of the total employment in this city. Third, the city has a lower volume of tourists than other Spanish World Heritage Cities of similar characteristics, such as Cáceres, Mérida, Úbeda, or Baeza. In fact, Cuenca is far from being considered a large tourist center since the number of annual visitors is less than 300,000 and hotel occupancies are less than 55%. Likewise, and although the hotel offer is high in relation to the number of its inhabitants, the proportion of foreign tourists is less than 20%, according to the latest report from the GCPHE Tourism Observatory by Braintrust.
Last, but not least, it should be mentioned that Cuenca is close to two large urban centers in Spain, namely Madrid and Valencia, and is part of an important land transport network (both by road and by train). For this reason, the city receives a large number of visitors but not tourists, since the average stay is a single overnight one [88]. This may result in their image of the city not being solid and may be changed through more visits, opinions from friends and family, or the influence of the media.
Thus, analyzing how online information platforms can help the image the city of Cuenca projects to tourists is of relevance, as it may allow us to know the aspects and attributes of the city that may most attract visitors and that can help increase its tourist significance as a heritage destination of reference. Overall, the city of Cuenca offers a good tourist destination to analyze the relationships proposed in this study.
We first pilot tested our survey by distributing it to web professionals, academics, members of Cuenca’s tourism office and marketing research students. Based on their feedback, we modified the wording of some items and then confirmed the survey’s adequacy with a group of three scholars who are experts in the fields of marketing and social media. After finalizing the survey, we made it accessible via several Internet avenues. First, via diverse online platforms (Facebook, Instagram, Twitter and WhatsApp), the choice of which was motivated by the differences between platforms in terms of use and co-creation behaviors reported in the literature [89]; second, via official Websites (http://www.cuenca.es, accessed on 15 June 2021); and third, via non-official Websites (the main unofficial tourist blog of the city, http://www.estoescuenca.com, accessed on 15 June 2021).
By the end of a five-week promotion period, we had received 640 questionnaires. After discarding some incomplete and incoherent questionnaires, we were left with 394 usable surveys. Because the study was cross-sectional and relied on self-reported measures, the results could have been affected by common method variance (CMV), evaluation apprehension and social desirability [90]. To mitigate these problems, we followed the recommendations of References [90,91] when designing the questionnaire. Before participants could answer the questions, the survey explicitly noted that honesty and frankness were strongly appreciated, and that individual and corporate anonymity would be guaranteed. Furthermore, in order to specifically limit CMV [91], the questionnaire (a) made predictors and criterion variables appear unrelated and part of different topic areas; (b) included various contextual variables to serve as distractors; and (c) included simple, specific and concise items that arose from the pilot test.
To test for non-response bias, we assumed that late respondents are more similar to non-respondents than to early ones [92]. Accordingly, we compared the first and last quartiles of submissions by conducting independent sample t-tests for all of the study variables. No significant differences appeared, so non-response bias does not appear to be a major problem in this study. In terms of demographics (see Table 1), the age of our respondents ranged from 18 to 70 years, although the sample was skewed relatively young: 61.77% of them were between 25 and 44. Meanwhile, around 75% of our sample had a university degree, and about 50% were working either in the private or the public industry. Finally, in terms of the place of residence of the tourists who responded to the questionnaire, 98% of tourists were from different parts of Spain (with only 2% from other countries). In the sample, there were also residents of diverse locations in the province of Cuenca (189 tourists, 48%), which is a large province (with an extension of 17,141 km2 and more than 238 population centers). Including tourists from different locations in the province of Cuenca does not alter the results obtained, as they were not from the World Heritage Site of Cuenca but from different towns or cities within the province of Cuenca. Furthermore, we conducted a t-test to compare the mean values of two independent groups (tourists from the province of Cuenca (n= 189) versus tourists from other locations (n = 205)) in the responses provided, regarding the cognitive, affective and conative images of the city of Cuenca. The results of this test revealed no significant differences between the means of the two groups for any of the image variables under study (cognitive image, F = 0.057, p = 0.404, not significant; affective image, F = 1.100, p= 0.392, not significant; conative image, F = 9.523, p = 0.150, not significant), thus indicating that having 189 respondents from different geographical points of the province of Cuenca province does not represent a bias in our findings.

Table 1.
Respondent profiles.
3.2. Measures
Following previous recommendations on how to treat latent variables in PLS [93], this study included formative and reflective first-order constructs, together with a second-order construct (motivation to co-create). The information sources were considered formative measurement constructs (arrows from the indicator variables to the latent variable), such that the indicator variables cause the measurement of the latent variable. The rest of the constructs (motivation to co-create and destination images) were reflective (i.e., linear combinations of the indicators based on correlation weights where arrows point from the construct to its indicators).
In order to measure the importance of online sources of information, we used a 5-point Likert scale similar to the one used by Reference [8]. Moreover, in line with Reference [8], we distinguished online sources of information according to three categories: social media sources (generic social networks and tourism blogs), online commercial sources (official website of the city and province, reservation websites with user ratings and tourism providers’ websites) and online non-commercial sources (maps, pictures and media websites).
