Enhanced Lung Disease Detection Using Double Denoising and 1D Convolutional Neural Networks on Respiratory Sound Analysis †
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The lung sound categorization system divides respiratory cycles into stages and uses the double denoising method to enhance information about unusual sounds.
- Enhance propagation and implementation: Encourage the use and approval of this beneficial technology in clinical settings.
- Suggest potential areas for future research: Propose potential pathways for progress and originality.
2. Related Works
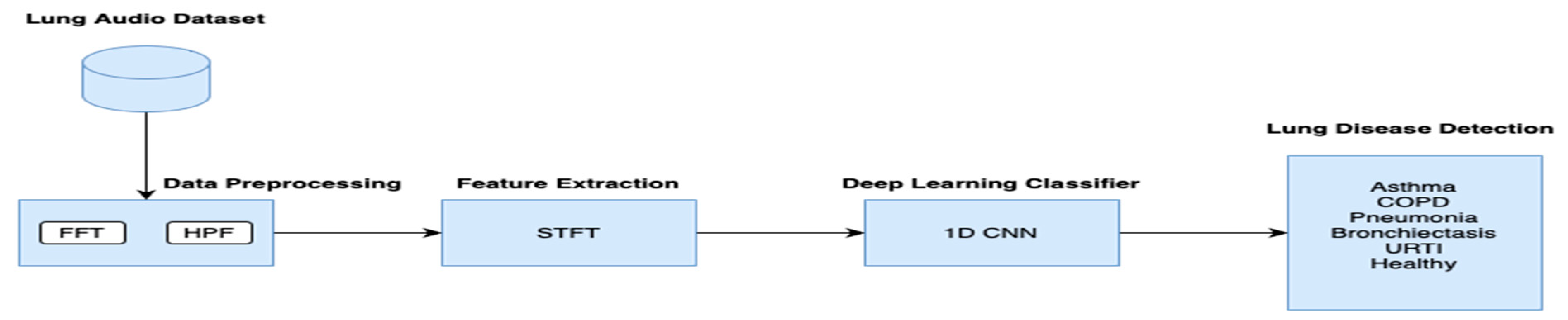
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Description
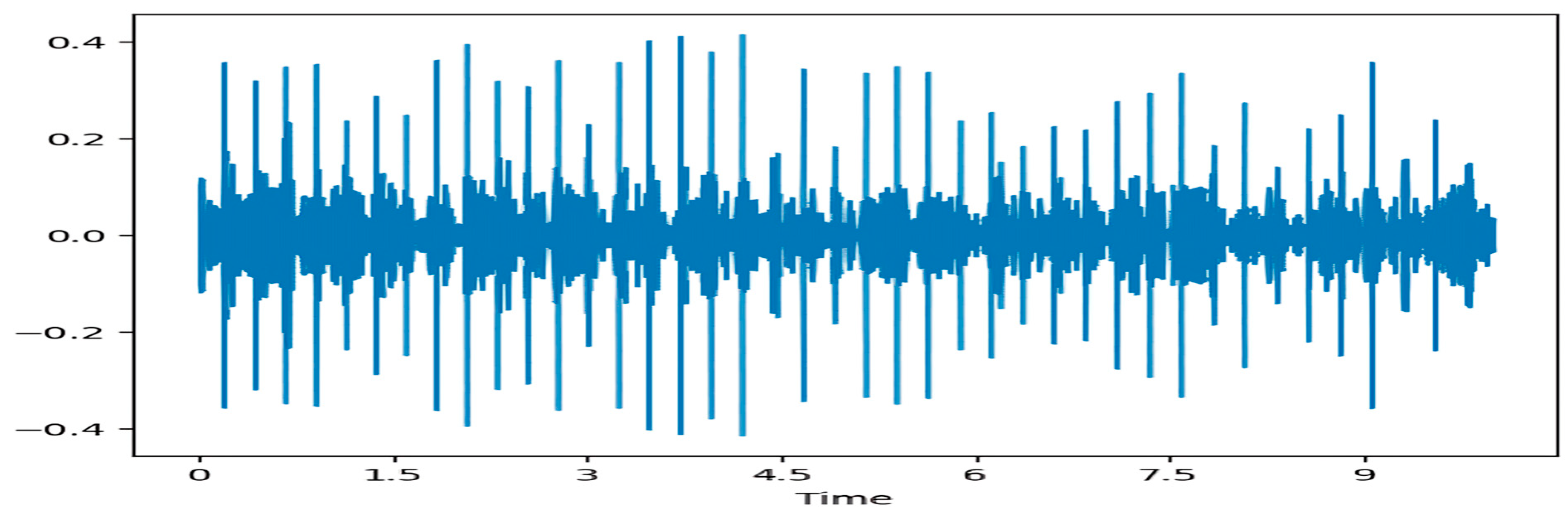
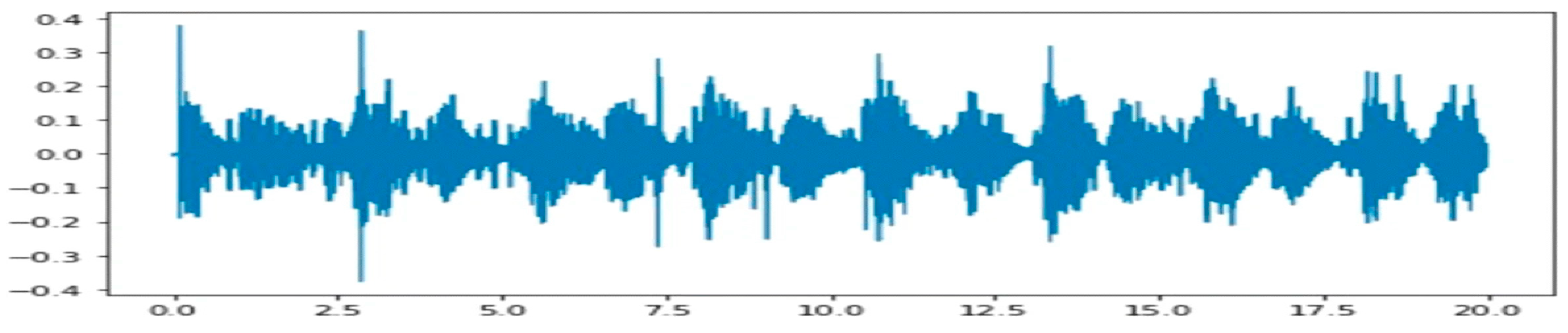
3.2. Preprocessing
3.3. Feature Extraction
3.4. Training and Testing
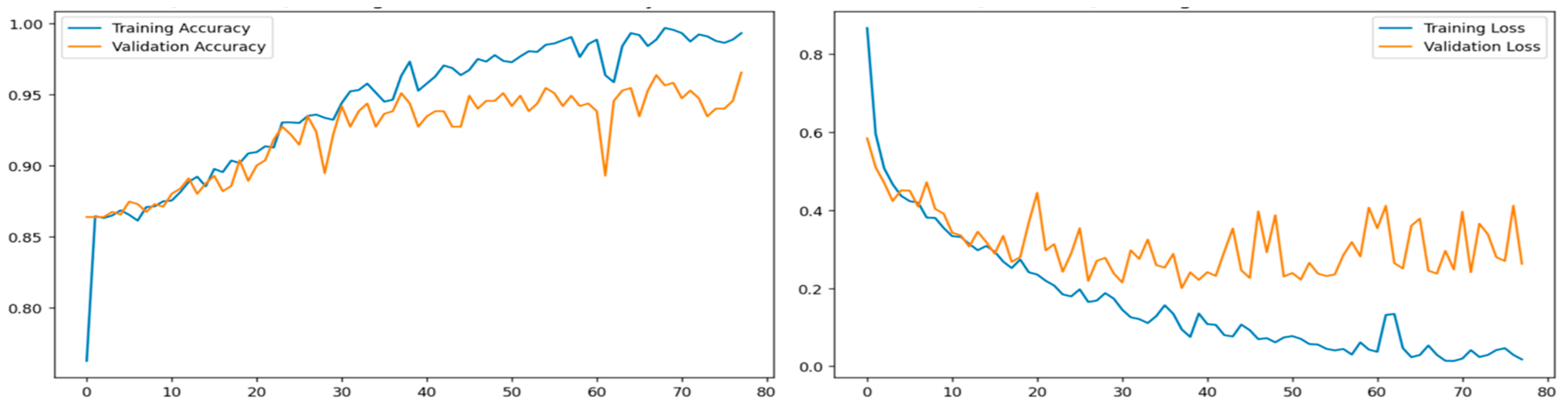
4. Result Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, Y.; Hyon, Y.; Jung, S.S.; Lee, S.; Yoo, G.; Chung, C.; Ha, T. Respiratory sound classification for crackles, wheezes, and rhonchi in the clinical field using deep learning. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horimasu, Y.; Ohshimo, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Masuda, T.; Nakashima, T.; Miyamoto, S.; Iwamoto, H.; Fujitaka, K.; Hamada, H.; et al. A machine-learning based approach to quantify fine crackles in the diagnosis of interstitial pneumonia. Medicine 2021, 100, e24738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, B.; Pessoa, D.; Marques, A.; Carvalho, P.; Paiva, R.P. Automatic Classification of Adventitious Respiratory Sounds: A (Un)Solved Problem? Sensors 2020, 21, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulfiqar, R.; Majeed, F.; Irfan, R.; Rauf, H.T.; Benkhelifa, E.; Belkacem, A.N. Abnormal Respiratory Sounds Classification Using Deep CNN Through Artificial Noise Addition. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 714811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aykanat, M.; Kılıç, Ö.; Kurt, B.; Saryal, S. Classification of lung sounds using convolutional neural networks. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2017, 2017, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, F.; Ismael, A.M.; Sengur, A. Classification of lung sounds with CNN model using parallel pooling structure. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 105376–105383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, R.; Majhi, S. Detecting respiratory diseases from recorded lung sounds by 2D CNN. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Security (ICCCS), Patna, India, 14–16 October 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraiwan, M.; Fraiwan, L.; Alkhodari, M.; Hassanin, O. Recognition of pulmonary diseases from lung sounds using convolutional neural networks and long short-term memory. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 13, 4759–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, H. Interpretation of lung disease classification with light attention connected module. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2023, 84, 104695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacanin, N.; Jovanovic, L.; Stoean, R.; Stoean, C.; Zivkovic, M.; Antonijevic, M.; Dobrojevic, M. Respiratory condition detection using audio analysis and convolutional neural networks optimized by modified metaheuristics. Axioms 2024, 13, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, Z. Performance evaluation of lung sounds classification using deep learning under variable parameters. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2024, 2024, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z. ICBHI 2017 Challenge; Harvard Dataverse; Harvard University: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1 January 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Deng, F.; Zhuang, H.; Yang, X.; Yu, J.; He, L. A Comparison of Image Denoising Methods. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.08990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; He, N. Research on ultrasound image of interventional catheterization processing method based on wavelet transform and fuzzy theory. Filomat 2020, 34, 5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Jain, S.; Miranda, R.; Patil, S.; Pandya, S.; Kotecha, K. Deep learning based respiratory sound analysis for detection of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casado, C.Á.; Cañellas, M.L.; Pedone, M.; Wu, X.; López, M.B. Audio-Based Classification of Respiratory Diseases using Advanced Signal Processing and Machine Learning for Assistive Diagnosis Support. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.07183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borwankar, S.; Verma, J.P.; Jain, R.; Nayyar, A. Improvise approach for respiratory pathologies classification with multilayer convolutional neural networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 39185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balamurali, B.T.; Hee, H.I.; Kapoor, S.; Teoh, O.H.; Teng, S.S.; Lee, K.P.; Herremans, D.; Chen, J.M. Deep Neural Network-Based Respiratory Pathology Classification Using Cough Sounds. Sensors 2021, 21, 5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, T.; Sinh, N.T.A.; Nguyen, C.; Phong, N.X. Sound-Dr: Reliable Sound Dataset and Baseline Artificial Intelligence System for Respiratory Illnesses. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.04581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabry, A.H.; Bashi, O.I.D.; Ali, N.N.; Al Kubaisi, Y.M. Lung disease recognition methods using audio-based analysis with machine learning. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albiges, T.; Sabeur, Z.; Arbab-Zavar, B. Compressed Sensing Data with Performing Audio Signal Reconstruction for the Intelligent Classification of Chronic Respiratory Diseases. Sensors 2023, 23, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sreejith, R.; Ramasamy, R.K.; Mohd-Isa, W.-N.; Abdullah, J. Enhanced Lung Disease Detection Using Double Denoising and 1D Convolutional Neural Networks on Respiratory Sound Analysis. Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 10, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010007
Sreejith R, Ramasamy RK, Mohd-Isa W-N, Abdullah J. Enhanced Lung Disease Detection Using Double Denoising and 1D Convolutional Neural Networks on Respiratory Sound Analysis. Computer Sciences & Mathematics Forum. 2025; 10(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleSreejith, Reshma, R. Kanesaraj Ramasamy, Wan-Noorshahida Mohd-Isa, and Junaidi Abdullah. 2025. "Enhanced Lung Disease Detection Using Double Denoising and 1D Convolutional Neural Networks on Respiratory Sound Analysis" Computer Sciences & Mathematics Forum 10, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010007
APA StyleSreejith, R., Ramasamy, R. K., Mohd-Isa, W.-N., & Abdullah, J. (2025). Enhanced Lung Disease Detection Using Double Denoising and 1D Convolutional Neural Networks on Respiratory Sound Analysis. Computer Sciences & Mathematics Forum, 10(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010007




