Impact of Colonic Fermentation of Plant Sterol-Enriched Rye Bread on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample and Oral Phase Digestion
2.2. Dynamic In Vitro Colonic Fermentation
2.3. Plate Count and Determination of SCFA and Ammonium Ion
2.4. Statistically Analysis
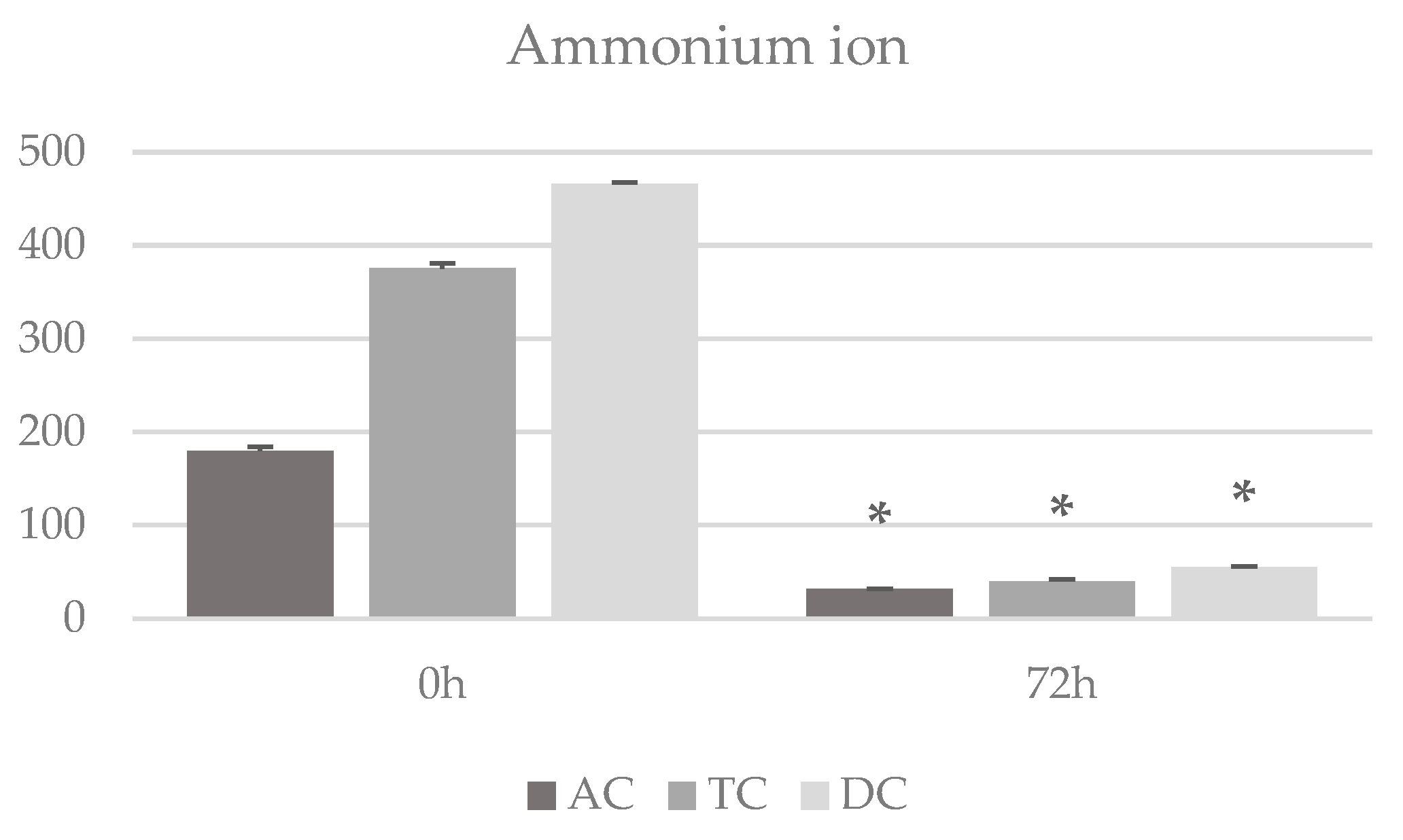
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Danneskiold-Samsøe, N.B.; Dias de Freitas Queiroz Barros, H.; Santos, R.; Bicas, J.L.; Cazarin, C.B.B.; Madsen, L.; Kristiansen, K.; Pastore, G.M.; Brix, S.; Maróstica Júnior, M.R. Interplay between food and gut microbiota in health and disease. Food Res. Int. 2019, 115, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åman, P.; Andersson, A.A.M.; Rakha, A.; Andersson, R. Rye, a healthy cereal full of dietary fiber. Cereal Foods World 2010, 55, 231–234. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, D.J.; Preston, T. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makran, M.; Cilla, A.; Haros, C.M.; Garcia-Llatas, G. Enrichment of wholemeal rye bread with plant sterols: Rheological analysis, optimization of the production, nutritional profile and starch digestibility. Foods 2022, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Wen, T.; Wang, J. Role of the microbiome in mediating health effects of dietary components. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 12820–12835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ounnas, F.; Privé, F.; Salen, P.; Gaci, N.; Tottey, W.; Calani, L.; Bresciani, L.; López-Gutiérrez, N.; Hazane-Puch, F.; Laporte, F.; et al. Whole rye consumption improves blood and liver n-3 fatty acid profile and gut microbiota composition in rats. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on dietetic products, nutrition, and allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to 3 g/day plant sterols/stanols and lowering blood LDL-cholesterol and reduced risk of (coronary) heart disease. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Quispe, C.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Cruz-Martins, N.; Nigam, M.; Mishra, A.P.; Konovalov, D.A.; Orobinskaya, V.; Abu-Reidah, I.M.; Zam, W.; et al. Phytosterols: From preclinical evidence to potential clinical applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 599959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas-Tena, M.; Alegría, A.; Lagarda, M.J. Relationship between dietary sterols and gut microbiota: A review. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2018, 120, 1800054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faubel, N.; Makran, M.; Cilla, A.; Alegría, A.; Barberá, R.; Garcia-Llatas, G. Bioaccessibility of plant sterols in wholemeal rye bread using the INFOGEST protocol: Influence of oral phase and enzymes of lipid metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 13223–13232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunçaõ, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrierè, F.; et al. INFOGEST static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamargo, A.; Cueva, C.; Taladrid, D.; Khoo, C.