Abstract
Mayonnaise has a long history as a representative of emulsified sauces. As people become more health-conscious, salad dressings (emulsified and non-emulsified) with lower fat content gradually appear in people’s lives. Both sauces are widely used in everyday life for meat marinades because they contain seasonings such as spices, salt, and vinegar. Although there are many studies on how condiments such as spices, salt, and vinegar affect meat, the effects of semi-solid/liquid emulsions and non-emulsified marinades on meat have yet to be further discussed and analyzed. Therefore, studying the physical and chemical effects of mayonnaise (semi-solid emulsified emulsion) and salad dressing (liquid emulsion and non-emulsified sauce) on meat is essential for improving food quality and safety. Thus, this paper examines the impacts of mayonnaise, emulsified salad dressing, and non-emulsified salad dressing on the physicochemical properties and sensory evaluations of meat. The results showed that the three sauces effectively reduced cooking losses when used as marinades for chicken breasts. In the juiciness and firmness tests, both mayonnaise and non-emulsified salad dressings positively affected the meat. This study also found that lower pH values were not always effective at reducing meat hardness and that emulsification may play a key role in reducing meat hardness.
1. Introduction
With the acceleration of modern life, the demand for ready-to-eat, convenient foods is growing, so processed and preserved foods have become an indispensable part of daily life [1]. Adding marinade to food is called marinating. The salt, sour substances, edible oil, phosphates, etc., added to a marinade can improve the flavor of the food, increase tenderness, extend the shelf life, improve water retention [2,3,4,5,6,7], and play a vital role in food quality and safety [8,9,10,11]. The marinades we use to marinate meat can be divided into biological, chemical, nanoparticle, and physical marinades [12]. Although emulsified semi-solid marinades, a mixture of biological and chemical marinades, are very common in daily life, there are very few studies on using semi-solid emulsions as marinades for meat. Most studies have focused on the liquid emulsion part. The emulsion and quality after marination have yet to be thoroughly analyzed and discussed [13,14,15,16].
Mayonnaise is one of the most commonly used sauces worldwide and has long been a favorite of consumers. According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), mayonnaise is an emulsified semi-solid sauce containing at least 65% vegetable oil, 2.5% or more acidifiers, and egg yolk as the main ingredient; it could also include other ingredients (salt, spices, and natural flavoring) [17]. Another sauce with a similar composition to mayonnaise is salad dressing. According to the FDA definition of salad dressing, it is an emulsified semi-solid food with vegetable oil, acidifier, egg yolk, and starch paste as the essential ingredients, with the addition of salt, spices, and thickening agents [18]. These two semi-solid emulsion seasonings can be used in various cooking occasions, including vegetable salad dressing, sauces, pizza, marinated meat, etc. However, the specific effects of these two semi-solid emulsions on meat quality still need to be made clear. Therefore, it is essential to understand how these two emulsion types affect meat because this can help us understand how emulsions affect the efficiency and sensory quality of pickling; this is essential for the future development of more complex composite emulsion pickled meats (W/O/W, O/W/O), aiming to reduce pickling time and improve pickling efficiency to improve meat quality.
This study aims to elucidate the effects of the corresponding composition and emulsification state of two semi-solid emulsions, mayonnaise and salad dressing, on meat quality. Doing so provides a new perspective for the study of meat marination. It offers practical insights that can be applied to the food industry, via the following:
- Using mayonnaise and salad dressing as marinades to marinate chicken breast meat and explore the effects of semi-solid emulsion marinades on their physicochemical properties and sensory evaluation.
- Studying the effects of emulsification and non-emulsification as marinades on the physical and chemical properties of chicken breast meat
- Employing the main ingredients of mayonnaise and salad dressing, vegetable oil, acidulant, and salt, as marinades at different concentrations to marinate chicken breast meat. The effects of the main ingredients on chicken breast meat were studied. The results of this study were compared and analyzed with the results of the above two studies to further explore the effects of semi-solid emulsion and emulsification on chicken breast meat.
The investigation into the effects of mayonnaise and salad dressing as marinades on meat quality constitutes the main experiment of this paper (referred to as Experiment 1). Experiment 2 and Experiment 3 are sub-experiments of Experiment 1. The purpose of Experiment 2 was to delve deeper into the effects of emulsified versus non-emulsified marinades on meat quality, and the purpose of Experiment 3 was to examine the impacts of the base marinades (salt, vegetable oil, and acetic acid) at different concentrations on meat quality.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
A whole chicken breast was used to measure cooking loss and pH value. Three pieces of the same size were taken from the middle of the chicken breast to measure juiciness, hardness, and sensory evaluation.
In Experiment 1, 9 chicken breasts were used for cooking loss, 2 for juiciness, 3 for firmness, 3 for pH, and 12 for sensory evaluation, for a total of 29 chicken breasts.
