Abstract
Substance P (SP), the first isolated neuropeptide, belongs to the family of tachykinin peptides and is the natural ligand of neurokinin-1 receptors (NK-1R), also named SP receptors. The undecapeptide activates the receptor after specifically binding to the protein and triggers intracellular signals leading to different biochemical events and subsequent physiological responses. This study reviews the main architectural features of this receptor, its interaction with natural and synthetic ligands, and the functional conformational states adopted after interacting with ligands and effector G proteins. The analysis of the main intracellular signaling pathways turned on by the activation of NK-1 receptors reveals the participation of different proteins supporting metabolic changes and genetic and epigenetic regulations. Furthermore, the analysis of receptor occupancy and receptor downregulation and internalization represents a complex and estimable field for basic and clinical research focused on the role of SP in physiopathology. Profound knowledge of the structural dynamics of NK-1R may help develop and assay new selective synthetic non-peptide antagonists as potential therapeutic agents applied to various pathologies and symptoms.
1. Introduction
In 1931, Von Euler and Gaddum reported the isolation of a standard preparation in a water-soluble powder (later named substance P) from horse tissues that induced the contraction of isolated rabbit jejunums. It also exerted “a temporary fall of blood pressure in the atropinized rabbit under ether” []. Afterward, the powder was characterized as a peptide, isolated from the bovine hypothalamus, and its sequence of amino acids was determined [,]. SP is an undecapeptide (H2N-RPKPQQFFGLM-CO-NH2) belonging to the family of tachykinin peptides (a large group of tachykinins and tachykinin-like peptides, including invertebrate tachykinin-related peptides and vertebrate tachykinins) []. Tachykinin expression refers to the fast-moving contractions of smooth muscle observed in the presence of SP []. Etymologically, the two Greek roots ταχύς and κίνησις (meaning rapid movement) form the word. Tachykinins encompass a family of peptides (more than forty peptides isolated from mammalian and non-mammalian species), including SP, neurokinin A (NKA), and neurokinin B (NKB), which are the three most representative species. The TAC1 gene on human chromosome 7 encodes four mRNA transcripts translated into four isoforms containing the SP sequence. Additionally, SP may be cleaved into different fragments with biological activity [].
Depending on the type and localization of neurokinin receptors, tachykinins influence numerous biological and pharmacological effects in all bilaterian organisms, from lower invertebrates to mammals, including humans []. Tachykinins have a pleiotropic impact on the central and peripheral nervous system, lungs, liver, skeletal muscle, skin, and gastrointestinal tract []. With other tachykinins, SP plays prominent physiological and pathological roles in pain, inflammation, carcinogenesis and cancer progression, major depression, and hematopoiesis, for example [].
The actions of tachykinins proceed through the activation of three receptors, namely NK-1R (for which SP shows the highest affinity), NK-2R (for which NKA shows the highest affinity), and NK-3R (for which NKB shows the highest affinity) [,,,]. Neurokinin receptors belong to the family of seven transmembrane G-coupled receptors and signal intracellularly by triggering different mechanisms (described below in this review). The internalization of the ligand–receptor complex and the subsequent enzymatic hydrolysis cease the signal. The three receptors have been pharmacologically characterized, and the affinity, selectivity, and binding properties were assessed using agonists and antagonists in cell membranes and isolated organs []. Additionally, their tissue distribution has been evaluated by autoradiography studies (see, for example, their distribution and ontogeny in the central nervous system, CNS []). NK-1R, NK-2R, and NK-3R are encoded by the TACR1, TACR2, and TACR3 genes.
The amino acid sequence of a human SP receptor was deduced from the nucleotide sequence of a cDNA. Protein expression in COS-7 cells facilitated the determination of the pharmacological properties of the protein and established that SP showed the highest affinity for the protein consisting of 407 residues and was confirmed as belonging to the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily []. Figure 1 presents the primary and secondary structures of the NK-1 receptor; it also shows the N-terminal, C-terminal, as well as the intracellular, extracellular, and transmembrane helical domains drawn in a snake plot.
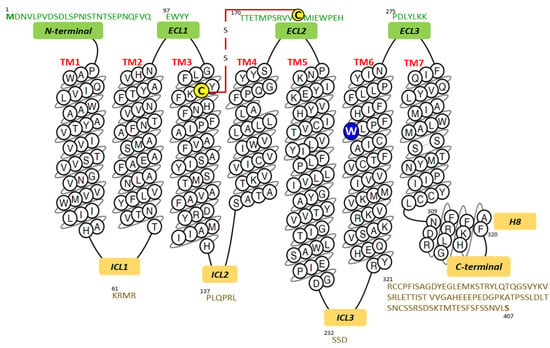
Figure 1.
Snake plot of the human NK-1 receptor depicting the amino acid sequences of the transmembrane (TM), in the color black; amino-terminal and extracellular loops (ECL), in the color green; intracellular loops, intracellular helix 8 (H8), and carboxy-terminal domains, in the color yellow. The numbers over the amino acid letters indicate their position within the entire receptor sequence from the N-terminal’s number 1 residue (Met). The red line depicts a disulfide bridge between Cys180 and Cys105 (in yellow). The W2616.48 residue in blue (superscript numbers correspond to Ballesteros and Weinstein numbering []) acts as a “molecular toggle” in the activation of GPCRs (G protein-coupled receptors) [,]. Image modified from the GPCRdb database [,].
Early studies on structure–activity relationships established the importance of the specific chemical characteristics of neurokinins that are necessary to trigger their receptors []. For example, aromatic or aliphatic residues in the C-terminal region of tachykinins and the amidation of the C-terminal residue to activate the receptor protein were considered essential for receptor activation [].
2. The Neurokinin-1 Receptor: Structure Dynamics and Interactions with Ligands
The NK-1R belongs to class A of GPCRs (G protein-coupled receptors). This family of seven transmembrane (7TM) receptors shares intrahelical and interhelical hydrogen bonding patterns, helping insert helices into the lipid bilayer and influencing their molecular contacts with other membrane-associated proteins and with agonists and antagonists. The dynamic establishment of hydrogen bonds and atomic displacements within the structure are requirements for their function. The interhelical forces also depend on the membrane’s lipid composition [,,]. Consequently, analyzing atomic events facilitating the displacement of atoms and structures within these membrane proteins is paramount to ascertaining their activity and regulation in physiological and pathological contexts.
The complete form of NK-1R consists of 407 amino acids and the truncated splice variant of 311 amino acids. The truncated isoform has a short cytoplasmic C-terminal domain lacking essential residues responsible for the anchoring of this domain to the internal bilayer of the plasma membrane []. Additionally, the C-terminal end of NK-1R full form serves as a substrate for essential modifications such as phosphorylation of specific amino acid residues [] required for receptor internalization and binding to β-arrestins and other transducers [,]. Notably, both isoforms may show differentiated expression, signaling profiles [], and roles in physiological and pathological processes [,]. Given the structural differences between both isoforms, substance P diversifies its activity and extends its influence in agreement with tissue and time-dependent expression of the NK-1R variants [].
2.1. SP Is the Natural Agonist of NK-1 Receptors
SP is the natural ligand of NK-1 receptors together with hemokinin-1 (HK-1) [,,]. The undecapeptide exhibits flexible random structures in an aqueous environment, and its 3D form is influenced by temperature, pH, and the presence of calcium ions under physiological conditions. The peptide’s randomly disordered structure is biologically inactive []. Neutron diffraction experiments carried out in bilayers composed of DOPC (dioleylphosphatidylcholine) and DOPG (dioleylphosphatidylglycerol) reported that SP interacts with both zwitterionic and anionic phospholipids. The C-terminal region of SP penetrates the bilayer, whereas the rest sets on the surface of the bilayer []. SP residues Pro-4, Gln-5, Phe-7, Phe-8, and Gly-9 determine the selectivity of the binding to the receptor [,]. Mutagenesis experiments unveiled important amino acid positions for the accommodation of the peptide to its site within the receptors, namely Asn-85, Asn-89, Tyr-92, and Asn-96, located in TM (transmembrane) domain 2, and Tyr-287 in TM domain 7 []. NMR determinations, docking experiments, molecular dynamics simulations, energy minimization, and the use of benzo-Phe-SP [,,] and the site-specific placement of benzoPhe [] addressed the possible contacts that the peptide ligand and the receptor establish during the binding action. The proposed models focused on the interaction between SP with the N-terminal domain of the receptor (residues 11 to 21) and with the extracellular loop 2 (ECL2) residues 173-177. Moreover, the C-terminal region of the peptide moved into deeper contact with the transmembrane regions TM5 and TM6 inside the receptor’s structure, and the central part of SP adopted a helical conformation that was favorably accommodated within the extracellular loops ECL2 and ECL3 (Figure 1 and Figure 2).
