Human Leukocyte Antigen Polymorphism and Blood Biomarker Profiles in Parkinson’s Disease: A Pilot Study in a Latvian Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
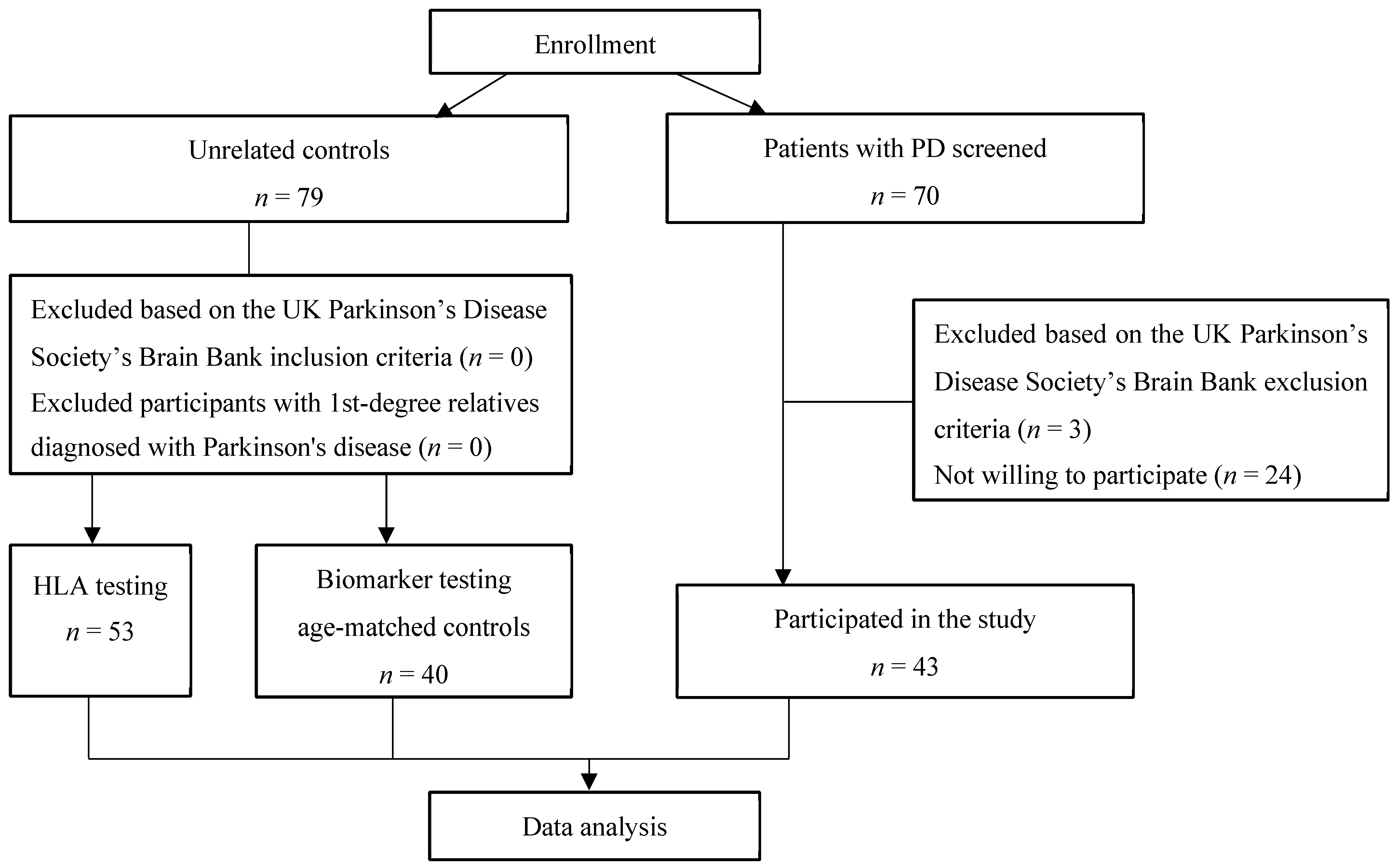
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Laboratory Analyses
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aliseychik, M.P.; Andreeva, T.V.; Rogaev, E.I. Immunogenetic Factors of Neurodegenerative Diseases: The Role of HLA Class II. Biochemistry 2018, 83, 1104–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wightman, D.P.; Savage, J.E.; Tissink, E.; Romero, C.; Jansen, I.E.; Posthuma, D. The genetic overlap between Alzheimer’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Lewy body dementia, and Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2023, 127, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lau, L.M.; Breteler, M.M. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbaz, A.; Carcaillon, L.; Kab, S.; Moisan, F. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 172, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldereschi, M.; Di Carlo, A.; Rocca, W.A.; Vanni, P.; Maggi, S.; Perissinotto, E.; Grigoletto, F.; Amaducci, L.; Inzitari, D. Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism in a longitudinal study: Two-fold higher incidence in men. ILSA Working Group. Italian Longitudinal Study on Aging. Neurology 2000, 55, 1358–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringsheim, T.; Jette, N.; Frolkis, A.; Steeves, T.D. The prevalence of Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D.K.; Tanner, C.M.; Brundin, P. Parkinson Disease Epidemiology, Pathology, Genetics, and Pathophysiology. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2020, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibb, W.R.; Lees, A.J. The relevance of the Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1988, 51, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.Y.; Xie, X.X.; Liu, R.T. The Role of α-Synuclein Oligomers in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schrag, A.E.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, M.K.; Damotte, V.; Hollenbach, J.A. The immunogenetics of neurological disease. Immunology 2018, 153, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollenhauer, B.; Dakna, M.; Kruse, N.; Galasko, D.; Foroud, T.; Zetterberg, H.; Schade, S.; Gera, R.G.; Wang, W.; Gao, F.; et al. Validation of Serum Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker of Parkinson’s Disease Progression. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 1999–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostapiuk, A.; Urbanska, E.M. Kynurenic acid in neurodegenerative disorders-unique neuroprotection or double-edged sword? CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2022, 28, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toleikis, Z.; Ziaunys, M.; Baranauskiene, L.; Petrauskas, V.; Jaudzems, K.; Smirnovas, V. S100A9 Alters the Pathway of Alpha-Synuclein Amyloid Aggregation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, B.; Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Elekhnawy, E.; Alharbi, H.; Alexiou, A.; Papadakis, M.; Batiha, G.E.-S. Role of GABA pathway in motor and non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease: A bidirectional circuit. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.J.; Daniel, S.E.; Kilford, L.; Lees, A.J. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: A clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1992, 55, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yan, R.; Su, D.; Zhao, D.; Wang, A.; Feng, T. Temporal trends in the prevalence of Parkinson’s disease from 1980 to 2023: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2024, 5, e464–e479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stebbins, G.T.; Goetz, C.G.; Burn, D.J.; Jankovic, J.; Khoo, T.K.; Tilley, B.C. How to identify tremor dominant and postural instability/gait difficulty groups with the movement disorder society unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale: Comparison with the unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 668–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahn, S.; Elton, R.L.; Members, U.P. Unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale. In Recent Developments in Parkinson’s Disease; Fahn, S., Marsden, C.D., Calne, D., Goldstein, M., Eds.; Macmillan Health Care Information: Florham Park, NJ, USA, 1987; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Goetz, C.G.; Tilley, B.C.; Shaftman, S.R.; Stebbins, G.T.; Fahn, S.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Poewe, W.; Sampaio, C.; Stern, M.B.; Dodel, R.; et al. Movement Disorder Society-sponsored revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS): Scale presentation and clinimetric testing results. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 2129–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, T.; Satake, W.; Ogawa, K.; Suzuki, K.; Hirata, J.; Foo, J.N.; Tan, E.K.; Toda, T.; Okada, Y. Trans-Ethnic Fine-Mapping of the Major Histocompatibility Complex Region Linked to Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 1805–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulzer, D.; Alcalay, R.N.; Garretti, F.; Cote, L.; Kanter, E.; Agin-Liebes, J.; Liong, C.; McMurtrey, C.; Hildebrand, W.H.; Mao, X.; et al. T cells from patients with Parkinson’s disease recognize α-synuclein peptides. Nature 2017, 546, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Tamouza, R.; Delord, M.; Krishnamoorthy, R.; Tzourio, C.; Mulot, C.; Nacfer, M.; Lambert, J.C.; Beaune, P.; Laurent-Puig, P.; et al. Association between Parkinson’s disease and the HLA-DRB1 locus. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandi, S.; Chinniah, R.; Sevak, V.; Ravi, P.M.; Raju, M.; Vellaiappan, N.A.; Karuppiah, B. Association of HLA-DRB1, DQA1 and DQB1 alleles and haplotype in Parkinson’s disease from South India. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 765, 136296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guen, Y.; Luo, G.; Ambati, A.; Damotte, V.; Jansen, I.; Yu, E.; Nicolas, A.; de Rojas, I.; Peixoto Leal, T.; Miyashita, A.; et al. Multiancestry analysis of the HLA locus in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases uncovers a shared adaptive immune response mediated by. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2302720120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wei, L.; Luo, F.