Trophoblast Organoids: Capturing the Complexity of Early Placental Development In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Early Placental Development
2.1. Trophoblast Diversity in Placental Development
2.2. In Vivo Models of Placental Development
2.3. In Vitro Models of Placental Development
3. Trophoblast Organoids as an In Vitro Model
3.1. Characterization of Trophoblast Organoids
3.2. Trophoblast Organoid Polarity
3.3. Trophoblast Cell Diversity Is Captured In Vitro by Trophoblast Organoids
3.4. Themes of Differentiation as Captured in Trophoblast Organoids
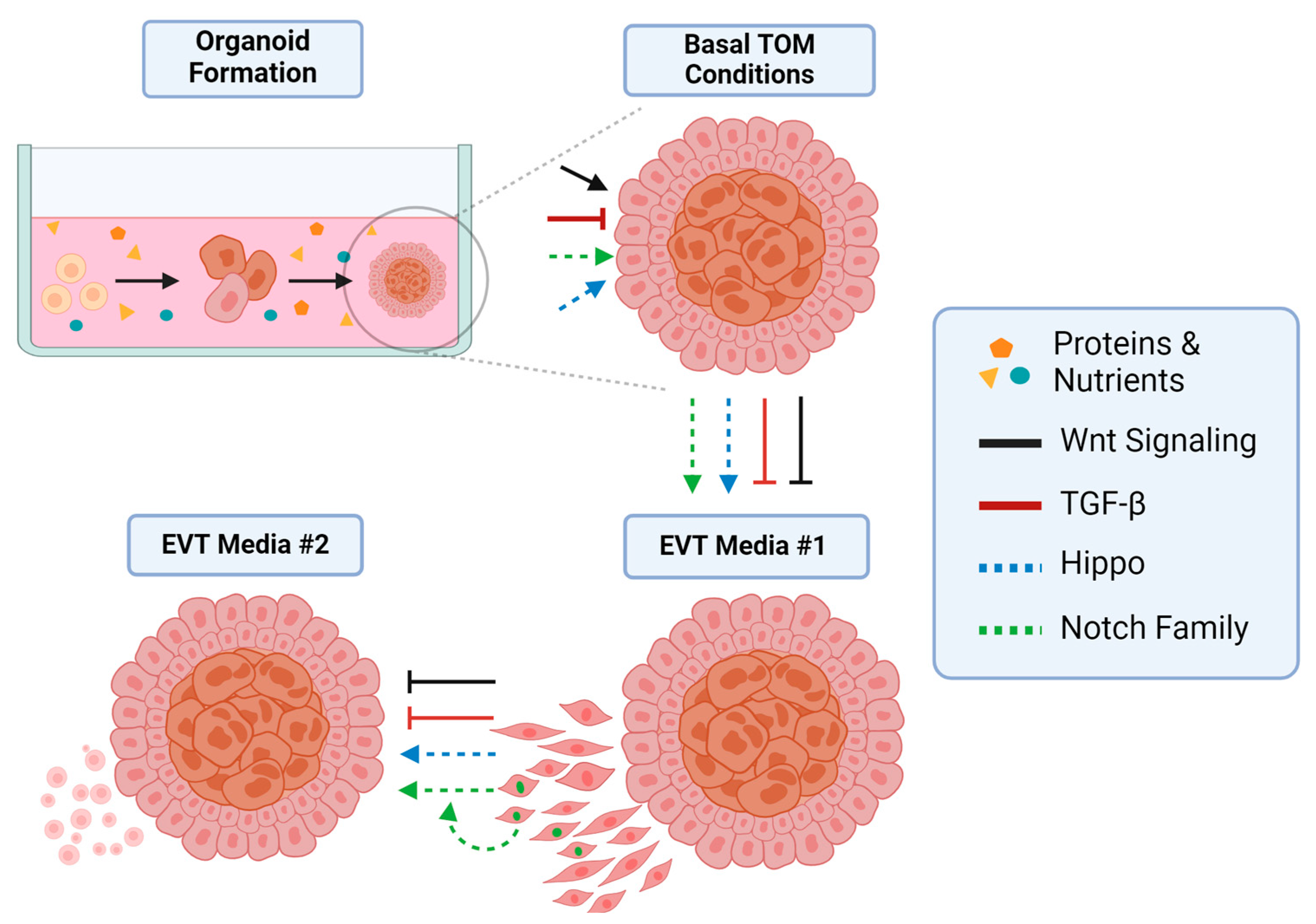
4. Signaling Pathways in Trophoblast Organoids
4.1. The Role of Wnt Signaling
4.2. The Role of TGF-β Signaling
4.3. The Hippo Pathway
4.4. Notch Family Signaling
5. Translational Potential
6. Future Directions and the Role of NHP Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Acronym | Definition |
| CTB | Cytotrophoblast |
| SYN | Syncytiotrophoblast |
| EVT | Extravillous Trophoblast |
| NHP | Nonhuman Primate |
| TO | Trophoblast Organoid |
| TSC | Trophoblast Stem Cell |
| fcCTB | Fusion-Competent Cytotrophoblast |
| CCC | Cytotrophoblast Cell Column |
| iEVT | Interstitial Extravillous Trophoblast |
| eEVT | Endovascular Extravillous Trophoblast |
| mTSC | Macaque Trophoblast Stem Cell |
| mCG | Macaque Chorionic Gonadotrophin |
| hCG | Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin |
| PTO | Primary Trophoblast Organoid |
| TSC-TO | Trophoblast Stem Cell Trophoblast Organoid |
| TTO | Term Trophoblast Organoid |
| GC | Giant Cell |
| ICD | Intracellular Domain |
| CVS | Chorionic Villous Sampling |
| CdLs | Cornelia de Lange Syndrome |
References
- Brosens, I.; Pijnenborg, R.; Vercruysse, L.; Romero, R. The “Great Obstetrical Syndromes” Are Associated with Disorders of Deep Placentation. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 204, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pijnenborg, R.; Vercruysse, L.; Hanssens, M. The Uterine Spiral Arteries in Human Pregnancy: Facts and Controversies. Placenta 2006, 27, 939–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baergen, R.N.; Burton, G.J.; Kaplan, C.G. (Eds.) Benirschke’s Pathology of the Human Placenta; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 978-3-030-84724-1. [Google Scholar]
- Shibata, S.; Kobayashi, E.H.; Kobayashi, N.; Oike, A.; Okae, H.; Arima, T. Unique Features and Emerging in Vitro Models of Human Placental Development. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2020, 19, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellery, P.M.; Cindrova-Davies, T.; Jauniaux, E.; Ferguson-Smith, A.C.; Burton, G.J. Evidence for Transcriptional Activity in the Syncytiotrophoblast of the Human Placenta. Placenta 2009, 30, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalla, A.M.; Tingari, M.D.; Abdalla, M.A. Histomorphometric Parameters of Normal Full Term Placenta of Sudanese