Genome-Wide Analysis of CPP Transcription Factor Family in Endangered Plant Phoebe bournei and Its Response to Adversity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of PbCPP Gene Family Members and Analysis of Physicochemical Properties
2.2. Chromosomal Localization of PbCPP Gene Family Members and Construction of Phylogenetic Tree
2.3. Tissue Expression Profile Analysis of PbCPP Genes
2.4. PbCPP Gene Family Motifs, Structural Domains, and Gene Structure Analysis
2.5. The Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements of the PbCPP Gene Family
2.6. Intraspecies and Interspecies Covariance Analysis of the PbCPP Gene Family
2.7. Plant Materials and Abiotic Stress Treatments
2.8. RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of PbCPP Gene Family and Analysis of Physicochemical Properties
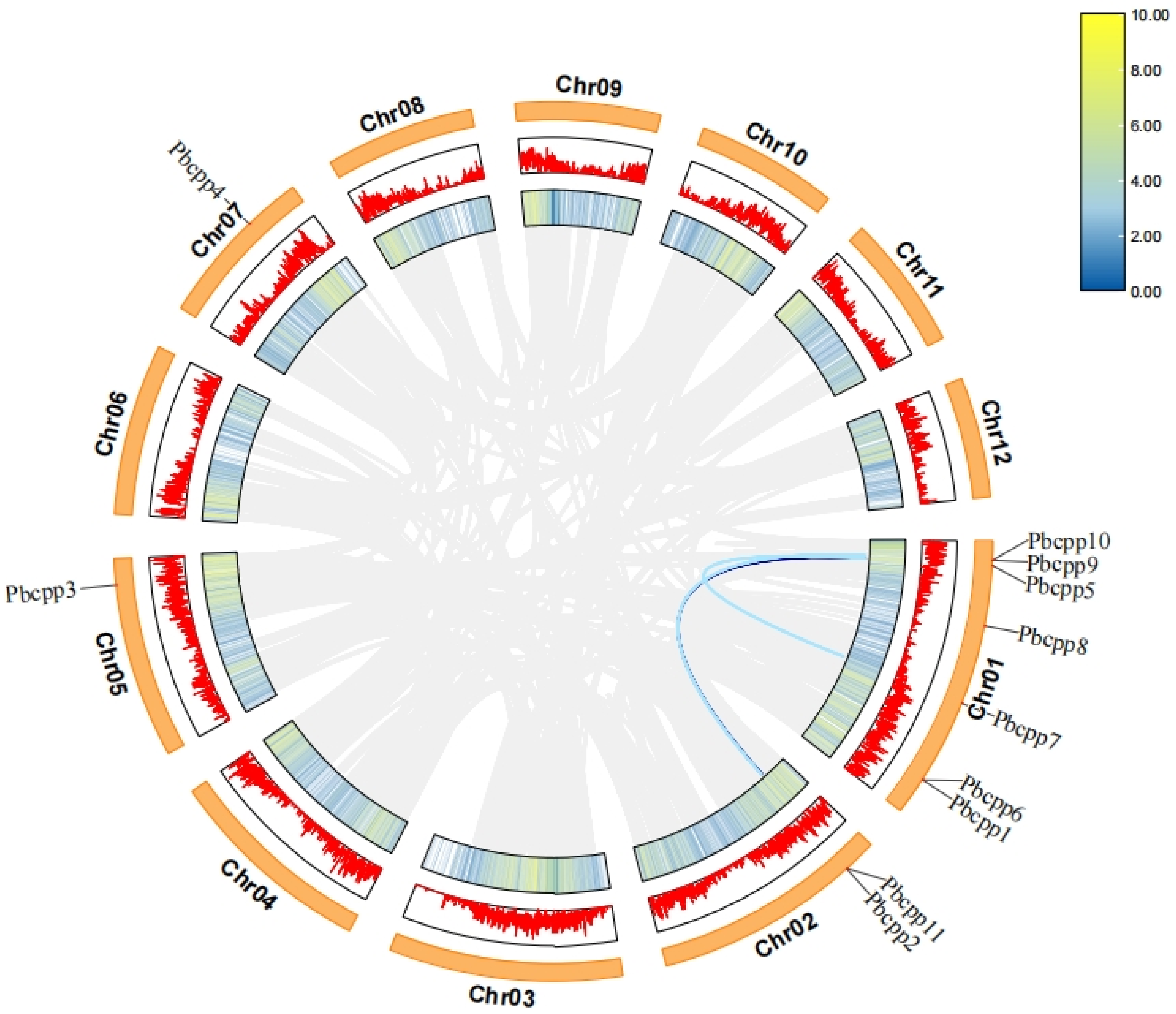
3.2. Chromosomal Localization Analysis of the PbCPP Gene Family
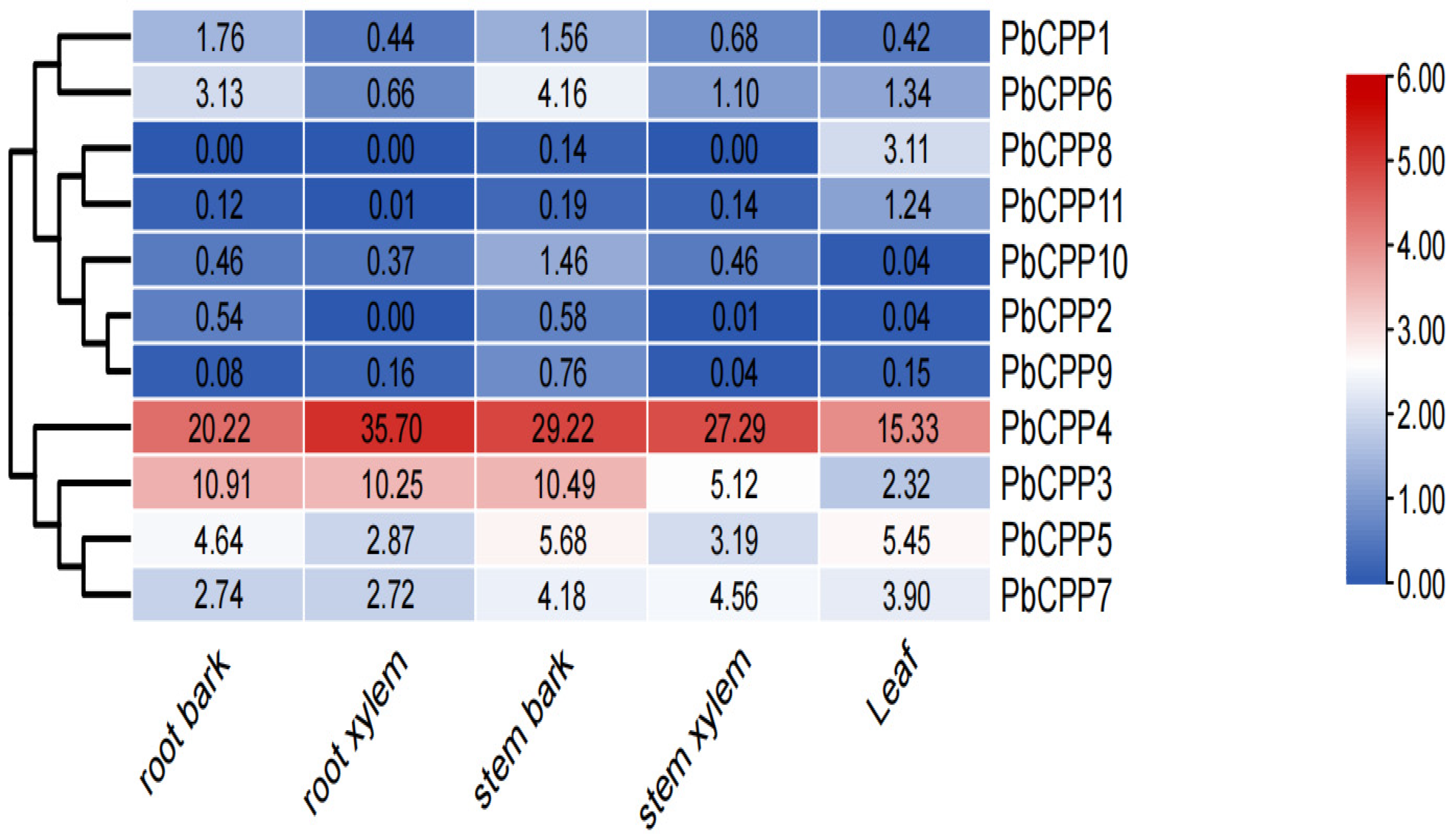
3.3. Analysis of Tissue-Specific Expression Patterns of PbCPP Gene Family
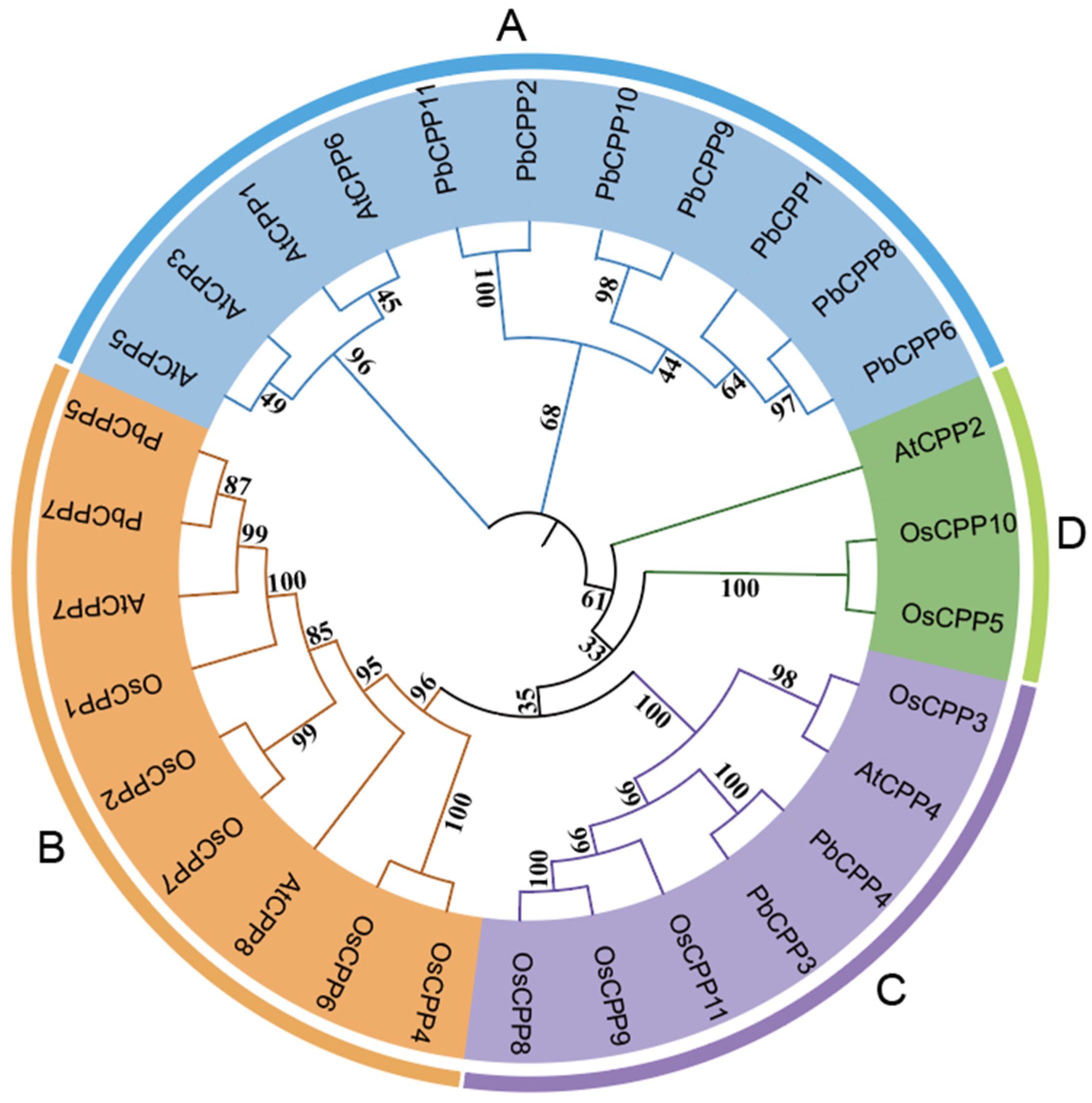
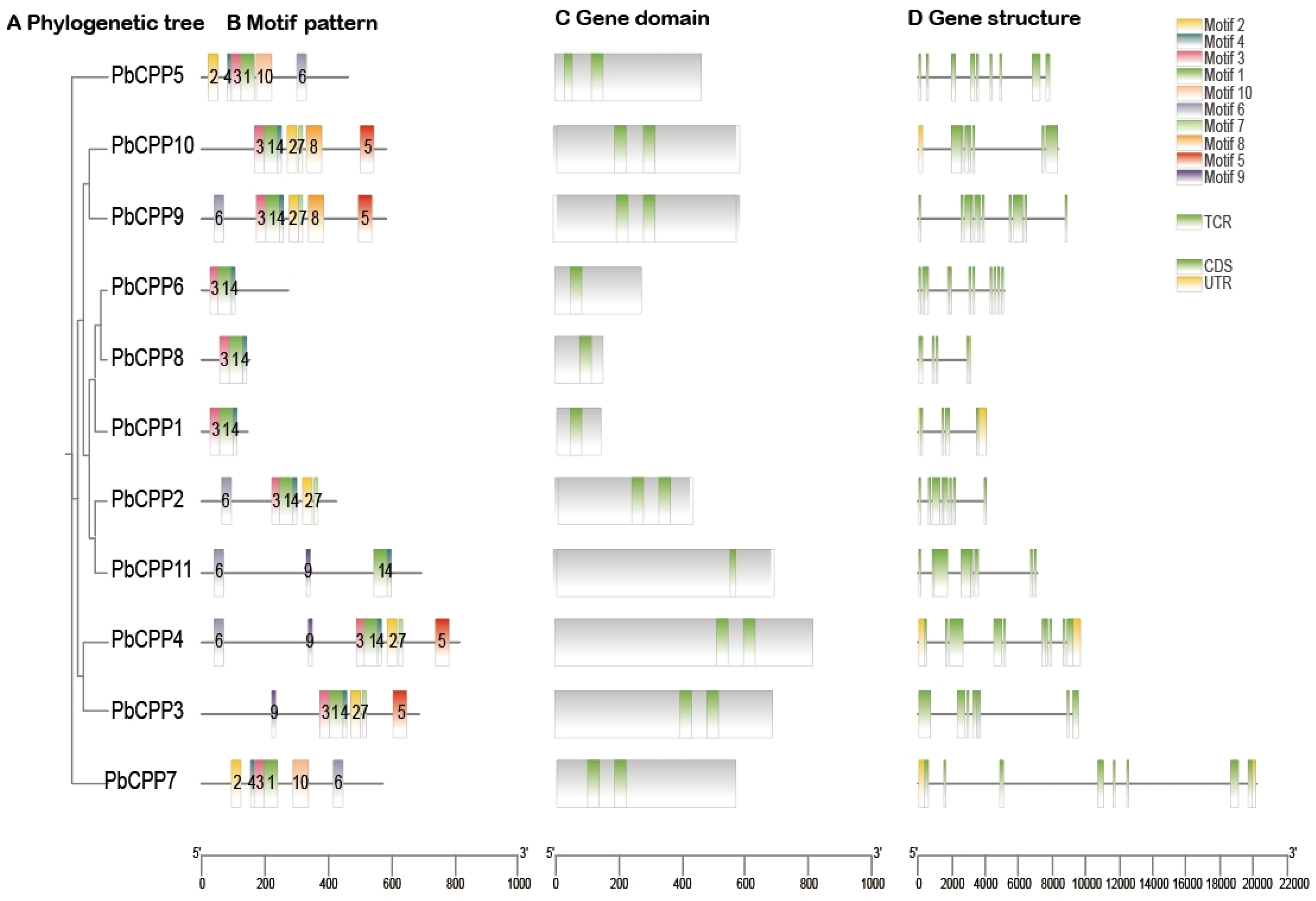
3.4. Phylogenetic Tree and Cis-Acting Element Analysis
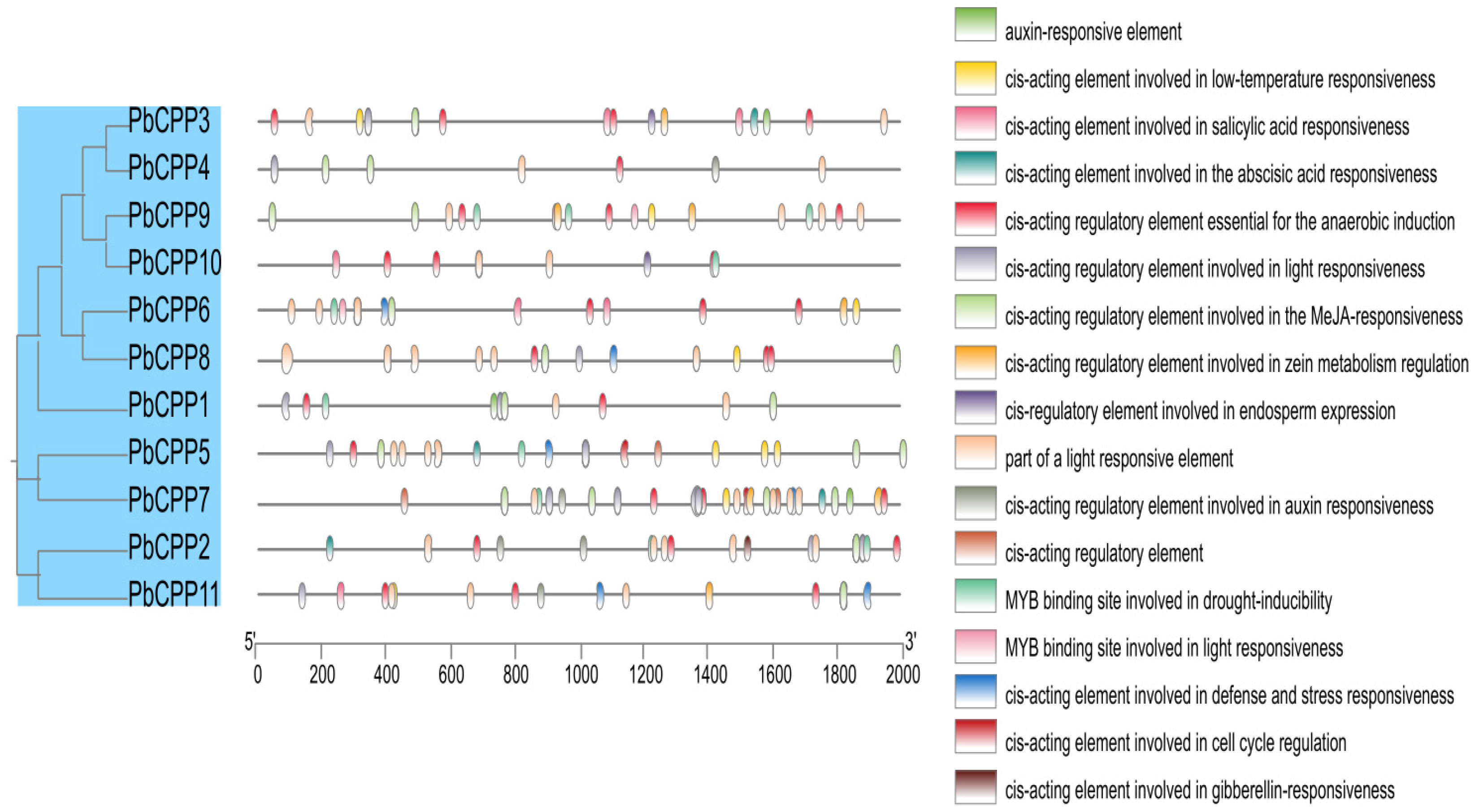
3.5. Analysis of Promoter Cis-Acting Elements of the PbCPP Gene Family
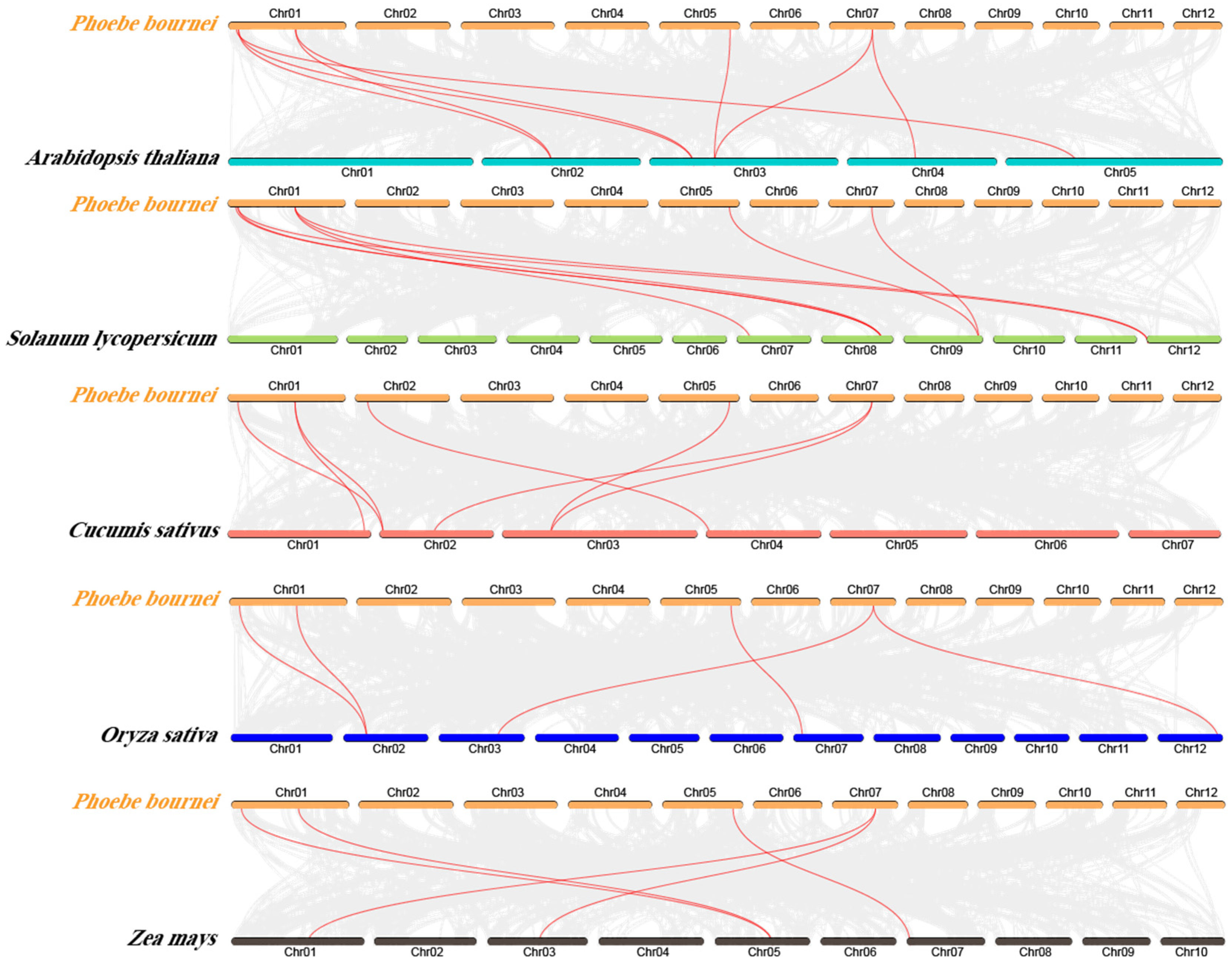
3.6. Analysis of Covariance Between Phoebe Bournei and Different Species
3.7. Analysis of PbCPP Gene Family Covariance
3.8. Analysis of PbCPP Gene Family Motifs, Structural Domains, and Gene Structures
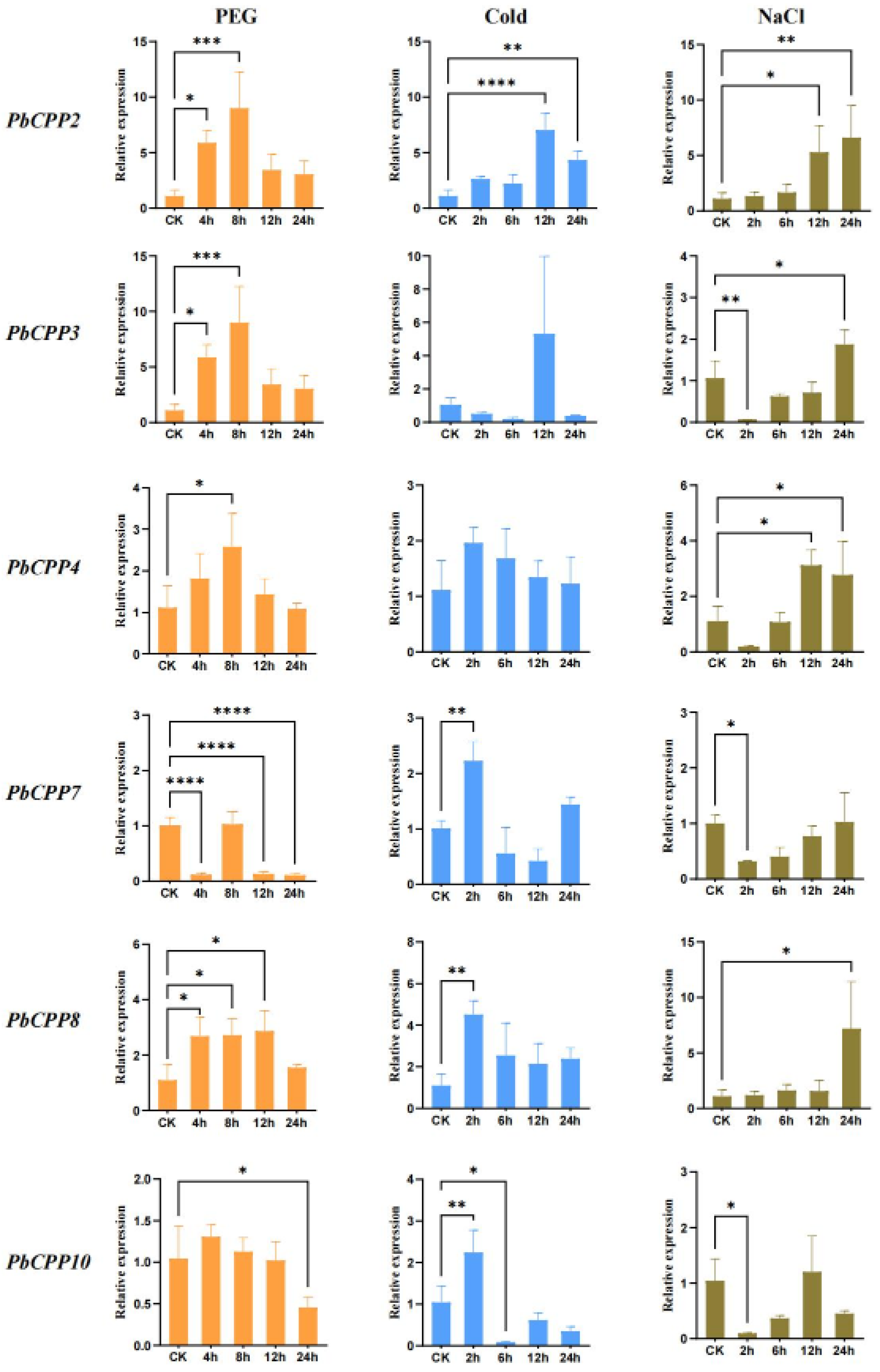
3.9. Expression Profiles of PbCPP Gene Family Under Cold Stress, Drought, and Salt Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Megha, S.; Pankaj, K.; Vipasha, V.; Rajnish, S.; Bhavya, B.; Mohammad, I. Understanding plant stress memory response for abiotic stress resilience: Molecular insights and prospects. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 173, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Latif, K. The phytomicrobiome: Solving plant stress tolerance under climate change. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1219366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Zhu, J.H.; Gong, Z.Z.; Zhu, J.K. Abiotic stress responses in plants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 23, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maïna, F.; Hany, M.; Elodie, L.; Christophe, R.; Benoît, M. Post-transcriptional Regulation of Gene Expression in Plants during Abiotic Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, H.; Knight, R.M. Abiotic stress signalling pathways: Specificity and cross-talk. Trends Plant Sci. 2001, 6, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, X.N.; Fan, S.G.; He, Y.; Wei, M.; Wang, J.Y.; Yin, Y.L.; Liu, Y.F. Combined genomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals the contribution of tandem duplication genes to low-temperature adaptation in perennial ryegrass. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1216048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.N.; Tan, Y.; Jacoby, R.P.; Millar, A.H. Abiotic environmental stress induced changes in the Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplast, mitochondria and peroxisome proteomes. J. Proteom. 2008, 72, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.D.; Wang, F.; Ma, J.Y.; Liu, H.Z.; Ye, H.; Zhao, P.; Wang, J.B. Comprehensive Evolutionary Analysis of CPP Genes in Brassica napus L. and Its Two Diploid Progenitors Revealing the Potential Molecular Basis of Allopolyploid Adaptive Advantage Under Salt Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 873071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.C.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.P.; Wang, Z.S.; Guo, Y.; Xu, C.; Guo, J.; He, T.; Ma, L.Y.; et al. Ancient plastid genomes solve the tree species mystery of the imperial woodNanmu” in the Forbidden City, the largest existing wooden palace complex in the world. Plants People Planet 2022, 4, 696–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Xiao, J.H.; Li, L.; Conran, J.G.; Li, J. Congruent species delimitation of two controversial gold-thread nanmu tree species based on morphological and restriction site-associated DNA sequencing data. J. Syst. Evol. 2019, 57, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.J.; Wu, X.H.; Grossnickle, S.C.; Chen, L.H.; Yu, X.X.; El-Kassaby, Y.A.; Feng, J.L. Formula Fertilization Promotes Phoebe bournei Robust Seedling Cultivation. Forests 2020, 11, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Liu, L.L.; Sun, S.X.; Li, Y.M.; Jia, L.; Ye, S.L.; Yu, Y.X.; Dossa, K.; Luan, Y.P. Leaf-transcriptome