Assessing the Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test with Spanish Adolescents
Abstract
1. Introduction
The Present Study
2. Method
2.1. Participants
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
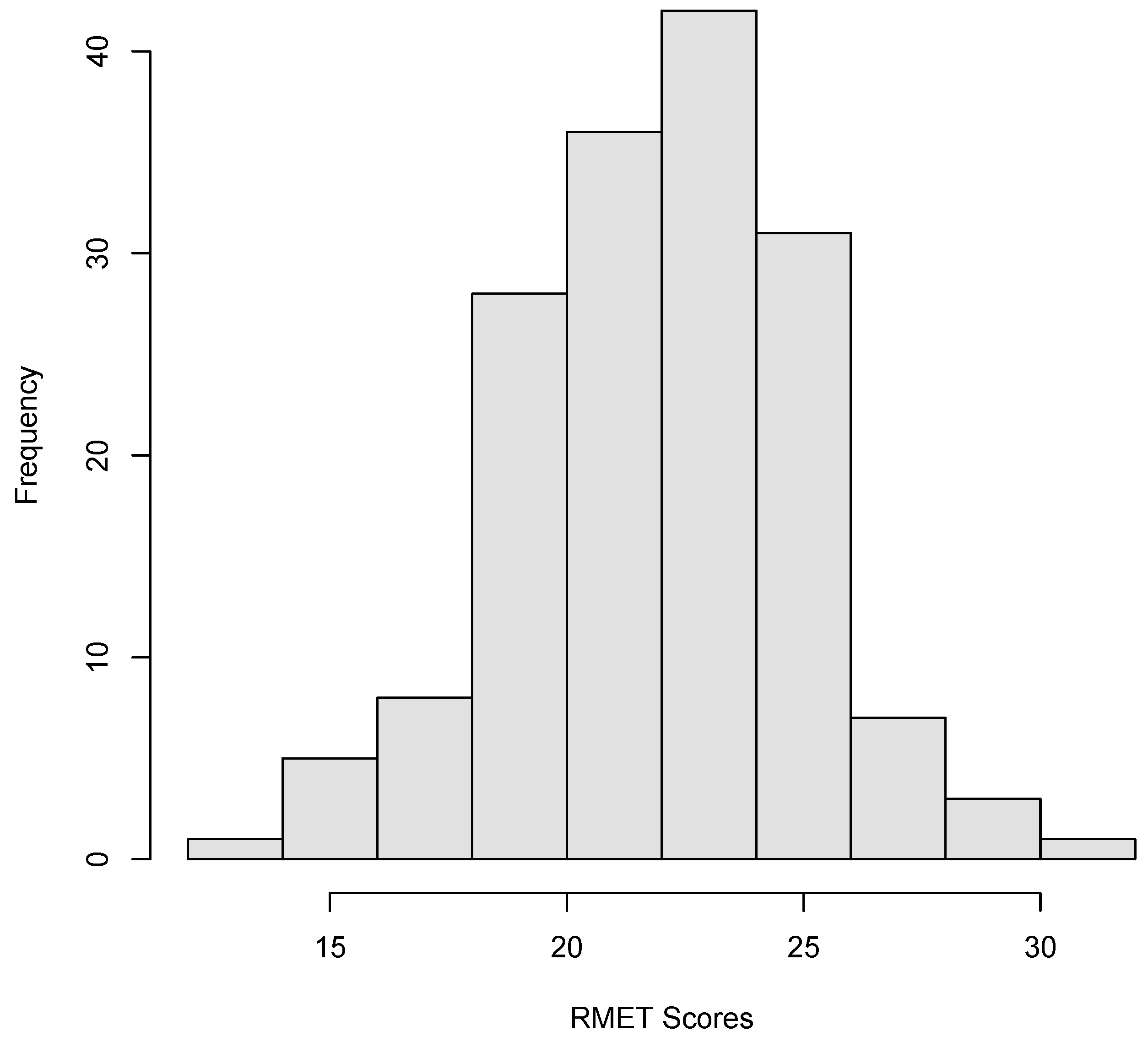
3.1. Descriptive Data, Reliability, and Exploratory Factor Analysis
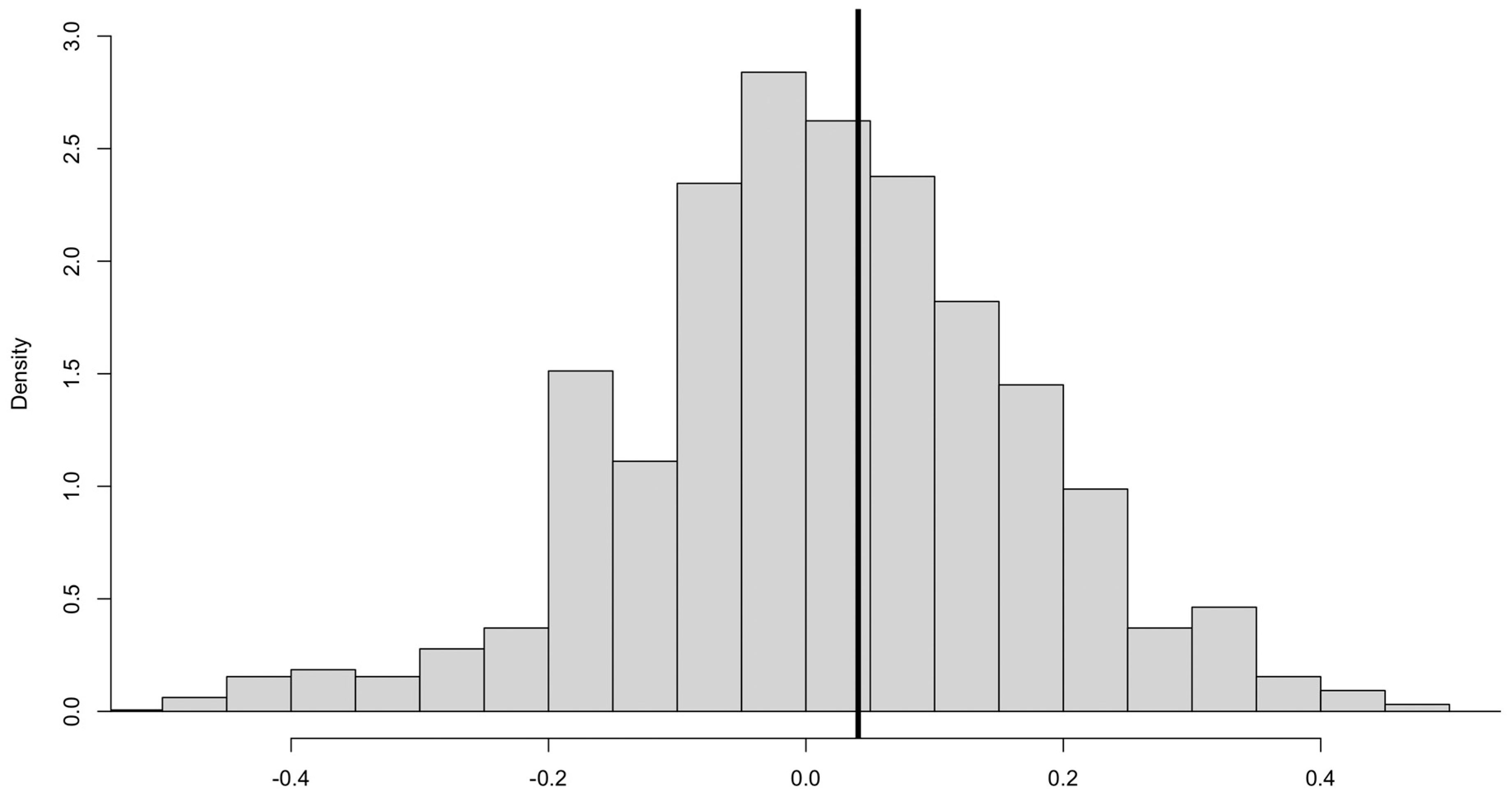
3.2. CFA
4. Discussion
4.1. Reliability
4.2. Factor Structure and Validity
4.3. RMET Administration
4.4. Implications for Counseling Practice and Research
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abu-Akel, A., & Shamay-Tsoory, S. (2011). Neuroanatomical and neurochemical bases of theory of mind. Neuropsychologia, 49(11), 2971–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adolphs, R., Baron-Cohen, S., & Tranel, D. (2002). Impaired recognition of social emotions following amygdala damage. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 14(8), 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, L. R. (2003). Tests psicológicos y evaluación. Pearson Educación. [Google Scholar]
- Altgassen, M., Vetter, N. C., Phillips, L. H., Akgun, C., & Kliegel, M. (2014). Theory of mind and switching predict prospective memory performance in adolescents. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 127, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron-Cohen, S., Campbell, R., Karmiloff-Smith, A., Grant, J., & Walker, J. (1995). Are children with autism blind to the mentalistic significance of the eyes? British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 13(4), 379–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron-Cohen, S., Jolliffe, T., Mortimore, C., & Robertson, M. (1997). Another advanced test of theory of mind: Evidence from very high functioning adults with autism or Asperger syndrome. The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 38(7), 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron-Cohen, S., Leslie, A. M., & Frith, U. (1985). Does the autistic child have a “theory of mind”? Cognition, 21(1), 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron-Cohen, S., O’riordan, M., Stone, V., Jones, R., & Plaisted, K. (1999). Recognition of faux pas by normally developing children and children with Asperger syndrome or high-functioning autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 29, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron-Cohen, S., Wheelwright, S., Spong, A., Scahill, V., & Lawson, J. (2001). Are intuitive physics and intuitive psychology independent? A test with children with Asperger Syndrome. Journal of Developmental and Learning Disorders, 5(1), 47–78. [Google Scholar]
