Association between Elevated De Ritis Ratio and Mortality Outcome in Adult Patients with Thoracoabdominal Trauma
Abstract
1. Introduction
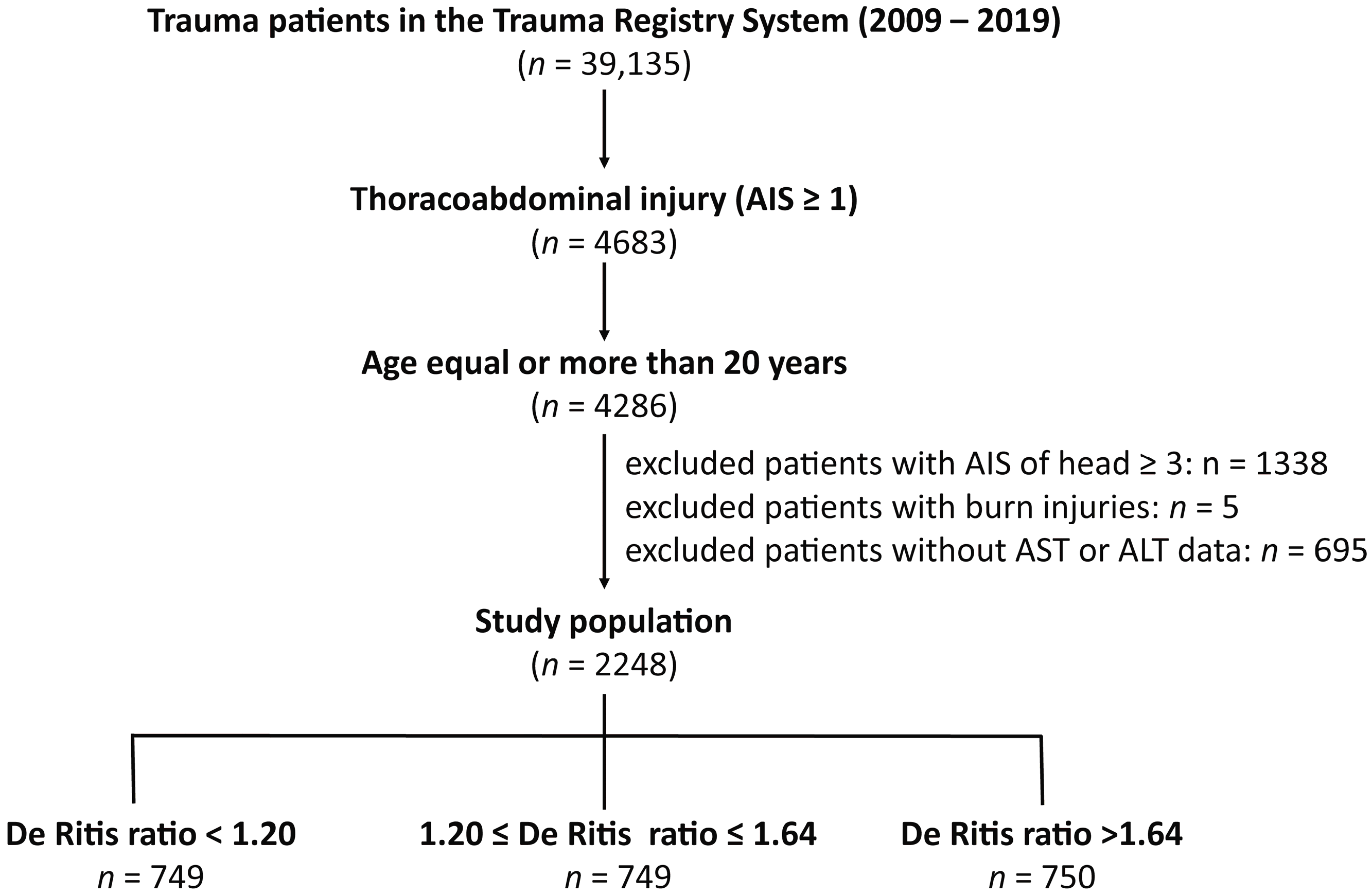
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient and Injury Characteristics
3.2. Adjusted Outcomes of the Propensity Score-Matched Patients
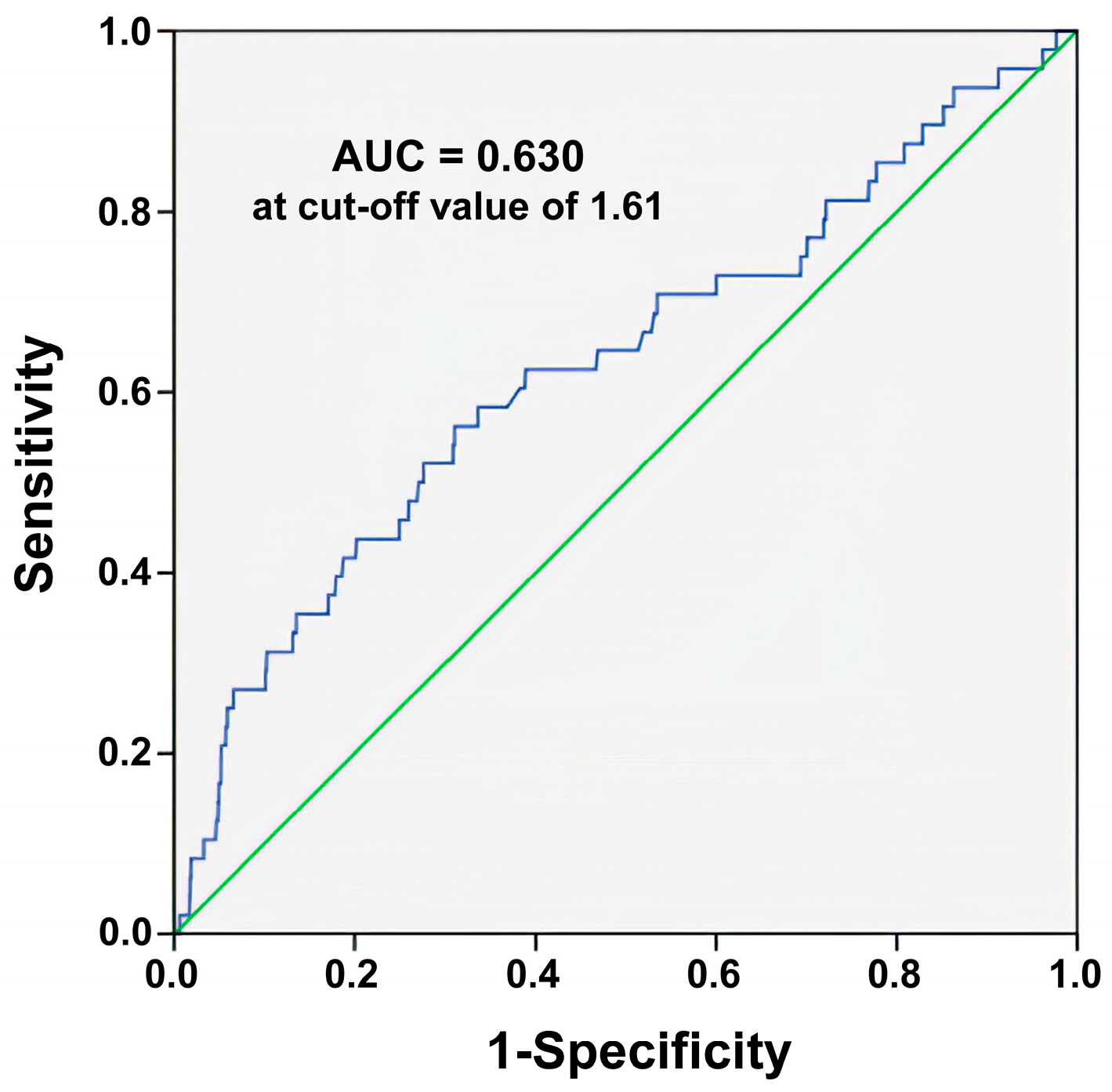
3.3. ROC Curve Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lecky, B.O.; Alexandrescu, R.; O’Brien, S.J. Changing Epidemiology of Polytrauma; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 3, pp. 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, R.J.; Okoye, O.; Teixeira, P.G.; Inaba, K.; Demetriades, D. The double jeopardy of blunt thoracoabdominal trauma. Arch. Surg. 2012, 147, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, B.; Şaşmaz, M.; Saglam Gurmen, E.; Bilge, A. Prognostic value of lactate to hematocrit ratio score in patients with severe thoracoabdominal trauma. Ulus. Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2022, 28, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriles, K.E.; Azer, S.A. Alanine Amino Transferase. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing, StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Otto-Ślusarczyk, D.; Graboń, W.; Mielczarek-Puta, M. Aspartate aminotransferase--key enzyme in the human systemic metabolism. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2016, 70, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suciu, A.; Abenavoli, L.; Pellicano, R.; Luzza, F.; Dumitrascu, D.L. Transaminases: Oldies but goldies. A narrative review. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2020, 66, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, P.C. Biochemical detection and monitoring of alcohol abuse and abstinence. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2001, 38, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botros, M.; Sikaris, K.A. The de ritis ratio: The test of time. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2013, 34, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Ritis, F.; Coltorti, M.; Giusti, G. An enzymic test for the diagnosis of viral hepatitis: The transaminase serum activities. 1957. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 369, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Li, R.; Gong, W.; Xiang, B.; Tang, W.; Yu, H. Prognostic Value of Aspartate Transaminase/Alanine Transaminase Ratio in Patients With Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma Undergoing Hepatectomy. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 876900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darstein, F.; Häuser, F.; Straub, B.K.; Wenzel, J.J.; Conradi, R.; Mittler, J.; Lang, H.; Galle, P.R.; Zimmermann, T. Hepatitis E virus genotype 3 is a common finding in liver-transplanted patients undergoing liver biopsy for elevated liver enzymes with a low De Ritis ratio and suspected acute rejection: A real-world cohort. Clin. Transpl. 2018, 32, e13411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghahari, M.; Salari, A.; Ghafoori Yazdi, M.; Nowroozi, A.; Fotovat, A.; Momeni, S.A.; Nowroozi, M.R.; Amini, E. Association Between Preoperative De Ritis (AST/ALT) Ratio and Oncological Outcomes Following Radical Cystectomy in Patients With Urothelial Bladder Cancer. Clin. Genitourin Cancer 2022, 20, e89–e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui-Kawaura, S.; Kawahara, T.; Araki, Y.; Nishimura, R.; Uemura, K.; Namura, K.; Mizuno, N.; Yao, M.; Uemura, H.; Ikeda, I. A higher De Ritis ratio (AST/ALT) is a risk factor for progression in high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janisch, F.; Klotzbücher, T.; Marks, P.; Kienapfel, C.; Meyer, C.P.; Yu, H.; Fühner, C.; Hillemacher, T.; Mori, K.; Mostafei, H.; et al. Predictive value of De Ritis ratio in metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with tyrosine-kinase inhibitors. World J. Urol. 2021, 39, 2977–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olcucu, M.T.; Karamik, K.; Yilmaz, K.; Okuducu, Y.; Cakir, S.; Ates, M. Preoperative Inflammation Markers and De Ritis Ratio in Predicting Clinical Presentation and Prognosis of Patients with Testicular Germ Cell Tumors. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2020, 30, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazo, M.; Clark, J.M. The epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A global perspective. Semin. Liver Dis. 2008, 28, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Ma, G.; Chen, L. De-Ritis Ratio Is Associated with Mortality after Cardiac Arrest. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 8826318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucukseymen, S.; Cekin, A.H.; Bayar, N.; Arslan, S.; Uygur Kucukseymen, E.; Mercan, T.; Ozdemir, S. A novel biomarker for prediction of atrial fibrillation susceptibility in patients with celiac disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.M.; He, C.; Zhang, S.C.; You, Z.B.; Lin, X.Q.; Luo, M.Q.; Lin, M.Q.; Guo, Y.S.; Zheng, W.P.; Lin, K.Y. Predictive value of aspartate aminotransferase-to-alanine aminotransferase ratio for contrast-associated acute kidney injury in patients undergoing elective percutaneous coronary intervention. J. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarczyk, K.; Carstens, H.; Heckmann, J.; Canbay, A.; Koch, A.; Pizanis, N.; Jakob, H.; Kamler, M. The aspartate transaminase/alanine transaminase (DeRitis) ratio predicts mid-term mortality and renal and respiratory dysfunction after left ventricular assist device implantation. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2017, 52, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Yu, J.; Hong, J.H.; Lim, B.; Kim, Y.; Hwang, J.H.; Kim, Y.K. Elevated De Ritis Ratio as a Predictor for Acute Kidney Injury after Radical Retropubic Prostatectomy. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.Y.; Yao, R.Q.; Ren, C.; Li, S.Y.; Li, Y.X.; Zhu, S.Y.; Yao, Y.M.; Du, X.H. De Ritis Ratio as a Significant Prognostic Factor in Patients with Sepsis: A Retrospective Analysis. J. Surg. Res. 2021, 264, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinellu, A.; Arru, F.; De Vito, A.; Sassu, A.; Valdes, G.; Scano, V.; Zinellu, E.; Perra, R.; Madeddu, G.; Carru, C.; et al. The De Ritis ratio as prognostic biomarker of in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, e13427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pranata, R.; Huang, I.; Lim, M.A.; Yonas, E.; Vania, R.; Lukito, A.A.; Nasution, S.A.; Siswanto, B.B.; Kuswardhani, R.A.T. Elevated De Ritis Ratio Is Associated With Poor Prognosis in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 676581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzey-Aras, Y.; Yazar, H.; Acar, T.; Kayacan, Y.; Acar, B.A.; Boncuk, S.; Eryilmaz, H.A. The Role of De Ritis Ratio as a Clinical Prognostic Parameter in COVID 19 Patients. Clin. Lab. 2021, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashashwini, A.; Vedavathi, R. The Study of De Ritis (Ast/Alt) Ratio in Comparision with Other Parameters for Predicting Poor Prognosis in Covid 19 Patients. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2022, 70, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Hu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, B.; Kong, W.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, K.