Artificial Intelligence for Forensic Image Analysis in Bullet Hole Comparison: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Non-Destructive Testing in Forensic Ballistics
2.1.1. Forensic Ballistics
- Internal ballistics investigates the phenomena that occur internally within the firearm.
- Intermediate ballistics (or transition ballistics) investigates the phenomena and behavior of the projectile, influenced by the gases remaining from the shot, immediately after leaving the gun barrel.
- External ballistics investigates the behavior of the bullet as it travels through the air in the distance between the weapon and the target surface of the shot.
- Terminal ballistics investigates the phenomena, behavior, and effects of the bullet as it collides with and pierces the target surface of the shot.
2.1.2. Evidence Collection in Forensic Science
2.1.3. Relevance
2.1.4. Guidelines for Carrying out Non-Destructive Testing
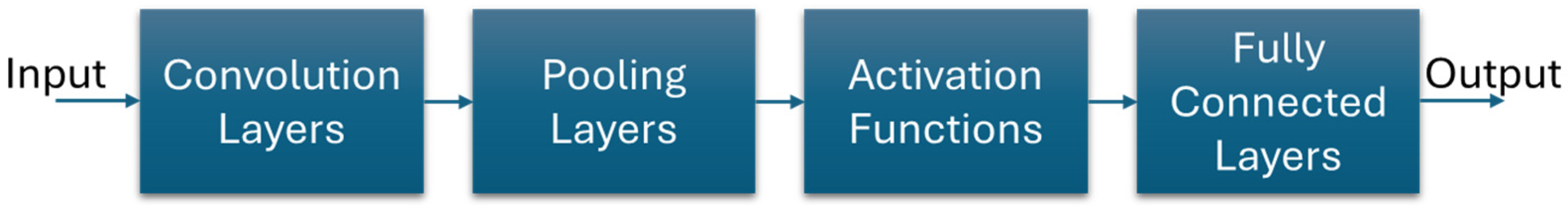
2.2. Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks
Structural Overview of Convolutional Neural Networks
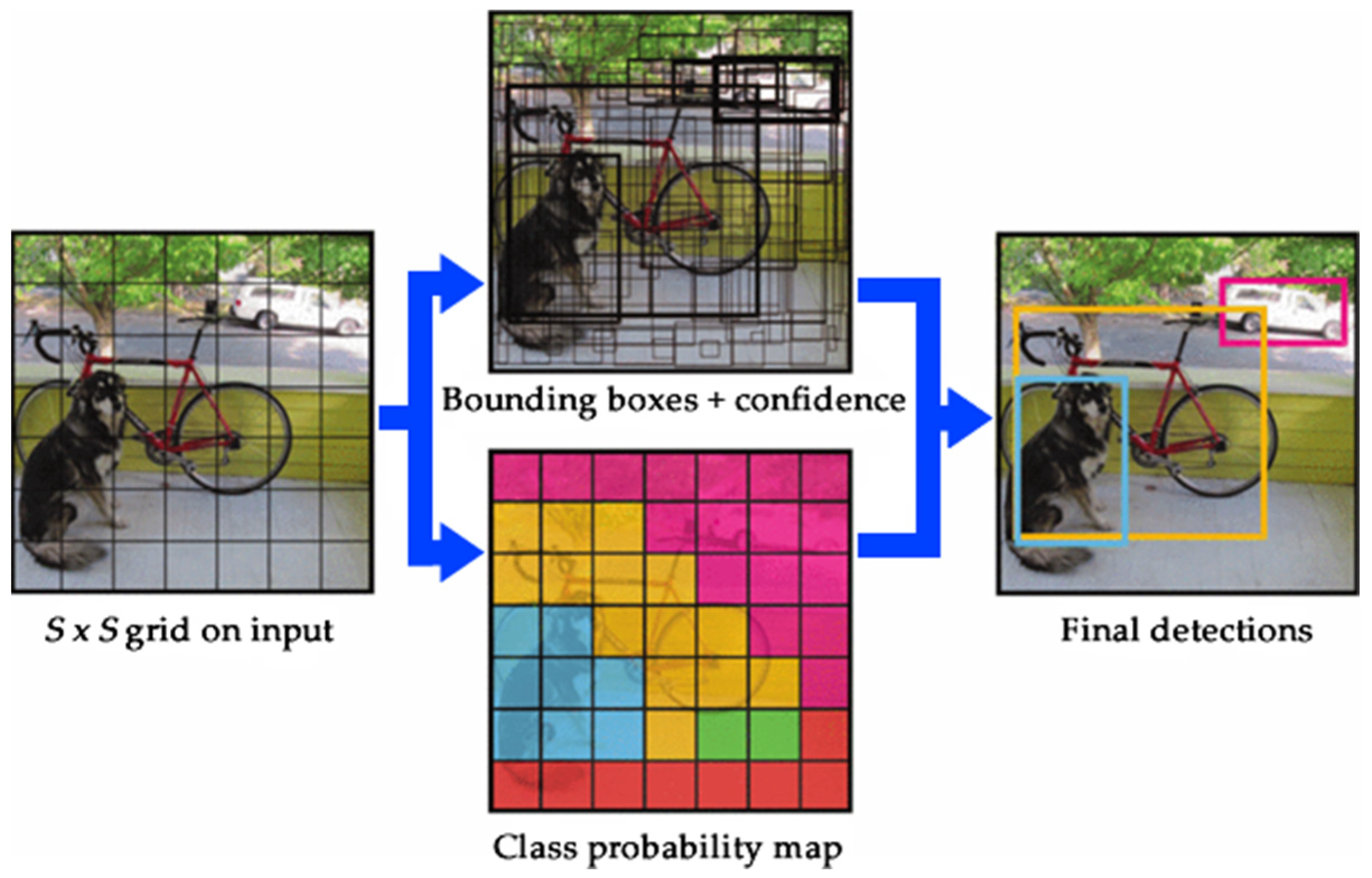
2.3. The YOLO (You Only Look Once) Algorithm
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.1.1. Forensic Equipment and Techniques for Creating Datasets
3.1.2. Datasets
3.2. Methods
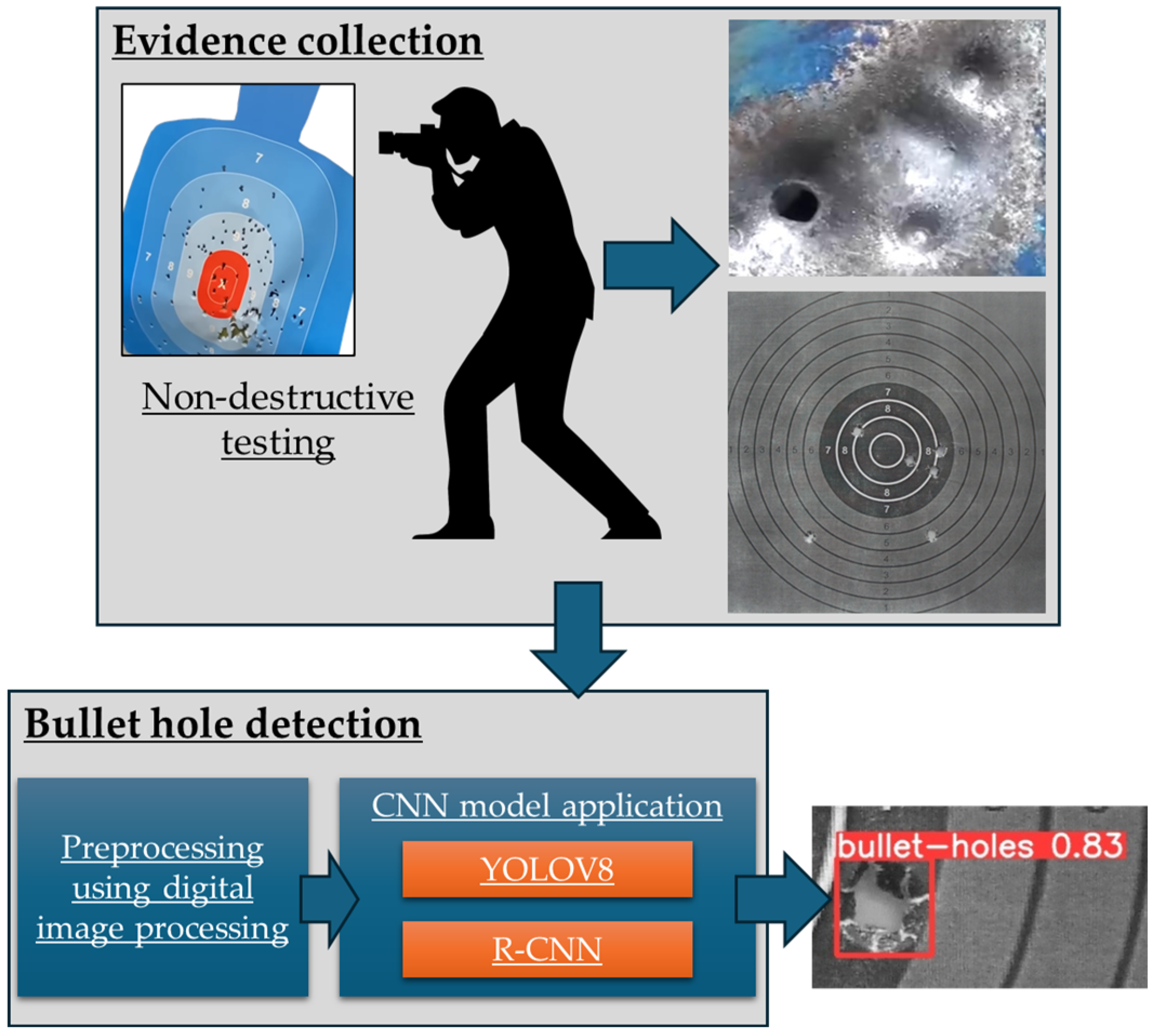
3.2.1. Evidence Collection
3.2.2. Bullet Hole Detection
Image Fetch and Preprocessing Using Digital Image Processing
CNN Model Application
3.2.3. Border Between the Parts of This Study
Mann–Whitney U Test
Kruskal–Wallis H Test
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.; An, C.; Yang, Y. Wind Turbine Surface Defect Detection Method Based on YOLOv5s-L. NDT 2023, 1, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armeni, A.; Loizos, A. Reporting the Bearing Capacity of Airfield Pavements Using PCR Index. NDT 2024, 2, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrin, P.; Fornasari, G.; Rizzo, E. Review of Ground Penetrating Radar Applications for Bridge Infrastructures. NDT 2024, 2, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, J.A.; Mirakovits, K. Forensic Science: The Basics, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; ISBN 9780367251499. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, R.M. Conceptualising Forensic Science and Forensic Reconstruction. Part I: A Conceptual Model. Sci. Justice 2017, 57, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations Office on Drugs. Crime Scene and Physical Evidence Awareness for Non-Forensic Personnel; United Nations Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferli, P. Forensic Evidence Field Guide: A Collection of Best Practices; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-0124201989. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, A.; Jamal, F.; Shikha; Ramesh, A.; Sojan, A.; Dileep, D. Collection, Preservation, and Packaging: Forensic Evidence Management. In Crime Scene Management Within Forensic Science; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 51–105. [Google Scholar]
- F.B.I. Laboratory Division. Handbook of Forensic Services; US Department of Justice, Federal Bureau of Investigation: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Federal Bureau of Investigation; Fish, J. FBI Handbook of Crime Scene Forensics: The Authoritative Guide to Navigating Crime Scenes; Fish, J., Ed.; Simon and Schuster: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; ISBN 9781632203229. [Google Scholar]
- Saferstein, R. Forensic Science: From the Crime Scene to the Crime Lab; Pearson Education Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; ISBN 9780131391871. [Google Scholar]
- Silva-Rivera, U.S.; Zúñiga-Avilés, L.A.; Vilchis-González, A.H.; Tamayo-Meza, P.A.; Wong-Angel, W.D. Internal Ballistics of Polygonal and Grooved Barrels: A Comparative Study. Sci. Prog. 2021, 104, 003685042110169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Mukherjee, D.; Moza, B. A Comprehensive Review of Wound Ballistics: Mechanisms, Effects, and Advancements. Int. J. Med. Toxicol. Leg. Med. 2023, 26, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berryman, H.E.; Smith, O.C.; Symes, S.A. Diameter of Cranial Gunshot Wounds as a Function of Bullet Caliber. J. Forensic Sci. 1995, 40, 751–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.H. Caliber Estimation from Cranial Entrance Defect Measurements. J. Forensic Sci. 1996, 41, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoso, R.I.; Freire, A.R.; Santos, L.S.D.M.; Daruge Junior, E.; Rossi, A.C.; Prado, F.B. Comparison of Gunshot Entrance Morphologies