Can Free AI Tools Replace Statistical Software in Data Analysis?
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| 95%CI | 95% confidence interval |
References
- Frangou, S.; Volpe, U.; Fiorillo, A. AI in scientific writing and publishing: A call for critical engagement. Eur. Psychiatry 2025, 68, e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Liang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, Q.; Huang, T.; Sun, F.; Liu, X.; Zhu, H.; Pan, H. Automated medical literature screening using artificial intelligence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2022, 29, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, T.I.; de Azevedo Cardoso, T.; Mavragani, A.; Eysenbach, G. Best Practices for Using AI Tools as an Author, Peer Reviewer, or Editor. J. Med. Internet Res. 2023, 25, e51584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, G.; Lackner, K.J.; Melichar, B.; Pan, S.; Schlattmann, P.; Greaves, R.; Gillery, P.; Plebani, M. Challenging the dogma: Why reviewers should be allowed to use AI tools. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2025, 63, 2349–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Software | Software Used for Statistics | Paired T-Test | Linear Regression | Correlation | Scatter Plot (YES/NO—Plot or Answer) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analyse.it | Analyse.it | t-statistic: 0.054 (p-value: 0.957) | [Population 2] = −0.112 × [Population 1] + 0.556 | r = −0.111 (95%CI −0.301 to 0.088; p = 0.272) | Yes: |
| Excel | Excel | p-value: 0.957 | [Population 2] = −0.112 × [Population 1] + 0.556 | r = −0.111 (No 95%CI and p-value) | Yes: |
| GEMINI | Python 3.13 (Statsmodels; Scipy) | t-statistic: 0.054 (p-value: 0.957) | [Population 2] = −0.112 × [Population 1] + 0.556 | r = −0.111 (95%CI, −0.301 to 0.088; p = 0.272) | No: I cannot directly generate or display a graph for you. The reason you can’t see the image in this conversation is due to a technical limitation of our current chat interface. I don’t have the ability to display or share those files directly in the chat window. |
| ChatGPT | Python 3.13 (Statsmodels; Scipy) | t-statistic: 0.054 (p-value: 0.957) | [Population 2] = −0.112 × [Population 1] + 0.556 | r = −0.111 (95%CI −0.301 to 0.088; p = 0.272) | Yes: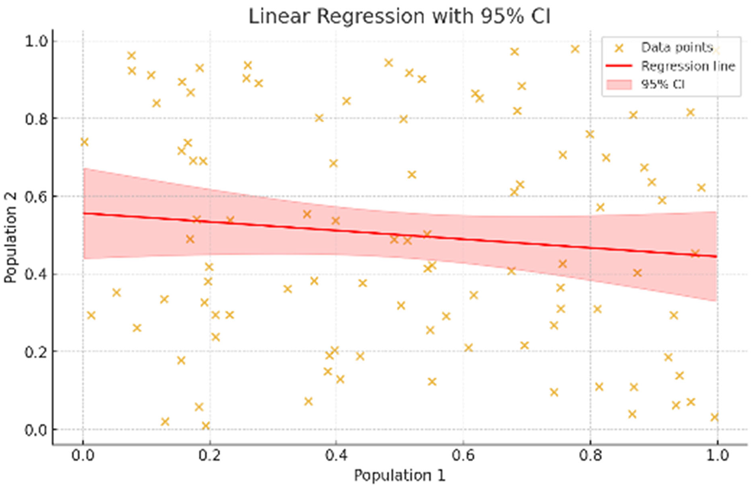 |
| Perplexity | Python 3.12 (Statsmodels; Scipy) | t-statistic: 0.054 (p-value: 0.957) | [Population 2] = −0.112 × [Population 1] + 0.556 | r = −0.111 (95%CI, −0.301 to 0.088; p = 0.272) | Yes: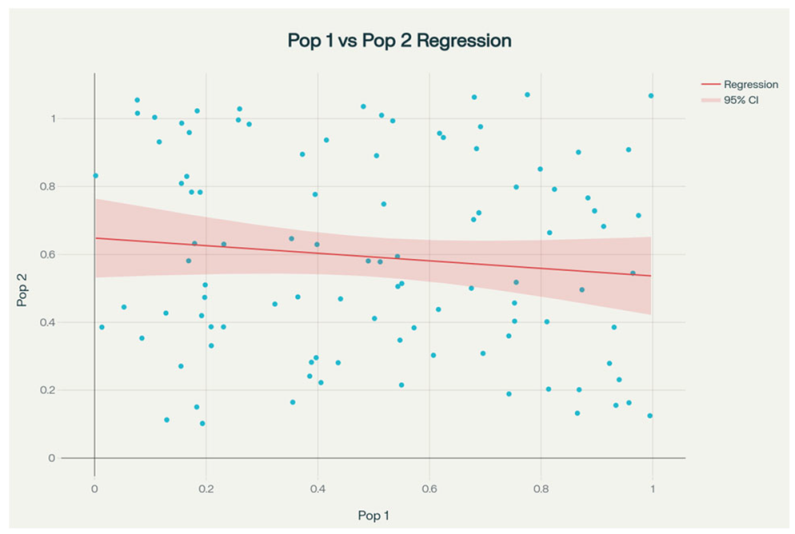 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lippi, G. Can Free AI Tools Replace Statistical Software in Data Analysis? LabMed 2025, 2, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2040027
Lippi G. Can Free AI Tools Replace Statistical Software in Data Analysis? LabMed. 2025; 2(4):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2040027
Chicago/Turabian StyleLippi, Giuseppe. 2025. "Can Free AI Tools Replace Statistical Software in Data Analysis?" LabMed 2, no. 4: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2040027
APA StyleLippi, G. (2025). Can Free AI Tools Replace Statistical Software in Data Analysis? LabMed, 2(4), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2040027





