Speech-Language Pathology Findings in Patients with Mouth Breathing: Multidisciplinary Diagnosis According to Etiology
Abstract
INTRODUCTION
METHODS
- Group 1. Allergic Rhinitis: subjects were assigned to this group when signs and symptoms characteristic of allergic rhinitis was documented in their clinical history and was accompanied by specific IgE results greater than or equal to Class 3, according ImmunoCAP - Phadia technique - level minimum 0.35 KU/ml - Class 0 (Lund, 1988).
- Group 2. Adenoidal Hypertrophy: subjects were assigned to this group when their X-rays indicated that the aerial column of the nasal cavity was decreased by ¾ (three quarters) or more, (i.e., obstruction of more than 80%;) or when in the nasofibroscopy it was determined that the adenoids occupied over three quarters of the nasopharynx, (i.e., 80% or more, for adenoidal hypertrophy) (Lund, 1998).
- Group 3. Allergic Rhinitis and Adenoidal Hypertrophy: subjects were assigned to this group when signs of both allergic rhinitis and adenoidal hypertrophy were diagnosed.
- Group 4. Functional Mouth Breathing (FMB): subjects were assigned to this group when mouth-breathing behavior was diagnosed with no signs of allergic rhinitis or obstruction (Di Francesco et al., 2004).
- Group 1 - Orofacial Myology: subjects were assigned to this group when orofacial myofunctional disorders were identified in one or more of the evaluated areas (for example: habitual position of lips and/or tongue, tonus, chewing and/or swallowing).
- Group 2 – Alterations in Orofacial Myology with Speech and/or Voice and/or Language: subjects were assigned to this group when orofacial myofunctional deficits were identified in conjunction with any other speech, voice and/or language impairments.
- Group 3 - Normal: subjects were assigned to this group when no deficiencies were identified in either orofacial myofunctional areas or speech-language areas.
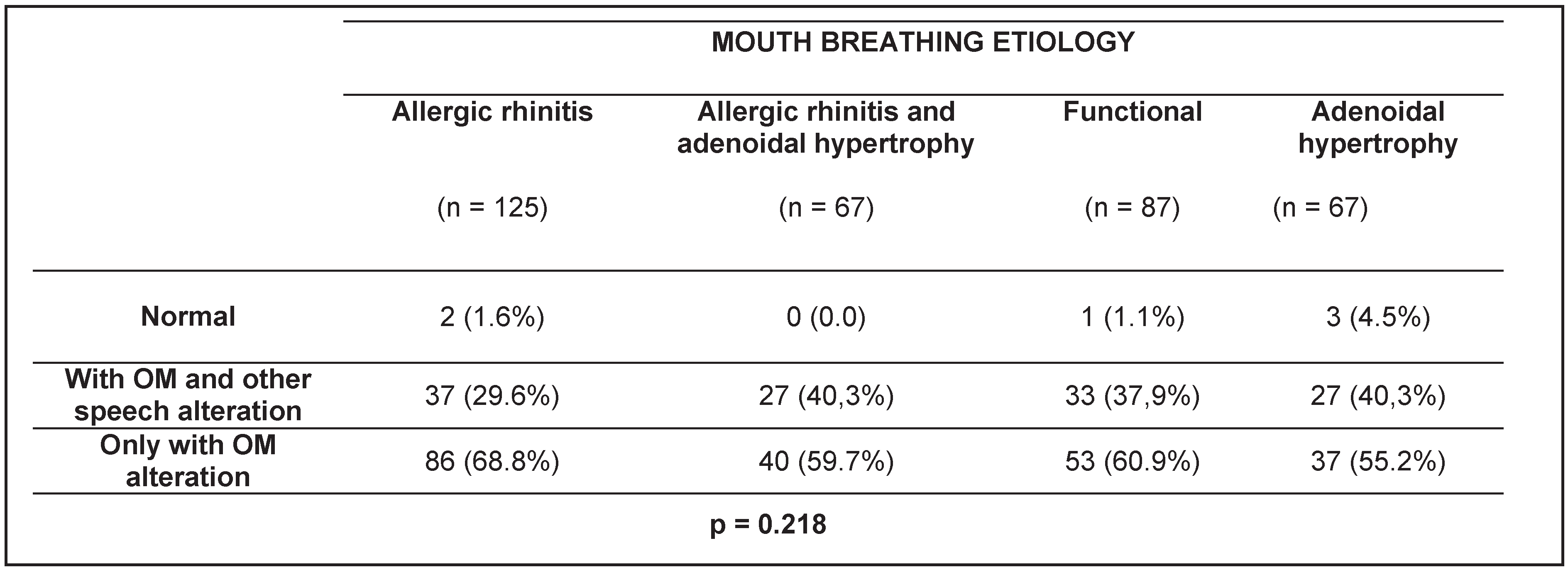
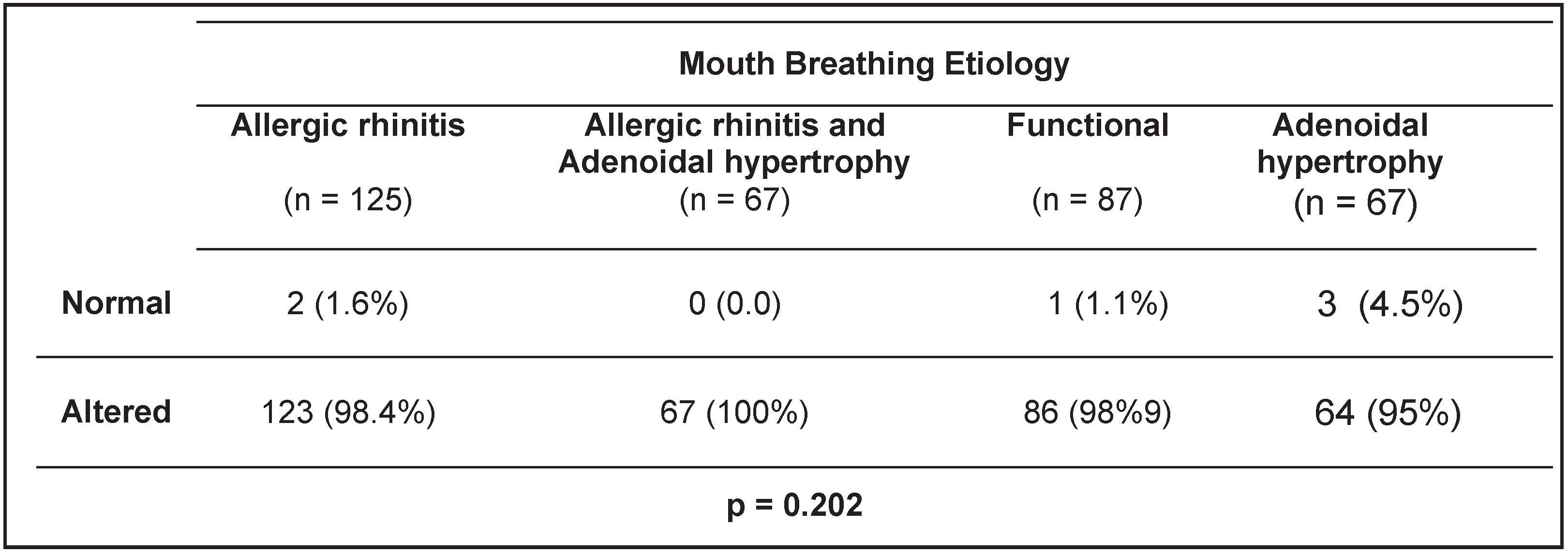
RESULTS
DISCUSSION
CONCLUSIONS
References
- Andrade, F.V., D.V. Andrade, A.S. Araújo, A.C.C. Ribeiro, L.D.G. Deccax, and K. Nemr. 2005. Alterações estruturais de órgãos fonoarticulatórios e más oclusões dentárias em respiradores orais de 6 a 10 anos. Revista Cefac 7: 318–25. [Google Scholar]
