A Study of Nematocyst Discharge of Physalia physalis and Venom Composition †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Nematocysts Assay
2.2. Count of Discharged Nematocysts
2.3. Crude Venom Extracts and Enzymatic Assays
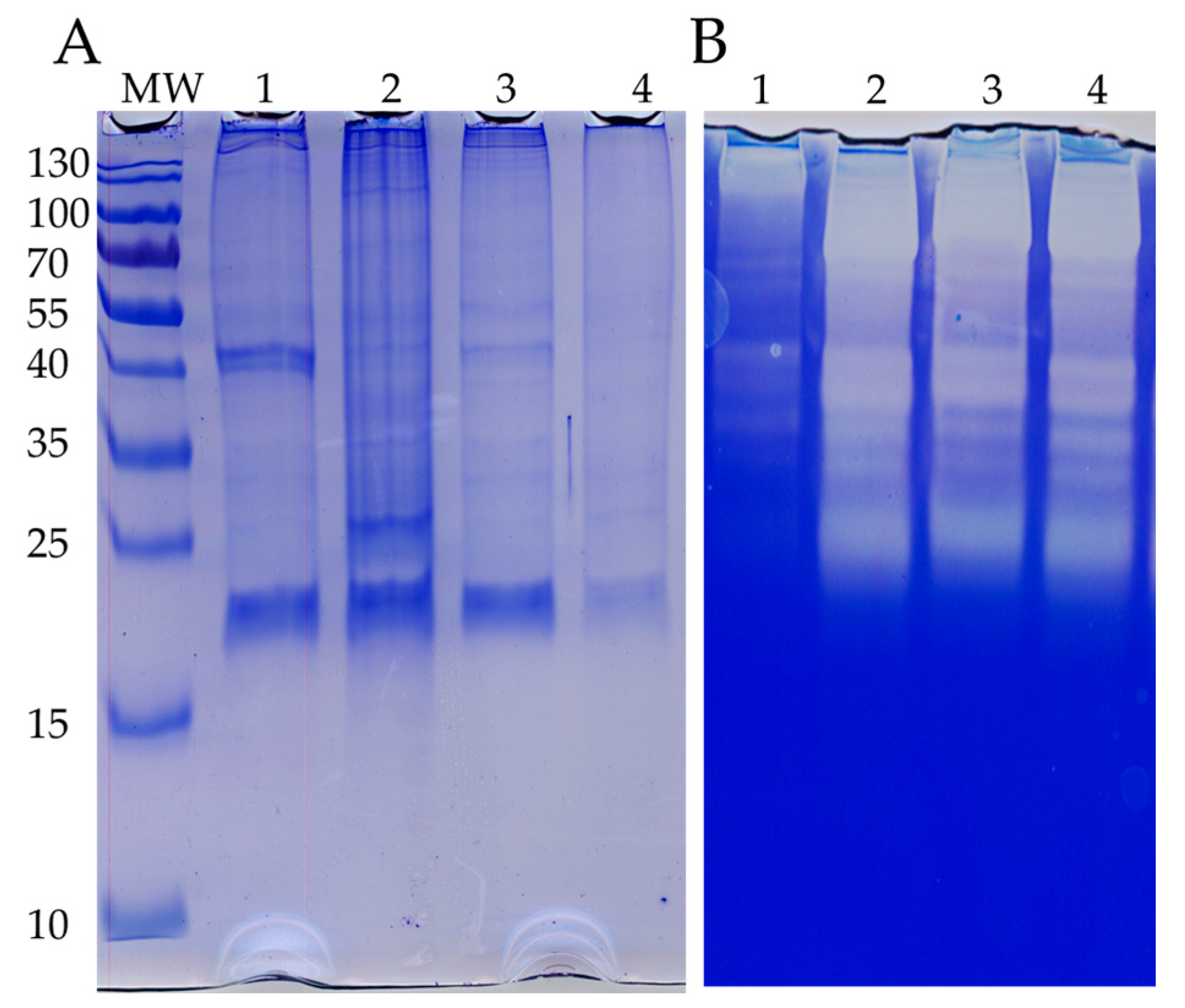
2.4. SDS-PAGE and Zymogram
3. Results
3.1. Ion Solutions Induce Nematocyst Discharge
3.2. Venom Released by Discharged Nematocysts Has Proteolytic Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dunn, C.W.; Pugh, P.R.; Haddock, S.H.D. Molecular Phylogenetics of the Siphonophora (Cnidaria), with Implications for the Evolution of Functional Specialization. Syst. Biol. 2005, 54, 916–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mapstone, G.M. Global Diversity and Review of Siphonophorae (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, C.; Vue, Z.; Behringer, R.R.; Dunn, C.W. Morphology and development of the Portuguese man of war, Physalia physalis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, G.O. Studies on Physalia physalis (L.). Part 2. Behavior and Histology; Discovery Reports; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1960; Volume 30, pp. 371–407. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, C.E.; Dodge, E. The Toxicity of Physalia Nematocysts. Biol. Bull. 1958, 115, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labadie, M.; Aldabe, B.; Ong, N.; Joncquiert-Latarjet, A.; Groult, V.; Poulard, A.; Coudreuse, M.; Cordier, L.; Rolland, P.; Chanseau, P.; et al. Portugueseman-of-war (Physalia physalis) envenomation on the Aquitaine Coast of France: An emerging health risk. Clin. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, S.A.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Raising Awareness on the Clinical and Forensic Aspects of Jellyfish Stings: A Worldwide Increasing Threat. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.A.; Bouchard, C. The regulation of cnidocyte discharge. Toxicon 2009, 54, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, R.B.; Anderson, P.A.V. Chemosensory pathways in the capitate tentacles of the hydroid Cladonema. Invert. Neurosci. 2006, 6, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gitter, A.H.; Oliver, D.; Thurm, U. Calcium- and voltage-dependence of nematocyst discharge in Hydra vulgaris. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1994, 175, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Americus, B.; Austin, B.M.; Lotan, T.; Bartholomew, J.L.; Atkinson, S.D. In vitro and in vivo assays reveal that cations affect nematocyst discharge in Myxobolus cerebralis (Cnidaria: Myxozoa). Parasitology 2020, 147, 1352–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, D.; Garg, N.; Grässle, S.; Vanderheiden, S.; Bergheim, B.G.; Bräse, S.; Jung, N.; Özbek, S. A small molecule screen identifies novel inhibitors of mechanosensory nematocyst discharge in Hydra. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesteros, A.; Trullas, C.; Jourdan, E.; Gili, J.-M. Inhibition of Nematocyst Discharge from Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa)—Prevention Measures against Jellyfish Stings. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birsa, L.M.; Verity, P.G.; Lee, R.F. Evaluation of the effects of various chemicals on discharge of and pain caused by jellyfish nematocysts. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 151, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrette, T.; Seymour, J. A rapid and repeatable method for venom extraction from Cubozoan nematocysts. Toxicon 2004, 44, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
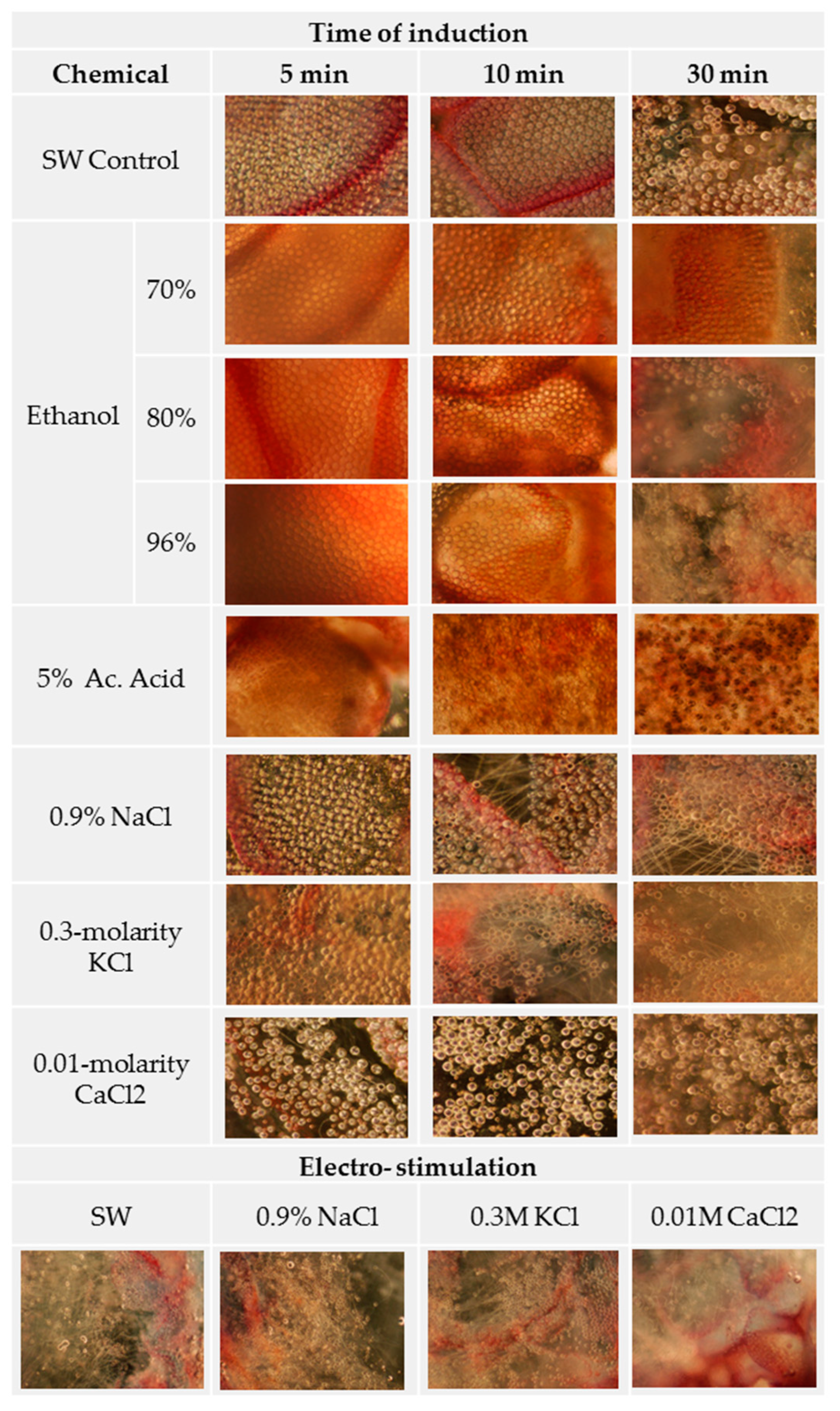
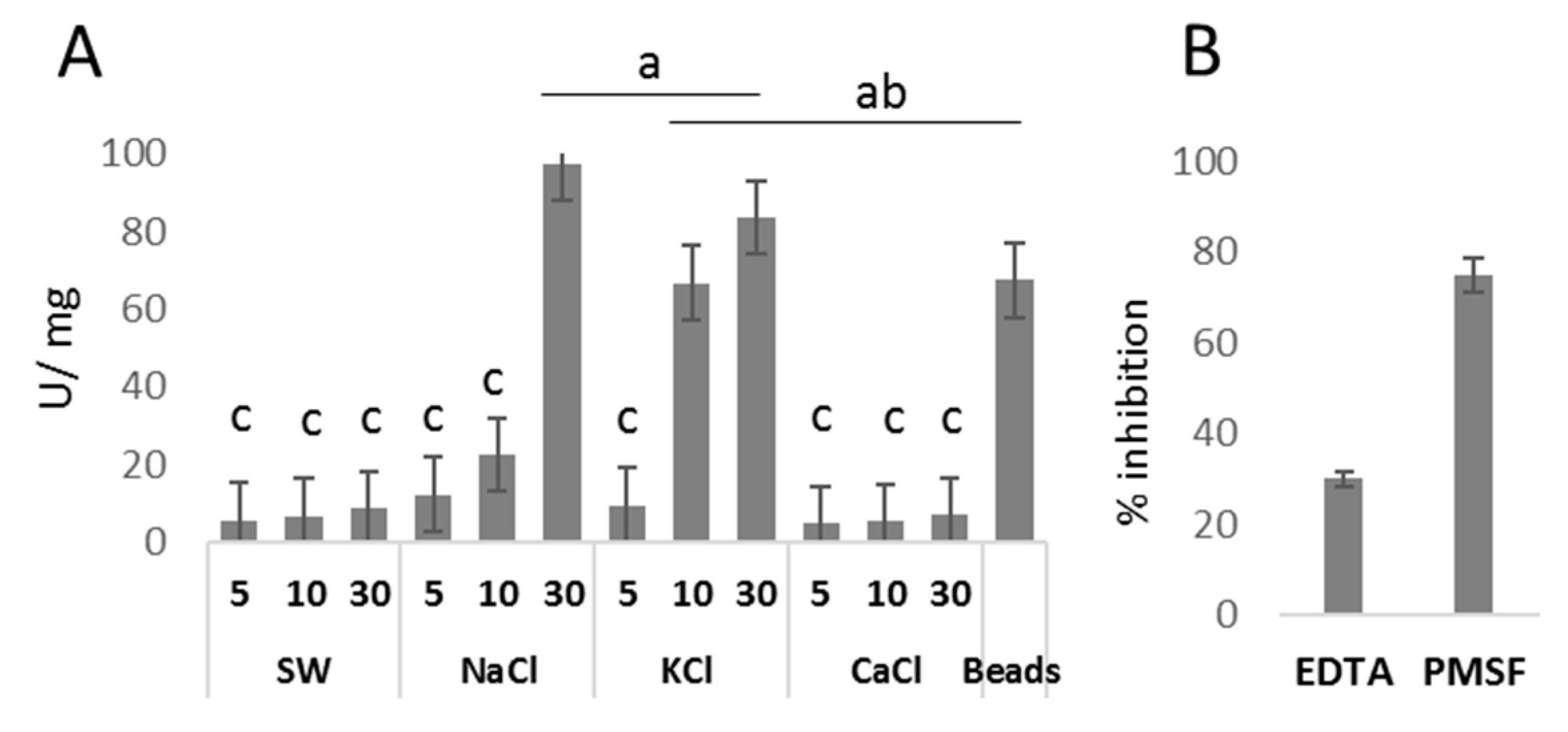
| Chemical | Induction (min.) | Discharge (%) | Protein (mg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SW Control | 5 | 4 ± 2 a | 0.08 | |
| (pH 7.8) | 15 | 8 ± 4 a | 0.05 | |
| 30 | 10 ± 2 a | 0.05 | ||
| Ethanol | 70% | 5 | 1.5 ± 1 a | 0.13 |
| 15 | 2 ± 2 a | 0.38 | ||
| 30 | 12 ± 5 a | 0.82 | ||
| 80% | 5 | 1 ± 1 a | 0.27 | |
| 15 | 15 ± 4 a | 0.82 | ||
| 30 | 25 ± 8 b | 0.96 | ||
| 96% | 5 | 5 ± 2 a | 0.67 | |
| 15 | 27 ± 6 b | 1.00 | ||
| 30 | 60 ± 12 c | 1.71 | ||
| Acetic acid 5% (pH 2.5) | 5 | 3 ± 2 a | 0.54 | |
| 15 | 20 ± 6 b | 0.61 | ||
| 30 | 30 ± 8 b | 0.64 | ||
| 0.9% NaCl (pH 5.8) | 5 | 3 ± 1 a | 0.37 | |
| 15 | 14 ± 8 ab | 0.29 | ||
| 30 | >90 d | 2.233 | ||
| 0.3-molarity KCl (pH 6.04) | 5 | 18 ± 4 ab | 0.64 | |