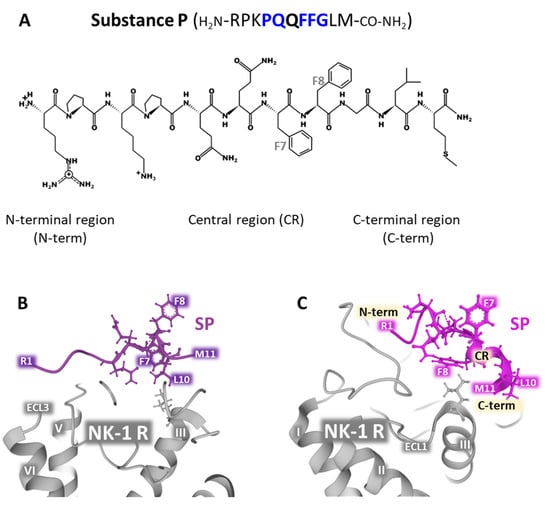
Figure 2.
Panel (A) shows SP’s sequence of amino acids and its two-dimensional structure drawn with KingDraw-Free software [], indicating the N-terminal, central, and C-terminal regions. Within the primary sequence shown, residues in blue are determinants of the selectivity of the ligand for its receptor [,]. The positions Phe7 and Phe8 are indicated within the chemical representation of the peptide. The lower panels (B,C) depict illustrative structures obtained from the Protein Data Bank [] (corresponding to the conformation of SP in artificial bilayers harboring the NK-1R in the presence of water (panel (B)) corresponding to PDB Id. 2KS9 or ganglioside GM1 (panel (C)), corresponding to PDB Id. 2KSA) []. Both structures were drawn with Mol* free web-based software [].
In vitro experiments using isotropic bicelles (structures composed of various phospholipids in different proportions) containing the ganglioside GM1 showed that SP assumed a stable turn/helical (extended 310 helix or turn III) conformation that facilitates binding to the membrane receptor. These artificial bicelles were designed and built to mimic the native membrane environment where NK-1 receptors are located in membrane caveolae rich in GM1 []. The undecapeptide shows a flexible and disordered conformation in the presence of water (Figure 2B; PDB Id. 2KS9). However, SP adopted a defined and ordered structure, corresponding to the bioactive conformation that interacts with NK-1 receptors in the presence of ganglioside GM1 (Figure 2C; PDB Id. 2KSA). Additionally, the assessment of hydrogen bonding with VADAR (Volume Area Dihedral Angle Reporter) [] and the determination of chemical shifts in bicelles by 1H-NMR in water alone or the presence of GM1 indicated that the C-terminal region of the peptide adopts a more defined conformation. In contrast, the N-terminal domain has a more flexible structure [] (Figure 2B, PDB Id 2KS9 and C PDB Id. 2KSA).
Cryo-electron microscopy studies revealed an active state of the NK-1 receptor complexed with Gq and Gs heterotrimeric proteins and bound to SP []. The occurrence of cholesterol molecules in the active form of the receptor (Figure 3, left panel) reinforces the reported importance of the organization of the plasma membrane with lipid rafts and caveolae where NK-1 receptors sit and recruit intracellular effectors after binding to SP []. The binding of SP to the receptor complexed with a heterotrimeric G protein indicates that the C-terminal region of the undecapeptide binds the receptor protein by interacting with its transmembrane core. In contrast, the N-terminal part extends towards the extracellular region (Figure 3, right panel) []. Additionally, the cryo-EM structural determination of the NK-1R-SP-G s/q70 complex showed that the N-terminal segment of SP establishes close contact with the extracellular loop 2 (ECL2) and the N-terminal portions of the receptor; the C-terminal region of SP comes into contacts with receptor residues N85 (in helix 2), N89 (in helix 2), H108 (in helix 3) and Y287 (in helix 7) through a network of hydrogen bonds []. The binding site of SP is different from the orthosteric pocket that NK-1R antagonists occupy, where the region of the receptor overlapped by the occupancy of SP and antagonists is scarce. For example, netupitant only shares a binding location with the amidated methionine at position 11 of the undecapeptide [].
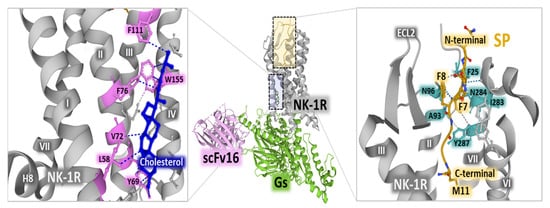
Figure 3.
The central panel represents NK-1R (gray) complexed with Gs heterotrimeric protein (green) and scFv16 (single-chain variable antibody fragment used to stabilize the complex) (light pink). The panel on the left shows the position of cholesterol (dark blue) within the receptor helices, indicating weak interactions with receptor residues (pink) with dashed lines. The right panel depicts SP’s position (yellow) within the receptor core. The C-terminal, N-terminal, and SP amino acids F7, F8, and M11 are indicated. Dashed lines represent weak interactions of the undecapeptide with NK-1R residues (light blue). The figure also shows the positioning of NK-1R, helices, and extracellular loop 2 (ECL2). The structures are from the Protein Data Bank [] (PDB, corresponding to PDB Id. 7P02) [], drawn with Mol* free web-based software [].
Examining the molecular structure of NK receptor subtypes and the interaction with their ligands brings attention to their unique role in physiological and pathological activities. The mode of interaction of agonists and antagonists with their respective receptors explains their selectivity, efficacy, and potency. A recent study [] compared the structures of SP bound to the complex NK-1R-Gq and neurokinin A (NKA) attached to NK-1R-Gq, at the atomic level. Interestingly, apparent differences concerning the interaction of the N-termini of neurokinins with the extracellular loop 2 (ECL) and other domains of their respective receptor explain different binding kinetics and physiological responses. This knowledge reports valuable information to understand structure–activity relationships and to design new compounds capable of modulating the activity of NK receptors in a specific and effective manner.
2.2. Antagonists of NK-1 Receptors
Early studies of crystal structures of NK-1R antagonists analyzed possible interactions of different pharmacophores (for example, quinuclidine derivatives, L-tryptophan benzyl esters, or piperidine rings) with the environment to obtain helpful information concerning their real contacts and binding capabilities to the receptor residues []. The analysis pointed to the importance of probable intermolecular interactions with some residues, including N165, H265, F268, and H197. However, determining the complex geometries between ligands and proteins requires the receptor protein’s presence. Later crystallographic and NMR structural studies provided more accurate information concerning ligand interactions with the receptor protein.
The synthesis of neurokinin receptor antagonists provided advances for studying the three types of NK receptors concerning binding, selectivity, and blocking activity. These compounds are also valuable for determining the structural properties and dynamics of the receptors by attaining crystal structures of the complex receptor-antagonist that permit unraveling the interactions with amino acid residues and defining three-dimensional orthosteric pockets with precision. The co-crystallization of the human NK-1 receptor fused with the thermostable PGS (Pyrococcus abysii glycogen synthase) with bound antagonists CP-99,994, aprepitant, and netupitant generated diffracting crystals that showed the structure of a type A GPCR (G protein-coupled receptor) in an inactive conformation with seven transmembrane domains, an extracellular N-terminal domain, three extracellular loops, and three intracellular loops, as well as an intracellular helix (helix 8) parallel to the plasma membrane, and a C-terminal intracellular domain [,]. A conserved disulfide bridge between Cys180 in extracellular loop two and Cys105 in transmembrane (TM) domain 3 connects the extracellular domain 2 (ECL2) with the transmembrane domain 3 (TM3) (Figure 1). The work of Schöppe et al. offers detailed information regarding the interatomic relationships between the receptor and the antagonist compounds. For example, netupitant sits in a hydrophobic cleft, establishing some essential weak interaction with residues within the receptor (Figure 4A,D). A longer linker in netupitant (compared with similar antagonists) between the di-trifluoromethylphenyl structure and the methylphenyl group approximates the compound towards F268 and H197, thus promoting π–π interactions between the methylphenyl ring and the imidazole of histidine (Figure 4D). These aromatic positions significantly influence the binding affinity of the antagonist netupitant for the NK-1 receptor. The accommodation of netupitant in a hydrophobic cavity within the NK-1 receptors creates unique weak interactions and anchors helices V and VI, leading to an inactivated protein conformation that impairs its function (see Figure 4D). In crystallographic structures of mutated E78D NK-1R bound to aprepitant and wild-type NK-1R attached to L-760735, a network of weak interactions with crucial residues, including H197, E193, F264, or W261, secures aprepitant (Figure 4B,E) [] and L-760735 (Figure 4C,F) [] into a hydrophobic cleft similar to the cavity occupied by netupitant where the antagonist orients perpendicularly to the plasma membrane, establishing interactions with TM3, TM5, and TM6 []. A recent study with carbohydrate (as a central scaffold)-based NK-1R antagonists revealed that the antagonist pocket of the receptor stabilizes the structure by arranging hydrophilic interactions between the pyranose moiety and amino acids Asn 109 and His108, thus improving and securing the stability of the binding and the affinity and selectivity of the compounds [].
