Aerosol Characteristics of Nebulized Tranexamic Acid 100 mg/mL for Hemoptysis Treatment—Proof-of-Concept Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
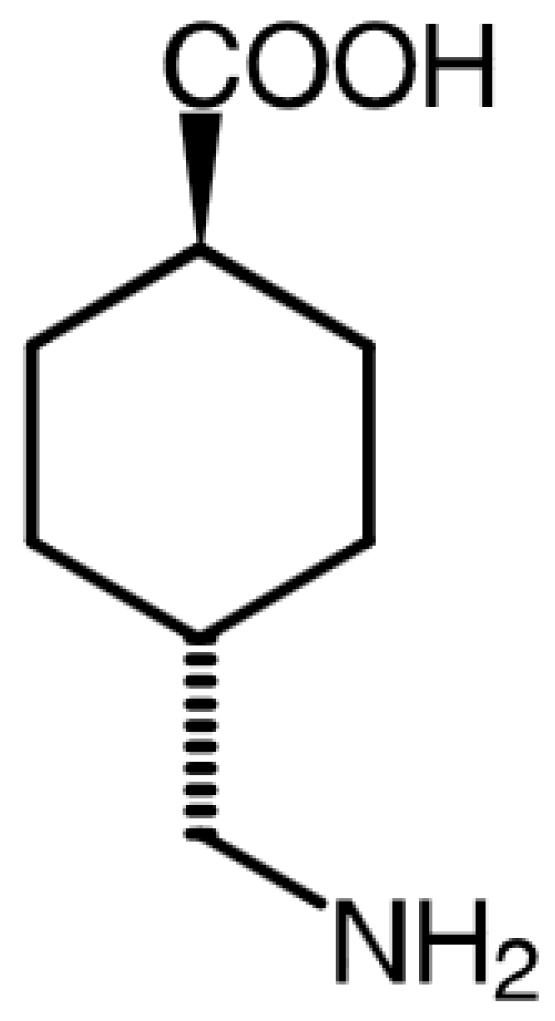
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Aerodynamic Assessment of TXA Aerosol by Cascade Impaction
2.2.2. Quantitative TXA Analysis by Anhydrous Titration
2.2.3. Data Processing
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCormack, P.L. Tranexamic Acid. Drugs 2012, 72, 585–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfizer. Fachinformation Cyklokapron®-Injektionslösung Frankfurt, Germany. 2024. Available online: https://figi.pfizer.de/sites/default/files/FI-8797.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Vitug, L.C.G.; Pempengco, M.S.A.; Santiaguel, J.M. Local Pulmonary Administration of Tranexamic Acid as Inhalational or Nebulized for the Control of Hemoptysis. Philipp. J. Chest Dis. 2022, 20, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wand, O.; Guber, E.; Guber, A.; Epstein Shochet, G.; Israeli-Shani, L.; Shitrit, D. Inhaled Tranexamic Acid for Hemoptysis Treatment: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Chest 2018, 154, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-S.; Hsu, L.-W.; Wu, M.-S.; Chen, K.-H.; Kang, Y.-N. Effects of Tranexamic Acid on Hemoptysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Clin. Drug Investig. 2020, 40, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadre, A.; Stoller, J.K. Tranexamic Acid for Hemoptysis: A Review. Clin. Pulm. Med. 2017, 24, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, B.; Mishra, P.R.; Aggarwal, P.; Nayaka, R.; Naik, S.R.; Kappagantu, V.; Shrimal, P.; Ramaswami, A.; Bhoi, S.; Jamshed, N.; et al. Nebulized vs IV Tranexamic Acid for Hemoptysis: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Chest 2023, 163, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, S.; Alam, S.F.; Islam, T. Inhaled Tranexamic Acid: A Therapeutic Option For Hemoptysis. Clin. Pulm. Med. 2019, 26, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adorni, G.; Seifert, G.; Buttini, F.; Colombo, G.; Stecanella, L.A.; Krämer, I.; Rossi, A. Aerosolization performance of jet nebulizers and biopharmaceutical aspects. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyder, J.; Gebhart, J.; Rudolf, G.; Schiller, C.F.; Stahlhofen, W. Deposition of particles in the human respiratory tract in the size range 0.005–15 μm. J. Aerosol Sci. 1986, 17, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darquenne, C. Deposition Mechanisms. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2020, 33, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.R.; Finlay, W.H. Nebulizers for drug delivery to the lungs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ph. Eur. Monograph 0875 Tranexamic Acid. In European Pharmacopeia; EDQM Council of Europe: Straßbourg, France, 2023; Volume 11.0.
