Structural Analysis of Saxitoxin and Neosaxitoxin Toxins with Potential Therapeutic Targets †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| STX | Saxitoxin |
| NeoSTX | Neosaxitoxin |
| PDB | Protein Data Bank |
| 5-HT6 | Serotonin 6 Receptor |
References
- Janik, E.; Ceremuga, M.; Saluk-Bijak, J.; Bijak, M. Biological Toxins as the Potential Tools for Bioterrorism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillotin, S.; Delcourt, N. Marine Neurotoxins’ Effects on Environmental and Human Health: An OMICS Overview. Mar. Drugs 2021, 20, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemical Weapons Convention—Annex on Chemicals: Schedule 1. Available online: https://www.opcw.org/chemical-weapons-convention/annexes/annex-chemicals/schedule-1 (accessed on 10 September 2025).
- Deng, H.; Shang, X.; Zhu, H.; Huang, N.; Wang, L.; Sun, M. Saxitoxin: A Comprehensive Review of Its History, Structure, Toxicology, Biosynthesis, Detection, and Preventive Implications. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Holguín, N.; Salas-Leiva, J.S.; Nuñes-Vázquez, E.J.; Tovar-Ramírez, D.; Glossman-Mitnik, D. Marine Toxins as Pharmaceutical Treasure Troves: A Focus on Saxitoxin Derivatives from a Computational Point of View. Molecules 2024, 29, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, C.; Riquelme, G.; Del Campo, M.; Lagos, N. Neosaxitoxin, a Paralytic Shellfish Poison Phycotoxin, Blocks Pain and Inflammation in Equine Osteoarthritis. Toxicon 2021, 204, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyaneder, L.; Lagos, N.; Dörner, C. Systemic, Hemodynamic and Neurological Effects of Caudal Epidural Administration of Neosaxitoxin in Horses. Toxicon 2025, 257, 108303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paggi, J.M.; Pandit, A.; Dror, R.O. The Art and Science of Molecular Docking. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2024, 93, 389–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.; Henrick, K.; Nakamura, H. Announcing the worldwide Protein Data Bank. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2003, 10, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gfeller, D.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. Shaping the interaction landscape of bioactive molecules. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 3073–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gfeller, D.; Grosdidier, A.; Wirth, M.; Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissTargetPrediction: A web server for target prediction of bioactive small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W32–W38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissTargetPrediction: Updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W357–W364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huang, S.; Xu, P.; Shen, D.D.; Simon, I.A.; Mao, C.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Harpsøe, K.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. GPCRs steer Gi and Gs selectivity via TM5-TM6 switches as revealed by structures of serotonin receptors. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 2681–2695.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, T.J.; Lolicato, M.; Thomas-Tran, R.; Du Bois, J.; Minor, D.L., Jr. Structure of the saxiphilin:saxitoxin (STX) complex reveals a convergent molecular recognition strategy for paralytic toxins. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 21117946, Neosaxitoxin. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/NeoSTX (accessed on 13 July 2024).
