Abstract
Dinitrotoluenes (DNTs) are byproducts of the explosive trinitrotoluene (TNT), and exist as a mixture of 2 to 6 isomers, with 2,4-DNT and 2,6-DNT being the most significant. The main route of human exposure at ammunition facilities is inhalation. The primary targets of DNTs toxicity are the hematopoietic system, cardiovascular system, nervous system and reproductive system. In factory workers, exposure to DNTs has been linked to many adverse health effects, including: cyanosis, vertigo, headache, metallic taste, dyspnea, weakness and lassitude, loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting. Other symptoms including pain or parasthesia in extremities, abdominal discomfort, tremors, paralysis, chest pain, and unconsciousness have been documented. An association between DNTs exposure and increased risk of hepatocellular carcinomas and subcutaneous tumors in rats, as well as renal tumors in mice, has been established. This research was therefore designed targeting the liver to assess the cellular and molecular responses of human liver carcinoma cells following exposure to 2,4-DNT and 2,6-DNT. Cytotoxicity was evaluated using the MTT assay. Upon 48 hrs of exposure, LC50 values of 245 ± 14.72μg/mL, and 300 ± 5.92μg/mL were recorded for 2,6-DNT and 2,4-DNT respectively, indicating that both DNTs are moderately toxic, and 2,6-DNT is slightly more toxic to HepG2 cells than 2,4-DNT. A dose response relationship was recorded with respect to the cytotoxicity of both DNTs. Western blot analysis resulted in a significant expression (p<0.05) of the 70-kDa heat shock protein in 2,6-DNT-treated cells compared to the control cells and at the 200 μg/mL dose for 2,4-DNT. A statistically significant expression in c-fos was also observed at the 200 and 250 μg/mL treatment level for 2,4- and 2,6-DNT, respectively. However, no statistically significant expression of this protooncogene-related protein was observed at the doses of 0, 100, or 300 μg/mL or within the dose range of 0–200 μg/mL for 2,6-DNT. The 45-kDa growth arrest and damage protein was significantly expressed at the dose range of 200 – 250μg/mL for 2,6-DNT and at the dose range of 200 – 400μg/mL for 2,4-DNT. Expression of 153-kDa growth arrest and DNA damage protein was significant at the 100, 200, and 250μg/mL doses for 2,6-DNT and at the 200 μg/mL dose for 2,4-DNT. Overall, these results indicate the potential of DNTs to induce cytotoxic, proteotoxic (HSP70), and genotoxic (GADD45/153) effects, as well as oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory reactions (c-fos).
Introduction
Dinitrotoluenes (DNTs) [CH3C6H3(NO2)2] are nitroaromatic compounds that are produced industrially and released into the environment as a result of human activities. DNTs appear as pale yellow crystalline solids and exist as a mixture of 2 to 6 isomers, among which 2,4-DNT and 2,6-DNT are the most significant at room temperature [1]. The compounds 2,4-dinitrotoluene (2,4-DNT; 1-methyl-2,4-dinirobenzene; CAS Reg No. 121-14-2) and 2,6-dinitrotoluene (2,6-DNT; 1-methyl-1,3-dinitrobezene; CAS Reg. No. 606-20-2) have a molecular weight of 182.14, melting points of 71 °C (2,4-DNT) and 66°C (2,6-DNT) and boiling points of 300 °C (2,4-DNT) and 260°C (2,6-DNT) [2]. They are soluble in alcohol, ether, acetone, and benzene, but only slightly soluble in water – 270 parts per million (ppm) at 22°C (2,4-DNT) and 180 ppm at 20°C (2,6-DNT) [2–5].
Although both 2,4-DNT and 2,6-DNT are transformation products of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene [4], the main pathway of their production is through the dinitration of toluene with nitric acid in the presence of sulfuric acid. This reaction produces a commercial grade mixture, also called technical grade (tg), containing about 75% 2,4-DNT isomer, 20% 2,6-DNT isomer, and 5% of the other DNT isomers [6–8]. Dinitrotoluenes are used in the manufacture of dyes, in munitions as smokeless propellant powder, and as gelatinizing and plasticizing agents in both commercial and military explosive compositions [6]. Their major use is in the synthesis of toluenediamine, the organic intermediate used in the production of polyurethane [7]. In the United States, about 500 persons are estimated to be potentially exposed yearly to 2,4-DNT and 2,6-DNT during the production of munitions and explosives.
Absorption of 2,4-DNT and 2,6-DNT occurs through the gastrointestinal tract, the respiratory tract, and the skin in most species [9]. From a study of 33 workers in a tg-DNT explosives factory, Woolen et al. [10] reported that the skin was probably the primary route of exposure in these workers, and the lungs constituted the secondary route because of low atmospheric levels of DNTs. Humans absorb both isomers of DNT following dermal or inhalation exposure. Urine is the primary route of elimination of both DNT isomers in most animals including rodents, rabbits, dogs, and monkeys; in CD-1 and B6C3F1 mice and in Wistar rats, but the main route of elimination is the feces. The percent absorption of the DNT isomers is difficult to assess because biliary excretion is significant in most animals; males excrete more of the 2,4-DNT isomer and its metabolites in the bile and less in urine than do females [7].
No systematic studies have been done on the distribution of DNTs in tissues of potentially exposed individuals. Trace amounts of 2,4-DNT and 2,6-DNT have been reported in blood samples of workers employed at a tg-DNT explosives factory [10]. Radiotracer studies with animals have shown small amounts of radioactivity were found in the liver, blood, kidneys, brain, and skeletal muscle of mice, rats, rabbits, dogs, and monkeys following oral exposure to radio labeled 2,4-DNT [6, 11]. Peak levels of radioactivity were observed in the blood of male rats 6 hours after a single oral dose of [3H] 2,4-DNT [12].
Although the main route of human exposure at ammunitions facilities is inhalation, dermal contact and inadvertent ingestion may also be substantial. Such exposures have been linked to many health effects in factory workers including cyanosis, vertigo, headache, metallic taste, dyspnea, weakness, and lassitude, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting [6, 13, 14]. Other symptoms including pain or parathesia in extremities, abdominal discomfort, tremors, paralysis, chest pain and unconsciousness have been reported [13, 9].
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and the U.S. EPA have classified DNT as a probable human carcinogen (Group B2). Epidemiologic data point to the possible urothelial carcinogenicity of DNT in highly and long term exposed miners. As a systemic toxicant, DNT has a potential of causing adverse health effects that target the hematopoietic system (pallor, cyanosis, anemia, and leukocytosis), the cardiovascular system (ischemic heart disease), the nervous system (muscular weakness, headache, dizziness, nausea, insomnia, and tingling pains in the extremities), and the reproductive system (reduction of sperm counts, alteration of sperm morphology and aspermatogenesis). The incidence of subcutaneous tumors and hepatocellular carcinomas in rats increased after exposure to 2,4-DNT and 2,6-DNT[14].
