Impaired Cerebral Hemodynamics in Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Stenosis Assessed by Resting-State Functional MRI
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. MRI Acquisition
2.3. Image Preprocessing
2.4. Resting-State Cerebrovascular Reactivity (RS-CVR)
2.5. Time Shift (TS)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
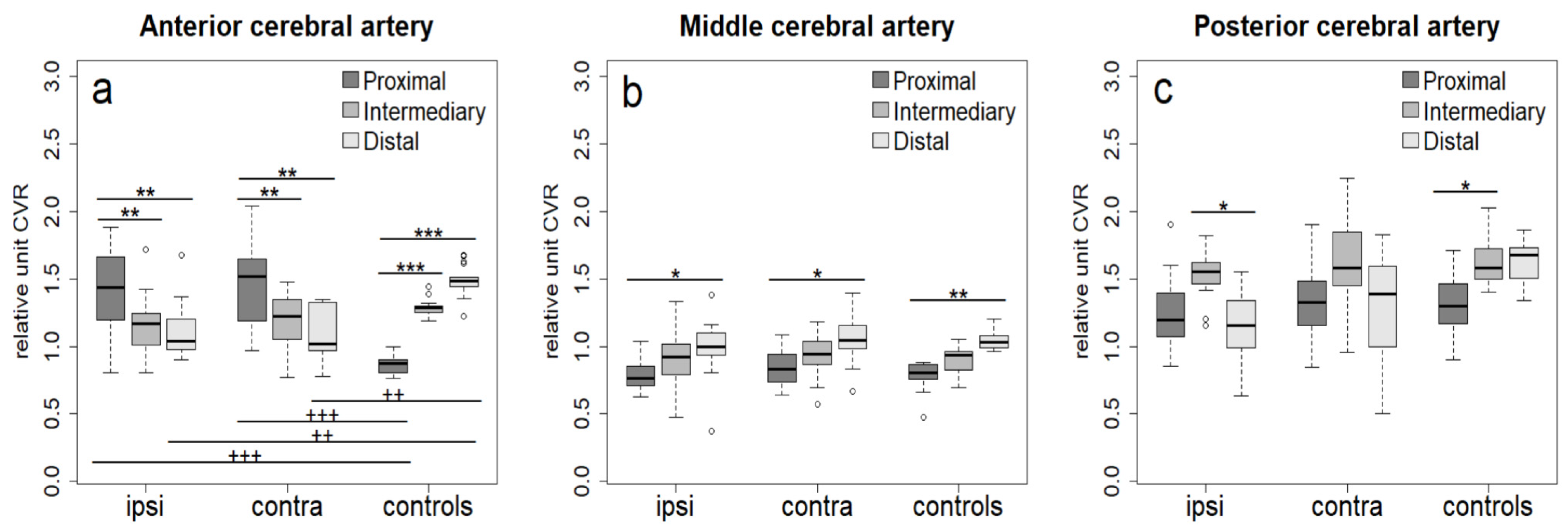
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACA | Anterior cerebral artery |
| ACAS | Asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis |
| ATT | Arterial transit time |
| BOLD | Blood-oxygenation-level-dependent |
| CBF | Cerebral blood flow |
| CVR | Cerebrovascular reactivity |
| EPI | Echo-planar imaging |
| FWHM | Full width at half maximum |
| ICA | Internal carotid artery |
| IRB | Institutional review board |
| MCA | Middle cerebral artery |
| MRA | Magnetic resonance angiography |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| MTT | Mean transit time |
| PCA | Posterior cerebral artery |
| ROIs | Regions of interest |
| RS-BOLD | Resting-state BOLD |
| RS-CVR | Resting-state cerebrovascular reactivity |
| rs-fMRI | Resting-state magnetic resonance imaging |
| sLFOs | Systemic low-frequency oscillations |
| TIA | Transient ischemic attack |
| TS | Time shift |
| TTP | Time to peak |
| VAs | Vertebral arteries |
References
- Hillen, T.; Coshall, C.; Tilling, K.; Rudd, A.G.; McGovern, R.; Wolfe, C.D.A. South London Stroke Register Cause of Stroke Recurrence Is Multifactorial: Patterns, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Stroke Recurrence in the South London Stroke Register. Stroke 2003, 34, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Weerd, M.; Greving, J.P.; Hedblad, B.; Lorenz, M.W.; Mathiesen, E.B.; O’Leary, D.H.; Rosvall, M.; Sitzer, M.; de Borst, G.J.; Buskens, E.; et al. Prediction of Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Stenosis in the General Population: Identification of High-Risk Groups. Stroke 2014, 45, 2366–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, G.W.; Brown, R.D., Jr.; Whisnant, J.P.; Sicks, J.D.; O’Fallon, W.M.; Wiebers, D.O. Ischemic Stroke Subtypes: A Population-Based Study of Incidence and Risk Factors. Stroke 1999, 30, 2513–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göttler, J.; Kaczmarz, S.; Nuttall, R.; Griese, V.; Napiórkowski, N.; Kallmayer, M.; Wustrow, I.; Eckstein, H.-H.; Zimmer, C.; Preibisch, C.; et al. The Stronger One-Sided Relative Hypoperfusion, the More Pronounced Ipsilateral Spatial Attentional Bias in Patients with Asymptomatic Carotid Stenosis. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2020, 40, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbuRahma, A.F.; Avgerinos, E.D.; Chang, R.W.; Darling, R.C., 3rd; Duncan, A.A.; Forbes, T.L.; Malas, M.B.; Murad, M.H.; Perler, B.A.; Powell, R.J.; et al. Society for Vascular Surgery Clinical Practice Guidelines for Management of Extracranial Cerebrovascular Disease. J. Vasc. Surg. 2022, 75, 4S–22S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, R.; Rerkasem, K.; Rothwell, P.M. Systematic Review of the Risks of Carotid Endarterectomy in Relation to the Clinical Indication for and Timing of Surgery. Stroke 2003, 34, 2290–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schollenberger, J.; Braet, D.J.; Hernandez-Garcia, L.; Osborne, N.H.; Figueroa, C.A. A Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Based Computational Analysis of Cerebral Hemodynamics in Patients with Carotid Artery Stenosis. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2023, 13, 1126–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hartog, A.G.; Achterberg, S.; Moll, F.L.; Kappelle, L.J.; Visseren, F.L.J.; van der Graaf, Y.; Algra, A.; de Borst, G.J. SMART Study Group Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Stenosis and the Risk of Ischemic Stroke according to Subtype in Patients with Clinical Manifest Arterial Disease. Stroke 2013, 44, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sun, D.; Liu, Y.; Mei, B.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J. The Impact of Carotid Artery Stenting on Cerebral Perfusion, Functional Connectivity, and Cognition in Severe Asymptomatic Carotid Stenosis Patients. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleißner, C.; Kaczmarz, S.; Kufer, J.; Schmitzer, L.; Kallmayer, M.; Zimmer, C.; Wiestler, B.; Preibisch, C.; Göttler, J. Hemodynamic MRI Parameters to Predict Asymptomatic Unilateral Carotid Artery Stenosis with Random Forest Machine Learning. Front. Neuroimaging 2022, 1, 1056503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, R.F.; Mazzetto-Betti, K.C.; Silva, A.C.; Dos Santos, A.C.; de Araujo, D.B.; Leite, J.P.; Pontes-Neto, O.M. Assessing Cerebrovascular Reactivity in Carotid Steno-Occlusive Disease Using MRI BOLD and ASL Techniques. Radiol. Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 268483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leoni, R.F.; Oliveira, I.A.F.; Pontes-Neto, O.M.; Santos, A.C.; Leite, J.P. Cerebral Blood Flow and Vasoreactivity in Aging: An Arterial Spin Labeling Study. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2017, 50, e5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vis, J.B.; Petersen, E.T.; Bhogal, A.; Hartkamp, N.S.; Klijn, C.J.M.; Kappelle, L.J.; Hendrikse, J. Calibrated MRI to Evaluate Cerebral Hemodynamics in Patients with an Internal Carotid Artery Occlusion. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geranmayeh, F.; Wise, R.J.S.; Leech, R.; Murphy, K. Measuring Vascular Reactivity with Breath-Holds after Stroke: A Method to Aid Interpretation of Group-Level BOLD Signal Changes in Longitudinal fMRI Studies. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 1755–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, G.W.; Thrippleton, M.J.; Shi, Y.; Hamilton, I.; Stringer, M.; Chappell, F.; Dickie, D.A.; Andrews, P.; Marshall, I.; Doubal, F.N.; et al. Intracranial Hemodynamic Relationships in Patients with Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Neurology 2020, 94, e2258–e2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastrup, A.; Li, T.Q.; Takahashi, A.; Glover, G.H.; Moseley, M.E. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Regional Cerebral Blood Oxygenation Changes during Breath Holding. Stroke 1998, 29, 2641–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burley, C.V.; Francis, S.T.; Thomas, K.N.; Whittaker, A.C.; Lucas, S.J.E.; Mullinger, K.J. Contrasting Measures of Cerebrovascular Reactivity between MRI and Doppler: A Cross-Sectional Study of Younger and Older Healthy Individuals. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 656746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebök, M.; Germans, M.R.; van Niftrik, C.H.B.; Kulcsár, Z.; Regli, L.; Fierstra, J. More Pronounced Hemodynamic Alterations in Patients with Brain Arteriovenous Malformation–associated Epilepsy. Neurosurg. Focus 2022, 53, E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Liu, P.; Yezhuvath, U.; Cheng, Y.; Marshall, O.; Ge, Y. MRI Mapping of Cerebrovascular Reactivity via Gas Inhalation Challenges. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 94, e52306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, Y.; Pinho, M.; Park, D.C.; Welch, B.G.; Lu, H. Cerebrovascular Reactivity Mapping without Gas Challenges. Neuroimage 2017, 146, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestani, A.M.; Wei, L.L.; Chen, J.J. Quantitative Mapping of Cerebrovascular Reactivity Using Resting-State BOLD fMRI: Validation in Healthy Adults. Neuroimage 2016, 138, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secchinato, K.F.; da Silva, P.H.R.; Camargo, A.P.A.; Pontes-Neto, O.M.; Leoni, R.F. Cerebrovascular reactivity mapping without hypercapnic challenge in patients with carotid artery stenosis. Rev. Bras. Fis. Med. 2019, 13, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amemiya, S.; Kunimatsu, A.; Saito, N.; Ohtomo, K. Cerebral Hemodynamic Impairment: Assessment with Resting-State Functional MR Imaging. Radiology 2014, 270, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Qi, Z.; An, Y.; Zhang, M.; Qian, T.; Lu, J. Detecting Perfusion Deficit in Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment Patients by Resting-State fMRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, S.; Aso, T.; Takaya, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Kikuchi, T.; Funaki, T.; Yoshida, K.; Okada, T.; Kunieda, T.; Togashi, K.; et al. Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Identifies Cerebrovascular Reactivity Impairment in Patients with Arterial Occlusive Diseases: A Pilot Study. Neurosurgery 2019, 85, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, K.; Lu, H.; Welch, B.G.; Thomas, B.P.; Pinho, M.; Lin, D.; Hillis, A.E.; Liu, P. Evaluation of Cerebrovascular Reserve in Patients with Cerebrovascular Diseases Using Resting-State MRI: A Feasibility Study. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 59, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, J.S.; Snyder, A.Z.; Ramsey, L.; Shulman, G.L.; Corbetta, M. The Effects of Hemodynamic Lag on Functional Connectivity and Behavior after Stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 2162–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, T.; Jahanian, H.; Ni, W.W.; Qiu, D.; Moseley, M.E.; Zaharchuk, G. Noncontrast Mapping of Arterial Delay and Functional Connectivity Using Resting-State Functional MRI: A Study in Moyamoya Patients. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 41, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Margulies, D.S.; Cameron Craddock, R.; Long, X.; Winter, B.; Gierhake, D.; Endres, M.; Villringer, K.; Fiebach, J.; Villringer, A. Identifying the Perfusion Deficit in Acute Stroke with Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 73, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.Q.; Kraft, A.W.; Wright, P.W.; Snyder, A.Z.; Lee, J.-M.; Culver, J.P. Optical Imaging of Disrupted Functional Connectivity Following Ischemic Stroke in Mice. Neuroimage 2014, 99, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovadia-Caro, S.; Margulies, D.S.; Villringer, A. The Value of Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Stroke. Stroke 2014, 45, 2818–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Zhou, F.; Wang, F.; Schwarz, C.G.; Liu, R.; Zhao, H.; Wu, W.; Zhang, X.; et al. The Value of Resting-State Functional MRI in Subacute Ischemic Stroke: Comparison with Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast-Enhanced Perfusion MRI. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutsaerts, H.J.M.M.; van Dalen, J.W.; Heijtel, D.F.R.; Groot, P.F.C.; Majoie, C.B.L.M.; Petersen, E.T.; Richard, E.; Nederveen, A.J. Cerebral Perfusion Measurements in Elderly with Hypertension Using Arterial Spin Labeling. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Sebök, M.; van Niftrik, C.H.B.; Winklhofer, S.; Wegener, S.; Esposito, G.; Stippich, C.; Luft, A.; Regli, L.; Fierstra, J. Mapping Cerebrovascular Reactivity Impairment in Patients with Symptomatic Unilateral Carotid Artery Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e020792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Hata, H.; Hara, T. Arterial Spin-Labeling Evaluation of Cerebrovascular Reactivity to Acetazolamide in Healthy Subjects. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIntosh, B.J.; Filippini, N.; Chappell, M.A.; Woolrich, M.W.; Mackay, C.E.; Jezzard, P. Assessment of Arterial Arrival Times Derived from Multiple Inversion Time Pulsed Arterial Spin Labeling MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 63, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutch, W.A.C.; Duffin, J. Differential Regional Cerebral Blood Flow Reactivity to Alterations in End-Tidal Gases in Healthy Volunteers. Can. J. Anesth. J. Can. D’anesthésie 2021, 68, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catchlove, S.J.; Parrish, T.B.; Chen, Y.; Macpherson, H.; Hughes, M.E.; Pipingas, A. Regional Cerebrovascular Reactivity and Cognitive Performance in Healthy Aging. J. Exp. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 1179069518785151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKetton, L.; Sobczyck, O.; Duffin, J.; Poublanc, J.; Sam, K.; Crawley, A.P.; Venkatraghavan, L.; Fisher, J.A.; Mikulis, D.J. The Aging Brain and Cerebrovascular Reactivity. Neuroimage 2018, 181, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cikrit, D.F.; Dalsing, M.C.; Harting, P.S.; Burt, R.W.; Lalka, S.G.; Sawchuk, A.P.; Solooki, B. Cerebral Vascular Reactivity Assessed with Acetazolamide Single Photon Emission Computer Tomography Scans before and after Carotid Endarterectomy. Am. J. Surg. 1997, 174, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cikrit, D.F.; Dalsing, M.C.; Lalka, S.G.; Burt, R.W.; Sawchuk, A.P.; Solooki, B.A. The Value of Acetazolamide Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Scans in the Preoperative Evaluation of Asymptomatic Critical Carotid Stenosis. J. Vasc. Surg. 1999, 30, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lombardi, J.V.; Hughes, G.C.; Appoo, J.J.; Bavaria, J.E.; Beck, A.W.; Cambria, R.P.; Charlton-Ouw, K.; Eslami, M.H.; Kim, K.M.; Leshnower, B.G.; et al. Society for Vascular Surgery (SVS) and Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) Reporting Standards for Type B Aortic Dissections. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 71, 723–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leoni, R.F.; Paiva, F.F.; Henning, E.C.; Nascimento, G.C.; Tannús, A.; de Araujo, D.B.; Silva, A.C. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Quantification of Regional Cerebral Blood Flow and Cerebrovascular Reactivity to Carbon Dioxide in Normotensive and Hypertensive Rats. Neuroimage 2011, 58, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rask-Madsen, C.; King, G.L. Vascular Complications of Diabetes: Mechanisms of Injury and Protective Factors. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, K.; Sreedharan, S.; Sudheer, J.; Abraham, M.; Sarma, S.; Sylaja, P.N. Malignant Middle Cerebral Artery Stroke Management in Developing World-Outcome Predictors. Neurol. Asia 2020, 25, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Molina, C.; Sabín, J.A.; Montaner, J.; Rovira, A.; Abilleira, S.; Codina, A. Impaired Cerebrovascular Reactivity as a Risk Marker for First-Ever Lacunar Infarction: A Case-Control Study. Stroke 1999, 30, 2296–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantin, S.; Villien, M.; Moreaud, O.; Tropres, I.; Keignart, S.; Chipon, E.; Le Bas, J.