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schake, P.; Bolz, S.N.; Linnemann, K.; Schroeder, M. PLIP 2025: Introducing protein-protein interactions to the protein-ligand interaction profiler. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, W463–W465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, T.; Barnes, N.M. Central 5-HT receptors and their function; present and future. Neuropharmacology 2020, 177, 108155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
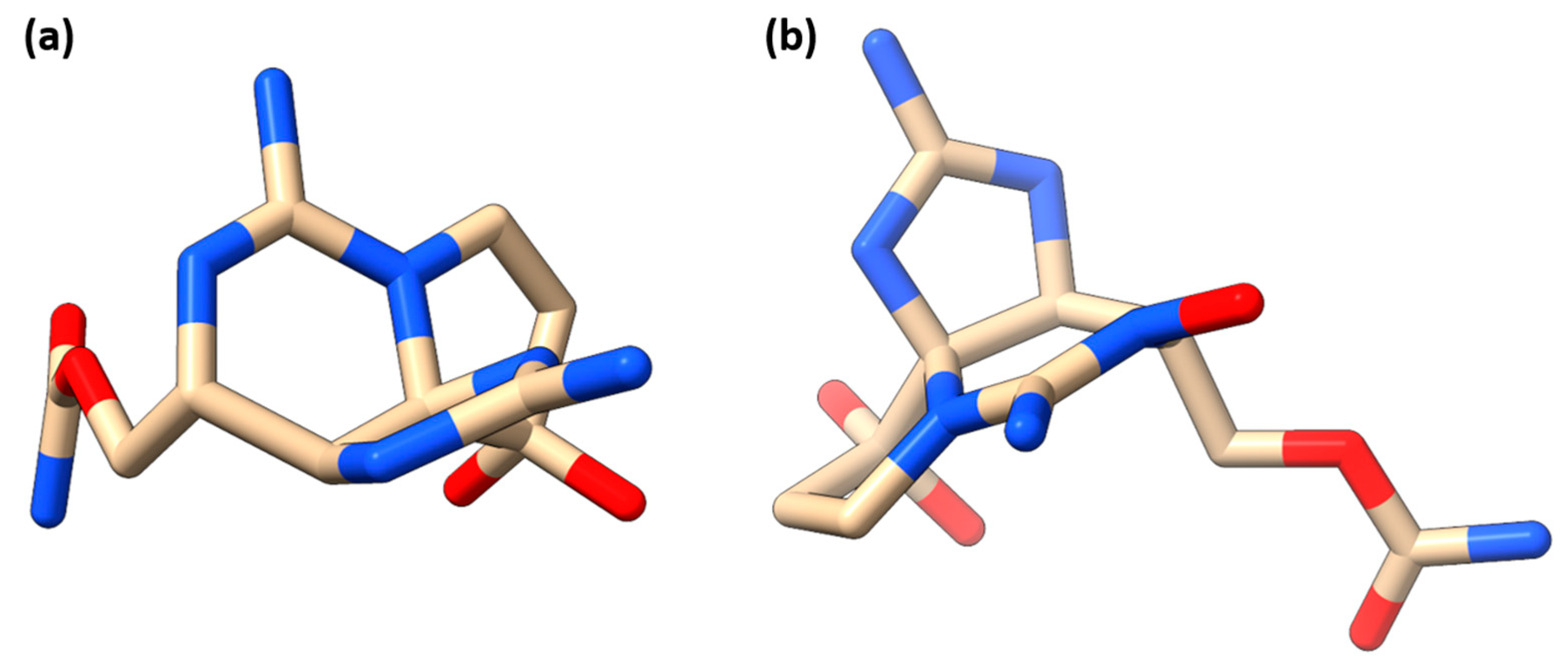
| Targets | UNIPROT ID |
|---|---|
| Serotonin 6 (5-HT6) receptor | P50406 |
| Carbonic anhydrase II | P00918 |
| Carbonic anhydrase I | P00915 |
| Carbonic anhydrase IX | Q16790 |
| Carbonic anhydrase VII | P43166 |
| Carbonic anhydrase XII | O43570 |
| Carbonic anhydrase XIV | Q9ULX7 |
| Steryl-sulfatase | P08842 |
| C-X-C chemokine receptor type 3 | P49682 |
| Carbonic anhydrase III | P07451 |
| Carbonic anhydrase VI | P23280 |
| Carbonic anhydrase IV | P22748 |
| Carbonic anhydrase VB | Q9Y2D0 |
| Carbonic anhydrase VA | P35218 |
| Carbonic anhydrase XIII (by homology) | Q8N1Q1 |
| Tyrosinase | P14679 |
| Nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 1 | P22736 |
| Protein tyrosine kinase 2 beta | Q14289 |
| Poses | Score (kcal/mol) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SRO—Native Ligand | STX | NeoSTX | |
| 1 | −6.3 | −5.5 | −5.7 |
| 2 | −6.1 | −5.2 | −5.4 |
| 3 | −6.0 | −5.0 | −5.1 |
| 4 | −5.9 | −4.9 | −4.8 |
| 5 | −5.9 | −4.7 | −4.6 |
| 6 | −5.7 | −4.6 | −4.5 |
| 7 | −5.7 | −4.6 | −4.4 |
| 8 | −4.3 | −4.5 | −4.2 |
| 9 | −5.4 | −4.2 | −4.0 |
| 10 | −4.3 | −4.1 | −3.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, V.d.S.; Mendes, B.d.P.; de Lima, D.V.N.; Nogueira, T.L.S.; do Amaral, V.S.G. Structural Analysis of Saxitoxin and Neosaxitoxin Toxins with Potential Therapeutic Targets. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2025, 52, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/blsf2025052001
Silva VdS, Mendes BdP, de Lima DVN, Nogueira TLS, do Amaral VSG. Structural Analysis of Saxitoxin and Neosaxitoxin Toxins with Potential Therapeutic Targets. Biology and Life Sciences Forum. 2025; 52(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/blsf2025052001
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Vanessa dos Santos, Beatriz de Paiva Mendes, Daniel Vinicius Neves de Lima, Tatiana Lúcia Santos Nogueira, and Virginia Sara Grancieri do Amaral. 2025. "Structural Analysis of Saxitoxin and Neosaxitoxin Toxins with Potential Therapeutic Targets" Biology and Life Sciences Forum 52, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/blsf2025052001
APA StyleSilva, V. d. S., Mendes, B. d. P., de Lima, D. V. N., Nogueira, T. L. S., & do Amaral, V. S. G. (2025). Structural Analysis of Saxitoxin and Neosaxitoxin Toxins with Potential Therapeutic Targets. Biology and Life Sciences Forum, 52(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/blsf2025052001