Caused by .40-Caliber Smith & Wesson, .380-Caliber, and 9-Mm Luger Bullets: A Finite Element Analysis Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pircher, R.; Preiß, D.; Pollak, S.; Thierauf-Emberger, A.; Perdekamp, M.G.; Geisenberger, D. The Influence of the Bullet Shape on the Width of Abrasion Collars and the Size of Gunshot Entrance Holes. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2017, 131, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Z. Determining Entrance-Exit Gunshot Holes on Skulls: A Real Time and In Situ Measurement Method. J. Forensic Pathol. 2018, 3, 113. [Google Scholar]
- Henwood, B.J.; Oost, T.S.; Fairgrieve, S.I. Bullet Caliber and Type Categorization from Gunshot Wounds in Sus Scrofa (Linnaeus) Long Bone. J. Forensic Sci. 2019, 64, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.K.; Walia, M.; Kaur Purba, M.; Sharma, Y.; Ahmad Beig, M.T. Understanding the Influence of 0.22 Caliber Bullets on Different Types of Clothing Materials for The Estimation of Possible Caliber of Projectile. Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol. 2021, 69, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Malik, S.A.; Nordin, F.A.; Mohd Ali, S.F.; Lim Abdullah, A.F.; Chang, K.H. Distinctive Bullet Impact Holes by 9-Mm Caliber Projectile on Sheet Metal Surfaces. J. Forensic Sci. Med. 2022, 8, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisenberger, D.; Große Perdekamp, M.; Pollak, S.; Thierauf-Emberger, A.; Thoma, V. Differing Sizes of Bullet Entrance Holes in Skin of the Anterior and Posterior Trunk. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2022, 136, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, S.; Pérez de los Ríos, M. Assessment of Bullet Holes through the Analysis of Mushroom-Shaped Morphology in Synthetic Fibres: Analysis of Six Cases. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2021, 135, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishshanka, B.; Shepherd, C.; Ariyarathna, R. AK Bullet (7.62 × 39 Mm) Holes on 1-mm Sheet Metal: A Forensic-related Study in Aid of Bullet Trajectory Reconstruction. J. Forensic Sci. 2021, 66, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.; Ali, A.; Ahmad, A.; Shehzad, M.; Malik, A. Forensic Investigation of Bullet Holes for Determining Distance from Glass Fracture Analysis. Austin J. Forensic Sci. Criminol. 