- U.S. Pharmacopeia National Formulary. USP-NF Monograph Tranexamic Acid Injection Electronic Version 2024. Available online: https://online.uspnf.com/uspnf/document/1_GUID-F8721089-4EFC-43A4-845A-781DAF48AEFE_8_en-US?source=Quick%20Search&highlight=tranexamic (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Loner, C.; Estephan, M.; Davis, H.; Cushman, J.T.; Acquisto, N.M. Effect of fluctuating extreme temperatures on tranexamic acid. Prehosp. Disaster Med. 2019, 34, 340–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ph. Eur. Monograph 0169 Water for injections. In European Pharmacopeia; EDQM Council of Europe: Straßbourg, France, 2023; Volume 11.0.
- Ph. Eur. Monograph 2.9.18. Preparations for inhalation: Aerodynamic Assessment of Fine Particles. In European Pharmacopeia; EDQM Council of Europe: Straßbourg, France, 2023; Volume 11.0.
- CEN: EN 13544-1:2007 + A1:2009; Respiratory Therapy Equipment: Nebulizing Systems and Their Components. British Standard Institute: London, UK, 2010.
- U.S. Pharmacopeia National Formulary. USP-NF Monograph Tranexamic Acid Electronic Version 2024. Available online: https://online.uspnf.com/uspnf/document/1_GUID-FEC38B38-8DD5-4B5D-B4CA-83865AC39C2B_6_en-US?source=Quick%20Search&highlight=tranexamic (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Marple, V.A.; Olson, B.A.; Santhanakrishnan, K.; Roberts, D.L.; Mitchell, J.P.; Hudson-Curtis, B.L. Next Generation Pharmaceutical Impactor: A New Impactor for Pharmaceutical Inhaler Testing. Part III. Extension of Archival Calibration to 15 L/min. J. Aerosol Med. 2004, 17, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arzneibuchkommentar zur, Ph. Eur. 5.2: 2.9.18. Zubereitungen zur Inhalation: Aerodynamische Beurteilung feiner Teilchen. In 2.Verzeichnis aller Texte der 11. Ausgabe; Deutscher Apotheker Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2006; p. 25.
- U.S. Pharmacopeia National Formulary. USP-NF <1601> Products for Nebulization—Characterization Tests Electronic Version 2021. Available online: https://online.uspnf.com/uspnf/document/1_GUID-6A8052DE-3176-4AAA-8293-EE07D28F0CA4_3_en-US?source=Quick%20Search&highlight=1601 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Aerogen Ltd. USB Controller System Instruction Manual for Use with Aerogen® Solo and Aerogen® Pro Galway, Ireland 2021. Available online: https://inspiration-medical.de/PDFs/Aeroneb_USB_Manual.