Non-Lethal Sequential Individual Monitoring of Viremia in Relation to DNA Vaccination in Fish–Example Using a Salmon Alphavirus DNA Vaccine in Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. DNA Vaccine
2.2. Ethical Statement
2.3. Experiment 1—Host Immune Response Following DNA Vaccination (Fish Not Challenged—Lethal Sampling)
2.4. Experiment 2—Non-Lethal Sampling, Vaccination Followed by Immersion Challenge
2.4.1. Vaccination
2.4.2. SPDv Challenge
2.5. Measurement of Viremia and Neutralising Antibodies by RTG-P1 Assay (Experiment 2)
2.6. SPDv Re-Isolation and Confirmation from Plasma Samples (Experiment 2)
2.7. Heart and Muscle Histopathology Scoring (Experiment 2)
2.8. RNA Extraction and Gene Expression (Immune Gene, Virus Load, Plasmid Load; Experiment 1 and/or 2)
2.9. Data and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
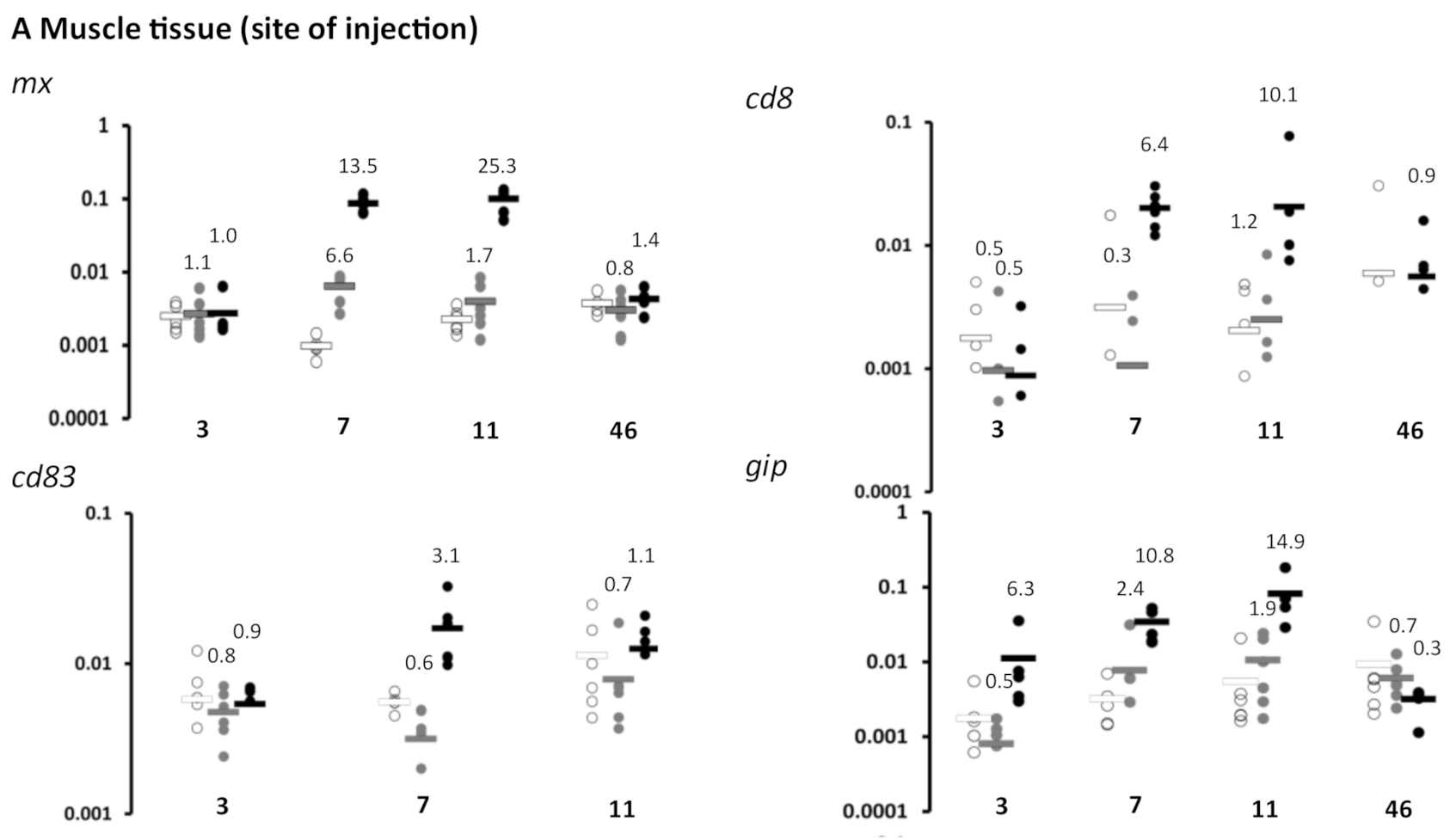
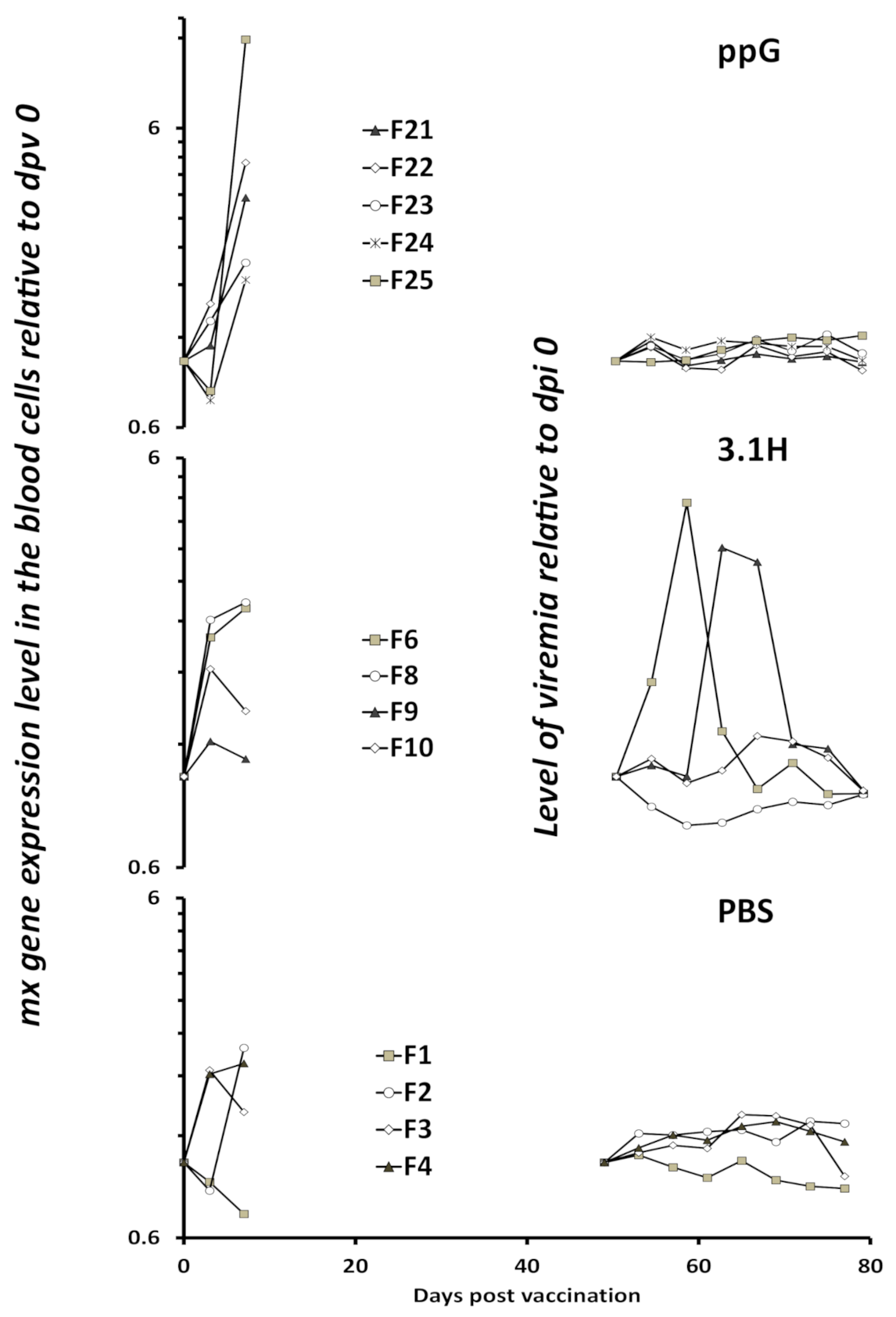
3.1. Immune Gene Expression Following Vaccination-Experiment 1 (Lethal Sampling)
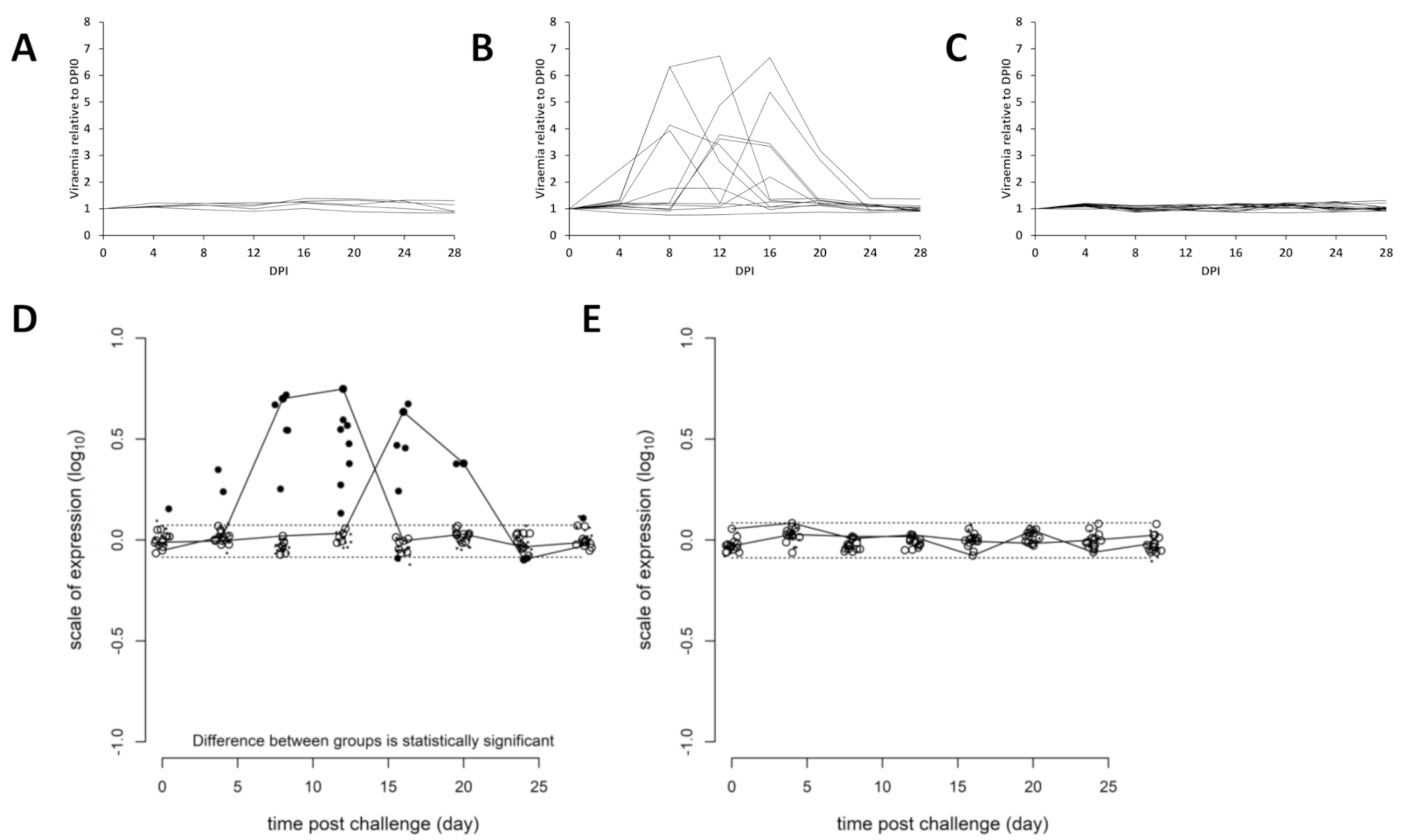
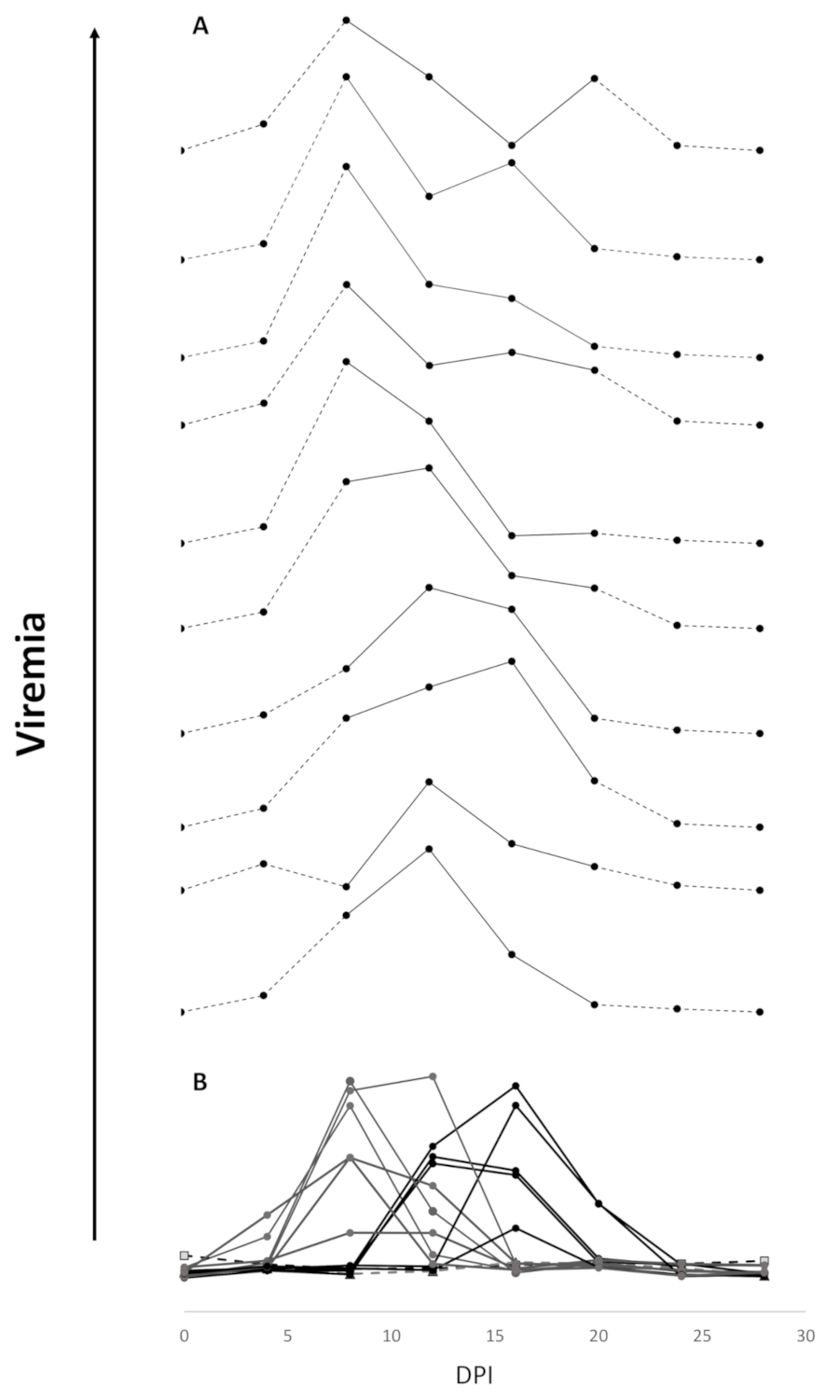
3.2. Efficacy of Sea Water Immersion Challenge and SPDv ppG DNA Vaccination–Experiment 2
3.3. Viremia and Mx Gene Expression in Blood Cells–Experiment 2
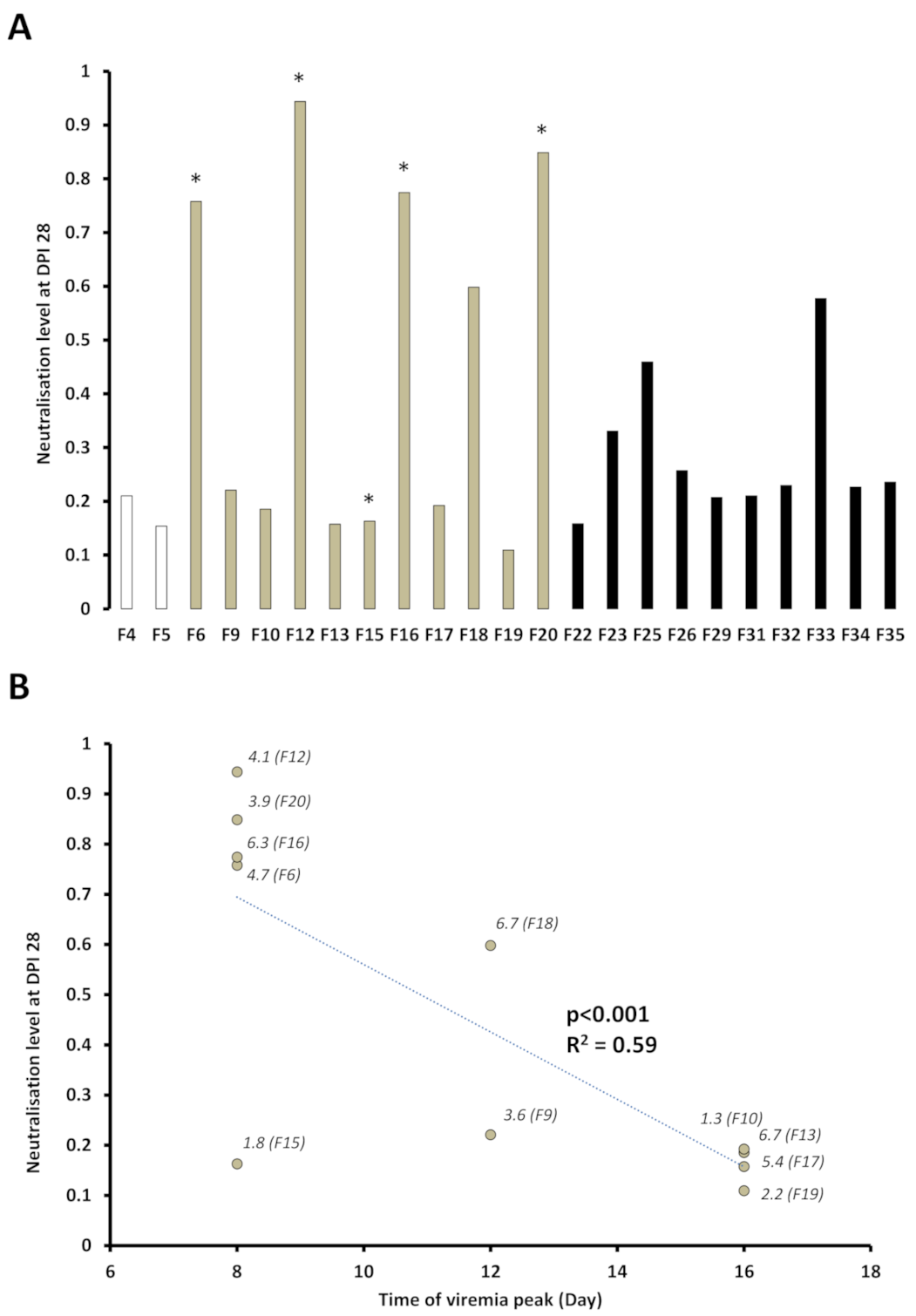
3.4. Presence of SPDv Plasma Neutralising Antibodies—Experiment 2
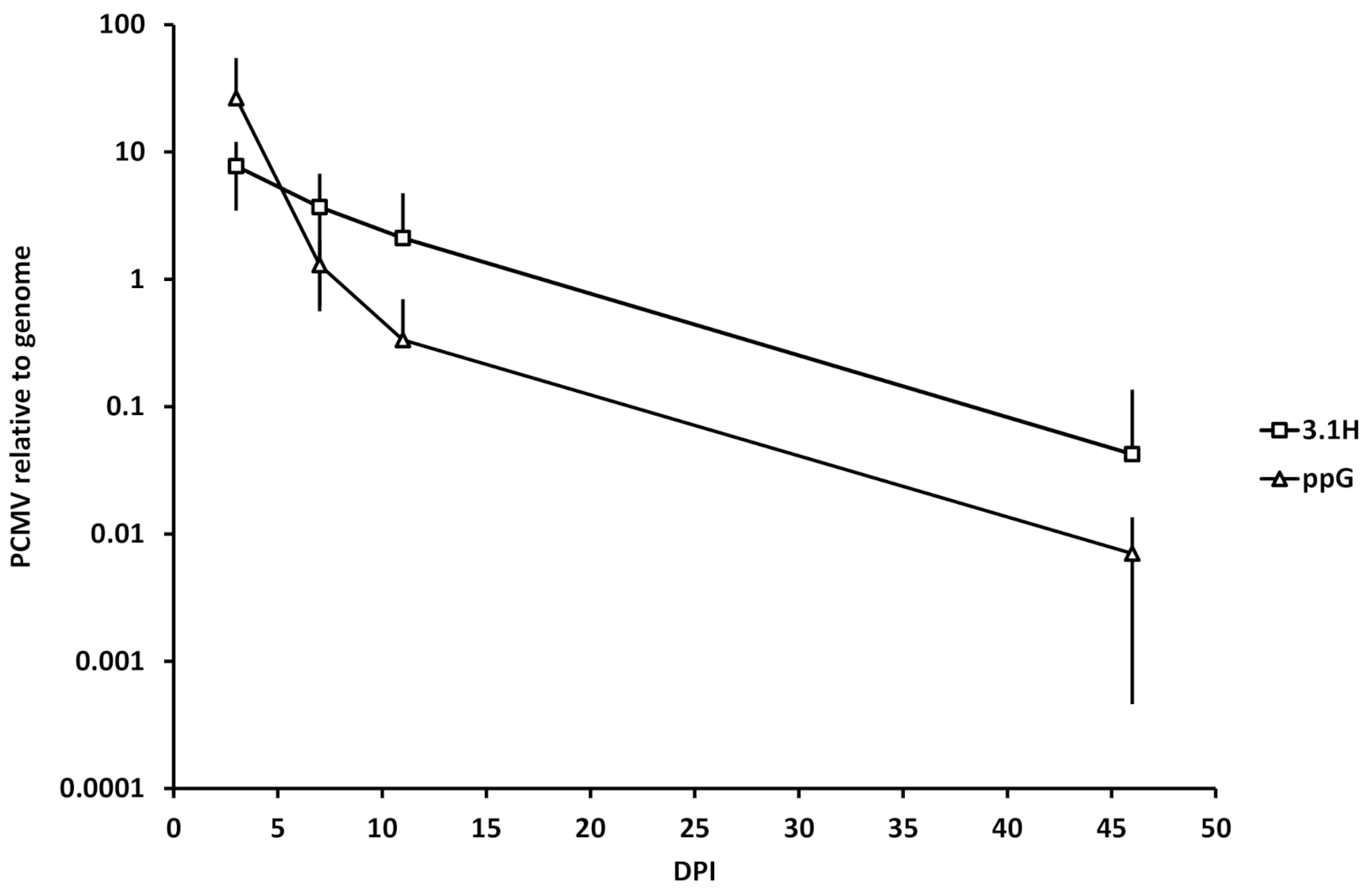
3.5. Kinetics of Plasmid Amount at the Site of Injection (Experiment 1)
4. Discussion
4.1. Viremia as a Proxy for Vaccine Efficacy
4.2. Viremia Kinetics
4.3. Plasma Neutralisation Levels
4.4. Plasmid Decay at the Site of Injection
4.5. Immersion SPDv Challenge
4.6. Early Type I Interferon and Later Vaccinal Protection
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jansen, M.D.; Jensen, B.B.; McLoughlin, M.F.; Rodger, H.D.; Taksdal, T.; Sindre, H.; Graham, D.A.; Lillehaug, A. The epidemiology of pancreas disease in salmonid aquaculture: Asummary of the current state of knowledge. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 40, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brudeseth, B.E.; Wiulsrød, R.; Fredriksen, B.N.; Lindmo, K.; Løkling, K.-E.; Bordevik, M.; Steine, N.; Klevan, A.; Gravningen, K. Status and future perspectives of vaccines for industrialised fin-fish farming. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evensen, Ø.; Leong, J.-A.C. DNA vaccines against viral diseases of farmed fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1751–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hølvold, L.B.; Myhr, A.I.; Dalmo, R.A. Strategies and hurdles using DNA vaccines to fish. Veter. Res. 2014, 45, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, V.; Espelid, S.; Mikkelsen, H. Vaccine efficacy in spotted wolffish Anarhichas minor: Relationship to molecular variation in A-layer protein of atypical Aeromonas salmoncida. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2003, 56, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikke, M.C.; Braaen, S.; Villoing, S.; Hodneland, K.; Geertsema, C.; Verhagen, L.; Frost, P.; Vlak, J.M.; Rimstad, E.; Pijlman, G. Salmonid alphavirus glycoprotein E2 requires low temperature and E1 for virion formation and induction of protective immunity. Vaccine 2014, 32, 6206–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.; Lorenzen, N.; Collet, B. DNA vaccination for finfish aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 85, 106–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.; Collins, C.; Collet, B. The potential benefits of repeated measure experiments for fish disease-challenge host-pathogen investigations. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 85, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collet, B.; Urquhart, K.; Monte, M.; Collins, C.; Perez, S.G.; Secombes, C.J.; Hall, M. Individual Monitoring of Immune Response in Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar following Experimental Infection with Infectious Salmon Anaemia Virus (ISAV). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, M.; Urquhart, K.; Evensen, Ø.; Secombes, C.J.; Collet, B. Individual monitoring of immune response in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar following experimental infection with piscine myocarditis virus (PMCV), agent of cardiomyopathy syndrome (CMS). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 99, 103406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teige, L.H.; Aksnes, I.; Røsæg, M.V.; Jensen, I.; Jørgensen, J.; Sindre, H.; Collins, C.; Collet, B.; Rimstad, E.; Dahle, M.K.; et al. Detection of specific Atlantic salmon antibodies against salmonid alphavirus using a bead-based immunoassay. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2020, 106, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collet, B.; Urquhart, K.; Noguera, P.; Larsen, K.H.; Lester, K.; Smail, D.; Bruno, D. A method to measure an indicator of viraemia in Atlantic salmon using a reporter cell line. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 191, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriette, C.; Leberre, M.; Boscher, S.K.; Castric, J.; Brémont, M. Characterization and mapping of monoclonal antibodies against the Sleeping disease virus, an aquatic alphavirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 3119–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.A.; Frost, P.; McLaughlin, K.; Rowley, H.M.; Gabestad, I.; Gordon, A.; McLoughlin, M.F. A comparative study of marine salmonid alphavirus subtypes 1-6 using an experimental cohabitation challenge model. J. Fish Dis. 2011, 34, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collet, B.; Collins, C. Comparative gene expression profile in two Atlantic salmon cell lines TO and SHK-1. Veter. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 130, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBeath, A.J.; Snow, M.; Secombes, C.; Ellis, A.; Collet, B. Expression kinetics of interferon and interferon-induced genes in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) following infection with infectious pancreatic necrosis virus and infectious salmon anaemia virus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 22, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodneland, K.; Endresen, C. Sensitive and specific detection of Salmonid alphavirus using real-time PCR (TaqMan®). J. Virol. Methods 2006, 131, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, D.; Collet, B.; Turnbull, A.; Kilburn, R.; Walker, A.; Pendrey, D.; McIntosh, A.; Urquhart, K.; Taylor, G. Evaluation and development of diagnostic methods for Renibacterium salmoninarum causing bacterial kidney disease (BKD) in the UK. Aquaculture 2007, 269, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate—A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.J.; Gu, J.; Robertsen, B. Protective effect and antibody response of DNA vaccine against salmonid alphavirus 3 (SAV3) in Atlantic salmon. J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-J.; Sun, B.; Robertsen, B. Adjuvant activity of fish type I interferon shown in a virus DNA vaccination