In Experiment 2, 3 chicken breasts were used for cooking loss, 2 for juiciness, 5 for hardness, and 4 for pH, for a total of 14 chicken breasts.
In Experiment 3, 3 chicken breasts were used for cooking loss, 2 for juiciness, 5 for hardness, and 4 for pH. A total of 14 chicken breasts were used in Experiment 3.
A total of 57 chicken breasts were used in the three experiments. Due to the large amount of data to be measured, and in order to minimize the impact of climate change on the results, the experiment was completed within three months. The experiment was divided into four stages, as follows: (1) Collection of physicochemical data for Experiment 1. (2) Sensory evaluation of Experiment 1. (3) Collection of physicochemical data for Experiment 2. (4) Collection of physicochemical data for Experiment 3.
In Experiment 1, we used three different marinades (mayonnaise, emulsified salad dressing (sesame flavor), and non-emulsified salad dressing (garlic flavor) to marinate chicken breasts for 24 h. The chicken breasts were then subjected to three hours of low-temperature heating at 60 °C, cooled down, and stored in a refrigerator at 4 °C for a further 24 h of marination. Physicochemical data were collected after refrigerated marination, and sensory evaluation tests were conducted. To eliminate pathogens in chicken breast meat, we controlled the thickness of the chicken breasts to less than 45 mm before heating them to ensure that the chicken meat eaten by the sensory evaluation panel was safe [19,20].
In Experiment 2, we used the same marination time and post-heating treatments as in Experiment 1, except that we changed from three marinades (mayonnaise, emulsified salad dressing, and non-emulsified salad dressing) to two homemade marinades (emulsified and non-emulsified sauces), and collected data on cooking loss, juiciness, firmness, and pH.
In Experiment 3, we used the same marinating time and post-heating treatment as in Experiment 1. Still, we changed the three marinades (mayonnaise, emulsified salad dressing, and non-emulsified salad dressing) into marinades with different concentrations of the three base ingredients (10, 30, 50% vegetable oil, 0.2, 0.6, 1% acetic acid, and 2, 5, 8% salt). We collected data on cooking loss, juiciness, firmness, and pH.
2.2. Sample Preparation
We purchased the chicken breast meat from Seiyu Supermarket via their online shopping site. The broiler chickens, one of Japan’s most common breeds, were raised on a large-scale farm for 50–60 days, slaughtered, cut up, packaged at the Sendai Pack Center, and then transported to the laboratory under rapid refrigeration at 3–5 °C. The chicken meat was then transported to the laboratory under rapid refrigeration. Chicken breasts weighing 350 ± 50 g were selected, and the skin and excess surface fat were removed manually.
The marinade and chicken breasts were then placed in a heat-resistant plastic bag, which was soaked in water to expel the internal air so that the marinade was in complete contact with the chicken, and then placed in the refrigerator at 4 °C for 24 h of marination, and then the samples were marinated for 3 h at 60 degrees Celsius, using a low-temperature cooker (Boniq 2.0: Hayama-Colony Inc. Hayama, Japan). The samples were heated at 60 °C for 3 h. At the end of heating, the samples were cooled with running water (15 ± 3 °C) for 30 min and stored in the refrigerator (4 °C) for 24 h of marination to collect physicochemical data.
2.3. Marinades Preparation
In Experiment 1, the salt content, pH, and oil content of the three marinades were calculated from the data on the packages as follows:
- Mayonnaise: 2% salt, pH 4.08, and 75% fat.
- Emulsified liquid salad dressing: 3% salt, pH 4.34, and 36% fat.
- Non-emulsified liquid salad dressing: 3% salt, pH 4.07, and 50% fat.
All three marinades mentioned above were purchased from Kewpie Corporation.
In Experiment 2, the composition of the homemade emulsified marinade was rapeseed oil, egg yolk, xanthan gum, and distilled water, corresponding to a ratio of 30:0.5:0.2:69.3. Homemade salad dressing was prepared with a first gear kitchen mixer (Acasas, Japan), according to the recipes. Egg yolks were mixed with xanthan gum and 1/3 of distilled water. In the beginning, rapeseed oil was added drop-by-drop with constant stirring. After obtaining stable consistency, rapeseed oil was added to a thin stream. The remaining distilled water was gradually added during mixing. The prepared samples maintained a stable consistency without phase separation. In contrast, the non-emulsified dressing, made without stirring and with the same composition as the salad dressing, remained separate and did not emulsify throughout the experiment.
In Experiment 3, rapeseed oil (10, 30, 50% (w/w)), vinegar (0.2, 0.6, 1.0% (w/w)), and salt (2, 5, 8% (w/w)) were used as a marinade in a proportional mixture with distilled water.
The weight of the marinade used in all three experiments mentioned above was 10% of the weight of the corresponding chicken breast, and the marinade used in the control group was distilled water.
