Abstract
This study aimed to assess the benefits of the solvent-free microwave extraction (SFME) on chamomile (Matricaria recutita L.) essential oil quality and yield compared to the extraction by steam distillation (SD). The oil obtained by SFME and SD presented a blue color, a solubility in 70% ethanol (v/v) of four, a relative density of 0.929–0.925 g/mL, a refractive index of 1.5013–1.4790, and an acidity value of 6.23 and 3.43, respectively. The yields were significantly different between extraction methods, being the highest (0.5 mL (0.083% v/w)) for SFME and 0.2 mL (0.03%) for SD. The GC-MS analysis showed a marked difference in sesquiterpenes, such as Chamazulene, α-bisabolol, α-bisabolol oxide A, and α-bisabolol oxide B. The SFME had 97% and 20% more content of chamazulene and α-bisabolol respectively, whilst SD had 88% and 12% more content of α-bisabolol oxide A and B, respectively. The results suggest that SME is an outstanding alternative for essential oil extraction due to much higher yield and quality compared to the steam distillation.
1. Introduction
Chamomile is probably the most widely used medicinal plant [1] due to many health benefits such as anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antiparasitic, antioxidant, and cytotoxic properties, among others, attributed mainly to its flavonoid, coumarin, and sesquiterpene content [2,3]. Thus, chamomile essential oil (EO) and extracts have been increasingly added to food products as a functional ingredient to increase their shelf life [4,5].
The solvent-free microwave extraction (SFME) method is considered a novel green technology that performs adequately in the extraction of essential oil from herbs or plants [6]. SFME combines the microwave heating and distillation in the absence of externally added solvents [7]. This technique can be completed in minutes instead of hours, presents high reproducibility, low energy consumption, and a usually higher quality of the final product due to less thermal degradation compounds [8].
The international price of M. recutita essential oil ranges between 850–1500 USD/kg, hence, suitable extraction methods for EO with high yields, strong aromatic profiles, and functional properties are needed. Therefore, this study aimed to assess the benefits of the solvent-free microwave extraction (SFME) on chamomile essential oil quality and yield compared to extraction by steam distillation (SD), which nowadays is the most widely used method.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Essential Oil Extraction
For both extraction methods solvent-free microwave extraction (SFME) and steam distillation (SD) were used for 600 g of fresh chamomile flowers (80–82% HR). Fresh plants of chamomile were bought to local companies, and flowers were separated manually to obtain a 14–15% yield (w/w), and they were immediately processed. Although usually essential oils are extracted from dried samples, in this study fresh flowers were used due to requirements of the extraction method [7] and due to better quality of final product [5,9]. The extraction of essential oil was performed during autumn with an average condition of 20 °C and 80% HR.
For SFME, flowers were placed in the reactor chamber of the Milestone’s Ethos X® (Sorisole, Italy). The setup used for extraction was 1200 W for 45 min and 8 °C of condensation temperature.
For the SD, flowers were placed in a Clevenger system using 2 L of water, and the extraction was performed for 2 h.
2.2. Physicochemical Analyses
Density was determined using a pycnometer, and the essential oil was taken to 20 °C for analysis. Refractive index was performed using a refractometer—Mettler Toledo´s RM40 LiquiPhysics® (Greifensee, Switzerland). The EO acidity value was performed following the AOAC Official Method 940.28 [10] and expressed as mg KOH/g EO).
2.3. GC-MS Analyses
The analysis was performed using a GC Agilent 7890 and a MS Agilent 5975 (California, United States of America) and a fused silica capillary HP-5 column (30 m length × 0.25 mm i.d., 0.25 μm film thickness). Helium was used as the carrier gas at a flow rate of 1.1 mL·min−1. The oven temperature was set for a gradient from 30 °C to 250 °C. The injection temperature was 250 °C and detection temperature 230 °C. The MS was set in TIC mode with an EI of 70 eV.
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Analyses
The essential oil obtained by SFME and SD presented a deep blue color, a solubility in 70% ethanol (v/v) of four, a relative density of 0.929–0.925 g/mL, and a refractive index of 1.5013–1.4790. The only difference was in the acidity index, showing higher values the SFME (6.23) against SD (3.43).
3.2. GC-MS Analyses
The GC-MS results showed that essential oils obtained by SFME (Figure 1) and SD (Figure 2) presented a similar chemical profile. Nevertheless, the quantity of each compound differs from each another (Table 1). In particular, chamazulene content is approximately two-fold in SFME compared to SD. On the other hand, SD presents slightly higher values for α-bisabolol oxide A and B.
