Bidirectional Relationships between Eating Disorders and Type 1 and 2 Diabetes: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
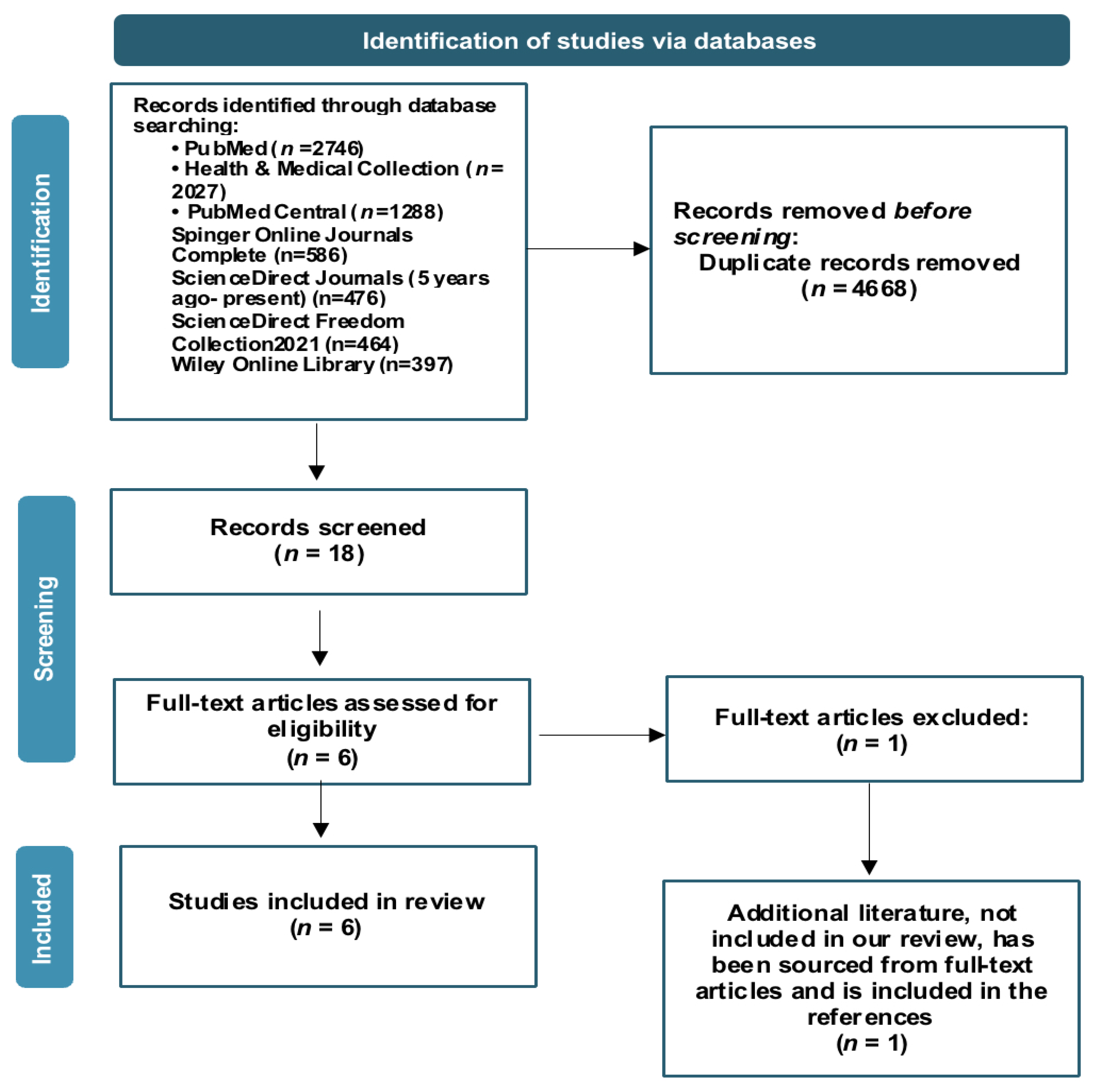
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategies
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
- a.
- Studies investigating the correlation between diabetes, treated with different types of insulin, such as insulin pens, intermediate-acting insulins and long-acting insulins and eating disorders in adults.