2021, 8, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eksinitkun, G.; Phungyimnoi, N.; Poogun, S. The Analysis of the Perforation of the Bullet 11 Mm. on the Metal Sheet. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Songkhla, Thailand, 6–7 June 2019; Volume 1380, p. 012085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, N.; Harshey, A.; Das, T.; Abhyankar, S.; Yadav, V.K.; Nigam, K.; Anand, V.R.; Srivastava, A. Evidential Significance of Multiple Fracture Patterns on the Glass in Forensic Ballistics. Egypt. J. Forensic Sci. 2019, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NE, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Naddaf-Sh, A.-M.; Baburao, V.S.; Zargarzadeh, H. Automated Weld Defect Detection in Industrial Ultrasonic B-Scan Images Using Deep Learning. NDT 2024, 2, 108–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, E.; Giacchetta, R.; Gonzalez, R.; Sanchez, D.; Sanchez-Sobrado, O.; Torre-Poza, A.; Cosarinsky, G.; Coelho, W. Ultrasonic Non-Contact Air-Coupled Technique for the Assessment of Composite Sandwich Plates Using Antisymmetric Lamb Waves. NDT 2023, 1, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardim, G.P.; Dias, M.A.; Noguti, R.H.; De Best, R.; da Silva, E.A. Mathematical Morphology Applied to Automation of Indoor Shooting Ranges. Int. J. Appl. Math. (Sofia) 2014, 27, 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, J.D. Deep Learning; The MIT Press Essential Knowledge Series; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; ISBN 9780262537551. [Google Scholar]
- Shinde, P.P.; Shah, S. A Review of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 Fourth International Conference on Computing Communication Control and Automation (ICCUBEA), Pune, India, 16–18 August 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, S.J.; Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 3rd ed.; Pearson: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep Learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieres, J.; Schemmel, J.; Meier, K. Training Convolutional Networks of Threshold Neurons Suited for Low-Power Hardware Implementation. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Network Proceedings, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 16–21 July 2006; pp. 