Epidemiologic studies of DNT toxicity have been limited to small groups of workers who were occupationally exposed at various ammunitions production facilities. It has therefore been difficult to clearly define the health effects of DNTs with a high degree of confidence because of the multigenic nature of occupational exposure.
Methemoglobinemia has been reported as the first clinical sign of DNT toxicity, followed by cyanosis when the methemoglobin concentration rises above 15 mg/L [13, 10]. Gastrointestinal effects of DNT exposure are characterized by nausea and vomiting, secondary to methemoglobinemia. In humans, long-term exposure can cause jaundice. Incidents of poisoning resulting from inhalation of 2,4-DNT are primarily described in the early literature; with symptoms including marked cyanosis, headache, palpitations, tightness in the chest, insomnia, lack of appetite, impaired reflexes, nystagmus, and tremors following exposure to 2,4-DNT [15].
Cellular response to systemic toxicants or other deleterious forms of stress is characterized by the activation of stress-inducible transcription factors that up-regulate target genes. The regulation of stress gene expression is intimately linked to signaling pathways that coordinate long-term cell adaptation or programmed cell death. Moreover, cytotoxic stresses can influence the synthesis of protective proteins that are associated with biotransformation activity, cell cycle progression, DNA-impairment, proliferative machinery, oxidative damage, and protein perturbations. Recent evidence in our laboratory has shown that DNT transcriptionally activates a novel set of stress genes in human liver carcinoma cells. In the present study, we hypothesize that DNT treatment of HepG2 cells will induce cytotoxicity and increase the level of stress proteins that may play a role in the molecular events leading to toxicity and tumorigenesis.
Materials and Methods
Chemicals
2,4-Dinitrotoluene (CH3C6H3(NO2)2, CAS Reg. No. 121-14-2, Lot No. 306-22A and 2,6-Dinitrotoluene (CH3C6H3(NO2)2, CAS Reg. No. 606-20-2, Lot No. 295-21A were purchased from Chem Service (West Chester, PA). All culture media and medium supplements, pre-cast SDS-PAGE gels, c-fos, HSP70, GADD45 and GADD153 primary and secondary antibodies, and BCIP/NBT color development substrate were purchased from commercially available sources.
Culture of HepG2 Cells
Human liver carcinoma, HepG2 cells were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA). In the laboratory, they were stored in liquid nitrogen until use. They were next thawed by gentle agitation of their containers (vials) for 2 minutes in a water bath at 37°C. After thawing, the content of each vial was transferred to a 75cm2 tissue culture flask, diluted with DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% streptomycin and penicillin, and incubated at 37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator to allow the cells to grow, and form a monolayer in the flask. Subsequently, cells grown to 80–95% confluence were washed with phosphate buffer saline (PBS), trypsinized with 10mL of 0.25% (w/v) trypsin-0.03% (w/v) EDTA, diluted, counted (1 × 106), and seeded in three 25 mm2 flasks prior to chemical treatment.
Cytotoxicity Experiment
The MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] assay was performed for assessing cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells exposed to serial doses (0–300μg/mL) of 2,4-DNT and (0–250 μg/mL) of 2,6-DNT. This experiment was conducted following the experimental protocol that is routinely used in our laboratory [16]. HepG2 cells are dosed with various concentrations of 2,4- and 2,6-DNT in 1% dimethyl suloxide DMSO and incubated at 37º C for 48 hrs, and the MTT assay for cell viability is performed using a microplate reader at 550mn to determine the cell viability of HepG2 to 2,4- and 2,6-DNT and the lethal concentration (LC50).
Western Blot Analysis
The Western Blot analysis was conducted to determine specific cellular response proteins (c-fos, GADD45, GADD153, HSP70) at 48 hrs of DNT exposure. About 1 × 106 HepG2 cells were grown to 80–95% confluency, and treated with 0, 100, 200, and 300 μg 2,4-DNT/mL and 0, 50, 100, 150, 200, and 250 μg 2,6-DNT/mL for 48 hrs. Control flasks were also made without DNT treatment. Five hundred μL of sample buffer (0.2 mol/L Tris, pH 6.8, 1% SDS, 30% glycerol, 7.5% β-mercaptoethanol, 0.1% bromophenol blue) was added to each flask and cells were mechanically dislodged and collected in microcentrifuge tubes. Whole cell extracts (20μg) from HepG2 cells containing an equal volume of sample buffer were heated at 100°C for 5 min and electrophoresed on a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel. Samples were then transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane on ice and the membrane blocked (Tris buffered saline with 5% nonfat dry milk, 0.1 Tween 20) for 1 hr at room temperature. Detection of membrane-bound proteins induced by DNT was carried out using specific primary antibodies that recognize the proteins of interest. Subsequently, the reaction was reprobed with an alkaline conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody for c-fos, GADD45, GADD153 and HSP70. BCIP/NBT color substrate was incorporated to develop protein bands. Immunoblot 1-D protein bands were assessed for relative abundance by Total Lab computer software (Nonlinear USA Inc. Durham, NC).
Results
Cytotoxicity Assay
The cytotoxic effect of 2,4-DNT on HepG2 cells is shown in Figure 1. A classical dose-response pattern was demonstrated with respect to the cytotoxicity of 2,4-dinitrotoluene. The percentages of cell viability were 100.0 ± 0%, 88.18 ± 3.31%, 74.51 ± 4.31%, 50.15 ± 5.31%, 22.00 ± 6.53%, 26.07 ± 7.08%, 23.40 ± 7.76, 20.00 ± 10.99, and 21.54 ± 8.14 for 0, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, and 800 μg/mL of 2,4-dinitrotoluene, respectively. Upon 48 hours of exposure the dose (LD50) required to produce 50% reduction in the viability of HepG2 cells was computed to be 300 ± 5.92 μg 2,4-DNT/mL. This result indicates that 2,4-DNT is moderately toxic to HepG2 cells.
