Proteomic Profiling and Artificial Intelligence for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Translational Medicine
Abstract
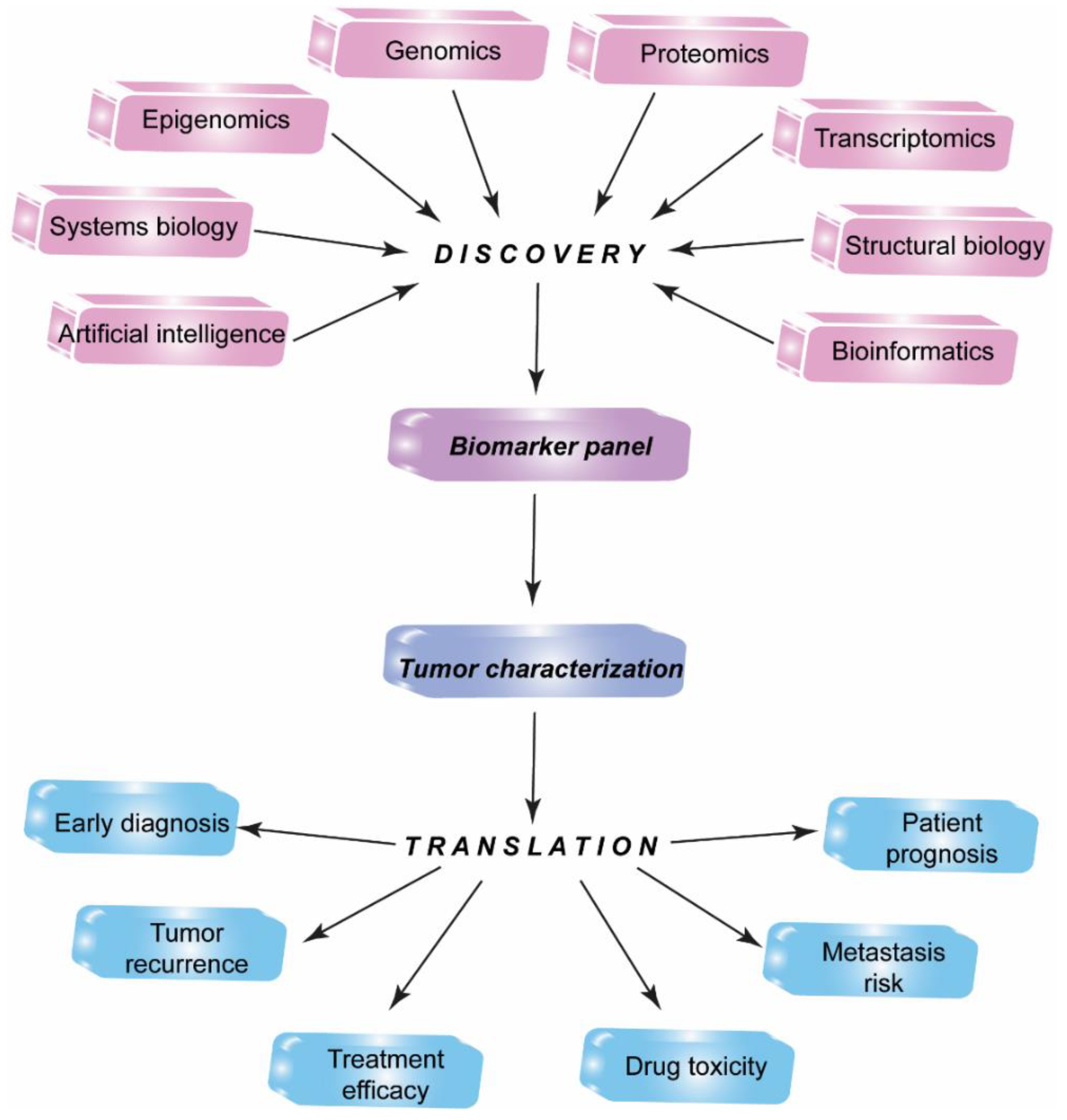
1. Introduction
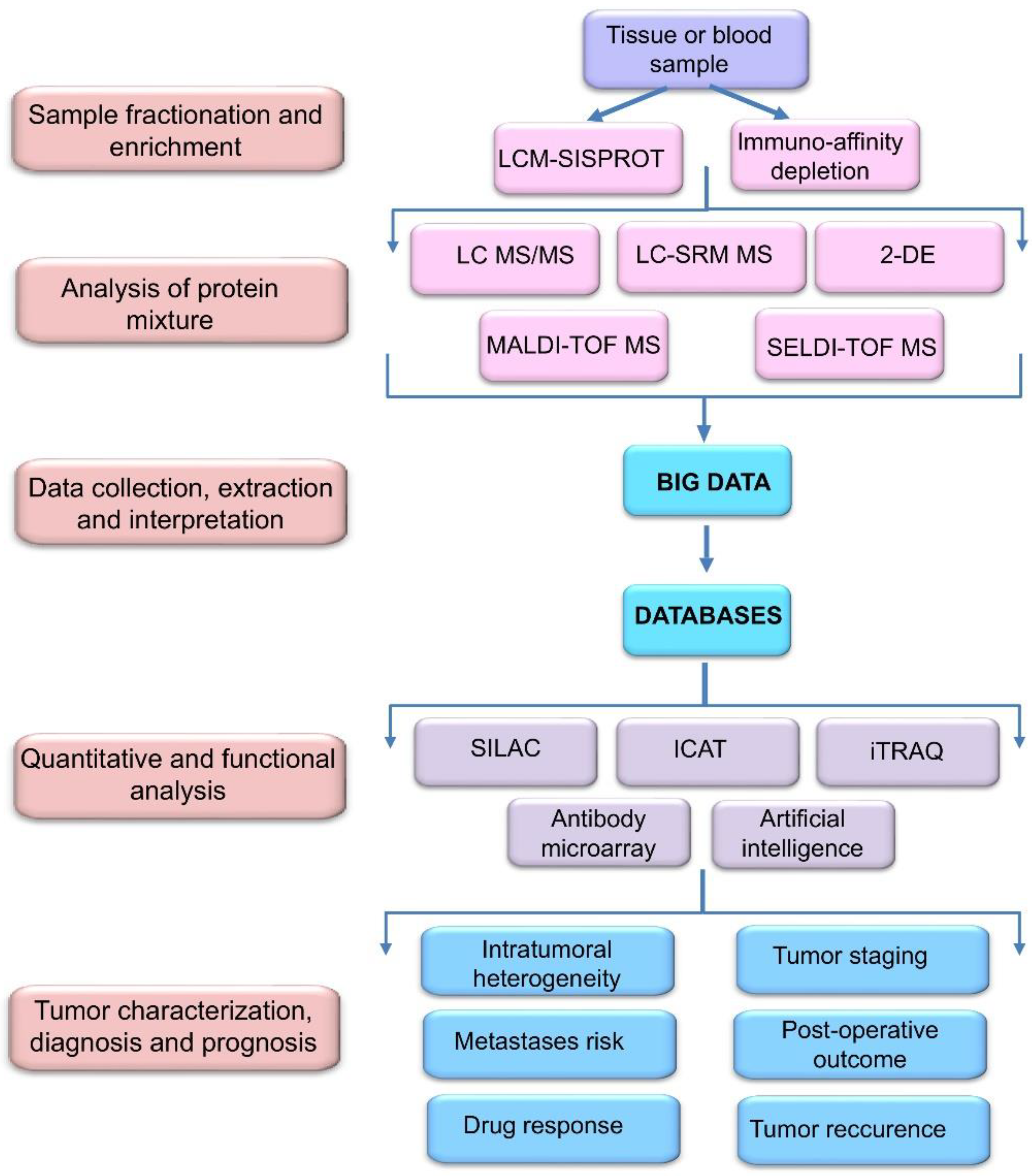
2. Proteomic Profiling Technologies and Big Data
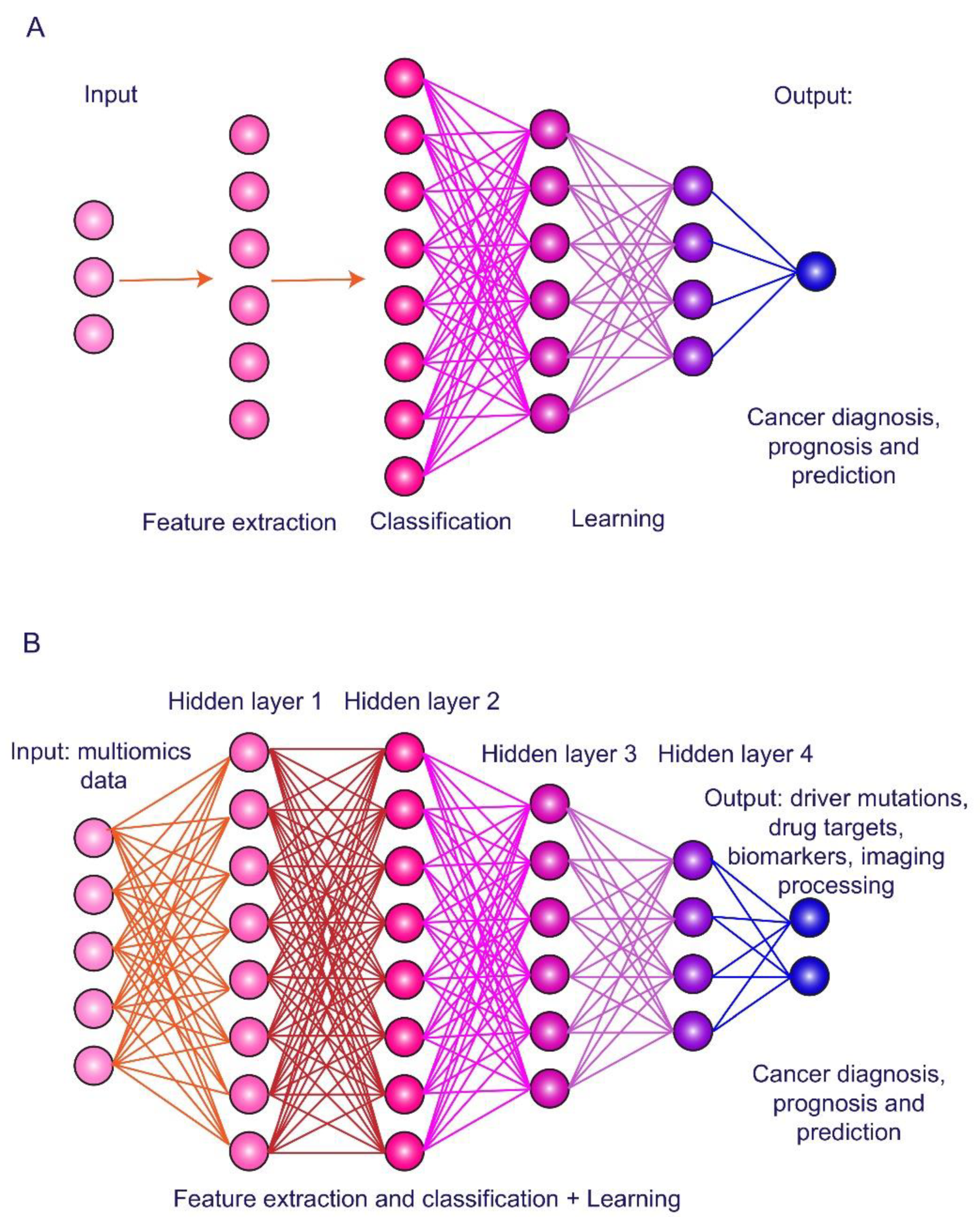
3. Artificial Intelligence in HCC Imaging and Biomarker Exploring
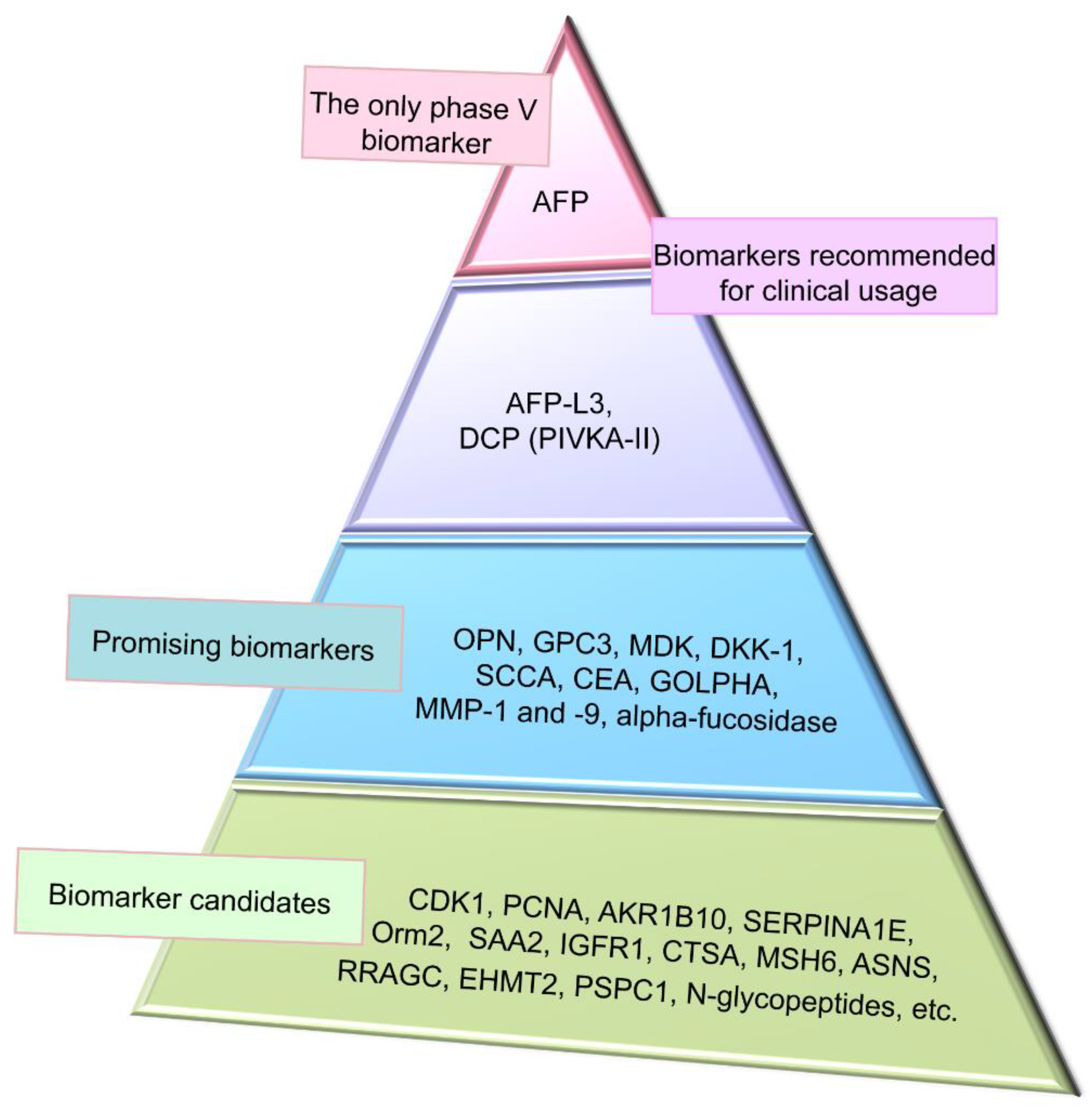
4. Conventional Biomarkers of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
4.1. Alpha-Fetoprotein and Its Glycoform
4.2. Des-Gamma-Carboxyprothrombin
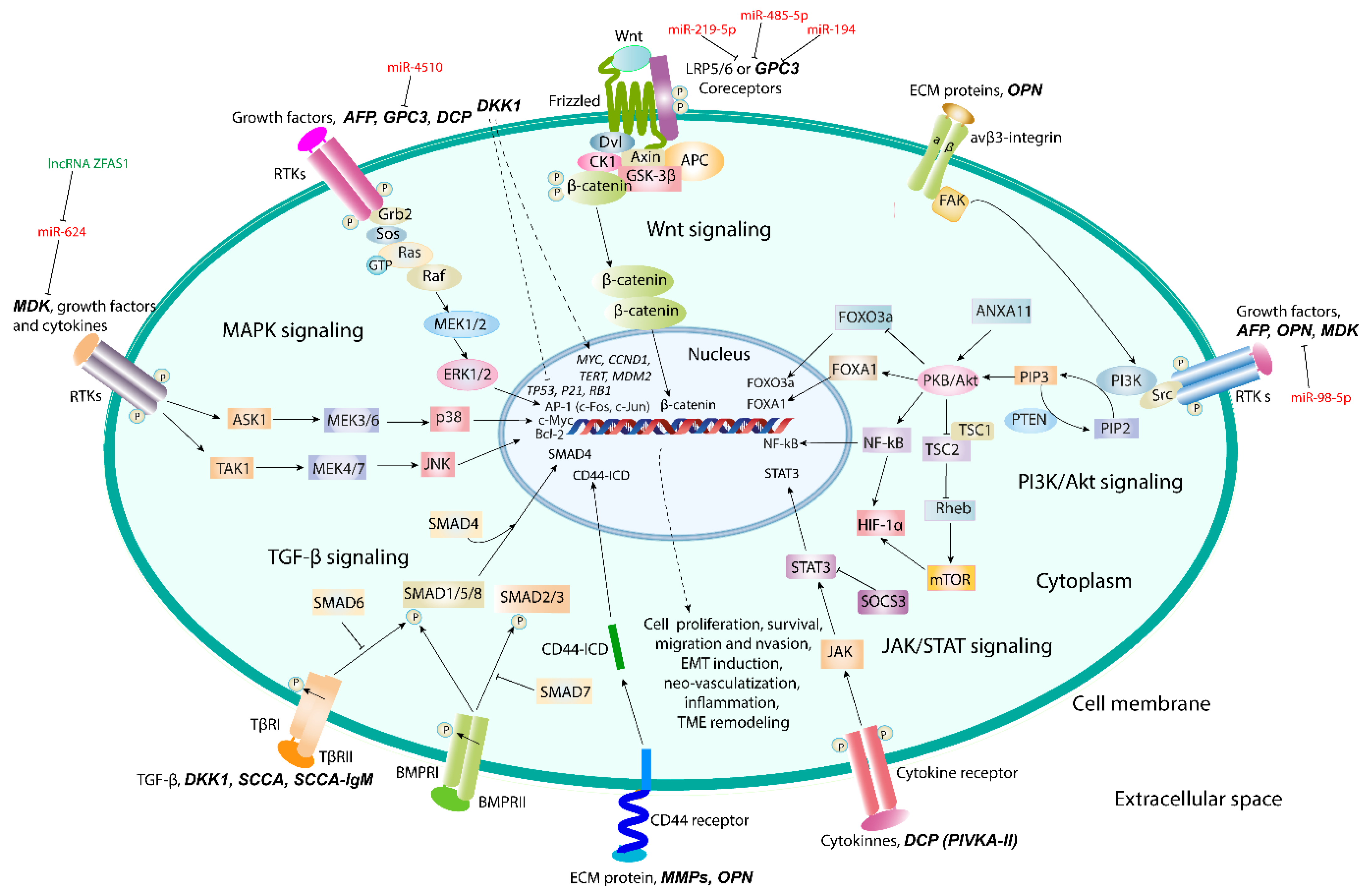
5. Promising Proteomic Biomarkers of HCC
5.1. Osteopontin
5.2. Glypican-3
5.3. Midkine
5.4. Dickkopf-1
5.5. Squamous Cell Carcinoma Antigen
6. Screening for Novel HCC Proteomic Biomarker Candidates
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.Y.; Han, K.H. Epidemiology and surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2012, 1, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Colomber, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñerous, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Rudolf, K.L. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2557–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, S.; Park, S.H. The epidemiology of hepatocellular cancer: From the perspectives of public health problem to tumor biology. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, W.S.; Steggerda, J.; Yang, J.D.; Kuo, A.; Sundaram, B.; Lu, S.C. Current status of hepatocellular carcinoma detection: Screening strategies and novel biomarkers. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835919869120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osho, A.; Rich, N.E.; Singal, A.G. Role of imaging in management of hepatocellular carcinoma: Surveillance, diagnosis, and treatment response. Hepatoma Res. 2020, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.K.; Tso, D.K.; Harris, A.C.; Malfair, D.; Chang, S.D. Extrahepatic metastases of hepatocellular carcinoma: A spectrum of imaging findings. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2014, 65, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, D.R.; Fraum, T.J.; Cannella, R.; Tsai, R.; Naeem, M.; LeBlanc, M.; Salter, A.; Tsung, A.; Fleckenstein, J.; Shetty, A.S.; et al. Expanding the Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System (LI-RADS) v2018 diagnostic population: Performance and reliability of LI-RADS for distinguishing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from non-HCC primary liver carcinoma in patients who do not meet strict LI-RADS high-risk criteria. HPB 2019, 21, 1697–1706. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, I.; Hatano, E.; Tada, M.; Kawabata, Y.; Tamagawa, S.; Kurimoto, A.; Iwama, H.; Toriguchi, K.; Sueoka, H.; Iida, K.; et al. Enhanced patterns on intraoperative contrast-enhanced ultrasonography predicts outcomes after curative liver resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Surg. Today 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, T.C.; Yip, T.T.; Chan, A.T.; Yap, C.; Yip, V.; Mok, T.S.; Lee, C.C.; Leung, T.W.; Ho, S.K.; Johnson, P.J. Comprehensive proteomic profiling identifies serum proteomic signatures for detection of hepatocellular carcinoma and its subtypes. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yang, Z.; Li, G.; Li, C.; Luo, Y.; Gong, Q.; Wu, X.; Li, T.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, B.; et al. Multi-omics analysis of primary cell culture models reveals genetic and epigenetic basis of intratumoral phenotypic diversity. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2019, 17, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.G.; Kim, Y.J. Multiplatform genomic roadmap of hepatocellular carcinoma: A matter of molecular heterogeneity. Hepatology 2018, 68, 2029–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristevski, B.; Chen, M. Big data analytics in medicine and healthcare. J. Integr. Bioinform. 2018, 15, 20170030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.S.; Grabowski, M.M.; Habboub, G.; Mroz, T.E. The impact of artificial intelligence on quality and safety. Glob. Spine J. 2020, 10, 99S–103S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.K.; George, B.; Rai, V. Artificial intelligence to decode cancer mechanism: Beyond patient stratification for precision oncology. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyers, M.; Mann, M. From genomics to proteomics. Nature 2003, 422, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, V.A.; Park, J.M.; Lee, H. Review of three-dimensional liquid chromatography platforms for bottom-up proteomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizcaíno, J.; Deutsch, E.; Wang, R.; Csordas, A.; Reisinger, F.; Rios, D.; Dianes, J.A.; Sun, Z.; Farrah, T.; Bandeira, N.; et al. ProteomeXchange provides globally coordinated proteomics data submission and dissemination. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, L.; Hermjakob, H.; Jones, P.; Adamski, M.; Taylor, C.; States, D.; Gevaert, K.; Vandekerckhove, J.; Apweiler, R. PRIDE: The proteomics identifications database. Proteomics 2005, 5, 3537–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, E.; Eng, J.; Zhang, H.; King, N.; Nesvizhskii, A.I.; Lin, B.; Lee, H.; Yi, E.; Ossola, R.; Aebersold, R. Human plasma peptide atlas. Proteomics 2005, 5, 3497–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohrs, R.J.; Martin, T.; Ghahramani, P.; Bidaut, L.; Higgens, P.J.; Shahzad, A. Translational medicine definition from the European Society for Translational Medicine. New Horiz. Transl. Med. 2015, 2, 86–88. [Google Scholar]
- Meerzaman, D.; Dunn, B.K.; Lee, M.; Chen, Q.; Yan, C.; Ross, S. The promise of omics-based approaches to cancer prevention. Semin. Oncol. 2016, 43, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, T.C.; Chan, A.T.; Zee, B.; Ho, S.K.; Mok, T.S.; Leung, T.W.; Johnson, P.J. Application of classification tree and neural network algorithms to the identification of serological liver marker profiles for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 2001, 61, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayon, L.; Núñez, G.A.; Cominetti, O.; Corthésy, J.; Kussmann, M. A highly automated shotgun proteomic workflow: Clinical scale and robustness for biomarker discovery in blood. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1619, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Lin, L.; Zhou, W.; Chen, W.; Tang, J.; Sun, X.; Huang, P.; Tian, R. Mixed-mode ion exchange-based integrated proteomics technology for fast and deep plasma proteome profiling. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1564, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Kong, Q.; Gao, W.; Chu, B.; Li, H.; Mao, Y.; Cai, Z.; Xu, R.; Tian, R. Spatial proteome profiling by immunohistochemistry-based laser capture microdissection and data-dependent acquisition proteomics. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1127, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Tang, J.; Deng, Q.; He, W.; Sun, X.; Xia, L.; Cheng, Z.; He, L.; You, S.; Hu, J.; et al. Spatial-resolution cell type proteome profiling of cancer tissue by fully integrated proteomics technology. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5879–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; An, Q.; Sheu, K.; Trejo, B.; Fan, S.; Guo, Y. Single cell multi-omics technology: Methodology and application. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, G.M.; Larry, D.; Petersen, J.R.; Elferink, C.J. Targeted proteomics for biomarker discovery and validation of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis C infected patients. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 1312–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafalko, A.; Dai, S.; Hancock, W.S.; Karger, B.L.; Hincapie, M. Development of a Chip/Chip/SRM platform using digital chip isoelectric focusing and LC-Chip mass spectrometry for enrichment and quantitation of low abundance protein biomarkers in human plasma. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Xing, X.; Zeng, J.; Cao, Y.; Cai, Z.; Xu, B.; Liu, X.; Huang, A.; Liu, J. Quantitative proteomics analysis of early recurrence/metastasis of huge hepatocellular carcinoma following radical resection. Proteome Sci. 2014, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Xue, R.; Huang, X.; Zhang, D.; Dong, L.; Wu, H.; Shen, X. Proteomic profiling of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma with magnetic bead-based matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sinica 2011, 43, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, M.G.; Petersen, J.R.; Ju, H.; Cicalese, L.; Snyder, N.; Haidacher, S.J.; Denner, L.; Elferink, C. Biomarker discovery for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis C-infected patients. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 3640–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Luo, R.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, C.L.; Huang, H.; Li, X.; Xie, Z.; et al. Screening differential expression of serum proteins in AFP-negative HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma using iTRAQ-MALDI-MS/MS. Neoplasma 2014, 61, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.T.; Ho, C.H. Plasma proteome atlas for differentiating tumor stage and post-surgical prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, S.K.; Sänger, H.; Krawczyk, M.; Julich-Haertel, H.; Willms, A.; Ligocka, J.; Azkargorta, M.; Mocan, T.; Kahlert, C.; Kruk, B.; et al. Synergistic effects of extracellular vesicle phenotyping and AFP in hepatobiliary cancer differentiation. Liver Int. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-Y.; Cheng, C.-W.; Kaddi, C.D.; Venugopalan, J.; Hoffman, R.; Wang, M.D. -Omic and electronic health record big data analytics for precision medicine. IEEE Transact. BioMed Engin. 2016, 64, 263–273. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, R.; Cortens, J.P.; Beavis, R.C. Open source system for analyzing, validating, and storing protein identification data. J. Proteome Res. 2004, 3, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrah, T.; Deutsch, E.W.; Kreisberg, R.; Sun, Z.; Campbell, D.S.; Mendoza, L.; Kusebauch, U.; Brusniak, M.-Y.; Hüttenhain, R.; Schiess, R.; et al. PASSEL: The PeptideAtlas SRMexperiment library. Proteomics 2012, 12, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, D.; Chen, X.; Jia, H. Computational data mining in cancer bioinformatics and cancer epidemiology. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2009, 2009, 582697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, L.J. Artificial intelligence and integrated genotype-phenotype identification. Genes 2018, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Qi, L.; Zou, Z.; Du, J.; Kong, W.; Zhao, L.; Wei, J.; Lin, L.; Ren, M.; Liu, B. Identification of a novel gene signature for the prediction of recurrence in HCC patients by machine learning of genome-wide databases. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, S.; Takeda, S.; Donadon, M.; Saiki, H.; Brunelli, L.; Pastorelli, R.; Cimino, M.; Soldani, C.; Franceschini, B.; Di Tommaso, L.; et al. Rapid automated diagnosis of primary hepatic tumour by mass spectrometry and artificial intelligence. Liver Int. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Vinvent, P. Representation learning: A review and new perspectives. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1798–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munir, K.; Elahi, H.; Ayub, A.; Frezza, F.; Rizzi, A. Cancer diagnosis using deep learning: A bibliographic review. Cancers 2019, 11, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Wang, L.; Gupta, S.; Goli, H.; Padmanabhan, P.; Gulyas, B. 3D deep learning on medical images: A review. Sensors 2020, 20, 5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azer, S.A. Deep learning with convolutional neural networks for identification of liver masses and hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2019, 11, 1218–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Jiang, H.; Pang, W. Joint multiple fully connected convolutional neural network with extreme learning machine for hepatocellular carcinoma nuclei grading. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 84, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Kang, S.; Ning, Z.; Deng, H.; Shen, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.; Li, X.; Gong, W.; et al. Residual convolutional neural network for predicting response of transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma from CT imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liu, F.; Xie, X.; Su, L.; Liu, M.; Xie, X.; Kuang, M.; Huang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; et al. Accurate prediction of responses to transarterial chemoembolization for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma by using artificial intelligence in contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 2365–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Kuang, S.; Cao, S.; Hu, B.; Xie, S.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; Gao, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Deep learning assisted differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma from focal liver lesions: Choice of four-phase and three-phase CT imaging protocol. Abdom. Radiol. (N. Y.) 2020, 45, 2688–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokrane, F.Z.; Lu, L.; Vavasseur, A.; Otal, P.; Peron, J.M.; Luk, L.; Yang, H.; Ammari, S.; Saenger, Y.; Rousseau, H.; et al. Radiomics machine-learning signature for diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients with indeterminate liver nodules. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, Q.; Iwamoto, Y.; Han, X.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, H.; Lin, L.; Chen, Y.W. Deep learning-based radiomics models early recurrence prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma with multi-phase CT images and clinical data. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2019, 2019, 4881–4884. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, K.; Poirion, O.B.; Lu, L.; Garmire, L.X. Deep learning-based multi-omics integration robustly predicts survival in liver cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1248–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Bae, J.; Chang, Y.; Cho, Y.; Sinn, D.H.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, S.H.; Yi, N.J.; Lee, K.W.; et al. Novel model to predict HCC recurrence after liver transplantation obtained using deep learning: A multicenter study. Cancers 2020, 12, E2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.W.; Zhu, F.P.; Xu, Q.; Wang, K.; Wu, M.Y.; Tang, W.W.; Li, X.C.; Wang, X.H. Machine-learning analysis of contrast-enhanced CT radiomics predicts recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection: A multi-institutional study. EBioMedicine 2019, 50, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.Y.; Wang, X.; Ding, G.Y.; Dong, Z.; Han, J.; Guan, Z.; Ma, L.J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, G.Z.; et al. Exploring prognostic indicators in the pathological images of hepatocellular carcinoma based on deep learning. Gut 2020, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debruyne, E.N.; Delange, J.R. Diagnosing and monitoring hepatocellular carcinoma with alpha-fetoprotein: New aspects and applications. Clin. Chim. Acta 2008, 395, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terentiev, A.A.; Moldogazieva, N.T. Alpha-fetoprotein: A renaissance. Tumor Biol. 2013, 34, 2075–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergstrand, C.G.; Czar, B. Demonstration of a new protein fraction in serum from the human fetus. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1956, 8, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelev, G.I.; Perova, S.D.; Kharkov, N.I.; Postnikova, Z.A.; Irlin, I.S. Production of embryonic alpha-globulin by the transplantable mouse hepatomas. Transplantation 1963, 1, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarinov, Y.S. Detection of embryo-specific alpha-globulin in the blood sera of patients with primary liver tumour. Vorprosy Meditsinskoi Khimii 1964, 10, 90–91. [Google Scholar]
- Jurišić, V.; Nikulina, D. The history of alpha-fetoprotein discovery. In Alpha-Fetoprotein: Functions and Clinical Applications; Lakhi, N., Moretti, M., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mizejewski, G.J. Alpha-fetoprotein structure and function: Relevance to isoforms, epitopes and conformational variants. Exp. Biol. Med. 2001, 226, 377–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizejewski, G.J. Biological role of alpha-fetoprotein in cancer: Prospects for anticancer therapy. Exp. Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2002, 2, 709–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizejewski, G.J. Alpha-fetoprotein and inflammation: Is AFP an acute and/or chronic phase reactant? J. Hematol. Thromboembol. Dis. 2015, 3, 1000191. [Google Scholar]
- Moldogazieva, N.T.; Terentiev, A.A. Alpha-fetoprotein in a protein interaction network: Systems biology approach in discovery biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. In Alpha-Fetoprotein: Functions and Clinical Applications; Lakhi, N., Moretti, M., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: New-York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 83–102. [Google Scholar]
- Moldogazieva, N.T.; Terentiev, A.A.; Shaitan, K.V. Relationship between structure and function of alpha-fetoprotein: Conformational status and biological activity. Biomed. Khim. 2005, 51, 127–151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moldogazieva, N.T.; Terentiev, A.A. Alpha-fetoprotein and growth factors. Structure/function relationships and analogies. Usp. Biol. Chim. 2006, 46, 99–148. [Google Scholar]
- Terentiev, A.A.; Moldogazieva, N.T. Cell adhesion proteins and alpha-fetoprotein. Similar structural motifs as prerequisites for common functions. Biochemistry 2007, 72, 920–935. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Zhou, S.; Guo, L.; Liu, H.; Jiang, W.; Liu, X.; Li, P.; McNutt, M.A.; et al. Alpha fetoprotein is a novel protein-binding partner for caspase-3 and blocks the apoptotic signaling pathway in human hepatoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 2845–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Jiang, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, S.; Liu, X.; McNutt, M.A.; Li, G. Alpha-fetoprotein: A new member of intracellular signal molecules in regulation of the PI3K/AKT signaling in human hepatoma cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Cai, C.; Gan, J.; Yang, X.; Shuang, Z.; Liu, M.; Li, S.; Tang, H. Mir-1236 down-regulates alpha-fetoprotein, thus causing PTEN accumulation, which inhibits the PI3K/AKT pathway and malignant phenotype in hepatoma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6014–6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Guo, J.; Xia, H.; Li, W.; Lu, Y.; Dong, X.; Chen, Y.; Xie, X.; Fu, S.; Li, M. Alpha-fetoprotein activates AKT/mTOR signaling to promote CXCR4 expression and migration of hepatoma cells. Oncoscience 2015, 2, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Parikh, N.D. Biomarker development for hepatocellular carcinoma early detection: Current and future perspectives. Hepat. Oncol. 2017, 4, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyson, G.L.; Duan, Z.; Kramer, J.R.; Davila, J.A.; Richardson, P.A.; El-Serag, H.B. Level of α-fetoprotein predicts mortality among patients with hepatitis C-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peng, S.Y.; Chen, W.J.; Lai, P.L.; Jeng, Y.M.; Shen, J.C.; Hsu, H.C. High alpha-fetoprotein level correlates with high stage, early recurrence and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: Significance of hepatitis virus infection, age, p53 and beta-catenin mutations. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 112, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, S.-L.; Li, L.