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Arel, I.; Rose, D.C.; Karnowski, T.P. Deep Machine Learning—A New Frontier in Artificial Intelligence Research [Research Frontier]. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2010, 5, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tivive, F.H.C.; Bouzerdoum, A. Efficient Training Algorithms for a Class of Shunting Inhibitory Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2005, 16, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavarani, S.; Ibarra-Castanedo, C.; Lopez, F.; Maldague, X.P.V. Deep Learning-Based Superpixel Texture Analysis for Crack Detection in Multi-Modal Infrastructure Images. NDT 2024, 2, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.B.; Cheon, S.; Kim, C.O. A Convolutional Neural Network for Fault Classification and Diagnosis in Semiconductor Manufacturing Processes. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2017, 30, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, S.; Giles, C.L.; Tsoi, A.C.; Back, A.D. Face Recognition: A Convolutional Neural-Network Approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1997, 8, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebauer, C. Evaluation of Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1998, 9, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Shi, Z.; Zou, Z. Maritime Semantic Labeling of Optical Remote Sensing Images with Multi-Scale Fully Convolutional Network. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y.-Q. Polarimetric SAR Image Classification Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1935–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felzenszwalb, P.F.; Girshick, R.B.; McAllester, D.; Ramanan, D. Object Detection with Discriminatively Trained Part-Based Models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 1627–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich Feature Hierarchies for Accurate Object Detection and Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 24–27 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Staggs, S. Crime Scene and Evidence Photography, 2nd ed.; Staggs Publishing: Wildomar, CA, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1933373072. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, S. Handbook of Forensic Photography; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; ISBN 9781003047964. [Google Scholar]