To measure the motivation to co-create variable, we adapted items suggested by Reference [10] based on Reference [94] and had respondents assess them on a 5-point Likert scale. These authors consider co-creation a creative activity in which the consumer actively produces a result. This creativity encompasses a wide range of activities, involving competence, autonomy and enjoyment.
In order to measure the three components of destination image, we analyzed the different attributes of each, using either a Likert scale or a differential semantic scale. First, the cognitive image analyzes different elements of the destination according to their quality, based on the work by References [95,96]. The cognitive image of the city of Cuenca was measured with a total of 20 indicators. Second, we adopted an 11-item semantic differential scale [97] to measure the affective image, in line with previous studies by References [2,8,40,72,98]. Lastly, we measured the conative image by using eight items that have been successfully applied in previous studies [98].
3.3. Data Analysis
We used Smart PLS 3.2.8 [99] to test the hypotheses. This is a powerful, robust structural equation modeling approach [100] with minimal requirements about how the variables are distributed [93] and well suited to testing mediation hypotheses [101]. Following [93], we used bootstrapping (5000 resamples) to generate standard errors and t-statistics for the hypothesis testing.
4. Results
4.1. Measurement Model
Table 2 and Table 3 show the reliability and validity for all the constructs. Specifically, Table 2 reports the FIV, weights, t-test results, p-values and confidence intervals for the formative constructs, while Table 3 reports the individual, construct reliability and convergent validity (average variance extracted, AVE) for the reflective constructs.

Table 2.
Formative constructs and their respective items.

Table 3.
Reflective constructs and their corresponding items.
According to the findings on our formative online sources of information constructs (Table 2), all items had significant weights to build the social media source construct (SMS). Regarding the online commercial source construct (OCS), all items also showed significant weights, with the only exception of OnlineSource5 (Reservation websites with user ratings). However, the t-value was positive and close to 1, so we followed Reference [93] and decided to keep this item. Finally, because all FIV values are below 3.3, we can affirm that our formative constructs are free of multicollinearity problems, and thus they all help build their corresponding formative constructs (SMS, OCS and ONCS).
With regard to findings on the measurement of our reflective variables, Table 3 indicates that most of the individual items achieved good reliability, with item loadings almost always exceeding the desired threshold of 0.707 [102]. Five items of cognitive image (cogni1, cogni2, cogni3, cogni4 and cogni14) and three items of affective image (afect5, afect7 and afect10) showed very low values (below the minimum required threshold of 0.55 [103]. We ultimately decided to remove those items, following previous recommendations [93]. In terms of construct reliability, the Cronbach’s alphas and Dijkstra–Henseler’s composite reliabilities (ρA) [104] were above 0.70 (Table 3), as recommended [93]. All the constructs also had convergent validity, as the AVE for each reflective variable was greater than 0.50 (Table 3) [93]. Finally, Table 4, which captures the correlations across all our research variables, shows that the heterotrait–monotrait (HTMT) values fell below the most restrictive threshold of 0.85 and were significantly different from 1 [105], thus confirming discriminant validity between each pair of variables. Discriminant validity was also met; according to the Fornell–Larcker criterion [84], the square roots of AVE for each variable were greater than the correlation of each variable with the others, as is required [93] (see Table 4).

Table 4.
Descriptive statistics, correlation matrix and square roots of AVE for the reflective constructs.
Regarding the measurement of our second-order construct, “motivation to co-create”, we followed recommendations by Reference [93] and built latent variable scores of first-order constructs, such as “Autonomy”, “Competence” and “Enjoyment” (Table 5). These items were adapted from References [10,94]. Ref. [94] considers that people involve themselves in creative activities because they seek experiences that give them feelings of competence, autonomy and enjoyment of the task, while Reference [10] shows that people with an interest in participating in creative activities are looking for pleasant, autonomous and competent co-creation experiences. More specifically, participants were asked about their motives for participating in co-creation activities related to the destination. We measured “autonomy” by using the item, “I am able to help improve the image of [Cuenca]”; “competence” was measured as “My participation in co-creation activities enhances my knowledge about [Cuenca]”; and “enjoyment” was measured as “The experience is a lot of fun and I am having a good time participating in co-creation activities”.

Table 5.
Motivation to co-create. Measurement model.
Table 5 shows the weights, loadings, reliability and convergent validity (AVE) for the construct. The first-order indicators that underlie the second-order construct achieved adequate loading values (i.e., in excess of 0.55, although enjoyment has a low value). In terms of reliability, they achieved adequate values for composite reliability, Cronbach’s Alpha and the Dijkstra–Henseler ratio (rho_A). Lastly, this construct met the convergent validity criterion, as the AVE exceeded the minimum 0.5 threshold.
