Effect of the Cooling Rate on the Solidification Structure and Phase of a 2:17 Samarium–Cobalt Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
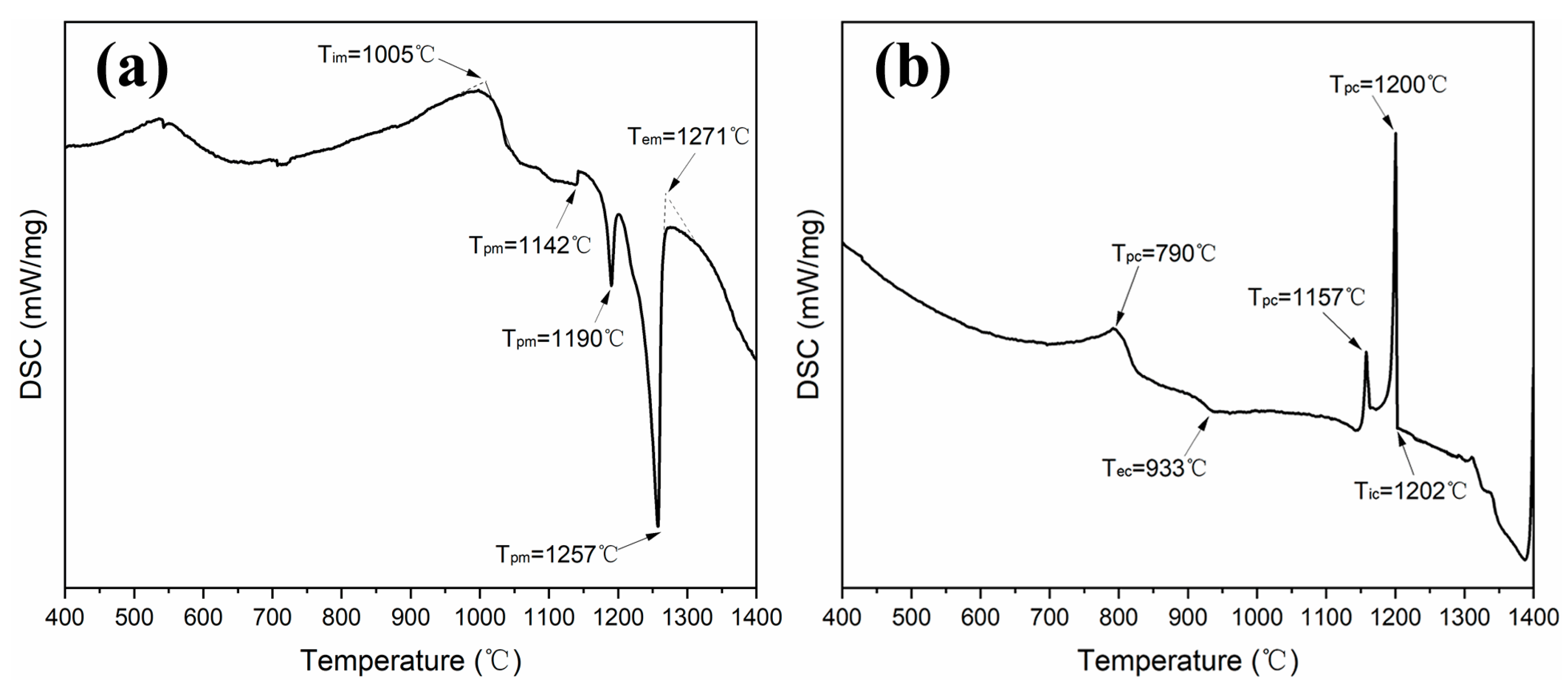
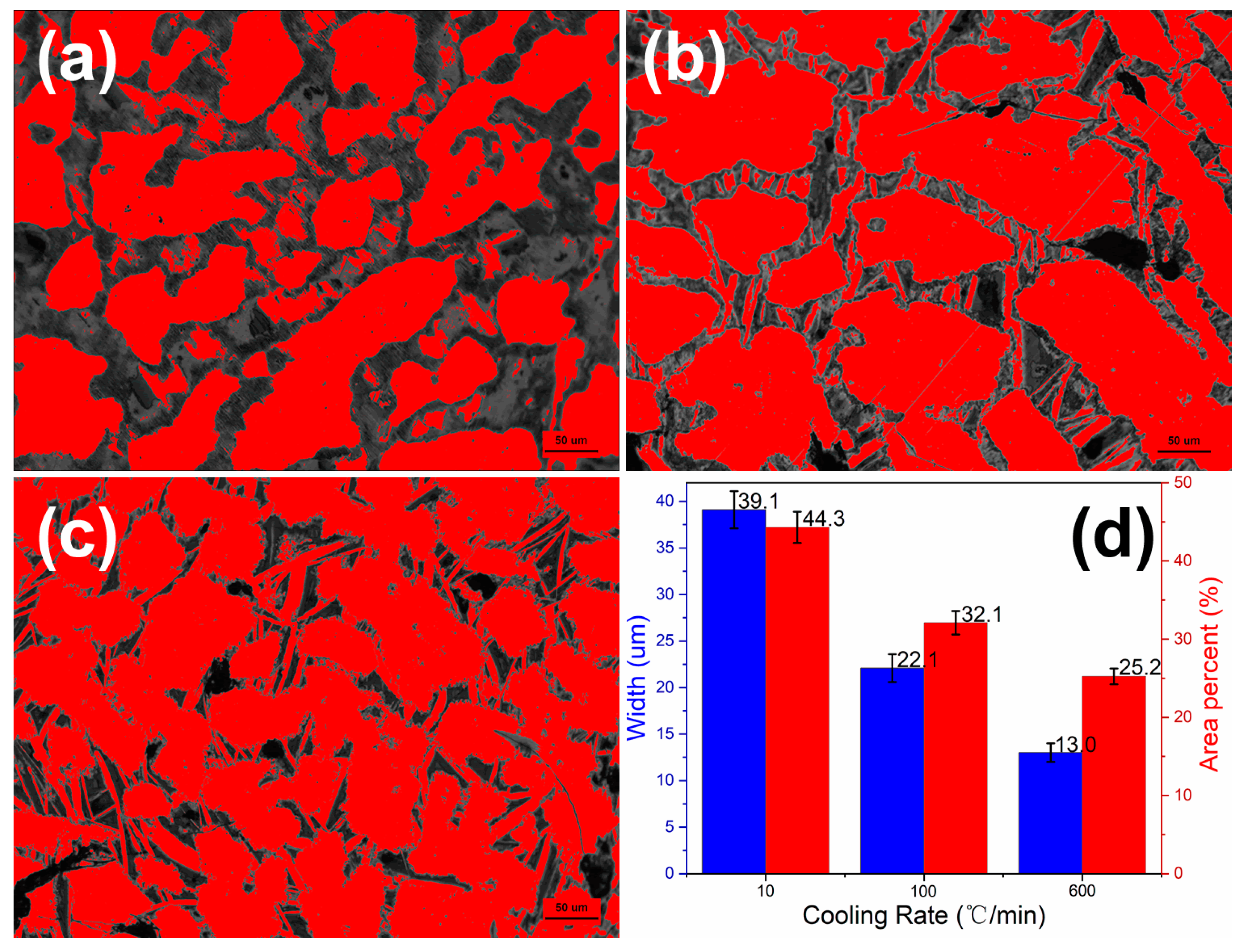
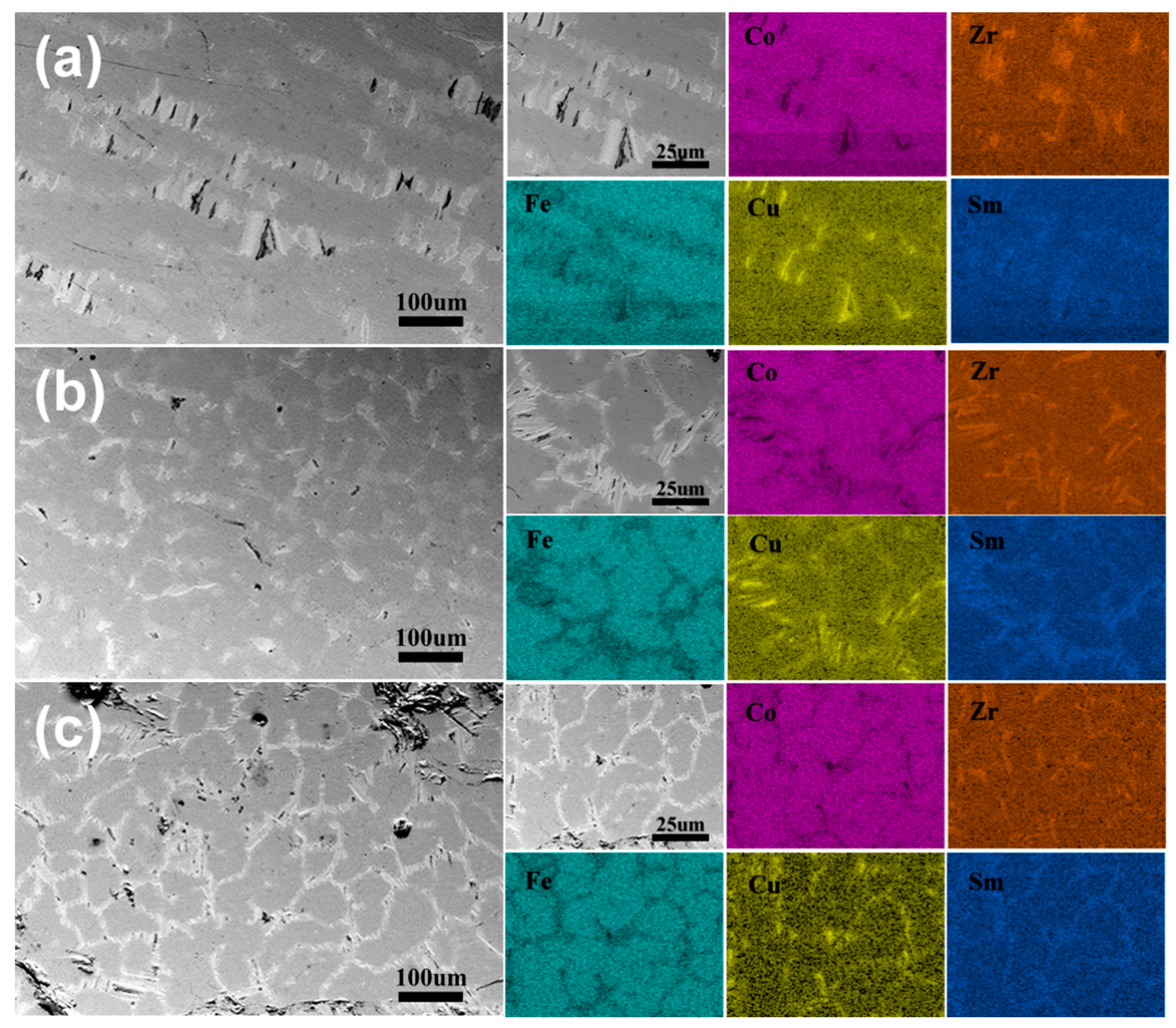
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, L.; Zuo, S.L.; Guan, C.S.; Liu, Z.H.; Hu, M.Y.; Kang, D.Z.; Zhao, M.J.; Liu, B.J.; Liu, J.H.; Peng, Y.; et al. Effect of interfacial stress on microchemistry and coercivity in 2:17-type SmCo sintered magnets. Acta Mater. 2024, 264, 119580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, Y.; Ilankoon, I.M.S.K.; Dushyantha, N.; Nwaila, G.T. Rare earth permanent magnets for the green energy transition: Bottlenecks, current developments and cleaner production solutions. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 212, 107966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islama, R.; Verob, K.; Borah, J.P. Historical overview and recent advances inpermanent magnet materials. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 110538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.L.; Liu, Y.; Jia, W.T.; Song, X.; Xiao, A.D.; Yuan, T.; Wang, F.; Fan, J.P.; Ma, T.Y. Revisiting the pinning sites in 2:17-type Sm-Co-Fe-Cu-Zr permanent magnets. J. Rare Earths 2021, 39, 1560–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.X.; Gao, C.M.; Liu, S.P.; Wang, J.B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zuo, W.L.; Li, J.; Ma, T.Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. Understanding of the enhanced coercivity and energy product in Sm(CobalFe0.27Cu0.05Zr0.02)z permanent magnets with lower z value. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1014, 178691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.H.; Lan, Q.F.; Zhang, X.L.; Niu, F.; Yang, Y.M. Preparation and Magnetic Properties of 2:17-Type SmCo Alloy by Transition Metal-Induced Calciothermic Reduction. JOM 2021, 73, 3885–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, Y.P.; Miao, X.F.; Shao, Y.Y.; Liu, C.Y.; Xu, F. Tunable microstructure and microwave absorption properties of the SmCo5/Sm2Co17 binary-phase magnetic absorbent prepared via a reduction diffusion method. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 973, 172843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.J.; Tao, S.W.; Qu, X.H.; Zhang, S.G. 2:17-type SmCo magnets prepared by powder injection molding using a water-based binder. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 2168–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Ormerod, J.; Parker, D.S.; Ott, R.; Palasyuk, A.; McCall, S.; Paranthaman, M.P.; Kesler, M.S.; Mcguire, M.A.; Nlebedim, C.; et al. Manufacturing Processes for Permanent Magnets: Part II—Bonding and Emerging Methods. JOM 2022, 74, 2492–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y.; Zuo, S.L.; Zhang, Q.; Dai, H.Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.H.; Jiang, C.B. 2:17-type SmCo permanent magnets with controllable remanence temperature coefficients via substitution of heavy rare earth elements. Rare Met. 2024, 43, 3990–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.F.; Wang, C.; Chen, H.S.; Fang, Y.K.; Wang, L.; Zheng, M.; Xiao, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.; Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Zhu, M.G.; et al. Influence of 1:7 H phase stability on the evolution of cellular microstructure in Fe-rich Sm-Co-Fe-Cu-Zr magnets. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 959, 170604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Dai, B.D.; Liu, L.; Hu, F.Q.; Sun, Y.L.; Ding, Y.; Yan, A.R. Study on the evolution of magnetic and mechanical properties in Sm2Co17 magnets at high temperatures. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2025, 628, 173162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.H.; Hu, F.Q.; Wang, J.B.; Wang, S.D.; Zhou, B.; Liu, L.; Sun, Y.L.; Ding, Y.; Yan, A.R. Study on correlation between mechanical properties and micro/nano-structure of Sm2Co17-type permanent magnets. Mater. Charact. 