- Barbaro, A.; Mishra, A. Manual of Crime Scene Investigation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; ISBN 9781003129554. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Wu, G.; Barth, M.J. Feature Corrective Transfer Learning: End-to-End Solutions to Object Detection in Non-Ideal Visual Conditions. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Etezadifar, M.; Karimi, H.; Aghdam, A.G.; Mahseredjian, J. Resilient Event Detection Algorithm for Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring Under Non-Ideal Conditions Using Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, M.; Fan, R.; Li, Y. Parametric Model-based Deinterleaving of Radar Signals with Non-ideal Observations via Maximum Likelihood Solution. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2022, 16, 1253–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, L.; Busso, C. AuxFormer: Robust Approach to Audiovisual Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 7357–7361. [Google Scholar]
- Bodla, N.; Singh, B.; Chellappa, R.; Davis, L.S. Soft-NMS—Improving Object Detection with One Line of Code. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 5561–5569. [Google Scholar]
- Jaccard, P. The Distribution of the Flora in the Alpine Zone. New Phytol. 1912, 11, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, N.; Keich, U. Reliability and Efficiency of Algorithms for Computing the Significance of the Mann–Whitney Test. Comput. Stat. 2009, 24, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divine, G.W.; Norton, H.J.; Barón, A.E.; Juarez-Colunga, E. The Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney Procedure Fails as a Test of Medians. Am. Stat. 2018, 72, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B.; Whitney, D.R. On a Test of Whether One of Two Random Variables Is Stochastically Larger than the Other. Ann. Math. Stat. 1947, 18, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargha, A.; Delaney, H.D. The Kruskal-Wallis Test and Stochastic Homogeneity. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 1998, 23, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurrier, J.D. On the Null Distribution of the Kruskal–Wallis Statistic. J. Nonparametr. Stat. 2003, 15, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Lee, J.W.; Huh, M.