Elucidation of Electrical Characteristics for Apples (Malus domestica) Using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Physical Properties
2.2.1. Dimensional Characteristics
2.2.2. Determination of Shape
2.2.3. Packing Coefficient
2.2.4. Gravimetric and Frictional Characteristics
2.3. Chemical Properties
2.3.1. Moisture Content
2.3.2. Total Soluble Solids (TSS)
2.3.3. pH
2.3.4. Acidity (%)
2.3.5. Ascorbic Acid (mg/100 g)
2.3.6. Brix Acid Ratio
2.4. Optical Properties
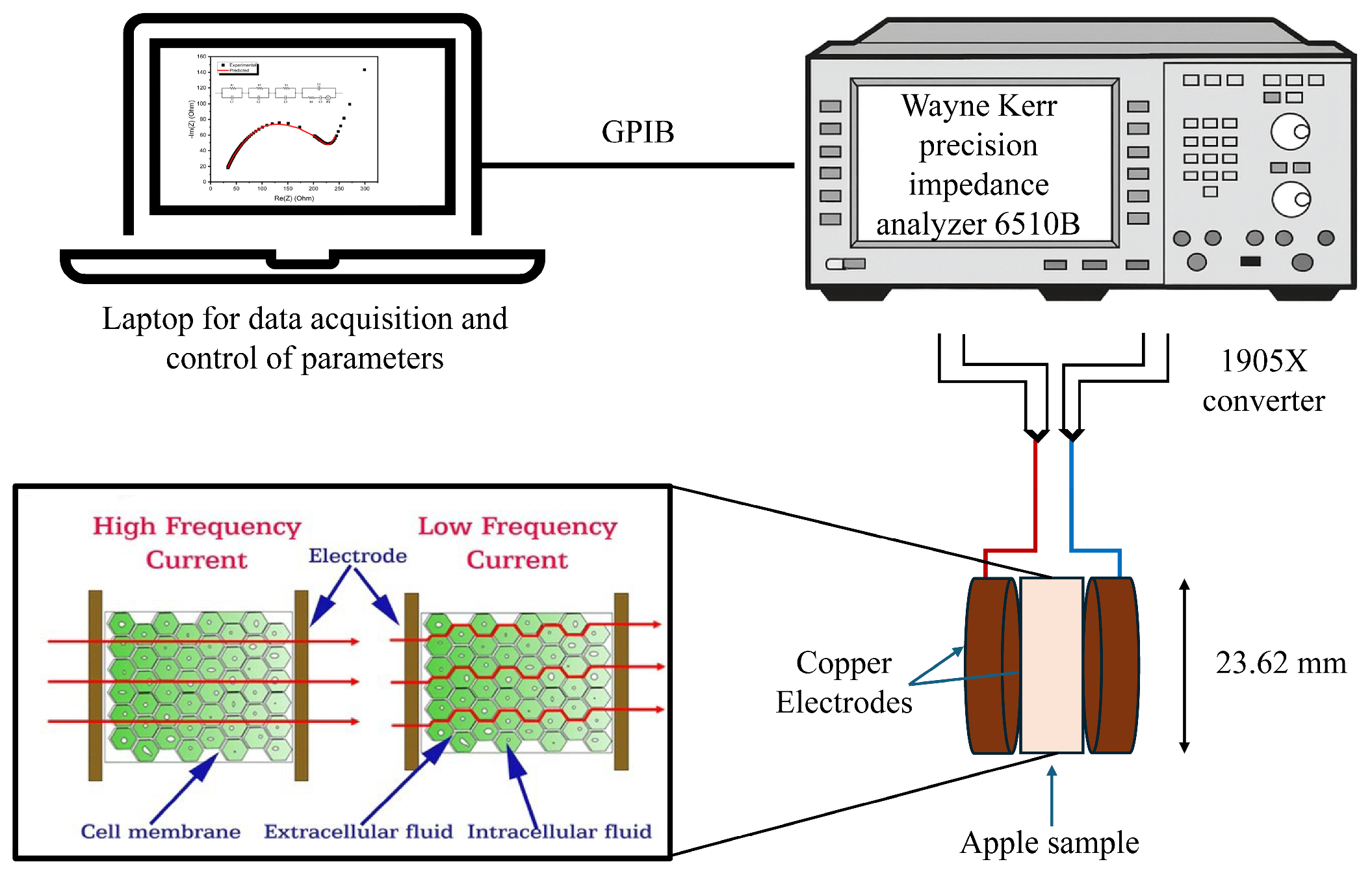
2.5. Measurement of Electrical Properties
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physico-Chemical and Optical Properties
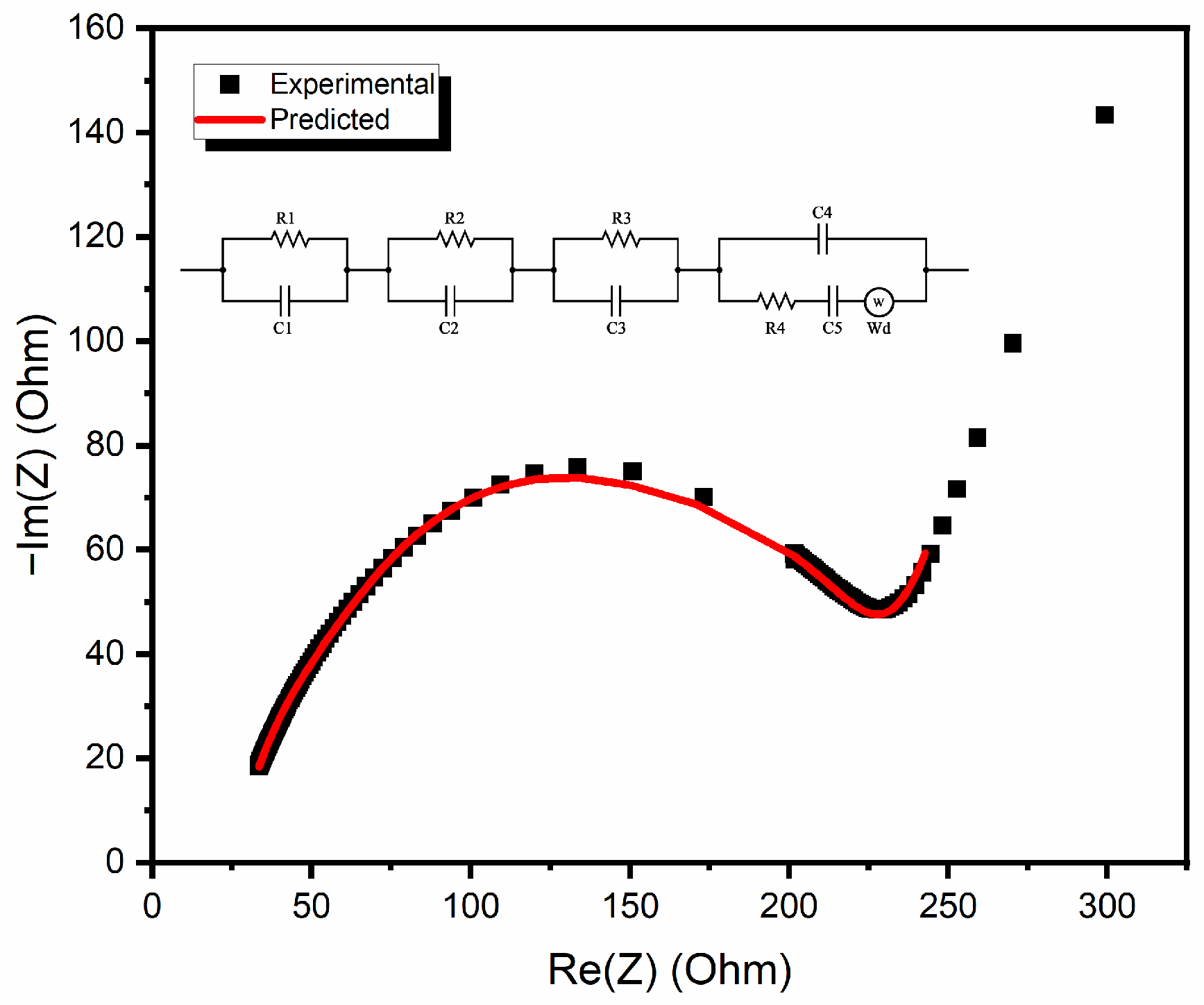
3.2. Nyquist Plot
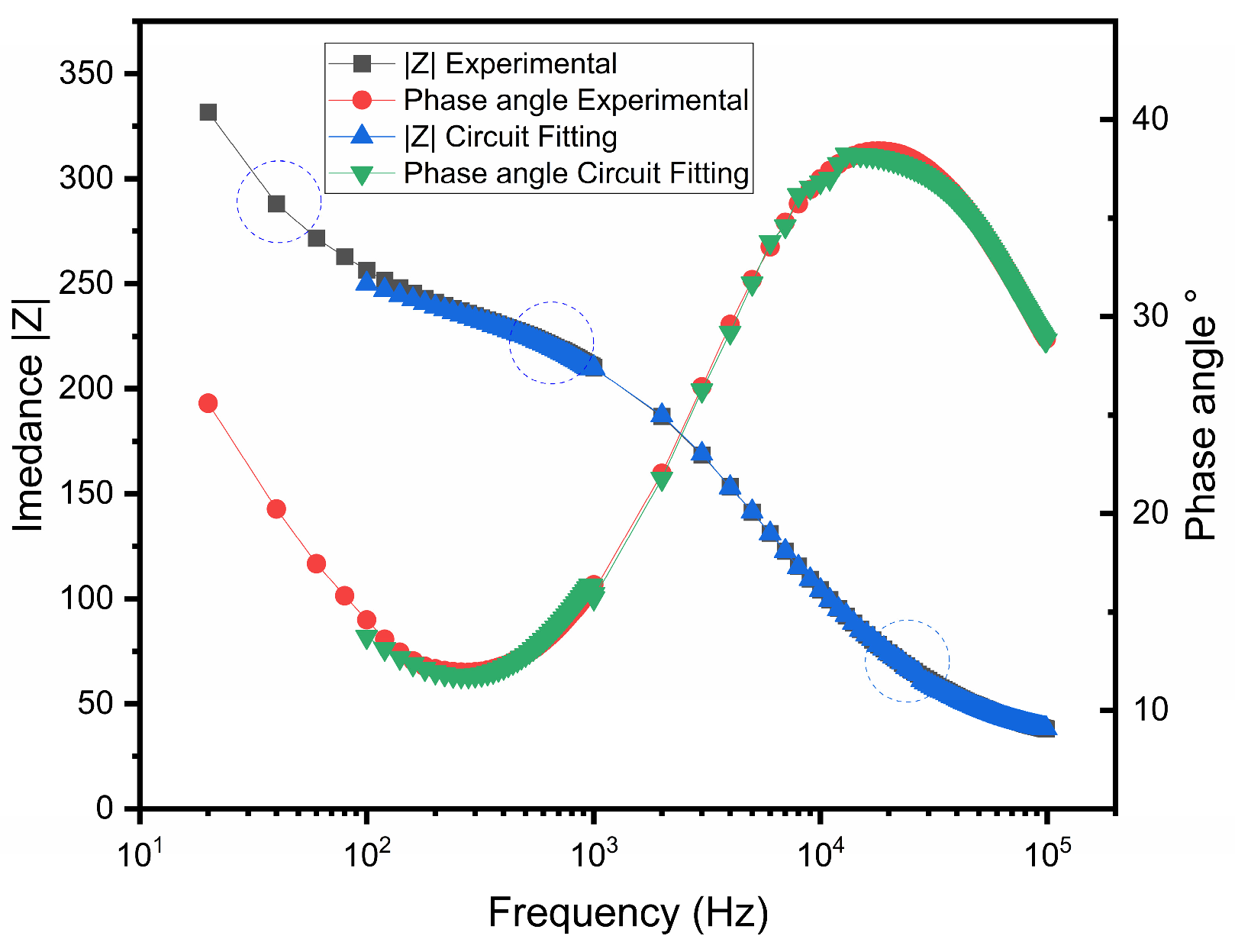
3.3. Bode Plot
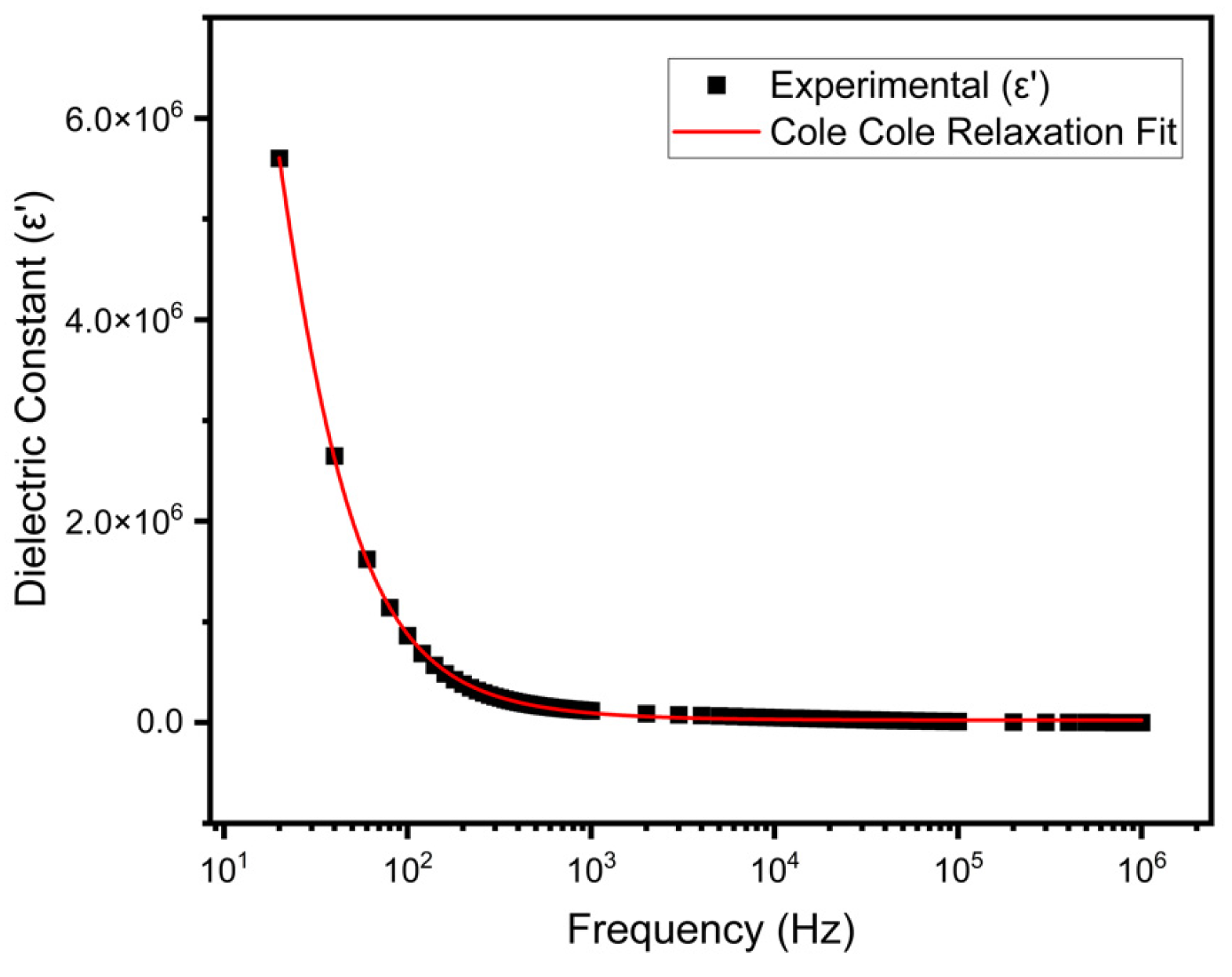
3.4. Dielectric Constant
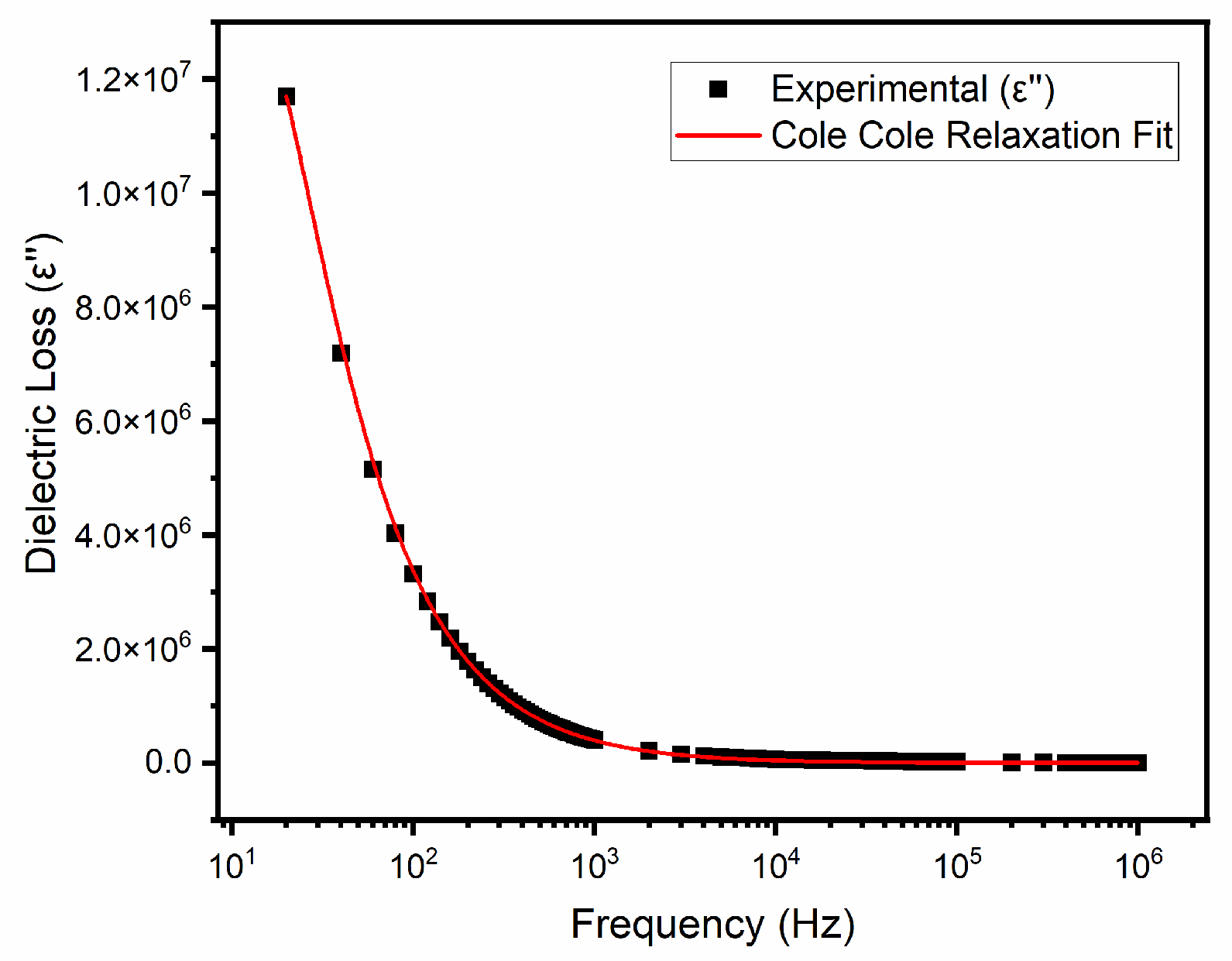
3.5. Relaxation Model and Cole–Cole Fitting
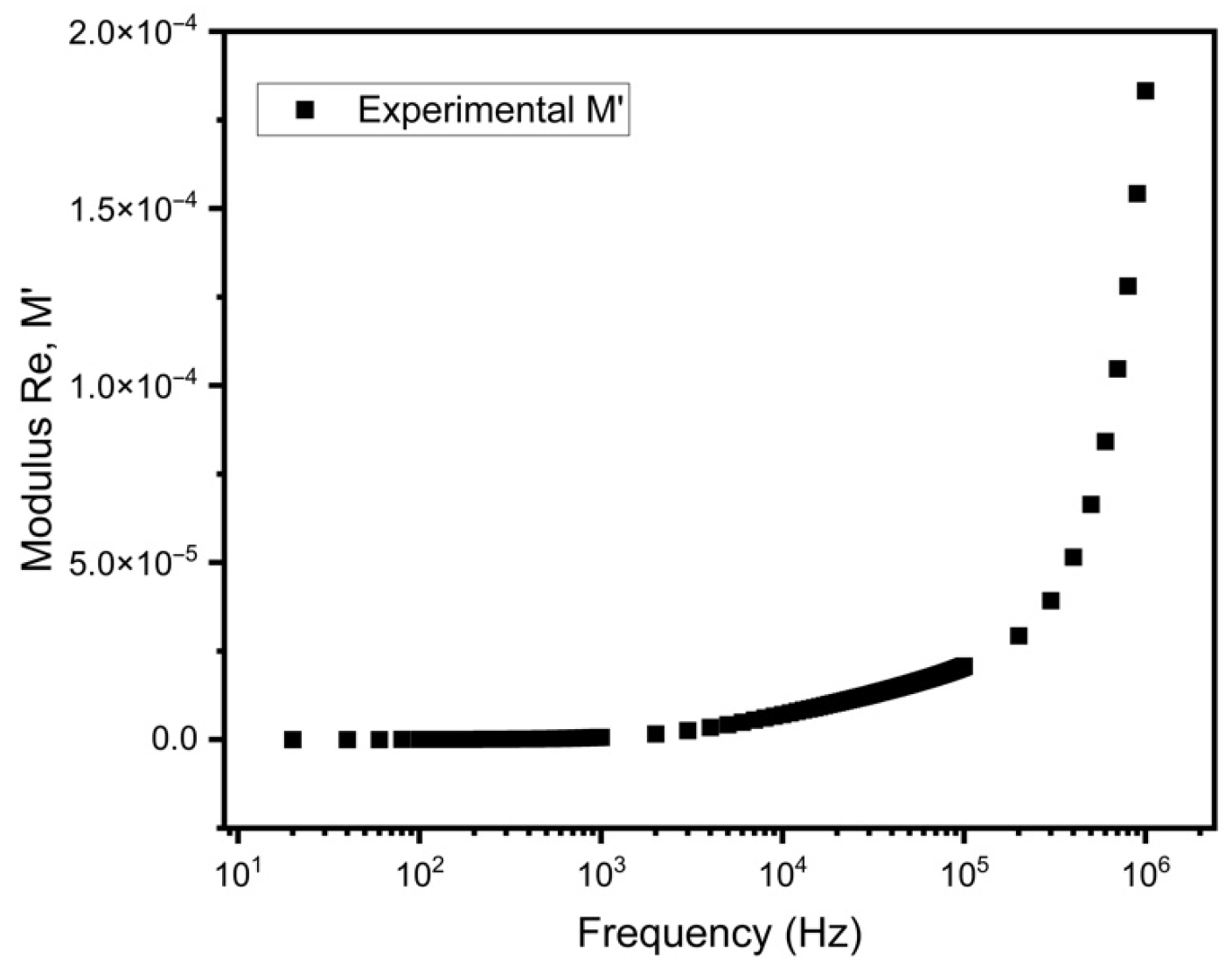
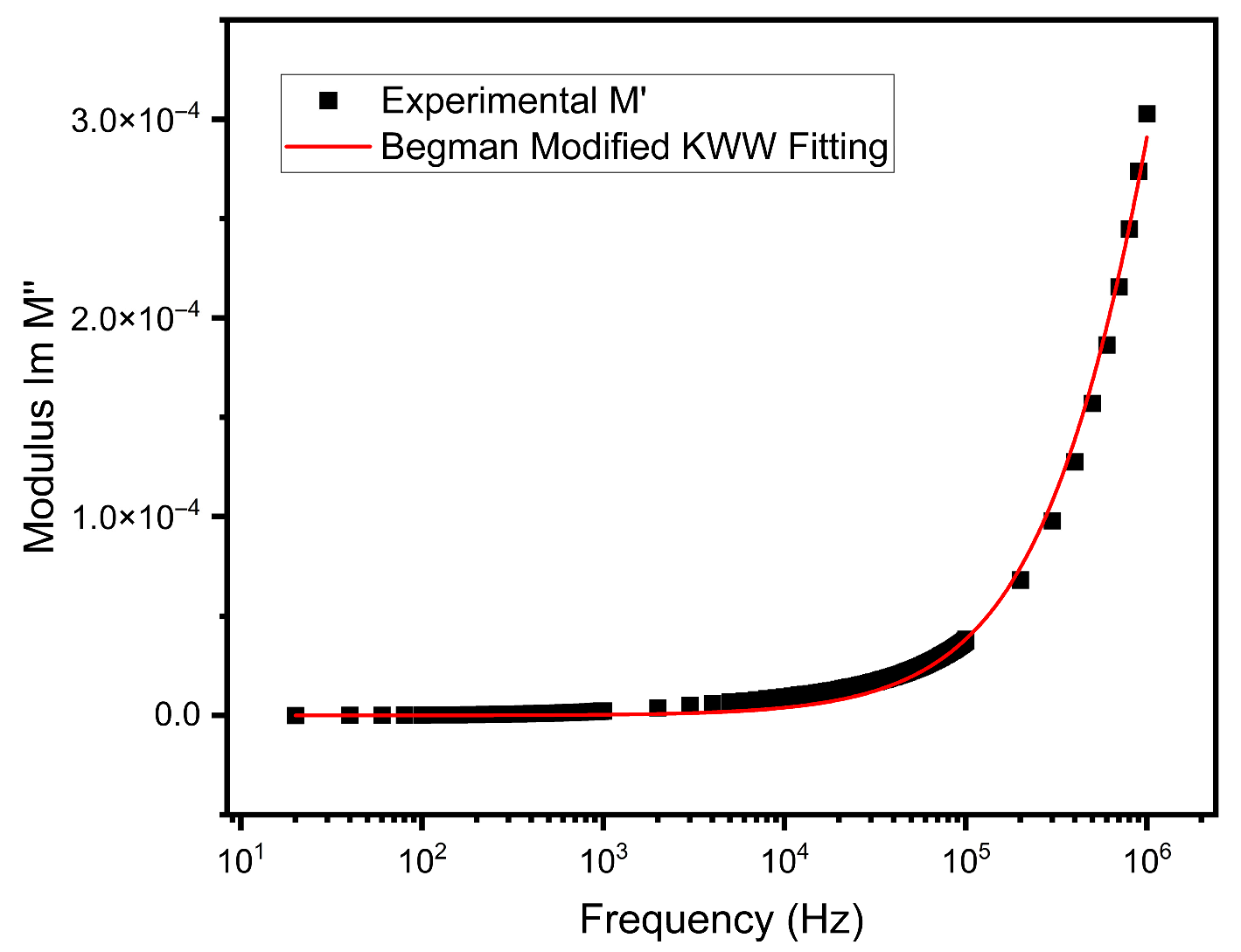
3.6. Electrical Modulus Analysis
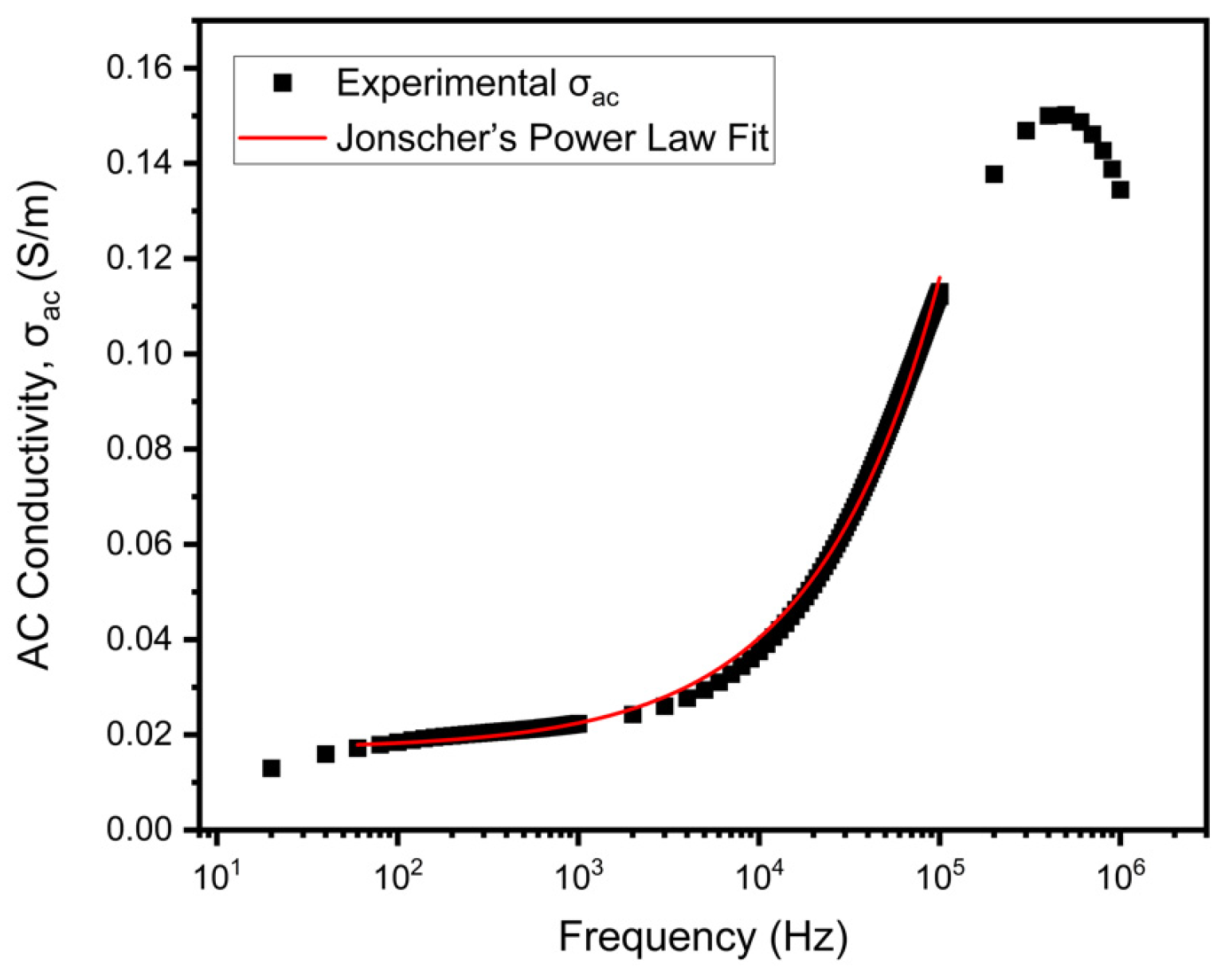
3.7. AC Conductivity
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAD | Average Absolute Deviation |
| EIS | Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy |
| GPIB | General-Purpose Interface Bus |
| MPE | Mean Percentage Error |
| MSE | Mean Square Error |
| NMSE | Normal Mean Square Error |
| NRMSE | Normal Root Mean Square |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| TA | Titratable Acidity |
| TSS | Total Soluble Solids |
| wwb | Weight Wet Basis |
References
- USDA. Supply and Distribution Online (PS&D). In United States Department of Agriculture Production Commodity Data; USDA: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.U.; Singh, Z.; Shah, H.M.S.; Kaur, J.; Woodward, A. Water Loss: A Postharvest Quality Marker in Apple Storage. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 17, 2155–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabska, J.; Beć, K.B.; Ueno, N.; Huck, C.W. Analyzing the Quality Parameters of Apples by Spectroscopy from Vis/NIR to NIR Region: A Comprehensive Review. Foods 2023, 12, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Fan, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhan, C.; Qing, R.; Li, K.; Kang, Z. Combining hyperspectral imaging technology and visible-near infrared spectroscopy with a data fusion strategy for the detection of soluble solids content in apples. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 137, 106996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathizadeh, Z.; Aboonajmi, M.; Beygi, S.R.H. Nondestructive firmness prediction of apple fruit using acoustic vibration response. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 262, 109073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempelaere, A.; Van Doorselaer, L.; He, J.; Verboven, P.; Nicolai, B.M. BraeNet: Internal disorder detection in ‘Braeburn’ apple using X-ray imaging data. Food Control 2024, 155, 110092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Jayan, H.; Majeed, U.; Ashiagbor, K.; Jiang, S.; Zou, X. Multi-sensor fusion and deep learning for batch monitoring and real-time warning of apple spoilage. Food Control 2025, 172, 111174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagüe, M.C.; Zhang, X.; Volpatti, M.; Wei, Y.; Lebedev, G.; Gamby, J.; Barakat, A.I. Noninvasive real-time monitoring of cellular spatiotemporal dynamics via machine learning–enhanced electrical impedance spectroscopy. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eadx4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazanas, A.C.; Prodromidis, M.I. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy—A Tutorial. ACS Meas. Sci. Au 2023, 3, 162–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, D.; Ramanathan, T.; Machado, D.; Sundararajan, R. Electrical impedance spectroscopy study of biological tissues. J. Electrost. 2008, 66, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Wahid, K.A.; Dinh, A.V.; Bhowmik, P. Model of dehydration and assessment of moisture content on onion using EIS. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 2814–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, G.; Rungraeng, N.; Han, J.H.; Jun, S. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy as an Alternative to Determine Dielectric Constant of Potatoes at Various Moisture Contents. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, E195–E201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, Y.; Mizutani, K.; Wakatsuki, N. Electrical impedance analysis of potato tissues during drying. J. Food Eng. 2014, 121, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fang, Q.; Zheng, S.; Cosic, I.; Cao, P. Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy Investigation on Cucumber Dehydration. Acta Hortic. 