Effects of Calcium Peroxide Dosage on Physicochemical Parameters, Organic Matter Degradation, Humification, and Microbial Community Succession During Food Waste Composting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
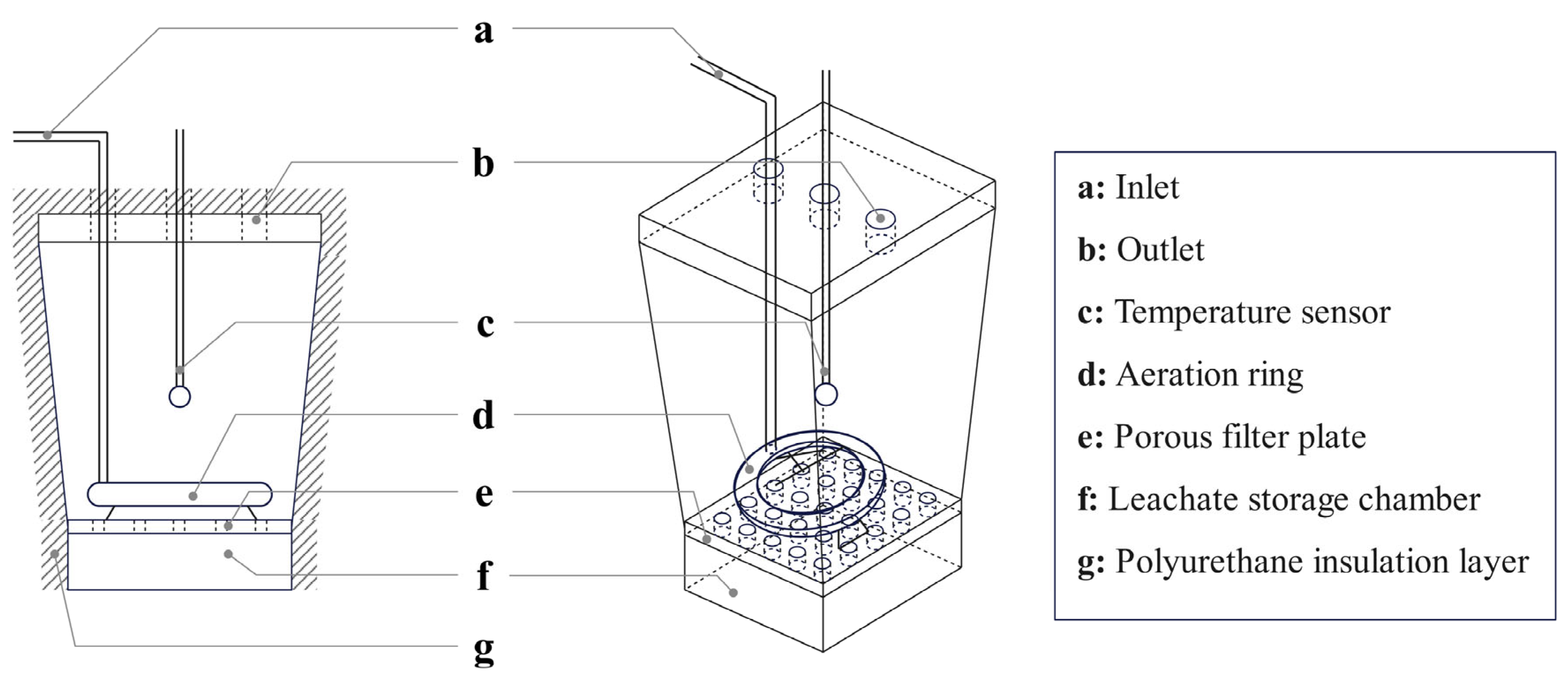
2.1. Composting Feedstock and Experimental Design
2.2. Measurement of Experimental Parameters During Composting
2.2.1. Basic Physiochemical Properties
2.2.2. Parameters Related to Organic Matter Degradation
2.2.3. Humus Dynamics
2.2.4. High-Throughput Sequencing
2.3. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Parameters
3.2. Organic Matter Degradation
3.3. Humification
3.4. Microbial Community Succession
3.4.1. Microbial Community Diversity
3.4.2. Bacterial Community Structure and Dynamics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J. Analysis and Research on the Current Status of Resource Recycling and Utilization of Municipal Food Waste. Resour. Econ. Environ. Prot. 2021, 10, 146–148. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Williams, P.N.; Zhan, Y.; Coughlin, S.A.; McGrath, J.W.; Chin, J.P.; Xu, Y. Municipal solid waste compost: Global trends and biogeochemical cycling. Soil Environ. Health 2023, 1, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Xie, M.; Yu, X.; Feng, H.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, T. A review of the definition, influencing factors, and mechanisms of rapid composting of organic waste. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 342, 123125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.N.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Awasthi, M.K.; He, Y.F.; Li, R.H.; Zhang, Z.Q. Improvement of humification and mechanism of nitrogen transformation during pig manure composting with Black Tourmaline. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 307, 123236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.X.; Liu, H.T.; Wu, S.B. Humic substances developed during organic waste composting: Formation mechanisms, structural properties, and agronomic functions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, H.G.; Thuy, B.T.P.; Lin, C.; Vo, D.N.; Tran, H.T.; Bahari, M.B.; Le, V.G.; Vu, C.T. The nitrogen cycle and mitigation strategies for nitrogen loss during organic waste composting: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jin, C.; Sun, S.; Yang, D.; He, Y.; Gan, P.; Nalume, W.G.; Ma, Y.; He, W.; Li, G. Recognizing the challenges of composting: Critical strategies for control, recycling, and valorization of nitrogen loss. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 198, 107172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, C.; Yu, D.; Franke-Whittle, I.; Kauppi, S.; Smars, S.; Insam, H.; Romantschuk, M.; Jonsson, H. Effects of pH and microbial composition on odour in food waste composting. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Wei, Y.Q.; Zhou, K.Y.; Gao, X.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Deng, J.; Zhan, Y.B.; Li, J.; Li, R.Q.; et al. Regulating pH and Phanerochaete chrysosporium inoculation improved the humification and succession of fungal community at the cooling stage of composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 384, 129291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Li, G.; Jiang, T.; Schuchardt, F.; Chen, T.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Y. Effect of aeration rate, C/N ratio and moisture content on the stability and maturity of compost. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 112, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.S.; Liu, X.P.; Yu, X.; Liu, L.M.; He, H.K.; Huang, C.; Hu, J.; Wang, Z.X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhai, Y.B. Enhancing bioavailable carbon sources and minimizing ammonia emissions in distillery sludge and distiller’s grains waste co-composting through deep eutectic solvent addition. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 397, 130491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Z.; Chen, X.; Yao, C.; Meng, Q.; Zhao, R. A novel method for removing heavy metals from composting system: The combination of functional bacteria and adsorbent materials. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 293, 122095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, H.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zou, B. Improving the humification by additives during composting: A review. Waste Manag. 