2.4. Measurement of Cooking Loss
After cooling for 24 h, the meat was removed from the bag, wiped dry with kitchen paper, and weighed. Cooking loss was calculated according to the following equation:
Cooking loss (%) = (weight of meat before cooking − weight of meat after cooking for 24 h)/weight of meat before cooking × 100.
2.5. Measurement of Juiciness
The juiciness was measured using the pressure filter paper method [21,22]. The meat was cut into 3 × 3 × 1 cm pieces parallel to the fibers in the center. Samples were taken from the center of the meat for testing. The meat was placed on top of three pieces of paper and underneath one piece (Filter Paper 110 mm, Advantec, Japan). Then, two 50 g vinyl sheets were placed on both sides, and a dumbbell (2.5 kg) was placed on top of the meat for 5 min (environmental temperature: 4 °C). The meat was then weighed, and the juiciness was calculated according to the following equation:
Juiciness (%) = (weight of meat before applying pressure − weight of meat after applying pressure)/weight of meat before applying pressure × 100.
2.6. Measurement of Hardness
The meat was cut into 3 × 3 × 1 cm pieces parallel to the fibers in the center. Three sub-samples were collected from each sample. Using a rheometer specialized for load measurement (Texture Analyzer, FRTS series: Imada Co., Ltd., Toyohashi, Japan), a flat probe (FR-HA-20J 5 N/50 N, Φ20 mm) was fixed to the machine, and the hamburger (cooked meat) mode was set (force-speed, 2 mm/s; force variable, 5.0 mm; returning speed, 5 mm/s; number of times force applied, once; graph format set to load-displacement with a start trigger at 2 digits).
After the settings were applied, the meat was placed on a platform, and the platform’s position was adjusted until there was no gap between the meat and the flat probe. Finally, displacement “zero” was pressed, the measurement screen returned, and the START button was pressed to measure hardness.
2.7. Measurement of pH
A 1.5 cm slice of meat from the center portion of the chicken breast was cut as a sample, and a pH meter (testo pH meter for food (specifically for semisolid products) model: Testo 206-pH2) was inserted 1 cm into the chicken meat to measure the pH directly. There were three measurement positions, as follows:
- A total of 5 mm from the surface of the chicken (later referred to as point A).
- Midway between point A and the center point (later referred to as point B).
- The center point (later referred to as point C).
(Refer to Figure 1.)
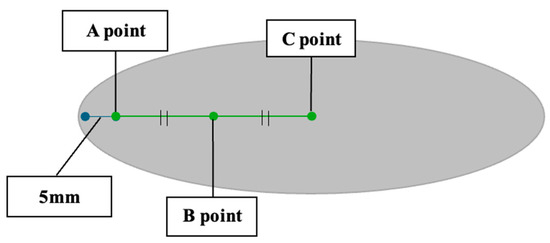
Figure 1.
Measurement of pH. A Point, 5 mm from the surface of the chicken; B Point, midway between the A point and the center point; C Point, the center point.
2.8. Sensory Evaluation
At Miyagi University, we randomly selected 12 untrained students for the experiment. Before experimenting, we confirmed that the members had healthy teeth and asked whether they had taken any medication in the last week; we prepared for the experiment after the check was completed. To prevent the different colors of the meat from affecting the results, we asked the group members to wear dark green glasses.
Marinated chicken breasts were cut into 2 × 2 × 1 cm cubes. The cubes were offered to the team members on white plates; each plate was labeled with a random number and arranged in a random order for each team member, and the team members were instructed to chew with their molars during the test. The test material was kept at a room temperature of 20 °C. Each panelist was given a cup of water between the two plates to rinse the mouth between samples. The evaluation form was designed on a seven-point scale (−3 to +3), with juiciness as the criterion; [+3] indicated very juicy compared to the control group, “0” indicated no difference compared to the control group, and [−3] indicated very dry compared to the control group.
The researcher explained the procedure and sequence of the experiment to all panelists, and after obtaining their consent, conducted the experiment. This study was conducted with the approval of the Research Ethics Committee of Miyagi University (approval no. 2022-261).
2.9. Statistical Analysis
In Experiment 1, significant differences among the physicochemical evaluation properties were calculated using the Tukey test via Kaleida Graph software (Hulinks Inc. Tpkyo, Japan); p < 0.05. The sensory evaluation (n = 12) of juiciness and firmness was performed using the Tukey test, and the data were analyzed to determine significant differences between mayonnaise, emulsified liquid salad dressing, and non-emulsified liquid salad dressing across different chewing intervals (3 chews, 10 chews, and before swallowing) (p < 0.05).
In Experiment 2, the t-test, a two-sample test assuming equal variances was used to determine if there were significant differences between the physicochemical effects of emulsified and non-emulsified marinades on meat quality (p < 0.05).