model. Vaccine 2015, 33, 2442–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-J.; Robertsen, C.; Sun, B.; Robertsen, B. Protection of Atlantic salmon against virus infection by intramuscular injection of IFNc expression plasmid. Vaccine 2014, 32, 4695–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjold, P.; Sommerset, I.; Frost, P.; Villoing, S. Vaccination against pancreas disease in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., reduces shedding of salmonid alphavirus. Veter. Res. 2016, 47, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, M.; Tingbø, T.; Solbakk, I.-T.; Evensen, Ø.; Furevik, A.; Aas-Eng, A. Efficacy and safety of an inactivated vaccine against Salmonid alphavirus (family Togaviridae). Vaccine 2012, 30, 5688–5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLoughlin, M.F.; Nelson, R.; Rowley, H.; Cox, D.; Grant, A. Experimental pancreas disease in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar post-smolts induced by salmon pancreas disease virus (SPDV). Dis. Aquat. Org. 1996, 26, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarungsriapisit, J.; Moore, L.J.; Taranger, G.L.; Nilsen, T.O.; Morton, H.C.; Fiksdal, I.U.; Stefansson, S.; Fjelldal, P.G.; Evensen, Ø.; Patel, S. Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) post-smolts challenged two or nine weeks after seawater-transfer show differences in their susceptibility to salmonid alphavirus subtype 3 (SAV3). Virol. J. 2016, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Urquhart, K.; Collins, C.; Monte, M.; Sokolowska, J.; Secombes, C.; Collet, B. Individual measurement of gene expression in blood cells from Rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J. Exp. Appl. Anim. Sci. 2016, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chance, R.J.; Cameron, G.A.; Fordyce, M.; Noguera, P.; Wang, T.; Collins, C.; Secombes, C.J.; Collet, B. Effects of repeated anaesthesia on gill and general health of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar. J. Fish Biol. 2018, 93, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, M.; Von Gegerfelt, A.; Roth, P.; Alicea, C.; Valentin, A.; Robert-Guroff, M.; Venzon, D.; Montefiori, D.C.; Markham, P.; Felber, B.K.; et al. DNA Vaccines Expressing Different Forms of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Antigens Decrease Viremia upon SIVmac251 Challenge. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8480–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belisle, S.E.; Yin, J.; Shedlock, D.J.; Dai, A.; Yan, J.; Hirao, L.; Kutzler, M.A.; Lewis, M.G.; Andersen, H.; Lank, S.M.; et al. Long-Term Programming of Antigen-Specific Immunity from Gene Expression Signatures in the PBMC of Rhesus Macaques Immunized with an SIV DNA Vaccine. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gao, N.; Song, Y.; Duan, S.; Wang, W.; Cong, Z.; Qin, C.; Jiang, C.; Yu, X.; Gao, F. Reduction of peak viremia by an integration-defective SIV proviral DNA vaccine in rhesus macaques. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 64, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rompay, K.K.A.; Keesler, R.I.; Ardeshir, A.; Watanabe, J.; Usachenko, J.; Singapuri, A.; Cruzen, C.; Bliss-Moreau, E.; Murphy, A.M.; Yee, J.L.; et al. DNA vaccination before conception protects Zika virus—Exposed pregnant macaques against prolonged viremia and improves fetal outcomes. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaay2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munang’Andu, H.M.; Evensen, Ø. Correlates of protective immunity for fish vaccines. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 85, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desvignes, L.; Quentel, C.; Lamour, F.; Le Ven, A. Pathogenesis and immune response in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) parr experimentally infected with salmon pancreas disease virus (SPDV). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2002, 12, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, K.; Graham, D.; McLoughlin, M.; Villoing, S.; Todd, D.; Knappskog, D. Experimental infection of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar pre-smolts by i.p. injection with new Irish and Norwegian salmonid alphavirus (SAV) isolates: A comparative study. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2007, 75, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.A.; Jewhurst, V.A.; Rowley, H.M.; McLoughlin, M.F.; Rodger, H.D.; Todd, D. Longitudinal serological surveys of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., using a rapid immunoperoxidase-based neutralization assay for salmonid alphavirus. J. Fish Dis. 2005, 28, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.A.; Jewhurst, H.; McLoughlin, M.F.; Sourd, P.; Rowley, H.; Taylor, C.; Todd, D. Sub-clinical infection of farmed Atlantic salmon Salmo salar with salmonid alphavirus? A prospective longitudinal study. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2006, 72, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.A.; Fringuelli, E.; Wilson, C.; Rowley, H.M.; Brown, A.; Rodger, H.D.; McLoughlin, M.F.; McManus, C.; Casey, E.; McCarthy, L.J.; et al. Prospective longitudinal studies of salmonid alphavirus infections on two Atlantic salmon farms in Ireland; evidence for viral persistence. J. Fish Dis. 2010, 33, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, T.M.; Drinan, E.M.; Gannon, F. Studies with an experimental model for pancreas disease of Atlantic salmon Salmo Salar L. Aquac. Res. 1995, 26, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, G.; Ellis, A. Pancreas disease in Atlantic salmon: Serum neutralisation and passive immunisation. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 1996, 6, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarzotti-Kelsoe, M.; Bailer, R.T.; Turk, E.; Lin, C.-L.; Bilska, M.; Greene, K.M.; Gao, H.; Todd, C.A.; Ozaki, D.A.; Seaman, M.S.; et al. Optimization and validation of the TZM-bl assay for standardized assessments of neutralizing antibodies against HIV-1. J. Immunol. Methods 2014, 409, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, D.E. Roles and reactivities of antibodies to alphaviruses. Semin. Virol. 1995, 6, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenberie, S.; Peñaranda, M.M.D.; Thim, H.L.; Styrvold, M.B.; Strandskog, G.; Jørgensen, J.B.; Jensen, I. Salmonid Alphavirus Subtype 3 Induces Prolonged Local B Cell Responses in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) After Intraperitoneal Infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertsen, B.; Chang, C.-J.; Bratland, L. IFN-adjuvanted DNA vaccine against infectious salmon anemia virus: Antibody kinetics and longevity of IFN expression. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 54, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laylor, R.; Porakishvili, N.; De Souza, J.; Playfair, J.; Delves, P.; Lund, T. DNA vaccination favours memory rather than effector B cell responses. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1999, 117, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmaljohn, A.L.; Johnson, E.D.; Dalrymple, J.M.; Cole, G.A. Non-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies can prevent lethal alphavirus encephalitis. Nat. Cell Biol. 1982, 297, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excler, J.-L.; Ake, J.; Robb, M.L.; Kim, J.H.; Plotkin, S.A. Nonneutralizing Functional Antibodies: A New “Old” Paradigm for HIV Vaccines. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2014, 21, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embregts, C.; Rigaudeau, D.; Veselý, T.; Pokorová, D.; Lorenzen, N.; Petit, J.; Houel, A.; Dauber, M.; Schütze, H.; Boudinot, P.; et al. Intramuscular DNA Vaccination of Juvenile Carp against Spring Viremia of Carp Virus Induces Full Protection and Establishes a Virus-Specific B and T Cell Response. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heppell, J.; Lorenzen, N.; Armstrong, N.K.; Wu, T.; Lorenzen, E.; Einer-Jensen, K.; Schorr, J.; Davis, H.L. Development of DNA vaccines for fish: Vector design, intramuscular injection and antigen expression using viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus genes as model. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 1998, 8, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, T.K.; Ashby, A.J.; Jayasuriya, N.S.; Bron, J.E.; Taylor, J.F.; Adams, A.; Richards, R.H.; Weidmann, M.; Ferguson, H.W.; Taggart, J.B.; et al. Impact of Salmonid alphavirus infection in diploid and triploid Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) fry. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano, I.; Joiner, C.; Bayley, A.; Rimmer, G.; Bateman, K.; Feist, S.W.; Stone, D.; Paley, R. An experimental means of transmitting pancreas disease in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L. fry in freshwater. J. Fish Dis. 2015, 38, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLoughlin, M.F.; Graham, D.A. Alphavirus infections in salmonids? A review. J. Fish Dis. 2007, 30, 511–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Mutoloki, S. Evensen, Øystein Superior protection conferred by inactivated whole virus vaccine over subunit and DNA vaccines against salmonid alphavirus infection in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Vaccine 2012, 30, 3918–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tough, D.F. Type I Interferon as a Link Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity through Dendritic Cell Stimulation. Leuk. Lymphoma 2004, 45, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Ohnemus, A.; Ong, L.C.; Gad, H.H.; Hartmann, R.; Lycke, N.; Staeheli, P. Type I and Type III Interferons Differ in Their Adjuvant Activities for Influenza Vaccines. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracci, L.; Canini, I.; Venditti, M.; Spada, M.; Puzelli, S.; Donatelli, I.; Belardelli, F.; Proietti, E. Type I IFN as a vaccine adjuvant for both systemic and mucosal vaccination against influenza virus. Vaccine 2006, 24, S56–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagao, Y.; Yamashiro, K.; Hara, N.; Horisawa, Y.; Kato, K.; Uemura, A. Oral-Mucosal Administration of IFN-α Potentiates Immune Response in Mice. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 1998, 18, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bon, A.; Durand, V.; Kamphuis, E.; Thompson, C.; Bulfone-Paus, S.; Rossmann, C.; Kalinke, U.; Tough, D.F. Direct Stimulation of T Cells by Type I IFN Enhances the CD8+T Cell Response during Cross-Priming. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 4682–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikalsen, A.B.; Sindre, H.; Torgersen, J.; Rimstad, E. Protective effects of a DNA vaccine expressing the infectious salmon anemia virus hemagglutinin-esterase in Atlantic salmon. Vaccine 2005, 23, 4895–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosser, D.M.; Edwards, J.P. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, U.; Klamp, T.; Groot, A.M.; Howard, J.C. Cellular responses to interferon-γ. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1997, 15, 749–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazirinejad, R.; Ahmadi, Z.; Arababadi, M.K.; Hassanshahi, G.; Kennedy, D. The Biological Functions, Structure and Sources of CXCL10 and Its Outstanding Part in the Pathophysiology of Multiple Sclerosis. Neuroimmunomodulation 2014, 21, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhkhez, M.; Krasnov, A.; Robertsen, B. Transcriptome analyses of Atlantic salmon muscle genes induced by a DNA vaccine against salmonid alphavirus, the causative agent of salmon pancreas disease (PD). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utke, K.; Kock, H.; Schuetze, H.; Bergmann, S.M.; Lorenzen, N.; Einer-Jensen, K.; Köllner, B.; Dalmo, R.A.; Vesely, T.; Ototake, M.; et al. Cell-mediated immune responses in rainbow trout after DNA immunization against the viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzemaekers, M.; Vanheule, V.; Janssens, R.; Struyf, S.; Proost, P. Overview of the Mechanisms that May Contribute to the Non-Redundant Activities of Interferon-Inducible CXC Chemokine Receptor 3 Ligands. Front. Immunol. 2018, 8, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.; Martin, S.A.; Bird, S.; Lamas, J.; Secombes, C.J. Characterisation of γ-interferon responsive promoters in fish. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 3454–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonheim, T.C.; Dalmo, R.A.; Bøgwald, J.; Seternes, T. Specific uptake of plasmid DNA without reporter gene expression in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) kidney after intramuscular administration. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 24, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, K.J.; Kawagoe, T.; Koyama, S.; Matsui, K.; Kumar, H.; Kawai, T.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O.; Takeshita, F.; Coban, C.; et al. TANK-binding kinase-1 delineates innate and adaptive immune responses to DNA vaccines. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 451, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, H.; Ma, Z.; Barber, G.N. STING regulates intracellular DNA-mediated, type I interferon-dependent innate immunity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 461, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, F.; Lu, M.; Roggendorf, M. Coadministration of Gamma Interferon with DNA Vaccine Expressing Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus (WHV) Core Antigen Enhances the Specific Immune Response and Protects against WHV Infection. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 5036–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Long, J.-E.; Huang, L.-N.; Qin, Z.-Q.; Wang, W.-Y.; Qu, D. IFN-γ increases efficiency of DNA vaccine in protecting ducks against infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 4967–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarradas, J.; Argilaguet, J.; Rosell, R.; Nofrarías, M.; Crisci, E.; Córdoba, L.; Pérez-Martín, E.; Díaz, I.; Rodríguez, F.; Domingo, M.; et al. Interferon-gamma induction correlates with protection by DNA vaccine expressing E2 glycoprotein against classical swine fever virus infection in domestic pigs. Veter. Microbiol. 