4.2. Hypothesis Testing
Table 6 contains the findings related to our hypotheses. The results show that social media sources did not relate to any component of the destination image, contrary to our predictions, and thus H1 (H1a, H1b and H1c) could not be accepted.

Table 6.
Hypothesis validation (H1–H4).
With regard to H2, the results confirm that online commercial sources (H2a, H2b and H2c) positively influence cognitive, affective and conative destination image. Therefore, the participants’ perceived image of the destination improved when the information about the destination came from sources such as official marketing campaigns. This result is consistent with the findings of (i) Reference [72], who found that travel agency staff acted as a commercial source with a positive influence on one of the cognitive image factors considered; (ii) Reference [106], who observed how certain US tour operators were having a major impact on the image of Russia as a US tourist destination, contributing to the positioning of the US as a primarily historical and cultural destination; (iii) Reference [107], who detected that commercial sources of information were having an impact on the perceived image of Mauritius as a vacation destination; and Reference [108], who found that commercial agents were one of the market forces that had dominated the process of forming the image of Yanyu (East China), helping to communicate an image of freedom, leisure and romance.
Regarding H3, the results also revealed that this hypothesis could not be accepted. Thus, contrary to expectations, we did not find that online non-commercial sources influenced the perceived image, so H3a, H3b and H3c could not be accepted.
Although neither H1 nor H3 could be accepted, the results obtained are consistent to some extent with those obtained by previous research. For example, although Reference [72] detected a certain influence of social media sources and online non-commercial sources information in the image (in particular, the cognitive image), this influence was quite small, since it only significantly influenced some components of the cognitive image.
For H4, we found that motivation to co-create positively influenced destination image. In particular, Table 6 and Figure 1 show that motivation to co-create positively influences cognitive image (β = 0.450, p < 0.001), affective image (β = 0.427, p < 0.001) and conative image (β = 0.494, p < 0.001). Thus, H4 (and therefore H4a, H4b and H4c) could be accepted.
In this regard, it is worth highlighting that the three categories of online information sources showed a significant relationship with the motivation to co-create. Social media sources were the most influential, followed by online commercial sources and online non-commercial sources.
Finally, with regard to H5, all our results suggest that motivation to co-create exerts a significant mediating effect on the relationship between online information sources (SMS, OCS and ONCS) and the image of the tourist destination (cognitive, affective and conative). In fact, the bias-corrected and accelerated (BCA) bootstrap method (with 5000 repetitions) revealed a significant indirect effect of social media sources, online commercial sources and online non-commercial sources on cognitive, affective and conative image (see Table 7). These results suggest that motivation to co-create does indeed mediate the relationship between informational online sources and destination images, in support of H5a, H5b and H5c; H6a, H6b and H6c; and H7a, H7b and H7c. With regard to H6a, H6b and H6c, the indirect effects of online commercial sources coexist with the significant direct effect of online commercial sources on cognitive (H2a), affective (H2b) and conative (H2c) destination image. Therefore, we can conclude that motivation to co-create partially mediates that particular relationship(s). Finally, albeit at a low level (p < 0.10), the indirect effects of online non-commercial sources on all three destination images are significant, thus suggesting the existence of such a mediation effect of motivation to co-create on the relationship between online non-commercial sources and destination image. Thus, we can also give support to H7a, H7b and H7c (Table 7).

Table 7.
Mediation hypothesis validation (H5–H7): direct, indirect, total effects and explained variance.
Table 8 is helpful to understand the quality of such mediation effects of motivation to co-create. For the mediation in the relationships between online sources of information and cognitive image, the data in the table show that the mediated model (R2mediated model = 0.255) triples the variance explained of cognitive image compared to an unmediated model (R2unmediated model = 0.083; ΔR2 = 0.172), which indicates that the mediation effect is medium in size (f2 = 0.23) [109] (Table 8). Of a similar size is the mediation effect of motivation to co-create in accounting for affective image (see Table 8); in this case, data show that the mediated model (R2mediated model = 0.254) has nearly triple the variance explained compared to an unmediated model (R2unmediated model = 0.097; ΔR2 = 0.157), indicating that the mediation effect is medium in size (f2 = 0.21) [109] (Table 8). Finally, regarding the mediation effect of motivation to co-create in the relationship between online sources of information and conative image (see Table 8), the results show that the mediated model (R2mediated model = 0.299) also triples the variance explained of conative image compared to an unmediated model (R2 unmediated model = 0.072; ΔR2 = 0.227), which indicates that the mediation effect is also medium in size (f2 = 0.32); [109].

Table 8.
Mediation effect size of motivation to co-create.