In Experiment 3, the Tukey test was used to determine if there were significant differences in the physicochemical effects of different concentrations of rapeseed oil, salt, and vinegar on meat quality (p < 0.05).
The above data were analyzed for differences between means using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with the SPSS statistical package (SPSS IBM, Urayasu, Chiba, Japan).
3. Results
3.1. Cooking Loss
In Experiment 1 (Table 1), the cooking losses of mayonnaise, salad dressing, and non-emulsified salad dressing significantly differed from the control (p < 0.001). All three marinades significantly reduced the moisture loss of the meat during heating, but there was no significant difference between the three marinades.

Table 1.
Effects of mayonnaise, salad dressing, and non-emulsified salad dressing on the physicochemical properties of chicken breast meat (Experiment 1).
In Experiment 2 (Table 2), no significant difference was observed between meat treated with homemade emulsified salad dressing and non-emulsified salad dressing as a marinade.

Table 2.
Effects of homemade emulsified versus non-emulsified salad dressing on the physicochemical properties of chicken breast meat (Experiment 2).
In Experiment 3 (Table 3), there was no significant difference in cooking losses between medium and high concentrations of acetic acid (0.6 and 1%) and the control. Still, there was a significant difference with the 0.2% concentration of acetic acid. Vegetable oil at a 50% concentration was not significantly different from the control in terms of cooking loss, but there was a significant reduction (p < 0.05) in cooking loss with decreasing concentrations (30% and 10%). Compared to vegetable oil with acetic acid, salt at concentrations of 2, 5, and 8% were significantly different from the control in terms of cooking losses; (p < 0.05).

Table 3.
Effects of different marinade ingredients and solution concentrations on the physicochemical properties of chicken breast meat (Experiment 3).
Analyzed from the three different marinades, the efficiency in reducing cooking losses ranked in descending order as salt, oil, and vinegar. Analyzed from various concentrations of marinades, salt reduced cooking losses at all three different concentrations, but a lower concentration (2%) had better results than a higher concentration (8%) compared to a 5% concentration. When vegetable oil was used as a marinade, lower and medium concentrations (30% and 10%) were more effective in reducing cooking losses than a high concentration (50%). When acetic acid was used as a marinade, the cooking losses of chicken breasts treated with the three different concentrations of acetic acid were not significantly different from those of the control group, but low (0.2%) concentrations of acetic acid resulted in less cooking losses than meat cured with medium to high (0.6 and 1%) concentrations of acetic acid (p < 0.05).
3.2. Juiciness
In Experiment 1 (Table 1), there was a significant group difference between the juiciness of the control, mayonnaise, emulsified salad dressing, and non-emulsified salad dressing; marinating meat in non-emulsified salad dressing significantly reduced the juiciness of the meat (p < 0.05).
In Experiment 2 (Table 2), there was no significant difference between meat treated with homemade emulsified salad dressing and non-emulsified salad dressing as marinade.
In Experiment 3 (Table 3), analyzed from the three different marinades, brine significantly increased the juiciness content in the meat. In contrast, using cooking oil as a marinade did not significantly affect the juice content in the meat, and a high concentration of acetic acid (1%) decreased the juice content in the meat (p < 0.05). Analyzing the different concentrations of marinade, the medium and high concentrations (5 and 8%) of brine significantly (p < 0.05) increased the juice in the meat compared to the control group. In comparison, there was no significant difference with the 2% brine. Low and medium concentrations (0.6 and 0.2%) of acetic acid were not significantly different from the control, but high acetic acid concentrations significantly decreased the meat’s juiciness. (p < 0.05). There was no significant difference between different concentrations of vegetable oil on the juiciness in the meat compared to the control.
3.3. Hardness
In Experiment 1 (Table 1), the hardness of the control, emulsified salad dressing, and non-emulsified salad dressing differed significantly from mayonnaise (p < 0.05). Mayonnaise significantly reduced the hardness of the meat, but there was no significant difference between the other three marinades.
In Experiment 2 (Table 2), the hardness of meat treated with emulsified salad dressing as a marinade was significantly reduced compared to non-emulsified salad dressing (p < 0.01).
In Experiment 3 (Table 3), there was no significant difference between meats marinated with different marinades and different marinade concentrations compared to the control. Meat marinated with 1% acetic acid was the hardest, and meat marinated with 0.6 and. 0.2% acetic acid, 8% brine, and 30% vegetable oil was softer. Although there was no significant difference when compared to the control, there was a significant difference between the meat marinated with 1% acetic acid (p < 0.05).
3.4. pH
In Experiment 1 (Table 1), the pH of mayonnaise-marinated meats was lower than that of the control, emulsified salad dressing, and non-emulsified salad dressing at point A (p < 0.01). There was no significant difference in pH between the control, mayonnaise, emulsified salad dressing, and non-emulsified salad dressing marinated meats at point B versus point C.