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Kamin, W.E.; Genz, T.; Roeder, S.; Scheuch, G.; Trammer, T.; Juenemann, R.; Cloes, R.M. Mass output and particle size distribution of glucocorticosteroids emitted from different inhalation devices depending on various inspiratory parameters. J. Aerosol Med. 2002, 15, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghi, M.; van den Oetelaar, W.; Moir, L.M.; Zhu, B.; Phillips, G.; Crapper, J.; Young, P.M.; Traini, D. Inhalable tranexamic acid for haemoptysis treatment. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean-Baptiste, E. Clinical assessment and management of massive hemoptysis. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 28, 1642–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, W.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Chung, T.W.; Kang, H.K. Bronchial and nonbronchial systemic artery embolization for life-threatening hemoptysis: A comprehensive review. Radiographics 2002, 22, 1395–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ittrich, H.; Bockhorn, M.; Klose, H.; Simon, M. Diagnostik und Therapie der Hämoptysen. Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int. 2017, 114, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.; Newman, S.; Knoch, M. Lung deposition from four nebulizers. Respir. Med. 1993, 87, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, G.; Krämer, I.; Rossi, A.; Kamin, W. Vergleichende Untersuchung von aktuell in Deutschland vermarkteten Druckluftverneblern und den damit erzeugten Aerosolen. Krankenhauspharmazie 2019, 40, 241–249. [Google Scholar]
- Boe, J.; Dennis, J.H.; O’Driscoll, B.R.; Bauer, T.T.; Carone, M.; Dautzenberg, B.; Diot, P.; Heslop, K.; Lannefors, L. European Respiratory Society Guidelines on the use of nebulizers. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 18, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arzu, A.; Orcin Telli, A.; Robert, H.; Meryl, M.S.; Essam, A.A.; James, B.F. Influence of Nebulizer Type, Position, and Bias Flow on Aerosol Drug Delivery in Simulated Pediatric and Adult Lung Models During Mechanical Ventilation. Respir. Care 2010, 55, 845. Available online: http://rc.rcjournal.com/content/55/7/845.abstract (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Hou, H.; Xu, D.; Dai, B.; Zhao, H.; Wang, W.; Kang, J.; Tan, W. Position of different nebulizer types for aerosol delivery in an adult model of mechanical ventilation. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 950569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
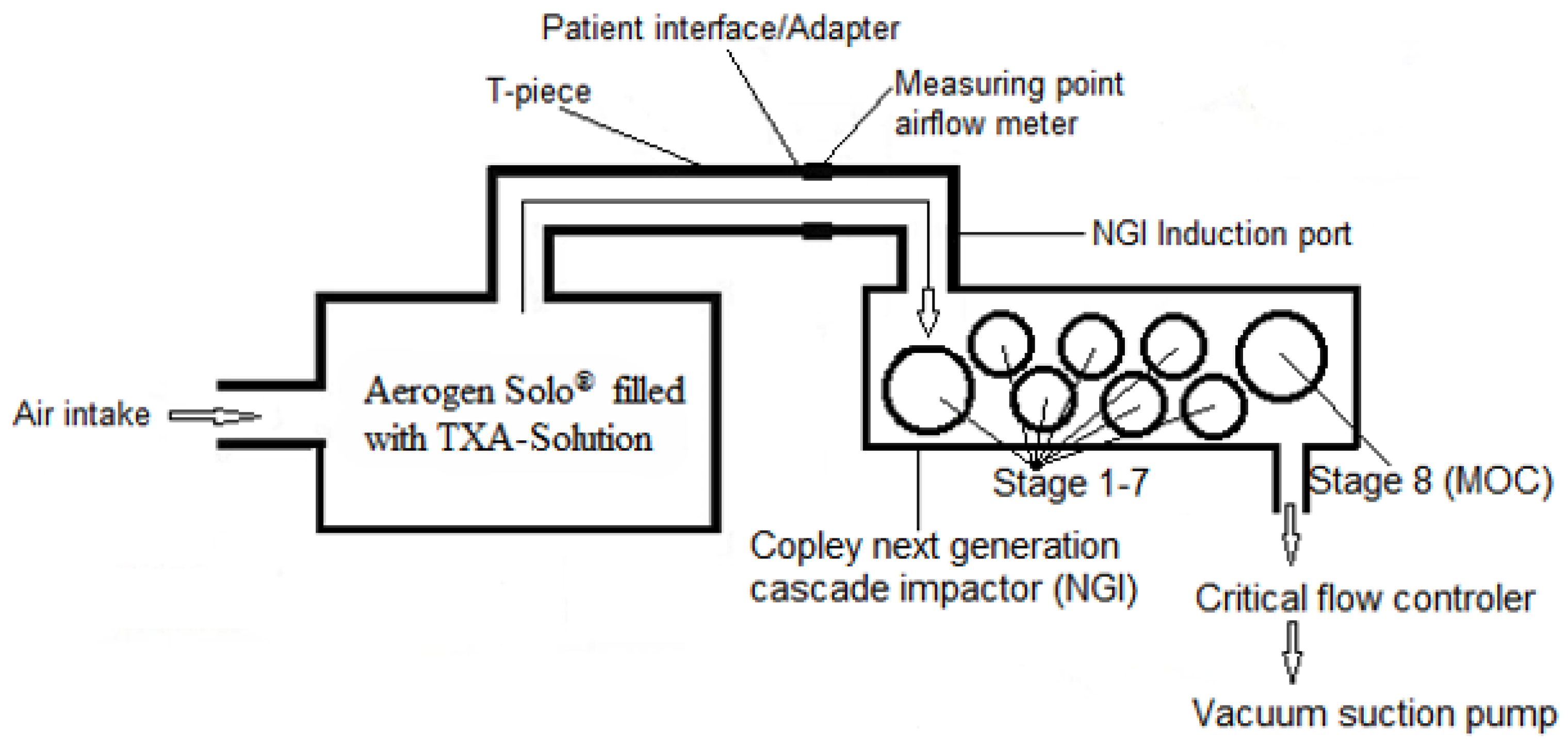

| Analysis Parameters [Unit] | Definition | Experimental Setup |
|---|---|---|
| Mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD) [µm] | MMAD refers to the aerodynamic diameter at which 50% of the particle population, based on mass, is larger and 50% is smaller. | Aerogen® Solo nebulizer 5 mL TXA 100 mg/mL injection solution Next Generation Cascade Impactor (NGI 0497; Copley Scientific) Air flow rate 15 L/min and 30 L/min 120 s nebulization time. About 0.7 mL of TXA solution was nebulized Quantitative analysis (anhydrous titration) of TXA deposited by cascade impaction [19] |
| Geometric standard deviation (GSD) | Measure of dispersion; quantifies the spread of the particle sizes around the MMAD | |
| Fine Particle Dose (FPD) [mg] | Cumulative drug content in particles < 5 µm | |
| Fine Particle Fraction (FPF < 5 µm) [%] | Fraction of fine particles < 5 µm related to the total dose |
|
Aerosol
Characteristic [Unit] | Test 1 | Test 2 | Test 3 | Test 4 | Mean ± SD (n = 4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMAD [µm] | 6.90 | 6.90 | 6.40 | 6.50 | 6.68 ± 0.23 |
| GSD | 1.72 | 1.86 | 2.15 | 2.02 | 2.02 ± 0.16 |
| FPD < 5 µm [mg] | 16.27 | 17.33 | 16.31 | 16.31 | 16.56 ± 0.45 |
| FPF < 5 µm [%] | 25.37 | 26.64 | 29.39 | 34.24 | 28.91± 3.40 |
|
Aerosol
Characteristic [Unit] | Test 1 | Test 2 | Test 3 | Test 4 | Mean ± SD (n = 4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMAD [µm] | 5.20 | 5.20 | 5.00 | 5.33 | 5.18 ± 0.12 |
| GSD | 2.31 | 2.10 | 2.10 | 2.05 | 2.14 ± 0.10 |
| FPD < 5 µm [mg] | 15.90 | 15.37 | 18.65 | 15.28 | 16.30 ± 1.38 |
| FPF < 5 µm [%] | 36.24 | 35.43 | 34.58 | 35.46 | 35.43 ± 0.59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seifert, G.; Erdnüß, F.; Kamin, W.; Krämer, I. Aerosol Characteristics of Nebulized Tranexamic Acid 100 mg/mL for Hemoptysis Treatment—Proof-of-Concept Study. J. Pharm. BioTech Ind. 2025, 2, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi2030012
Seifert G, Erdnüß F, Kamin W, Krämer I. Aerosol Characteristics of Nebulized Tranexamic Acid 100 mg/mL for Hemoptysis Treatment—Proof-of-Concept Study. Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry. 2025; 2(3):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi2030012
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeifert, Gerrit, Frank Erdnüß, Wolfgang Kamin, and Irene Krämer. 2025. "Aerosol Characteristics of Nebulized Tranexamic Acid 100 mg/mL for Hemoptysis Treatment—Proof-of-Concept Study" Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry 2, no. 3: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi2030012
APA StyleSeifert, G., Erdnüß, F., Kamin, W., & Krämer, I. (2025). Aerosol Characteristics of Nebulized Tranexamic Acid 100 mg/mL for Hemoptysis Treatment—Proof-of-Concept Study. Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry, 2(3), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi2030012