Finally, regarding the model’s explanatory power, the R2 and Q2 (predictive relevance of the endogenous variable) yielded satisfactory values (Table 8). The R2 adjusted values were 0.255 for cognitive image, 0.254 for affective image and 0.299 for conative image. The R2 adjusted value for motivation to co-create was low (R2 adjusted = 0.084), but the abovementioned R2 adjusted values show the model has substantial power to explain these main dependent variables [93]. Interestingly, the Stone–Geisser blindfolding sample reuse technique, with an omission distance of 7, revealed Q2 values larger than zero for all the cases. This indicates that the model we tested has good predictive power for motivation to co-create (Q2 = 0.043), cognitive image (Q2 = 0.128), affective image (Q2 = 0.122) and general conative image (Q2 = 0.185) [93].
5. Discussion
The main purpose of this research was to contribute to the marketing literature by analyzing the relationship between online sources of information, co-creation and destination image. More specifically, beyond the direct relationship between the importance of online sources of information and destination image, the current study analyzed the mediating effect of motivation to co-create in the relationship between online sources of information and destination image, responding to recent calls to analyze the role of motivation in the image of the destination [110,111].
Our findings reveal a significant indirect effect of social media sources, online commercial sources and online non-commercial sources on cognitive, affective and conative image, through motivation to co-create. The mediation value was also significant. It reveals that tourists contribute more effectively to the formation of the image when they are motivated. This study calls on tourist companies and destination managers to consider incentives to promote motivation among consumers to engage in value co-creation through informational online sources. In this process, consumers participate in the building of the destination image, so companies can develop their marketing strategies to motivate consumers to promote positive aspects of the destination. As a result, value co-creation may reinforce the image projected and perceived by other users and make tourists prefer to visit and get to know that destination instead of other competing destinations. These results are consistent with recent studies that show how co-creation has a positive effect on the image of the destination. For example, it has been found that the co-creation experience has a positive and significant impact on the cognitive and affective image of the destination through UGC platforms [112]. Authors have also shown that the publications shared by users themselves on Instagram are the most influential in promoting the attractiveness of the destination and attracting other travelers [113].
The results additionally showed that the three categories of online sources of information were also directly related to motivation to co-create. The greater the perceived importance of the online source among users, the greater is the motivation to co-create. Social media sources, such as the recommendations of family and friends, exerted the greatest influence on such motivation, followed by online commercial sources and online non-commercial sources. These results substantiate previous findings [8,40] indicating that word-of-mouth is the most effective and accurate communication channel for tourists, particularly when the source is friends and family.
Moreover, the findings reveal a positive relationship between the importance of online commercial sources for the individual and all image dimensions, albeit in the following order: conative, affective and cognitive image. These findings highlight the importance of the information provided by public officials, sources and private companies through their website. Thus, based on the results obtained, the official website of the destination and tourist reservation portals are the online source considered most important by users to search for tourist information about Cuenca. This conclusion is consistent with the findings of previous studies that indicate a greater influence of induced sources on the image of the destination [8,114]. In particular, the results indicate that online commercial sources have a significant positive impact on conative image. In contrast to previous studies, we have been unable to verify the influence of social media sources and online non-commercial sources on the destination image. These results are consistent with the findings of a number of papers, however. For example, although Reference [72] detected a certain influence of social media sources and online non-commercial sources on image (in particular, cognitive image), this influence was quite small, influencing only some components of the cognitive image. Sociodemographic characteristics lead tourist provider websites to be more important for middle-aged users (45–64 years), in contrast to younger people, who report not using this type of social media or using it very little. Thus, while younger generations are influenced by the opinions of other users on platforms such as TripAdvisor or Booking, retired people prefer to obtain information directly from the official source. A possible explanation is that older people may have greater knowledge and experience in life and are thus are more likely to want to be careful with what they communicate and transmit to other people.
Lastly, the results also showed that the effect of motivation to co-create was greatest on conative image, followed by cognitive image and affective image. These results are consistent with the works of References [59,64], who showed that conative image plays a fundamental role in the decision and/or recommendation to visit a destination [59,64,98], and with Reference [40], who found that the psychological motivation of travelers positively impacts on cognitive and affective image. Regarding the motivation to co-create, 48% of respondents consider that their main motivation is to contribute to improving the image of Cuenca, while 46% consider it is to inform and advise other tourists about the activities and places to visit in Cuenca. If we consider conative image, the respondents said that Cuenca constitutes a dream destination to visit at some point (39.3%) and an adequate vacation option (34.5%). For affective image, users highlight that Cuenca is “pleasant”, “relaxing”, “pretty” and “interesting”. If the cognitive image is considered, Cuenca is a destination of nature (71.8%), artistic–cultural interest (56.3%) and mountains (55.8%), with a relaxed and safe environment, important monuments and opportunities for sports.
6. Managerial Implications
From a practical perspective, this study makes several important contributions to the tourism literature. At present, destinations face great competition, so the directors of DMOs and tourism companies must find and know how to manage effective communication tools to transmit and to position a favorable image in the minds of tourists. Many articles have examined the role of online information sources in image formation. However, this article goes a step further by providing empirical evidence on the mediating effect of motivation to co-create on the relationship between both concepts. The active role of consumers influences not only the decisions that destinations make in image management, but also directly influences the image that other users perceive of the destination through different online platforms.