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, F.; Kang, P.; Xu, R.; Xiao, L.; Liu, Z.; et al. HLA-DRB1 alleles are associated with the susceptibility to sporadic Parkinson’s disease in Chinese Han population. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissemann, W.T.; Hill-Burns, E.M.; Zabetian, C.P.; Factor, S.A.; Patsopoulos, N.; Hoglund, B.; Holcomb, C.; Donahue, R.J.; Thomson, G.; Erlich, H.; et al. Association of Parkinson disease with structural and regulatory variants in the HLA region. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.; Ambati, A.; Andersen, M.S.; Krohn, L.; Estiar, M.A.; Saini, P.; Senkevich, K.; Sosero, Y.L.; Sreelatha, A.A.K.; Ruskey, J.A.; et al. Fine mapping of the HLA locus in Parkinson’s disease in Europeans. npj Parkinson’s Dis. 2021, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenbach, J.A.; Norman, P.J.; Creary, L.E.; Damotte, V.; Montero-Martin, G.; Caillier, S.; Anderson, K.M.; Misra, M.K.; Nemat-Gorgani, N.; Osoegawa, K.; et al. A specific amino acid motif of. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7419–7424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.Y.; Ho, P.W.; Liu, H.F.; Leung, C.T.; Li, L.; Chang, E.E.S.; Ramsden, D.B.; Ho, S.L. The interplay of aging, genetics and environmental factors in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2019, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, I.; Iashchishyn, I.A.; Moskalenko, R.A.; Wang, C.; Wärmländer, S.K.T.S.; Wallin, C.; Gräslund, A.; Kovacs, G.G.; Morozova-Roche, L.A. Co-aggregation of pro-inflammatory S100A9 with α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease: Ex vivo and in vitro studies. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Song, R.; Wang, Z.; Jing, Z.; Ma, J. S100A8/A9 in Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, D.; Iyer, M.; Narayanasamy, A.; Siva, K.; Vellingiri, B. Kynurenine pathway in Parkinson’s disease—An update. eNeurologicalSci 2020, 21, 100270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, M.; Vakili, K.; Yaghoobpoor, S.; Tavasol, A.; Jazi, K.; Hajibeygi, R.; Shool, S.; Sodeifian, F.; Klegeris, A.; McElhinney, A.; et al. Dynamic changes in metabolites of the kynurenine pathway in Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease: A systematic Review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 997240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilman, P.L.; Wang, E.W.; Lewis, M.M.; Krzyzanowski, S.; Capan, C.D.; Burmeister, A.R.; Du, G.; Escobar Galvis, M.L.; Brundin, P.; Huang, X.; et al. Tryptophan Metabolites Are Associated with Symptoms and Nigral Pathology in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 2028–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.H.; Cheng, M.L.; Tang, H.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Wu, Y.R.; Chen, C.M. Alternations of Metabolic Profile and Kynurenine Metabolism in the Plasma of Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 6319–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmans, P.; Moskvina, V.; Jones, L.; Sharma, M.; Vedernikov, A.; Buchel, F.; Saad, M.; Bras, J.M.; Bettella, F.; Nicolaou, N.; et al. A pathway-based analysis provides additional support for an immune-related genetic susceptibility to Parkinson’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murueta-Goyena, A.; Andikoetxea, A.; Gómez-Esteban, J.C.; Gabilondo, I. Contribution of the GABAergic System to Non-Motor Manifestations in Premotor and Early Stages of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terkelsen, M.H.; Hvingelby, V.S.; Pavese, N. Molecular Imaging of the GABAergic System in Parkinson’s Disease and Atypical Parkinsonisms. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2022, 22, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auteri, M.; Zizzo, M.G.; Serio, R. GABA and GABA receptors in the gastrointestinal tract: From motility to inflammation. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 93, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Lee, B.C.; Lin, C.H. Integrated Plasma and Neuroimaging Biomarkers Associated with Motor and Cognition Severity in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Parkinson’s Dis. 2020, 10, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhle, J.; Barro, C.; Andreasson, U.; Derfuss, T.; Lindberg, R.; Sandelius, Å.; Liman, V.; Norgren, N.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H. Comparison of three analytical platforms for quantification of the neurofilament light chain in blood samples: ELISA, electrochemiluminescence immunoassay and Simoa. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Dewit, N.; Jacobs, D.; Pijnenburg, Y.A.L.; In ‘t Veld, S.G.J.G.; Coppens, S.; Quaglia, M.; Hirtz, C.; Teunissen, C.E.; Vanmechelen, E. A Novel Neurofilament Light Chain ELISA Validated in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease, Frontotemporal Dementia, and Subjective Cognitive Decline, and the Evaluation of Candidate Proteins for Immunoassay Calibration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Demographics and Clinical Characteristics | Total (n = 43) |
|---|---|
| Age (years), mean ± SD | 65.2 ± 8.94 |
| Age at onset, median (Q1–Q3) | 59 (49–64) |
| Gender, n (%) | |
| Male | 20 (46.5%) |
| Female | 23 (53.5%) |
| Duration of PD (years), median (Q1–Q3) | 6 (4–10) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 18 (41.9%) |
| Disorders of the thyroid gland, n (%) | 15 (34.9%) |
| Cancer, n (%) | 4 (9.3%) |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 3 (7%) |
| Clinical subgroups, n (%) | |
| Tremor-dominant | 14 (32.6%) |
| PIGD | 25 (58.1%) |
| Mixed | 4 (9.3%) |
| Hoehn and Yahr stage, n (%) | |
| HY—1 | 17 (39.5%) |
| HY—2 | 15 (34.9%) |
| HY—3 | 11 (25.6%) |
| HLA Alleles | Controls | PD | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 53 | n = 43 | |||
| DRB1 | ||||
| 01 | 24 (45.3%) | 10 (23.3%) | 0.366 (0.15–0.892) | 0.032 |
| 04 | 3 (5.7%) | 16 (37.2%) | 9.88 (2.64–36.9) | <0.001 |
| 07 | 10 (18.9%) | 16 (37.2%) | 2.55 (1.01–6.43) | 0.064 |
| 08 | 7 (13.2%) | 0 | 0.0713 (0.003–1.29) | 0.016 |
| 09 | 1 (1.9%) | 0 | 0.402 (0.016–10.1) | 1.0 |
| 11 | 12 (22.6%) | 9 (20.9%) | 0.904 (0.341–2.4) | 1.0 |
| 12 | 1 (1.9%) | 4 (9.3%) | 5.33 (0.573–49.6) | 0.17 |
| 13 | 18 (34%) | 8 (18.6%) | 0.444 (0.171–1.16) | 0.11 |
| 14 | 7 (13.2%) | 3 (7%) | 0.493 (0.119–2.03) | 0.504 |
| 15 | 5 (9.4%) | 10 (23.3%) | 2.91 (0.911–9.29) | 0.09 |
| 16 | 8 (15.1%) | 2 (4.7%) | 0.274 (0.055–1.37) | 0.177 |
| 17 | 6 (11.3%) | 7 (16.3%) | 1.52 (0.471–4.93) | 0.556 |