In Experiment 2 (Table 2), at points A, B, and C, there was no significant difference between meat treated with homemade emulsified salad dressing and meat treated with non-emulsified salad dressing as a marinade.
In Experiment 3 (Table 3), at points A, B, and C, only the meat marinated with 1% acetic acid had a lower pH than the meat marinated with the other marinades (p < 0.05), and there was no significant difference between the other marinades (except 1% acetic acid).
3.5. Sensory Evaluation
In Experiment 1, there was no significant difference in juiciness and firmness across different chewing intervals (3 chews, 10 chews, and before swallowing) of chicken breasts marinated with the same marinade (mayonnaise, emulsified salad dressing versus non-emulsified salad dressing). There was no significant difference in juiciness and firmness between chicken breasts marinated in three marinades (mayonnaise, emulsified salad dressing versus non-emulsified salad dressing) with the same number of chews (3 chews, 10 chews, and before swallowing).
Experiments 2 and 3 were not subjected to sensory evaluation.
4. Discussion
4.1. Cooking Loss
From the analysis of cooking loss and water retention in Table 1, the three marinades showed a significant increase in water retention compared to the control (p < 0.001). However, the effects of different concentrations of oil, salt, and acetic acid on meat cooking losses are presented in Table 3. The factors that may have a greater impact on the cooking losses of meat marinated with mayonnaise and salad dressings are salt and the medium concentration (30%) of vegetable oil. The lateral expansion of tendon fibers during brine curing allows more water to enter the meat [23]; moreover, salt also dissolves myofibrillar proteins, resulting in the formation of viscous secretions on the surface of the meat. These secretions combine during cooking to form a thermo-coagulant protein matrix, encapsulating the free water, resulting in a decrease in cooking losses and an increase in the juiciness of the meat [24].
The 30% vegetable oil improved water retention capacity, consistent with Shtonda’s findings. Fats and oils reduce the free water content of the meat and are more effective at encapsulating and sealing in moisture during marination, thus preventing water loss during cooking [25]. When fats were mixed with spices as a marinade for meat, the spices could dissolve into the fats and the spices could penetrate the meat [26].
pH can directly affect the negative charges on proteins that bind to water molecules. So, pH values below or above the isoelectric point can expand the space in the muscle filaments by enhancing hydrophilic properties, resulting in increased water retention [27]. However, according to the results of cooking loss in Table 3, the increase in acetic acid concentration did not lead to a decrease in cooking loss of the meat, and there was no significant difference compared to the control. The pH values of Table 3 also showed a significant difference (p < 0.05) in the pH values of meat marinated with a 1% concentration of acetic acid at points A, B, and C compared to other marinades, which means that even though the acetic acid penetrated the interior of the meat, it did not improve the water retention of the meat, which may be due to the insufficient concentration of acetic acid. As mentioned above, moving away from the isoelectric point improves water retention. Still, from the actual pH measured in the acetic acid marinated meat, the absolute difference was only about 0.2 compared to the pH measured in the control group. Although there is a statistically significant difference in the pH between the control group and the meat marinated in the 1% acetic acid, when the difference is less than 0.2, it may not result in a significant difference in cooking loss.
4.2. Juiciness
Cooking losses involve water [28], and higher cooking losses mean more water escapes from the meat during cooking and less water content in the meat. However, in Table 1, the cooking loss of the control group was two times higher than that of the experimental group (p < 0.001). At the same time, the juiciness was not significantly different from that of mayonnaise and non-emulsified salad dressings. The juiciness of emulsified salad dressings was higher than the control, mayonnaise, and non-emulsified salad dressings (p < 0.05), which, when combined with the non-significant difference in juiciness between homemade emulsified and non-emulsified salad dressings measured in Table 2, suggests that the difference in juiciness between emulsified and non-emulsified salad dressings may be independent of the emulsification status. From the juiciness data in Table 3, brine was effective at increasing juiciness, but the juiciness of meat marinated in oil (10, 30, 50%) and acetic acid (0.2, 0.6%) was not significantly different from that of the control group, whereas 1% acetic acid decreased juiciness (p < 0.05). Therefore, the inconsistency between cooking losses and juiciness that led to the control and experimental groups may be due to the different contents of free and immobilized water in meat, where the reduction in free water leads to an increase in the water-binding capacity, which in turn increases the proportion of immobilized water [29]. Meat is classified into three types, based on water content:
- Held water, which usually cannot be removed during food processing and is tightly bound to proteins.
- Immobilized water, which constitutes 80% of meat, is weakly bound to proteins and can be lost during food processing.
- Free water, which exists in the part of the water between capillaries and between the capillaries and proteins, which is more easily lost in food processing.