2023, 158, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, A.; Wang, L. Enhancing the quantity and quality of short-chain fatty acids production from waste activated sludge using CaO2 as an additive. Water Res. 2015, 83, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Chen, Z.; Wen, Q.; Wu, Y.; Fu, Q. Effect of calcium peroxide dosage on organic matter degradation, humification during sewage sludge composting and application as amendment for Cu (II)-polluted soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Guo, R.; Feng, Q.; Qin, K.; Zhang, F.; Shi, X. Effect of calcium peroxide assisted microwave irradiation pretreatment on humus formation and microbial community in straw and dairy manure composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 374, 128780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Shu, L.L.; Yang, Y.Y.; Kumar, S.; Tripathi, P.; Mishra, S.; Qiu, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.J.; Yang, Z.C. Microbial agents obtained from tomato straw composting effectively promote tomato straw compost maturation and improve compost quality. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 270, 115884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Ryan Penton, C.; Liu, C.; Shen, Z.; Ou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, X.; Li, R.; Shen, Q. Key extracellular enzymes triggered high-efficiency composting associated with bacterial community succession. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of China. Organic Fertilizer; NY/T 525–2021; Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of China: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Che, J.; Lin, W.; Ye, J.; Liao, H.; Yu, Z.; Lin, H.; Zhou, S. Insights into compositional changes of dissolved organic matter during a full-scale vermicomposting of cow dung by combined spectroscopic and electrochemical techniques. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, C.; Xi, B.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, X. Assessment of humification degree of dissolved organic matter from different composts using fluorescence spectroscopy technology. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cong, H.; Zhang, C.; Wu, J. Quantifying the contribution of lignin to humic acid structures during composting. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 492, 152204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, A.S.; Hafen, P.S.; Brault, J.J. Liquid chromatography method for simultaneous quantification of ATP and its degradation products compatible with both UV-Vis and mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2022, 1206, 123351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Li, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, X.; Ho Daniel Tang, K.; Emmanuel Scriber, K.; Zhang, Z.; Quan, F. Molecular mechanisms of humus formation mediated by new ammonifying microorganisms in compost. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 483, 149341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108 (Suppl. 1), 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousk, J.; Baath, E.; Brookes, P.C.; Lauber, C.L.; Lozupone, C.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Du, G.; Wu, C.; Li, Q.; Zhou, P.; Shi, J.; Zhao, Z. Effect of thermophilic microbial agents on nitrogen transformation, nitrogen functional genes, and bacterial communities during bean dregs composting. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 31846–31860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Selvam, A.; Chan, M.T.; Wong, J.W.C. Nitrogen conservation and acidity control during food wastes composting through struvite formation. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 147, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, W.H.; Li, G.X.; Wang, K.; Gong, X.Y. Performance of phosphogypsum and calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer for nitrogen conservation in pig manure composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C. A negative-pressure aeration system for composting food wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7651–7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Ma, J. Overview of the mechanisms regulating the humification process of agricultural organic waste composting. Agric. Technol. 2023, 43, 108–111. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Jiang, H.; Luo, X.; Tang, P.; Chen, L.; Yan, H. Evolution of humic substances and the forms of heavy metals during co-composting of rice straw and sediment with the aid of Fenton-like process. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 333, 125170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Awasthi, M.K.; Bao, H.; Bie, J.; Lei, S.; Lv, J. Exploring the microbial mechanisms of organic matter transformation during pig manure composting amended with bean dregs and biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 313, 123647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Zhou, K.; Yang, T.; Zhao, X.; Li, R.; Li, J.; Xu, S.; Feng, Z.; Ding, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. Bacillus licheniformis inoculation promoted humification process for kitchen waste composting: Organic components transformation and bacterial metabolic mechanism. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 117016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.C.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, R.X.; Lu, Q.; Wu, J.Q.; Zhang, D.Y.; Nie, Z.F.; Wei, Z.M. Effect of the addition of exogenous precursors on humic substance formation during composting. Waste Manag. 2018, 79, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Ootsuka, K.; Komai, T.; Aramaki, T.; Ueda, S.; Horiya, S. Effects of the maturity of wood waste compost on the structural features of humic acids. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.P.; Tang, S.Q.; Ke, X.; Zhou, H.Y.; Zou, S.P.; Xue, Y.P.; Zheng, Y.G. Hyperthermophilic pretreatment significantly accelerates thermophilic composting humification through improving bacterial communities and promoting microbial cooperation. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 385, 129467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, G.; Huda, N.; Zhang, B.; Wang, M.; Luo, W. Effects of moisture and carbon/nitrogen ratio on gaseous emissions and maturity during direct composting of cornstalks used for filtration of anaerobically digested manure centrate. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, G.; Nghiem, L.D.; Luo, W. Bacterial dynamics for gaseous emission and humification in bio-augmented composting of kitchen waste. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Food Waste Components (Wet Weight) | Mass (g) | Percentage (%) | Moisture Content (%) | C/N Ratio | OM (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cooked rice | 1750 | 25 | 58.62 ± 0.09 | 38.26 ± 0.24 | 99.64 ± 0.09 |
| Cooked noodles | 1050 | 15 | 45.00 ± 0.15 | 17.75 ± 0.33 | 98.17 ± 0.12 |
| Cooked chicken breast | 350 | 5 | 68.17 ± 0.23 | 3.52 ± 0.36 | 97.54 ± 0.11 |
| Cabbage | 700 | 10 | 91.96 ± 0.19 | 16.10 ± 0.25 | 93.13 ± 0.21 |
| Celery | 700 | 10 | 94.69 ± 0.17 | 12.77 ± 0.22 | 89.59 ± 0.13 |
| Potato | 1050 | 15 | 61.19 ± 0.14 | 29.65 ± 0.31 | 95.41 ± 0.14 |
| Apple | 700 | 10 | 85.60 ± 0.14 | 80.04 ± 0.25 | 97.34 ± 0.09 |
| Banana | 700 | 10 | 82.66 ± 0.21 | 33.75 ± 0.24 | 94.71 ± 0.12 |
| TOTAL | 7000 | 100 | 71.21 ± 0.76 | 22.98 ± 1.12 | 94.97 ± 0.82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, K.; Zhou, G.; Chen, J.; Wafula, N.G.; Li, G. Effects of Calcium Peroxide Dosage on Physicochemical Parameters, Organic Matter Degradation, Humification, and Microbial Community Succession During Food Waste Composting. Waste 2025, 3, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3010003
Hu K, Zhou G, Chen J, Wafula NG, Li G. Effects of Calcium Peroxide Dosage on Physicochemical Parameters, Organic Matter Degradation, Humification, and Microbial Community Succession During Food Waste Composting. Waste. 2025; 3(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Kun, Guoning Zhou, Jia Chen, Nalume Gerald Wafula, and Guangming Li. 2025. "Effects of Calcium Peroxide Dosage on Physicochemical Parameters, Organic Matter Degradation, Humification, and Microbial Community Succession During Food Waste Composting" Waste 3, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3010003
APA StyleHu, K., Zhou, G., Chen, J., Wafula, N. G., & Li, G. (2025). Effects of Calcium Peroxide Dosage on Physicochemical Parameters, Organic Matter Degradation, Humification, and Microbial Community Succession During Food Waste Composting. Waste, 3(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3010003