- Bicalho, G.P., A.R. Motta, and L.C. Vicente. 2006. Avaliação da deglutição em crianças respiradoras orais. Revista Cefac 8: 50–5. [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky, L. 1993. Tonsillitis, tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy. In Head and Neck Surgery-Otolaryngology. Edited by B.J. Bailey. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott, pp. 838–47. [Google Scholar]
- Cintra, C.F., F.F. Castro, and P.P. Cintra. 2000. As alterações orofaciais apresentadas em pacientes respiradores bucais. Revista Brasileira de Alergia e Imunopatologia 23: 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Di Francesco, R.C., G. Passeroti, B. Paulucci, and A. Miniti. 2004. Respiração oral na criança: repercussões diferentes de acordo com o diagnóstico. Revista Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia 70, 5: 667–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessa, F.C., C. Enoki, M.F. Feres, F.C. Valera, W.T. Lima, and M.A. Matsumoto. 2005. Influência do padrão respiratório na morfologia craniofacial. Revista Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia 71: 156–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, V. 1998. Allergic rhinitis: making the correct diagnosis. Journal of the British Society for Allergy & Clinical Immunology 28, 6: 25–8. [Google Scholar]
- Marchesan, I.Q. 2003. Protocolo de Avaliação Miofuncional Orofacial. In Respiração Oral. Edited by L.H. Krakauer, R.C. Di Francesco and I.Q. Marchesan. Ed. Pulso: pp. 55–80. [Google Scholar]
- Motonaga, S.M., L.C. Berti, and W.T. Anselmo-Lima. 2000. Respiração bucal: causas e conseqüências. Revista Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia 66: 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Paulo, C.B., and C.A. Conceição. 2003. Sintomatologia do respirador oral. Revista Cefac 5: 219–22. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo, C., S. Hauache, C. Naspitz, S. Pignatari, P. Junqueira, and M. Hallinan. 2002. Characteristics of children with allergic rhinitis and chronic mouth breathing. Journal of the British Society for Allergy & Clinical Immunology 109: S263. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, S., T. Ono, Y. Ishiwata, and T. Kuroda. 