It inhibits protein denaturation and changes the pH value to make its principal isoelectric point. Low-temperature preservation and other methods can make the free water converted to immobilized water to immobilized water retention capacity [30]. Due to the interaction of salt, acidifiers, and spices contained in the three marinades (mayonnaise, emulsified salad dressing, and non-emulsified salad dressing), which converted the free water that was easily lost to immobilized water, the water retention capacity of the meat increased. The meat could retain water even when a certain amount of pressure was applied. Although the control group lost twice as much water to cooking as the experimental group, this may have resulted in no significant difference in the number of meat juices released from the control and experimental groups when the same pressure was applied, as more of the bound water was converted to easily lost free water in the control group under heating conditions. The conversion of a portion of the free water into immobilized water during marination improved water retention in the experimental group, resulting in twice as much cooking loss in the control group as in the experimental group.
4.3. Hardness and pH
The results of the hardness test are in Table 1. We can see that mayonnaise significantly improved the tenderness of the meat (p < 0.05). Still, there was no significant difference between the emulsified and non-emulsified salad dressing and the control group. In contrast, regarding pH, the meat marinated with mayonnaise as a marinade differed significantly from the other two experimental groups at point A, while there was no significant difference between the meat marinated with mayonnaise at points B and C. The hardness test results in Table 1 show that the meat marinated with mayonnaise as a marinade significantly differed from the other two experimental groups. The acidic substances of the mayonnaise only penetrated 5 mm of the meat. Still, they did not penetrate the inside of the meat, so the internal pH value was not significantly different from the other two experimental groups and the control group. For the hardness test, we cut the meat in the center (points B and C), so the hardness of the meat at the center was less affected by the pH value. The decrease in pH at point A alone does not explain why the meat at the center also became less firm.
Moreover, the pH values of the three seasonings from low to high are 4.07 for non-emulsified salad dressing, 4.08 for mayonnaise, and 4.34 for emulsified salad dressing. The pH of non-emulsified salad dressing is nearly the same as that of mayonnaise, as shown in Table 1. According to the results, the pH values of meat marinated in non-emulsified salad dressing at points A, B, and C after heating are not significantly different from the control group. Therefore, the change in pH value in the meat is not only related to the pH value of the marinade but may also be related to other factors, requiring further research.
Numerous studies also show that low-pH marinades can improve meat tenderness [31,32,33,34]. Still, there is no significant difference in the pH values of the three marinades. Thus, it is impossible to explain why only mayonnaise could reduce the pH at point A and improve the tenderness of meat from the pH value alone. Combining the relationship between pH and hardness of homemade emulsified and non-emulsified salad dressings in Table 2, we can see that—although there is no significant difference in pH between the two marinades at points A, B, and C—after heating, there is a substantial improvement in the tenderness of meat marinated in emulsified salad dressing (p < 0.01). The three marinated raw materials from Table 3 were analyzed; there were no significant differences between the hardness values of all experimental and the control groups.
In contrast to Experiment 1, where the acidity of mayonnaise penetrated only to point A of the meat, the high concentration (1%) of acetic acid marinated meat in Experiment 3 had significantly lower (p < 0.05) pH values than the other marinades at points A, B, and C. This proves that the high concentration of acetic acid penetrated the internal part of the meat but did not positively affect its softness, which is the same as the results of Seuss’s study [35]. This suggests that mayonnaise as a marinade may have a positive effect on the softening of the meat, with emulsification playing a more significant role, but the mechanism of how the emulsified marinade affected the meat is unclear and requires further research and discussion.
4.4. Sensory Evaluation
In sensory evaluation, there are two stages of juiciness assessment: The early stage of chewing (3–10 chews) is used to determine the water content of the meat, and the latter stage of chewing (between 10 chews and swallowing) is used to determine the water content of the meat, the fat, and the saliva secreted during chewing [36]. In experiments where a similar measurement (TI method) was used to measure the change in hardness over time during chewing, the toughness of meat decreased with increasing chewing times [37].
In the sensory evaluation, we tested the juiciness and hardness of meat marinated in three marinades at the same number of chewing times. We found no significant difference between the three marinades. However, in Experiment 1, there was no considerable difference in the cooking loss of meat marinated in the three marinades, but in the physicochemical evaluation of juiciness, the meat marinated in non-emulsified salad dressing was significantly less juicy than the other two marinades (p < 0.05). In the physicochemical evaluation, the hardness of meat marinated in mayonnaise was substantially lower than the other two marinades (p < 0.05). This illustrates that sensory, physical, and chemical evaluations will produce inconsistencies under specific conditions. Although the chemical evaluation shows significant differences between meats, ordinary people cannot test the differences between samples as accurately as machines can, so when testers taste a sample below their perception threshold, they cannot accurately tell the difference between the two samples.
