A Comparison of Green Extraction Techniques for the Recovery of Bioactive Compounds from Grapevine By-Products †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Extraction Techniques
- SWE: 2.0 g of sample was mixed with 140 mL of water for 20 min at three temperatures (100, 150, and 200 °C) [7];
2.3. Total Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity
2.4. Qualitative and Quantitative Polyphenol Characterization via HPLC-PDA
3. Results and Discussion
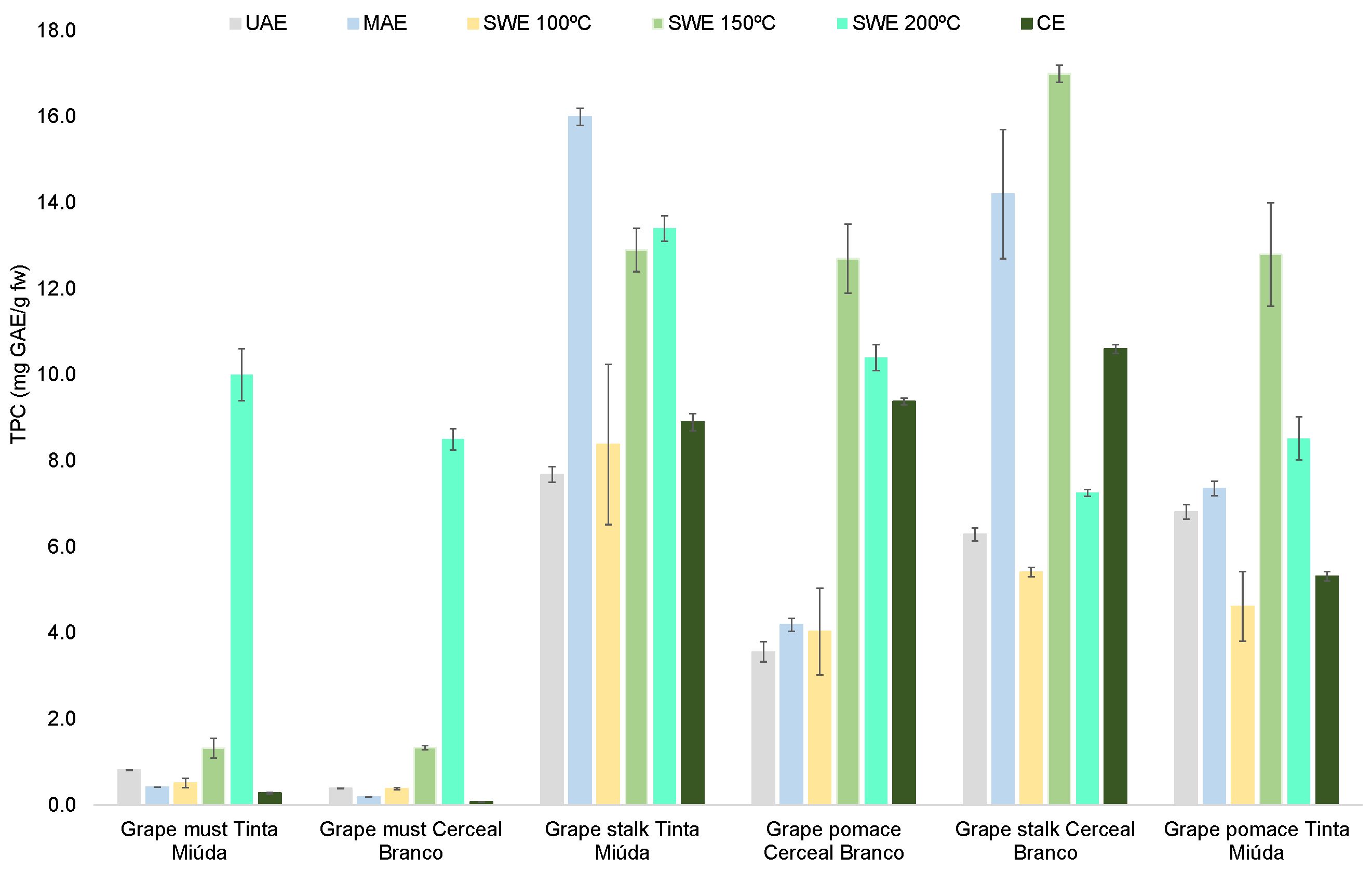
3.1. Total Phenolic Content
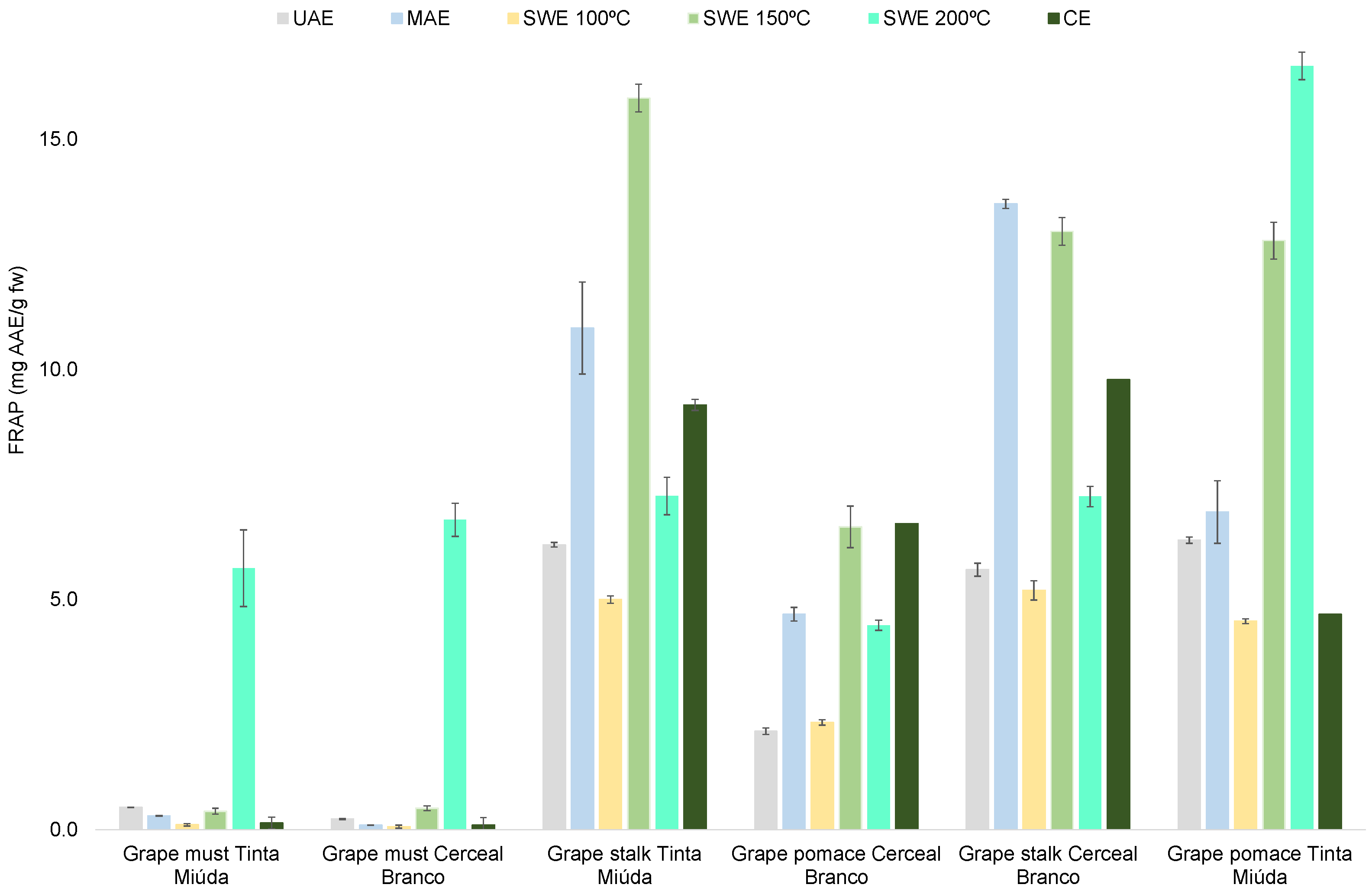
3.2. Antioxidant Activity
3.3. Phenolic Profile via HPLC-DAD Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dorosh, O.; Rodrigues, F.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Moreira, M.M. Increasing the added value of vine-canes as a sustainable source of phenolic compounds: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troilo, M.; Difonzo, G.; Paradiso, V.; Summo, C.; Caponio, F. Bioactive Compounds from Vine Shoots, Grape Stalks, and Wine Lees: Their Potential Use in Agro-Food Chains. Foods 2021, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, M.M.; Barroso, M.F.; Porto, J.V.; Ramalhosa, M.J.; Švarc-Gajić, J.; Estevinho, L.; Morais, S.; Delerue-Matos, C. Potential of Portuguese vine shoot wastes as natural resources of bioactive compounds. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natolino, A.; Da Porto, C. Kinetic models for conventional and ultrasound assistant extraction of polyphenols from defatted fresh and distilled grape marc and its main components skins and seeds. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 156, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, T.; Gizdavic-Nikolaidis, M.; Leceta, I.; Urdanpilleta, M.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K.; Kilmartin, P.A. Optimizing the extraction process of natural antioxidants from chardonnay grape marc using microwave-assisted extraction. Waste Manag. 2019, 88, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiatkowski, M.; Kravchuk, O.; Skouroumounis, G.K.; Taylor, D.K. Microwave-assisted and conventional phenolic and colour extraction from grape skins of commercial white and red cultivars at veraison and harvest. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 122671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidossi, R.; Yammine, S.; Delsart, C.; Xavier, V.; Mietton-Peuchot, M. Characterisation of polyphenols and antioxidant potential of red and white pomace by-product extracts using subcritical water extraction. Oeno One 2020, 54, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorosh, O.; Moreira, M.M.; Pinto, D.; Peixoto, A.F.; Freire, C.; Costa, P.; Rodrigues, F.; Delerue-Matos, C. Evaluation of the Extraction Temperature Influence on Polyphenolic Profiles of Vine-Canes (Vitis vinifera) Subcritical Water Extracts. Foods 2020, 9, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, M.; Carvalho, A.P.; Magalhães, J.M.C.S.; Moreira, M.; Guido, L.; Gomes, A.M.; Delerue-Matos, C. Response surface evaluation of microwave-assisted extraction conditions for Lycium barbarum bioactive compounds. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 33, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milinčić, D.D.; Stanisavljević, N.S.; Kostić, A.Ž.; Soković Bajić, S.; Kojić, M.O.; Gašić, U.M.; Barać, M.B.; Stanojević, S.P.; Lj Tešić, Ž.; Pešić, M.B. Phenolic compounds and biopotential of grape pomace extracts from Prokupac red grape variety. LWT 2021, 138, 110739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
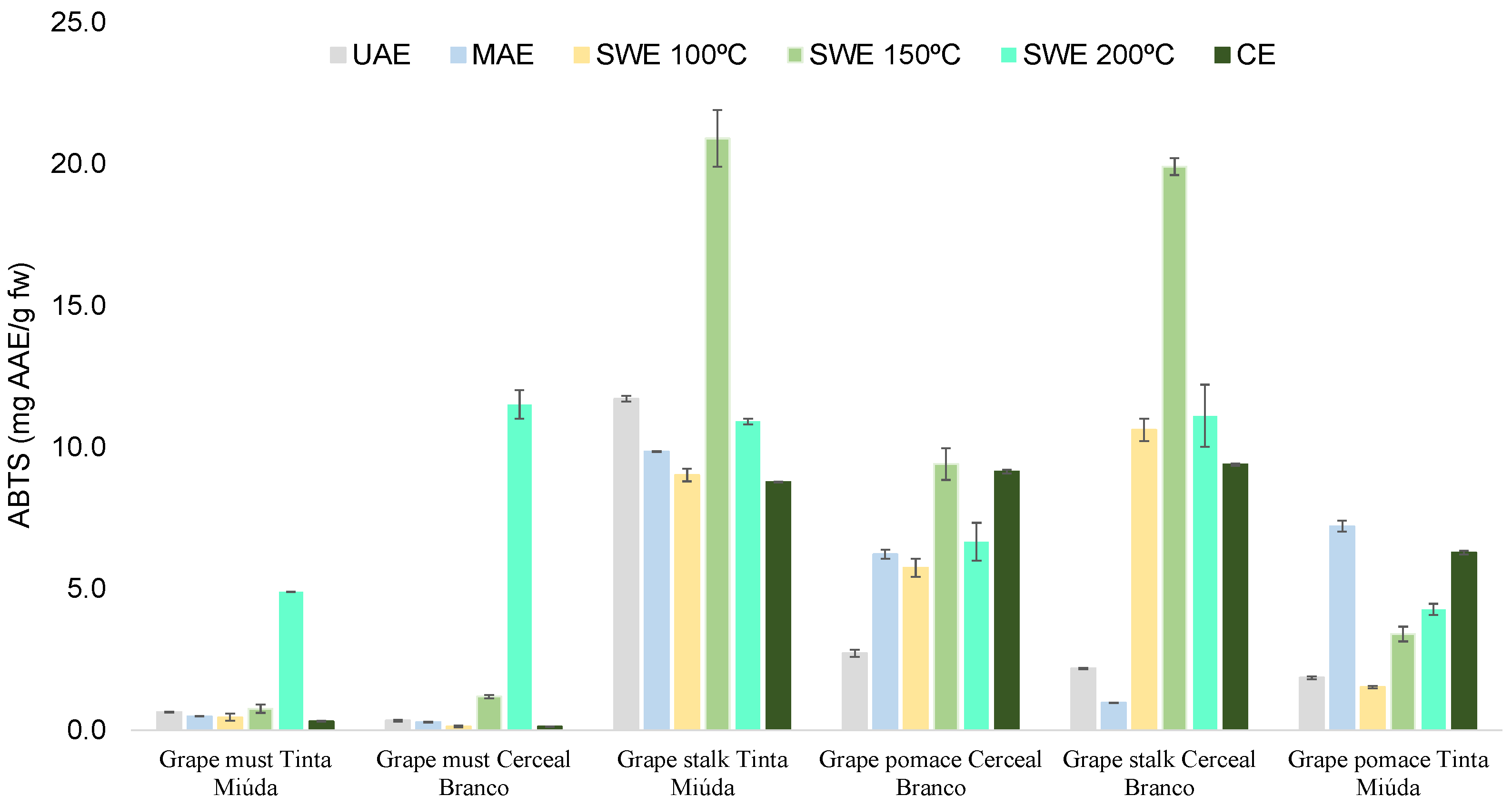
| Phenolic Compounds | Mean ± SD (mg of Compound/100 g fw) |
|---|---|
| Gallic acid | 38.8 ± 1.9 |
| Protocatechuic acid | ND a |
| Neochlorogenic acid | 123 ± 6 |
| Caftaric acid | 18.5 ± 0.9 |
| (+)-Catechin | 467 ± 23 |
| Caffeine | 105 ± 5 |
| Chlorogenic acid | 154 ± 8 |
| 4-O-caffeyolquinic acid | 48.0 ± 2.4 |
| Vanillic acid | 47.3 ± 2.4 |
| Caffeic acid | 21.2 ± 1.1 |
| Syringic acid | 30.2 ± 1.5 |
| (−)-Epicatechin | 129 ± 6 |
| p-Coumaric acid | 8.66 ± 0.43 |
| trans-Ferulic acid | 2.67 ± 0.13 |
| Sinapic acid | ND |
| trans-polydatin | <LOQ b |
| Naringin | 4.25 ± 0.21 |
| 3,5-di-caffeoylquinic acid | 1.30 ± 0.06 |
| Quercetin-3-O-galactoside | 25.6 ± 1.3 |
| Resveratrol | <LOD c |
| Rutin | ND |
| Phloridzin | 8.42 ± 0.42 |
| Ellagic acid | 3.62 ± 0.18 |
| 3,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 21.4 ± 1.1 |
| Myricetin | 7.50 ± 0.38 |
| Cinnamic acid | ND |
| Kaempferol-3-O-glucoside | ND |
| Kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside | ND |
| Naringenin | ND |
| trans-ε viniferin | 22.1 ± 1.1 |
| Quercetin | 44.3 ± 2.2 |
| Phloretin | ND |
| Tiliroside | 1.55 ± 0.08 |
| Kaempferol | 1.31 ± 0.07 |
| Apigenin | <LOD |
| Chrysin | ND |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira, E.; Soares, C.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Moreira, M.M. A Comparison of Green Extraction Techniques for the Recovery of Bioactive Compounds from Grapevine By-Products. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2023, 26, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2023-15050
Ferreira E, Soares C, Delerue-Matos C, Moreira MM. A Comparison of Green Extraction Techniques for the Recovery of Bioactive Compounds from Grapevine By-Products. Biology and Life Sciences Forum. 2023; 26(1):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2023-15050
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira, Eduarda, Cristina Soares, Cristina Delerue-Matos, and Manuela M. Moreira. 2023. "A Comparison of Green Extraction Techniques for the Recovery of Bioactive Compounds from Grapevine By-Products" Biology and Life Sciences Forum 26, no. 1: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2023-15050
APA StyleFerreira, E., Soares, C., Delerue-Matos, C., & Moreira, M. M. (2023). A Comparison of Green Extraction Techniques for the Recovery of Bioactive Compounds from Grapevine By-Products. Biology and Life Sciences Forum, 26(1), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2023-15050