-Q. Diagnostic accuracy of midkine for hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8, e1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Edward, S.; Singal, A.G.; Lavieri, M.S.; Volk, M. Improving screening for hepatocellular carcinoma by incorporating data on levels of alpha-fetoprotein over time. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoo, T.; Patel, A.D.; Lev-Cohain, N.; Singal, A.G.; Yopp, A.C.; Pedrosa, I. Extrahepatic metastasis risk of hepatocellular carcinoma based on α-fetoprotein and tumor staging parameters at cross-sectional imaging. Cancer Manag. Res. 2017, 9, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Bent, S.; Kohlwes, J. Test characteristics of alpha-fetoprotein for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C. A systematic review and critical analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 139, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, C.; Zhou, L.; Tian, F.; Tai, M.H.; Wei, J.C.; Qu, K.; Meng, F.D.; Zhang, L.Q.; Wang, Z.X.; et al. Distinctions between clinicopathological factors and prognosis of alpha-fetoprotein negative and positive hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Asian Pacific J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, J.D.; Dai, J.; Singal, A.G.; Gopal, P.; Addissie, B.D.; Nguyen, M.H.; Befeler, A.S.; Reddy, K.R.; Schwartz, M.; Harnois, D.M.; et al. Improved performance of serum alpha-fetoprotein for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis in HCV cirrhosis with normal alanine transaminase. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2017, 26, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Zhang, R.; Qian, H.; Cao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, J.; Wu, M.; Yin, Z. Serum profiling based on fucosylated glycoproteins for differentiating between chronic hepatitis B and hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 240, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Lv, Y.; Wang, B. Prognostic role of pre-treatment serum AFP-L3% in hepatocellular carcinoma: Systemic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.J.; Ahmed, A.; Gish, R.G. Elevated alpha-fetoprotein: Differential diagnosis-hepatocellular carcinoma and other disorders. Clin. Liver Dis. 2015, 19, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inagaki, Y.; Tang, W.; Makuuchi, M.; Hasegawa, K.; Sugawara, Y.; Kokudo, N. Clinical and molecular insights into the hepatocellular carcinoma tumour marker des-γ-carboxyprothrombin. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikawa, T.; Shiraha, H.; Yanamoto, K. Significance of des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin production in hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Med. Okayama 2009, 63, 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara, M.; Shiraha, M.; Kataoka, J.; Iwamuro, M.; Horiguchi, S.; Nishina, S.; Takaoka, N.; Uemura, M.; Takaki, A.; Nakamura, S.; et al. Des-γ-carboxyl prothrombin is associated with tumor angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 1602–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, P.; Gao, Z.-H.; Xue, X.; Cui, S.-X.; Zhao, C.-R.; Yuan, Y.; Yin, Z.; Inagaki, Y.; Kokudo, N.; Tang, W.; et al. Des-γ-carboxyl prothrombin induces matrix metalloproteinase activity in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by involving the ERK1/2 MAPK signalling pathway. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, G.; Chattopadhyay, D.; Gray, J.; Stewart, S.; Hudson, M.; Day, C.; Trerotoli, P.; Giannelli, G.; Manas, D.; Reeves, H. AFP, PIVKAII, GP3, SCCA-1 and follisatin as surveillance biomarkers for hepatocellular cancer in non-alcoholic and alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Dong, J.; Ma, L.; Liao, A.; Rong, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Cao, L.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; et al. mTOR and ERK regulate VKORC1 expression in both hepatoma cells and hepatocytes which influence blood coagulation. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 19, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.I.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, W.J.; Shin, W.G.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, K.H.; Jang, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, H.Y.; et al. Diagnostic value of PIVKA-II and alpha-fetoprotein in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 3928–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lok, A.S.; Sterling, R.K.; Everhart, J.E.; Wright, E.C.; Hoefs, J.C.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Morgan, T.R.; Kim, H.-Y.; Lee, W.M.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; et al. Des-γ-carboxy prothrombin and α-fetoprotein as biomarkers for the early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, H.; Kumada, T.; Kiriyama, S.; Sone, Y.; Tanikawa, M.; Hisanaga, Y.; Yamaguchi, A.; Isogai, M.; Kaneoka, Y.; Washizu, J. Prognostic significance of simultaneous measurement of three tumor markers in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Jang, J.Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Cho, Y.K.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.G.; Cha, S.-W.; Kim, Y.S.; Cho, Y.D.; Kim, H.S.; et al. Usefulness of AFP, AFP-L3, and PIVKA-II, and their combinations in diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma. Medicine 2017, 96, e5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.S.; Kim, D.Y.; Han, K.H.; Kim, H.S.; Shin, S.H.; Jung, K.S.; Kim, B.K.; Kim, S.U.; Park, J.Y.; Ahn, S.H. Combined use of AFP, PIVKA-II, and AFP-L3 as tumor markers enhances diagnostic accuracy for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeji, S.; Hirooka, M.; Koizumi, Y.; Tokumoto, Y.; Abe, M.; Ikeda, Y.; Nadano, S.; Hiasa, Y.; Onji, M. Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin identified by P-11 and P-16 antibodies reflects prognosis for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, A.; Akiba, J.; Ogasawara, S.; Nakayama, M.; Nomura, Y.; Yasumoto, M.; Sanada, S.; Nakashima, O.; Abe, T.; Yano, H. Des-γ-carboxyprothrombin (DCP) and NX-DCP expressions and their relationship with clinicopathological features in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsura, T.; Nishimura, Y. Usefulness of the novel oncofetal antigen for diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and melanoma. BioDrug 2005, 19, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Lin, Y.; Yi, H.C.; Niu, J.J. The diagnostic performance of lncRNAs from blood specimens in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Lab. Med. 2021, 52, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Liang, Q.; Song, X. Diagnostic value of alpha-L-fucosidase for hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 3953–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.P.; Ariizumi, S.; Nakano, M.; Yamamoto, M. Positive glypican-3 expression in early hepatocellular carcinoma predicts recurrence after hepatectomy. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schizas, D.; Mastoraki, A.; Routsi, E.; Papapanou, M.; Tsapralis, D.; Vassiliu, P.; Toutouzas, K.; Felekouras, E. Combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma: An update on epidemiology, classification, diagnosis and management. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2020, 19, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, H.; Lu, X.; Sang, X.; Du, S.; Zhao, H.; Chen, W.; Xu, Y.; Chi, T.; et al. Golgi protein 73 (GOLPH2) is a valuable serum marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2010, 59, 1687–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Wang, J.; Katayama, H.; Sen, S.; Liu, S.-M. Circulating microRNAs (cmiRNAs) as novel potential biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Neoplasma 2013, 60, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Ling, S.; Zheng, S.; Xu, X. Liquid biopsy in hepatocellular carcinoma: Circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor DNA. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, N.; Sawada, Y.; Endo, I.; Saito, K.; Uemura, Y.; Nakatsura, T. Biomarkers for the early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 10573–10583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, S.; Plymoth, A.; Feng, Z.; Rosen, H.R.; Sangrajrang, S.; Hainaut, P.; Marrero, J.A.; Beretta, L. Identification of osteopontin as a novel marker for early hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2012, 55, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L. Osteopontin is a promoter for hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis: A summary of 10 years of studies. Front. Med. 2014, 8, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zheng, J.; Wu, F.; Kang, B.; Liang, J.; Heskia, F.; Zhang, X.; Shan, Y. OPN is a promising serological biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis. J. Med. Virol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denhardt, D.T.; Guo, X. Osteopontin: A protein with diverse functions. FASEB J. 1993, 7, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tanani, M.K. Role of osteopontin in cellular signaling and metastatic phenotype. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 4276–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anborgh, P.H.; Mutrie, J.C.; Tuck, A.B.; Chambers, A.F. Role of the metastasis-promoting protein osteopontin in the tumour microenvironment. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 2037–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangaswami, H.; Bulbule, A.; Kundu, G.C. Osteopontin: Role in cell signaling and cancer progression. Trends Cell Biol. 2006, 16, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Fan, X.; Tang, M.; Chen, R.; Wang, H.; Jia, R.; Zhou, X.; Jing, W.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. Osteopontin induces autophagy to promote chemo-resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2016, 383, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Fan, X.; Jing, W.; Liang, Y.; Chen, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Jia, R.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. Osteopontin promotes a cancer stem cell-like phenotype in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via integrin-κB-HIF-1α pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6627–6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Fang, S.; Weng, Q.; Lv, X.; Meng, M.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, L.; Hu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wu, X.; et al. Integrated analysis reveals critical regulators in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, X.; Gao, X.; Wang, C.; Sheng, Y.; Cheng, W.; Qin, L.; Ren, N.; Jia, H.; et al. Osteopontin promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via the PI3K/AKT/Twist signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 5299–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Gao, X.M.; Yang, J.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Sheng, Y.Y.; Li, J.H.; Yu, X.X.; Zheng, Y.; Dong, Q.Z.; et al. C-C chemokine receptor type 1 mediates osteopontin-promoted metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, D.; Gao, X.-M.; Zhang, Z.; Hsu, J.L.; Li, C.-W.; Lim, S.-O.; Sheng, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Disruption of tumour-associated macrophage trafficking by the osteopontin-induced colony-stimulating factor-1 signalling sensitises hepatocellular carcinoma to anti-PD-L1 blockade. Gut 2019, 68, 1653–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.G.; Xu, H.; Gu, Y.M.; Wang, H.; Xu, W.; Zu, M.H. Comparison osteopontin vs AFP for the diagnosis of HCC: A meta-analysis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2014, 38, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, S.A.; Mohamed, N.A.G.; Fawzy, M.W.; Moustafa, D.A. Plasma osteopontin level in chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepat. Mon. 2015, 15, e30753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, X.; Dai, M.; Huang, S.; Chen, J.; Dai, S. Diagnostic accuracy of osteopontin plus alpha-fetoprotein in the hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2017, 41, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Tang, Y.; Sun, D.; Bu, Q.; Li, P. Osteopontin versus alpha-fetoprotein as a diagnostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 8925–8935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronald, J.; Nixon, A.B.; Marin, D.; Gupta, R.T.; Janas, G.; Chen, W.; Suhocki, P.V.; Pabon-Ramos, W.; Sopko, D.R.; Starr, M.D.; et al. Pilot evaluation of angiogenesis signaling factor response after transcatheter arterial embolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology 2017, 285, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Rong, W.; Xiao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, F.; Qi, J.; Zhao, X.; et al. Secretory/releasing proteome-based identification of plasma biomarkers in HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. China Life Sci. 2013, 56, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa, A.N.; Plymoth, A.; Santos-Silva, D.; Ortiz-Cuaran, S.; Camey, S.; Guilloreau, P.; Sangrajrang, S.; Khuhaprema, T.; Mendy, M.; Lesi, O.A.; et al. Osteopontin and latent-TGF β binding-protein 2 as potential diagnostic markers for HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Yang, L.; Rong, W.; Feng, L.; Han, N.; Zhang, K.; Cheng, S.; Wu, J.; Xiao, T.; Gao, Y. Latent transforming growth factor-beta binding protein-1 in circulating plasma as a novel biomarker for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 16046–16054. [Google Scholar]