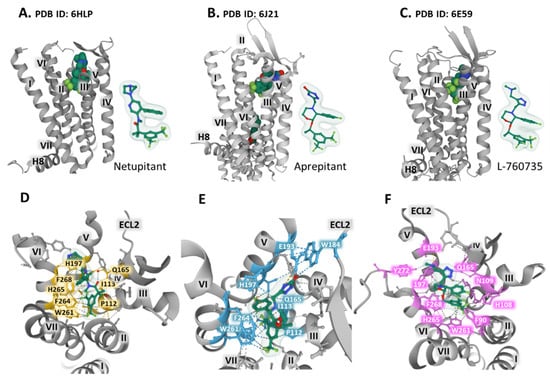
Figure 4.
The antagonists (space fill representation) nenupitant (A,D), aprepitant (B,E), and L-760735 (C,F) occupy an NK-1 receptor hydrophobic pocket. The upper pictures, (A–C), present a view of the co-crystalized complex parallel to the plasma membrane plane, together with a representation of the antagonists’ ball and stick and the Gaussian volume (light green). The lower panels (D–F) depict a more detailed view of the complex observed from the extracellular space and relate to the (A–C) structures. Dashed lines represent weak antagonist bonding with receptor residues (yellow for netupitant, blue for aprepitant, and pink for L-760735). Transmembrane (TM) helices appear in roman numbers. ECL2 is extracellular loop 2. The figure displays the structures obtained from the Protein Data Bank [], corresponding to NK-1R bound to netupitant (PDB Id. 2HLP, A and D), the E782.50D mutant bound to aprepitant (PDB Id. 6J21, B and E) [] and NK-1R attached to L-760735 (PDB Id. 6E59, C and F) [], viewed with the Mol* free web-based software [].
The structural analysis provides the basis for understanding the role of some residue positions that bear crucial functions. For example, Figure 4D–F and Figure 1 show the place of residue W261, situated in TM6, lying in the inferior region of the antagonist pocket []. The displacement of this conserved tryptophan functions as a rotameric switch in the activation of class A GPCRs [] and may act as an essential component of an allosteric interface necessary for regulating receptor function []. The indole ring of W261 interacts with the trifluoromethyl-benzyl group of the antagonists and stabilizes the complex (Figure 4F).
2.3. Insurmountable Antagonism of NK-1 Receptors
The displacement of agonist dose–response curves to the right and the reduction of the maximal agonist response define insurmountable antagonism. This antagonism correlates with structural adjustments between the antagonist drug and the receptor protein. Many different mechanisms may account for this antagonist effect, for instance, the stability and binding kinetics of the antagonist–receptor complex. Additionally, slow change rates between receptor conformations, allosteric regulation, or the internalization of the protein in the antagonist–receptor complex may explain this phenomenon. Recent co-crystallization and X-ray diffraction studies with the selective antagonists aprepitant, netupitant, and NK-1R show that when the antagonists bind to the NK-1 R, a new hydrogen bonding network ties up the transmembrane helices TMVI and TMVII to become closer.
Consequently, the whole structure loses conformational flexibility. This structural restriction imposed by the interaction of the antagonist with NK-1R may explain the observed insurmountable antagonism exerted by both aprepitant and netupitant in experimental settings. A comparison of crystal structures of NK-1R bound to insurmountable antagonists and structures of NK-1R bound to Gα and Gq proteins [] revealed that the receptor’s conformation with the antagonists prevents SP binding due to steric hindrance contacting ECL2 and the imposed difficulty for the movement of TMVI to facilitate receptor activation.
2.4. The Amino Acid Position 2.50 in NK-1 Receptors
In contrast to the majority of GPCRs, where the 2.50 position (according to Ballesteros and Weinstein numbering, []) is aspartic acid (D782.50), the NK-1R has a glutamic acid residue (E782.50). The variant relates to the absence of constitutive NK-1R signaling []. The NK-1 receptor bound to netupitant reveals a network of direct and water-mediated hydrogen bonds established by E782.50, mostly with residues S1193.39, N3017.49, and N501.50. (Figure 5). These weak bonds are responsible for the inactive conformation of the receptor. The extended carbon atom chain in glutamic acid situates the residue in an advantageous position compared with aspartic acid, thus permitting the creation of interactions similar to those observed between D782.50 and sodium in other GPCRs, where partially hydrated sodium ions act as negative allosteric modulators (Figure 6) [,]. Mutational studies provided evidence of a unique interface formed by residues E782.50, S1193.39, and N307.49 that triggers differential signaling pathways [,]. Moreover, in a recent report, mutations at the wild-type amino acid position E782.50 to aspartic acid (D782.50) or asparagine (N782.50) revealed that the hydrogen bond between E/D782.50 and N3017.49 disappears when asparagine occupies the X2.50 position (Figure 5B,C). For that reason, a consequent displacement of a short sequence where residue N3017.49 sits may affect essential interactions for receptor activation []. Additionally, the hydrogen bond between the X2.50 position and S1193.39 is less robust with either aspartic acid or asparagine at position 2.50 than glutamic acid (Figure 5). The studies mentioned above indicate that the X2.50, X3.39, and X7.49 posts form an interface that plays an essential role in the activation states of the receptors dependent on weak interactions with neighboring residues [].
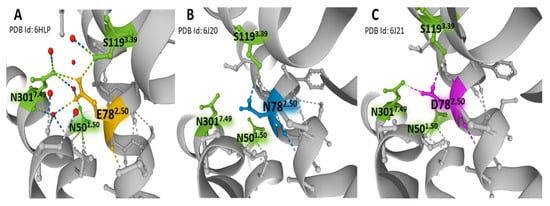
Figure 5.
Weak bonding interactions of different residues occupying the X2.50 position with neighboring S1193.39, N3017.49, and N501.50 in the structure of NK-1R. Panel (A) represents the position of E782.50 in a wild-type NK-1R bound to antagonist netupitant (PDB Id: 6HLP), defining the basal inactive state of NK-1 receptors. Panel (B) represents the position of N782.50 in a mutated NK-1R bound to antagonist aprepitant (PDB Id: 6J20) []. Panel (C) illustrates the situation of D782.50 in a mutated NK-1R attached to the antagonist aprepitant (PDB Id: 6J21) []. Receptor helices are depicted in gray. The figures are from the Protein Data Bank [] and were drawn with the Mol* free web-based software [].
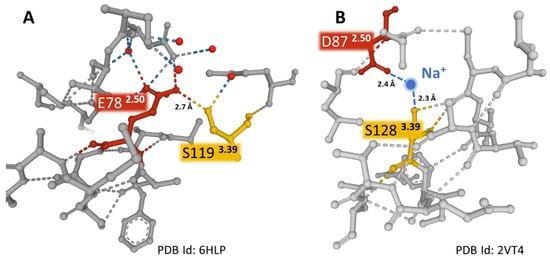
Figure 6.
The weak interactions (dashed lines) between positions 2.50 and 3.39 in two different GPCRs. Panel (A) shows E782.50 directly interacting with S1193.39 in the NK-1R (PDB Id 6HLP). Panel (B) depicts the interaction of D872.50 with S1283.39 coordinated with a sodium ion in the turkey β-1 adrenergic receptor (PDB Id 2VT4) []. The sodium ion is blue, and the water molecules are red-colored spheres. The figures were obtained from the Protein Data Bank [] and drawn with the Mol* free web-based software [].