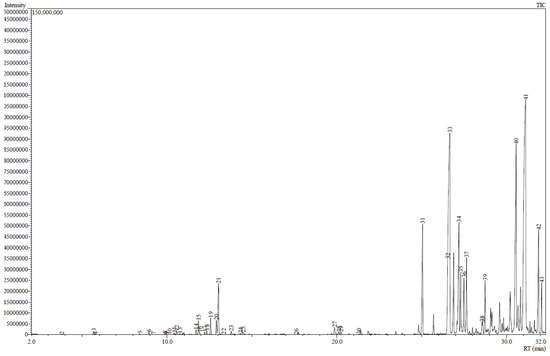
Figure 1.
Chromatogram of M. recutita essential oil obtained by solvent-free microwave extraction.
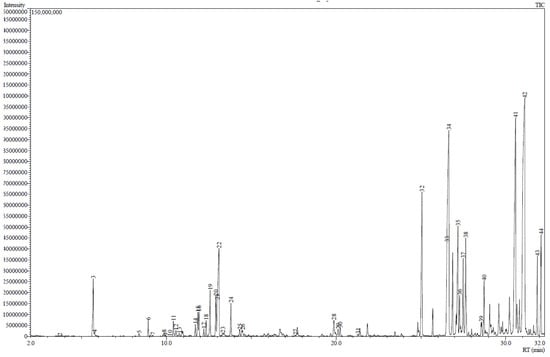
Figure 2.
Chromatogram of M. recutita essential oil obtained by steam distillation.

Table 1.
Physicochemical characterization of chamomile essential oil obtained by solvent-free microwave extraction (SFME) and steam distillation (SD).
3.3. Yield
The yields were significantly different between extraction methods, being the highest (0.5 mL (0.083% v/w)) for SFME and 0.2 mL (0.03%) for SD.
4. Discussions
4.1. Physicochemical Analyses
Acidity value of EO obtained by SFME is almost twice that of EO from SD. This difference can be attributed to the high microwave power (1200 w) used in the extraction, since increasing microwave power has been associated with more free fatty acid content [11,12].
4.2. GC-MS Analyses
The main difference in the chemical profile of essential oils obtained by SFME and SD is the sesquiterpenes content. The SFME showed 97% more content of chamazulene and 20% more α-Bisabolol than SD. These results are remarkable since α-bisabolol and chamazulene are considered to be the most valuable components [4], especially due to their contribution to aroma profile and bioactivity [13,14].
Chamazulene derives from matricin [4,5] and has been reported as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antispasmodic [15]. On the other hand, α-bisabolol apparently prevents oxidative stress, inflammatory disorders, infections, neurodegenerative diseases, cancers, and metabolic disorders [15,16].
One study showed that microwave-assisted hydrodistillation achieved 15.08% of chamazulene, while hydro-distillation achieved only 1.67% from dried flowers of M. recutita [17]. In Damask rose extracts obtained by SFME, a massive difference in the sesquiterpenes amount was found—38.55% against 2.97% obtained by hydrodistillation and 3.37% by steam distillation [8]. Thus, apparently, microwave exerts a positive effect in the quantity of sesquiterpenes due to is improved energy transfer compared to traditional heating methods.
Regarding the quality of essential oil, microwave methods have shown to present better quality than traditional extractions. The lemongrass oil obtained by SFME had a higher amount of citral (74%) in comparison to hydrodistillation (60%) [18]. In another study, although the T. mastichina essential oil extracted by SFME did not show significant difference compared to steam distillation or hydrodistillation, the microwave method was quicker and had higher yield [7].
4.3. Yields
The SFME yield was 150% higher than SD, and the time for maximum extraction of essential oil was reduced in approximately 60%. This can be due to the effect of microwaves in the cell walls of chamomile, as demonstrated in C. camphora fruit peels [19]. Moreover, SMFE has been reported as highly effective in essential oil extraction compared to other methods, such as hydrodistillation, salt-assisted extraction, ultrasound-assisted extraction, and enzymes-assisted extraction [18,20].