- Capurro, M.; Wanless, I.R.; Sherman, M.; Deboer, G.; Shi, W.; Miyoshi, E.; Filmus, J. Glypican-3: A novel serum and histochemical marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morford, L.A.; Davis, C.; Jin, L.; Dobierzewska, A.; Peterson, M.L.; Spear, B.T. The oncofetal gene glypican-3 is regulated in the postnatal liver by zinc fingers and homeoboxes 2 and in the regenerating liver by alpha-fetoprotein regulator 2. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capurro, M.I.; Xiang, Y.Y.; Lobe, C.; Filmus, J. Glypican-3 promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by stimulating canonical Wnt signaling. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6245–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhai, D.; Liu, J.; Cai, J.; Wang, Y.; Jing, L.; Du, Z. Assessment of the clinical utility of glypican 3 as a serum marker for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 15, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.; Jang, E.S.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, J.-W.; Jeong, S.-H. Glypican-3 level assessed by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is inferior to alpha-fetoprotein level for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2016, 22, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Xie, Y.; Wei, J.; Li, W.; Ye, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, J.; Li, X. MRI-based radiomics signature: A potential biomarker for identifying glypican 3-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 52, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yao, M.; Pan, L.H.; Qian, Q.; Yao, D.F. Glypican-3 is a biomarker and a therapeutic target of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2015, 14, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghousein, A.; Mosca, N.; Cartier, F.; Charpentier, J.; Dupuy, J.-W.; Raymond, A.-A.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Grosset, C.F. miR-4510 blocks hepatocellular carcinoma development through RAF1 targeting and RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signalling inactivation. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, T.; Ning, X.; Deng, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhou, B.; Chen, X.; Huang, S.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Luo, R. Propofol-induced miR-219-5p inhibits growth and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma through suppression of GPC3-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signalling activation. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 16934–16945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Dai, C.; Yu, X.; Yin, X.B.; Zhou, F. microRNA-485-5p inhibits the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through blocking the WBP2/Wnt signaling pathway. Cell. Signal. 2020, 66, 09466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gao, F.; Jiang, L.; Jia, M.; Ao, L.; Lu, M.; Gou, L.; Ho, M.; Jia, S.; Chen, F.; et al. 32A9, a novel human antibody for designing an immunotoxin and CAR-T cells against glypican-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Shi, Y.; Kaseb, A.O.; Qi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chi, J.; Lu, Q.; Gao, H.; Jiang, H.; Wang, H.; et al. Chimeric antigen receptor-glypican-3 T-cell therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Results of phase I trials. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3979–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koide, N.; Hada, H.; Shinji, T.; Ujike, K.; Hirasaki, S.; Yumoto, Y.; Hanafusa, T.; Kadomatsu, K.; Muramatsu, H.; Muramatsu, T.; et al. Expression of the midkine gene in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatogastroenterology 1999, 46, 3189–3196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Hu, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Xiong, J.; Ma, J.; Chen, L.; Qian, H.; Luo, X.; et al. Midkine promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by elevating anoikis resistance of circulating tumor cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 32523–32535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Li, C.; Wang, F.; Han, F.; Zhu, L. The long noncoding RNA ZFAS1 potentiates the development of hepatocellular carcinoma via the microRNA-624/MDK/ERK/JNK/P38 signaling pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 4431–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.-W.; Guo, J.-J.; Guo, L.; Jia, H.L.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, J.B.; Loffredo, C.A.; Forgues, M.; Huang, H.; Xing, X.J.; et al. Evaluation of midkine as a diagnostic serum biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3944–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodeib, H.; Elshora, O.; Selim, A.; Sabry, N.M.; El-Ashry, H.M. Serum midkine and osteopontin levels as diagnostic biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma. Electron. Physician 2017, 9, 3492–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, K.Y.A.; Abdel-Mageed, A.I.; Safwat, E.; Albreedy, A.M. The value of serum midkine level in diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Hepatol. 2015, 2015, 146389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vongsuvanh, R.; van Der Poorten, D.; Iseli, T.; Strasser, S.I.; McCaughan, G.W.; George, J. Midkine increases diagnostic yield in AFP negative and NASH-related hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Li, J.; Cao, H.; Lv, C.; Wang, X.; Cao, S. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of midkine and AFP for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BioSci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20192424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, G.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Gan, D.; Cao, X.; Han, M.; Du, H.; Ye, Y. The threshold of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinka, A.; Wu, W.; Delius, H.; Monaghan, A.P.; Blumenstock, C.; Niehrs, C. Dickkopf-1 is a member of a new family of secreted proteins and functions in head induction. Nature 1998, 391, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.W.; Park, J.S.; Han, J.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Ahn, M.S.; Lee, H.W.; Kang, S.Y.; Choi, J.-H.; Jeong, S.H. Strong immunoexpression of dickkopf-1 is associated with response to bortezomib in multiple myeloma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018, 59, 2670–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamuk, G.E.; Uyanik, M.S.; Pamuk, O.N.; Maden, M.; Tapan, U. Decreased dickkopf-1 levels in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and increased osteopontin levels in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma at initial diagnosis: Could they be playing roles in pathogenesis? Hematology 2015, 20, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, B.; Qi, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y. Dickkopf-1 expression is down-regulated during the colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence and correlates with reduced microvessel density and VEGF expression. Histopathology 2015, 67, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; He, H.; Lv, R.; Zhang, M.; Huang, H.; An, Z.; Li, S. Preliminary mechanism on the methylation modification of Dkk-1 and Dkk-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2014, 36, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakabe, T.; Azumi, J.; Umekita, Y.; Toriguchi, K.; Hatano, E.; Hirooka, Y.; Shiota, G. Expression of cancer stem cell-associated DKK1 mRNA serves as prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 4881–4888. [Google Scholar]
