Vitamin Compatibility with the Marek’s Disease Vaccine †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Injection Solution Precreation
2.2. MDV Integrity (Live/Dead CEF-MDV Ratio)
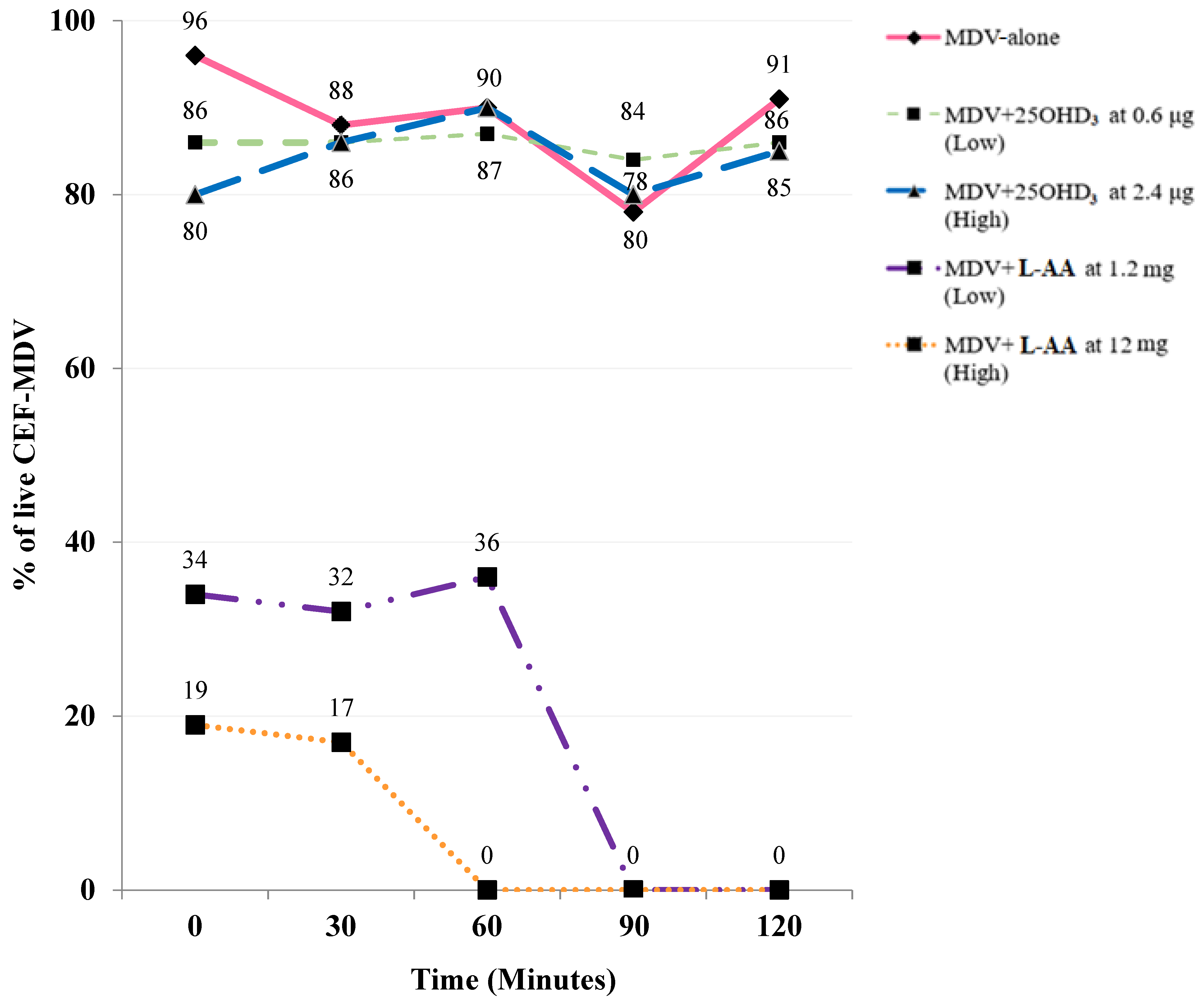
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hein, R.; Koopman, R.; García, M.; Armour, N.; Dunn, J.R.; Barbosa, T.; Martinez, A. Review of poultry recombinant vector vaccines. Avian Dis. 2021, 65, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negash, T.; Al-Garib, S.O.; Gruys, E. Comparison of in ovo and post-hatch vaccination with particular reference to infectious bursal disease. A review. Vet. Q. 2004, 26, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razib, D.; Pravin, M.; Rajesh, J. In ovo feeding as a tool for improving performance and gut health of poultry: A review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 754246. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, J.M. Introduction to poultry vaccines and immunity. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 1999, 41, 481–493. [Google Scholar]
- Van Hulten, M.C.W.; Cruz-Coy, J.; Gergen, L.; Pouwels, H.; Ten Dam, G.B.; Verstegen, I.; de Groof, A.; Morsey, M.; Tarpey, I. Efficacy of a turkey herpesvirus double construct vaccine (HVT-ND-IBD) against challenge with different strains of Newcastle disease, infectious bursal disease and Marek’s disease viruses. Avian Pathol. 2021, 50, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peebles, E.D.; Barbosa, T.M.; Cummings, T.S.; Gerard, P.D.; Williams, C.J.; Wilson, F.D. Comparative effects of in ovo versus subcutaneous administration of the Marek’s disease vaccine and pre-placement holding time on the intestinal villus to crypt ratios of Ross 708 broilers during early post-hatch development. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, I.M.; Glaize, A.; Cortes, A.L. Effect of Marek’s disease vaccines on interferon and toll like receptors when administered in ovo. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2018, 201, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uni, Z.; Ferket, P.R.; Tako, E.; Kedar, O. In ovo feeding improves energy status of late-term chicken embryos. Poult. Sci. 2005, 84, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uni, Z.; Ferket, P.R. Methods for early nutrition and their potential. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2004, 60, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritts, C.A.; Waldroup, P.W. Effect of source and level of vitamin D on live performance and bone development in growing broilers. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2003, 12, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narbaitz, R.; Tsang, C.P.; Grunder, A.A. Effects of vitamin D deficiency in the chicken embryo. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1987, 40, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignale, K.; Greene, E.S.; Caldas, J.V.; England, J.; Boonsinchai, N.; Sodsee, P.; Pollock, E.D.; Dridi, S.; Coon, C.N. 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol enhances male broiler breast meat yield through the mTOR pathway. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.S.; Hewison, M. Unexpected actions of vitamin D: New perspectives on the regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 42, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, A.; Hester, P.Y.; Gerard, P.D.; Zhai, W.; Peebles, E.D. Effects of commercial in ovo injection of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol on bone development and mineralization in male and female broilers. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 2734–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatemi, S.A.; Elliott, K.E.C.; Bello, A.; Durojaye, O.A.; Zhang, H.; Alqhtani, A.H.; Peebles, E.D. Effects of the in ovo injection of vitamin D3 and 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 in Ross 708 broilers subsequently fed commercial or calcium and phosphorus-restricted diets. I. performance, carcass characteristics, and incidence of woody breast myopathy. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, S.A.; Elliott, K.E.C.; Bello, A.; Macklin, K.S.; Peebles, E.D. Effects of the in ovo injection of vitamin D3 and 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 in Ross 708 broilers subsequently challenged with coccidiosis: II. Immunological and inflammatory responses and small intestine histomorphology. Animals 2022, 12, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, T.; Shakeri, M.; Zaghari, M.; Kohram, H. Growth performance parameters, bone calcification and immune response of in ovo injection of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol and vitamin K3 in male ross 308 broilers. Theriogenology 2017, 90, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Elliott, K.E.C.; Durojaye, O.A.; Fatemi, S.A.; Schilling, M.W.; Peebles, E.D. Effects of in ovo injection of L-ascorbic acid on growth performance, carcass composition, plasma antioxidant capacity, and meat quality in broiler chickens. Poult Sci. 2019, 98, 3617–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Senousey, H.K.; Chen, B.; Wang, J.Y.; Atta, A.M.; Mohamed, F.R.; Nie, Q.H. In ovo injection of ascorbic acid modulates antioxidant defense system and immune gene expression in newly hatched local Chinese yellow broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousstaaid, A.; Fatemi, S.A.; Levy, A.W.; Purswell, J.L.; Olanrewaju, H.A.; Baughman, B.; McNulty, K.; Gerard, P.D.; Peebles, E.D. Effects of the in ovo administration of L-ascorbic acid on tissue L-ascorbic acid concentrations, systemic inflammation, and tracheal histomorphology of Ross 708 Broilers subjected to elevated levels of atmospheric ammonia. Poultry 2023, 2, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousstaaid, A.; Fatemi, S.A.; Elliott, K.E.C.; Levy, A.W.; Miller, W.W.; Olanrewaju, H.A.; Purswell, J.L.; Gerard, P.D.; Peebles, E.D. Effects of the in ovo administration of L-ascorbic acid on the performance and incidence of corneal erosion in Ross 708 broilers subjected to elevated levels of atmospheric ammonia. Animals 2023, 13, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, A.; Zhai, W.; Gerard, P.D.; Peebles, E.D. Effects of the commercial in ovo injection of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol on the hatchability and hatching chick quality of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 2551–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatemi, S.A.; Elliott, K.E.C.; Bello, A.; Zhang, H.; Peebles, E.D. Effects of the in ovo injection of vitamin D3 and 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 in Ross 708 broilers subsequently fed commercial or calcium and phosphorous-restricted diets: II. Immunity and small intestine morphology. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatemi, S.A.; Macklin, K.S.; Zhang, L.; Mousstaaid, A.; Poudel, S.; Poudel, I.; Peebles, E.D. Improvement in the immunity- and vitamin D3 activity-related gene expression of coccidiosis-challenged Ross 708 broilers in response to the in ovo injection of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3. Animals 2022, 12, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, S.A.; Alqhtani, A.H.; Elliott, K.E.C.; Bello, A.; Zhang, H.; Levy, A.W.; Peebles, E.D. Improvement in the performance and inflammatory reaction of Ross 708 broilers in response to the in ovo injection of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Elliott, K.E.C.; Durojaye, O.A.; Fatemi, S.A.; Peebles, E.D. Effects of in ovo-administration of L-ascorbic acid on broiler hatchability and its influence on the effects of pre-placement holding time on broiler quality characteristics. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 1941–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, T.; Salarmoini, M.; Afsharmanesh, M.; Tasharrofi, S. The effects of in ovo injection of ascorbic acid on hatchability, growth performance, intestinal morphology, and tibia breaking strength in 36h post hatch fasted broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. J. 2019, 7, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Bodinga, M.B.; Zhou, J.H.; Zhu, L.Q.; Cao, Y.L.; Ren, Z.Z.; Yang, X.J. Effects of in ovo injection of vitamin C on heat shock protein and metabolic genes expression. Animal 2020, 14, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Li, S.Z.; Sun, Q.Z.; Yang, X.J. Effect of in ovo feeding of vitamin C on antioxidation and immune function of broiler chickens. Animal 2019, 13, 1927–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buranathai, C.; Rodriguez, J.; Grose, C. Transformation of primary chick embryo fibroblasts by Marek’s disease vaccine. Virology 1997, 239, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fatemi, S.A.; Elliott, K.E.C.; Bello, A.; Durojaye, O.A.; Zhang, H.J.; Peebles, E.D. The effects of in ovo-injected vitamin D3 sources on the eggshell temperature and early post-hatch performance of Ross 708 broilers. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatemi, S.A.; Elliott, K.E.C.; Bello, A.; Durojaye, O.; Zhang, H.; Turner, B.; Peebles, E.D. Effects of source and level of in ovo-injected vitamin D3 on the hatchability and serum 25-hydroxycholecalciferol concentrations of Ross 708 broilers. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 3877–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, W.; Gerard, P.D.; Pulikanti, R.; Peebles, E.D. Effects of in ovo injection of carbohydrates on embryonic metabolism, hatchability, and subsequent somatic characteristics of broiler hatchlings. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 2134–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Hu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, D.; Lie, B.; Du, R.; Lei, B.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Improvement in the early growth, immune system and tibia development of broilers in response to the in ovo injection of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2023, 51, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, T.; Shiraishi, J.; Ohta, Y. Effects of in ovo vitamin D3 injection on subsequent growth of broilers. J. Poult. Sci. 2019, 56, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, D.S.; El-Senosi, Y.A.; Mohamed, M.I.; Amer, M.M.; Elaroussi, M.A. Effects of injecting vitamin D3 or an active metabolite in ovo on chick embryonic development and calcium homeostasis. W. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 6, 1454–1467. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fatemi, S.A.; Williams, C.J.; Deines, J.; Peebles, E.D. Vitamin Compatibility with the Marek’s Disease Vaccine. Poultry 2023, 2, 442-448. https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry2040033
Fatemi SA, Williams CJ, Deines J, Peebles ED. Vitamin Compatibility with the Marek’s Disease Vaccine. Poultry. 2023; 2(4):442-448. https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry2040033
Chicago/Turabian StyleFatemi, Seyed Abolghasem, Christopher J. Williams, Joshua Deines, and Edgar David Peebles. 2023. "Vitamin Compatibility with the Marek’s Disease Vaccine" Poultry 2, no. 4: 442-448. https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry2040033
APA StyleFatemi, S. A., Williams, C. J., Deines, J., & Peebles, E. D. (2023). Vitamin Compatibility with the Marek’s Disease Vaccine. Poultry, 2(4), 442-448. https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry2040033