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V.; Bartolomé, B.; González de Llano, D. Simulated gastrointestinal digestion of cranberry polyphenols under dynamic conditions. Impact on antiadhesive activity against uropathogenic bacteria. Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivieri, K.; de Oliveira, S.M.; de Souza Marquez, A.; Pérez-Jiménez, J.; Diniz, S.N. Insights of β-glucan as a prebiotic coadjuvant in the treatment of diabetes mellitus: A review. Food Hydrocoll. Health 2022, 2, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Tena, M.; Alegria, A.; Lagarda, M.J.; Venema, V. Impact of plant sterols enrichment dose on gut microbiota from lean and obese subjects using TIM-2 in vitro fermentation model. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 54, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diether, N.E.; Willing, B.P. Microbial fermentation of dietary protein: An important factor in diet-microbe-host interaction. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Microorganisms | 0 h | 72 h 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus spp. | AC | 4.28 ± 0.01 | 8.98 ± 0.05 |
| TC | 5.67 ± 0.01 | 7.88 ± 0.05 | |
| DC | 5.64 ± 0.06 | 8.77 ± 0.01 | |
| Lactobacillus spp. | AC | 6.01 ± 0.02 | 9.23 ± 0.07 |
| TC | 6.15 ± 0.03 | 9.17 ± 0.02 | |
| DC | 5.71 ± 0.03 | 8.67 ± 0.02 | |
| Bifidobacterium spp. | AC | 6.37 ± 0.01 | 9.34 ± 0.02 |
| TC | 7.25 ± 0.04 | 9.18 ± 0.09 | |
| DC | 7.14 ± 0.08 | 9.23 ± 0.12 | |
| Enterococcus spp. | AC | 5.80 ± 0.03 | 9.44 ± 0.04 |
| TC | 6.42 ± 0.02 | 9.29 ± 0.01 | |
| DC | 5.71 ± 0.01 | 8.86 ± 0.03 |
| SCFA | 0 h | 72 h | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acetate | AC | 15.11 ± 0.02 | 3.66 ± 0.05 * |
| TC | 35.25 ± 0.36 | 35.46 ± 0.22 | |
| DC | 40.29 ± 0.59 | 29.88 ± 0.25 * | |
| Propionate | AC | 1.07 ± 0.03 | 0.31 ± 0.12 * |
| TC | 12.03 ± 0.09 | 2.51 ± 0.03 * | |
| DC | 15.42 ± 0.22 | 9.06 ± 0.02 * | |
| Butyrate | AC | 0.04 ± 0.002 | 0.06 ± 0.001 * |
| TC | 2.33 ± 0.01 | 1.98 ± 0.17 * | |
| DC | 3.79 ± 0.11 | 44.89 ± 0.02 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faubel, N.; Blanco-Morales, V.; Barberá, R.; Garcia-Llatas, G. Impact of Colonic Fermentation of Plant Sterol-Enriched Rye Bread on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2023, 26, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2023-15012
Faubel N, Blanco-Morales V, Barberá R, Garcia-Llatas G. Impact of Colonic Fermentation of Plant Sterol-Enriched Rye Bread on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Biology and Life Sciences Forum. 2023; 26(1):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2023-15012
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaubel, Nerea, Virginia Blanco-Morales, Reyes Barberá, and Guadalupe Garcia-Llatas. 2023. "Impact of Colonic Fermentation of Plant Sterol-Enriched Rye Bread on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites" Biology and Life Sciences Forum 26, no. 1: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2023-15012
APA StyleFaubel, N., Blanco-Morales, V., Barberá, R., & Garcia-Llatas, G. (2023). Impact of Colonic Fermentation of Plant Sterol-Enriched Rye Bread on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Biology and Life Sciences Forum, 26(1), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2023-15012