profiles of Phoebe bournei provide insights into temporal drought stress responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1010314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.J.; Yin, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, J.H.; Han, X.; Tong, Z.K. Co-expression network analysis reveals PbTGA4 and PbAPRR2 as core transcription factors of drought response in an important timber species Phoebe bournei. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1297235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.M.; Hu, L.J. WRKY Transcription Factor Responses and Tolerance to Abiotic Stresses in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, N.N.; Wang, L.; Sun, Q.L.; Wang, Q.G.; Zhang, Y.T.; Han, X.; Yang, Q.; Ma, W.J.; Tong, Z.K.; Zhang, J.H. Genome-wide identification of the bHLH transcription factor family and the regulatory roles of PbbHLH74 in response to drought stress in Phoebe bournei. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghpanah, M.; Hashemipetroudi, S.; Arzani, A.; Araniti, F. Drought Tolerance in Plants: Physiological and Molecular Responses. Plants 2024, 13, 2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.J.; Wu, X.J.; Li, N.; Nie, H.S.; Ma, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.C.; Ma, Y.H. The StbHLH47 transcription factor negatively regulates drought tolerance in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenchanmane Raju, S.K.; Zhang, Y.; Mahboub, S.; Ngu, D.W.; Qiu, Y.; Harmon, F.G.; Schnable, J.C.; Roston, R.L. Low-temperature tolerance in land plants: Are transcript and membrane responses conserved? Plant Sci. 2018, 276, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Sarwar, R.; Zhang, W.; Geng, R.; Zhu, K.M.; Tan, X.L. Research progress on the physiological response and molecular mechanism of cold response in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1334913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi, S.; Delangiz, N.; Lajayer, A.B.; Saghafi, D.; Maggi, F. Review and future prospects on the mechanisms related to cold stress resistance and tolerance in medicinal plants. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.Y.; Yang, W.B.; Ma, J.