-H.; Kang, S.-H. An Algorithm for Computing the Exact Distribution of the Kruskal–Wallis Test. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 2003, 32, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of Ranks in One-Criterion Variance Analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafi, M.M.; Chakma, S.; Mahmud, A.; Rozario, R.X.; Munna, R.U.; Wohra, M.A.A.; Joy, R.H.; Mahmud, K.R.; Paul, B. Performance Analysis of Deep Learning YOLO Models for South Asian Regional Vehicle Recognition. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2022, 13, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.; Glas, N.; Monsuur, J.; Stoop, R.; de Keijzer, A. Application of YOLOv8 and Detectron2 for Bullet Hole Detection and Score Calculation from Shooting Cards. AI 2023, 5, 72–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W.; Yang, L. Bullet Hole Detection Using Series Faster-RCNN and Video Analysis. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Machine Vision (ICMV 2018), Munich, Germany, 1–3 November 2018; pp. 190–197. [Google Scholar]
- Vilchez, R.F.; Mauricio, D. Bullet Impact Detection in Silhouettes Using Mask R-CNN. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 129542–129552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widayaka, P.D.; Kusuma, H.; Attamimi, M. Automatic Shooting Scoring System Based on Image Processing. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 29–30 January 2019; Volume 1201, p. 012047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
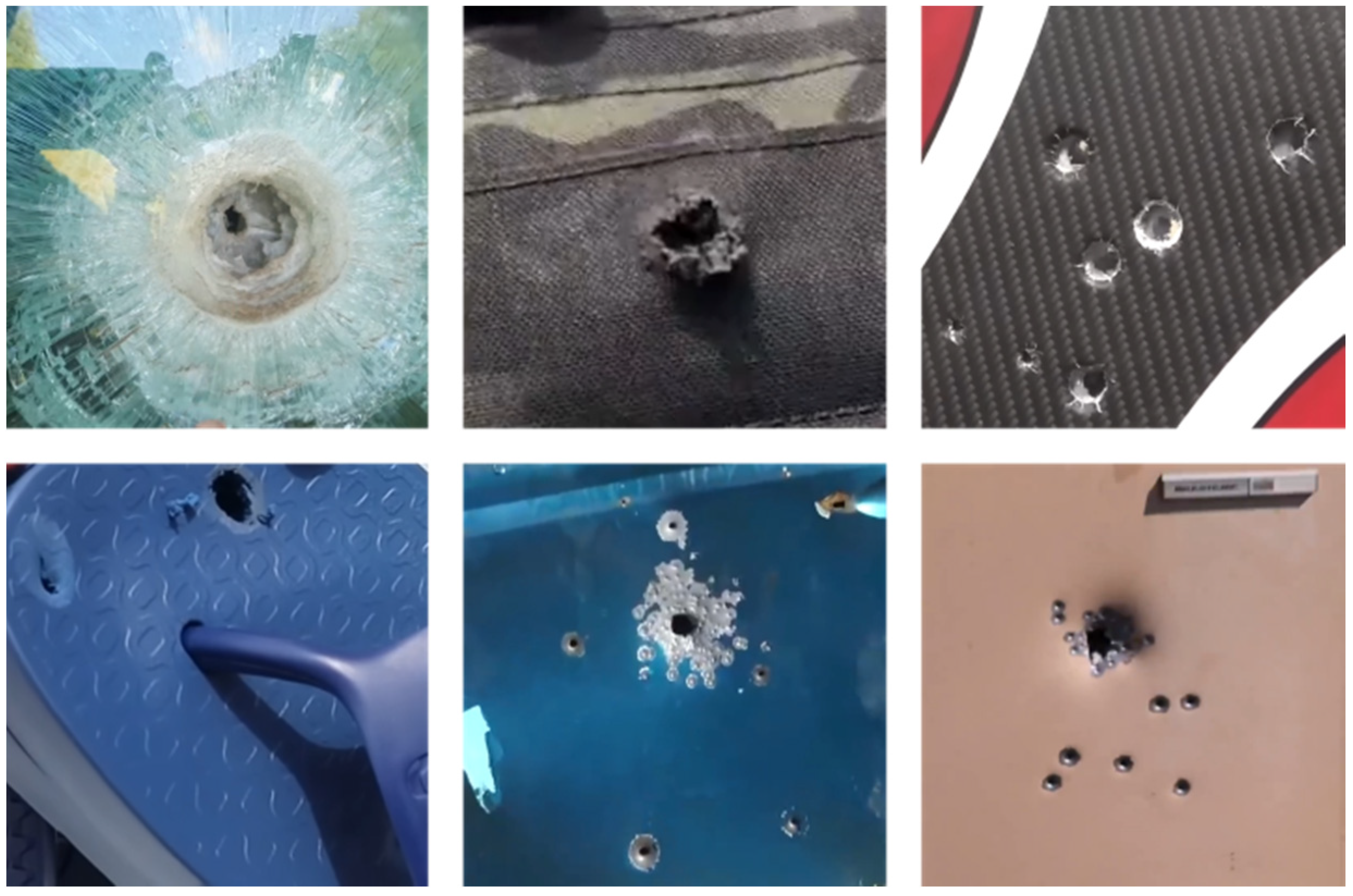







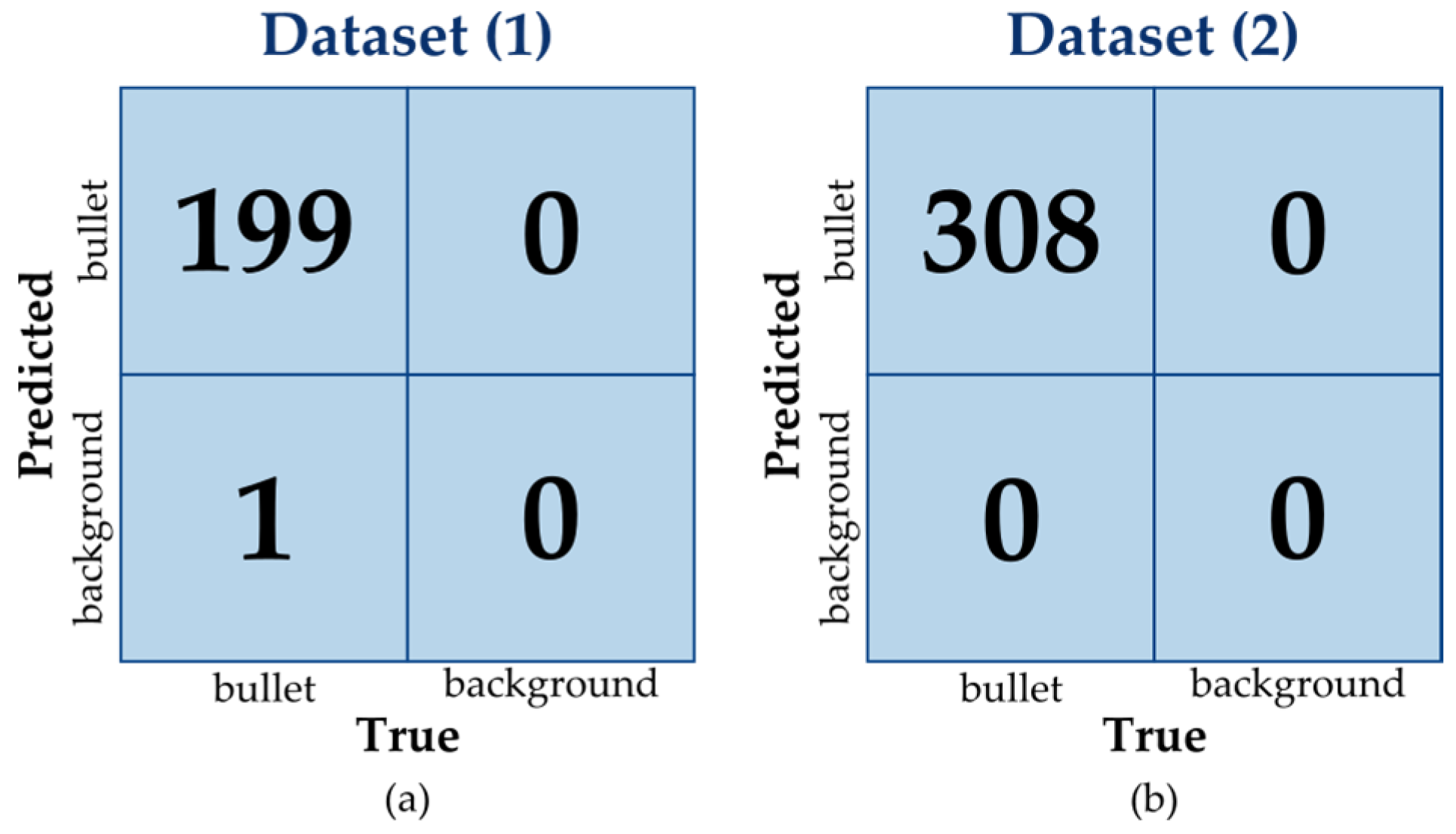

| Metric | Dataset (1) | Dataset (2) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train | Val. | Test | Gen. | Train | Val. | Test | Gen. | ||
| YOLOV8 | Accuracy | 0.995 | 0.983 | 1.000 | 0.993 | 1.000 | 0.459 | 0.463 | 0.759 |
| Precision | 1.000 | 0.983 | 1.000 | 0.997 | 1.000 | 0.873 | 0.926 | 0.966 | |
| Recall | 0.995 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.997 | 1.000 | 0.492 | 0.481 | 0.780 | |
| F1 score | 0.997 | 0.992 | 1.000 | 0.997 | 1.000 | 0.629 | 0.633 | 0.863 | |