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wu, G.; et al. Aspartate transaminase/alanine transaminase (De Ritis ratio) predicts survival in major burn patients. Burns 2022, 48, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Kim, H.Y.; Kong, Y.G.; Park, J.H.; Seo, Y.J.; Kim, Y.K. De Ritis ratio as a predictor of 1-year mortality after burn surgery. Burns 2021, 47, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Man, C.; Liao, S.; Qiu, H. The Prognosis Role of AST/ALT (De Ritis) Ratio in Patients with Adult Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 5719751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steininger, M.; Winter, M.P.; Reiberger, T.; Koller, L.; El-Hamid, F.; Forster, S.; Schnaubelt, S.; Hengstenberg, C.; Distelmaier, K.; Goliasch, G.; et al. De-Ritis Ratio Improves Long-Term Risk Prediction after Acute Myocardial Infarction. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rief, P.; Pichler, M.; Raggam, R.; Hafner, F.; Gerger, A.; Eller, P.; Brodmann, M.; Gary, T. The AST/ALT (De-Ritis) ratio: A novel marker for critical limb ischemia in peripheral arterial occlusive disease patients. Medicine 2016, 95, e3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Hsu, S.Y.; Hsieh, H.Y.; Chen, Y.C. Differences between the sexes in motorcycle-related injuries and fatalities at a Taiwanese level I trauma center. Biomed. J. 2017, 40, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Liu, H.T.; Hsu, S.Y.; Hsieh, H.Y.; Chen, Y.C. Motorcycle-related hospitalizations of the elderly. Biomed. J. 2017, 40, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Hsu, S.Y.; Hsieh, H.Y.; Chien, P.C. Defining polytrauma by abbreviated injury scale >/= 3 for a least two body regions is insufficient in terms of short-term outcome: A cross-sectional study at a level I trauma center. Biomed. J. 2018, 41, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opio, C.K.; Seremba, E.; Ocama, P.; Lalitha, R.; Kagimu, M.; Lee, W.M. Diagnosis of alcohol misuse and alcoholic liver disease among patients in the medical emergency admission service of a large urban hospital in Sub-Saharan Africa; a cross sectional study. Pan. Afr. Med. J. 2013, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torkadi, P.P.; Apte, I.C.; Bhute, A.K. Biochemical Evaluation of Patients of Alcoholic Liver Disease and Non-alcoholic Liver Disease. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 29, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldstein, A.E.; Canbay, A.; Angulo, P.; Taniai, M.; Burgart, L.J.; Lindor, K.D.; Gores, G.J. Hepatocyte apoptosis and fas expression are prominent features of human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| De Ritis Ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | <1.20 (Tertile 1) n = 749 | 1.20–1.64 (Tertile 2) n = 749 | >1.64 (Tertile 3) n = 750 | p |