Thus, managers can intervene in order to address problems in motivation and understand the determinants that lead consumers to share their perceptions about the destination and, consequently, contribute effectively to the creation and projection of the destination image in online form. Therefore, for destinations to transmit a stable and consistent message on online information platforms, different stakeholders must collaborate to correctly identify the image that users perceive about the destination, and then implement a coherent marketing strategy to appropriately promote the online position of the tourist destination [115]. In this sense, knowing what type of online source is most important for users when looking for tourist information can lead to the destination’s marketing efforts being better targeted and more tailored to the characteristics and needs of potential tourists. It is from co-creation that destinations can transmit the most positive image of the destination, since, according to existing studies, well-formed destination images are positively associated with the level of satisfaction of travelers and their behavioral predisposition to visit the destination [116].
7. Limitations of the Study and Directions for Future Research
The present work features some limitations that may serve to inspire future lines of research. First, we only analyzed the image of Cuenca according to three dimensions: cognitive, affective and conative image. However, the literature also highlights other dimensions, such as the overall, unique and multisensory image. Future studies should thus accommodate a fuller set of dimensions, as well as delve deeper into the existing relationship between the dimensions studied in the current paper.
Second, future research should seek to identify other online sources of information beyond those included here. Web platforms and web tendencies are constantly changing and evolving in the market, with new features and attributes to offer users a better online experience. Some of today’s types of online platforms will increase their number of users in the coming years, and others will maintain their position in the future. However, other types of information sources will disappear due to the lack of user participation.
Third, as detailed, our study analyzed the image of the city of Cuenca. The province of Cuenca is very large, but only the city is considered a World Heritage site. For this reason, although 48% of respondents are from Cuenca, this refers to the province of Cuenca, so most are not residents of the city itself. However, the results should be interpreted with caution, since residents’ perceptions of the city likely differ from that of outsiders.
Therefore, future work should attempt to replicate our study, while differentiating between residents and non-residents of the province of Cuenca. Relatedly, it would be interesting to apply this model to other destinations and see if the results hold. Finally, we acknowledge that the PLS method, which we used to verify the empirical model and test the hypotheses, presents a number of limitations. Despite its methodological rigor, the method is more exploratory than confirmatory, and should thus be complemented with other more confirmatory methods.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: M.A.G.-H. and M.P.M.-R.; methodology and software: R.M.-C. and P.R.-P.; validation: R.M.-C. and P.R.-P.; formal analysis, M.P.M.-R.; R.M.-C. and P.R.-P.; investigation, M.A.G.-H. and M.P.M.-R.; data curation: R.M.-C. and P.R.-P.; writing—review and editing, M.A.G.-H., M.P.M.-R., R.M.-C. and P.R.-P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the University of Castilla-La Mancha Research Group: Innovation observatory in commercial distribution.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Baloglu, S.; Mangaloglu, M. Tourism destination images of Turkey, Egypt, Greece, and Italy as perceived by US-based tour operators and travel agents. Tour. Manag. 2001, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacout, O.M.; Hefny, L.I. Use of Hofstede’s cultural dimensions, demographics, and information sources as antecedents to cognitive and affective destination image for Egypt. J. Vacat. Mark. 2015, 21, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzigeorgiou, C.; Christou, E. Promoting agrotourism resorts online: An assessment of alternative advertising approaches. Int. J. Technol. Mark. 2020, 14, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinerean, S. Importance of strategic social media marketing. Expert J. Mark. 2017, 5, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Emadi, F.A.; Yahia, I.B. Ordinary celebrities related criteria to harvest fame and influence on social media. J. Res. Interact. Mark. 2020, 14, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Gretzel, U. Role of social media in online travel information search. Tour. Manag. 2010, 31, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Fesenmaier, D.R. Sharing tourism experiences: The posttrip experience. J. Travel Res. 2017, 56, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llodrá-Riera, I.; Martínez-Ruiz, M.P.; Jiménez-Zarco, A.I.; Izquierdo-Yusta, A. A multidimensional analysis of the information sources construct and its relevance for destination image formation. Tour. Manag. 2015, 48, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambisan, S.; Nambisan, P. How to profit from a better’virtual customer environment. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2008, 49, 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Füller, J.; Hutter, K.; Faullant, R. Why co-creation experience matters? Creative experience and its impact on the quantity and quality of creative contributions. RandD Manag. 2011, 41, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkhorst, E.; Den Dekker, T. Agenda for co-creation tourism experience research. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2009, 18, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G. Modeling Consumers’ Co-Creation in Tourism Innovation; Temple University: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Suntikul, W.; Jachna, T. The co-creation/place attachment nexus. Tour. Manag. 2016, 52, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciasullo, M.V.; Carrubbo, L. System Theory and Service Science: Integrating Three Perspectives in a New Service Agenda. Tourist Systems Co-Creation Exchanges: Service Research and System Thinking Insights for Destination Competitiveness. 2011. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=1903956 (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Neuhofer, B.; Buhalis, D.; Ladkin, A. Co-creation through technology: Dimensions of social connectedness. In Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 339–352. [Google Scholar]