- Kagey, M.H.; He, X. Rationale for targeting the Wnt signalling modulator Dickkopf-1 for oncology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 4637–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fezza, M.; Moussa, M.; Aoun, R.; Haber, R.; Hilal, G. DKK1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma inflammation, migration and invasion: Implication of TGF-β1. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Fan, J.; Yang, X.R.; Tan, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xu, Y.; Wang, N.; Niu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, J.; et al. Serum DKK1 as a protein biomarker for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A large-scale, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.S.; Jeong, S.-H.; Kim, J.-W.; Choi, Y.S.; Leissner, P.; Brechot, C. Diagnostic performance of alpha-fetoprotein, protein Induced by vitamin K absence, osteopontin, dickkopf-1 and its combinations for hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Mou, L.; Gao, H.; Zeng, Y.; Tang, X.; Deng, X.; Pu, Z.; Ni, Y.; Zhan, Y. Diagnostic accuracy of serum dickkopf-1 protein in diagnosis hepatocellular carcinoma: An updated meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e16725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, T.; Shen, Q.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, Z.; Chu, W.; Lv, X.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, W.; Fan, J.; et al. Diagnostic values of alpha-fetoprotein, dickkopf-1, and osteopontin for hepatocellular carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byeon, H.; Lee, S.D.; Hong, E.-K.; Lee, D.E.; Kim, B.H.; Seo, Y.; Joo, J.; Han, S.-S.; Kim, S.H.; Park, S.-J. Long-term prognostic impact of osteopontin and Dickkopf-related protein 1 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suminami, Y.; Kishi, F.; Sekiguchi, K.; Kato, H. Squamous cell carcinoma antigen is a new member of the serine protease inhibitors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 181, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suminami, Y.; Kishi, F.; Murakami, A.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Nawata, S.; Numa, F.; Kato, H. Novel forms of squamous cell carcinoma antigen transcripts produced by alternative splicing. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1519, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataltepe, S.; Gornstein, E.R.; Schick, C.; Kamachi, Y.; Chatson, K.; Fries, J.; Silverman, G.A.; Upton, M.P. Co-expression of the squamous cell carcinoma antigens 1 and 2 in normal adult human tissues and squamous cell carcinomas. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2000, 48, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turato, C.; Vitale, A.; Fasolato, S.; Ruvoletto, M.; Terrin, L.; Quarta, S.; Ramirez Morales, R.; Biasiolo, A.; Zanus, G.; Tan, P.S.; et al. SERPINB3 is associated with TGF-β1 and cytoplasmic β-catenin expression in hepatocellular carcinomas with poor prognosis. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2708–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontisso, P. Role of SERPINB3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Hepatol. 2014, 13, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenmayer, A.; Alsinet, C.; Savic, R.; Cabellos, L.; Toffanin, S.; Hoshida, Y.; Vilanueva, A.; Minquez, B.; Newell, P.; Tsai, H.W.; et al. Wnt-pathway activation in two molecular classes of hepatocellular carcinoma and experimental modulation by sorafenib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4997–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernanda, P.Y.; Chen, K.; Das, A.M.; Sideras, K.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Cao, W.; Bots, S.J.; Kodach, L.L.; de Man, R.A.; et al. SMAD4 exerts a tumor-promoting role in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5055–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannito, S.; Turato, C.; Paternostro, C.; Biasiolo, A.; Colombatto, S.; Cambieri, I.; Quarta, S.; Novo, E.; Morello, E.; Villano, G.; et al. Hypoxia up-regulates SERPINB3 through HIF-2α in human liver cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 2206–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannito, S.; Foglia, B.; Villano, G.; Turato, C.; Delgado, T.C.; Morello, E.; Pin, F.; Novo, E.; Napione, L.; Quarta, S.; et al. SerpinB3 differently up-regulates hypoxia inducible factors-1α and -2α in hepatocellular carcinoma: Mechanisms revealing novel potential therapeutic targets. Cancers 2019, 11, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarta, S.; Vidalino, L.; Turato, C.; Ruvoletto, M.; Calabrese, F.; Valente, M.; Cannito, S.; Fassina, G.; Parola, M.; Gatta, A.; et al. SERPINB3 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Pathol. 2010, 221, 343–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beneduce, L.; Castaldi, F.; Marino, M.; Quarta, S.; Ruvoletto, M.; Benvegnu, L.; Calabrese, F.; Gatta, A.; Pontisso, P.; Fassina, G. Squamous cell carcinoma antigen-immunoglobulin M complexes as novel biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2005, 103, 2558–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossad, N.A.; Mahmoud, E.H.; Osman, E.A.; Mahmoud, S.H.; Shousha, H.I. Evaluation of squamous cell carcinoma antigen-immunoglobulin M complex (SCCA-IGM) and alpha-L-fucosidase (AFU) as novel diagnostic biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 11559–11564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Shao, C.; Zhou, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Tu, C. Diagnostic accuracy of serum squamous cell carcinoma antigen and squamous cell carcinoma antigen-immunoglobulin M for hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 3, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, Z.-J.; Chen, L.-H.; Dong, W.