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.M.; Wu, X.L.; Zhang, J.H. An integrated Framework for Drought Stress in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.L.; Hwarari, D.; Korboe, H.M.; Ahmad, B.; Cao, Y.W.; Movahedi, A.; Yang, L.M. Low temperature stress-induced perception and molecular signaling pathways in plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2023, 207, 105190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.S.; Zhang, Q.K.; Liu, M.Y.; Zhou, H.P.; Ma, C.L.; Wang, P.P. Regulation of Plant Responses to Salt Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.R.; Fan, D.J.; Lan, S.X.; Cheng, S.Z.; Chen, S.P.; Lin, Y.L.; Cao, S.J. Genome-Wide Identification, Expression and Stress Analysis of the GRAS Gene Family in Phoebe bournei. Plants 2023, 12, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.H.; Li, M.; Yang, Z.C.; He, C.Y.; Wu, Z.K.; Tong, Z.K.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Cao, S.J. The Vital Role of the CAMTA Gene Family in Phoebe bournei in Response to Drought, Heat, and Light Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.D.; Ahammed, G.J.; Guo, D.L. Plant transcriptional memory and associated mechanism of abiotic stress tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 10, 7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.H.; Tang, X.H.; Li, J.S.; Zheng, Q.M.; Wang, T.; Cheng, S.Z.; Chen, S.P.; Cao, S.J.; Cao, G.Q. Genome wide investigation of Hsf gene family in Phoebe bournei: Identification, evolution, and expression after abiotic stresses. J. For. Res. 2024, 35, 3456–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, T.; Tahir, M.H.N.; Iqbal, S.; Sajjad, M.; Nadeem, M.A.; Qanmber, G.; Baig, A.; Khan, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Geng, Z.; et al. Genome-wide characterization and sequence polymorphism analyses of cysteine-rich poly comb-like protein in Glycine max. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 996265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riechmann, J.L.; Heard, J.; Martin, G.; Reuber, L.; Jiang, C.; Keddie, J.; Adam, L.; Pineda, O.; Ratcliffe, O.J.; Samaha, R.R.; et al. Arabidopsis Transcription Factors: Genome-Wide Comparative Analysis Among Eukaryotes. Science 2000, 290, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.U.; Algreen-Petersen, R.G.; Hoedl, M.; Jurkiewicz, A.; Cvitanich, C.; Braunschweig, U.; Schauser, L.; Oh, S.A.; Twell, D.; Jensen, E.