- Garay, L. #Visitspain. Breaking down affective and cognitive attributes in the social media construction of the tourist destination image. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2019, 32, 100560. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, C.; Fidgeon, P.; Page, S.J. Maritime tourism and terrorism: Customer perceptions of the potential terrorist threat to cruise shipping. Curr. Isues Tour. 2014, 17, 610–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grissemann, U.S.; Stokburger-Sauer, N.E. Customer co-creation of travel services: The role of company support and customer satisfaction with the co-creation performance. Tour. Manag. 2012, 33, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Költringer, C.; Dickinger, A. Analyzing destination branding and image from online sources: A web content mining approach. J. Bus. Res. 2015, 68, 1836–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.Y.M. Repurchase loyalty for customer social co-creation e-marketplaces. J. Fash. Mark. Manag. 2014, 18, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See-To, E.W.K.; Ho, K.K.W. Value co-creation and purchase intention in social network sites: The role of electronic Word-of-Mouth and trust–A theoretical analysis. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 31, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, T.; Yang, M.H.; Wu, J.T.B.; Cheng, Y.Y. Co-creating value with consumers through social media. J. Serv. Mark. 2016, 30, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.Y.T.; Peko, G.; Sundaram, D.; Piramuthu, S. Mobile environments and innovation co-creation processes and ecosystems. Inf. Manag. 2016, 53, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayapal, P.; Omar, A. The Role of Value Co-Creation on Brand Image: A Conceptual Framework for the Market. In Digital Marketing and Consumer Engagement: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications; IGI Global, Hershey: Hershey, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 326–348. [Google Scholar]
- Prebensen, N.; Chen, J.; Uysal, M. Creating Experience Value in Tourism, 2nd ed.; Cab International: Boston, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sugathan, P.; Ranjan, K.R. Co-creating the tourism experience. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 100, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepaniuk, K. The relation between destination image and social media user engagement–theoretical approach. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 213, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.; Hughes, M.; Kertbo, K. Exploring consumers’ motivations to engage in innovation through co-creation activities. Eur. J. Mark. 2014, 48, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletta, R.; Servidio, R. Tourists’ opinions and their selection of tourism destination images: An affective and motivational evaluation. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2012, 4, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, K.; Rashid, B.; Zainol, N.A. Beyond the motivation theory of destination image. Tour. Hosp. Manag. 2016, 22, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crompton, J.L. Motivations for pleasure vacation. Ann. Tour. Res. 1979, 6, 408–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cai, L.A.; Lehto, X.Y.; Huang, J. A missing link in understanding revisit intention—The role of motivation and image. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2010, 27, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marine-Roig, E.; Ferrer-Rosell, B. Measuring the gap between projected and perceived destination images of Catalonia using compositional analysis. Tour. Manag. 2018, 68, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshardoost, M.; Eshaghi, M.S. Destination image and tourist behavioural intentions: A meta-analysis. Tour. Manag. 2020, 81, 104154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Real, J.L.; Uribe-Toril, J.; Gázquez-Abad, J.C. Destination branding: Opportunities and new challenges. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2020, 17, 100453. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, W.W.; Li, X.R.; Pan, B.; Witte, M.; Doherty, S.T. Tracking destination image across the trip experience with smartphone technology. Tour. Manag. 2015, 48, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.K.; Wu, C.E. An investigation of the relationships among destination familiarity, destination image and future visit intention. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2016, 5, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H. A structural model to examine how destination image, attitude, and motivation affect the future behavior of tourists. Leis. Sci. 2009, 31, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J.D. Image as a factor in tourism development. J. Travel Res. 1975, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloglu, S.; McCleary, K.W. A model of destination image formation. Ann. Tour. Res. 1999, 26, 868–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Alcázar, C.; Sicilia, M.; De Ruiz Maya, S. La imagen de un producto turístico rural a través del acceso al contenido generado por otros usuarios en internet: Diferencias por género. J. Technol. Manag. Innov. 