The juiciness and firmness of meat marinated in the same marinade tested at different chewing times were not significantly different. The pre-chewing stage may influence the evaluation of the meat texture and hardness by ordinary individuals, overlooking the secretion of saliva and changes in meat texture hardness during chewing. Consequently, they may need to accurately perceive changes in juiciness and hardness while tasting samples. Therefore, significant differences in the physicochemical evaluation of meat occurred, which may not necessarily reflect mirror differences in sensory evaluation [38].
5. Conclusions
In Experiment 1, the use of mayonnaise and emulsified versus non-emulsified salad dressing was influential in the physicochemical evaluation to reduce cooking losses and increase the moisture in the meat after cooking. In many papers, salt and acidifiers as marinade for marinating meat play a crucial role in juiciness and firmness. Still, according to the physicochemical evaluation in Experiment 1, salt content and acidifiers did not explain the inconsistency between cooking loss and juiciness, pH and moisture content, and pH and firmness. Therefore, we combined the data from Experiments 2 and 3 to demonstrate that it is not only cooking loss that affects juiciness but also the ratio of free water to immobilized water. A lower pH does not necessarily positively affect meat tenderness and moisture content, and the type and concentration of acidifiers should be considered. Emulsifying marinades have a positive impact on the tenderization of meat.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.Y. and S.-i.I.; methodology, N.S., H.O. and Y.O.; formal analysis, N.S. and H.O.; investigation, N.S. and H.O.: resources, Y.O.; writing—original draft preparation, N.S. and H.O.; writing—review and editing, J.L. and S.-i.I.; supervision, S.-i.I.; project administration, S.-i.I.; funding acquisition, S.-i.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We wish to thank Kewpie Corporation for their generous financial assistance [grant number R05KYKE9].
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Miyagi University (approval number: 2022-261).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Patients consented via an informed consent process that was reviewed by the Ethics Committee of Miyagi University.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that this study received funding from Kewpie Corporation. The funder had the following involvement with the study: Conceptualization, methodology, resources.
References
- Alvarado, C.Z.; Sams, A.R. Early postmortem injection and tumble marination effects on broiler breast meat tenderness. Poult. Sci. 2004, 83, 1035–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertbjerg, P.; Mielche, M.M.; Larsen, L.M.; Møller, A.J. Relationship between proteolytic changes and tenderness in prerigor lactic acid marinated beef. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R.M.; Monahan, F.J. The tenderisation of shin beef using a citrus juice marinade. Meat Sci. 2003, 63, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latoch, A.; Libera, J.; Stasiak, D.M. Physicochemical properties of pork loin marinated in kefir, yoghurt or buttermilk and cooked sous vide. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2019, 18, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latoch, A. Effect of meat marinating in kefir, yoghurt and buttermilk on the texture and color of pork steaks cooked sous-vide. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2020, 65, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.Z.; Talib, N.H.; Hasnol, N.D.S. Heterocyclic aromatic amines in deep fried lamb meat: The influence of spices marination and sensory quality. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.M.; De Kock, H.L.; Dykes, G.A.; Coorey, R.; Buys, E.M. Enhancement of poultry meat, nutritional profile, legislation and challenges. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 48, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Fandos, E.; Herrera, B. Efficacy of malic acid against Listeria monocytogenes attached to poultry skin during refrigerated storage. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 1936–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayaka, R.M.U.S.K. Antibacterial Effect of Malic Acid Against Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella enteritidis and Escherichia coli in Mango, Pineapple and Papaya Juices. Am. J. Food Technol. 2013, 8, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, R.J.; Stratford, M. Weak-acid preservatives: Modelling microbial inhibition and response. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 86, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.R.; Hall, C.J. Growth inhibition of food-borne pathogens by lactic and acetic acids and their mixtures. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1988, 23, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsanur Rahman, S.M.; Islam, S.; Pan, J.; Kong, D.; Xi, Q.; Du, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Oh, D.H.; Han, R. Marination ingredients on meat quality and safety—A review. Food Qual. Saf. 2023, 7, fyad027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahova-Vangelova, D.B.; Dragoev, S.G.; Balev, D.K.; Assenova, B.K.; Amirhanov, K.J. Quality, microstructure, and technological properties of sheep meat marinated in three different ways. J. Food Qual. 2017, 2017, 5631532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahova-Vangelova, D.B.; Abjanova, S.; Dragoev, S.G. Influence of the marinating type on the morphological and sensory properties of horse meat. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2014, 13, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siroli, L.; Baldi, G.; Soglia, F.; Bukvicki, D.; Patrignani, F.; Petracci, M.; Lanciotti, R. Use of essential oils to increase the safety and the quality of marinated pork loin. Foods 2020, 9, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargiotou, C.; Katsanidis, E.; Rhoades, J.; Kontominas, M.; Koutsoumanis, K. Efficacies of soy sauce and wine base marinades for controlling spoilage of raw beef. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Sec. 169.140 Mayonnaise. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/cfrsearch.cfm?fr=169.140 (accessed on 9 June 2024).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Sec. 169.150 Salad Dressing. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/cfrsearch.cfm?fr=169.150 (accessed on 9 June 2024).