- Black, J. E. (2019). An IRT analysis of the reading the mind in the eyes test. Journal of Personality Assessment, 101(4), 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakemore, S. J. (2008). The social brain in adolescence. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 9(4), 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, E., Eryavuz, A., Kayahan, B., Sungu, G., & Veznedaroglu, B. (2006). Social functioning, theory of mind and neurocognition in outpatients with schizophrenia; mental state decoding may be a better predictor of social functioning than mental state reasoning. Psychiatry Research, 145(2–3), 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Abascal, E. G., Cabello, R., Fernández-Berrocal, P., & Baron-Cohen, S. (2013). Test-retest reliability of the ‘Reading the Mind in the Eyes’ test: A one-year follow-up study. Molecular Autism, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flora, D. B., & Curran, P. J. (2004). An empirical evaluation of alternative methods of estimation for confirmatory factor analysis with ordinal data. Psychological Methods, 9(4), 466–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frith, U., Morton, J., & Leslie, A. M. (1991). The cognitive basis of a biological disorder: Autism. Trends in Neurosciences, 14(10), 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavilán-Ibáñez, J. M., & García-Albea, J. E. (2013). Theory of mind and language comprehension in schizophrenia. Psicothema, 25(4), 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girli, A. (2014). Psychometric properties of the Turkish child and adult form of “Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test”. Psychology, 5(11), 1321–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkness, K., Sabbagh, M., Jacobson, J., Chowdrey, N., & Chen, T. (2005). Enhanced accuracy of mental state decoding in dysphoric college students. Cognition and Emotion, 19, 999–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, W. C., Kaplan, D. M., Deschrijver, E., & Ross, R. M. (2024). Construct validity evidence reporting practices for the reading the mind in the eyes test: A systematic scoping review. Clinical Psychology Review, 108, 102378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, R. J., Chura, L. R., Lai, M. C., Suckling, J., Von Dem Hagen, E., Calder, A. J., Bullmore, E. T., Baron-Cohen, S., & Spencer, M. D. (2014). ‘Reading the Mind in the Eyes’: An fMRI study of adolescents with autism and their siblings. Psychological Medicine, 44(15), 3215–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Ramos, E., Ferrer-Quintero, M., Gómez-Benito, J., González-Higueras, F., Cuadras, D., del Rey-Mejías, Á. L., Usall, J., & Ochoa, S. (2021). Traducción y validación del test de caras de Baron Cohen en población española. Actas Españolas de Psiquiatría, 49(3), 106. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, B. N., Kivity, Y., Rosenstein, L. K., LeBreton, J. M., & Levy, K. N. (2022). The association between mentalizing and psychopathology: A meta-analysis of the reading the mind in the eyes task across psychiatric disorders. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 29(4), 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbe, E., Grabenhorst, F., Brand, M., Kessler, J., Hilker, R., & Markowitsch, H. J. (2007). Elevated emotional reactivity in affective but not cognitive components of theory of mind: A psychophysiological study. Journal of Neuropsychology, 1(1), 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittel, A. F. D., Olderbak, S., & Wilhelm, O. (2022). Sty in the mind’s eye: A meta-analytic investigation of the nomological network and internal consistency of the “Reading the Mind in the Eyes” test. Assessment, 29(5), 872–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konrath, S., Corneille, O., Bushman, B. J., & Luminet, O. (2014). The relationship between narcissistic exploitativeness, dispositional empathy, and emotion recognition abilities. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 38, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghi, F., Lonigro, A., Levanto, S., Ferraro, M., Baumgartner, E., & Baiocco, R. (2016). The role of nice and nasty theory of mind in teacher-selected peer models for adolescents with autism spectrum disorders. Measurement and Evaluation in Counseling and Development, 49(3), 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, W. L., Huang, I. C., & Marcoulides, G. A. (2008). Item selection for the development of short forms of scales using an ant colony optimization algorithm. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 43, 411–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriguchi, Y., Ohnishi, T., Mori, T., Matsuda, H., & Komaki, G. (2007). Changes of brain activity in the neural substrates for theory of mind during childhood and adolescence. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 61, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nader-Grosbois, N., & Simon, P. (2023). Adaptation and validation of a french version of the griffith empathy measure. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessmnet, 45, 993–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olderbak, S., Wilhelm, O., Olaru, G., Geiger, M., Brenneman, M. W., & Roberts, R. D. (2015). A psychometric analysis of the reading the mind in the eyes test: Toward a brief form for research and applied settings. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, M. A., & Sokolov, A. A. (2022). Reading language of the eyes. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 140, 104755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premack, D., & Woodruff, G. (1978). Does the chimpanzee have a theory of mind? Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 1(4), 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevost, M., Carrier, M. E., Chowne, G., Zelkowitz, P., Joseph, L., & Gold, I. (2014). The Reading the Mind in the Eyes test: Validation of a French version and exploration of cultural variations in a multi-ethnic city. Cognitive Neuropsychiatry, 19(3), 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. (2022). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 11 September 2022).