2008, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y.; Maeda, Y.; Mizutani, K.; Wakatsuki, N.; Hagiwara, S.; Nabetani, H. Effect of air-dehydration pretreatment before freezing on the electrical impedance characteristics and texture of carrots. J. Food Eng. 2016, 169, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, S.; Prasad, K. Nondestructive Evaluation of Moisture Content for Spinach Leaf Powder Using Complex Impedance Spectroscopy. J. ASABE 2023, 66, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, L.K.R.; dos Santos, I.T.C.; da Silva, B.D.L.; dos Anjos, V.C.; Bell, M.J.V.; Nascimento, W. Electrical characterization of milk samples by Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS). Quarks Braz. Electron. J. Phys. Chem. Mater. Sci. 2022, 4, e022003. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, C.; Machado, J.T.; Lopes, A.M.; Vieira, E.; Delerue-Matos, C. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy characterization of beverages. Food Chem. 2020, 302, 125345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossi, M.; Parolin, C.; Vitali, B.; Riccò, B. Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) characterization of saline solutions with a low-cost portable measurement system. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2019, 22, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Bera, T.K.; Ghoshal, D.; Chakraborty, B. Electrical Impedance Variations in Banana Ripening: An Analytical Study with Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy. J. Food Process Eng. 2016, 40, 12387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Singh, P.; Bera, T.K.; Ghoshal, D.; Chakraborty, B. Electrical impedance spectroscopic study of mandarin orange during ripening. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 1654–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, A.F.; Olivier, N.C.; Cordeiro, E.R.; de Oliveira, H.P. Determination of mango ripening degree by electrical impedance spectroscopy. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 143, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Wahid, K.; Dinh, A. Assessment of Ripening Degree of Avocado by Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy and Support Vector Machine. J. Food Qual. 2018, 2018, 4706147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Wei, X.; Sun, H. Maturity assessment of tomato fruit based on electrical impedance spectroscopy. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2019, 12, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Shekhar, S.; Kumar, P.; Prasad, K. Image analysis as a non-destructive approach in selective characterization of promising Indian chickpea cultivars. Biol. Life Sci. Forum. 2021, 6, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.; Vairagar, P.; Bera, M. Temperature dependent hydration kinetics of Cicer arietinum splits. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Rockville, MD, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ranganna, S. Handbook of Analysis and Quality Control for Fruit and Vegetable Products; Tata McGraw-Hill Education: Noida, India, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Shekhar, S.; Prasad, K. Impedance Analyser Fixture for Testing Electrical Properties of Solid, Liquid, and Powder Materials. GB Patent 6,420,816, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, T.; Ando, Y.; Orikasa, T.; Kasai, S.; Shiina, T. Electrical impedance estimation for apple fruit tissues during storage using Cole–Cole plots. J. Food Eng. 2018, 221, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Orikasa, T.; Shono, H.; Koide, S.; Ando, Y.; Shiina, T.; Tagawa, A. The influence of inhibit avoid water defect responses by heat pretreatment on hot air drying rate of spinach. J. Food Eng. 2016, 168, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, K.S. Permeability and Impermeability of Cell Membranes for Ions. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1940, 8, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, R.I.; Moyse, C.A.; Calder, F.W.; Crawford, D.P.; Fensom, D.S. Electrical Impedance Studies on Potato and Alfalfa Tissue. J. Exp. Bot. 1969, 20, 177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.I.N.; Willison, J.H.M. Electrical Impedance Analysis in Plant Tissues8. J. Exp. Bot. 1993, 44, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibba, P.; Falco, A.; Abera, B.D.; Cantarella, G.; Petti, L.; Lugli, P. Bio-impedance and circuit parameters: An analysis for tracking fruit ripening. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 159, 110978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheiralipour, K.; Tabatabaeefar, A.; Mobli, H.; Rafiee, S.; Sharifi, M.; Jafari, A.; Rajabipour, A. Some physical and hydrodynamic properties of two varieties of apple [Malus domestica Borkh L.]