2010, 142, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Bourgine, M.; Zhang, X.M.; Bayard, F.; Deng, Q.; Michel, M.-L. Plasmid Vector-Linked Maturation of Natural Killer (NK) Cells Is Coupled to Antigen-Dependent NK Cell Activation during DNA-Based Immunization in Mice. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 10201–10212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassity, E.; Clark, T.G. Functional Identification of Dendritic Cells in the Teleost Model, Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granja, A.G.; Leal, E.; Pignatelli, J.; Castro, R.; Abós, B.; Kato, G.; Fischer, U.; Tafalla, C. Identification of Teleost Skin CD8α+ Dendritic-like Cells, Representing a Potential Common Ancestor for Mammalian Cross-Presenting Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 1825–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer-Barber, K.D.; Yan, B. Clash of the Cytokine Titans: Counter-regulation of interleukin-1 and type I interferon-mediated inflammatory responses. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braceland, M.; Bickerdike, R.; Tinsley, J.; Cockerill, D.; McLoughlin, M.; Graham, D.; Burchmore, R.; Weir, W.; Wallace, C.; Eckersall, P.D. The serum proteome of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar, during pancreas disease (PD) following infection with salmonid alphavirus subtype 3 (SAV3). J. Proteom. 2013, 94, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreassen, R.; Woldemariam, N.T.; Egeland, I.Ø.; Agafonov, O.; Sindre, H.; Høyheim, B. Identification of differentially expressed Atlantic salmon miRNAs responding to salmonid alphavirus (SAV) infection. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attaya, A.; Jiang, Y.; Secombes, C.J.; Wang, T. Distinct response of immune gene expression in peripheral blood leucocytes modulated by bacterin vaccine candidates in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss: A potential in vitro screening and batch testing system for vaccine development in aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 93, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


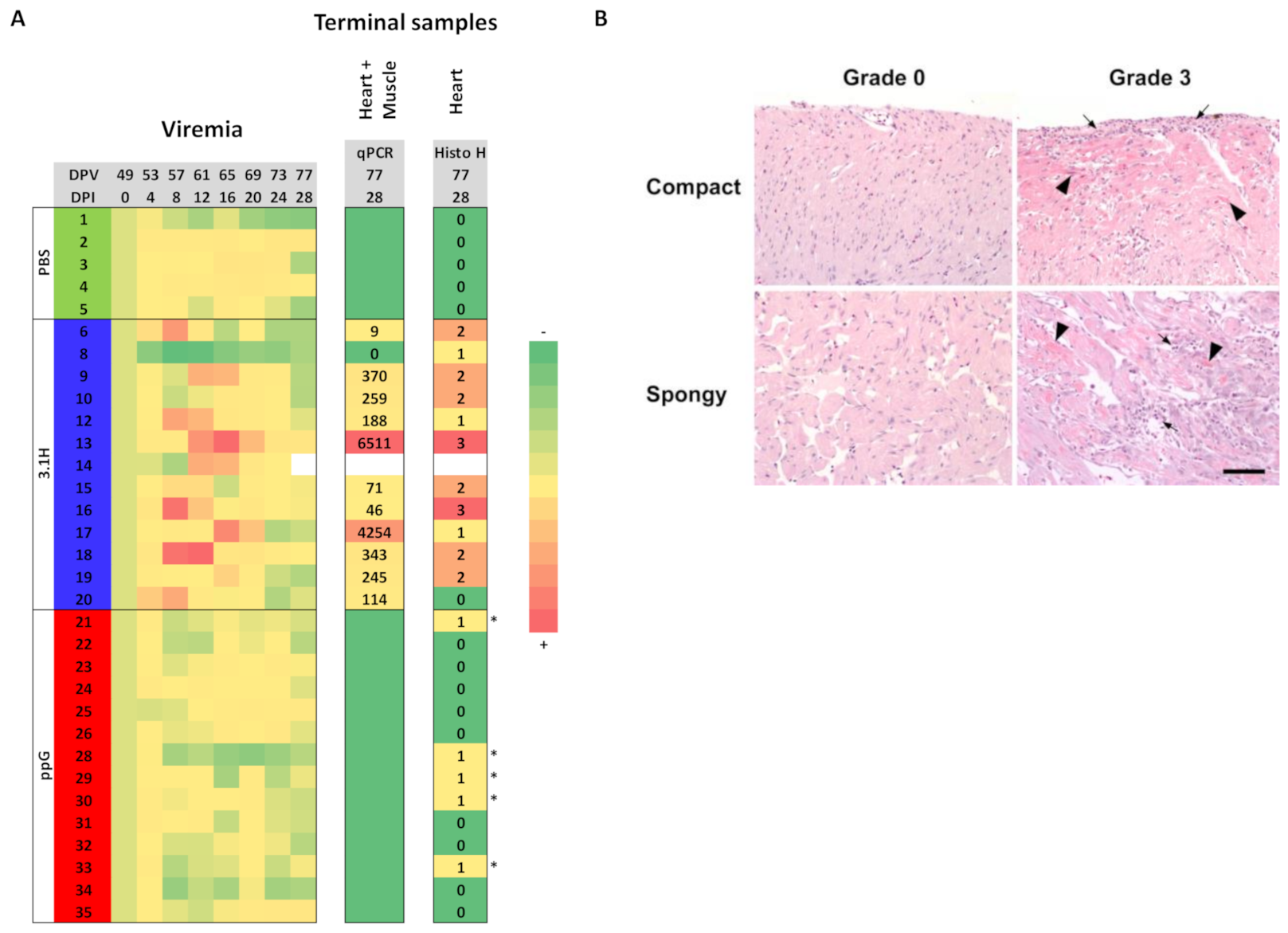
| Tissue | Score | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Heart | 0 | Normal appearance |
| 1 | Focal myocardial degeneration ± inflammation (<7 fibres affected) | |
| 2 | Focal myocardial degeneration ± inflammation (<15% of heart affected) | |
| 3 | Multifocal myocardial degeneration ± inflammation (>15 and <50% of heart affected) | |
| 4 | Severe diffuse myocardial degeneration ± inflammation (<50% of heart affected) | |
| R | Repair | |
| Red and white skeletal muscle | 0 | Normal appearance |
| 1 | Focal myocytic degeneration ± inflammation | |
| 2 | Multifocal myocytic degeneration ± inflammation | |
| 3 | Severe diffuse myocytic degeneration ± inflammation | |
| R | Repair |
| Muscle (Site of Injection) | Head Kidney | Blood Cells | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dpv | gene | Uncorrected p-Value | Corrected p-Value | Uncorrected p-Value | Corrected p-Value | Uncorrected p Value | Corrected p-Value | ||||||||||||
| PBS v 3.1H | PBS v ppG | 3.1H v ppG | PBS v 3.1H | PBS v ppG | 3.1H v ppG | PBS v 3.1H | PBS v ppG | 3.1H v ppG | PBS v 3.1H | PBS v ppG | 3.1H v ppG | PBS v 3.1H | PBS v ppG | 3.1H v ppG | PBS v 3.1H | PBS v ppG | 3.1H v ppG | ||
| 3 | mx | 0.8435 | 0.8401 | 0.9774 | ns | ns | ns | 0.2363 | 0.8740 | 0.0479 | ns | ns | ns | ||||||