2015, 10, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tasci, A.D.; Kozak, M. Destination brands vs destination images: Do we know what we mean? J. Vacat. Mark. 2006, 12, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, S.; Rowley, J. Towards a strategic place brand-management model. J. Mark. Manag. 2011, 27, 458–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urry, J. The Tourist Gaze; Sage: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ruzzier, M. Clarifying the concept of customer-based brand equity for a tourism destination. Ann. Ser. Hist. Sociol. 2013, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, K.L.; Kotler, P. Branding in B2B firms. In Handbook of Business-to-Business Marketing; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Agapito, D.; do Valle, P.; Mendes, J. The cognitive-affective-conative model of destination image: A confirmatory analysis. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2013, 30, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marine-Roig, E. Identity and authenticity in destination image construction. Anatolia 2015, 26, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroudi, P.; Cuomo, M.T.; Foroudi, M.M.; Katsikeas, C.S.; Gupta, S. Linking identity and heritage with image and a reputation for competition. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 113, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcázar, C.H.; Sicilia, M. How web interactivity influences the image of a tourist destination. J. Urban Regen. Renew. 2015, 8, 356–366. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazali, R.M.; Cai, L. Social media sites in destination image formation. In Tourism Social Media: Transformations in Identity, Community and Culture; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2014; pp. 73–86. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, A.; Haenlein, M. Users of the world, unite! The challenges and opportunities of Social Media. Bus. Horiz. 2010, 53, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.; Sicilia, M. Use of online versus offline information sources by tourists. Catalan J. Commun. Cult. Stud. 2011, 3, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, I.S.; McKercher, B.; Lo, A.; Cheung, C.; Law, R. Tourism and online photography. Tour. Manag. 2011, 32, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.S.; Liang, Y.; Xue, J.X.; Pan, B.; Schroeder, A. Destination image through social media analytics and survey method. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2021, 33, 2219–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Gerritsen, R. What do we know about social media in tourism? A review. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2014, 10, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucco, F.; Falaster, C.; Gadotti dos Anjos, S.J.; Belli Kraus, C. Destination image in virtual social networks. Anagramas-Rumbos Sentidos Comun. 2019, 17, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, W.C. The social construction of tourism online destination image: A comparative semiotic analysis of the visual representation of Seoul. Tour. Manag. 2016, 54, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, W.C. Image formation process. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 1994, 2, 191–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fu, X.; Cai, L.A.; Lu, L. Destination image and tourist loyalty. Tour. Manag. 2014, 40, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, C.A.; Andereck, K.L. Destination perceptions across a vacation. J. Travel Res. 2003, 41, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massara, F.; Severino, F. Psychological distance in the heritage experience. Ann. Tour. Res. 2013, 42, 108–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.E.; Lee, K.Y.; Shin, S.I.; Yang, S.B. Effects of tourism information quality in social media on destination image formation: The case of Sina Weibo. Inf. Manag. 2017, 54, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kladou, S.; Mavragani, E. Assessing destination image: An online marketing approach and the case of TripAdvisor. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2015, 4, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlović, D.K.; Belullo, A. Internet—An agent of tourism destination image formation: Content and correspondence analysis of Istria travel related websites. Ekon. Istraz. 2011, 24, 541–556. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, J.K.S.; Munar, A.M. Tourist information search and destination choice in a digital age. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2012, 1, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderSchee, B.A.; Peltier, J.; Dahl, A.J. Antecedent consumer factors, consequential branding outcomes and measures of online consumer engagement: Current research and future directions. J. Res. Interact. Mark. 2020, 14, 239–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narangajavana, Y.; Fiol, L.J.C.; Tena, M.A.; Artola, R.M.R.; García, J.S. The influence of social media in creating expectations. An empirical study for a tourist destination. Ann. Tour. Res. 2017, 65, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenot, G. Blogging as a social media. Tour. Hosp. Res. 2007, 7, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.; Nassanbekova, S.; Pérez, L.M.; Uruzbayeva, N. The impact of information quality in DMOs’ Facebook pages on the formation of destination image in the Silk Road: The case of Almaty, Kazakhstan. Curr. Issues Tour. 2020, 23, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, S.; Duarte, P.; Henriques, C. Travelers’ use of social media: A clustering approach. Ann. Tour. Res. 2016, 59, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerli, A.; Martín, J.D. Factors influencing destination image. Ann. Tour. Res. 2004, 31, 657–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pymesonline. Available online: http://www.pymesonline.com/uploads/tx_icticontent/agentes_destinos.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2021).
