Omics Description (Metabolome and Microbiome) from Centuroides suffusus and Centuroides vittatus (Arachnida: Scorpiones)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Scorpions Sample Collection
2.2. Metabolome Analysis
2.3. Microbiome Determination
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Metabolome
4.1.1. Amino Acid Profile
4.1.2. Differential Display from Acylcarnitines Between Centruroides
4.2. Microbiome
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beccaloni, J. Arachnids; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2009; p. 320. [Google Scholar]
- Polis, G.A. The Biology of Scorpions; Stanford University Press: Redwood City, CA, USA, 1990; p. 587. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hao, P.; Di, Z.; He, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yang, W.; Shen, Z.; He, X.; et al. The genome of Mesobuthus martensii reveals a unique adaptation model of arthropods. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhao, R.; Di, Z.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Hong, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, W.; Cao, Z. Molecular diversity of Chaerilidae venom peptides reveals the dynamic evolution of scorpion venom components from Buthidae to non-Buthidae. J. Proteom. 2013, 89, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.J.; Ellsworth, S.A.; Nystrom, G.S. A global accounting of medically significant scorpions: Epidemiology, major toxins, and comparative resources in harmless counterparts. Toxicon 2018, 151, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.S.; Silva, C.G.; Neto, B.S.; Grangeiro-Júnior, C.R.; Lopes, V.H.; Teixeira-Júnior, A.G.; Bezerra, D.A.; Luna, J.V.C.; Crdeiro, J.B.; Goncalves Junior, J.; et al. Clinical and epidemiological aspects of scorpionism in the world: A systematic review. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2016, 27, 504–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niermann, C.N.; Tate, T.G.; Suto, A.L.; Barajas, R.; White, H.A.; Guswiler, O.D.; Secor, S.M.; Rowe, A.H.; Rowe, M.P. Defensive venoms: Is pain sufficient for predator deterrence? Toxins 2020, 12, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santibáñez-López, C.E.; Aharon, S.; Ballesteros, J.A.; Gainett, G.; Baker, C.M.; González-Santillán, E.; Harvey, M.S.; Kassan, M.K.; Almaaty, A.H.A.; Aldeyarbi, S.M.; et al. Phylogenomics of scorpions reveal contemporaneous diversification of scorpion mammalian predators and mammal-active sodium channel toxins. Syst. Biol. 2022, 71, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce-Saavedra, J.; Linares-Guillén, J.W.; Quijano-Ravell, A.F. Una nueva especie de alacrán del género Centruroides Marx (Scorpiones: Buthidae) de la costa noroeste de México. Acta Zool. Mex. 2022, 38, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Saavedra, J.; Francke, O.F. Clave para la identificación de especies de alacranes del género Centruroides Marx 1890 (Scorpiones: Buthidae) en el centro occidente de México. Biológicas 2013, 15, 52–62. [Google Scholar]