. Int. Agrophysics 2008, 22, 225–229. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Gao, H.; Zhao, L.; Liao, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, Z.; Hu, X. Chemical compositional characterization of some apple cultivars. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzanski, B.; Rybczynski, R. Colour change of apple as a result of storage, shelf-life, and bruising. Int. Agrophysics 2002, 16, 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- Motshakeri, M.; Sharma, M.; Phillips, A.R.J.; Kilmartin, P.A. Electrochemical Methods for the Analysis of Milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 2427–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, C.M.A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy in the Characterisation and Application of Modified Electrodes for Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors. Molecules 2022, 27, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allagui, A.; Benaoum, H.; Olendski, O. On the Gouy–Chapman–Stern model of the electrical double-layer structure with a generalized Boltzmann factor. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2021, 582, 126252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M. Importance of impedance spectroscopy technique in materials characterization: A brief review. Mech. Mater. Sci. Eng. MMSE J. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Rout, S.K.; Bera, J. Grain and Grain-Boundary Study of Acceptor Doped SrTiO3 Ceramics Using Impedance Spectroscopy. Ferroelectrics 2005, 323, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschuk, N.O.; Easton, E.B.; Zenkina, O.V. Reducing the resistance for the use of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analysis in materials chemistry. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 27925–27936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bera, T.K.; Bera, S.; Chowdhury, A.; Ghoshal, D.; Chakraborty, B. Electrical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) based fruit characterization: A technical review. In Computer, Communication and Electrical Technology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 279–288. [Google Scholar]