2025, 223, 114936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.H.F.; Mancilha, P.H.S.; Reyes, R.A.V.; Gouveia, G.L.D.; Bolfarini, C.; Spinelli, J.E.; Coury, F.G. Influence of the cooling rate on the solidification path and microstructure of a AlCoCrFeNi2.1 alloy. Mater. Charact. 2023, 203, 113121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.N.; Zou, D.N.; Chen, W.W.; Zhang, Y.B.; Zhang, W.; Xu, F.H. Effect of Cooling Rate on Solidifcation and Segregation Characteristics of 904L Super Austenitic Stainless Steel. Met. Mater. Int. 2022, 28, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.T.; Wang, S.H.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Y.K. SmFe12-based permanent magnet master alloy prepared efficiently by vacuum induction melting. China Metall. 2023, 33, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.H.; Wang, S.H.; Song, C.Y.; Liu, K. Effects of Superheat Degree on Smelting of Sm-Fe Alloy. Rare Met. Cem. Carbides 2019, 47, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Bao, S.X.; Lai, W.M.; Zhang, X.W.; Wang, Z.W.; Shen, A.G.; Zhang, M. Studies on ingot casting of Sm2Co17 type permanent magnet materials. J. Magn. Mater. Devices 2014, 45, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, W.M.; Bao, S.X.; Zhang, X.W.; Wang, Z.W.; Cheng, L.L.; Zhang, M. Studies on corrosion conditions of metallographic sample of Sm2Co17 permanent magnet materials. J. Magn. Mater. Devices 2012, 4, 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, L.; Cui, H.; Yang, S.F.; Lv, S.M.; Xie, X.F.; Qu, J.L. Effect of the cooling rates on the microstructure and segregation characteristics in directionally solidified GH4151 superalloy. Mater. Charact. 