| DQA1 | ||||
| 01:01 | 15 (28.3%) | 7 (16.3%) | 0.493 (0.18–1.35) | 0.223 |
| 01:02 | 23 (43.4%) | 14 (32.6%) | 0.63 (0.272–1.46) | 0.3 |
| 01:03 | 0 | 9 (20.9%) | 29.5 (1.66–523) | <0.001 |
| 02:01 | 12 (22.6%) | 19 (44.2%) | 2.7 (1.12–6.53) | 0.03 |
| 03:01 | 9 (17%) | 20 (46.5%) | 4.25 (1.67–10.8) | 0.003 |
| 04:01 | 1 (1.9%) | 3 (7%) | 3.9 (0.391–38.9) | 0.322 |
| 05:01 | 29 (54.7%) | 13 (30.2%) | 0.359 (0.154–0.836) | 0.023 |
| DQB1 | ||||
| 02:01:02 | 16 (30.2%) | 21 (48.8%) | 2.21 (0.955–5.1) | 0.091 |
| 03:01 | 23 (43.4%) | 12 (27.9%) | 0.505 (0.214–1.19) | 0.139 |
| 03:02 | 5 (9.4%) | 3 (7%) | 0.72 (0.162–3.2) | 0.727 |
| 03:03 | 5 (9.4%) | 6 (14%) | 1.56 (0.441–5.5) | 0.534 |
| 03:04 | 0 | 4 (9.3%) | 12.2 (0.638–233) | 0.037 |
| 04:01 | 0 | 1 (2.3%) | 3.78 (0.15–95.1) | 0.448 |
| 04:01:02 | 3 (5.7%) | 1 (2.3%) | 0.397 (0.039–3.96) | 0.625 |
| 05:01 | 15 (28.3%) | 13 (30.2%) | 1.1 (0.454–2.66) | 1.0 |
| 05:02:04 | 7 (13.2%) | 6 (14%) | 1.07 (0.33–3.44) | 1.0 |
| 06:02:08 | 19 (35.8%) | 12 (27.9%) | 0.693 (0.29–1.66) | 0.511 |
| HLA Alleles | PD | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age < 60 (n = 22) | Age ≥ 60 (n = 21) | ||
| DRB1 | |||
| 01 | 5 (22.7%) | 5 (23.8%) | 1 |
| 04 | 10 (45.5%) | 6 (28.6%) | 0.347 |
| DQA1 | |||
| 02:01 | 6 (27.3%) | 13 (61.9%) | 0.033 |
| 03:01 | 12 (54.5%) | 8 (38.1%) | 0.364 |
| 05:01 | 7 (31.8%) | 6 (28.6%) | 1 |
| Blood Biomarkers | Age-Matched Controls n = 40 | PD n = 43 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean ± SD | 62 ± 7.3 | 65.2 ± 8.9 | 0.079 |
| Gender, male, n (%) | 19 (47.5%) | 20 (46.5%) | 1 |
| Neurofilament light chain, pg/mL, median (Q1–Q3) | 303.5 (211.25–460.35) | 335.3 (255.8–415.5) | 0.88 |
| S100 calcium-binding protein A9, ng/mL, median (Q1–Q3) | 2.71 (1.1–4.02) | 3.51 (2.56–6.04) | 0.005 |
| Kynurenic acid, ng/mL, mean ± SD | 183.08 ± 9.18 | 177.4 ± 8.86 | 0.005 |
| Glutamate decarboxylase (GAD1), ng/mL, median (Q1–Q3) | 0.34 (0.0–0.76) | 0.37 (0.27–0.67) | 0.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minibajeva, O.; Karelis, G.; Zolovs, M.; Ķēniņa, V. Human Leukocyte Antigen Polymorphism and Blood Biomarker Profiles in Parkinson’s Disease: A Pilot Study in a Latvian Cohort. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2709. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122709
Minibajeva O, Karelis G, Zolovs M, Ķēniņa V. Human Leukocyte Antigen Polymorphism and Blood Biomarker Profiles in Parkinson’s Disease: A Pilot Study in a Latvian Cohort. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2709. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122709
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinibajeva, Olga, Guntis Karelis, Maksims Zolovs, and Viktorija Ķēniņa. 2024. "Human Leukocyte Antigen Polymorphism and Blood Biomarker Profiles in Parkinson’s Disease: A Pilot Study in a Latvian Cohort" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2709. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122709
APA StyleMinibajeva, O., Karelis, G., Zolovs, M., & Ķēniņa, V. (2024). Human Leukocyte Antigen Polymorphism and Blood Biomarker Profiles in Parkinson’s Disease: A Pilot Study in a Latvian Cohort. Biomedicines, 12(12), 2709. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122709