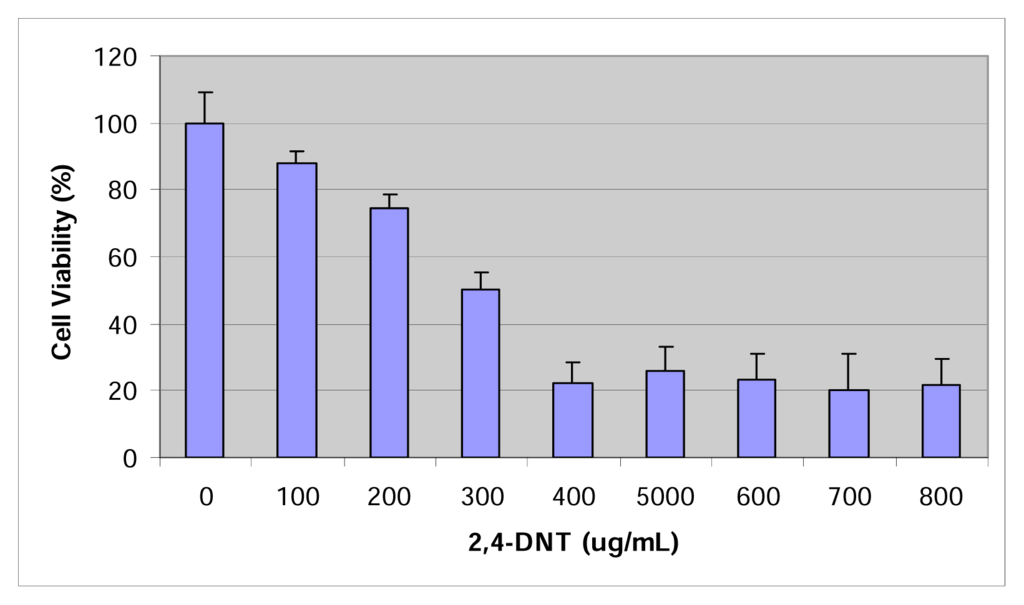
Figure 1.
Cytotoxicity of 2,4-dinitrotoluene to HepG2 cells
The MTT result of the cytotoxic effect of 2,6-dinitrotoluene on human liver carcinoma cells (HepG2) following 48 hours of exposure is shown in Figure 2. This figure also indicates a strong dose-response relationship with respect to 2,6-dinitrotoluene toxicity to HepG2 cells. The percentages of cell viability were 100.0 ± 0.0%, 109.25 ± 15.42%, 105.73 ± 25.69%, 86.60 ± 16.89 %, 59.43 ± 19.10%, 45.45 ± 31.93%, 21.75 ± 37.22, 14.74 ± 23.62, and 8.94 ± 8.46 for 0, 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, and 400 μg/mL of 2,6-dinitrotoluene, respectively. There was a gradual decrease in cell viability with increasing doses of 2,6-dinitrotoluene. Upon 48 hours of exposure the dose (LD50) required to produce 50% reduction in the viability of HepG2 cells was computed to be 245.0 ± 14.72μg/mL. This result indicates that 2,6-DNT is moderately toxic to HepG2 cells.
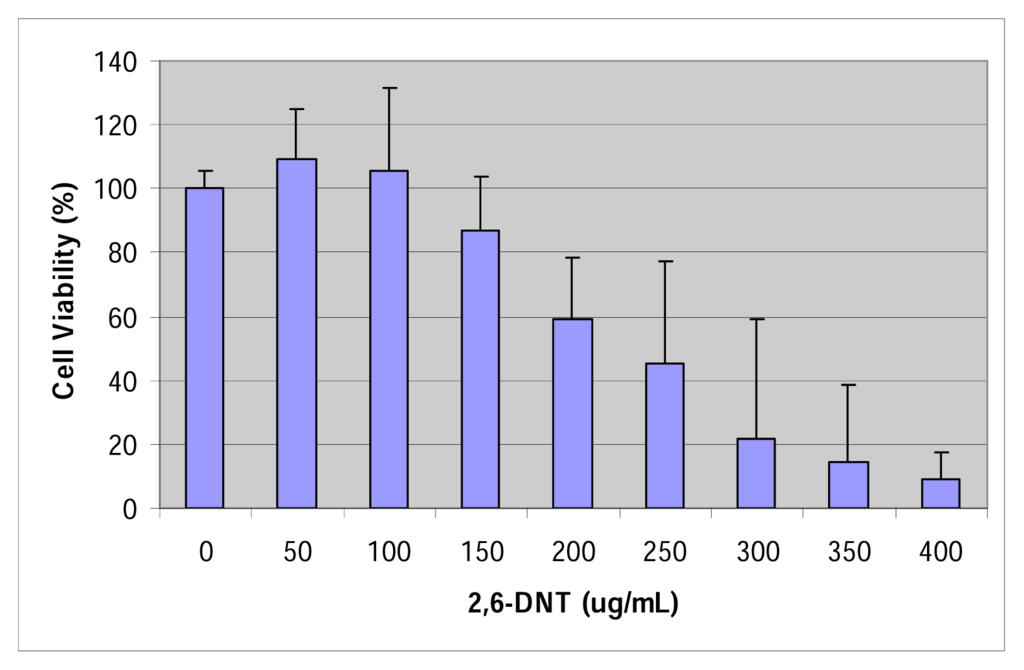
Figure 2.
Cytotoxicity of 2,6-dinitrotoluene to HepG2 cells.
Western and Densitometric Analyses
c-fos expressions in 2,4- and 2–6-DNT-treated HepG2 cells are shown in figures 3 & 4. c-fos was significantly expressed in the western blot and densitometric analysis of 2–4 and 2–6-dinitrotoluene at the 200μg/mL and 250μg/mL treatment levels, respectively. However, no statistically significant expression of this protooncogene-related protein was observed at the doses of 0, 100, or 300μg/mL for 2,4-dinitrotuluene or within the dose ranges of 0–200μg/mL for 2,6-dinitrotoluene.