Ø. The conserved cysteine-rich domain of a tesmin/TSO1-like protein binds zinc in vitro and TSO1 is required for both male and female fertility in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 3657–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, M.; Arshi, A.S.; Narayanan, N.; Arfin, U.H.; Sharma, A. A mechanistic insight on how Compromised Hydrolysis of Triacylglycerol 7 (CHT7) restrains the involvement of it’s CXC domain from quiescence repression. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 265, 130844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.Q.; Xuan, X.Y.; Su, S.Y.; Jiao, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Z.J. Comprehensive analysis of the CPP gene family in Moso bamboo: Insights into their role in rapid shoot growth. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yrurla, I. Plant development regulation: Overview and perspectives. J. Plant Physiol. 2015, 182, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.Y.; Fan, H.F.; Li, Y.P.; Guo, Y.T.; Liu, C.; Chai, L.A.; Du, C.X. Cucumis sativus PHLOEM PROTEIN 2-A1 like gene positively regulates salt stress tolerance in cucumber seedlings. Plant Mol. Biol. 2023, 111, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Yang, L.; Chang, R.Z.; Gaut, B.S.; Qiu, L.J. Genetic diversity in domesticated soybean (Glycine max) and its wild progenitor (Glycine soja) for simple sequence repeat and single-nucleotide polymorphism loci. New Phytol. 2010, 188, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, H.; Lin, Y.L.; Wang, X.H.; Gao, L.Z. Comprehensive genomic analysis and expression profiling of cysteine-rich polycomb-like transcription factor gene family in tea tree. Hortic. Plant J. 2021, 7, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.G.; Jia, X.Y.; Chen, D.X.; Fu, Q.J.; Chen, J.X.; Yang, W.H.; Yang, H.H.; Xu, X.Y. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Cysteine-Rich Polycomb-like Protein (CPP) Gene Family in Tomato. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, B.A.; Villanueva, J.M.; Gasser, C.S. Arabidopsis TSO1 regulates directional processes in cells during floral organogenesis. Genetics 1998, 150, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, B.A.; He, J.Q.; Park, S.Q.; Gasser, C.S. TSO1 is a novel protein that modulates cytokinesis and cell expansion in Arabidopsis. Development 2000, 127, 2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Dou, Y.C.; Zhang, C. Fuzzy clustering of CPP family in plants with evolution and interaction analyses. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Wang, Y.C.; Chen, W.F.; Xu, M.L.; Zhou, R.H.; Shou, H.X.; Chen, J. High-resolution Anatomical and Spatial Transcriptome Analyses Reveal Two Types of Meristematic Cell Pools within the Secondary Vascular Tissue of Poplar Stem. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 809–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Gebali, S.; Mistry, J.; Bateman, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Luciani, A.; Potter, S.C.; Qureshi, M.; Richardson, L.J.; Salazar, G.A.; Smart, A.; et al. The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 41, D427–D432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Bo, Y.; Han, L.Y.; He, J.E.; Lanczycki, C.J.; Lu, S.N.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonza-les, N.R.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: Functional classification of proteins via subfamily domain ar-chitectures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D200–D203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit De-veloped for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhang, J.H.; Han, S.; Chong, S.L.; Meng, G.L.; Song, M.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.C.; Liu, C.C.; Lou, L.H.; et al. The chromosome-scale genome of Phoebe bournei reveals contrasting fates of terpene synthase (TPS)-a and TPS-b subfamilies. Plant Commun. 2022, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.Y.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, H.L.; Qian, W.; Gao, W.J.; She, H.B. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of MYB Gene Family and Analysis of Its Sex-Biased Expression Pattern in Spinacia oleracea L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.Z.; Yang, H.; Zheng, Q.M.; Liao, W.H.; Chen, L.; Lian, Y.R.; Lin, Q.M.; Huo, S.H.; Obaid, U.R.; Liu, W.; et al. Identification and Expression Analysis of TCP Transcription Factors Under Abiotic Stress in Phoebe bournei. Plants 2024, 13, 3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckett, S.; Steve, E.; Jeremy, G.W. An account of conserved functions and how biologists use them to integrate cell and evolutionary biology. Biol. Philos. 