- b.
- All studies published in PubMed, Health & Medical Collection, PubMed Central, Springer Online Journals Complete, ScienceDirect Journals, Science direct Freedom Collection 2021 and Wiley Online Library.
- a.
- Studies published in non-scientific or non-peer-reviewed sources.
- b.
- All articles explore the association between diabetes and eating disorders with a focus on adolescents.
- c.
- Articles of which the full text cannot be found.
2.3. Data Collection
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Included Studies
3.2. Eating Disorders in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
3.3. Eating Disorders in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Invernizzi, G.; Bressi, C. Manuale di Psichiatria e Psicologia Clinica; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- De-Bacco, C.; Marzola, E.; Fassino, S.; Abbate-Daga, G. Psychodynamic psychotherapies for feeding and eating disorders. Minerva Psychiatry 2017, 58, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conviser, J.H.; Fisher, S.D.; McColley, S.A. Are children with chronic illnesses requiring dietary therapy at risk for disordered eating or eating disorders? A systematic review. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2018, 51, 187–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colton, P.A.; Olmsted, M.P.; Daneman, D.; Rodin, G.M. Depression, disturbed eating behavior, and metabolic control in teenage girls with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2013, 14, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custal, N.; Arcelus, J.; Aguera, Z.; Wales, J.; Granero, R.; Sanchez, I.; Riesco, N.; Alonso, P.; Virgili, N. Treatment outcome of patients with comorbid type 1 diabetes and eating disorders. BMC Psychiatry 2014, 14, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.M.; Lawson, M.L.; Daneman, D.; Olmsted, M.P.; Rodin, G. Eating disorders in adolescent females with and without type 1 diabetes: Cross sectional study. BMJ 2000, 320, 1563–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Candler, T.; Murphy, R.; Pigott, A. Fifteen-minute consultation: Diabulimia and disordered eating in childhood diabetes. Arch. Dis. Child.-Educ. Pract. 2018, 103, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treasure, J.; Stein, D.; Maguire, S. Has the time come for a staging model to map the course of eating disorders from high risk to severe enduring illness? An examination of the evidence. Early Interv. Psychiatry 2015, 9, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddard, G.; Oxlad, M. Insulin restriction or omission in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A meta-synthesis of individuals’ experiences of diabulimia. Health Psychol. Rev. 2023, 17, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poos, S.; Faerovitch, M.; Pinto, C.; Jamalkhani, N.; Chaudhri, F.; Khan, S.; Lo, D.F.; McGowan, K.; Martin, A. The role of diabetes distress in Diabulimia. J. Eat. Disord. 2023, 11, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Guideline Alliance (UK). Eating Disorders: Recognition and Treatment; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE): London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rydall, A.C.; Rodin, G.M.; Olmsted, M.P.; Devenyi, R.G.; Daneman, D. Disordered eating behavior and microvascular complications in young women with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1849–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muley, A.; Deshmane, A.; Mahajan, A.; Shah, J. Eating Disorders: Assessing Its Prevalence and Pattern Among Adults with Type 2 Diabetes. Cureus 2024, 16, e52425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroni, M.; Barbanti, F.; Bonadonna, R.; Bruno, G.; Caletti, M.; Croci, M.; D’eusebio, C.; Dei Cas, A.; Invitti, C.; Merlo, F.; et al. Dysfunctional eating in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A multicenter Italian study of socio-demographic and clinical associations. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 29, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, S.; Dindol, N.; Tahrani, A.A.; Piya, M.K. Binge eating disorder and night eating syndrome in adults with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. J. Eat. Disord 2018, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworski, M.; Panczyk, M.; Śliwczyński, A.M.; Brzozowska, M.; Janaszek, K.; Małkowski, P.; Gotlib, J. A Ten-Year Longitudinal Study of Prevalence of Eating Disorders in the General Polish Type 2 Diabetes Population. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 9204–9212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvia, M.G.; Ritholz, M.D.; Craigen, K.L.E.; Quatromoni, P.A. Managing type 2 diabetes or prediabetes and binge eating disorder: A qualitative study of patients’ perceptions and lived experiences. J. Eat. Disord. 2022, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dotti, A.; Lazzari, R. Validation and reliability of the Italian EAT-26. Eat. Weight. Disord. 1998, 3, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gormally, J.; Black, S.; Daston, S.; Rardin, D. The assessment of binge eating severity among obese persons. Addict. Behav. 1982, 7, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanik, R. Insulin manipulation and eating disorders in young people with type 1 diabetes: Implications for schools. J. Diabetes Nurs. 2014, 18, 238–242. [Google Scholar]
- Kinik, M.F.; Gönûllü, F.V.; Vatansever, Z.; Karakaya, I. Diabulimia, a type I diabetes mellitus-specific eating disorder. Turk. Arch. Pediatr. 2017, 52, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipot, U. Eating disorders in young people with diabetes: Development, diagnosis and management. J. Diabetes Nurs. 2013, 17, 228–232. [Google Scholar]
- Goebel-Fabbri, A.E.; Fikkan, J.; Franko, D.L.; Pearson, K.; Anderson, B.K.; Weinger, K. Insulin restriction and associated morbidity and mortality in women with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcão, M.A.; Francisco, R. Diabetes, eating disorders and body image in young adults: An exploratory study about “diabulimia”. Eat. Weight Disord. 2017, 22, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, S.E.; Caswell, N. Diabetes and eating disorders: An exploration of ‘Diabulimia’. BMC Psychol. 2020, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenardy, J.; Mensch, M.; Bowen, K.; Pearson, S.A. A comparison of eating behavior in newly-diagnosed NIDDM patients and casematched control subjects. Diabetes Care 1994, 17, 1197–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papelbaum, M.; Appolinario, J.C.; Moreira Rde, O.; Ellinger, V.C.; Kupfer, R.; Coutinho, W.F. Prevalence of eating disorders and psychiatric comorbidity in a clinical sample of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Rev. Praz. Psiquatr. 2005, 27, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenardy, J.; Mensch, M.; Bowen, K.; Green, B.; Walton, J.; Dalton, D. Disordered eating behaviours in women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eat. Behav. 2001, 2, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannucci, E.; Tesi, F.; Ricca, V.; Pierazzuoli, E.; Barciulli, E.; Moretti, S.; Di Bernardo, M.; Travaglino, R.; Carrara, S.; Zucchi, T.; et al. Eating behavior in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26, 848–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharaj, S.I.; Rodin, G.M.; Olmsted, M.P.; Connolly, J.A.; Daneman, D. Eating disturbances in girls with diabetes: The contribution of adolescent self-concept, maternal weight and shape concerns and mother-daughter relationships. Psychol. Med. 2003, 33, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaremba, N.; Harrison, A.; Brown, J.; Allan, J.; Pillay, D.; Treasure, J.; Ayis, S.; Hopkins, D.; Ismail, K.; Stadler, M. Protocol for the STEADY intervention for type 1 diabetes and disordered eating: Safe management of people with Type 1 diabetes and EAting Disorders studY. Diabet. Med. 2024, 41, e15273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, C.; Belanger, C.; Aime, A. Predictors of Comorbid Eating Disorders and Diabetes in People with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Can. J. Diabetes 2017, 41, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larrañaga, A.; Docet, M.F.; García-Mayor, R.V. Disordered eating behaviors in type 1 diabetic patients. World J. Diabetes 2011, 2, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sammut, R.; Grech, J.; Polosa, R.; Campagna, D.; Di Ciaula, A.; Dugal, T.; Kenge, A.; Misra, A.; Abbas Raza, S.; Russo, C.; et al. Behavioral Therapy for People With Diabetes Who Smoke: A Scoping Review. J. Prim. Care Community Health 2024, 15, 21501319241241470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author | Year | Title | Type of Study | Focus | Sample | Measures | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Falcao M. A., Francisco R. | 2017 | Diabetes, eating disorders and body image in young adults: an exploratory study about “diabulimia”. | Case–control analytic study. | To