| Gender | 0.001 | |||
| Male, n (%) | 558 (69.8) * | 474 (61.2) | 456 (67.7) * | |
| Female, n (%) | 242 (30.2) * | 300 (38.8) | 218 (32.3) * | |
| Age (years) | 47.0 ± 16.4 * | 50.4 ± 17.6 | 49.9 ± 18.1 | <0.001 |
| AST (U/L) | 115.8 ± 174.9 | 115.7 ± 262.0 | 140.5 ± 209.7 | 0.049 |
| ALT (U/L) | 115.9 ± 158.1 * | 74.5 ± 107.0 | 61.9 ± 86.0 | <0.001 |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| DM, n (%) | 104 (13.0) | 88 (11.4) | 79 (11.7) | 0.580 |
| HTN, n (%) | 181 (22.6) | 160 (20.7) | 160 (23.7) | 0.361 |
| CAD, n (%) | 16 (2.0) | 20 (2.6) | 13 (1.9) | 0.633 |
| CVA, n (%) | 7 (0.9) | 12 (1.6) | 16 (2.4) | 0.068 |
| CHF, n (%) | 2 (0.2) | 4 (0.5) | 5 (0.7) | 0.399 |
| ESRD, n (%) | 10 (1.2) | 4 (0.5) | 6 (0.9) | 0.301 |
| ISS, median (IQR) | 10 (8–16) * | 13 (8–18) | 13 (9–18) * | <0.001 |
| 1–15, n (%) | 581 (72.6) * | 508 (65.6) | 413 (61.3) | <0.001 |
| 16–24, n (%) | 161 (20.1) * | 196 (25.3) | 189 (28.0) | 0.001 |
| ≥25, n (%) | 58 (7.2) | 70 (9.0) | 72 (10.7) | 0.069 |
| Mortality, n (%) | 13 (1.6) | 10 (1.3) | 25 (3.7) * | 0.003 |
| Propensity Score Matched-Cohort | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| De Ritis Ratio | OR (95% CI) | p | Standardized Difference | |||||
| >1.64 (Tertile 3) n = 604 | 1.20–1.64 (Tertile 2) n = 604 | |||||||
| Male, n (%) | 403 | (66.7) | 403 | (66.7) | 1.00 | (0.79–1.27) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| Age (years) | 48.9 | ±17.9 | 48.7 | ±18.0 | - | 0.839 | 1.17% | |
| DM, n (%) | 59 | (9.8) | 59 | (9.8) | 1.00 | (0.68–1.46) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| HTN, n (%) | 126 | (20.9) | 126 | (20.9) | 1.00 | (0.76–1.32) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| CAD, n (%) | 8 | (1.3) | 8 | (1.3) | 1.00 | (0.37–2.68) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| CVA, n (%) | 6 | (1.0) | 6 | (1.0) | 1.00 | (0.32–3.12) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| CHF, n (%) | 1 | (0.2) | 1 | (0.2) | 1.00 | (0.06–16.02) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| ESRD, n (%) | 0 | (0.0) | 0 | (0.0) | - | - | - | |
| GCS | 15 | (15–15) | 15 | (15–15) | - | 0.479 | −4.07% | |
| ISS | 13 | (9–18) | 13 | (9–18) | - | 0.966 | −0.24% | |
| Mortality | 19 | (3.1) | 5 | (0.8) | 3.89 | (1.44–10.50) | 0.004 | - |