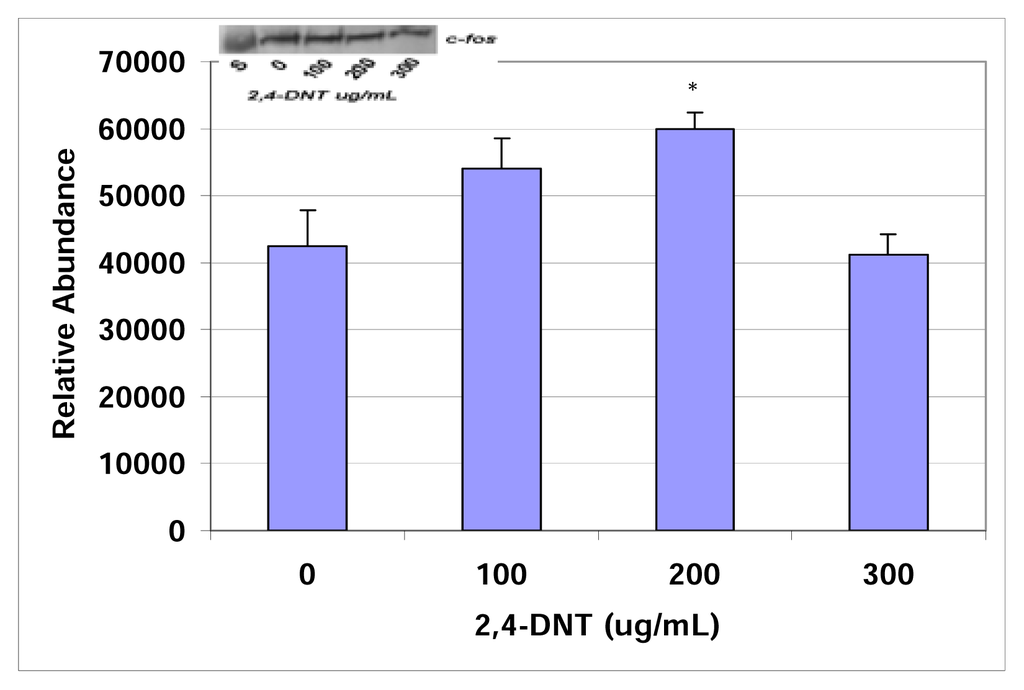
Figure 3.
Western Blot and densitometric analysis of c-fos expression in 2,4-DNT treated HepG2 cells.
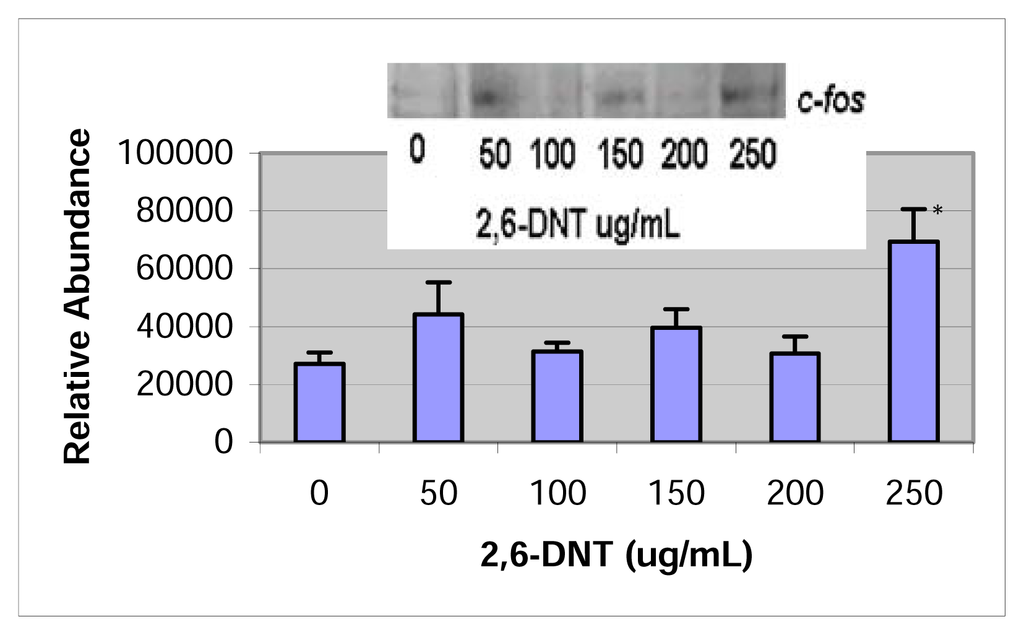
Figure 4.
Western Blot and densitometric analysis of c-fos expression in 2,6-DNT treated HepG2 cells.
Growth arrest and DNA damage (GADD) expressions in HepG2 cells treated with 2,4- and 2,6-DNT are shown in figures 5 & 6. The 45-kDa GADD protein was significantly over expressed at the 100 – 400 μg/mL dose range for 2,4-dinitrotoluene and at the dose levels of 200 and 250 μg/mL for 2,6-dinitrotoluene.
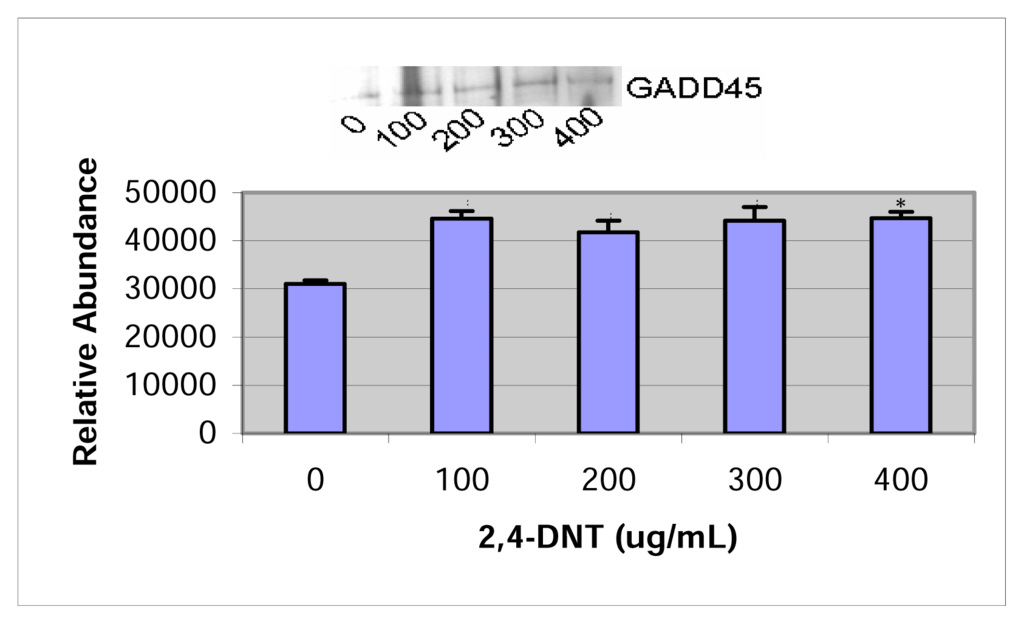
Figure 5.
Western Blot and densitometric analysis of GADD45 expression in 2,4-DNT treated HepG2 cells.