- Ikyumbur, J.T.; McAsule, A.A.; Akiiga, N.S.; Andrawus, Z.E.; Kungur, S.T. The Analysis of Dielectric Constant, Loss Factor and Q-Factor of Selected Fruits at Microwave Frequency Range. J. Sci. Res. Rep. 2020, 26, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juansah, J.; Budiastra, I.W.; Dahlan, K.; Seminar, K.B. Electrical properties of garut citrus fruits at low alternating current signal and its correlation with physicochemical properties during maturation. Int. J. Food Prop. 2014, 17, 1498–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, M.; Zhou, W.; Chen, Z. Radio-frequency dielectric relaxation behavior of selected vegetable tissues: Spectra analysis with logarithmic derivative method and simulation with double-shell model. J. Food Eng. 2020, 277, 109914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafarski, M.; Wilczek, A.; Szypłowska, A.; Lewandowski, A.; Pieczywek, P.; Janik, G.; Skierucha, W. Evaluation of apple maturity with two types of dielectric probes. Sensors 2018, 18, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, J.; Kumar, S.; Kaur, S.; Malhi, P.S.; Kumar, Y.; Singh, M.; Singh, A. Study of the magnetic, electrical and magneto-dielectric properties and dielectric relaxation in 0.8BiFeO3-0.2Ba0·8Sr0·2TiO3 solid solution. Solid State Sci. 2020, 103, 106193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafé, S.; Manzanares, J.A.; Ramirez, P. Modeling of surface vs. bulk ionic conductivity in fixed charge membranes. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2003, 5, 376–383. [Google Scholar]
- Tıraş, B.; Dede, S.; Altay, F. Dielectric properties of foods. J. Agric. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 7, 1805–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainardi, F.; Barelli, E. Dielectric Relaxation in Biological Materials. In Scuola di Scienze; Alma Mater Studiorum Universita di Bologna: Bologna, Italy, 2015; p. 101. [Google Scholar]
- Havriliak, S.; Negami, S. A complex plane analysis of α-dispersions in some polymer systems. J. Polym. Sci. Part C Polym. Symp. 2007, 14, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhao, C.Z.; Werner, M.; Taylor, S.; Chalker, P. Dielectric relaxation of high-k oxides. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Arora, M.; Sharma, L.; Kumar, S.; Malhi, P.S.; Singh, M.; Singh, A. Hopping Mechanism and Impedance Properties of Mg Doped NBT-KBT Solid Solution near Ambient Temperature. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2022, 11, 103010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, J.R. Impedance spectroscopy. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 1992, 20, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenari, H.M.; Golzan, M.; Sedghi, H.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Talebian, M. Frequency dependence of dielectric properties and electrical conductivity of Cu/nano-SnO2 thick film/Cu arrangement. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2011, 11, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, R. General susceptibility functions for relaxations in disordered systems. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 88, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, V.; Choudhary, S.; Sinha, T. Dielectric relaxation in complex perovskite oxide BaCo1/2W1/2O3. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2008, 403, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonscher, A.K. The ‘universal’ dielectric response. Nature 1977, 267, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, S.; Bhuyan, S.; Choudhary, R. Structural, dielectric and electrical characteristics of lead-free electro-ceramic:Bi(Ni2/3Ta1/3)O3. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2019, 22, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K. Advances in Nondestructive Quality Measurement of Fruits and Vegetables. Postharvest Biol. Technol. Hortic. Crops Princ. Pract. Qual. Maint. 2015, 51, 51–87. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X. Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy Applied in Plant Physiology Studies. Master’s Thesis, RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia, 2024; p. 102. [Google Scholar]


| Physical Property | Red Delicious |
|---|---|
| Length (cm) | 7.53 ± 0.64 |
| Width (cm) | 7.53 ± 0.55 |
| Thickness (cm) | 8.37 ± 0.45 |
| Geometric mean diameter (Dg) cm | 7.87 ± 0.56 |
| Equivalent Diameter (Dp) cm | 7.88 ± 0.67 |
| Arithmetic diameter (Da) cm | 7.88 ± 0.87 |
| Surface Area (S) cm2 | 196 ± 28 |
| Sphericity (Sp) % | 1.03 ± 0.02 |
| Aspect Ratio (Ra) | 1.05 ± 0.07 |
| Mass of fruit (g) | 233 ± 33 |
| Volume (mL) | 266 ± 43 |
| Density (kg/m3) | 879 ± 34 |
| Bulk Density (kg/m3) | 645 ± 90 |
| Porosity (%) | 26 ± 11 |
| Packaging coefficient (v/v) | 0.74 ± 0.14 |
| Coefficient of static friction on: | |
| Glass | 0.70 ± 0.02 |
| Steel | 0.49 ± 0.04 |
| Plywood with Grains perpendicular | 0.46 ± 0.05 |
| Plywood with grains parallel. | 0.46 ± 0.02 |
| Moisture, % w.b | 84.00 ± 1.40 |
| TSS, (°B) | 14.58 ± 0.28 |