5. Conclusions
Solvent-free microwave extraction is a remarkable alternative for chamomile essential oil extraction due to much higher yield and quality compared to the steam distillation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.H.; methodology, E.H.; validation, L.O.-M. and E.H.; formal analysis, L.O.-M. and E.H.; investigation, C.P.; resources, C.P. and E.H.; data curation, L.O.-M. and E.H.; writing—original draft preparation, C.P., L.O.-M. and E.H.; writing—review and editing, E.H.; visualization, L.O.-M.; supervision, E.H.; project administration, E.H.; funding acquisition, E.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We want to thank the Esencias Quimicas SAC company for its support in the research, as well as Maria Julia Llontop and Cesar Cotera for their contributions in experimental trials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Stanojevic, L.P.; Marjanovic-Balaban, Z.R.; Kalaba, V.D.; Stanojevic, J.S.; Cvetkovic, D.J. Chemical Composition, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of Chamomile Flowers Essential Oil (Matricaria Chamomilla L.). J. Essent. Oil-Bear. Plants 2016, 19, 2017–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mihyaoui, A.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.G.; Charfi, S.; Candela Castillo, M.E.; Lamarti, A.; Arnao, M.B. Chamomile (Matricaria Chamomilla L.): A Review of Ethnomedicinal Use, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Uses. Life 2022, 12, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.; González-Burgos, E.; Gómez-Serranillos, M.P. The Pharmacology and Clinical Efficacy of Matricaria Recutita L.: A Systematic Review of in Vitro, in Vivo Studies and Clinical Trials. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 38, 1668–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Nazaruk, J.; Polito, L.; Morais-Braga, M.F.B.; Rocha, J.E.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; Salehi, B.; Tabanelli, G.; Montanari, C.; del Mar Contreras, M.; et al. Matricaria Genus as a Source of Antimicrobial Agents: From Farm to Pharmacy and Food Applications. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 215, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, R.; Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, A.; Kumari, A.; Rathore, S.; Kumar, R.; Singh, S. A Comprehensive Review on Biology, Genetic Improvement, Agro and Process Technology of German Chamomile (Matricaria Chamomilla L.). Plants 2022, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalili, G.; Mazloomifar, A.; Larijani, K.; Tehrani, M.S.; Azar, P.A. Solvent-Free Microwave Extraction of Essential Oils from Thymus Vulgaris L. and Melissa Officinalis L. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 119, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, A.R.T.S.; Périno, S.; Fernandez, X.; Cunha, C.; Rodrigues, M.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Jordao, L.; Silva, L.A.; Rodilla, J.; Coutinho, P.; et al. Solvent-free Microwave Extraction of Thymus Mastichina Essential Oil: Influence on Their Chemical Composition and on the Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, C.; Robustelli Della Cuna, F.S.; Russo, E.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Grignani, E.; Preda, S. Microwave-Assisted and Conventional Extractions of Volatile Compounds from Rosa x Damascena Mill. Fresh Petals for Cosmetic Applications. Molecules 2022, 27, 3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, M.; Rezwanee, F.; Hassanzadeh Khayyat, M.; Lackzian, A. The Effect of Different Levels of Vermicompost and Irrigation on Morphological Properties and Essential Oil Content of German Chamomile (Matricaria Recutita) C.V. Goral. Planta Med. 2008, 74, PE3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International; AOAC: Rockville, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Musa Özcan, M.; Al-Juhaimi, F.Y.; Mohamed Ahmed, I.A.; Osman, M.A.; Gassem, M.A. Effect of Different Microwave Power Setting on Quality of Chia Seed Oil Obtained in a Cold Press. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydinkaptan, E.; Mazi, B.G.; Barutçu Mazi, I. Microwave Heating of Sunflower Oil at Frying Temperatures: Effect of Power Levels on Physicochemical Properties. J. Food Process Eng. 2017, 40, e12402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Joumaa, M.M.; Borjac, J.M. Matricaria Chamomilla: A Valuable Insight into Recent Advances in Medicinal Uses and Pharmacological Activities. Phytochem. Rev. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radivojac, A.; Bera, O.; Micić, D.; Đurović, S.; Zeković, Z.; Blagojević, S.; Pavlić, B. Conventional versus Microwave-Assisted Hydrodistillation of Sage Herbal Dust: Kinetics Modeling and Physico-Chemical Properties of Essential Oil. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 123, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddin, L.B.; Jha, N.K.; Goyal, S.N.; Agrawal, Y.O.; Subramanya, S.B.; Bastaki, S.M.A.; Ojha, S. Health Benefits, Pharmacological Effects, Molecular Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Potential of α-Bisabolol. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramazani, E.; Akaberi, M.; Emami, S.A.; Tayarani-Najaran, Z. Pharmacological and Biological Effects of Alpha-Bisabolol: An Updated Review of the Molecular Mechanisms. Life Sci. 2022, 304, 120728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homami, S.S.; Jaimand, K.; Rezaee, M.B.; Afzalzadeh, R. Comparative Studies of Different Extraction Methods of Essential Oil from Matricaria Recutita L. in Iran. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2016, 61, 2982–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhatem, M.N.; Ferhat, M.A.; Rajabi, M.; Mousa, S.A. Solvent-Free Microwave Extraction: An Eco-Friendly and Rapid Process for Green Isolation of Essential Oil from Lemongrass. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 664–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, D.; Qi, Y.; Ma, C.; Zou, Z.; Ni, H. Cinnamomum Camphora Fruit Peel as a Source of Essential Oil Extracted Using the Solvent-Free Microwave-Assisted Method Compared with Conventional Hydrodistillation. LWT 2022, 153, 112549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taktak, O.; Ben Youssef, S.; Abert Vian, M.; Chemat, F.; Allouche, N. Physical and Chemical Influences of Different Extraction Techniques for Essential Oil Recovery from Citrus Sinensis Peels. J. Essent. Oil-Bear. Plants 2021, 24, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).