Consumption and Preferences of Dairy Products by Taiwanese and Polish Students †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
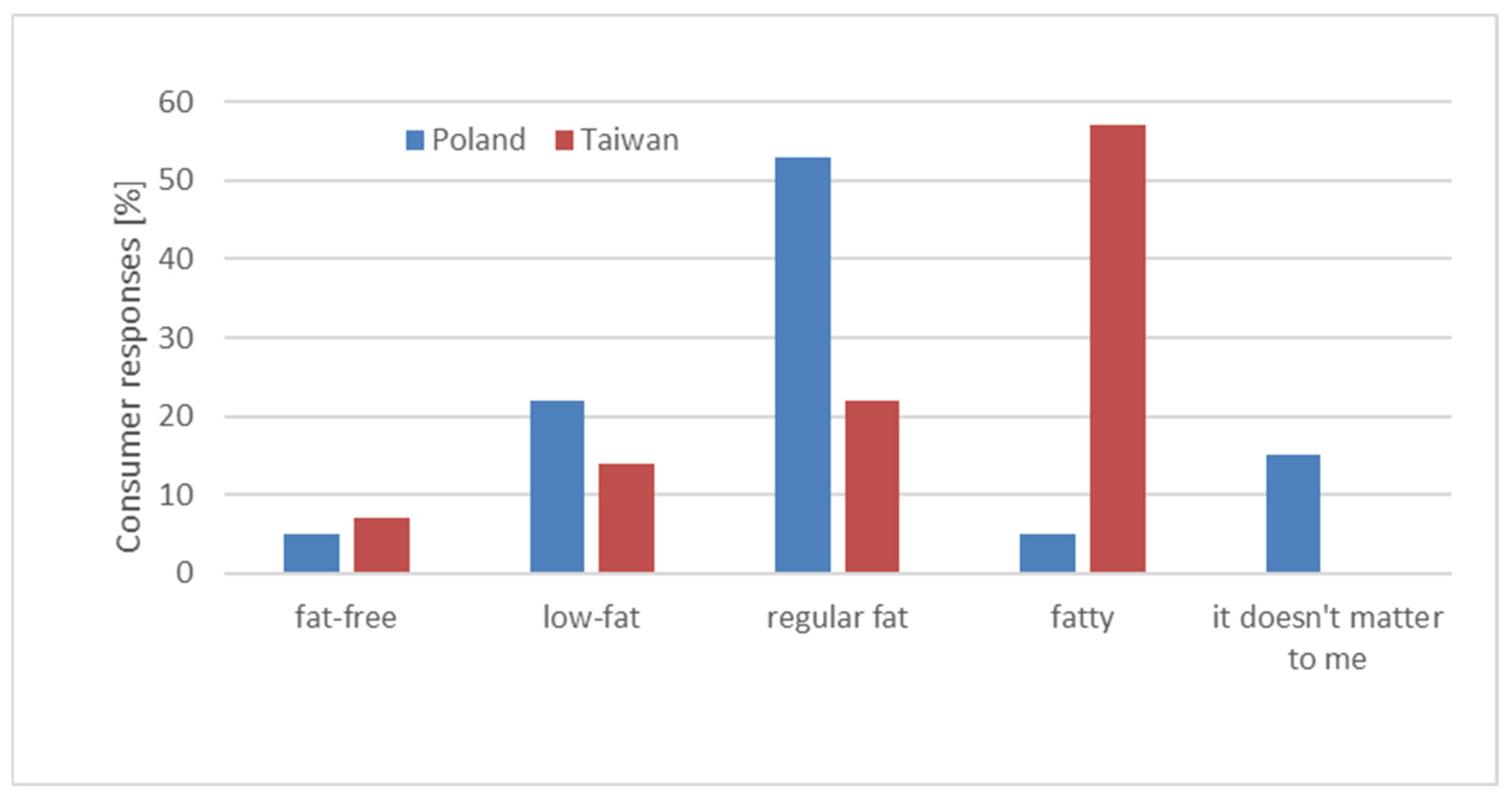
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, M.S.; Huang, L.Y.; Chen, M.C.; Wahlqvist, M.L. The demography of food in health security: Current experience with dairy consumption in Taiwan. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 18, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grębowiec, M.; Korytkowska, A. Zachowania konsumenckie na rynku wyborów mleczarskich. Rocz. Nauk. Stowarzyszenia Ekon. Rol. I Agrobiz. 2017, 19, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- HPA. Daily Dietary Guidelines. Taiwan. Available online: https://www.hpa.gov.tw/EngPages/Detail.aspx?nodeid=4106&pid=11729 (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Lee, M.-S.; Wahlqvist, M.L.; Peng, C.-J. Dairy foods and health in Asians: Taiwanese considerations. APJCN 2015, 24 (Suppl. 1), S14–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouamra-Mechemache, Z.; Réquillart, V.; Soregaroli, C.; Trévisiol, A. Demand for dairy products in the EU. Food Policy 2008, 33, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzejski, T.; Lizińska, W.; Jakubowska, D. Consumption and internationalization: Determinants for the development of the dairy market in Poland. ERSJ 2020, 23, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosz, M. Piramida Zdrowego Żywienia i Aktywności Fizycznej dla osób Dorosłych Utworzone Przez. Available online: https://ncez.pzh.gov.pl/abc-zywienia/piramida-zdrowego-zywienia-i-aktywnosci-fizycznej-dla-osob-doroslych/ (accessed on 10 September 2021).



| Sample Characteristics | Poland (%) | Taiwan (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 79 | 43 |
| Male | 21 | 57 | |
| Age | 19–22 | 38 | 86 |
| 23–25 | 62 | 14 | |
| Economic situation | Very good | 11 | 2 |
| Good | 53 | 10 | |
| Average | 34 | 82 | |
| Bad | 0 | 5 | |
| Very bad | 2 | 1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Świąder, K.; Banach, R.; Tan, F.-J. Consumption and Preferences of Dairy Products by Taiwanese and Polish Students. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2021, 6, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2021-10984
Świąder K, Banach R, Tan F-J. Consumption and Preferences of Dairy Products by Taiwanese and Polish Students. Biology and Life Sciences Forum. 2021; 6(1):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2021-10984
Chicago/Turabian StyleŚwiąder, Katarzyna, Renata Banach, and Fa-Jui Tan. 2021. "Consumption and Preferences of Dairy Products by Taiwanese and Polish Students" Biology and Life Sciences Forum 6, no. 1: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2021-10984
APA StyleŚwiąder, K., Banach, R., & Tan, F.-J. (2021). Consumption and Preferences of Dairy Products by Taiwanese and Polish Students. Biology and Life Sciences Forum, 6(1), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2021-10984