| TA, (%) | 0.64 ± 0.02 |
| pH | 4.81 ± 0.25 |
| Vitamin C (mg/100 g) | 12.30 ± 3.13 |
| Brix: Acid ratio | 22.64 ± 0.16 |
| Optical parameters | |
| L* | 32 ± 8 |
| a* | 43 ± 6 |
| b* | 21 ± 4 |
| R-C Circuit | Resistance (Ohm) | Capacitance (F) | Warburg Element (Ohm∙s−1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17.84 | 2.343 × 10−9 | - |
| 2 | 240.8 | 23.39 × 10−6 | - |
| 3 | 43.33 | 0.491 × 10−6 | - |
| 4 | 176.2 | 4.713 × 10−6 | 11,693 |
| 0.668 × 10−6 |
| Model Parameters | Harvrialiak–Negami Relaxation Model |
|---|---|
| ε* | |
| τ | 0.024 |
| α | 0.892 |
| Model Parameters | John’s Power Law |
|---|---|
| σdc | 0.016 |
| n | 0.627 |
| Statistical Parameters | Cole Model | Hyden Model | Double-Shell Model | P. Ibba et al. [35] | Proposed Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 11.481 | 10.080 | 7.433 | 6.852 | 6.610 |
| NMSE | 0.103 | 0.091 | 0.067 | 0.062 | 0.059 |
| MSE | 131.824 | 101.616 | 55.254 | 46.950 | 43.696 |
| NRMSE | 1.184 | 0.913 | 0.496 | 0.422 | 0.392 |
| MPE | 0.059 | 0.055 | 0.044 | 0.052 | 0.025 |
| AAD | 7.169 | 6.572 | 5.183 | 4.914 | 2.857 |
| R | 0.9906 | 0.9939 | 0.9958 | 0.9972 | 0.9973 |
| R2 | 0.9813 | 0.9879 | 0.9917 | 0.9944 | 0.9946 |
| Adj. R2 | 0.9809 | 0.9876 | 0.9915 | 0.9943 | 0.9945 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shekhar, S.; Trujillo, F.J.; Kaur, S.; Prasad, K. Elucidation of Electrical Characteristics for Apples (Malus domestica) Using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. NDT 2025, 3, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ndt3040025
Shekhar S, Trujillo FJ, Kaur S, Prasad K. Elucidation of Electrical Characteristics for Apples (Malus domestica) Using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. NDT. 2025; 3(4):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ndt3040025
Chicago/Turabian StyleShekhar, Shubhra, Francisco J. Trujillo, Shubhpreet Kaur, and Kamlesh Prasad. 2025. "Elucidation of Electrical Characteristics for Apples (Malus domestica) Using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy" NDT 3, no. 4: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ndt3040025
APA StyleShekhar, S., Trujillo, F. J., Kaur, S., & Prasad, K. (2025). Elucidation of Electrical Characteristics for Apples (Malus domestica) Using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. NDT, 3(4), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ndt3040025