The work mentioned above points to a specific structure of the ligand SP and a defined membrane environment to successfully bind to the receptor. Recent structural studies using specific NK-1R antagonists precisely show the properties of the receptors, their binding to ligands and G proteins, and the dynamic movements that secure their effective and fine-tuned function. Defining specific sites for antagonists facilitates the design of new structures that may improve the receptors’ binding effectivity and blocking capacity. The evidence provided may help design antagonists more efficaciously and in a way that is specifically suitable for application in numerous pathologies, from pain relief to the treatment of alcohol use disorders, cancer, emesis, and depression []. Designed antagonists attached to hydrophobic structures or new compounds without this requirement, targeting NK-1 endosomal signaling, may represent another sound approach to controlling NK-1R function. With this goal in mind, a consideration of the conformational fitting induced by antagonists on the receptor structure is paramount, and research in this field may report on new effective drugs for the treatment of different pathologies or the alleviation of symptoms, including pain [].
3. The Neurokinin-1 Receptor: Structure Dynamics and Signaling
3.1. G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs)
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are abundant and ubiquitous membrane proteins that respond to stimuli from photons to ions, small organic compounds, peptides, and macromolecules. They are responsible for multiple cellular responses and share a serpentine architecture with a package of seven transmembrane helices, alternate intracellular and extracellular loops, the C-terminus lying in the cytoplasm, and the N-terminus expanding towards the extracellular space [,,,,,,]. GPCRs activate different G protein and β-arrestin-dependent mechanisms that control many physiological and pathological outcomes [] related to immune responses, mood, cognition, blood pressure control, pain control, taste, vision, and olfaction [,,,]. Signaling can also occur via endosomal membranes that facilitate the activation of localized signals [,,]. The group is subdivided into classes considering their sequences’ similarities and structural features: A (rhodopsin), B (secretin), B2 (adhesion), C (glutamate receptors), D1 (Ste2-like fungal pheromone), family F (frizzled, FZD, and smoothened, SMO), and T (taste) [,]. Extensive and meticulous structural studies of GPCRs provide essential information that allows for a better understanding of their function. They also improved drug design based on the knowledge of protein conformational movements linked to activation and inactivation states and biased agonist signaling [,,,,]. X-ray crystallography studies, molecular dynamics simulations, and the mutational analysis of allosteric interfaces with hydrogen bonding networks in transmembrane helices determine states of activity that trigger intracellular signaling [,,,,]. Updated information on the structural studies of GPCRs can be found in the GPCRs database [,]. GPCRs serve as a target for pharmacological intervention. Approximately 35% of officially approved drugs target GPCRs directly or GPCR-associated proteins [,]. The list may grow more prominent due to new methods of drug design exploration based on novel receptor regulation concepts, allosteric changes, biased signaling, and receptor heteromerization [,,,]. Additionally, post-translational modifications (phosphorylation, glycosylation, ubiquitination, and palmitoylation) influence receptor folding, dimerization, and function []. Soundly, these modifications should also be focused on when studying the pharmacological manipulation of GPCRs.
Class A GPCRs (to which NK-1 receptors belong) are the most abundant and studied. They have an enormous influence on human physiology and pathology. Agonist binding to these receptors activates G protein recruitment by moving helix number 6 towards the exterior of the receptor bundle caused by a common activation mechanism affecting specific residues []. The first structures defined with X-ray diffraction data were bovine rhodopsin [] and human β-adrenergic receptors [,]. More than a hundred structures of GPCRs have been resolved to date. Conserved sequence motifs, such as D(E)R3.50Y in TM3 and D/E6.30 in TM6, are responsible for the inactivation state of the receptors by establishing an ionic bridge tightening TM3 and TM6 together, thus preventing the flexible outward movement of TM6 necessary for activation and signaling.
3.2. NK-1R Signaling Pathways
The NK-1 receptor belongs to class A of GPCRs. Upon activation, it signals through different pathways depending on its intrinsic performance, topology within the membrane bilayer, tissue localization, and the type of ligand. Agonist ligands of NK-1R include SP, SP analogs, and neurokinin A (NKA) [,,,]. The main signaling routes activate Gq and Gs heterotrimeric proteins, causing intracellular variations in second messenger concentrations, such as calcium, cAMP, or IP3 [,]. Figure 7 depicts the main signaling pathways activated by NK-1 receptors, leading to operative protein phosphorylation cascades and metabolic regulations responsible for physiological and pathological consequences.
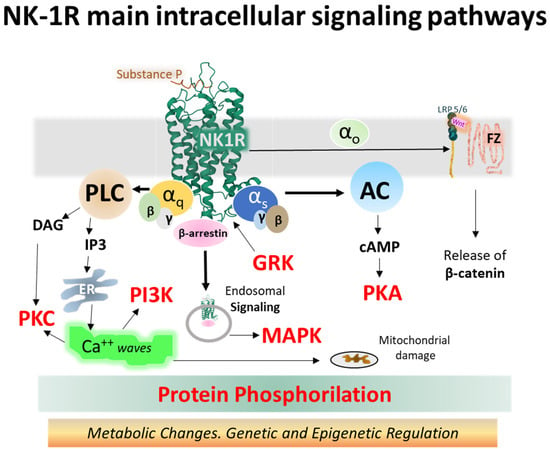
Figure 7.
Intracellular NK-1R signaling pathways turned on after binding SP and activating different alpha subunits (Gq and Gs, mainly) and beta-gamma dimers of heterotrimeric G proteins (the structure of NK-1R in green is from the Protein Data Bank [], PDB Id. 2KS9) []. Abbreviations: AC (adenylyl cyclase), cAMP (cyclic 3′-5′ adenosine monophosphate), DAG (diacylglycerol), ER (endoplasmic reticulum), FZ (frizzled), GRK (G protein-coupled receptor kinase), IP3 (inositol 1,4,5 trisphosphate), LRP 5/6 (low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein), MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase), NK-1R (neurokinin-1 receptor), PI3K (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase), PKA (protein kinase A), PKC (protein kinase C), PLC (phospholipase C), and Wnt (wingless-related integration site) [,,,,,,,,,,].
The observed differential activation of NK-1R signaling cascades by agonists may be caused by structural coupling between the receptor and agonist, where efficacy and selectivity lie in different architectural settings. The interface formed by amino acid positions E2.50, S3.39, and N7.49 sets in a net of hydrogen bonds (Figure 5) and facilitates receptor conformations leading to biased receptor activation (Gs, Gq, and β-arrestin) []. In this hydrogen bond network built by the amino acid lateral chains, the alanine substitution of E2.50 abolished SP-activated Gq signaling measured by the accumulation of inositol 1, 4,5 trisphosphate (IP3). However, the alanine substitution of N7.49 and S3.39 had a marginal effect on Gq stimulation.
SP and neurokinin A (NKA) and neurokinin B (NKB) bind NK-1 receptors; however, differences in the charge distribution and amino acid composition of the peptides and their interaction with the anionic surface formed by acidic residues in extracellular loops 2 and 3 favor SP binding (higher affinity) over the other two tachykinins []. The structural resolution of NK-1 receptors bound to Gs and Gq proteins contributed to determining that the receptor similarly binds to both G proteins []. However, the binding to Gq is slightly favored and accords with the observed preference of Gq over Gs signaling []. Mutagenesis experiments and the structural dynamics analysis of ligand–receptor interactions [,,] showed that SP and its truncated form SP6-11 (lacking the N-terminal region of the undecapeptide) triggered calcium signaling with similar potency when bound to wild-type NK-1 receptors. However, NKA and SP6-11 induce a weaker cAMP accumulation response than SP. Additionally, experiments with NK-1R bearing conservative mutations of amino acids establishing hydrogen bonding nets deeper inside the pocket (N852.57, N892.61, H1083.28, and Y2877.35) with the C-terminal region of SP (Figure 8) did not affect the potency and maximal response of the undecapeptide. In contrast, truncated SP6-11-dependent responses significantly decreased [].
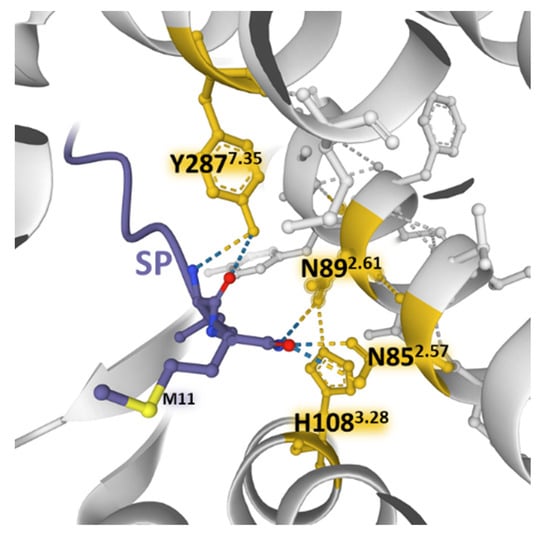
Figure 8.