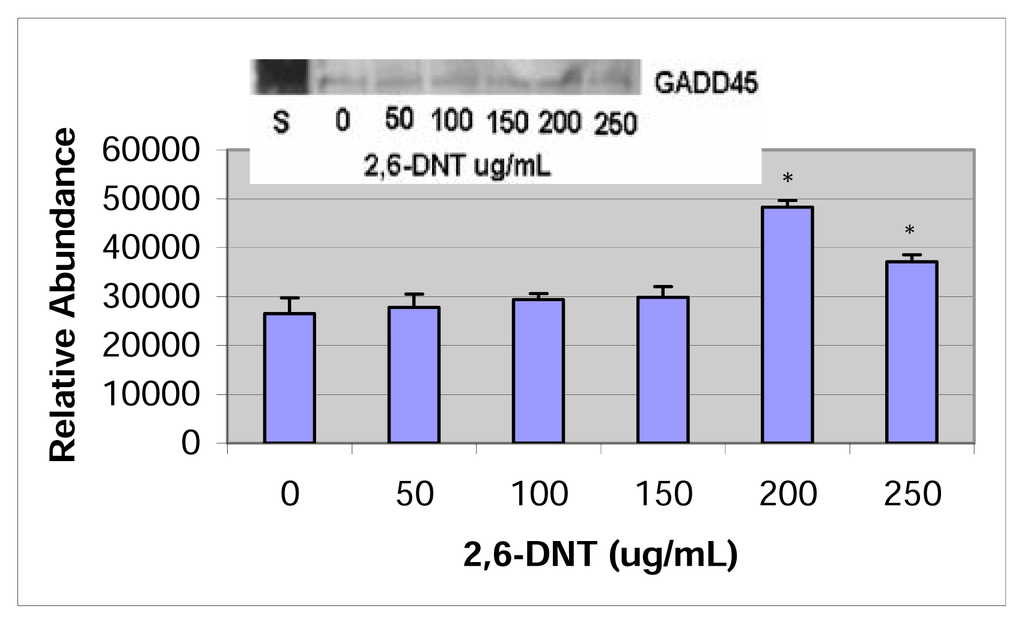
Figure 6.
Western Blot and densitometric analysis of GADD45 expression in 2,6-DNT treated HepG2 cells.
Expression of GADD153 protein was significant at the 200μg/mL dose for 2,4-dinitrotoluene and at the 100, 200, and 250 μg/mL doses for 2,6-dinitrotoluene. The western blot and densitometric analysis are shown in figures 7 & 8.
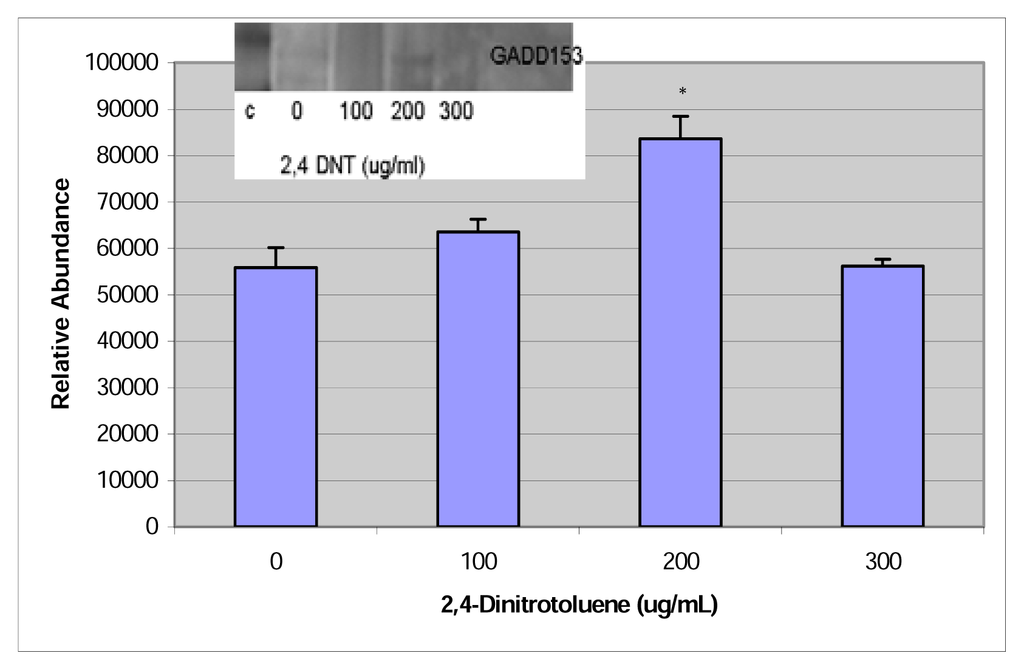
Figure 7.
Western Blot and densitometric analysis of GADD153 expression in 2,4-DNT treated HepG2 cells.
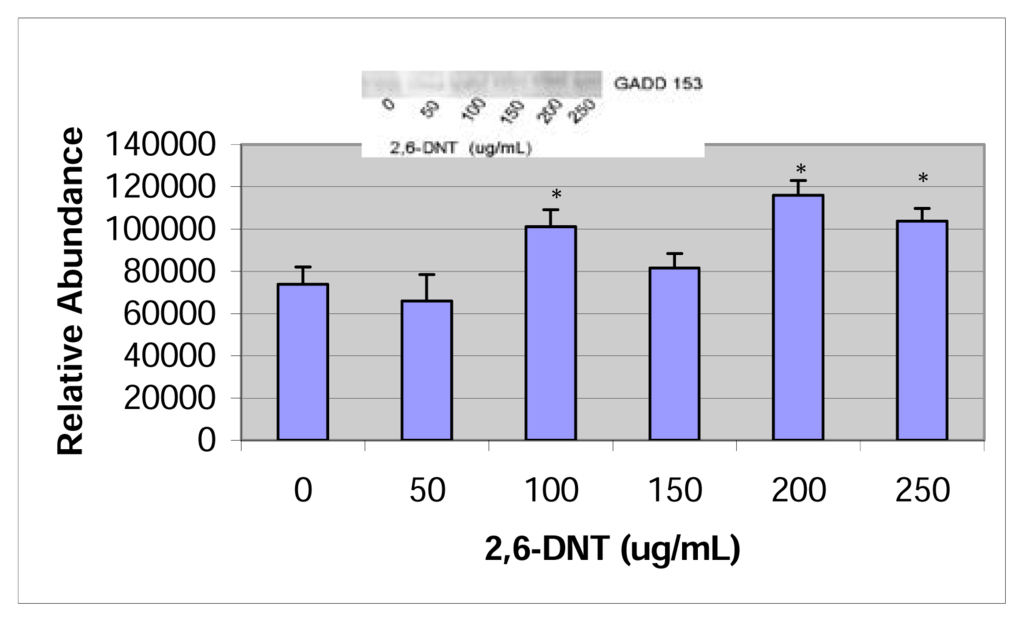
Figure 8.