| 15 | 80 ± 11 d | 1.214 | ||
| 30 | >90 d | 2.646 | ||
| 0.01-molarity CaCl2 (pH 6.4) | 5 | 2 ± 1 a | 0.42 | |
| 15 | 2 ± 1 a | 0.57 | ||
| 30 | 9 ± 4 a | 0.76 | ||
| SW | Electro-stimulated | 50 ± 11 c | 0.212 | |
| 0.9% NaCl | >90 d | 0.47 | ||
| 0.3-molarity KCl | >90 d | 0.59 | ||
| 0.01-molarity CaCl2 | 50 ± 12 c | 0.17 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toubarro, D.; Tomkielska, Z.; Silva, L.; Borges, M.; Simões, N. A Study of Nematocyst Discharge of Physalia physalis and Venom Composition. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2023, 24, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECT2023-14810
Toubarro D, Tomkielska Z, Silva L, Borges M, Simões N. A Study of Nematocyst Discharge of Physalia physalis and Venom Composition. Biology and Life Sciences Forum. 2023; 24(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECT2023-14810
Chicago/Turabian StyleToubarro, Duarte, Zuzanna Tomkielska, Liliana Silva, Margarida Borges, and Nelson Simões. 2023. "A Study of Nematocyst Discharge of Physalia physalis and Venom Composition" Biology and Life Sciences Forum 24, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECT2023-14810
APA StyleToubarro, D., Tomkielska, Z., Silva, L., Borges, M., & Simões, N. (2023). A Study of Nematocyst Discharge of Physalia physalis and Venom Composition. Biology and Life Sciences Forum, 24(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECT2023-14810