Women. Heliyon 2016, 2, e00135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doughty, I.M.; Glazier, J.D.; Powell, T.L.; Jansson, T.; Sibley, C.P. Chloride Transport across Syncytiotrophoblast Microvillous Membrane of First Trimester Human Placenta. Pediatr. Res. 1998, 44, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, M.J.; McNeill, G.L.; Koksal, B.; Baltayeva, J.; Wächter, J.; Castellana, B.; Peñaherrera, M.S.; Robinson, W.P.; Leung, P.C.K.; Beristain, A.G. Single-Cell Assessment of Primary and Stem Cell-Derived Human Trophoblast Organoids as Placenta-Modeling Platforms. Dev. Cell 2024, 59, 776–792.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheridan, M.A.; Zhao, X.; Fernando, R.C.; Gardner, L.; Perez-Garcia, V.; Li, Q.; Marsh, S.G.E.; Hamilton, R.; Moffett, A.; Turco, M.Y. Characterization of Primary Models of Human Trophoblast. Development 2021, 148, dev199749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karvas, R.M.; Khan, S.A.; Verma, S.; Yin, Y.; Kulkarni, D.; Dong, C.; Park, K.-M.; Chew, B.; Sane, E.; Fischer, L.A.; et al. Stem-Cell-Derived Trophoblast Organoids Model Human Placental Development and Susceptibility to Emerging Pathogens. Cell Stem Cell 2022, 29, 810–825.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, X.; Wang, R.; Lu, X.; Dang, Y.-L.; Wang, H.; Lin, H.-Y.; Zhu, C.; Ge, H.; Cross, J.C.; et al. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Reveals the Diversity of Trophoblast Subtypes and Patterns of Differentiation in the Human Placenta. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 819–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vento-Tormo, R.; Efremova, M.; Botting, R.A.; Turco, M.Y.; Vento-Tormo, M.; Meyer, K.B.; Park, J.-E.; Stephenson, E.; Polański, K.; Goncalves, A.; et al. Single-Cell Reconstruction of the Early Maternal–Fetal Interface in Humans. Nature 2018, 563, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, S.; Meinhardt, G.; Saleh, L.; Fiala, C.; Pollheimer, J.; Knöfler, M. Notch1 Controls Development of the Extravillous Trophoblast Lineage in the Human Placenta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E7710–E7719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, W.J.; Boyd, J.D. Development of the Human Placenta in the First Three Months of Gestation. J. Anat. 1960, 94, 297–328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burton, G.J.; Jauniaux, E. The Cytotrophoblastic Shell and Complications of Pregnancy. Placenta 2017, 60, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arutyunyan, A.; Roberts, K.; Troulé, K.; Wong, F.C.K.; Sheridan, M.A.; Kats, I.; Garcia-Alonso, L.; Velten, B.; Hoo, R.; Ruiz-Morales, E.R.; et al. Spatial Multiomics Map of Trophoblast Development in Early Pregnancy. Nature 2023, 616, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, G.J.; Charnock-Jones, D.S.; Jauniaux, E. Regulation of Vascular Growth and Function in the Human Placenta. Reproduction 2009, 138, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loukeris, K.; Sela, R.; Baergen, R.N. Syncytial Knots as a Reflection of Placental Maturity: Reference Values for 20 to 40 Weeks’ Gestational Age. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2010, 13, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Sun, R.; Liu, F.; Li, J.; Yan, L.; Zhang, J.; Xie, X.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. Single-Nucleus Multi-Omic Profiling of Human Placental Syncytiotrophoblasts Identifies Cellular Trajectories during Pregnancy. Nat. Genet. 2024, 56, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.Q.E.; Gardner, L.; Turco, M.; Zhao, N.; Murray, M.J.; Coleman, N.; Rossant, J.; Hemberger, M.; Moffett, A. What Is Trophoblast? A Combination of Criteria Define Human First-Trimester Trophoblast. Stem Cell Rep. 2016, 6, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, M.J.; Baltayeva, J.; Castellana, B.; Wächter, J.; McNeill, G.L.; Yoon, J.S.; Treissman, J.; Le, H.T.; Lavoie, P.M.; Beristain, A.G. Cell Trajectory Modeling Identifies a Primitive Trophoblast State Defined by BCAM Enrichment. Development 2022, 149, dev199840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damsky, C.H.; Librach, C.; Lim, K.-H.; Fitzgerald, M.L.; McMaster, M.T.; Janatpour, M.; Zhou, Y.; Logan, S.K.; Fisher, S.J. Integrin Switching Regulates Normal Trophoblast Invasion. Development 1994, 120, 3657–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Lamki, R.S.; Skepper, J.N.; Burton, G.J. Are Human Placental Bed Giant Cells Merely Aggregates of Small Mononuclear Trophoblast Cells? An Ultrastructural and Immunocytochemical Study. Human. Reprod. 1999, 14, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.J.P.; Aplin, J.D. A Re-Examination of the Origins of Placental Bed Giant Cells. Placenta 2021, 114, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, A.M. Animal Models of Human Pregnancy and Placentation: Alternatives to the Mouse. Reproduction 2020, 160, R129–R143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, S.; Kuroda, Y.; Sugiyama, A. A Comparison of the Histological Structure of the Placenta in Experimental Animals. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2014, 27, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, V.H.J.; Castro, J.N.; Wessel, B.M.; Conrad, D.F.; Lewis, A.D.; Lo, J.O. Rhesus Macaque Fetal and Placental Growth Demographics: A Resource for Laboratory Animal Researchers. Am. J. Primatol. 2023, 85, e23526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schabel, M.C.; Roberts, V.H.J.; Lo, J.O.; Platt, S.; Grant, K.A.; Frias, A.E.; Kroenke, C.D. Functional Imaging of the Nonhuman Primate Placenta with Endogenous Blood Oxygen Level–Dependent Contrast. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 76, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenship, T.N.; King, B.F. Macaque Intra-Arterial Trophoblast and Extravillous Trophoblast of the Cell Columns and Cytotrophoblastic Shell Express Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule (NCAM). Anat. Rec. 1996, 245, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, A.C.; Blankenship, T.N.; Fazleabas, A.T.; Jones, C.J.P. Structure of Anchoring Villi and the Trophoblastic Shell in the Human, Baboon and Macaque Placenta. Placenta 2001, 22, 284–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, G.J.; Jauniaux, E. The Human Placenta: New Perspectives on Its Formation and Function during Early Pregnancy. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2023, 290, 20230191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, A.M.; Enders, A.C.; Pijnenborg, R. The Role of Invasive Trophoblast in Implantation and Placentation of Primates. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slukvin, I.I.; Boyson, J.E.; Watkins, D.I.; Golos, T.G. The Rhesus Monkey Analogue of Human Lymphocyte Antigen-G Is Expressed Primarily in Villous Syncytiotrophoblasts1. Biol. Reprod. 1998, 58, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhai, J.; Xiao, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhang, D.; Wan, H.; Xu, Y.; Qi, L.; Wang, M.; Yu, D.; et al. Identifying a Dynamic Transcriptomic Landscape of the Cynomolgus Macaque Placenta during Pregnancy at Single-Cell Resolution. Dev. Cell 2023, 58, 806–821.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.K.; Keding, L.T.; Block, L.N.; Wiepz, G.J.; Koenig, M.R.; Meyer, M.G.; Dusek, B.M.; Kroner, K.M.; Bertogliat, M.J.; Kallio, A.R.; et al. Placenta-Derived Macaque Trophoblast Stem Cells: Differentiation to Syncytiotrophoblasts and Extravillous Trophoblasts Reveals Phenotypic Reprogramming. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgen, G.D.; Tullner, W.W.; Vaitukaitis, J.L.; Ward, D.N.; Ross, G.T. Specific Radioimmunoassay of Chorionic Gonadotropin During Implantation in Rhesus Monkeys. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1974, 39, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raha, S. Trophoblasts Methods and Protocols; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; Volume 2728, ISBN 978-1-07-163494-3. [Google Scholar]
- Di Santo, S.; Malek, A.; Sager, R.; Andres, A.-C.; Schneider, H. Trophoblast Viability in Perfused Term Placental Tissue and Explant Cultures Limited to 7–24 Hours. Placenta 2003, 24, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simán, C.M.; Sibley, C.P.; Jones, C.J.; Turner, M.A.; Greenwood, S.L. The Functional Regeneration of Syncytiotrophoblast in Cultured Explants of Term Placenta. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2001, 280, R1116–R1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, M.; Satoh, M.; Kinoshita, K.; Satoh, K.; Mizuno, M.; Sakamoto, S. Viability of the Human Placental Villi in Organ Culture. Arch. Gynecol. 1984, 234, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.E.; Watson, A.L.; Burton, G.J. Morphological Analysis of Degeneration and Regeneration of Syncytiotrophoblast in First Trimester Placental Villi during Organ Culture. Hum. Reprod. 1997, 12, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaga-Clavellina, V. In Vitro Culturing of Human Term Placental Explants. In Maternal Placental Interface; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; Volume 2781, pp. 39–45. ISBN 978-1-07-163745-6. [Google Scholar]
