Time Series Forecasting for Touristic Policies †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Time Series Forecasting
2.2. Time Series Forecasting in Smart Cities
3. Materials and Methods
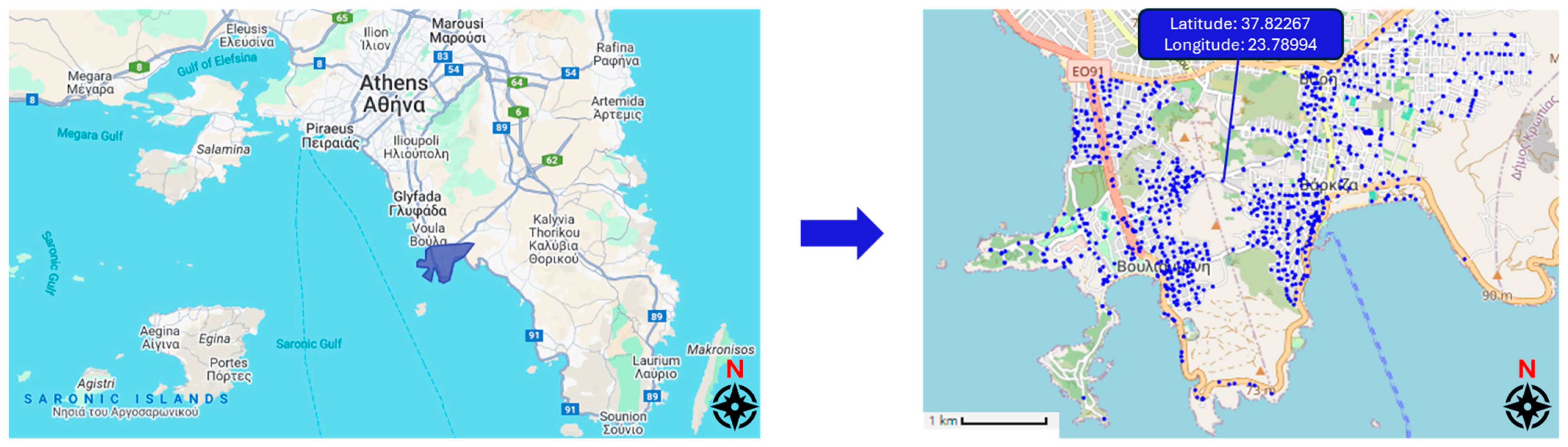
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Preprocessing and Data Cleaning
3.3. Algorithms
3.4. Proposed Approach Architecture
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Statista. Countries with the Highest Number of International Tourist Arrivals in Europe (2019–2023). Available online: www.statista.com/statistics/261729/countries-in-europe-ranked-by-international-tourist-arrivals/ (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Hellenic Statistical Authority. Available online: https://www.statistics.gr/en/home/ (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Municipality of Vari, Voula. Vouliagmeni—Waste and Recycling Policies. Available online: https://www.vvv.gov.gr/index.php/environment-and-planning/waste-and-recycling/kanonismos-kathariotitas (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Manias, G.; Apostolopoulos, D.; Athanassopoulos, S.; Borotis, S.; Chatzimallis, C.; Chatzipantelis, T.; Compagnucci, M.C.; Draksler, T.Z.; Fournier, F.; Goralczyk, M. AI4Gov: Trusted AI for Transparent Public Governance Fostering Democratic Values. In Proceedings of the 2023 19th International Conference on Distributed Computing in Smart Systems and the Internet of Things (DCOSS-IoT), Pafos, Cyprus, 19–21 June 2023; pp. 548–555. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, J. Crossformer: Transformer utilizing cross-dimension dependency for multivariate time series forecasting. In Proceedings of the The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Weerakody, P.B.; Wong, K.W.; Wang, G.; Ela, W. A review of irregular time series data handling with gated recurrent neural networks. Neurocomputing 2021, 441, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderpour, E.; Dadkhah, H.; Dabiri, H.; Bozzano, F.; Scarascia Mugnozza, G.; Mazzanti, P. Precipitation time series analysis and forecasting for Italian regions. Eng. Proc. 2023, 39, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, F.; Frías, M.P.; Pérez, M.D.; Rivera, A.J. A methodology for applying k-nearest neighbor to time series forecasting. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2019, 52, 2019–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, R.K.; Nguyen, T.N.; Cengiz, K.; Sharma, A. Fine-tuned support vector regression model for stock predictions. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 23295–23309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirisci, M.; Cagcag Yolcu, O. A new CNN-based model for financial time series: TAIEX and FTSE stocks forecasting. Neural Process. Lett. 2022, 54, 3357–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewamalage, H.; Bergmeir, C.; Bandara, K. Recurrent neural networks for time series forecasting: Current status and future directions. Int. J. Forecast. 2021, 37, 388–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, F.; Guijarro, F.; Oliver, J.; Tamošiūnienė, R. Foreign exchange forecasting models: ARIMA and LSTM comparison. Eng. Proc. 2023, 39, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, A.; Chen, M.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Q. Are transformers effective for time series forecasting? In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 11121–11128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.N.; Wu, S.-B.; Tian, Y.-J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.