Weak bonding interactions of different amino acid residues (yellow) coming into contact with the C-terminal region of SP (blue) deep inside the orthosteric pocket of the NK-1 receptor (gray) (PDB Id: 7RMG []). Conservative mutations of the depicted positions do not affect the SP-induced increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentrations. The figure also indicates residue M11 of the undecapeptide. The structure is from the Protein Data Bank [], drawn with the Mol* software [].
The findings point out that the calcium signaling depended on the interaction of the C-terminal region of SP with the receptor. However, the findings also showed that contact between the central and N-terminal parts of SP with the extracellular domains of NK-1R (ECL2 and N-terminus area) is essential for signaling through Gs and not only for ligand recognition and selectivity. Molecular dynamics simulations reported that the residues F7 and M11 in SP6-11-truncated peptide adopt more orientations than F7 and M11 in SP undecapeptide and establish differential contacts with TM7 and TM6 of the NK-1R []. It is worth noting that preferential Gq activation obtained with SP6-11 reinforces the assumption that connections between the N-terminal region of SP with the exterior of NK-1R determined receptor activation-dependent signaling.
Other GPCRs also exhibit biased agonism responsible for activating singular intracellular metabolic reactions, producing a signaling signature at a given time and in a particular target cell [,].
The truncated NK-1 receptor isoform lacks the intracellular C-terminal region [,]. Full (NK-1R-F) and truncated NK-1 (NK-1R-T) receptor isoforms display functional differences affecting intracellular signaling []. The exclusion of the C-terminal tail impairs receptor internalization, making the protein resistant to desensitization []. Additionally, the interaction with transducer G proteins is weaker, and calcium release, protein kinase C (PKC) activation, and other phosphorylation events appear delayed [,,].
The so-called canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways encompass a group of membrane-bound and intracellular proteins, and the route is closely related to the control of immunomodulation and cell proliferation. The activation of the FZ/LRP 5/6 complex (frizzled/low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6) by secreted cysteine-rich glycoproteins Wnt (wingless-related integration site) (see Figure 7) mobilizes an effector G protein, disrupts the Axin-GSK3-APC-CK1 complex and impedes the phosphorylation of β-catenin by the kinases GSK-3β and CK1 (casein kinase 1). Consequently, β-catenin accumulates in the cytosol and moves to the nucleus, where it associates with TCFs/LEF (T-cell factor/lymphoid-enhancer-binding factor) proteins and other transcription factors and co-triggers the transcription of target genes by binding to specific promoter sequences [,,,,]. β-catenin may also translocate to the membrane and stabilize it by building cell adhesion complexes [,].
Experimental studies using agonists and antagonists of NK-1R showed that the agonist turning-on of NK-1R induced an increased expression of β-catenin and GSK3β and diminished the expression of DKK1 (Dickkopf 1), an inhibitor of Wnt []. Additionally, selective antagonists of NK-1 receptors inhibited cell proliferation in several experimental scenes by influencing Wnt/β-catenin pathways [,,,].
The NK-1R system controls numerous intracellular processes, including cell growth, cytoskeletal organization, metabolic reaction, or gene expression through biochemical reactions that contribute to cell homeostasis []. Malfunction of the receptor induces dysregulation of intracellular signaling cascades, and disease may appear. NK-1R-triggered signaling complexes participating in cell disruption led to inflammation, calcium overloads, altered cell metabolism and growth, and disrupted cell migration conveying to cancer, pain, psychiatric disorders, and other pathologies. Molecular complexes responsible include the Wnt/β-catenin [], β-arrestins scaffolds [], JNK and p38/MAPK [], NF-kB [,], PKCδ/ERK/P65 [], or metalloproteases MMP-2/MMP-9 [], to mention a few (Figure 7).
Aside from fine structural studies revealing activated and inactivated conformations of the receptors induced by movements of receptor domains, determining the binding kinetics of both agonist and antagonist ligands deserves attention to ascertain signal transduction outcomes and determine new drugs’ specificity, efficacy, modulation, and potency [].
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
State agencies have only approved using human NK-1R antagonists for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting []. Basic experimental research provided much information on the potential efficacy of NK-1R antagonists in other pathological entities related to substance abuse, pain, some types of cancer, and psychiatric disorders, among others [,,,,]. The drawbacks have come from the poor efficacy observed in some clinical assays, possibly associated with low receptor occupancy or other factors, and the need to simultaneously target different types of NK receptors for specific pathologies to attain effectiveness []. Receptor occupancy determines drug responses []. It is an important issue when considering using NK-1R antagonists in therapy, from psychiatric disorders to malignancies [,]. Clinical trials that used NK-1R antagonists to treat individuals with major depressive disorder (MDD) [] reported low efficacy results, leading to a discontinuation of the studies. A possible explanation for the negative outcomes appeared associated with the observation that only receptor occupancy close to 100% determined the efficacy of NK-1R antagonists [,]. Consequently, contemplating dose, route of administration, pharmacokinetics, and tissue penetration to attain required receptor occupancy, the design of specific antagonists that may interfere with activated states of the receptors, and careful selection of patients, demands additional basic and clinical research [,].
The accurate determination of structural changes defined by agonist and antagonist contacts at the atomic level governing selectivity, potency, and efficacy is essential for detecting NK-1 receptors to block or lessen given signaling routes and alleviate the effects of NK-1R-dependent malfunction. Biased agonist activation through the same receptor structure that triggers different signals opens new lines for the design of drugs in a way that is more specific, more effective, and addressed to tackling certain disorders related to particular signaling pathways [,,]. Additionally, the heteromerization of NK-1 receptors is a mechanism worth exploring to design specific drugs that modulate the action of the receptor complexes []. Furthermore, the role of the NK-1R truncated isoform merits attention in the design of new drugs.