Western blot and densitometric analysis of GADD153 expression in 2,6-DNT treated HepG2 cells.
HSP70 expressions for 2,4-and 2,6-dinitrotoluene are shown in figures 9 & 10 respectively. There was a significant expression of the 70-kDa heat shock protein from western blot analysis (p<0.05) at the 200 μg/mL dose for 2,4-dinitrotoluene and a significant expression of the 70-kDa heat shock protein (p<0.05) of 2,6-dinitrotoluene compared to the control cells.
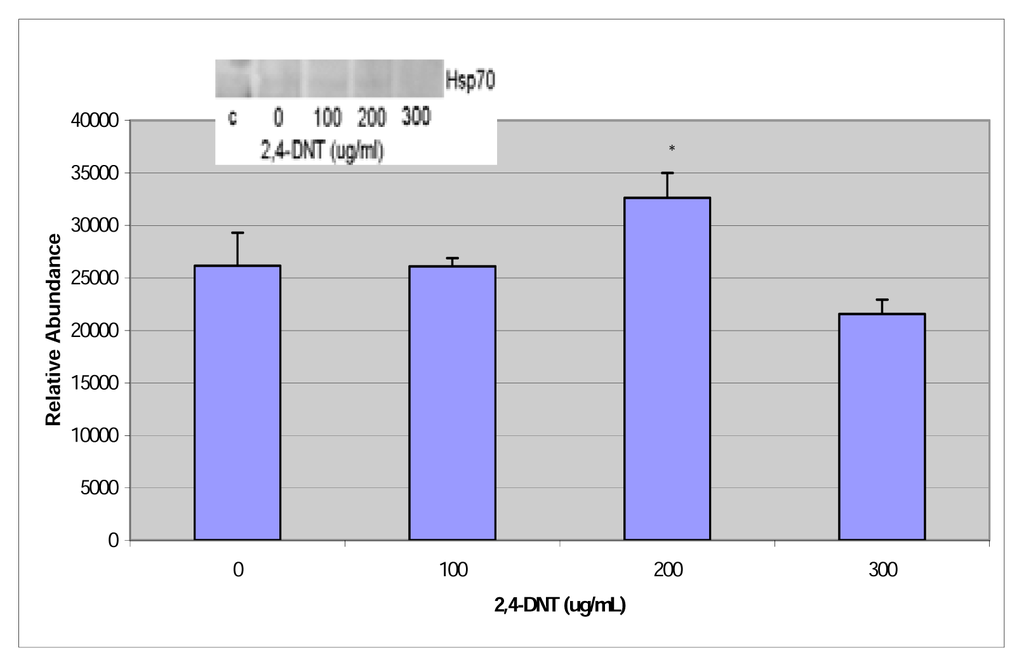
Figure 9.
Western blot and densitometric analysis of HSP70 expression in 2,4-DNT treated HepG2 cells.
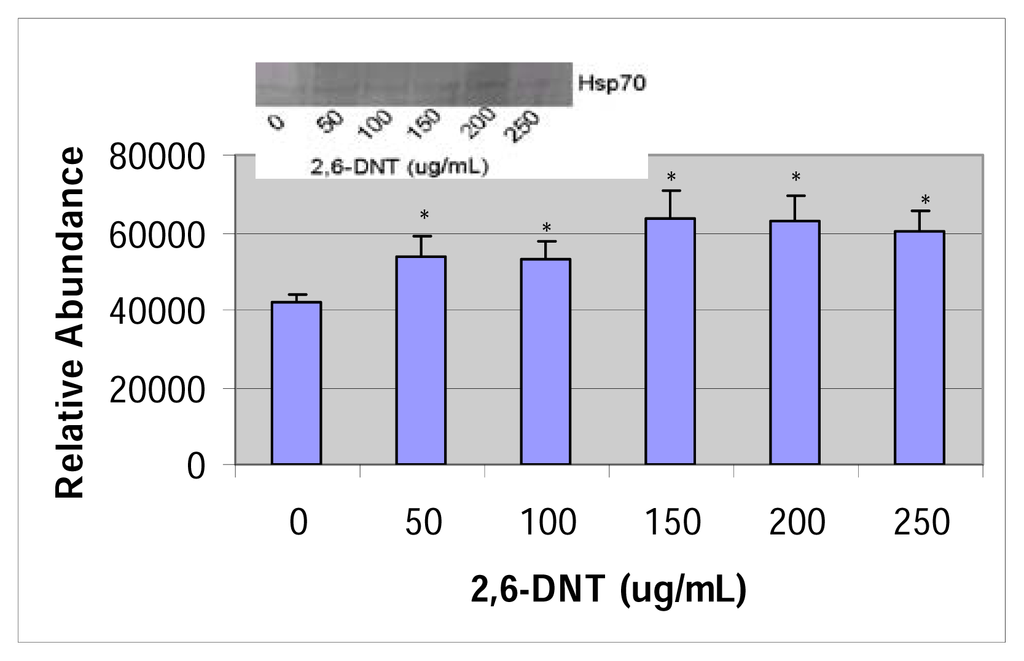
Figure 10.
Western blot and densitometric analysis of HSP70 expression in 2,6-DNT treated HepG2 cells.
Discussion
Cytotoxicity
Cytotoxicity has been defined as the cell killing property of a chemical compound independent from the mechanism of death. Cytotoxicity assays measure the negative effects of the isomers, 2,4- and 2,6-dinitrotoluene, on cells. In the present study, it was demonstrated that different doses of 2,4- and 2,6-DNT induce cytotoxicity in human liver carcinoma cells. Data obtained from this research clearly demonstrate that under similar exposure conditions, the cytotoxicity of the dinitrotoluenes is dose-dependent with LD50 values of 300 ± 5.92μg/mL for 2,4-DNT and 245 ± 14.72μg/mL for 2,6-DNT. The primary targets of DNT toxicity are the hematopoietic system (pallor, cyanosis, anemia, and leukocytosis), the cardiovascular system (ischemic heart disease), the nervous system muscular weakness, headache, dizziness, nausea, insomnia, and tingling pains in the extremities), and the reproductive system (reduction of sperm counts, alteration of sperm morphology, and aspermatogenesis) [6, 13, 7, 9]. Subchronic and chronic oral toxicity studies with experimental animals indicate that the blood, liver, nervous system, and reproductive system are the targets affected by 2,4-DNT. The most common hematogic findings are methemoglobinemia, anemia, reticulocytosis, and an increase in Heinz bodies. Hepatotoxic effects include liver discoloration, and proliferative alterations of hepatocytes and bile duct epithelium. Neuromuscular effects, ranging from tremors and ataxia to convulsions, are more severe in dogs than in rodents. Reproductive effects are characterized by alterations of spermatogenesis, testicular atrophy, and ovarian dysfunction [17, 14, 18, 11, 19, 20].
