Telehealth-Based Health Coaching Produces Significant Weight Loss over 12 Months in a Usual Care Setting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virtual Health Coaching Group (VHC)
2.2. Usual Care Group
2.3. Statistical Analysis
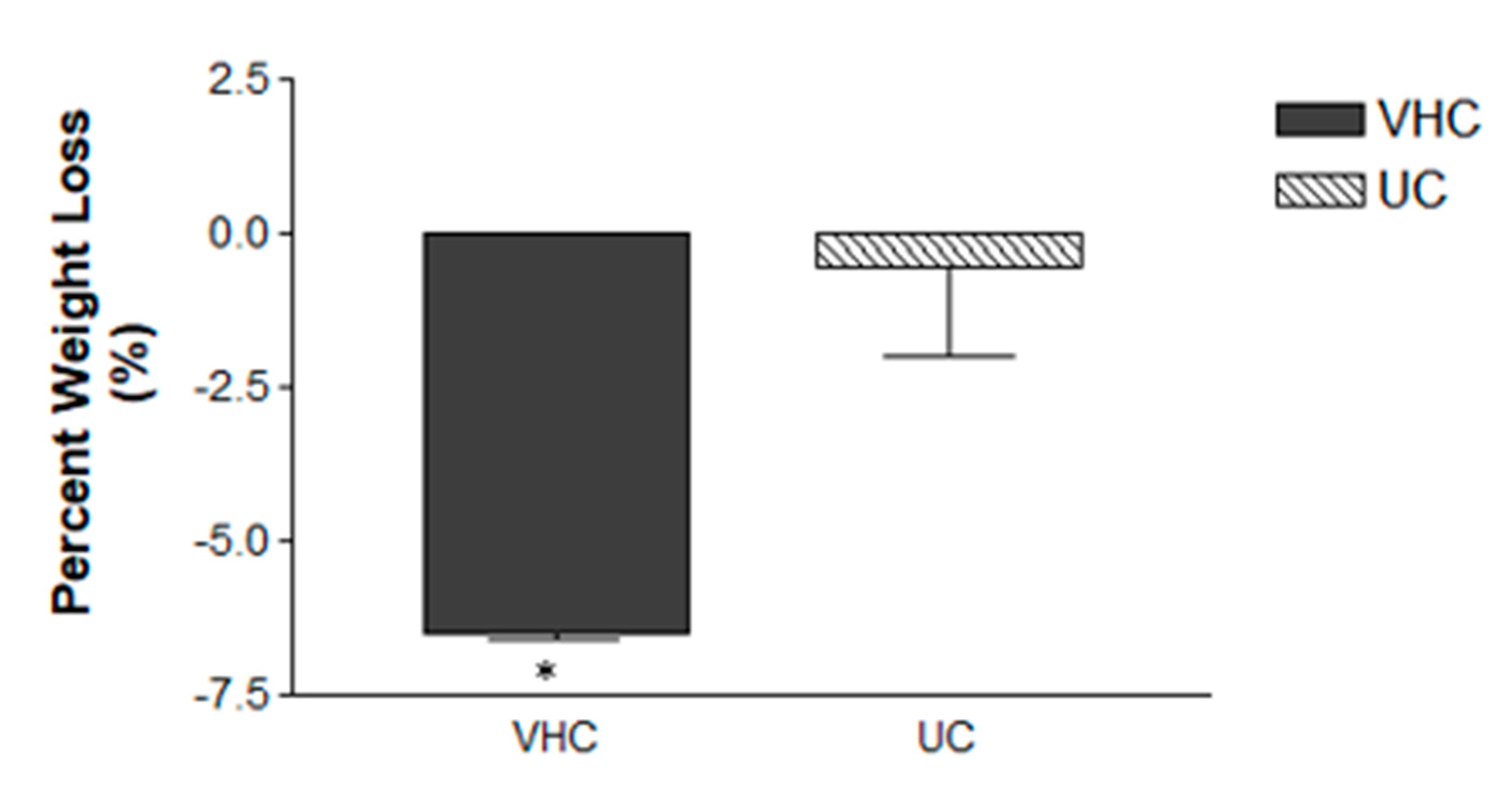
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tronieri, J.S.; Wadden, T.A.; Chao, A.M.; Tsai, A.G. Primary Care Interventions for Obesity: Review of the Evidence. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, C.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Fryar, C.D.; Ogden, C.L. Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity among Adults: United States, 2017–2018; NCHS Data Brief, No 360; The National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cawley, J.; Biener, A.; Meyerhoefer, C.; Ding, Y.; Zvenyach, T.; Smolarz, G.B.; Ramasamy, A. Direct Medical Costs of Obesity in the United States and the Most Populous States. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2021, 27, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.C.; Burley, V.J.; Nykjaer, C.; Cade, J.E. Adherence to a Smartphone Application for Weight Loss Compared to Website and Paper Diary: Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 2013, 15, e2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadden, T.A.; Butryn, M.L.; Hong, P.S.; Tsai, A.G. Behavioral Treatment of Obesity in Patients Encountered in Primary Care Settings: A Systematic Review. JAMA 2014, 312, 1779–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, V.L.; Wadden, T.A. Intensive Lifestyle Intervention for Obesity: Principles, Practices, and Results. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1752–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.G.; Warner, E.T.; Glasgow, R.E.; Askew, S.; Goldman, J.; Ritzwoller, D.P.; Emmons, K.M.; Rosner, B.A.; Colditz, G.A. Obesity Treatment for Socioeconomically Disadvantaged Patients in Primary Care Practice. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 565–574. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, C.K.; Gilmore, A.L.; Apolzan, J.W.; Myers, C.A.; Thomas, D.M.; Redman, L.M. Smartloss: A Personalized Mobile Health Intervention for Weight Management and Health Promotion. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2016, 4, e5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, D.A. Fifty Years of Behavioral/Lifestyle Interventions for Overweight and Obesity: Where Have We Been and Where Are We Going? Obesity 2017, 25, 1867–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.J.; Leahey, T.M.; Wing, R.R. An Automated Internet Behavioral Weight-Loss Program by Physician Referral: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, B.; Pellegrini, C.A.; Pfammatter, A.; Duncan, J.M.; Pictor, A.; McFadden, H.; Siddique, J.; Hedeker, D. Effects of an Abbreviated Obesity Intervention Supported by Mobile Technology: The Engaged Randomized Clinical Trial. Obesity 2017, 25, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.K.; Miller, A.C.; Thomas, D.M.; Champagne, C.M.; Han, H.; Church, T. Efficacy