Refined structural determinations and basal functional research concerning the interaction of NK-1 receptors with proteins involved in cellular signaling and cross-talk pathways are necessary to unveil their participation in numerous processes such as cell proliferation, inflammation, melanogenesis, pain control, and mood and stress-related disorders and to design modulation strategies that would eventually permit targeted therapies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, design, bibliography analysis, draft preparation, writing and review, F.D.R. and R.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
Support from Programa XIII de la Universidad de Salamanca to the GIR group (Bases Moleculares del Desarrollo) is acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Euler, U.S.V.; Gaddum, J.H. An unidentified depressor substance in certain tissue extracts. J. Physiol. 1931, 72, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.M.; Leeman, S.E. Isolation of a Sialogogic Peptide from Bovine Hypothalamic Tissue and Its Characterization as Substance P. J. Biol. Chem. 1970, 245, 4784–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.M.; Leeman, S.E.; Niall, H.D. Amino-acid Sequence of Substance P. Nat. New Biol. 1971, 232, 86–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severini, C.; Improta, G.; Falconieri-Erspamer, G.; Salvadori, S.; Erspamer, V. The Tachykinin Peptide Family. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002, 54, 285–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.; Canning, B.; Coulson, J.; Dombrowsky, E.; Douglas, S.D.; Fong, T.M.; Heyward, C.Y.; Leeman, S.E.; Remeshwar, P. Tachykinin receptors (version 2019.4) in the IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology Database. IUPHAR/BPS Guide Pharmacol. CITE 2019, 2019, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nässel, D.R.; Zandawala, M.; Kawada, T.; Satake, H. Tachykinins: Neuropeptides That Are Ancient, Diverse, Widespread and Functionally Pleiotropic. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, B.; Nygaard, R.; Valentin-Hansen, L.; Bach, A.; Engelstoft, M.S.; Petersen, P.S.; Frimurer, T.M.; Schwartz, T.W. A Conserved Aromatic Lock for the Tryptophan Rotameric Switch in TM-VI of Seven-transmembrane Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 3973–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preininger, A.M.; Meiler, J.; Hamm, H.E. Conformational Flexibility and Structural Dynamics in GPCR-Mediated G Protein Activation: A Perspective. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 2288–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussap, C.J.; Geraghty, D.P.; Burcher, E. Tachykinin Receptors: A Radioligand Binding Perspective. J. Neurochem. 1993, 60, 1987–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennefather, J.N.; Lecci, A.; Candenas, M.L.; Patak, E.; Pinto, F.M.; Maggi, C.A. Tachykinins and tachykinin receptors: A growing family. Life Sci. 2004, 74, 1445–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regoli, D.; Drapeau, G.; Dion, S.; Couture, R. New selective agonists for neurokinin receptors: Pharmacological tools for receptor characterization. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1988, 9, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, T.-V.; Escher, E.; Quirion, R. Evidence for the existence of three classes of neurokinin receptors in brain. Differential ontogeny of neurokinin-1, neurokinin-2 and neurokinin-3 binding sites in rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1988, 453, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Chou, K.B.; Takeda, J.; Sachais, B.S.; Krause, J.E. Molecular cloning, structural characterization and functional expression of the human substance P receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 179, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erspamer, V. Bioactive Secretions of the Integument. Amphibian Biology I. The Integuments; Heatwole, H., Barthalmus, G., Eds.; Surrey Beatty & Sons: Chipping Norton, NSW, Australia, 1994; pp. 178–350. [Google Scholar]
- Ballesteros, J.A.; Weinstein, H. Integrated methods for the construction of three-dimensional models and computational probing of structure-function relations in G protein-coupled receptors. Methods Neurosci. 1995, 25, 366–428. [Google Scholar]
- GPCR Database. GPCR Database. 2022. Available online: https://gpcrdb.org (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Pándy-Szekeres, G.; Esguerra, M.; Hauser, A.S.; Caroli, J.; Munk, C.; Pilger, S.; Keserű, G.M.; Kooistra, A.J.; Gloriam, D.E. The G protein database, GproteinDb. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D518–D525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondar, A.-N.; White, S.H. Hydrogen bond dynamics in membrane protein function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.X.; Cocco, M.J.; Russ, W.P.; Brunger, A.T.; Engelman, D.M. Interhelical hydrogen bonding drives strong interactions in membrane proteins. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Chun, E.; Thompson, A.A.; Chubukov, P.; Xu, F.; Katritch, V.; Han, G.W.; Roth, C.B.; Heitman, L.H.; Ijzerman, A.P.; et al. Structural Basis for Allosteric Regulation of GPCRs by Sodium Ions. Science 2012, 337, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, T.M.; Anderson, S.A.; Yu, H.; Huang, R.R.; Strader, C.D. Differential activation of intracellular effector by two isoforms of human neurokinin-1 receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 1992, 41, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen, R.; Holliday, N.D.; Hansen, J.L.; Vrecl, M.; Heding, A.; Schwartz, T.W.; Elling, C.E. Characterization of G-Protein Coupled Receptor Kinase Interaction with the Neurokinin-1 Receptor Using Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilger, D.; Masureel, M.; Kobilka, B.K. Structure and dynamics of GPCR signaling complexes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, D.D.; Lieu, T.; Halls, M.L.; Veldhuis, N.A.; Imlach, W.L.; Mai, Q.N.; Poole, D.P.; Quach, T.; Aurelio, L.; Conner, J.; et al. Neurokinin 1 receptor signaling in endosomes mediates sustained nociception and is a viable therapeutic target for prolonged pain relief. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaal3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.-P.; Lai, S.; Tuluc, F.; Tansky, M.F.; Kilpatrick, L.E.; Leeman, S.E.; Douglas, S.D. Differences in the length of the carboxyl terminus mediate functional properties of neurokinin-1 receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12605–12610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitsin, S.; Pappa, V.; Douglas, S.D. Truncation of neurokinin-1 receptor-Negative regulation of substance P signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 103, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinos-Quintana, A.; Trujillo-Hacha, P.; Piruat, J.I.; Bejarano-García, J.A.; García-Guerrero, E.; Pérez-Simón, J.A.; Muñoz, M. Human acute myeloid leukemia cells express Neurokinin-1 receptor, which is involved in the antileukemic effect of Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists. Investig. New Drugs 2019, 37, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Frakich, N.; Filippini, P.; Edwards, L.J.; Vinkemeier, U.; Gran, B.; Tanasescu, R.; Bayraktutan, U.; Colombo, S.; Constantinescu, C.S. Effects of substance P on human cerebral microvascular endothelial cell line hCMEC/D3 are mediated exclusively through a truncated NK-1 receptor and depend on cell confluence. Neuropeptides 2022, 95, 102265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morteau, O.; Lu, B.; Gerard, C.; Gerard, N.P. Hemokinin 1 is a full agonist at the substance P receptor. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borbély, É.; Helyes, Z. Role of hemokinin-1 in health and disease. Neuropeptides 2017, 64, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, L.; Furlonger, C.; Wu, G.E.; Paige, C.J. Hemokinin is a hematopoietic-specific tachykinin that regulates B lymphopoiesis. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurasekova, Z.; Garcia-Leis, A.; Sanchez-Cortes, S.; Tinti, A.; Torreggiani, A. Structural analysis of the neuropeptide substance P by using vibrational spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 7419–7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, J.P.; Davies, S.M.; Hauss, T. Interaction of Substance P with Phospholipid Bilayers: A Neutron Diffraction Study. Biophys. J. 1998, 75, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, T.A.; Rojo, J.; Nieto, P.M.; Pinto, F.M.; Hernandez, M.; Martín, J.D.; Candenas, M.L. Tachykinins and Tachykinin Receptors: Structure and Activity Relationships. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 2045–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.R.C.; Yu, H.; Strader, C.D.; Fong, T.M. Interaction of Substance P with the Second and Seventh Transmembrane Domains of the Neurokinin-1 Receptor. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 3007–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrini, M.; Bremer, A.A.; Ulfers, A.L.; Boyd, N.D.; Mierke, D.F. Molecular characterization of the substance P*neurokinin-1 receptor complex: Development of an experimentally based model. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 22862–22867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, A.A.; Leeman, S.E.; Boyd, N.D. Evidence for Spatial Proximity of Two Distinct Receptor Regions in the Substance P (SP)·Neurokinin-1 Receptor (NK-1R) Complex Obtained by Photolabeling the NK-1R withp-Benzoylphenylalanine3-SP. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 22857–22861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, N.D.; Kage, R.; Dumas, J.J.; Krause, J.E.; Leeman, S.E. The peptide binding site of the substance P (NK-1) receptor localized by a photoreactive analogue of substance P: Presence of a disulfide bond. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin-Hansen, L.; Park, M.; Huber, T.; Grunbeck, A.; Naganathan, S.; Schwartz, T.W.; Sakmar, T.P. Mapping Substance P Binding Sites on the Neurokinin-1 Receptor Using Genetic Incorporation of a Photoreactive Amino Acid. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 18045–18054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KingDraw Free Software. 2022. Available online: https://www.kingdraw.cn/en/index.html (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- PDB. Protein Data Bank (PDB). 2022. Available online: https://pdb101.rcsb.org (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Gayen, A.; Goswami, S.K.; Mukhopadhyay, C. NMR evidence of GM1-induced conformational change of Substance P using isotropic bicelles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1808, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehnal, D.; Bittrich, S.; Deshpande, M.; Svobodová, R.; Berka, K.; Bazgier, V.; Velankar, S.; Burley, S.K.; Koča, J.; Rose, A.S. Mol* Viewer: Modern web app for 3D visualization and analysis of large biomolecular structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W431–W437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willard, L.; Ranjan, A.; Zhang, H.; Monzavi, H.; Boyko, R.F.; Sykes, B.D.; Wishart, D.S. VADAR: A web server for quantitative evaluation of protein structure quality. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3316–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, C.; Ehrenmann, J.; Vacca, S.; Waltenspühl, Y.; Schöppe, J.; Medalia, O.; Plückthun, A. Structures of neurokinin 1 receptor in complex with G q and G s proteins reveal substance P binding mode and unique activation features. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabk2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monastyrskaya, K.; Hostettler, A.; Buergi, S.; Draeger, A. The NK1 Receptor Localizes to the Plasma Membrane Microdomains, and Its Activation Is Dependent on Lipid Raft Integrity. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 7135–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.A.; Faust, B.; Gondin, A.B.; Dämgen, M.A.; Suomivuori, C.-M.; Veldhuis, N.A.; Cheng, Y.; Dror, R.O.; Thal, D.M.; Manglik, A. Selective G protein signaling driven by substance P–neurokinin receptor dynamics. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yang, F.; Ling, S.; Luo, Y.; Lv, P.; Xu, H.E.; Tian, C.; Yin, W.; et al. Structural insights into the activation of neurokinin 2 receptor by neurokinin A. Cell Discov. 2022, 8, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boks, G.J.; Tollenaere, J.P.; Kroon, J. Possible ligand-receptor interactions for NK1 antagonists as observed in their crystal structures. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 1997, 5, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lu, M.; Liu, D.; Yang, L.; Yi, C.; Ma, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Frimurer, T.M.; Wang, M.-W.; et al. Human substance P receptor binding mode of the antagonist drug aprepitant by NMR and crystallography. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Chapman, K.; Clark, L.D.; Shao, Z.; Borek, D.; Xu, Q.; Wang, J.; Rosenbaum, D.M. Crystal structure of the human NK(1) tachykinin receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 13264–13269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recio, R.; Lerena, P.; Pozo, E.; Calderón-Montaño, J.M.; Burgos-Morón, E.; López-Lázaro, M.; Valdivia, V.; Leal, M.P.; Mouillac, B.; Organero, J.Á.; et al. Carbohydrate-Based NK1R Antagonists with Broad-Spectrum Anticancer Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 10350–10370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-De-Terán, H.; Massink, A.; Rodríguez, D.; Liu, W.; Han, G.W.; Joseph, J.S.; Katritch, I.; Heitman, L.H.; Xia, L.; Ijzerman, A.P.; et al. The Role of a Sodium Ion Binding Site in the Allosteric Modulation of the A(2A) Adenosine G Protein-Coupled Receptor. Structure 2013, 21, 2175–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katritch, V.; Fenalti, G.; Abola, E.E.; Roth, B.L.; Cherezov, V.; Stevens, R.C. Allosteric sodium in class A GPCR signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentin-Hansen, L.; Frimurer, T.M.; Mokrosinski, J.; Holliday, N.D.; Schwartz, T.W. Biased Gs Versus Gq Proteins and β-Arrestin Signaling in the NK1 Receptor Determined by Interactions in the Water Hydrogen Bond Network. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 24495–24508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warne, T.; Serrano-Vega, M.J.; Baker, J.G.; Moukhametzianov, R.; Edwards, P.C.; Henderson, R.; Leslie, A.G.W.; Tate, C.G.; Schertler, G.F.X. Structure of a beta1-adrenergic G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature 2008, 454, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilger, D. The role of structural dynamics in GPCR-mediated signaling. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 2461–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, R.; Lagerström, M.C.; Lundin, L.G.; Schiöth, H.B. The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Mol Pharmacol. 2003, 63, 1256–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.K.; Prosser, R.S. Dynamics and Mechanistic Underpinnings to Pharmacology of Class A GPCRs—An NMR Perspective. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 322, C739–C753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, K.L.; Eddy, M.T.; Gao, Z.-G.; Han, G.W.; Lian, T.; Deary, A.; Patel, N.; Jacobson, K.A.; Katritch, V.; Stevens, R.C. Structural Connection between Activation Microswitch and Allosteric Sodium Site in GPCR Signaling. Structure 2018, 26, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, D.M.; Rasmussen, S.G.; Kobilka, B.K. The structure and function of G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature 2009, 459, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katritch, V.; Cherezov, V.; Stevens, R.C. Structure-Function of the G Protein–Coupled Receptor Superfamily. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 531–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defea, K. Beta-arrestins and heterotrimeric G-proteins: Collaborators and competitors in signal transduction. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153 (Suppl. 1), 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salon, J.A.; Lodowski, D.T.; Palczewski, K. The Significance of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Crystallography for Drug Discovery. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 901–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Basith, S.; Choi, S. Recent Advances in Structure-Based Drug Design Targeting Class A G Protein-Coupled Receptors Utilizing Crystal Structures and Computational Simulations. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 61, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantas, I.; Saarinen, M.; Xu, Z.D.; Svenningsson, P. Update on GPCR-based targets for the development of novel antidepressants. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 534–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.G.; DeVree, B.T.; Zou, Y.; Kruse, A.C.; Chung, K.Y.; Kobilka, T.S.; Thian, F.S.; Chae, P.S.; Pardon, E.; Calinski, D.; et al. Crystal structure of the β2 adrenergic receptor–Gs protein complex. Nature 2011, 477, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichel, K.; von Zastrow, M. Subcellular Organization of GPCR Signaling. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutkeviciute, I.; Vilardaga, J.-P. Structural insights into emergent signaling modes of G protein–coupled receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 11626–11642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wold, E.A.; Chen, J.; Cunningham, K.A.; Zhou, J. Allosteric Modulation of Class A GPCRs: Targets, Agents, and Emerging Concepts. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 88–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, B. Structural Studies of G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Mol. Cells 2015, 38, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, D.; Wu, M.; Guo, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhong, L.; Cai, X.; Dai, A.; Jang, W.; Shakhnovich, E.I.; et al. Common activation mechanism of class A GPCRs. eLife 2019, 8, e50279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, R.; Frimurer, T.M.; Holst, B.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Schwartz, T.W. Ligand binding and micro-switches in 7TM receptor structures. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisler, J.W.; Xiao, K.; Thomsen, A.R.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Recent developments in biased agonism. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2013, 27, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkilde, M.M.; Smit, M.J.; Waldhoer, M. Structure, function and physiological consequences of virally encoded chemokine seven transmembrane receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153 (Suppl. 1), 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, K.; Insel, P.A. G Protein-Coupled Receptors as Targets for Approved Drugs: How Many Targets and How Many Drugs? Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 93, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, A.S.; Attwood, M.M.; Rask-Andersen, M.; Schiöth, H.B.; Gloriam, D.E. Trends in GPCR drug discovery: New agents, targets and indications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 829–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, R.; Martinez-Pinilla, E.; Lanciego, J.L.; Navarro, G. Basic Pharmacological and Structural Evidence for Class A G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Heteromerization. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaitonde, S.A.; González-Maeso, J. Contribution of heteromerization to G protein-coupled receptor function. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 32, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, I.; Ayoub, M.A.; Fujita, W.; Jaeger, W.C.; Pfleger, K.D.; Devi, L.A. G Protein–Coupled Receptor Heteromers. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 56, 403–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, M.; Kirscht, S.; Stumm, R.; Koch, T.; Wu, D.; Laugsch, M.; Schröder, H.; Höllt, V.; Schulz, S. Heterodimerization of substance P and mu-opioid receptors regulates receptor trafficking and resensitization. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 51630–51637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, S.; Shui, W. Post-Translational Modifications of G Protein–Coupled Receptors Revealed by Proteomics and Structural Biology. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 843502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palczewski, K.; Kumasaka, T.; Hori, T.; Behnke, C.A.; Motoshima, H.; Fox, B.A.; Le Trong, I.; Teller, D.C.; Okada, T.; Stenkamp, R.E.; et al. Crystal Structure of Rhodopsin: A G Protein-Coupled Receptor. Science 2000, 289, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherezov, V.; Rosenbaum, D.M.; Stevens, R.C.; Hanson, M.A.; Rasmusen, S.G.F.; Thian, S.S.; Kobilka, T.S.; Choi, H.; Kuhn, P.; Weis, W.I.; et al. High-Resolution Crystal Structure of an Engineered Human β2 -Adrenergic G Protein–Coupled Receptor. Science 2007, 318, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagan, S.; Chassaing, G.; Pradier, L.; Lavielle, S. Tachykinin peptides affect differently the second messenger pathways after binding to CHO-expressed human NK-1 receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1996, 276, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Riitano, D.; Werge, T.M.; Costa, T. A Mutation Changes Ligand Selectivity and Transmembrane Signaling Preference of the Neurokinin-1 Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 7646–7655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurada, T.; Yamada, T.; Tan-No, K.; Manome, Y.; Sakurada, S.; Kisara, K.; Ohba, M. Differential effects of substance P analogs on neurokinin 1 receptor agonists in the mouse spinal cord. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1991, 259, 205–210. [Google Scholar]