| R-CNN | Accuracy | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.848 | 0.385 | 0.500 | 0.651 |
| Precision | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.848 | 0.640 | 0.660 | 0.778 | |
| Recall | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.492 | 0.673 | 0.799 | |
| F1 score | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.918 | 0.556 | 0.667 | 0.788 | |
| Authors | Model | Accuracy | Precision |
|---|---|---|---|
| The experiments performed on Dataset (1) | YOLOV8 | 0.993 | 0.997 |
| R-CNN | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| The experiments performed on Dataset (2) | YOLOV8 | 0.759 | 0.966 |
| R-CNN | 0.651 | 0.778 | |
| Butt et al. [65] | YOLOV8n | - | 0.921 |
| YOLOV8s | - | 0.947 | |
| YOLOV8m | - | 0.937 | |
| Du et al. [66] | Faster R-CNN | - | 0.632 |
| Series Network | - | 0.835 | |
| Vilchez and Mauricio [67] | R-CNN | 0.976 | 0.995 |
| Widayaka et al. [68] | Image Processing | 0.910 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cardim, G.P.; de Souza Duarte, T.; Cardim, H.P.; Casaca, W.; Negri, R.G.; Cabrera, F.C.; Santos, R.J.d.; da Silva, E.A.; Dias, M.A. Artificial Intelligence for Forensic Image Analysis in Bullet Hole Comparison: A Preliminary Study. NDT 2025, 3, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ndt3030016
Cardim GP, de Souza Duarte T, Cardim HP, Casaca W, Negri RG, Cabrera FC, Santos RJd, da Silva EA, Dias MA. Artificial Intelligence for Forensic Image Analysis in Bullet Hole Comparison: A Preliminary Study. NDT. 2025; 3(3):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ndt3030016
Chicago/Turabian StyleCardim, Guilherme Pina, Thiago de Souza Duarte, Henrique Pina Cardim, Wallace Casaca, Rogério Galante Negri, Flávio Camargo Cabrera, Renivaldo José dos Santos, Erivaldo Antônio da Silva, and Mauricio Araujo Dias. 2025. "Artificial Intelligence for Forensic Image Analysis in Bullet Hole Comparison: A Preliminary Study" NDT 3, no. 3: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ndt3030016
APA StyleCardim, G. P., de Souza Duarte, T., Cardim, H. P., Casaca, W., Negri, R. G., Cabrera, F. C., Santos, R. J. d., da Silva, E. A., & Dias, M. A. (2025). Artificial Intelligence for Forensic Image Analysis in Bullet Hole Comparison: A Preliminary Study. NDT, 3(3), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ndt3030016









