Abstract
In recent years, the prevalence of chronic non-communicable diseases has increased. In females, there is a close relationship in the development of these diseases after menopause to estrogenic signaling occurring in various tissues; such is the case for the bladder, compromising its physiology in females. We sought to analyze the effect of diet-induced metabolic syndrome on the bladder epithelium. Eighteen 12-week-old Wistar rats were divided into an intact control group (C, n = 6), a cafeteria diet SMet group (CAF, n = 6), and a high-fat/high-sugar diet SMet group (HF/HS, n = 6). Atrophy and hyperplasia in the bladder epithelium were observed in the case of the CAF diet, while only inflammation was observed in the other schemes.
1. Introduction
In recent years, there has been a constant growth in the prevalence of chronic non-communicable diseases, which even appear increasingly at an earlier age [1]. However, there is a close relationship in the development of these diseases in females, and the role of estrogen fluctuation in reproductive stages such as gestation and menopause has been widely discussed [2,3], compromising its physiology in females. Urinary incontinence (UI) is a common experience throughout a woman’s life and has a significant impact on well-being and quality of life [4]. The prevalence of urinary incontinence worldwide is reported to be 8.5%; it is the most common urinary tract disease affecting adult women. The main risk factors associated with stress UI include age, pregnancy and parity, a history of hysterectomy, obesity, and pelvic radiation [5]. Most related studies focus on analyzing the morphophysiology of the pelvic floor and bladder musculature, neglecting effects on the urothelium [6,7]. Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a set of disorders characterized by low-grade inflammation that alters various systems and is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease [8]. Diet plays a crucial role in the development of MetS, with the combination of high caloric intake, poor nutrient quality, and unhealthy food choices contributing to its negative impact on overall health [9]. Considering that women are more affected by bladder diseases such as UI, it is of relevance to analyze the effect of metabolic syndrome (MS) models of diet, using a cafeteria diet (CAF) or high-fat/high-sugar diet (HF/HS), on the bladder urothelia of female rats.
2. Materials and Methods
Eighteen 12-week-old Wistar rats were divided into an intact control group (C, n = 6), a cafeteria diet SMet group (CAF, n = 6), and a high-fat/high-sugar diet SMet group (HF/HS, n = 6). The rats were housed with controlled temperature and artificial illumination (20 ± 2 C; light/dark from 7 AM to 9 PM). This light condition was used. All animal procedures followed the Guidelines of Mexican Law of Production, Care, and Use of Laboratory Animals (NOM-062-ZOO-1999) and were approved by the research committee of the division de Ciencias de la Salud from Universidad Cristóbal Colón (registration code: COVID-100).
The control group had access to water and feed (23% protein, 50% carbohydrates, and 27% lipids) ad libitum; the cafeteria group had a designed diet (approximately 11% protein, 60% carbohydrates, and 29% lipids) in which ultra-processed feeds were used; the high-fat/high-sugar diet (HF/HS) was designed, and pellets were prepared with a composition of 18% protein, 55% carbohydrates, and 27% lipids. In the case of the CAF group, the animals had access to chow and water along with the diet, which consisted of bread rolls, French fries, soft drinks, and sausages, among others. The duration of the treatment was 10 weeks. All rats used in the experimental procedures were euthanized with an overdose of sodium pentobarbital (60 mg/kg). Blood was obtained via cardiac puncture for biochemical measures.
The bladders were fixed in formaline, histologically processed, and then embedded in Paraplast X-tra (Sigma-Aldrich). Each bladder was transversally cut at a thickness of 5 µ using a microtome (Thermo Scientific, Model 325). Tissue sections were mounted on gelatin-coated slides. Each tissue section was stained with Masson’s trichrome and PAS, and photographs were taken at 10×, 40×, and 100×. Data were analyzed statistically, and differences were considered when p < 0.05, using graph Pad v.6 statistical packages.
3. Results
The cafeteria diet was effective at generating metabolic syndrome, with the presence of hyperglycemia, elevated cholesterol and triglycerides, as well as higher body weight gain (Table 1), while the HF/HS diet generated increased body weight and hypercholesterolemia.

Table 1.
Parameters measured to identify metabolic syndrome.
With respect to the bladder epithelium in the case of the HF/HS diet, it generated a detachment of umbrella cells and areas of desquamation, and it can be observed that there are foci of inflammation. In the case of the CAF diet, it generated an important disarrangement of the epithelium, with many pyknotic nuclei and changes in basal cells, as well as blank spaces that do not appear in the other groups (Figure 1).
