Metabolites Differentiating Asymptomatic and Symptomatic Grapevine Plants (Vitis vinifera ‘Malvasia-Fina’) Infected with Esca Complex Disease-Associated Fungi †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
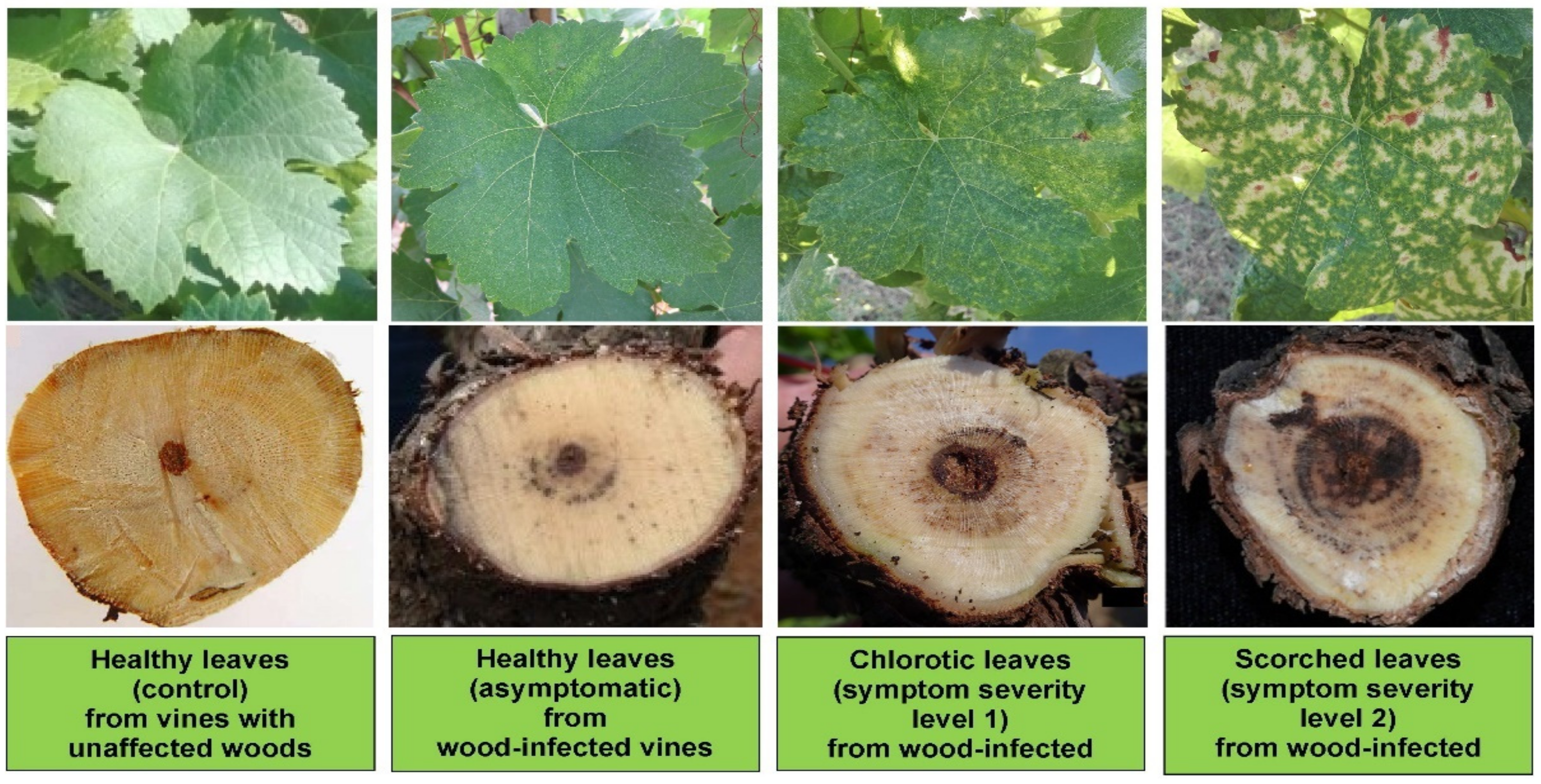
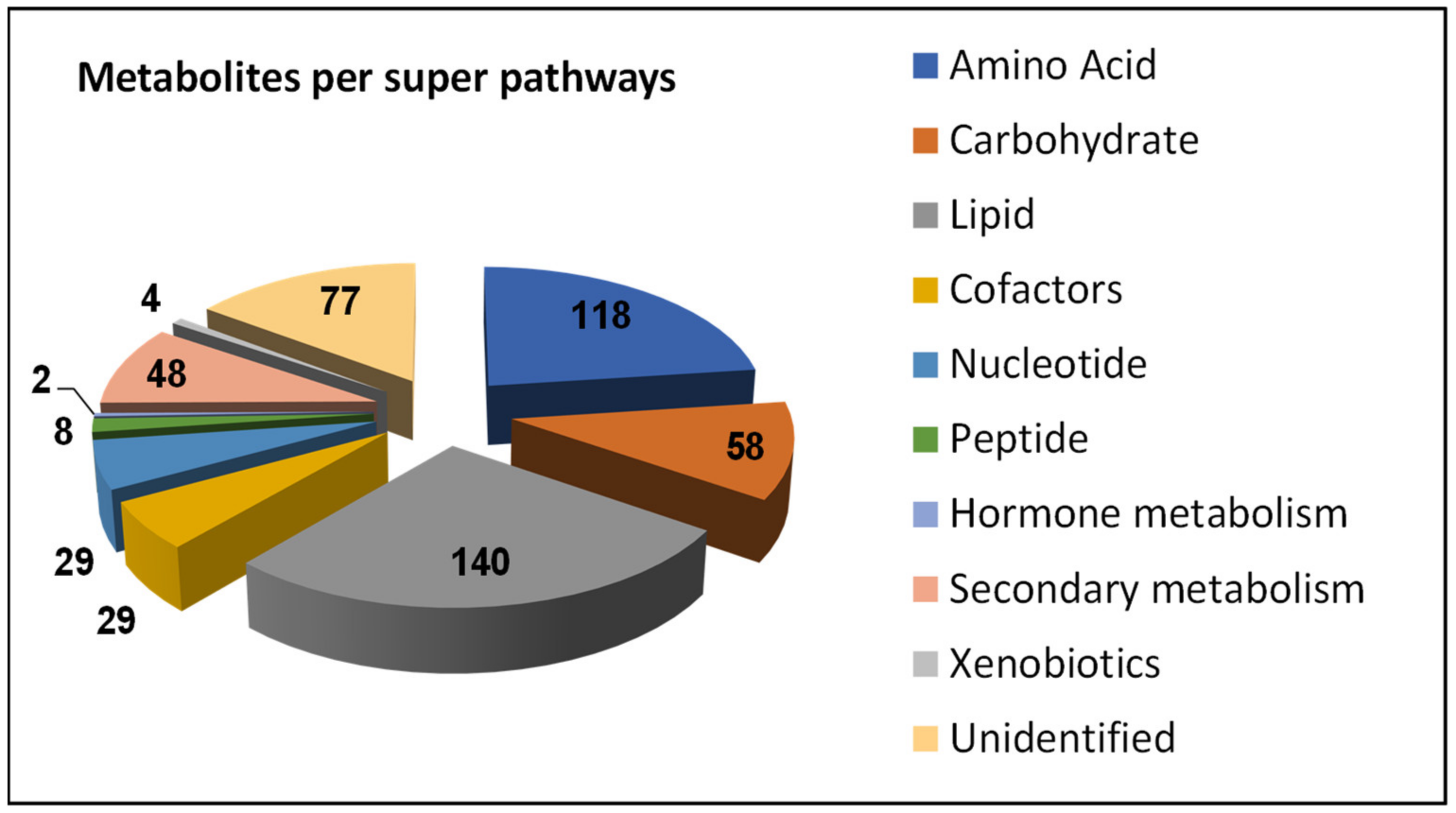
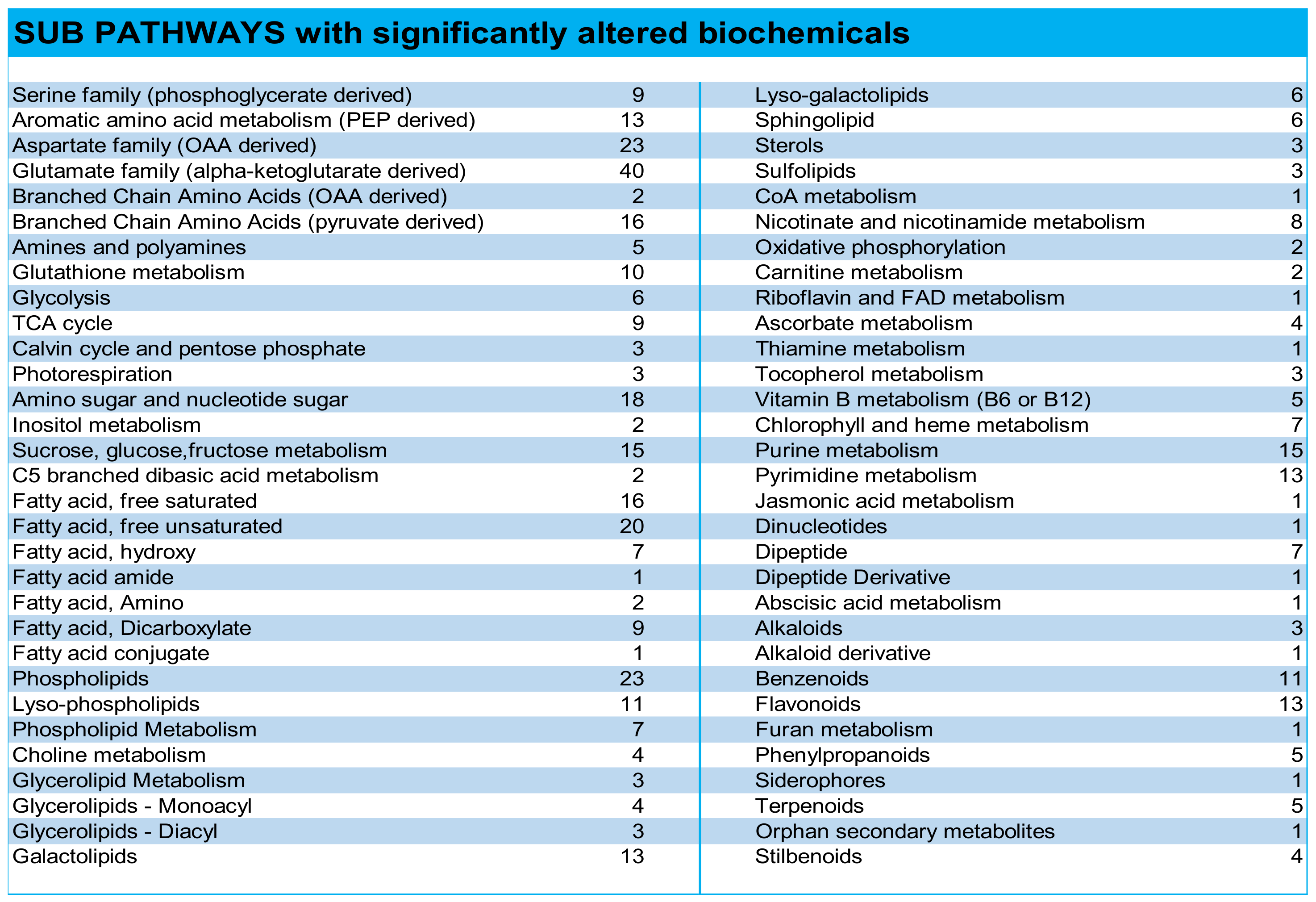
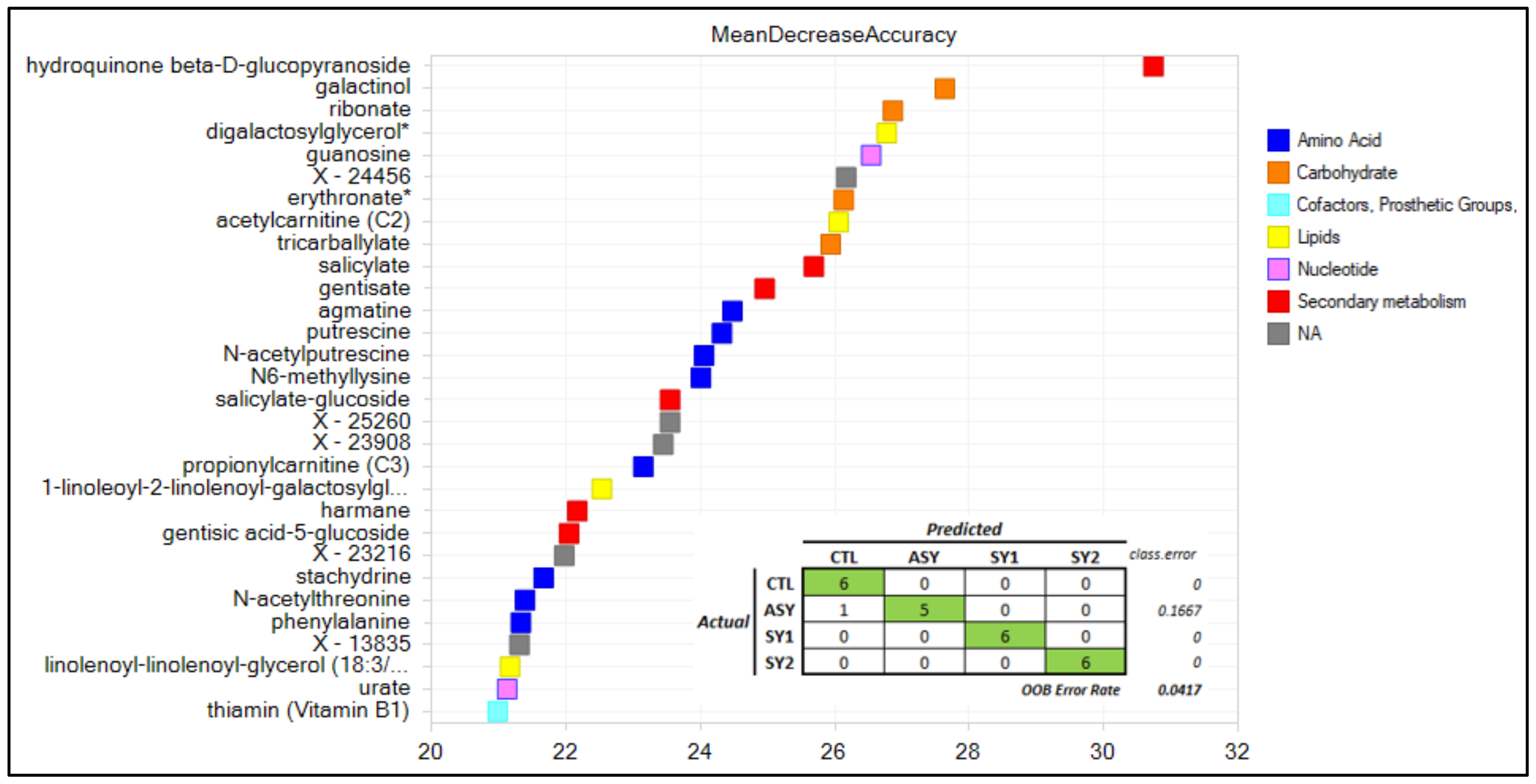
3. Results and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nerva, L.; Turina, M.; Zanzotto, A.; Gardiman, M.; Gaiotti, F.; Gambino, G.; Chitarra, W. Isolation, molecular characterization and virome analysis of culturable wood fungal endophytes in esca symptomatic and asymptomatic grapevine plants. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 2886–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofia, J.; Mota, M.; Gonçalves, T.M.; Rego, C. Response of four Portuguese grapevine cultivars to infection by Phaeomoniella chlamydospora. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2018, 57, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Frari, G.; Gobbi, A.; Aggerbeck, M.R.; Oliveira, H.; Hansen, L.H.; Ferreira, R.B. Characterization of the wood mycobiome of Vitis vinifera in a vineyard affected by esca. Spatial distribution of fungal communities and their putative relation with leaf symptoms. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rusjan, D.; Persic, M.; Likar, M.; Biniari, K.; Mikulic-Petkovsek, M. Phenolic responses to esca-associated fungi in differently decayed grapevine woods from different trunk parts of ‘Cabernet Sauvignon’. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6615–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouadi, L.; Bruez, E.; Bastien, S.; Yacoub, A.; Coppin, C.; Guérin-Dubrana, L.; Fontaine, F.; Domec, J.-C.; Rey, P. Sap flow disruption in grapevine is the early signal predicting the structural, functional, and genetic responses to esca disease. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 695846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cholet, C.; Bruez, E.; Lecomte, P.; Barsacq, A.; Martignon, T.; Giudici, M.; Simonit, M.; Rey, P.; Dubourdieu, D.; Gény, L. Plant resilience and physiological modifications induced by curettage of Esca-diseased grapevines. OENO One 2021, 55, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, G.L.; Ippolito, M.P.; Mannerucci, F.; Bragazzi, L.; Tommasi, F. Physiological responses of ‘Italia’ grapevines infected with Esca pathogens. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2021, 60, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtaud, C.; Thibault, F.; Larignon, P.; Bertsch, C.; Fleurat-lessard, P.; Bourbouloux, A. Systemic damage in leaf metabolism caused by esca infection in grapevines. Aus. J. Grape Wine Res. 2011, 17, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, L.; Fontaine, F.; Castañoa, J.F.; Songy, A.; Roda, R.; Vallet, J.; Ferrer-Gallego, R. Specific profile of Tempranillo grapevines related to Esca-leaf symptoms and climate conditions. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquier, G.; Lapaillerie, D.; Vilain, S.; Dupuy, J.-W.; Lomenech, A.-M.; Claverol, S.; Gény, L.; Bonneu, M.; Teissedre, P.-L.; Donèche, B. Impact of foliar symptoms of “Esca proper” on proteins related to defense and oxidative stress of grape skins during ripening. Proteomics 2013, 13, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goufo, P.; Marques, C.A.; Cortez, I. Exhibition of local but not systemic induced phenolic defenses in Vitis vinifera L. affected by brown wood streaking, grapevine leaf stripe, and apoplexy (Esca complex). Plants 2019, 8, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magnin-Robert, M.; Adrian, M.; Trouvelot, S.; Spagnolo, A.; Jacquens, L.; Letousey, P.; Rabenoelina, F.; Harir, M.; Roullier-Gall, C.; Clément, C.; et al. Alterations in grapevine leaf metabolism occur prior to esca apoplexy appearance. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2017, 30, 946–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnin-Robert, M.; Spagnolo, A.; Boulanger, A.; Joyeux, C.; Clément, C.; Abou-Mansour, E.; Fontaine, F. Changes in plant metabolism and accumulation of fungal metabolites in response to Esca proper and apoplexy expression in the whole grapevine. Phytopathology 2016, 106, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnin-Robert, M.; Spagnolo, A.; Alayi, D.T.; Cilindre, C.; Mercier, L.; Schaeffer-Reiss, C.; Van Dorsselaer, A.; Clément, H.C.; Fontaine, F. Proteomic insights into changes in grapevine wood in response to esca proper and apoplexy. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2014, 53, 168–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moret, F.; Delorme, G.; Clément, G.; Grosjean, C.; Lemaître-Guillier, C.; Trouvelot, S.; Adrian, M.; Fontaine, F. Esca-affected grapevine leaf metabolome is clone- and vintage-dependent. Physiol. Plant. 2020, 171, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goufo, P.; Cortez, I. A Lipidomic analysis of leaves of esca-affected grapevine suggests a role for galactolipids in the defense response and appearance of foliar symptoms. Biology 2020, 9, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goufo, P.; Cortez, I. Dataset of levels and masses of lipid species in healthy, asymptomatic and symptomatic leaves of Vitis vinifera L. ’Malvasia Fina´ affected by Esca complex disease. Data Brief 2020, 33, 106469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekulić, A.; Kilibarda, M.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Nikolić, M.; Bajat, B. Random Forest spatial interpolation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goufo, P.; Moutinho-Pereira, J.; Jorge, T.F.; Correia, C.M.; Oliveira, M.R.; Rosa, E.A.S.; Antonio, C.; Trindade, H. Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) Metabolomics: Osmoprotection as a physiological strategy for drought stress resistance and improved yield. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goufo, P.; Singh, R.K.; Cortez, I. A Reference list of phenolic compounds (including stilbenes) in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) roots, woods, canes, stems, and leaves. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goufo, P.; Singh, R.K.; Cortez, I. Metabolites Differentiating Asymptomatic and Symptomatic Grapevine Plants (Vitis vinifera ‘Malvasia-Fina’) Infected with Esca Complex Disease-Associated Fungi. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2022, 11, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECPS2021-11923
Goufo P, Singh RK, Cortez I. Metabolites Differentiating Asymptomatic and Symptomatic Grapevine Plants (Vitis vinifera ‘Malvasia-Fina’) Infected with Esca Complex Disease-Associated Fungi. Biology and Life Sciences Forum. 2022; 11(1):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECPS2021-11923
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoufo, Piebiep, Rupesh Kumar Singh, and Isabel Cortez. 2022. "Metabolites Differentiating Asymptomatic and Symptomatic Grapevine Plants (Vitis vinifera ‘Malvasia-Fina’) Infected with Esca Complex Disease-Associated Fungi" Biology and Life Sciences Forum 11, no. 1: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECPS2021-11923
APA StyleGoufo, P., Singh, R. K., & Cortez, I. (2022). Metabolites Differentiating Asymptomatic and Symptomatic Grapevine Plants (Vitis vinifera ‘Malvasia-Fina’) Infected with Esca Complex Disease-Associated Fungi. Biology and Life Sciences Forum, 11(1), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECPS2021-11923