2023, 38, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, S.; Schulfer, A.F.; Di Stilio, V.S. A eudicot MIXTA family ancestor likely functioned in both conical cells and trichomes. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1288961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, F.; Brian, C.T. Gene-balanced duplications, like tetraploidy, provide predictable drive to increase morphological complexity. Genome Res. 2006, 16, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, S.B.; Mitra, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Young, N.D.; May, G. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Puente, P.; Deng, X.W.; Wei, N. Combinatorial interaction of light-responsive elements plays a critical role in determining the response characteristics of light-regulated promoters in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 1998, 15, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.L.; Lau, O.S.; Deng, X.W. Light-regulated transcriptional networks in higher plants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, R.; Nawaz, M.S.; Siddique, M.J.; Hakim, S.; Imran, A. Plant survival under drought stress: Implications, adaptive responses, and integrated rhizosphere management strategy for stress mitigation. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 242, 126626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, S.M.; Karimi, M.; Venditti, A.; Zahra, N.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Farooq, M. Plant Adaptation to Drought Stress: The Role of Anatomical and Morphological Characteristics in Maintaining the Water Status. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 13, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Ding, R.S.; Du, T.S.; Kang, S.Z.; Tong, L.; Gu, S.J.; Gao, S.Y.; Gao, J. Stomatal conductance modulates maize yield through water use and yield components under salinity stress. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 294, 108717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene Name | Gene ID | AA/aa | MW/kDa | pI | II | AI | GRAVY | Subcellular Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OF11936-RA | PbCPP1 | 142 | 15,718.56 | 5.46 | 45.27 | 53.66 | −0.81 | Nucleus |