- O’Bryan, C.A.; Crandall, P.G.; Martin, E.M.; Griffis, C.L.; Johnson, M.G. Heat resistance of Salmonella spp., Listeria monocytogenes, Escherichia coli 0157: H7, and Listeria innocua M1, a potential surrogate for Listeria monocytogenes, in meat and poultry: A review. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, R23–R30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, P.D.; Alonso, M.D.; Mascheroni, R.H. Thermophysical properties of meat products: General bibliography and experimental values. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kauffman, R.G.; Eikelenboom, G.; Van der Wal, P.G.; Merkus, G.; Zaar, M. The use of filter paper to estimate drip loss of porcine musculature. Meat Sci. 1986, 18, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.T. Determination of water-holding capacity of porcine musculature based on released water method using optimal load. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2018, 38, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offer, G.; Knight, P.; Jeacocke, R.; Almond, R.; Cousins, T.; Elsey, J.; Parsons, N.; Sharp, A.; Starr, R.; Purslow, P. The structural basis of the water-holding, appearance and toughness of meat and meat products. Food Struct. 1989, 8, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Z.L.; Zhang, X.H.; Li, X.; Song, Z.J.; Ma, H.J.; Lu, F.; Zhu, M.M.; Zhao, S.M.; Wang, Z.R. The effects of sodium chloride on proteins aggregation, conformation and gel properties of pork myofibrillar protein. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 2258–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shtonda, O.; Semeniuk, K. Aspects of the influence of vegetable-oil-based marinade on organoleptic and physicochemical indicators of the quality of semi-finished natural marinated meat products. Slovak J. Food Sci. 2021, 15, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vişan, V.G.; Chiş, M.S.; Păucean, A.; Mureșan, V.; Pușcaș, A.; Stan, L.; Vodnar, D.C.; Dulf, F.V.; Tibulca, D.; Vlaic, B.A.; et al. Influence of marination with aromatic herbs and cold pressed oils on black angus beef meat. Foods 2021, 10, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, V.D.; Mule, B.D.; Machewad, G.M. Effect of marination with ginger rhizome extract on properties of raw and cooked chevon. J. Muscle Foods 2007, 18, 349–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymann, H.; Hedrick, H.B.; Karrasch, M.A.; Eggeman, M.K.; Ellersieck, M.R. Sensory and chemical characteristics of fresh pork roasts cooked to different endpoint temperatures. J. Food Sci. 1990, 55, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarenko, A.; Mushtruk, M.; Rudyk-Leuska, N.; Kononenko, I.; Shevchenko, P.; Khyzhniak, M.; Martseniuk, N.; Glebova, J.; Bazaeva, A.; Khalturin, M. The study of the variability of morphobiological indicators of different size and weight groups of hybrid silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys spp.) as a promising direction of development of the fish processing industry. Slovak J. Food Sci. 2021, 15, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, M.S. Water holding capacity. Encycl. Meat Sci. 2004, 1, 242–249. [Google Scholar]
- Żochowska-Kujawska, J.; Kotowicz, M.; Lachowicz, K.; Sobczak, M. Influence of marinades on shear force, structure and sensory properties of home-style jerky. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2017, 16, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arganosa, G.C.; Marriott, N.G. Organic acids as tenderizers of collagen in restructured beef. J. Food Sci. 1989, 54, 1173–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktaş, N.; Kaya, M. The influence of marinating with weak organic acids and salts on the intramuscular connective tissue and sensory properties of beef. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2001, 213, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Singh, P.; Tanwar, V.K.; Ponnusamy, P.; Singh, P.K.; Shukla, P. Augmentation of quality attributes of chicken tikka prepared from spent hen meat with lemon juice and ginger extract marination. Nutr. Food Sci. 2015, 45, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seuss, I.; Martin, M. The influence of marinating with food acids on the composition and sensory properties of beef. Fleischwirtschaft 1993, 73, 292–295. [Google Scholar]
- Aaslyng, M.D.; Bejerholm, C.; Ertbjerg, P.; Bertram, H.C.; Andersen, H.J. Cooking loss and juiciness of pork in relation to raw meat quality and cooking procedure. Food Qual. Prefer. 2003, 14, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimoch, J.; Gullett, E.A. Temporal aspects of perception of juiciness and tenderness of beef. Food Qual. Prefer. 1997, 8, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjelkner-Modig, S.T. Sensory properties of pork, as influenced by cooking temperature and breed. J. Food Qual. 1986, 9, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).