- Kovařík, F.; Teruel, R.; Lowe, G. Two new scorpions of the genus Chaneke Francke, Teruel et Santibáñez-López, 2014 (Scorpiones: Buthidae) from southern Mexico. Euscorpius 2016, 218, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santibáñez-López, C.E.; Francke, O.F.; Ureta, C.; Possani, L.D. Scorpions from Mexico: From species diversity to venom complexity. Toxins 2016, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaño-Umbarila, L.; Gómez-Ramírez, I.V.; García-Arredondo, A.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, E.R.; Possani, L.D. Identification and molecular modeling of novel toxins from scorpion venom gland transcriptomes. Toxicon 2017, 138, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corzo, G.; Prochnicka-Chalufour, A.; García, B.I.; Possani, L.D.; Delepierre, M. Solution structure of Cn5, a crustacean toxin found in the venom of the scorpions Centruroides noxius and Centruroides suffusus suffusus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2009, 1794, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espino-Solis, G.; Estrada, P.; Olamendi-Portugal, G.; Villegas, T.; Zamudio, E.; Cestele, F.; Possani, L.; Corzo, G. Isolation and molecular cloning of beta-neurotoxins from the venom of the scorpion Centruroides suffusus suffusus. Toxicon 2011, 57, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Rhoads, D.; Pummill, J. The complete mitochondrial genome of the scorpion Centruroides vittatus (Arachnida: Scorpiones). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2017, 2, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, L.A.; Prendini, L. Island ancestors and new world biogeography: A case study from the scorpions (Buthidae: Centruroidinae). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Carmona, M.; Montaña-Lozano, P.; Quiroga, C.F.P.; Baeza, J.A. Comparative analysis of mitochondrial genomes reveals family-specific architectures and molecular features in scorpions (Arthropoda: Arachnida: Scorpiones). Gene 2023, 859, 147189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botana, L.M.; Hess, P.; Munday, R.; Nathalie, A.; DeGrasse, S.L.; Feeley, M.; Toshiyuki, S.; van den Berg, M.; Fattori, V.; Garrido Gamarro, E.; et al. Derivation of toxicity equivalency factors for marine biotoxins associated with Bivalve Molluscs. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 59, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, M.E.; Bernasconi, S. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals in human fetal growth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Park, A.; Gomez-Govea, M.A.; Lopez-Monroy, B.; Treviño-Alvarado, V.M.; Torres-Sepúlveda, M.D.R.; López-Uriarte, G.A.; Villanueva-Segura, O.K.; Ruiz-Herrera, M.d.C.; Martinez-Fierro, M.d.l.L.; Delgado-Enciso, I.; et al. Profiles of amino acids and acylcarnitines related with insecticide exposure in Culex quinquefasciatus (Say). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169514. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Sánchez, I.P.; Treviño-Alvarado, V.M.; Torres-Sepúlveda, M.D.R.; López-Saldaña, L.A.; Ponce-García, G.; López-Uriarte, G.A.; Ruiz-Herrera, M.d.C.; Zamora-Avila, D.E.; Villareal-Perez, J.; Davalos-Guillermo, G.; et al. Reference values for amino acids and acylcarnitines in peripheral blood in Quarter horses and American Miniature horses. Acta Vet. Scand. 2015, 57, 62. [Google Scholar]
- Abellan-Borja, A.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, I.P.; Carrera-Treviño, R.; Villanueva-Segura, O.K.; Zapata-Morin, P.A.; Martinez-de-Villareal, L.E.; Barboza-Aranda, L.J.; Gomez-Govea, M.A.; MArtinez-Fierro, M.L.; Delgado-Enciso, I.; et al. Free amino acid and acylcarnitine values in Ursus americanus Pallas 1780 (black bear) from Northeastern Mexico. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0272979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal-Pérez, J.Z.; Villarreal-Martínez, J.Z.; Lavalle-González, F.J.; Torres-Sepúlveda, M.D.R.; Ruiz-Herrera, C.; Cerda-Flores, R.M.; Castillo-Garcia, E.R.; Rostriguez-Sanchez, I.P.; Martinez de Villareal, L.E. Plasma and urine metabolic profiles are reflective of altered beta-oxidation in non-diabetic obese subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimwell, C.; Atkinson, L.; Graham, M.R.; Murdoch, B. A first molecular characterization of the scorpion telson microbiota of Hadrurus arizonensis and Smeringurus mesaensis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabezas-Cruz, A. Grand challenges in arachnid microbiota and diseases. Front. Arachnid Sci. 2023, 2, 1215831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2012; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods. 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glur, C. data.tree: To Manage Hierarchical Data and Tree Structures. R Package Version 1.0.0. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=data.tree (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Tennekes, M. treemap: Treemap Visualization. R Package Version 2.4-2. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=treemap (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Paradis, E.; Schliep, K. ape 5.0: An environment for modern phylogenetics and evolutionary analyses in R. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G. Data Integration, Manipulation and Visualization of Phylogenetic Trees; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. Available online: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Martins, J.C.S.; Assunção Romão, H.A.; Canettieri, C.K.; Cercilian, A.C.; Oliveira, P.R.O.; Ferreira, C.; Terra, W.R.; de Oliveira Dias, R. The loss of the urea cycle and ornithine metabolism in different insect orders: An omics approach. Insect Mol. Biol. 2025, 34, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeMoine, C.M.; Walsh, P.J. Evolution of urea transporters in vertebrates: Adaptation to urea’s multiple roles and metabolic sources. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218 Pt 12, 1936–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Foderaro, T.; Kramer, L.; Markley, A.L.; Lee, J.; Traylor, M.J.; Fox, J.M. Evolution-guided biosynthesis of terpenoid inhibitors. ACS Synth. Biol. 2022, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElroy, T.; McReynolds, C.N.; Gulledge, A.; Knight, K.R.; Smith, W.E.; Albrecht, E.A. Differential toxicity and venom gland gene expression in Centruroides vittatus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Aardt, W.J.; le Roux, J.M.; Lindeque, J.Z.; Mason, S.; Louw, R. The effect of temperature on the respiration and metabolism of the African burrowing scorpion (Opistophthalmus latimanus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D Genom. Proteom. 2016, 20, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J. Venomous animals: Clinical toxinology. EXS 2010, 100, 233–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, U.C.; Nishiyama, M.Y., Jr.; Dos Santos, M.B.; Pinto, J.R.A.S.; Souza-Imberg, A.; Lopes, A.H.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.L.M. Proteomic endorsed transcriptomic profiles of venom glands from Tityus obscurus and T. serrulatus scorpions. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa Laboratories. KEGG Phenylalanine Metabolism-Centruroides sculpturatus (Bark Scorpion). Available online: https://www.kegg.jp/pathway/cscu00360 (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Laparie, M.; Larvor, V.; Frenot, Y.; Renault, D. Starvation resistance and effects of diet on energy reserves in a predatory ground beetle (Merizodus soledadinus; Carabidae) invading the Kerguelen Islands. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2012, 161, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce, G.; Cantú, P.C.; Flores, A.; Badii, M.; Zapata, R.; López Ildefonso, B. Modo de Acción de los Insecticidas. Available online: https://respyn.uanl.mx/index.php/respyn/article/view/178/160 (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Kanehisa Laboratories. KEGG Tyrosine Metabolism-Centruroides sculpturatus (Bark Scorpion). Available online: https://www.kegg.jp/pathway/cscu00350 (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Barmore, W.; Azad, F.; Stone, W. Physiology, Urea Cycle. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513323/ (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Dambrova, M.; Liepinsh, E. Acylcarnitines in health and disease: Biomarkers and drug targets. Maced. Pharm. Bull. 2022, 68 (Suppl. S1), 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobassum, S.; Tahir, H.M.; Zahid, M.T.; Gardner, Q.A.; Ahsan, M.M. Effect of Milking Method, Diet, and Temperature on Venom Production in Scorpions. J. Insect Sci. 2018, 18, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indiveri, C.; Iacobazzi, V.; Tonazzi, A.; Giangregorio, N.; Infantino, V.; Convertini, P.; Console, L.; Palmieri, F. The mitochondrial carnitine/acylcarnitine carrier: Function, structure and physiopathology. Mol. Aspects Med. 2011, 32, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucca, M.B.; Cerni, F.A.; Pinheiro Junior, E.L.; Bordon, K.C.; Amorim, F.G.; Cordeiro, F.A.; Longhim, H.T.; Cremonez, C.M.; Oliveira, G.H.; Arantes, E.C. Tityus serrulatus venom—A lethal cocktail. Toxicon 2015, 108, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezellou, P.; Jakob, K.; Atashi, J.; Ghassempour, A.; Spengler, B. Mass-spectrometry-based lipidome and proteome profiling of Hottentotta saulcyi (Scorpiones: Buthidae) venom. Toxins 2022, 14, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Delalibera, I.; Handelsman, J.O.; Raffa, K.F. Bacteria associated with the guts of two wood-boring beetles: Anoplophora glabripennis and Saperda vestita (Cerambycidae). Environ. Entomol. 2006, 35, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Freitak, D.; Vogel, H.; Ping, L.; Shao, Y.; Cordero, E.A.; Andersen, G.; Westermann, M.; Heckel, D.; Boland, W. Complexity and variability of gut commensal microbiota in polyphagous lepidopteran larvae. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.C.; Chaston, J.M.; Douglas, A.E. The inconstant gut microbiota of Drosophila species revealed by 16S rRNA gene analysis. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1922–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.Y.; Leone, V.A.; Devkota, S.; Wang, Y.; Brady, M.J.; Chang, E.B. Composition of dietary fat source shapes gut microbiota architecture and alters host inflammatory mediators in mouse adipose tissue. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2013, 37, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanthakumar, A.; Handelsman, J.O.; Schloss, P.D.; Bauer, L.S.; Raffa, K.F. Gut microbiota of an invasive subcortical beetle, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, across various life stages. Environ. Entomol. 2008, 37, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.N.A.; Ng, P.; Douglas, A.E. Low-diversity bacterial community in the gut of the fruitfly Drosophila melanogaster. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corby-Harris, V.; Pontaroli, A.C.; Shimkets, L.J.; Bennetzen, J.L.; Habel, K.; Promislow, D.E.L. Geographical distribution and diversity of bacteria associated with natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3470–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M.D.; Chan, E.R.; Molyneaux, N.D.; Bonomo, R.A. Genomewide analysis of divergence of antibiotic resistance determinants in closely related isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3569–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klepzig, K.D.; Adams, A.S.; Handelsman, J.; Raffa, K.F. Symbioses: A key driver of insect physiological processes, ecological interactions, evolutionary diversification, and impacts on humans. Environ. Entomol. 2009, 38, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.X.; Li, M.; Wu, B. Metagenomic profiles and antibiotic resistance genes in gut microbiota of mice exposed to arsenic and iron. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, E.V.; Wong, A.C.; Westmiller, S.; Douglas, A.E. Impact of the resident microbiota on the nutritional phenotype of Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werren, J.H.; Baldo, L.; Clark, M.E. Wolbachia: Master manipulators of invertebrate biology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, G.; Segal, D.; Ringo, J.M.; Hefetz, A.; Zilber-Rosenberg, I.; Rosenberg, E. Commensal bacteria play a role in mating preference of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20051–20056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasimhan, S.; Rajeevan, N.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.O.; Heisig, J.; Pan, J.; Eppler-Epstein, R.; Deponte, K.; Fish, D.; Fikrig, E. Gut microbiota of the tick vector Ixodes scapularis modulate colonization of the Lyme disease spirochete. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brune, A.; Ohkuma, M. Role of the Termite Gut Microbiota in Symbiotic Digestion. In Biology of Termites: A Modern Synthesis; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 439–475. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.C.; Tang, M.S.; Lim, Y.A.; Choy, S.H.; Kurtz, Z.D.; Cox, L.M.; Gundra, U.M.; Cho, I.; Bonneau, R.; Blaser, M.J.; et al. Helminth colonization is associated with increased diversity of the gut microbiota. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkuma, M. Symbioses of flagellates and prokaryotes in the gut of lower termites. Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Jiménez, J.; Vera-Ponce de León, A.; García-Domínguez, A.; Martínez-Romero, E.; Zúñiga, G.; Hernández-Rodríguez, C. Nitrogen-fixing and uricolytic bacteria associated with the gut of Dendroctonus rhizophagus and Dendroctonus valens (Curculionidae: Scolytinae). Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Hayatsu, M.; Hosokawa, T.; Nagayama, A.; Tago, K.; Fukatsu, T. Symbiont-mediated insecticide resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8618–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Ceron, L.; Santillan, F.; Rodriguez, M.H.; Mendez, D.; Hernandez-Avila, J.E. Bacteria in midguts of field-collected Anopheles albimanus block Plasmodium vivax sporogonic development. J. Med. Entomol. 2003, 40, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, R.J.; Vennard, C.T.; Buckling, A.; Charnley, A.K. Diversity of locust gut bacteria protects against pathogen invasion. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirimotich, C.M.; Ramirez, J.L.; Dimopoulos, G. Native microbiota shape insect vector competence for human pathogens. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 10, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadley, N.F. Water relations of the desert scorpion, Hadrurus arizonensis. J. Exp. Biol. 1970, 53, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadley, N.F. Adaptational biology of desert scorpions. J. Arachnol. 1974, 2, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Bolaños, L.M.; Rosenblueth, M.; Castillo-Ramírez, S.; Figuier-Huttin, G.; Martinez-Romero, E. Species-specific diversity of novel bacterial lineages and differential abundance of predicted pathways for toxic compound degradation in scorpion gut microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1364–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, P.; Moran, N.A. The gut microbiota of insects–diversity in structure and function. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 699–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.H.; Roh, S.W.; Whon, T.W.; Jung, M.J.; Kim, M.S.; Park, D.S.; Yoon, C.; Nam, Y.; Kim, Y.; Choi, J.; et al. Insect gut bacterial diversity determined by environmental habitat, diet, developmental stage, and phylogeny of host. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5254–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmnasri, K.; Hamdi, C.; Ettoumi, B.; Crotti, E.; Guesmi, A.; Najjari, A.; Doudoumis, V.; Boudabous, A.; Daffonchio, D.; Tsiamis, G.; et al. Highly divergent Mollicutes symbionts coexist in the scorpion Androctonus australis. J. Basic Microbiol. 2018, 58, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, K.L.; Carniol, K.; Manson, J.M.; Heiman, D. High-quality draft genome sequences of 28 Enterococcus sp. isolates. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 2469–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellegaard, K.M.; Tamarit, D.; Javelind, E.; Olofsson, T.C. Extensive intra-phylotype diversity in lactobacilli and bifidobacteria from the honeybee gut. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilanova, C.; Baixeras, J.; Latorre, A.; Porcar, M. The generalist inside the specialist: Gut bacterial communities of two insect species feeding on toxic plants are dominated by Enterococcus sp. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