Recent studies on the cytotoxicity of selected munitions compounds reported that 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene has a relatively higher toxicity to human liver carcinoma cells (showing a LC50 of 105 ± 6 μg/mL) compared to its two metabolites, 2,4- and 2,6-DNT with LC50’s greater than 300 μg/mL at 48 hours of exposure [34]. Other organic compounds such as pentachlorophenol (PCP), a biocidal chemical used in agriculture and as a wood preservative, have shown similar but greater cytotoxic effects to HepG2 cells than 2,4- and 2,6-DNT. PCP has a LD50 of 23.0 ± 5.6 μg/mL compared to 300 ± 5.92 μg/mL and 245 ± 14.72 μg/mL for 2,4- and 2,6-DNT respectively. Based on this information, it can be stated that 2,4- and 2,6-DNT are less toxic than PCP and 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene. The order of toxicity is PCP>TNT>2,6-DNT>2,4-DNT.
An association between DNT exposure and increased risk of hepatobiliary cancer has been reported from a retrospective mortality study involving 4,989 workers exposed to DNT (isomer composition not specified) and 7,436 unexposed controls at an U.S. Army Munitions facility [19]. Exposure to 2,4-DNT containing trace amounts of 2,6-DNT was found to induce an increased incidence of hepatocellular carcinomas and subcutaneous tumors in rats and of renal tumors in male mice [14]. Exposure to tg-DNT induced hepatocellular carcinomas in rats [20, 21]. The results of isomer-specific DNT carcinogenicity studies have suggested, however, that 2,6-DNT rather than 2,4-DNT is the primary hepato-carcinogen in tg-DNT [20–23].
It has been reported that 2,6-DNT must undergo reduction in the gastrointestinal tract to become genotoxic [24, 25]. The compound is absorbed in the small intestine and metabolized in the liver to 2,6-dinitrobenzyl alcohol, which is then conjugated with gluroronic acid before excretion in the bile. The gastrointestinal flora then hydrolyzes the gluronide linkage and reduces one or both of the nitro groups. The amino derivative is then reabsorbed and oxidized in the liver where it binds to DNA [4].
Western blot and Densitometric Analysis
Substantial expressions of GADD45 were observed for 2,4- and 2,6-DNT. Densitometric analysis revealed significant expressions at the 100 – 400 μg/mL dose range and the dose range of 200 – 250 μg/mL for 2,4- and 2,6-DNT, respectively. Substantial expressions of GADD153 were observed for 2,4- and 2,6-DNT. Densitometric analysis revealed significant expressions at the 200μg/mL dose and the doses of 100, 200 and 250 μg/mL for 2,4- and 2,6-DNT, respectively. These proteins are associated with cell cycle regulation and genotoxicity. The expression of these proteins indicates a potential damage at the genomic level. This damage may be associated with alterations in DNA sequence, as well as conformational changes in its helical structure [26].
The c-fos has been indicated as a mammalian UV response pathway, which appears to have an important role in the response to DNA damaging agents such as methyl methane sulfonate and 4-nitroquinoline N-oxide [27]. From our studies, we found strong expressions at the doses of 200 μg/mL and 250 μg/mL for 2,4- and 2,6-DNT, respectively. This protein is an integral part of the AP-1 transcriptional complex along with other nuclear proto-oncogenes including c-jun[28, 29]. The c-fos protein responds to DNA damage and oxidative stress [30].
Increased heat shock protein expression may be a result of alterations in protein structure through adducts formation [31]. DNT-induced expression of heat shock is an indication of its proteotoxic effects in HepG2 cells [16, 32, 33]. The significant expression of the 70-kDa heat shock protein (HSP70) was shown at the 200 μg/mL and the dose range of 50 – 250 μg/mL for 2,4- and 2,6-DNT, respectively. This protein’s biological function is to act as a cytoplasmic protein chaperone.
Conclusions
Data obtained from this research indicate that 2,4- and 2,6-dinitrotoluene are moderately cytotoxic to transformed human liver cells, with 48 hrs-LD50 values of 300 ± 5.92 μg/mL and 245 ± 14.72 μg/mL, respectively. Western Blot and densitometric analyses resulted in a strong dose-response relationship with respect to GADD153 and HSP70 expression in HepG2 cells for 2,6-dinitroluene. At the molecular level, the proteotoxic and genotoxic effects, and oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory reactions of 2,4- and 2,6-DNT were characterized by the over expression HSP70, GADD45/153, and c-fos proteins.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported in part by the U.S. Department of the Army, Grant # DACA-42-02-C-0057 through the MACERAC Program, and in part by NIH Grant # 1G12RR13459 through the RCMI-Center for Environmental Health.
References
- Beard, R. R.; Noe, J. T. Aromatic nitro and amino compounds. Clayton, G. D., Clayton, F. E., Eds.; In Patty’s Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology, 3rd Edition; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1981; Volume 2A, pp. 2462–2463. [Google Scholar]
- Hazardous Substance Data Bank (HSDB); Bethesda, Maryland, USA; National Library of Medicine, 1998.
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health/Occupational Safety and Health Administration (NIOSH/OSHA), Dinitrotoluene (DNT); Current Intelligence Bulletin 44; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Public Health Review DHHS/NIOSH, Publ. No. 85–109; 1985.
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR), Toxicological Profile for 2,4-Dinitrotoluene and 2,6-Dinitrotoluene; U.S. Public Health Service, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1989.