| gIP | 0.2984 | 0.2016 | 0.1671 | ns | ns | ns | 0.3184 | 0.0491 | 0.1077 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| cd8 | 0.4611 | 0.3760 | 0.9204 | ns | ns | ns | 0.0046 | 0.0051 | 0.8038 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| cd83 | 0.5908 | 0.8532 | 0.6386 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||||||
| il1b | 0.1822 | 0.0305 | 0.6475 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||||||
| 7 | mx | 0.0131 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | ns | * | * | 0.5843 | 0.0010 | 0.0011 | ns | * | * | 0.0810 | 0.0149 | 0.0194 | ns | ns | ns |
| gIP | 0.3994 | 0.0043 | 0.0086 | ns | ns | ns | 0.2039 | 0.7465 | 0.0071 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| cd8 | 0.5121 | 0.0017 | 0.0007 | ns | ns | * | 0.2387 | 0.6095 | 0.7348 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| cd83 | 0.0248 | 0.0219 | 0.0100 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||||||
| il1b | 0.3671 | 0.6218 | 0.1698 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||||||
| 11 | mx | 0.2075 | 0.0048 | 0.0050 | ns | ns | ns | 0.6453 | 0.0010 | 0.0011 | ns | * | * | 0.1288 | 0.0180 | 0.0130 | ns | ns | ns |
| gIP | 0.3259 | 0.0439 | 0.0534 | ns | ns | ns | 0.3677 | 0.0297 | 0.0172 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| cd8 | 0.7784 | 0.1697 | 0.1791 | ns | ns | ns | 0.1708 | 0.2485 | 0.7811 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| cd83 | 0.3940 | 0.8094 | 0.2950 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||||||
| il1b | 0.9824 | 0.8759 | 0.8680 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||||||
| 46 | mx | 0.4706 | 0.5430 | 0.1777 | ns | ns | ns | 0.4432 | 0.1412 | 0.4686 | ns | ns | ns | ||||||
| gIP | 0.5673 | 0.2851 | 0.1196 | ns | ns | ns | 0.2002 | 0.1227 | 0.3344 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| cd8 | 0.2869 | 0.9520 | 0.0669 | ns | ns | ns | 0.7191 | 0.7936 | 0.4058 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| 60 | mx | 0.3101 | 0.2542 | 0.7686 | ns | ns | ns | ||||||||||||
| cd8 | 0.5566 | 0.9337 | 0.7346 | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Collins, C.; Lester, K.; Del-Pozo, J.; Collet, B. Non-Lethal Sequential Individual Monitoring of Viremia in Relation to DNA Vaccination in Fish–Example Using a Salmon Alphavirus DNA Vaccine in Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar. Vaccines 2021, 9, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020163
Collins C, Lester K, Del-Pozo J, Collet B. Non-Lethal Sequential Individual Monitoring of Viremia in Relation to DNA Vaccination in Fish–Example Using a Salmon Alphavirus DNA Vaccine in Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar. Vaccines. 2021; 9(2):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020163
Chicago/Turabian StyleCollins, Catherine, Katherine Lester, Jorge Del-Pozo, and Bertrand Collet. 2021. "Non-Lethal Sequential Individual Monitoring of Viremia in Relation to DNA Vaccination in Fish–Example Using a Salmon Alphavirus DNA Vaccine in Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar" Vaccines 9, no. 2: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020163
APA StyleCollins, C., Lester, K., Del-Pozo, J., & Collet, B. (2021). Non-Lethal Sequential Individual Monitoring of Viremia in Relation to DNA Vaccination in Fish–Example Using a Salmon Alphavirus DNA Vaccine in Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar. Vaccines, 9(2), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020163