-F.; Warnking, J.; Krainik, A. Impaired Cerebral Vasoreactivity to CO2 in Alzheimer’s Disease Using BOLD fMRI. Neuroimage 2011, 58, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-Z.; Zhang, J.-J.; Liu, H.; Wu, G.-Y.; Xiong, L.; Shu, M. Regional Cerebral Blood Flow and Cerebrovascular Reactivity in Alzheimer’s Disease and Vascular Dementia Assessed by Arterial Spinlabeling Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2013, 10, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrikse, J.; Petersen, E.T.; van Laar, P.J.; Golay, X. Cerebral Border Zones between Distal End Branches of Intracranial Arteries: MR Imaging. Radiology 2008, 246, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarz, S.; Göttler, J.; Petr, J.; Hansen, M.B.; Mouridsen, K.; Zimmer, C.; Hyder, F.; Preibisch, C. Hemodynamic Impairments within Individual Watershed Areas in Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Stenosis by Multimodal MRI. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2021, 41, 380–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipp, I.; Murphy, K.; Caseras, X.; Wise, R.G. Agreement and Repeatability of Vascular Reactivity Estimates Based on a Breath-Hold Task and a Resting State Scan. Neuroimage 2015, 113, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| ID | Sex | Age | Left ICAS (%) | Right ICAS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p1 | Male | 62 | >70 | <50 |
| p2 | Female | 59 | >70 | no |
| p3 | Female | 56 | no | >70 |
| p4 | Male | 68 | no | >70 |
| p5 | Female | 81 | >70 | <30 |
| p6 | Female | 82 | 30 | >70 |
| p7 | Female | 68 | >70 | no |
| p8 | Male | 65 | 50 | >70 |
| p9 | Male | 77 | >70 | <30 |
| p10 | Male | 83 | >70 | <30 |
| p11 | Male | 77 | no | >70 |
| p12 | Female | 67 | >50 | >70 |
| p13 | Female | 67 | >70 | no |
| p14 | Female | 65 | >70 | 50 |
| p15 | Female | 71 | no | >70 |
| p16 | Male | 61 | no | >70 |
| p17 | Female | 52 | >70 | no |
| p18 | Male | 70 | no | >75 |
| p19 | Female | 53 | >70 | no |
| p20 | Female | 53 | no | >70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Secchinato, K.F.; da Silva, P.H.R.; Rodrigues, G.R.; Ferreira, A.P.A.C.; Pontes-Neto, O.M.; Leoni, R.F. Impaired Cerebral Hemodynamics in Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Stenosis Assessed by Resting-State Functional MRI. J. Vasc. Dis. 2025, 4, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd4020015
Secchinato KF, da Silva PHR, Rodrigues GR, Ferreira APAC, Pontes-Neto OM, Leoni RF. Impaired Cerebral Hemodynamics in Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Stenosis Assessed by Resting-State Functional MRI. Journal of Vascular Diseases. 2025; 4(2):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd4020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleSecchinato, Kaio F., Pedro H. R. da Silva, Guilherme R. Rodrigues, Ana P. A. C. Ferreira, Octavio M. Pontes-Neto, and Renata F. Leoni. 2025. "Impaired Cerebral Hemodynamics in Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Stenosis Assessed by Resting-State Functional MRI" Journal of Vascular Diseases 4, no. 2: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd4020015
APA StyleSecchinato, K. F., da Silva, P. H. R., Rodrigues, G. R., Ferreira, A. P. A. C., Pontes-Neto, O. M., & Leoni, R. F. (2025). Impaired Cerebral Hemodynamics in Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Stenosis Assessed by Resting-State Functional MRI. Journal of Vascular Diseases, 4(2), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd4020015