- Trafton, J.A.; Abbadie, C.; Basbaum, A.I. Differential Contribution of Substance P and Neurokinin A to Spinal Cord Neurokinin-1 Receptor Signaling in the Rat. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 3656–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calebiro, D.; Godbole, A. Internalization of G-protein-coupled receptors: Implication in receptor function, physiology and diseases. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 32, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Recio, S.; Gascón, P. Biological and Pharmacological Aspects of the NK1-Receptor. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 495704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Y.-L.; Liu, S.; Yan, W.-W.; Dong, B. Wnt/β-catenin signaling as a useful therapeutic target in hepatoblastoma. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20192466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, J.E.; Bu, J.Y.; Takeda, Y.; Blount, P.; Raddatz, R.; Sachais, B.S.; Chou, K.B.; Takeda, J.; McCarson, K.; DiMaggio, D. Structure, expression and second messenger-mediated regulation of the human and rat substance P receptors and their genes. Regul. Pept. 1993, 46, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartara, L.; Maggi, C.A. The tachykinin NK1 receptor. Part I: Ligands and mechanisms of cellular activation. Neuropeptides 1997, 31, 537–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhoff, M.S.; von Mentzer, B.; Geppetti, P.; Pothoulakis, C.; Bunnett, N.W. Tachykinins and Their Receptors: Contributions to Physiological Control and the Mechanisms of Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 265–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieglgänsberger, W. Substance P and pain chronicity. Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 375, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistrova, E.; Kruzliak, P.; Chottova Dvorakova, M.C. Role of substance P in the cardiovascular system. Neuropeptides 2016, 58, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, S.; Javid, H.; Alaei, A.; Hashemy, S.I. New insight into the role of substance P/neurokinin-1 receptor system in breast cancer progression and its crosstalk with microRNAs. Clin. Genet. 2020, 98, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javid, H.; Mohammadi, F.; Zahiri, E.; Hashemy, S.I. The emerging role of substance P/neurokinin-1 receptor signaling pathways in growth and development of tumor cells. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 75, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eapen, P.M.; Rao, C.M.; Nampoothiri, M. Crosstalk between neurokinin receptor signaling and neuroinflammation in neurological disorders. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 30, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, B.; Hastrup, H.; Raffetseder, U.; Martini, L.; Schwartz, T.W. Two Active Molecular Phenotypes of the Tachykinin NK1 Receptor Revealed by G-protein Fusions and Mutagenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 19793–19799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suomivuori, C.-M.; Latorraca, N.R.; Wingler, L.M.; Eismann, S.; King, M.C.; Kleinhenz, A.L.W.; Skiba, M.A.; Staus, D.P.; Kruse, A.C.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; et al. Molecular mechanism of biased signaling in a prototypical G protein–coupled receptor. Science 2020, 367, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kage, R.; Leeman, S.E.; Boyd, N.D. Biochemical Characterization of Two Different Forms of the Substance P Receptor in Rat Submaxillary Gland. J. Neurochem. 1993, 60, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuluc, F.; Lai, J.P.; Kilpatrick, L.E.; Evans, D.L.; Douglas, S.D. Neurokinin 1 receptor isoforms and the control of innate immunity. Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, S.G.; Carneiro, B.A.; Mota, J.M.; Costa, R.; Leite, C.A.; Barroso-Sousa, R.; Kaplan, J.B.; Chae, Y.K.; Giles, F.J. Wnt/beta-catenin pathway: Modulating anticancer immune response. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagotto, F. Looking beyond the Wnt pathway for the deep nature of β-catenin. EMBO Rep. 2013, 14, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronkov, A.; Krauss, S. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and small molecule inhibitors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 634–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bienz, M. Beta-Catenin: A pivot between cell adhesion and Wnt signalling. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnier, A.; Vykoukal, J.; Hubertus, J.; Alt, E.; von Schweinitz, D.; Kappler, R.; Berger, M.; Ilmer, M. Targeting the neurokinin-1 receptor inhibits growth of human colon cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Ling, J.; Song, H.; Lv, B.; Wang, L.; Shang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chang, C.; Ping, F.; Qian, J. Neurokinin-1 receptor is a novel positive regulator of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in melanogenesis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 81268–81280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilmer, M.; Garnier, A.; Vykoukal, J.; Alt, E.; von Schweinitz, D.; Kappler, R.; Berger, M. Targeting the Neurokinin-1 Receptor Compromises Canonical Wnt Signaling in Hepatoblastoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 2712–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.-L.; Hou, J.-F.; Li, J.-X. The NK1 receptor antagonist NKP608 inhibits proliferation of human colorectal cancer cells via Wnt signaling pathway. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, Y.K.; Luttrell, L.M. The Diverse Roles of Arrestin Scaffolds in G Protein–Coupled Receptor Signaling. Pharmacol. Rev. 2017, 69, 256–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Xu, X.; Ge, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, G.-Q.; Miao, L.; Deng, X. Aprepitant Inhibits JNK and p38/MAPK to Attenuate Inflammation and Suppresses Inflammatory Pain. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 811584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumaravel, S.; Dhole, S.; Roy, S.; Pavan, V.; Chakraborty, S. Neuropeptide Substance P Enhances Inflammation-Mediated Tumor Signaling Pathways and Migration and Proliferation of Head and Neck Cancers. Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 12 (Suppl. 1), 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhong, Y.; Tang, Z.; Pu, Y.; Lu, C.; Yin, G.; et al. Cinacalcet Targets the Neurokinin-1 Receptor and Inhibits PKCδ/ERK/P65 Signaling to Alleviate Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 735194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golestaneh, M.; Firoozrai, M.; Javid, H.; Hashemy, S.I. The substance P/neurokinin-1 receptor signaling pathway mediates metastasis in human colorectal SW480 cancer cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 4893–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nederpelt, I.; Kuzikov, M.; De Witte, W.E.A.; Schnider, P.; Tuijt, B.; Gul, S.; Ijzerman, A.P.; De Lange, E.C.M.; Heitman, L.H. From receptor binding kinetics to signal transduction; a missing link in predicting in vivo drug-action. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14169–14174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthaus, M.; Schiel, X.; Ruhlmann, C.H.; Celio, L. Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists: Review of their role for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in adults. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 661–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, M.; Coveñas, R. Involvement of substance P and the NK-1 receptor in human pathology. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 1727–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandweiss, A.J.; McIntosh, M.I.; Moutal, A.; Davidson-Knapp, R.; Hu, J.; Giri, A.K.; Yamamoto, T.; Hruby, V.J.; Khanna, R.; Largent-Milnes, T.M.; et al. Genetic and pharmacological antagonism of NK(1) receptor prevents opiate abuse potential. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 1745–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olive, M.F. Neurokinin-1 (NK1) receptor antagonists as possible therapeutics for psychostimulant use disorders. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2015, 14, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupniak, N.M.; Kramer, M.S. NK1 receptor antagonists for depression: Why a validated concept was abandoned. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 223, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonville, L.; Paterson, L.; Herlinger, K.; Hayes, A.; Hill, R.; Nutt, D.; Lingford-Hughes, A. Functional evaluation of NK(1) antagonism on cue reactivity in opiate dependence; An fMRI study. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021, 221, 108564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallakh, R.S.E.; Kim, E.; McCoy, B. Receptor occupancy and drug response: Understanding the relationship. Curr. Psychiatry 2018, 17, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domi, E.; Domi, A.; Adermark, L.; Heilig, M.; Augier, E. Neurobiology of alcohol seeking behavior. J. Neurochem. 2021, 157, 1585–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Muñoz, M.E.; Morell, F.; Coveñas, R. Why Use Aprepitant Only as a Cough Suppressant in Lung Cancer When at Higher Doses it Could Also Exert an Antitumor Action? Arch. Bronconeumol. 2022; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.; Montgomery, S.; Ball, W.; Morrison, M.; Snavely, D.; Liu, G.; Hargreaves, R.; Hietala, J.; Lines, C.; Beebe, K.; et al. Lack of Efficacy of the Substance P (Neurokinin1 Receptor) Antagonist Aprepitant in the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratti, E.; Bettica, P.; Alexander, R.; Archer, G.; Carpenter, D.; Evoniuk, G.; Gomeni, R.; Lawson, E.; Lopez, M.; Millns, H.; et al. Full central neurokinin-1 receptor blockade is required for efficacy in depression: Evidence from orvepitant clinical studies. J. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 27, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Fabio, R.; Alvaro, G.; Griffante, C.; Pizzi, D.A.; Donati, D.; Mattioli, M.; Cimarosti, Z.; Guercio, G.; Marchioro, C.; Provera, S.; et al. Discovery and Biological Characterization of (2R,4S)-1′-Acetyl-N-{(1R)-1-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethyl}-2-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-N-methyl-4,4′-bipiperidine-1-carboxamide as a New Potent and Selective Neurokinin 1 (NK1) Receptor Antagonist Clinical Candidate. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).