compare ED and BID among young adults with type 1 diabetes and their peers without diabetes, to investigate the consequences of diabetes for food, body image, and weight in individuals with diabetes and to identify the behavior of insulin omission as a weight loss strategy. | A total of 55 young adults with diabetes and 73 without diabetes. | Demographic and personal data questionnaire, EDE-Q, CDRS, questionnaire on personal experience about found and body image. | Several changes resulting from diabetes in terms of food, body image and weight that interfere with the day-to-day life of individuals with diabetes; 7.3% of these participants reported insulin omission as a weight loss strategy. |
| Jaworki M., Panczyk M., Silwczynski A., Brzozowska M., Janaszek K., Malkowski P., Gotlib J. | 2018 | A ten-year longitudinal study of prevalence of eating disorders in the general Polish type 2 diabetes population. | Longitudinal study. | Evaluate the prevalence of ED in T2DM in the years 2008–2017 in state medical care. | 3071 (In 10 years) | NFZ, GUS, ICD-10. | The prevalence of EDs in T2DM patients in the whole patient population with diagnosed T2DM ranged from 0.059% (in 2017) to 0.086% patients (in 2010). Differences in subcategories of EDs were noted. |
| Petroni M.L., Barbanti F.A., Bonadonna R., Bruno G., Caletti M.T., Croci M., D’Eusebio C., Dei Cas A., Invitti C., Merlo F., Molteni A., Pontiroli A., Trento M., Veronelli A., Vigli de Kreutzenberg S., Marchesini G. | 2019 | Dysfunctional eating in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A multicenter Italian study of socio-demographic and clinical associations. | Cross-sectional observational study | Assess the prevalence of dysfunctional eating in a large population of people with T2DM in Italy recruited in a real-life multicenter clinical setting, as well as its association with socio-demographic characteristics. | 895 | Body weight, height, waist circumference, biochemical data, EAT-26, BES, NEQ, MDS, QMV. | Critical EAT and BES values were associated with higher BMI and dysfunctional eating is present across the whole spectrum of T2DM. |
| Coleman S.E. Caswell N. | 2020 | Diabetes and eating disorders: an exploration of “Diabulimia”. | Qualitative study. | The aim of this study was to conduct an exploratory analysis into the views and experience of diabulimia. | 55 | EDE-Q; 16 open-ended questions analyzed using thematic analysis. | EDE-Q score 3.96; weight concerns, coping issues, trauma, negative healthcare experiences, diabulimia consequences noted. |
| Salvia M.G., Ritholz M.D. Craigen K.L.E, Quattromoni P.A. | 2022 | Managing type 2 diabetes or prediabetes and binge eating disorder: a qualitative study of paties’ perceptions and lived experiences. | Qualitative study | Qualitatively explore the experiences of women concurrently managing T2DM/prediabetes and BED. | 21 | EDE-Q and semi-structured interviews. | BED often predates diabetes diagnosis; BED treatment helps manage diabetes. |
| Muley A., Deshmane A., Mahajan A., Shah J. | 2024 | Eating disorders: assessing its prevalence and pattern among adults with type 2 diabetes | Cross-sectional study | To assess the risk of EDs among T2DM. | 254 | SCOFF, EDE-Q | The 35% of the total population with T2DM had a high risk of EDs. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bottari, A.; La Giglia, F.; Magrì, R.; Marletta, L.; Prezzavento, G.C. Bidirectional Relationships between Eating Disorders and Type 1 and 2 Diabetes: A Scoping Review. Psychol. Int. 2024, 6, 685-694. https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint6030042
Bottari A, La Giglia F, Magrì R, Marletta L, Prezzavento GC. Bidirectional Relationships between Eating Disorders and Type 1 and 2 Diabetes: A Scoping Review. Psychology International. 2024; 6(3):685-694. https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint6030042
Chicago/Turabian StyleBottari, Alessia, Fabiana La Giglia, Rachele Magrì, Lucrezia Marletta, and Graziella Chiara Prezzavento. 2024. "Bidirectional Relationships between Eating Disorders and Type 1 and 2 Diabetes: A Scoping Review" Psychology International 6, no. 3: 685-694. https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint6030042
APA StyleBottari, A., La Giglia, F., Magrì, R., Marletta, L., & Prezzavento, G. C. (2024). Bidirectional Relationships between Eating Disorders and Type 1 and 2 Diabetes: A Scoping Review. Psychology International, 6(3), 685-694. https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint6030042