of Smartlosssm, a Smartphone-Based Weight Loss Intervention: Results from a Randomized Controlled Trial. Obesity 2015, 23, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahan, S.I. Practical Strategies for Engaging Individuals with Obesity in Primary Care. In Mayo Clinic Proceedings; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Foley, P.; Steinberg, D.; Levine, E.; Askew, S.; Batch, B.C.; Puleo, E.M.; Svetkey, L.P.; Bosworth, H.B.; DeVries, A.; Miranda, H. Track: A Randomized Controlled Trial of a Digital Health Obesity Treatment Intervention for Medically Vulnerable Primary Care Patients. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2016, 48, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, L.J.; Clark, J.M.; Yeh, H.C.; Wang, N.Y.; Coughlin, J.W.; Daumit, G.; Miller, E.R., 3rd; Dalcin, A.; Jerome, G.J.; Geller, S.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Weight-Loss Interventions in Clinical Practice. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.D.; Hales, S.; Evans, T.E.; Turner, T.; Sword, D.O.; O’Neil, P.M.; Ballentine, S.; Lovelace, O.; DuBose-Morris, R.A. Description, Utilisation and Results from a Telehealth Primary Care Weight Management Intervention for Adults with Obesity in South Carolina. J. Telemed. Telecare 2018, 26, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alencar, M.K.; Johnson, K.; Mullur, R.; Gray, V.; Gutierrez, E.; Korosteleva, O. The Efficacy of a Telemedicine-Based Weight Loss Program with Video Conference Health Coaching Support. J. Telemed. Telecare 2019, 25, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.O.; Keith, N.; Weiner, M.; Xu, H. Outcomes of an Rct of Videoconference Vs. In-Person or in-Clinic Nutrition and Exercise in Midlife Adults with Obesity. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2019, 5, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.E.; Alencar, M.K.; Coakley, K.E.; Swift, D.L.; Cole, N.H.; Mermier, C.M.; Kravitz, L.; Amorim, F.T.; Gibson, A.L. Telemedicine-Based Health Coaching Is Effective for Inducing Weight Loss and Improving Metabolic Markers. Telemed. e-Health 2019, 25, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.M.; Nesbitt, B.J. Health Coaching to Improve Healthy Lifestyle Behaviors: An Integrative Review. Am. J. Health Promot. 2010, 25, e1–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.G.; Steinberg, D.; Askew, S.; Levine, E.; Foley, P.; Batch, B.C.; Svetkey, L.P.; Bosworth, H.B.; Puleo, E.M.; Brewer, A. Effectiveness of an App and Provider Counseling for Obesity Treatment in Primary Care. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2018, 55, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, K.; Hayoz, S.; Maurer-Wiesner, S. Effectiveness and Feasibility of a Remote Lifestyle Intervention by Dietitians for Overweight and Obese Adults: Pilot Study. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2019, 7, e12289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.D.; Ryan, D.H.; Apovian, C.M.; Ard, J.D.; Comuzzie, A.G.; Donato, K.A.; Yanovski, M. Aha/Acc/Tos Guideline for the Management of Overweight and Obesity in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Obesity Society. Circulation 2014, 129, S139–S140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, D.F.; Jackvony, E.H.; Wing, R.R. A Randomized Trial Comparing Human E-Mail Counseling, Computer-Automated Tailored Counseling, and No Counseling in an Internet Weight Loss Program. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, D.F.; Wing, R.R.; Winett, R.A. Using Internet Technology to Deliver a Behavioral Weight Loss Program. JAMA 2001, 285, 1172–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadden, T.A.; Butryn, M.L.; Wilson, C. Lifestyle Modification for the Management of Obesity. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2226–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total Group (n = 70) | Video Health Group (VHC) (n = 38) | Usual Care Group (UC) (n = 32) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Baseline | 12 Months | Baseline | 12 Months | Baseline | 12 Months |
| Age (yrs) | 58.1 ± 14.6 | - | 57.0 ± 17.6 | - | 60.6 ± 9.8 | - |
| Body Weight (kg) | 109.9 ± 32.9 | - | 106.0 ± 27.5 | 98.9 ± 25.2 | 111.9 ± 38.3 | 111.7 ± 45.5 |
| Height (cm) | 169.8 ± 10.6 | - | 170.3 ± 11.7 | - | 169.3 ± 10.7 | - |
| Weight loss (kg) | - | - | 8.24 ± 9.8 * | 0.16 ± 10.64 | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 35.5 ± 7.80 | - | 36.9 ± 10.07 | 34.4 ± 9.13 | 38.4 ± 10.40 | 38.2 ± 12.53 |
| Weight loss (%) | - | - | 6.5 ± 0.1 * | 0.53 ± 1.45 | ||
| Gender | Male = 32 Female = 38 | - | Male = 17 Female = 21 | - | Male = 14 Female = 18 | - |
| VHC Group: | |
|---|---|
Medical Doctor (MD) Consultations
| Health Coach (HC) Coaching Sessions
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Johnson, K.; Gutierrez, E.; Dionicio, P.; McConnell, J.; Sauls, R.; Alencar, M. Telehealth-Based Health Coaching Produces Significant Weight Loss over 12 Months in a Usual Care Setting. Int. Med. Educ. 2022, 1, 79-84. https://doi.org/10.3390/ime1020010
Johnson K, Gutierrez E, Dionicio P, McConnell J, Sauls R, Alencar M. Telehealth-Based Health Coaching Produces Significant Weight Loss over 12 Months in a Usual Care Setting. International Medical Education. 2022; 1(2):79-84. https://doi.org/10.3390/ime1020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohnson, Kelly, Elizabeth Gutierrez, Patricia Dionicio, Jeremy McConnell, Rachel Sauls, and Michelle Alencar. 2022. "Telehealth-Based Health Coaching Produces Significant Weight Loss over 12 Months in a Usual Care Setting" International Medical Education 1, no. 2: 79-84. https://doi.org/10.3390/ime1020010
APA StyleJohnson, K., Gutierrez, E., Dionicio, P., McConnell, J., Sauls, R., & Alencar, M. (2022). Telehealth-Based Health Coaching Produces Significant Weight Loss over 12 Months in a Usual Care Setting. International Medical Education, 1(2), 79-84. https://doi.org/10.3390/ime1020010