| Propensity Score Matched-Cohort | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| De Ritis Ratio | OR (95% CI) | p | Standardized Difference | |||||
| <1.20 (Tertile 1) n = 647 | 1.20–1.64 (Tertile 2) n = 647 | |||||||
| Male, n (%) | 426 | (65.8) | 426 | (65.8) | 1.00 | (0.80–1.26) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| Age (years) | 48.0 | ±16.2 | 48.6 | ±16.7 | - | 0.539 | −3.42% | |
| DM, n (%) | 71 | (11.0) | 71 | (11.0) | 1.00 | (0.71–1.42) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| HTN, n (%) | 136 | (21.0) | 136 | (21.0) | 1.00 | (0.77–1.31) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| CAD, n (%) | 9 | (1.4) | 9 | (1.4) | 1.00 | (0.39–2.54) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| CVA, n (%) | 4 | (0.6) | 4 | (0.6) | 1.00 | (0.25–4.02) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| CHF, n (%) | 0 | (0.0) | 0 | (0.0) | - | - | - | |
| ESRD, n (%) | 2 | (0.3) | 2 | (0.3) | 1.00 | (0.14–7.12) | 1.000 | 0.00% |
| GCS | 15 | (15–15) | 15 | (15–15) | - | 0.655 | −2.48% | |
| ISS | 11 | (8–17) | 12 | (8–17) | - | 0.703 | −2.12% | |
| Mortality | 11 | (1.7) | 6 | (0.9) | 1.85 | (0.68–5.03) | 0.222 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, W.-T.; Rau, C.-S.; Chou, S.-E.; Tsai, C.-H.; Liu, H.-T.; Hsu, S.-Y.; Hsieh, C.-H. Association between Elevated De Ritis Ratio and Mortality Outcome in Adult Patients with Thoracoabdominal Trauma. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2082. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10102082
Su W-T, Rau C-S, Chou S-E, Tsai C-H, Liu H-T, Hsu S-Y, Hsieh C-H. Association between Elevated De Ritis Ratio and Mortality Outcome in Adult Patients with Thoracoabdominal Trauma. Healthcare. 2022; 10(10):2082. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10102082
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Wei-Ti, Cheng-Shyuan Rau, Sheng-En Chou, Ching-Hua Tsai, Hang-Tsung Liu, Shiun-Yuan Hsu, and Ching-Hua Hsieh. 2022. "Association between Elevated De Ritis Ratio and Mortality Outcome in Adult Patients with Thoracoabdominal Trauma" Healthcare 10, no. 10: 2082. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10102082
APA StyleSu, W.-T., Rau, C.-S., Chou, S.-E., Tsai, C.-H., Liu, H.-T., Hsu, S.-Y., & Hsieh, C.-H. (2022). Association between Elevated De Ritis Ratio and Mortality Outcome in Adult Patients with Thoracoabdominal Trauma. Healthcare, 10(10), 2082. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10102082