- Seeho, S.K.M.; Park, J.H.; Rowe, J.; Morris, J.M.; Gallery, E.D.M. Villous Explant Culture Using Early Gestation Tissue from Ongoing Pregnancies with Known Normal Outcomes: The Effect of Oxygen on Trophoblast Outgrowth and Migration. Human. Reprod. 2008, 23, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okae, H.; Toh, H.; Sato, T.; Hiura, H.; Takahashi, S.; Shirane, K.; Kabayama, Y.; Suyama, M.; Sasaki, H.; Arima, T. Derivation of Human Trophoblast Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 50–63.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Beltcheva, M.; Gontarz, P.; Zhang, B.; Popli, P.; Fischer, L.A.; Khan, S.A.; Park, K.-M.; Yoon, E.-J.; Xing, X.; et al. Derivation of Trophoblast Stem Cells from Naïve Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. eLife 2020, 9, e52504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandevoort, C.A.; Thirkill, T.L.; Douglas, G.C. Blastocyst-Derived Trophoblast Stem Cells from the Rhesus Monkey. Stem Cells Dev. 2007, 16, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Porter, C.J.; Ogasawara, N.; Iwatani, C.; Tsuchiya, H.; Seita, Y.; Chang, Y.-W.; Okamoto, I.; Saitou, M.; Ema, M.; et al. Establishment of Macaque Trophoblast Stem Cell Lines Derived from Cynomolgus Monkey Blastocysts. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, M.Y.; Gardner, L.; Kay, R.G.; Hamilton, R.S.; Prater, M.; Hollinshead, M.S.; McWhinnie, A.; Esposito, L.; Fernando, R.; Skelton, H.; et al. Trophoblast Organoids as a Model for Maternal-Fetal Interactions during Human Placentation. Nature 2018, 564, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Meinhardt, G.; Saleh, L.; Kunihs, V.; Gamperl, M.; Kaindl, U.; Ellinger, A.; Burkard, T.R.; Fiala, C.; Pollheimer, J.; et al. Self-Renewing Trophoblast Organoids Recapitulate the Developmental Program of the Early Human Placenta. Stem Cell Rep. 2018, 11, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloria, A.J.; Haider, S.; Dietrich, B.; Kunihs, V.; Oberhofer, S.; Knöfler, M.; Leitgeb, R.; Liu, M.; Drexler, W.; Haindl, R. Ultra-High-Resolution 3D Optical Coherence Tomography Reveals Inner Structures of Human Placenta-Derived Trophoblast Organoids. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 68, 2368–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, T.; Okae, H.; Shibata, S.; Kobayashi, N.; Kobayashi, E.H.; Oike, A.; Sekiya, A.; Arima, T.; Kaji, H. Trophoblast Stem Cell-Based Organoid Models of the Human Placental Barrier. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Semmes, E.C.; Ovies, C.; Megli, C.; Permar, S.; Gilner, J.B.; Coyne, C.B. Innate Immune Signaling in Trophoblast and Decidua Organoids Defines Differential Antiviral Defenses at the Maternal-Fetal Interface. eLife 2022, 11, e79794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liang, P.; Yang, H.; Coyne, C.B. Trophoblast Organoids with Physiological Polarity Model Placental Structure and Function. J. Cell Sci. 2023, 137, jcs261528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConkey, C.A.; Delorme-Axford, E.; Nickerson, C.A.; Kim, K.S.; Sadovsky, Y.; Boyle, J.P.; Coyne, C.B. A Three-Dimensional Culture System Recapitulates Placental Syncytiotrophoblast Development and Microbial Resistance. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheridan, M.A.; Fernando, R.C.; Gardner, L.; Hollinshead, M.S.; Burton, G.J.; Moffett, A.; Turco, M.Y. Establishment and Differentiation of Long-Term Trophoblast Organoid Cultures from the Human Placenta. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 3441–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, B.; Ganguly, A.; Home, P.; Bhattacharya, B.; Ray, S.; Ghosh, A.; Rumi, M.A.K.; Marsh, C.; French, V.A.; Gunewardena, S.; et al. TEAD4 Ensures Postimplantation Development by Promoting Trophoblast Self-Renewal: An Implication in Early Human Pregnancy Loss. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 17864–17875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackers, I.; Malgor, R. Interrelationship of Canonical and Non-Canonical Wnt Signalling Pathways in Chronic Metabolic Diseases. Diab Vasc. Dis. Res. 2018, 15, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knöfler, M.; Pollheimer, J. Human Placental Trophoblast Invasion and Differentiation: A Particular Focus on Wnt Signaling. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, H. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Trophoblasts and Abnormal Activation in Pre-eclampsia (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinhardt, G.; Saleh, L.; Otti, G.R.; Haider, S.; Velicky, P.; Fiala, C.; Pollheimer, J.; Knöfler, M. Wingless Ligand 5a Is a Critical Regulator of Placental Growth and Survival. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, S.; Lackner, A.I.; Dietrich, B.; Kunihs, V.; Haslinger, P.; Meinhardt, G.; Maxian, T.; Saleh, L.; Fiala, C.; Pollheimer, J.; et al. Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling Governs the Differentiation Program of Extravillous Trophoblasts in the Developing Human Placenta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2120667119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soncin, F.; Parast, M.M. Role of Hippo Signaling Pathway in Early Placental Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 20354–20356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D. The Hippo Signaling Pathway in Development and Cancer. Dev. Cell 2010, 19, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Hu, Y.; Lan, T.; Guan, K.