-Z. Diagnostic value of serum squamous cell carcinoma antigen for hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2017, 77, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-H.; Gil-Gomez, A.; Ampuero, J.; Romero-Gomez, M. Diagnostic accuracy of SCCA and SCCA-IgM for hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 1820–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertino, G.; Neri, S.; Bruno, C.M.; Ardiri, A.M.; Calvagno, G.S.; Malaguarnera, M.; Toro, A.; Malaguarnera, M.; Clementi, S.; Bertino, N.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of alpha-fetoprotein, des-γ-carboxyprothrombin and squamous cell carcinoma antigen immunoglobulin M complexes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Minerva Med. 2011, 102, 363–371. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, I.; Kim, G.A.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.H.; Sohn, A.; Gwak, G.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lim, Y.S.; Kim, Y. Proteome multimarker panel with multiple reaction monitoring-mass spectrometry for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Liu, X.; Wei, X.; Luo, H.; Li, P.; Shi, M.; Guo, B.; Cui, Y.; Su, Z.; Zeng, J.; et al. Quantitative proteomics identifies a plasma multi-protein model for detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Wang, G.; Wang, T.; Fu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L.; Deng, Y.; Chen, G.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the transglutaminase 2-dependent IL-6/IL6R/STAT3 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2542–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.H.; Yang, D.L. Identification of a protein signature for predicting overall survival of hepatocellular carcinoma: A study based on data mining. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, K.; Makjaroen, J.; Robinson, J.; Khoomrung, S.; Pisitkun, T. Deep proteomic deconvolution of interferons and HBV transfection effects on a hepatoblastoma cell line. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 16796–16810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, X.; Yuan, H.; Chen, G.; Ouyang, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Xing, X.; Zhao, B. Proteomic analyses reveal divergent ubiquitylation patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with different metastasis potential. J. Proteomics 2020, 225, 103834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, K.; Yeom, J.; Park, S.; Kim, I. Euchromatin histone methyltransferase II (EHMT2) regulates the expression of Ras-related GTP binding C (RRAGG) protein. BMB Rep. 2020, 20, 4978. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, X.; Dong, J.; Wang, L.; Ye, M. A new workflow for the analysis of phosphosite occupancy in paired samples by integration of proteomics and phosphoproteomics data sets. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 3807–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jen, H.W.; Gu, D.L.; Lang, Y.D.; Jou, Y.S. PSPC1 potentiates IGF1R expression to augment cell adhesion and motility. Cells 2020, 9, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Jia, L.; Li, J.; Ma, C.; Wu, J.; Shen, J.; Dang, L.; Zhu, B.; Li, P.; Zhi, Y.; et al. Heterogeneities of site-specific N-glycosylation in HCC tumors with low and high AFP concentrations. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Lin, Y.; Grigorean, G.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; Singal, A.G.; Parikh, N.D.; et al. Glycopeptide biomarkers in serum haptoglobin for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 3452–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Rong, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, N.; Pu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, X.; Lei, C.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X.; et al. Proteomic analysis revealed common, unique and systemic signatures in gender-dependent hepatocarcinogenesis. Biol. Sex Dif. 2020, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Biomarker | Chemical Nature | Functions | Signaling Pathways | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFP and AFL-L3 | Embryo-specific and tumor-associated glycoprotein | Dual regulation of cell proliferation and survival | MAPK- an PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling | [69,70,71,72,73] |
| DCP | Abnormal prothrombin without carboxylation of γ-carbon atom in Glu residues in γ-carboxyglutamic (Gla) domain | Growth factor activity and DNA synthesis | JAK/STAT3, Raf/MEK1/2/ERK1/2 (MAPK) signaling | [89,90,91] |
| OPN | Acidic chemokine-like secreted ECM-specific phosphoglycoprotein | Cell adhesion, migration, invasion, and survival, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition | Integrin αvβ3/NF-κB/HIF-1α and PI3K/Akt/NF-κB and CD44-mediated signaling | [117,118,119,120,121] |
| GPC3 | Heparan sulfate proteoglycan | Cell proliferation and tumor growth | Co-receptor of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling; Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling | [138,139,140] |
| MDK | Small heparin-binding growth factor | HCC progression and metastasis, resistance of CTCs to anoikis | PI3K/Akt/NF-kB/TrkB and ERK/JNK/p38-mediated signaling | [143,144,145] |
| DKK1 | Secreted glycoprotein | TME remodeling, promotion of inflammation, cell migration and invasion | TGF-β1-mediated pathway | [158,159] |
| SCCA and SCCA-IgM | Member of serine protease inhibitor (serpin) family | Inhibition of apoptosis and intra-tumor infiltration by NK cells; induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, cell proliferation and invasion | c-Myc and Ras/TGF-β/SMAD4 signaling | [169,170,171] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moldogazieva, N.T.; Mokhosoev, I.M.; Zavadskiy, S.P.; Terentiev, A.A. Proteomic Profiling and Artificial Intelligence for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Translational Medicine. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020159
Moldogazieva NT, Mokhosoev IM, Zavadskiy SP, Terentiev AA. Proteomic Profiling and Artificial Intelligence for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Translational Medicine. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(2):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020159
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoldogazieva, Nurbubu T., Innokenty M. Mokhosoev, Sergey P. Zavadskiy, and Alexander A. Terentiev. 2021. "Proteomic Profiling and Artificial Intelligence for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Translational Medicine" Biomedicines 9, no. 2: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020159
APA StyleMoldogazieva, N. T., Mokhosoev, I. M., Zavadskiy, S. P., & Terentiev, A. A. (2021). Proteomic Profiling and Artificial Intelligence for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Translational Medicine. Biomedicines, 9(2), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020159