-T. Application of machine learning methods for the prediction of organic solid waste treatment and recycling processes: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.K.A.; Ibraheem, A.M.; Abd-Ellah, M.K. Forecasting of municipal solid waste multi-classification by using time-series deep learning depending on the living standard. Results Eng. 2022, 16, 100655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayeleru, O.O.; Fajimi, L.; Oboirien, B.; Olubambi, P. Forecasting municipal solid waste quantity using artificial neural network and supported vector machine techniques: A case study of Johannesburg, South Africa. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, R. Application of machine learning algorithms in municipal solid waste management: A mini review. Waste Manag. Res. 2022, 40, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogiorgos, K.; Kiourtis, A.; Mavrogiorgou, A.; Guček, A.; Menychtas, A.; Kyriazis, D. Mitigating Bias in Time Series Forecasting for Efficient Wastewater Management. In Proceedings of the 2024 7th International Conference on Informatics and Computational Sciences (ICICoS), Semarang, Indonesia, 17–18 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- El-Rawy, M.; Abd-Ellah, M.K.; Fathi, H.; Ahmed, A.K.A. Forecasting effluent and performance of wastewater treatment plant using different machine learning techniques. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 44, 102380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.; Fernandes, B.; Analide, C.; Novais, P. Forecasting energy consumption of wastewater treatment plants with a transfer learning approach for sustainable cities. Electronics 2021, 10, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, M.; Wu, J.-Z.; Chakrabortty, R.K.; Alahmadi, A.; Ansari, M.F.; Ryan, M.J. Attention-based STL-BiLSTM network to forecast tourist arrival. Processes 2021, 9, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Wang, L.; Ai, X.-Y.; Zeng, Y.-R. Forecasting tourist arrivals via random forest and long short-term memory. Cogn. Comput. 2021, 13, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.C.; Ji, L.; He, K.; Tso, K.F.G. Forecasting tourist daily arrivals with a hybrid Sarima–Lstm approach. J. Hosp. Tour. Res. 2021, 45, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.W.; Bergmeir, C.; Petitjean, F.; Webb, G.I. Time series extrinsic regression: Predicting numeric values from time series data. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2021, 35, 1032–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogiorgos, K.; Kiourtis, A.; Mavrogiorgou, A.; Kleftakis, S.; Kyriazis, D. A multi-layer approach for data cleaning in the healthcare domain. In Proceedings of the 2022 8th International Conference on Computing and Data Engineering, Bangkok, Thailand, 11–13 January 2022; pp. 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Mavrogiorgou, A.; Kiourtis, A.; Manias, G.; Kyriazis, D. Adjustable data cleaning towards extracting statistical information. In Public Health and Informatics; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 1013–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrabi, N.; Morstatter, F.; Saxena, N.; Lerman, K.; Galstyan, A. A survey on bias and fairness in machine learning. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2021, 54, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogiorgos, K.; Kiourtis, A.; Mavrogiorgou, A.; Menychtas, A.; Kyriazis, D. Bias in Machine Learning: A Literature Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Python Darts Documentation. Available online: https://unit8co.github.io/darts/ (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Kodinariya, T.M.; Makwana, P.R. Review on determining number of Cluster in K-Means Clustering. Int. J. 2013, 1, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Mavrogiorgou, A.; Kiourtis, A.; Kyriazis, D.; Themistocleous, M. A comparative study in data mining: Clustering and classification capabilities. In Information Systems, Proceedings of the 14th European, Mediterranean, and Middle Eastern Conference, EMCIS 2017, Coimbra, Portugal, 7–8 September 2017; Proceedings 14; Springer: Cham, Switherland, 2017; pp. 82–96. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Yu, X.; Zhou, Y. Lstm and gru neural network performance comparison study: Taking yelp review dataset as an example. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Workshop on Electronic Communication and Artificial Intelligence (IWECAI), Shanghai, China, 12–14 June 2020; pp. 98–101. [Google Scholar]


| NN Type | Optimizer | Learning Rate | Epochs | MAE | Training Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | Adam | 0.01 | 3 | 0.0052 | 3.03 |
| 0.001 | 3 | 0.00489 | 4.09 | ||
| 0.0001 | 3 | 0.014 | 3.57 | ||
| SGD | 0.01 | 3 | 0.0283 | 2.57 | |
| 0.001 | 3 | 0.196 | 3.30 | ||
| 0.0001 | 5 | 0.253 | 4.55 | ||
| AdamW | 0.01 | 3 | 0.00363 | 3.15 | |
| 0.001 | 3 | 0.00542 | 3.15 | ||
| 0.0001 | 3 | 0.00861 | 3.18 | ||
| Adamax | 0.01 | 3 | 0.00324 | 2.57 | |
| 0.001 | 3 | 0.00622 | 3.24 | ||
| 0.0001 | 3 | 0.0117 | 3.09 | ||
| Adagrad | 0.01 | 3 | 0.00943 | 3.12 | |
| 0.001 | 3 | 0.0467 | 2.57 | ||
| 0.0001 | 12 | 0.274 | 13.10 | ||
| Adadelta | 0.01 | 3 | 0.0368 | 2.57 | |
| 0.001 | 5 | 0.206 | 4.50 | ||
| 0.0001 | 16 | 0.313 | 18.24 | ||
| Adafactor | 0.01 | 3 | 0.00902 | 3.39 | |
| 0.001 | 3 | 0.00568 | 3.03 | ||
| 0.0001 | 4 | 0.0668 | 4.36 | ||
| RMSprop | 0.01 | 3 | 0.00928 | 3.03 | |
| 0.001 | 3 | 0.00396 | 3.03 | ||
| 0.0001 | 3 | 0.0056 | 3.09 | ||
| Nadam | 0.01 | 3 | 0.00401 | 2.57 | |
| 0.001 | 3 | 0.00439 | 3.03 | ||
| 0.0001 | 3 | 0.0148 | 3.12 | ||
| GRU | Adam | 0.01 | 3 | 0.0032 | 3.03 |
| 0.001 | 3 | 0.00418 | 2.44 | ||
| 0.0001 | 3 | 0.0112 | 2.57 | ||
| SGD | 0.01 | 3 | 0.0238 | 2.54 | |
| 0.001 | 3 | 0.0469 | 2.51 | ||
| 0.0001 | 5 | 0.216 | 4.45 | ||
| AdamW | 0.01 | 3 | 0.0053 | 2.51 | |
| 0.001 | 3 | 0.00411 | 2.54 | ||
| 0.0001 | 3 | 0.0111 | 2.51 | ||
| Adamax | 0.01 | 3 | 0.00318 | 2.51 | |
| 0.001 | 3 | 0.00523 | 2.51 | ||
| 0.0001 | 3 | 0.00972 | 2.51 | ||
| Adagrad | 0.01 | 3 | 0.00599 | 3.12 | |
| 0.001 | 3 | 0.0359 | 3.00 | ||
| 0.0001 | 9 | 0.326 | 9.45 | ||
| Adadelta | 0.01 | 3 | 0.0302 | 2.46 | |
| 0.001 | 4 | 0.187 | 3.44 | ||
| 0.0001 | 10 | 0.337 | 10.10 | ||
| Adafactor | 0.01 | 3 | 0.0135 | 2.51 | |
| 0.001 | 3 | 0.0067 | 2.48 | ||
| 0.0001 | 5 | 0.0351 | 4.20 | ||
| RMSprop | 0.01 | 3 | 0.0144 | 2.51 | |
| 0.001 | 3 | 0.00645 | 3.03 | ||
| 0.0001 | 3 | 0.00629 | 2.45 | ||
| Nadam | 0.01 | 3 | 0.0068 | 3.09 | |
| 0.001 | 3 | 0.00521 | 3.21 | ||
| 0.0001 | 3 | 0.00919 | 2.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mavrogiorgos, K.; Kiourtis, A.; Mavrogiorgou, A.; Apostolopoulos, D.; Menychtas, A.; Kyriazis, D. Time Series Forecasting for Touristic Policies. Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 11, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025011004
Mavrogiorgos K, Kiourtis A, Mavrogiorgou A, Apostolopoulos D, Menychtas A, Kyriazis D. Time Series Forecasting for Touristic Policies. Computer Sciences & Mathematics Forum. 2025; 11(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025011004
Chicago/Turabian StyleMavrogiorgos, Konstantinos, Athanasios Kiourtis, Argyro Mavrogiorgou, Dimitrios Apostolopoulos, Andreas Menychtas, and Dimosthenis Kyriazis. 2025. "Time Series Forecasting for Touristic Policies" Computer Sciences & Mathematics Forum 11, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025011004
APA StyleMavrogiorgos, K., Kiourtis, A., Mavrogiorgou, A., Apostolopoulos, D., Menychtas, A., & Kyriazis, D. (2025). Time Series Forecasting for Touristic Policies. Computer Sciences & Mathematics Forum, 11(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025011004