- Redondo, I., & Herrero-Fernández, D. (2018). Validation of the Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test in a healthy Spanish sample and women with anorexia nervosa. Cognitive Neuropsychiatry, 23(4), 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastian, C. L., Fontaine, N. M., Bird, G., Blakemore, S. J., De Brito, S. A., McCrory, E. J., & Viding, E. (2012). Neural processing associated with cognitive and afective theory of mind in adolescents and adults. Social Cognitive and Afective Neuroscience, 7(1), 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellante, M., Baron-Cohen, S., Melis, M., Marrone, M., Petretto, D. R., Masala, C., & Preti, A. (2013). The “Reading the Mind in the Eyes” test: Systematic review of psychometric properties and a validation study in Italy. Cognitive Neuropsychiatry, 18(4), 326–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voracek, M., & Dressler, S. G. (2006). Lack of correlation between digit ratio (2D:4D) and Baron-Cohen’s ‘‘Reading the Mind in the Eyes’’ test, empathy, systemising, and autism-spectrum quotients in a general population sample. Personality and Individual Differences, 41, 1481–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, H., & Perner, J. (1983). Beliefs about beliefs: Representation and constraining function of wrong beliefs in young children’s understanding of deception. Cognition, 13(1), 103–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Model | KR 20 | Split Half | CFA Alpha | CFA Omega | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full test | 0.28 | 0.49 | --- | --- | |
| Delete as Baron-Cohen et al. b | 0.36 | 0.46 | --- | --- | |
| Sex of the model Male | 0.07 | 0.43 | --- | --- | |
| Sex of the model Female | 0.2 | 0.36 | --- | --- | |
| ACO | 0.10 | 0.25 | 0.09 | 0.11 | |
| MML | 0.02 | 0.27 | 0.02 | 0.06 | |
| NEG | −0.01 | 0.28 | --- | --- | |
| HARKNESS | POS | 0.37 | 0.41 | --- | --- |
| NEU | 0.27 | 0.42 | --- | --- |
| Item | Correct Answer ENG | Correct Answer ESP | Model Sex | MML | ACO | HARKNESS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POSITIVE | NEGATIVE | NEUTRAL | ||||||
| 1 | Playful | Juguetón | H | --- | --- | 0.265 * | --- | --- |
| 2 | Upset | Molesto | H | --- | --- | --- | 0.045 | --- |
| 3 | Desire | Deseo | M | --- | --- | --- | --- | 0.102 |
| 4 | Insisting | Insistente | H | --- | --- | --- | --- | −0.229 * |
| 5 | Worried | Preocupado | H | --- | --- | --- | 0.219 | --- |
| 6 | Fantasizing | Fantasiosa | M | --- | --- | 0.332 ** | --- | --- |
| 7 | Uneasy | Intranquilo | H | --- | --- | --- | --- | −0.08 |
| 8 | Despondent | Abatido | H | −0.01 | 0.267 * | --- | --- | −0.163 |
| 9 | Preoccupied | Angustiada | M | --- | 0.332 ** | --- | --- | −0.142 |
| 10 | Cautious | Prudente | H | −0.195 | --- | --- | --- | −0.334 *** |