-L.; Luo, T.; Luo, M. The Hippo Signalling Pathway and Its Implications in Human Health and Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinhardt, G.; Haider, S.; Kunihs, V.; Saleh, L.; Pollheimer, J.; Fiala, C.; Hetey, S.; Feher, Z.; Szilagyi, A.; Than, N.G.; et al. Pivotal Role of the Transcriptional Co-Activator YAP in Trophoblast Stemness of the Developing Human Placenta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 13562–13570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.; Saha, A.; Ghosh, A.; Roy, N.; Kumar, R.P.; Meinhardt, G.; Mukerjee, A.; Gunewardena, S.; Kumar, R.; Knöfler, M.; et al. Hippo Signaling Cofactor, WWTR1, at the Crossroads of Human Trophoblast Progenitor Self-Renewal and Differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2204069119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopan, R. Notch Signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a011213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, B.; Haider, S.; Meinhardt, G.; Pollheimer, J.; Knöfler, M. WNT and NOTCH Signaling in Human Trophoblast Development and Differentiation. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, B.; Kunihs, V.; Lackner, A.I.; Meinhardt, G.; Koo, B.-K.; Pollheimer, J.; Haider, S.; Knöfler, M. NOTCH3 Signalling Controls Human Trophoblast Stem Cell Expansion and Differentiation. Development 2023, 150, dev202152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plessl, K.; Haider, S.; Fiala, C.; Pollheimer, J.; Knöfler, M. Expression Pattern and Function of Notch2 in Different Subtypes of First Trimester Cytotrophoblast. Placenta 2015, 36, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Meinhardt, G.; Velicky, P.; Otti, G.R.; Whitley, G.; Fiala, C.; Pollheimer, J.; Knöfler, M. Notch Signaling Plays a Critical Role in Motility and Differentiation of Human First-Trimester Cytotrophoblasts. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaffers, O.J.; Dupont, C.; Bindels, E.M.; Van Opstal, D.; Dekkers, D.H.; Demmers, J.A.; Gribnau, J.; van Rijn, B.B. Single-Cell Atlas of Patient-Derived Trophoblast Organoids in Ongoing Pregnancies. Organoids 2022, 1, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.M.; Montero, F.J. Chorionic Villus Sampling. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Reilly, K.; Doyle, S.; Hamilton, S.J.; Kilby, M.D.; Mone, F. Pitfalls of Prenatal Diagnosis Associated with Mosaicism. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2023, 25, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, B.; Castro, J.; Scottoline, B.; Roberts, V. Development of a Nonhuman Primate Trophoblast Organoid Model Resource. Reprod. Sci. 2024, 31, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Salati, J.A.; Roberts, V.H.J.; Schabel, M.C.; Lo, J.O.; Kroenke, C.D.; Lewandowski, K.S.; Lindner, J.R.; Grove, K.L.; Frias, A.E. Maternal High-Fat Diet Reversal Improves Placental Hemodynamics in a Nonhuman Primate Model of Diet-Induced Obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, A.J.; Smith, J.L.; Haese, N.N.; Broeckel, R.M.; Parkins, C.J.; Kreklywich, C.; DeFilippis, V.R.; Denton, M.; Smith, P.P.; Messer, W.B.; et al. Zika Virus Infection of Rhesus Macaques Leads to Viral Persistence in Multiple Tissues. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helms, C.M.; Rau, A.; Shaw, J.; Stull, C.; Gonzales, S.W.; Grant, K.A. The Effects of Age at the Onset of Drinking to Intoxication and Chronic Ethanol Self-Administration in Male Rhesus Macaques. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 1853–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, G.J.; Cindrova-Davies, T.; Yung, H.W.; Jauniaux, E. HYPOXIA AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH: Oxygen and Development of the Human Placenta. Reproduction 2021, 161, F53–F65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.A.; Bondarenko, G.I.; Gerami-Naini, B.; Drenzek, J.G.; Durning, M.; Garthwaite, M.A.; Schmidt, J.K.; Golos, T.G. Trophoblast Differentiation, Invasion and Hormone Secretion in a Three-Dimensional in Vitro Implantation Model with Rhesus Monkey Embryos. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2018, 16, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, M.Y.; Gardner, L.; Hughes, J.; Cindrova-Davies, T.; Gomez, M.J.; Farrell, L.; Hollinshead, M.; Marsh, S.G.E.; Brosens, J.J.; Critchley, H.O.; et al. Long-Term, Hormone-Responsive Organoid Cultures of Human Endometrium in a Chemically Defined Medium. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
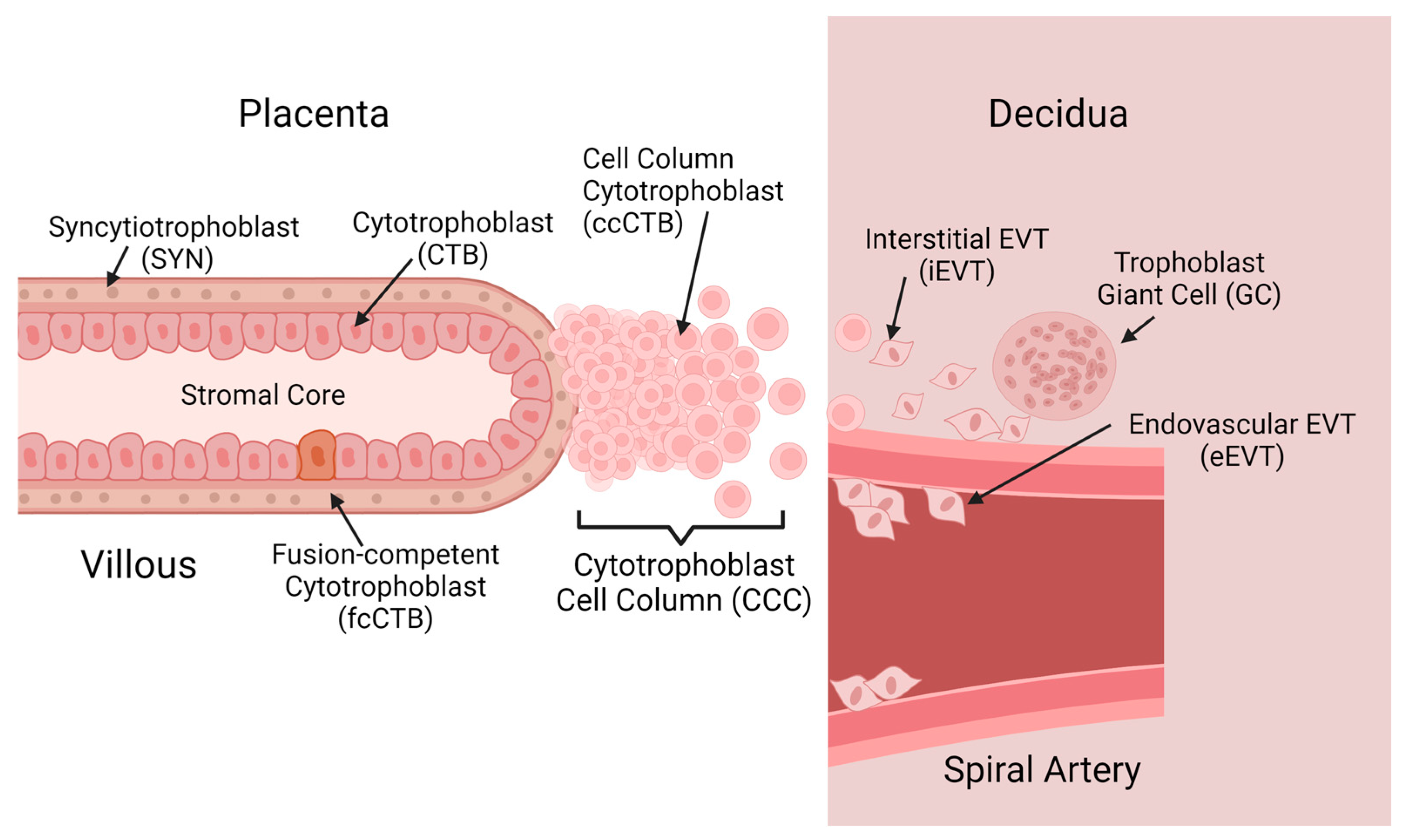
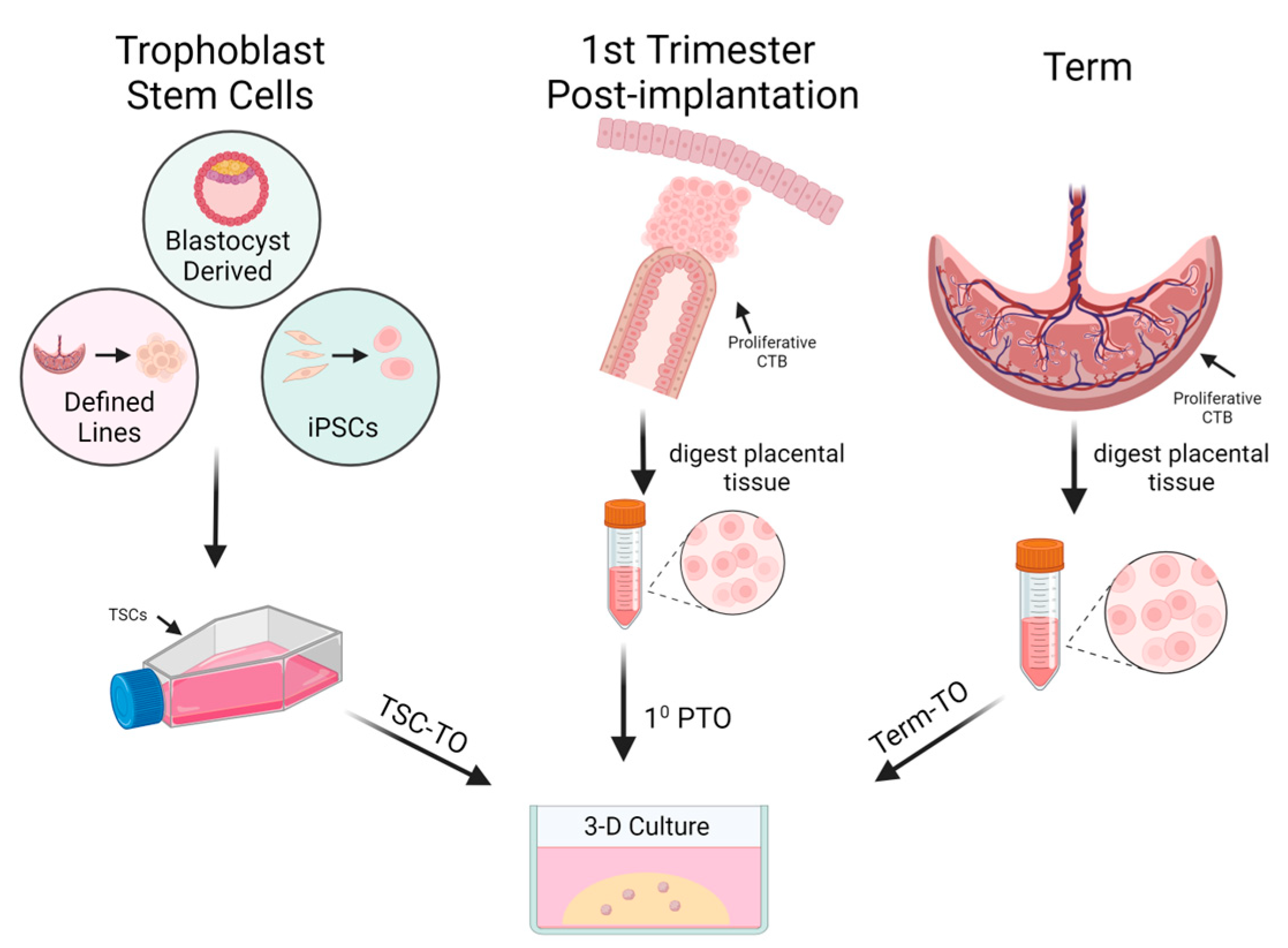
| Cell Type | Human | Rhesus Macaque |
|---|---|---|
| Trophoblast | KRT7 | KRT7 |
| CTB | GATA3, TP63, TEAD4, CDH1 | KI67, TEAD4 |
| fcCTB | ERVFRD-1 | ERVFRD-1 |
| ccCTB | Notch1, KI67, ITGA1/2 | Notch1, KI67 |
| SYN | GCM1, SDC1 | SDC1, Mamu-AG |
| EVT | HLA-G, ITGA5 | NCAM1, ITGA5 Mamu-AG |
| iEVT | PAPPA, DAO, SERPINE1 | N/A |
| eEVT | NCAM1 | N/A |
| GC | CD81, RAC11 | Unknown |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wessel, B.M.; Castro, J.N.; Roberts, V.H.J. Trophoblast Organoids: Capturing the Complexity of Early Placental Development In Vitro. Organoids 2024, 3, 174-193. https://doi.org/10.3390/organoids3030012
Wessel BM, Castro JN, Roberts VHJ. Trophoblast Organoids: Capturing the Complexity of Early Placental Development In Vitro. Organoids. 2024; 3(3):174-193. https://doi.org/10.3390/organoids3030012
Chicago/Turabian StyleWessel, Brady M., Jenna N. Castro, and Victoria H. J. Roberts. 2024. "Trophoblast Organoids: Capturing the Complexity of Early Placental Development In Vitro" Organoids 3, no. 3: 174-193. https://doi.org/10.3390/organoids3030012
APA StyleWessel, B. M., Castro, J. N., & Roberts, V. H. J. (2024). Trophoblast Organoids: Capturing the Complexity of Early Placental Development In Vitro. Organoids, 3(3), 174-193. https://doi.org/10.3390/organoids3030012