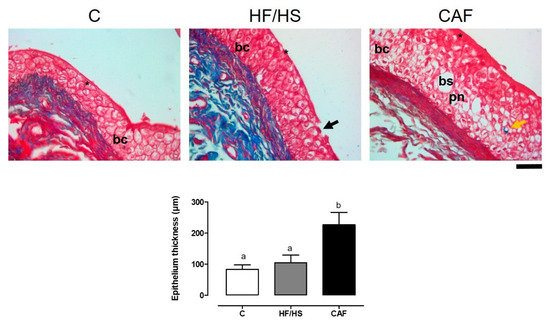
Figure 1.
Bladder epithelium samples from the control, HF/HS, and CAF groups. Data are means ± SEMs. Different letters indicate significant differences between groups. Scale: 50 µ. Abbreviations: * umbrella cells; black arrows, areas of desquamation; bc, basal cells, pn, pyknotic nuclei; yellow arrows, fibrosis; bs, blank space.
4. Discussion
Several studies have shown that different diet patterns can emulate the clinical manifestations of MetS. In the case of high-fat/high-sugar (HF/HS) diets, we find similarities to what was shown previously in which the diet appears to be less effective in females [10]. In the case of the cafeteria diet, it was shown to be an excellent model with the classical manifestations of MetS: hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and higher adiposity. The treatment time was adjusted to 10 weeks, derived from the fact that as indicated above, pathogenesis in females is slower due to the protective effect of estrogens [8]. The manifestations observed in the bladder coincide with problems such as cystitis [9], in which there is desquamation and a loss of umbrella cells. In the case of the CAF diet, in addition, disarray and many pyknotic nuclei were found, suggesting an increase in cell death. While histology alone does not indicate urinary incontinence, other studies show that the cafeteria diet leads to changes in the electrophysiological profile [11,12]. The results show that the cafeteria diet is a model that could be more useful for analyzing metabolic syndrome in females than other diet-generated models. Further studies are required to analyze the relationship of bladder alterations in females.
Author Contributions
Methodology and data curation, V.V.-F.; methodology and data curation, M.R.-L.; methodology, and data curation, S.S.M.; analysis and curation, F.L.-V.; writing, conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation, and review and editing, J.R.-C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of División de ciencias de la Salud, Universidad Cristóbal Colón (protocol code 005/2023, 29 March 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Laura Nataly Bober Ramírez, Fany Machuca Roa, and Omar Ugarte Álvarez for technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Di Cesare, M. Global trends of chronic non-communicable diseases risk factors. Eur J Public Health 2019, 29 (Suppl. S4), ckz185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Carrasco, V.; Soriano-Lerma, A.; Soriano, M.; Gutiérrez-Fernández, J.; Garcia-Salcedo, J.A. Urinary microbiome: Yin and yang of the urinary tract. Front. Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021, 11, 617002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paoli, M.; Zakharia, A.; Werstuck, G.H. The role of estrogen in insulin resistance: A review of clinical and preclinical data. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 1490–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Maldonado, L.A.; Erosa-Villarreal, R.A.; Janssen-Aguilar, R.; Laviada-Molina, H.A.; Méndez-Domínguez, N.I. Incontinencia urinaria: Factores de riesgo y frecuencia en mujeres mayores de 60 años, en el sureste de México. Rev. Mex. Urol. 2019, 79, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milsom, I.; Gyhagen, M. The prevalence of urinary incontinence. Climacteric 2019, 22, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falah-Hassani, K.; Reeves, J.; Shiri, R.; Hickling, D.; McLean, L. The pathophysiology of stress urinary incontinence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Urogynecol. 2021, 32, 501–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.D.; Chen, S.J.; Chen, H.Y.; Chiu, K.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, W.C. Review of animal models to study urinary bladder function. Biology 2021, 10, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahed, G.; Aoun, L.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Allam, S.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Bouferraa, Y.; Assi, H.I. Metabolic Syndrome: Updates on Pathophysiology and Management in 2021. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fourny, N.; Lan, C.; Bernard, M.; Desrois, M. Male and Female Rats Have Different Physiological Response to High-Fat High-Sucrose Diet but Similar Myocardial Sensitivity to Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguéns-Gómez, A.; Sierra-Cruz, M.; Pérez-Vendrell, A.M.; Rodríguez-Gallego, E.; Beltrán-Debón, R.; Terra, X.; Ardévol, A.; Pinent, M. Differential effects of a cafeteria diet and GSPE preventive treatments on the enterohormone secretions of aged vs. young female rats. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 10491–10500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedlander, J.I.; Shorter, B.; Moldwin, R.M. Diet and its role in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS) and comorbid conditions. BJU Int. 2012, 109, 1584–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Wang, M.; Maher, S.; Fu, P.; Cai, D.; Wang, B.; Gupta, S.; Hijaz, A.; Daneshgari, F.; Liu, G. Effects of different diets used to induce obesity/metabolic syndrome on bladder function in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2023, 324, R70–R81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).