2024, 209, 113735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Z.; Long, H.B.; Sun, M.; Yang, G.; Wei, H.; Mao, S.C.; Zhang, Z.; Han, X.D. Effect of directional solidification methods on solid solution window in Ni-based single-crystal superalloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 8307–8319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.J.; Shen, C.L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, C.Y.; Tian, X.Y.; Xu, M.Q.; Yi, J.J. Designing TixZrNbMoV refractory high entropy alloys with improved properties by reducing intermetallic compound and dendritic segregation. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1036, 181913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Han, J.; Ge, F.Y.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Y.C.; Cui, Y. Design of eutectic high-entropy alloys in the Co-Cr-Ni-V-Ti-Al system using Scheil solidification path optimization. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1002, 175327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.D.; Sun, W.W. Enhancing classical Scheil–Gulliver model calculations by predicting generated phases and corresponding compositions through machine learning techniques. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 95, 104516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Element | Sm | Co | Fe | Cu | Zr | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | 25 | 48.5 | 19 | 4.8 | 2.7 | 100 |
| Sample | Segregation Parameter | Sm | Co | Fe | Cu | Zr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | Dendrite/wt.% | 22.1 | 46.5 | 20.4 | 7.3 | 3.7 |
| Inter-dendrite/wt.% | 25.8 | 42.8 | 14.7 | 12.1 | 4.6 | |
| K | 1.16 | 0.92 | 0.72 | 1.66 | 1.24 | |
| 100 | Dendrite/wt.% | 22 | 48.6 | 20.3 | 6.4 | 2.7 |
| Inter-dendrite/wt.% | 24.6 | 44.5 | 17.5 | 10.4 | 3 | |
| K | 1.12 | 0.92 | 0.86 | 1.63 | 1.11 | |
| 600 | Dendrite/wt.% | 21.9 | 45.7 | 22 | 7.8 | 2.6 |
| Inter-dendrite/wt.% | 27.8 | 40.5 | 15.1 | 13.3 | 3.3 | |
| K | 1.27 | 0.89 | 0.69 | 1.71 | 1.30 |
| ID | Phase | Element/wt% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co | Sm | Fe | Cu | Zr | ||
| 1 | Sm2(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)17 | 48.3 | 22.1 | 20.4 | 7.3 | 1.9 |