- Weast, R. C.; Spadaro, J. A.; Becker, R. O.; et al. Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 69th Edition ed; CRC Press Inc: Boca Raton, Florida, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Etnier, E. Water Quality Criteria for 2,4-Dinitrotoluene and 2,6-Dinitrotoluene. In Final Report ORNL-6312; Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Brower, M. E.; Roberts, W. C.; Hartley, W. R.; Abernathy, C. 2,4- and 2,6-Dinitrotoluene (DNT). Hartley, W. R., Roberts, W. C., Commons, B. J., Eds.; In Drinking Water Health Advisory; Munitions II; Professional Administrative Service, 1994; pp. 39–153. [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap, K. L. Nitrobenzene and nitrotoluenes. Grayson, M., Eckroth, D., Eds.; In Kirk Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 3rd Edition; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1978; Volume 15, pp. 930–931. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C. C.; Dilley, J. V.; Hogdson, H. R.; Helton, D. O.; Wiegand, W. J.; Roberts, D. N.; et al. Mammalian Toxicity of Munition Compounds. Phase I: Acute Oral Toxicity, Primary Skin and Eye Irritation, Dermal Sensitization, and Disposition and Metabolism. In AD BO11 150; Kansas City, Missouri, USA; Midwest Research Institute; DAMD17-14-C-4073; U.S. Army Medical Bioengineering Research and Development Laboratory, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Woolen, B. H.; Hall, M. G.; Craig, R.; Steel, G. T. Dinitrotoluene: An assessment of occupational absorption during the manufacture of blasting explosives. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 1995, 55, 319–330. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C. C.; Ellis, H. V.; Kowalski, J. J.; Hodgson, J. R.; Hwang, J. R.; Hwang, S. W.; et al. Mammalian Toxicity of Munition Compounds. Phase II: Effects of Multiple Doses. Part II: 2,4-Dinitrotoluene. In DAMD17-74-C-4073; U.S. Army Medical Bioengineering Research and Development Laboratory; Report AD AO47 067; Midwest Research Institute: Kansas City, Missouri, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, M.; Yaruse, N.; Kozuka, H. Studies on the metabolism and toxicity of dinitrotoluenes. Absorption and excretion of tritium-labeled 2,4-Dinitrotoluene (3H-2,4-dinitrotoluene) in rats. Radioisotopes 1978, 27, 715–719. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Health Effects Assessment for 2,4- and 2,6-Dinitrotoluene; Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, Environmental Criteria and Assessment Office: Cincinnati, Ohio, EPA ECAO-CIN-HO69, 1987.
- Ellis, H. V.; Hagensen, J. H.; Hogdson, J. R.; Minor, J. L.; Hong, C. B.; Ellis, E. R.; et al. Mammalian Toxicity of Munitions Compounds. Phase III: Effects of Lifetime Exposure. Part 1: 2,4-Dinitrotoluene. In DAMD17-74-C-4073; U.S. Army Medical Bioengineering Research and Development Laboratory; Report AD AO77 692; Midwest Research Institute: Kansas City, Missouri, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Floret, F. Medical opinions on industrial poisonings; Centr Gewerbehyg Unfallverhut, 1989; Volume 16, p. 280. [Google Scholar]
- Tchounwou, P. B.; Ishaque, A. B.; Schneider, J. Cytotoxicity and transcriptional activation of stress genes in human liver carcinoma cells exposed to cadmium chloride. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 2001, 222, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C. C.; Hong, C. B.; Ellis, H. V.; Dacre, J. C.; Glennon, J. P. Subchronic and chronic toxicity studies of 2,4-dinitrotoluene, Part H. CD rats. J. Am Coll Toxicol 1985, 4, 243–246. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, H. V.; Hong, C. B.; Lee, C. C.; Dacre, J. C.; Glennon, J. P. Subchronic and chronic toxicity studies of 2,4-dinitrotoluene, Part 1. Beagle dogs. J. Am Coll Toxicol 1985, 4, 233–242. [Google Scholar]
- Stayner, L. T.; Dannenberg, A. L.; Bloom, T.; Thun, M. Excess hepatobiliary cancer mortality among munitions workers exposed to dinitrotoluene. J. Occup Med 1993, 35, 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, T. B.; Graichen, M. E.; Popp, J. A. Dinitrotoluene isomer-specific hepatocarcinogenesis in F344 rats. J. Natl Cancer Inst 1987, 79, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Chemical Industry Institute of Toxicology (CIIT), 104-Week Chronic Toxicity Study in Rats: Dinitrotoluene. In Final Report; Volume 1 and 2, CIIT Docket No. 12362; CIIT: Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, USA, 1982.
- National Cancer Institute, Bioassay of 2,4-Dinitrotoluene for Possible Carcinogenicity; Technical Support Series No. 54; U.S. Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, Public Health Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Leonard, T. B.; Lyght, C.; Popp, J. A. Dinitrotoluene structure dependent initiation of hepatocytes in vivo. Carcinogenesis 1983, 4, 1059–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Mirsalis, J. C.; Butterworth, B. E. Induction of unscheduled DNA synthesis in rat hepatocytes following in vivo treatment with dinitrotoluene. Carcinogenesis 1982, 3, 241–245. [Google Scholar]
- Mirsalis, J. C.; Tyson, C. K.; Butterworth, B. E. Detection of genotoxic carcinogens in the in vivo/in vitro hepatocyte DNA repair assay. Environ Mutagen 1982, 4, 553–562. [Google Scholar]
- Luethy, J. D.; Holbrook, N. J. Activation of GADD153 promoter by genotoxic agents: A rapid and specific response to DNA damage. Cancer Res 1992, 52, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Barlett, J. D.; Luethy, J. D.; Carlson, S. G.; Sollott, S. J.; Holbrook, N. M. Calcium ionophore binding protein (C/EDP)-related gene, GADD153. J. Biol. Chem 1992, 267, 20465–20470. [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi, P.; Sission, J. C.; Verma, I. M. Transcriptional autoregulation of the proto-oncogene fos. Nature 1988, 334, 314–319. [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli, E.; Montmayeur, J. P.; Foulkes, N. S.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Signal transduction and gene control: cAMP pathway. Crit. Rev. Onco 1992, 3, 321–338. [Google Scholar]
- Hollander, M. C.; Fornace, A. J. Induction of fos RNA by DNA damaging agents. Cancer Res 1989, 29, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Lightfoot, R.; Stevens, J. L. Activation of heat shock factor by alkylating agent is triggered by glutathione depletion in oxidation of protein thiols. J. Biol. Chem 1996, 271, 4805–4812. [Google Scholar]
- Todd, M. D.; Lee, M. J.; Williams, J. L.; Lalennalenzy, J. M.; Gee, P.; Benjamin, M. B.; Farr, S. B. The Cat-Tox assay: A sensitive and specific measure of stress induced transcription in human liver carcinoma cells. Fund Appl. Tox 1995, 28, 118–128. [Google Scholar]
- Jolly, C.; Murimoto, R. I. Role of the heat shock response and molecular chaperones in onconogenesis in cell death. J. Natl Cancer Inst 2000, 982, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar]
- Tchounwou, P. B.; Wilson, B. A.; Ishaque, A.; Schneider, J. Transcriptional activation of stress genes and Cytotoxicity in human liver carcinoma cells exposed to 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene, 2,4-Dinitrotoluene, and 2,6-Dinitrotoluene. Environ. Toxicol 2001, 16(3), 209–216. [Google Scholar]
© 2005 MDPI. All rights reserved.