2002. Breathing modes, body positions, and suprahyoid muscle activity. Journal Orthodontic 29: 307–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Valera, F.C.P., L.V.V. Trawitzk, and W.T. Anselmo-Lima. 2006. Myofunctional evaluation after surgery for tonsils hypertrophy and its correlation to breathing pattern: A 2-year-follow up. International Journal Pediatric Otorhinolayngology 70: 221–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valera, F.C.P., L.V.V. Trawitzki, S.E.M. Mattar, A.M. Matsumoto, W.T. Elias, and W.T. Anselmo-Lima. 2003. Muscular, functional and orthodontic changes in preschool children with enlarged adenoids and tonsils. International Journal Pediatric Otorhinolayngology 67: 761–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera, C.F.D., G.E. Conde, R. Wajnsztejn, and K. Nemr. 2006. Transtornos de aprendizagem e presença de respiração oral em indivíduos com diagnóstico de transtornos de déficit de atenção/hiperatividade (TDAH). Revista Cefac 8: 441–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 |
 |
© 2010 by the author. 2010 Patricia Junqueira, Irene Queiroz Marchesan, Luciana Regina de Oliveira, Emilio Ciccone, Leonardo Haddad, Maria Cândida Rizzo
Share and Cite
Junqueira, P.; Marchesan, I.Q.; de Oliveira, L.R.; Ciccone, E.; Haddad, L.; Rizzo, M.C. Speech-Language Pathology Findings in Patients with Mouth Breathing: Multidisciplinary Diagnosis According to Etiology. Int. J. Orofac. Myol. Myofunct. Ther. 2010, 36, 27-32. https://doi.org/10.52010/ijom.2010.36.1.3
Junqueira P, Marchesan IQ, de Oliveira LR, Ciccone E, Haddad L, Rizzo MC. Speech-Language Pathology Findings in Patients with Mouth Breathing: Multidisciplinary Diagnosis According to Etiology. International Journal of Orofacial Myology and Myofunctional Therapy. 2010; 36(1):27-32. https://doi.org/10.52010/ijom.2010.36.1.3
Chicago/Turabian StyleJunqueira, Patricia, Irene Queiroz Marchesan, Luciana Regina de Oliveira, Emilio Ciccone, Leonardo Haddad, and Maria Cândida Rizzo. 2010. "Speech-Language Pathology Findings in Patients with Mouth Breathing: Multidisciplinary Diagnosis According to Etiology" International Journal of Orofacial Myology and Myofunctional Therapy 36, no. 1: 27-32. https://doi.org/10.52010/ijom.2010.36.1.3
APA StyleJunqueira, P., Marchesan, I. Q., de Oliveira, L. R., Ciccone, E., Haddad, L., & Rizzo, M. C. (2010). Speech-Language Pathology Findings in Patients with Mouth Breathing: Multidisciplinary Diagnosis According to Etiology. International Journal of Orofacial Myology and Myofunctional Therapy, 36(1), 27-32. https://doi.org/10.52010/ijom.2010.36.1.3