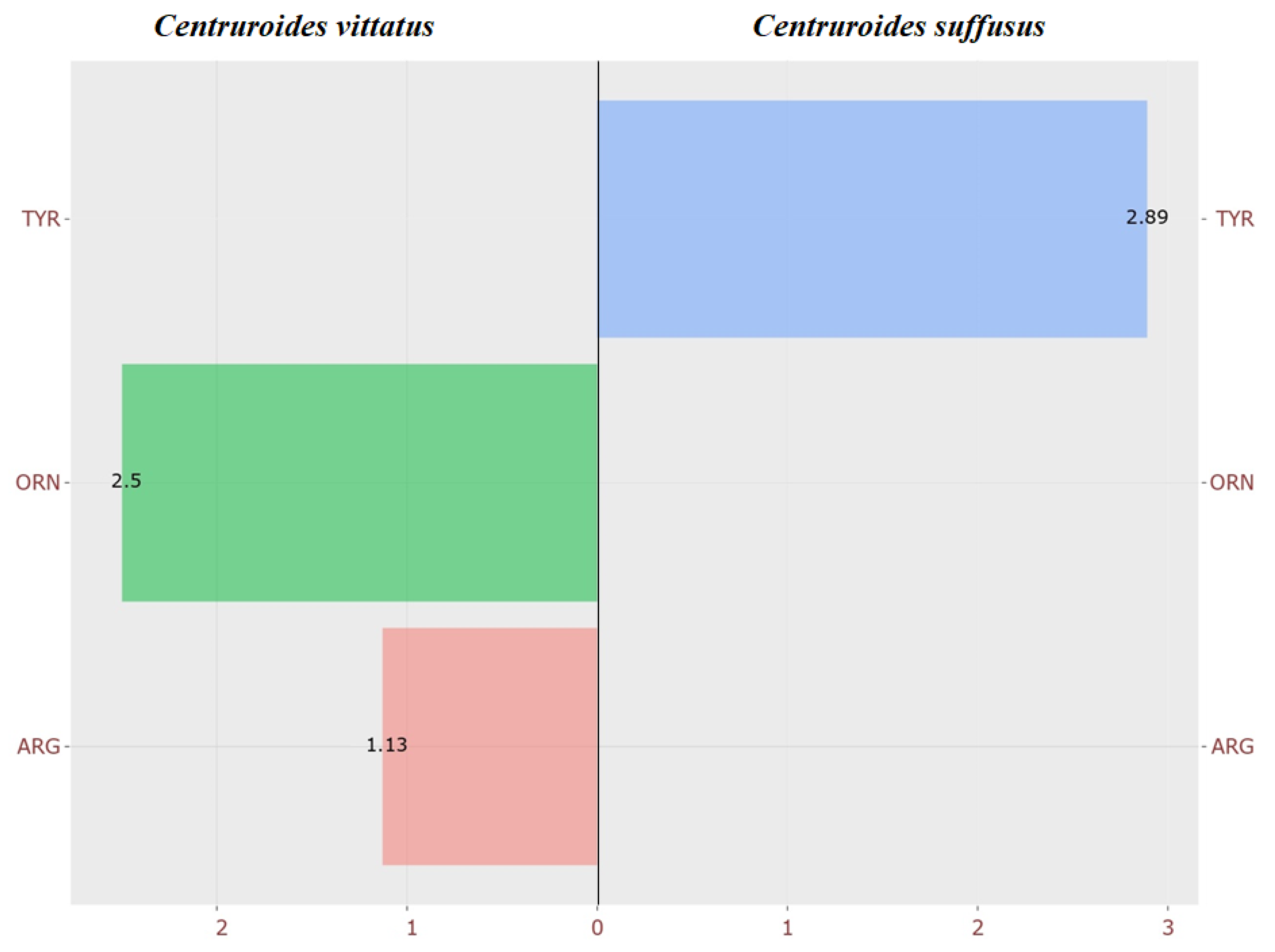
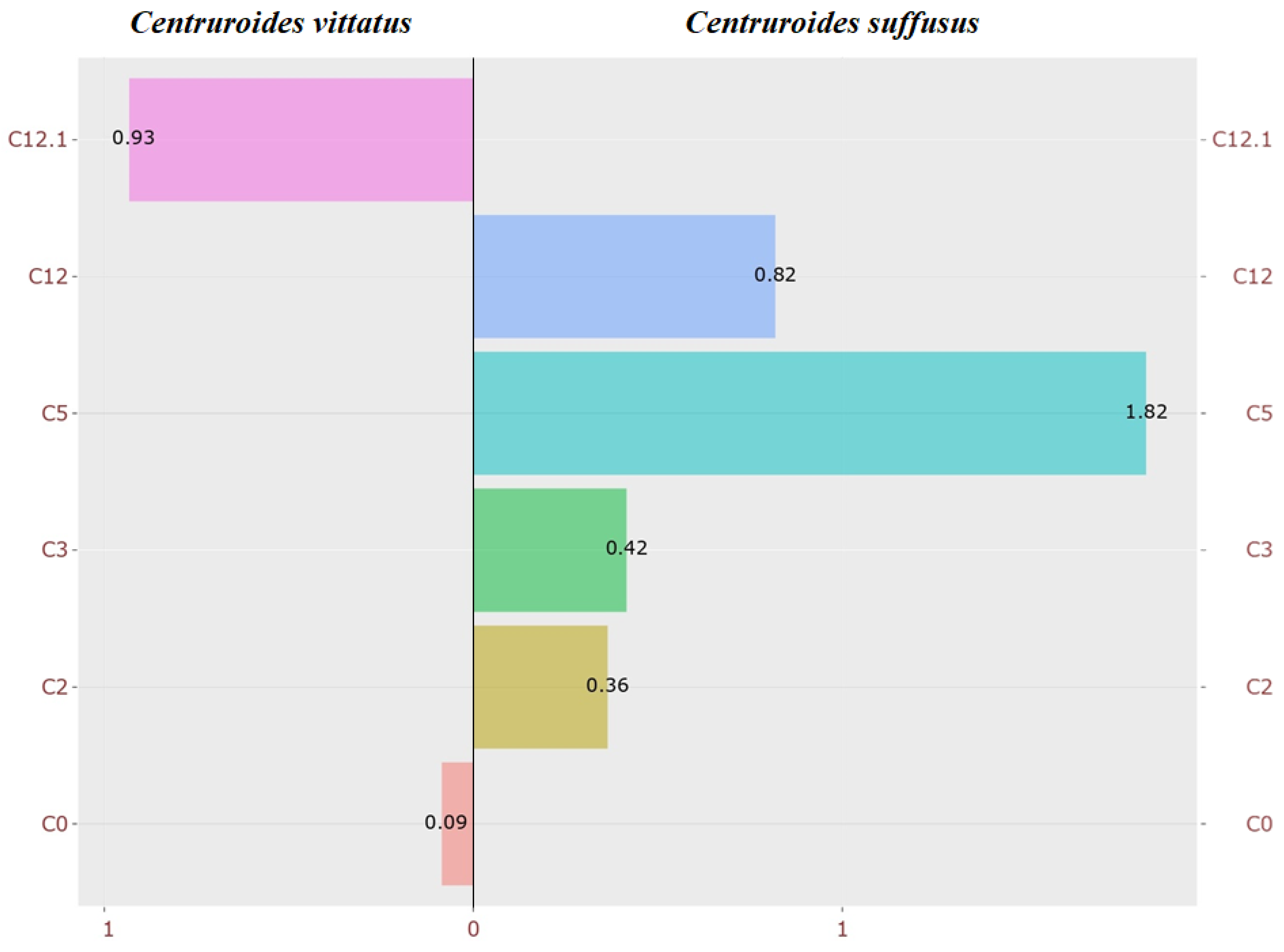
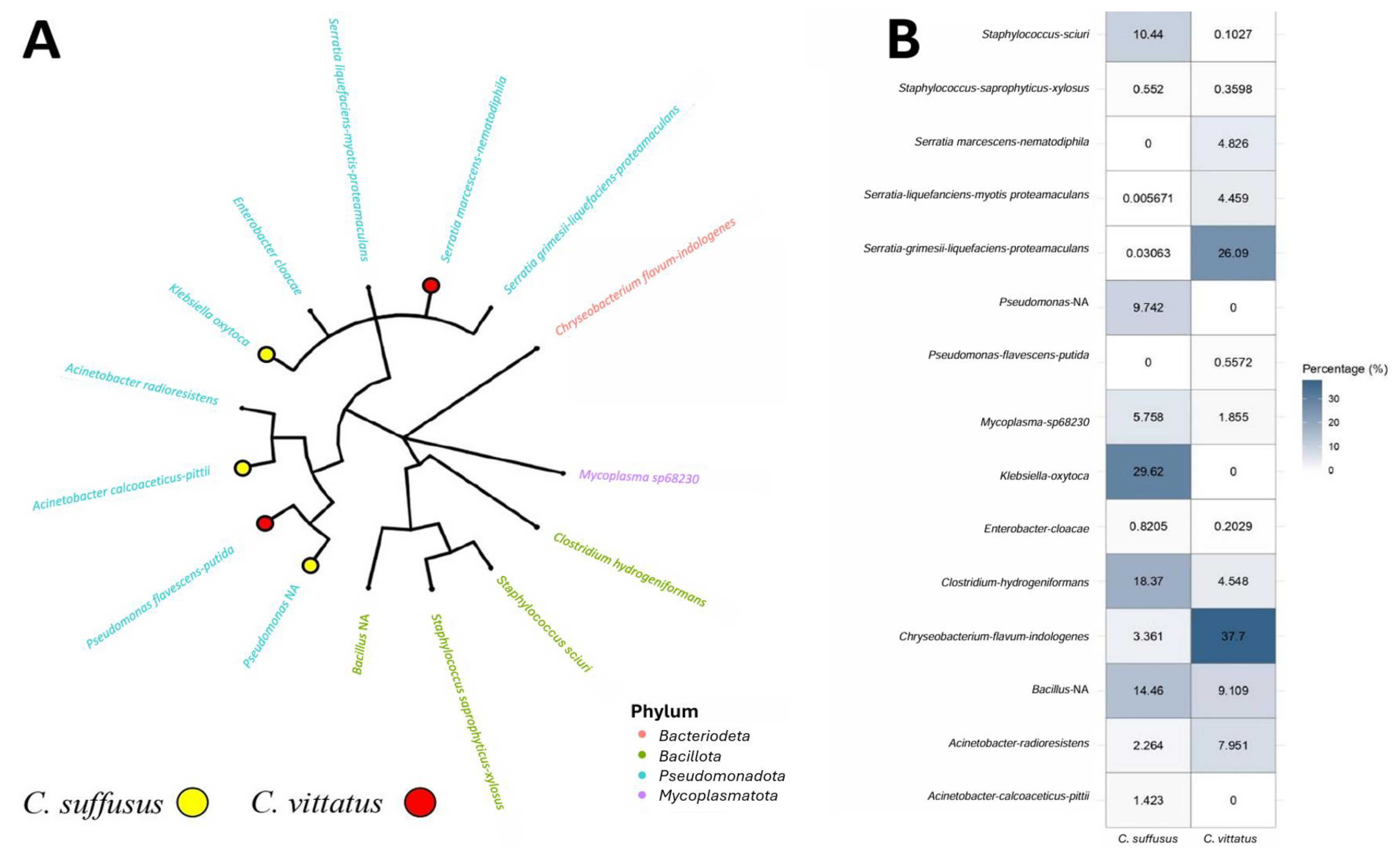
| Phylum | Species | C. suffusus | C. vittatus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteriodeta | Chryseobacterium flavum-indologenes | × | × |
| Pseudomonadota | Pseudomonas NA | × | |
| Pseudomonas flavescens-putida | × | ||
| Acinetobacter calcoacetius-pittii | × | ||
| Acinetobacter radioresistens | × | × | |
| Klebsiella oxytoca | × | ||
| Enterobacter cloacae | × | × | |
| Serratia liquafaciens-myotis-protemaculans | × | × | |
| Serratia marcescens-nematodiphila | × | ||
| Serratia grimesii-liquefaciens-protemaculans | × | × | |
| Bacillota | Clostridium hydrogeniformans | × | × |
| Staphylococcus sciuri | × | × | |
| Staphylococcus saprophyticus-xylosus | × | × | |
| Bacillus NA | × | × | |
| Mycoplasmatota | Mycoplasma sp.68230 | × | × |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiménez-Martínez, M.L.; Zapata-Morin, P.A.; Ramírez-Ahuja, M.d.L.; de Luna, M.; Meneses-Morales, I.; Trujillo-Rodríguez, G.d.J.; Ruiz-Baca, E.; Martínez-Garza, L.E.; Ovando-Vazquez, C.M.; Solis-Rojas, C.; et al. Omics Description (Metabolome and Microbiome) from Centuroides suffusus and Centuroides vittatus (Arachnida: Scorpiones). Arthropoda 2025, 3, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda3040014
Jiménez-Martínez ML, Zapata-Morin PA, Ramírez-Ahuja MdL, de Luna M, Meneses-Morales I, Trujillo-Rodríguez GdJ, Ruiz-Baca E, Martínez-Garza LE, Ovando-Vazquez CM, Solis-Rojas C, et al. Omics Description (Metabolome and Microbiome) from Centuroides suffusus and Centuroides vittatus (Arachnida: Scorpiones). Arthropoda. 2025; 3(4):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda3040014
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiménez-Martínez, Mariana Lizbeth, Patricio Adrián Zapata-Morin, María de Lourdes Ramírez-Ahuja, Manuel de Luna, Ivan Meneses-Morales, Gerardo de Jesús Trujillo-Rodríguez, Estela Ruiz-Baca, Laura Elia Martínez-Garza, Cesaré Moises Ovando-Vazquez, Carlos Solis-Rojas, and et al. 2025. "Omics Description (Metabolome and Microbiome) from Centuroides suffusus and Centuroides vittatus (Arachnida: Scorpiones)" Arthropoda 3, no. 4: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda3040014
APA StyleJiménez-Martínez, M. L., Zapata-Morin, P. A., Ramírez-Ahuja, M. d. L., de Luna, M., Meneses-Morales, I., Trujillo-Rodríguez, G. d. J., Ruiz-Baca, E., Martínez-Garza, L. E., Ovando-Vazquez, C. M., Solis-Rojas, C., Guzman-Velasco, A., Martinez-Fierro, M. L., Delgado-Enciso, I., Flores-Suarez, A. E., Lopez-Rodriguez, A., & Rodríguez-Sánchez, I. P. (2025). Omics Description (Metabolome and Microbiome) from Centuroides suffusus and Centuroides vittatus (Arachnida: Scorpiones). Arthropoda, 3(4), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda3040014