| 11 | Regretful | Arrepentido | H | --- | --- | --- | 0.098 | --- |
| 12 | Skeptical | Escéptico | H | --- | 0.511 ** | --- | --- | −0.135 |
| 13 | Anticipating | Expectante | H | --- | --- | --- | --- | −0.240 * |
| 14 | Accusing | Acusante | H | --- | 0.226 | --- | 0.004 | --- |
| 15 | Contemplative | Abstraída | M | 0.277 * | −0.073 | --- | --- | 0.024 |
| 16 | Thoughtful | Considerado | H | --- | --- | 0.042 | --- | --- |
| 17 | Doubtful | Insegura | M | --- | --- | --- | 0.053 | --- |
| 18 | Decisive | Decidida | M | --- | --- | --- | --- | −0.490 * |
| 19 | Tentative | Vacilante | M | 0.052 | −0.116 | --- | --- | 0.054 |
| 20 | Friendly | Amistoso | H | --- | --- | 0.395 *** | --- | --- |
| 21 | Fantasizing | Fantasiosa | M | --- | --- | 0.350 ** | --- | --- |
| 22 | Preoccupied | Angustiada | M | --- | −0.027 | --- | −0.036 | --- |
| 23 | Defiant | Desafiante | H | --- | --- | --- | −0.038 | --- |
| 24 | Pensive | Abstraído | H | 0.048 | −0.001 | --- | --- | −0.141 |
| 25 | Interested | Interesada | M | --- | --- | 0.290 ** | --- | --- |
| 26 | Hostile | Hostil | H | --- | --- | --- | −0.024 | --- |
| 27 | Cautious | Prudente | M | --- | --- | --- | 0.140 | --- |
| 28 | Interested | Interesada | M | --- | --- | --- | --- | −0.514 *** |
| 29 | Reflective | Reflexiva | M | --- | --- | --- | --- | −0.187 |
| 30 | Flirtatious | Seductora | M | --- | --- | 0.257 * | --- | --- |
| 31 | Confident | Segura | M | --- | --- | 0.249 * | --- | --- |
| 32 | Serious | Serio | H | --- | 0.121 | --- | --- | −0.105 |
| 33 | Concerned | Preocupado | H | --- | --- | --- | --- | 0.219 |
| 34 | Distrustful | Recelosa | M | −0.285 * | --- | --- | 0.430 *** | --- |
| 35 | Nervous | Nerviosa | M | 0.76 4 ** | --- | --- | −0.276 * | --- |
| 36 | Suspicious | Desconfiado | H | --- | −0.185 | --- | −0.443 *** | --- |
| χ2 (df) | 7.569 (14) | 30.735 (35) | 641.062 (591) | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez, A.; Romero, A.; Malas, O.; Blanch, A. Assessing the Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test with Spanish Adolescents. Psychol. Int. 2025, 7, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint7020041
Martínez A, Romero A, Malas O, Blanch A. Assessing the Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test with Spanish Adolescents. Psychology International. 2025; 7(2):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint7020041
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez, Albert, Alicia Romero, Olga Malas, and Angel Blanch. 2025. "Assessing the Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test with Spanish Adolescents" Psychology International 7, no. 2: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint7020041
APA StyleMartínez, A., Romero, A., Malas, O., & Blanch, A. (2025). Assessing the Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test with Spanish Adolescents. Psychology International, 7(2), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint7020041