| 2 | (Sm, Zr)(Co, Fe, Cu)3 | 46.9 | 19.4 | 12.4 | 2.5 | 18.8 |
| 3 | Sm(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)5 | 36.99 | 33.5 | 9.36 | 16.01 | 4.15 |
| 4 | Sm(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)7 | 42.8 | 27.54 | 14.71 | 12.1 | 2.86 |
| 5 | Sm2(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)17 | 48.6 | 21.6 | 20.1 | 6.4 | 3.3 |
| 6 | (Sm, Zr)(Co, Fe, Cu)3 | 44.8 | 27.6 | 12.5 | 3.8 | 11.3 |
| 7 | Sm(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)5 | 33 | 34.7 | 10.1 | 17.4 | 4.8 |
| 8 | Sm(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)7 | 45 | 25.4 | 17.1 | 9.3 | 3.1 |
| 9 | Sm2(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)17 | 48.8 | 21.6 | 20.3 | 6.4 | 2.8 |
| 10 | (Sm, Zr)(Co, Fe, Cu)3 | 45.9 | 23.3 | 12.1 | 3 | 15.6 |
| 11 | Sm(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)5 | 40.2 | 32.7 | 11.5 | 10.4 | 5.1 |
| 12 | Sm(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)7 | 40.5 | 27.8 | 15.1 | 14.3 | 2.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Z.; Fang, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhao, B. Effect of the Cooling Rate on the Solidification Structure and Phase of a 2:17 Samarium–Cobalt Alloy. Alloys 2025, 4, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/alloys4040023
Zhu Z, Fang Y, Wu W, Zhao B. Effect of the Cooling Rate on the Solidification Structure and Phase of a 2:17 Samarium–Cobalt Alloy. Alloys. 2025; 4(4):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/alloys4040023
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Zhi, Yikun Fang, Wei Wu, and Bo Zhao. 2025. "Effect of the Cooling Rate on the Solidification Structure and Phase of a 2:17 Samarium–Cobalt Alloy" Alloys 4, no. 4: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/alloys4040023
APA StyleZhu, Z., Fang, Y., Wu, W., & Zhao, B. (2025). Effect of the Cooling Rate on the Solidification Structure and Phase of a 2:17 Samarium–Cobalt Alloy. Alloys, 4(4), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/alloys4040023