| OF04268-RA | PbCPP2 | 423 | 46,902.83 | 5.68 | 72.08 | 51.65 | −0.799 | Nucleus |
| OF21316-RA | PbCPP3 | 685 | 75,008.06 | 5.49 | 64.13 | 57.36 | −0.822 | Nucleus |
| OF27418-RA | PbCPP4 | 813 | 88,999.17 | 5.69 | 54.63 | 62.46 | −0.699 | Nucleus |
| OF13684-RA | PbCPP5 | 460 | 49,459.6 | 7.17 | 51.88 | 61.22 | −0.61 | Nucleus |
| OF11935-RA | PbCPP6 | 272 | 30,496.31 | 8.57 | 41.51 | 59.85 | −0.681 | Nucleus |
| OF22648-RA | PbCPP7 | 568 | 60,799.64 | 7.94 | 52.3 | 68.08 | −0.445 | Nucleus |
| OF27954-RA | PbCPP8 | 149 | 16,915.16 | 8.31 | 69.08 | 55.64 | −0.721 | Nucleus |
| OF00758-RA | PbCPP9 | 580 | 64,246.22 | 8.43 | 63.73 | 61.02 | −0.696 | Nucleus |
| OF00759-RA | PbCPP10 | 580 | 64,940.85 | 8.92 | 67.23 | 57.45 | −0.864 | Nucleus |
| OF04279-RA | PbCPP11 | 690 | 76,270.21 | 5.59 | 61.23 | 68.99 | −0.586 | Nucleus |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, R.; Feng, Y.; Li, Q.; Wu, H.; Guo, S.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Cao, S. Genome-Wide Analysis of CPP Transcription Factor Family in Endangered Plant Phoebe bournei and Its Response to Adversity. Plants 2025, 14, 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050803
Liu R, Feng Y, Li Q, Wu H, Guo S, Li J, Liu X, Zhang Y, Tang X, Cao S. Genome-Wide Analysis of CPP Transcription Factor Family in Endangered Plant Phoebe bournei and Its Response to Adversity. Plants. 2025; 14(5):803. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050803
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ronglin, Yizhuo Feng, Qingyan Li, Hua Wu, Shengzhou Guo, Junnan Li, Xiaomin Liu, Yanlin Zhang, Xinghao Tang, and Shijiang Cao. 2025. "Genome-Wide Analysis of CPP Transcription Factor Family in Endangered Plant Phoebe bournei and Its Response to Adversity" Plants 14, no. 5: 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050803
APA StyleLiu, R., Feng, Y., Li, Q., Wu, H., Guo, S., Li, J., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Tang, X., & Cao, S. (2025). Genome-Wide Analysis of CPP Transcription Factor Family in Endangered Plant Phoebe bournei and Its Response to Adversity. Plants, 14(5), 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050803