- Murphy, L.; Mascardo, G.; Benckendorff, P. Exploring word-of-mouth influences on travel decisions: Friends and relatives vs. other travellers. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2007, 31, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.C.; Kim, Y. Determinants of consumer engagement in electronic word-of-mouth (eWOM) in social networking sites. Int. J. Advert. 2011, 30, 47–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirakaya, E.; Sonmez, S. Gender images in state tourism brochures: An overlooked area in socially responsible tourism marketing. J. Travel Res. 2010, 38, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Lehto, X.Y.; Morrison, A.M. Destination image representation on the web: Content analysis of Macau travel related websites. Tour. Manag. 2007, 28, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandvik, T.; Rindell, A. Value of Image in Service; Hanken School of Economics: Helsinki, Finland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mäläskä, M.; Saraniemi, S.; Tähtinen, J. Co-creation of branding by network actors. In Proceedings of the 10th Annual EBRF Conference on Co-Creation as a Way Forward, Nokia, Finland, 15–17 September 2010; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Revilla-Hernández, M.; Santana-Talavera, A.; Parra-López, E. Effects of co-creation in a tourism destination brand image through twitter. J. Tour. Herit. Serv. Mark. 2016, 2, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Saraniemi, S. Destination brand identity development and value system. Tour. Rev. 2010, 65, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, E.; Panyik, E. Content, context and co-creation: Digital challenges in destination branding with references to Portugal as a tourist destination. J. Vacat. Mark. 2015, 21, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhofer, B. An Exploration of the Technology Enhanced Tourist Experience; Bournemouth University: Bournemouth, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mladenovic, D.; Dolenec, S. Theoretical overview of social media-value (co) creation bond. In Economic and Social Development: Book of Proceedings; Varazdin Development and Entrepreneurship Agency (VADEA): Varazdin, Croatia, 2016; pp. 187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Dolan, R.; Seo, Y.; Kemper, J. Complaining practices on social media in tourism: A value co-creation and co-destruction perspective. Tour. Manag. 2019, 73, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambisan, S.; Baron, R.A. Virtual customer environments: Testing a model of voluntary participation in value co-creation activities. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2009, 26, 388–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confederation of Employers of Cuenca (CEOE CEPYME). Available online: http://www.ceoecuenca.es/ (accessed on 10 January 2021).
- Berhanu, K.; Raj, S. The trustworthiness of travel and tourism information sources of social media: Perspectives of international tourists visiting Ethiopia. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, M.J.; Krallman, A.; Adams, F.G.; Hancock, T. One size doesn’t fit all: A uses and gratifications analysis of social media platforms. J. Res. Interact. Mark. 2020, 14, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, J.M.; Lance, C.E. What reviewers should expect from authors regarding common method bias in organizational research. J. Bus. Psychol. 2010, 25, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, J.S.; Overton, T.S. Estimating Non Response Bias in Mail Surveys. J. Mark. Res. 1977, 14, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.; Hult, G.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM), 2nd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dahl, D.W.; Moreau, C.P. Thinking inside the box: Why consumers enjoy constrained creative experiences. J. Mark. Res. 2007, 44, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konecnik, M.; Gartner, W. Customer-based brand equity for a destination. Ann. Tour. Res. 2007, 34, 400–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo-Martínez, S.; Garau-Vadell, J.B.; Martínez-Ruiz, M.P. Factors influencing repeat visits to a destination: The influence of group composition. Tour. Manag. 2010, 31, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.A.; Pratt, G. A description of the affective quality attributed to environments. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1980, 38, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylos, N.; Vassiliadis, C.A.; Bellou, V.; Andronikidis, A. Destination images, holistic images and personal normative beliefs: Predictors of intention to revisit a destination. Tour. Manag. 2016, 53, 40–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringle, C.; Wende, S.; Will, A. Smart PLS 2.0; University of Hamburg: Hamburg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.; Sarstedt, M. Testing measurement invariance of composites using partial least squares. Int. Mark. Rev. 2016, 33, 405–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, D.P.; Coxe, S.; Baraldi, A.N. Guidelines for the investigation of mediating variables in business research. J. Bus. Psychol. 2012, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sinkovics, R.R. The use of partial least squares path modeling in international marketin. In New Challenges to International Marketing; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2009; pp. 277–319. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra, T.K.; Henseler, J. Consistent partial least squares path modeling. MIS Q. 2015, 39, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, R.F.; Miller, N.B. A Primer for Soft Modeling; University of Akron Press: Akron, OH, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phau, I.; Shanka, T.; Dhayan, N. Destination image and choice intention of university student travellers to Mauritius. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2010, 22, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ye, T. Dynamic destination image formation and change under the effect of various agents: The case of Lijiang, The Capital of Yanyu. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2018, 7, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power for the Behavioral Sciences; Erlbaum: Hillsdale, MI, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Giannopoulos, A.; Piha, L.; Skourtis, G. Destination branding and co-creation: A service ecosystem perspective. J. Prod. Brand Manag. 2020, 30, 148–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Chelliah, S.; Ahmed, S. Factors influencing destination image and visit intention among young women travellers: Role of travel motivation, perceived risks, and travel constraints. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2017, 22, 1139–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.M.; Ismail, H.; Lee, S. From desktop to destination: User-generated content platforms, co-created online experiences, destination image and satisfaction. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2020, 18, 100490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Sánchez, P.P.; Correia, M.B.; Jambrino-Maldonado, C.; de las Heras-Pedrosa, C. Instagram as a co-creation space for tourist destination image-building: Algarve and Costa del Sol case studies. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Las Noticias de Cuenca. Available online: https://www.lasnoticiasdecuenca.es/provincia/turismo-crece-cuenca-pero-como-destino-fin-semana-43070 (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Kneesel, E.; Baloglu, S.; Millar, M. Gaming destination images: Implications for branding. J. Travel Res. 2010, 49, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Tsai, D. How destination image and evaluative factors affect behavioral intentions? Tour. Manag. 2007, 28, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).