Abstract
This scoping review study examines seven governments and some non-governmental organisations’ youth development mechanisms in response to drug and alcohol abuse among their youth. This scoping review, including sources from 39 studies and 16 government or organisational reports, are reviewed to investigate youth development measures to mitigate drug and alcohol abuse. This study revealed that youth development mechanisms, such as outreach youth work, digital youth work, and detached youth work, lead to significant changes in risky behaviours. The study further revealed that non-governmental organisations play a critical role in solving drug- and alcohol-related challenges among youth by deterring local merchants from selling drugs and alcohol to underage customers and by strictly regulating their promotion and advertising. Effective mechanisms to develop self-efficacy, purpose, and meaning in life among youth are needed. This study also highlights the need for a joint effort between government departments, local municipalities, non-governmental youth-focused organisations, and schools to come up with effective youth work strategies. This study concludes by proposing the establishment of a Southern African Development Community (SADC) Youth Work Association and the professionalisation of youth work in the region. This will ensure that intervention programmes are implemented by professional youth workers who have the skills and knowledge to work with vulnerable young people.
1. Introduction
Substance abuse among young people has become a pressing public health and social concern in Southern Africa, with drug and alcohol use contributing significantly to poor health, crime, school dropout, and unemployment. The problem is not confined to individual behaviour but reflects broader structural, cultural, and economic conditions that shape youth development across the region (Dzinamarira et al., 2023; Mukwenha et al., 2022; Watson et al., 2023). High levels of substance abuse are reported in both urban and rural contexts, with marginalised communities particularly affected due to poverty, unemployment, limited recreational opportunities, and weak family support structures (Mulaudzi, 2018; Setlalentoa et al., 2015). These realities demand multi-sectoral and culturally responsive interventions, grounded in both community and school-based strategies, to curb the prevalence of drug and alcohol misuse among the youth.
Globally, adolescent drug and alcohol use is recognised as a developmental risk that undermines educational attainment, psychosocial wellbeing, and long-term health (WHO, 2014). In sub-Saharan Africa, youth constitute the majority of the population, and the growing burden of substance abuse threatens to derail progress toward social and economic development goals (United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime [UNODC], 2018). Recent evidence links substance uses to risky sexual behaviour, gender-based violence, and exposure to HIV/AIDS, further exacerbating the vulnerabilities of young people in the region (Letamo et al., 2016; Riva et al., 2018). Against this backdrop, Southern African Development Community (SADC) countries have intensified prevention efforts through national drug control policies, youth development initiatives, and community engagement programmes (Department of Social Development, 2013; Ndawonde, 2020).
In South Africa, the prevalence of youth drug and alcohol use remains alarmingly high. Studies identify boredom, poverty, and social dislocation as major risk factors, particularly in low-income townships where recreational alternatives are scarce (Van ZuI, 2013; Chauke, 2023). Corruption has also hindered the construction of youth centres intended to equip young people with entrepreneurial and life skills (Mulaudzi, 2018). Community-based interventions, such as chess clubs, ecological recovery projects, and dance groups, have been promoted as innovative ways to engage youth positively and divert them from substance misuse (Setlalentoa et al., 2015). Collaboration between religious organisations and civil society has further strengthened anti-drug efforts, while government investment in recreational facilities continues to be advocated (Ndawonde, 2020). At the family level, empowering parents with the skills to raise resilient children is considered central to prevention, as supportive home environments foster higher self-esteem and reduce susceptibility to peer pressure (Mudavanhu & Schenck, 2014). Non-governmental organisations (NGOs) also play a vital role in monitoring local merchants, preventing the sale of drugs and alcohol to minors, and regulating advertising (Department of Social Development, 2013).
Botswana faces similar challenges, with research showing high levels of alcohol and drug use among adolescents, often accompanied by ignorance of associated risks (Letamo et al., 2016; Diraditsile & Rasesigo, 2018). Substance abuse has been linked to teenage pregnancy, sexually transmitted infections, and HIV (Letamo et al., 2016). In response, the government introduced a national alcohol policy and the presidential alcohol levy, combining regulatory measures with awareness campaigns (Pitso & Obot, 2011). Studies show that while these initiatives have improved public knowledge and influenced attitudes, behavioural change remains a complex process requiring stronger community participation (Riva et al., 2018).
Zimbabwean youth are similarly vulnerable, with substance abuse escalating in recent years due to socio-economic hardship, trauma, and the psychological toll of the COVID-19 pandemic (Dzinamarira et al., 2023; Mukwenha et al., 2022). Easy access to drugs, coupled with a lack of recreational facilities in urban areas, has contributed to the crisis. The migration of parents in search of work has further weakened family support systems, leaving many children unsupervised and exposed to peer influence (Makwanise, 2023; Pufall et al., 2017). The government’s response has included the National Drug Master Plan 2020–2025 and law enforcement initiatives, complemented by interventions from NGOs, churches, and the Tariro Youth Drug Abuse Intervention Module (TYDAIM), which is informed by Christian Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (Koenig, 2012; Maraire et al., 2022). These initiatives highlight the importance of integrating psychological, spiritual, and community dimensions in tackling drug abuse.
Namibia also reports high levels of alcohol consumption, with more than half of young people aged 13–30 engaging in drinking (Barth & Hubbard, 2009). Alcohol misuse contributes to violence, legal troubles, and HIV risk-taking (WHO, 2014; Netope et al., 2023). Community-based responses, such as the Drug Action Group (DAG), Christelike Alkoholiste Diens (CAD), and the Horizon Project, provide aftercare and prevention services, often in collaboration with schools and health institutions (Strijdom, 1992). However, the scale of these efforts is limited compared to the magnitude of the problem, underscoring the need for more comprehensive strategies.
In Zambia, drug and alcohol misuse among secondary school learners poses a serious threat to educational outcomes. Research shows that substance use undermines academic performance, increases absenteeism, and raises the likelihood of school dropout (Masiye & Ndhlovu, 2015; Zemba, 2022). Peer influence, low self-esteem, and poor refusal skills are identified as major contributing factors (Nyimbili et al., 2019). However, peer education programmes have shown considerable promise, with trained peer educators serving as role models and providing counselling support (Midford et al., 2000; Mertens & Wilson, 2012). These interventions leverage the fact that young people are more likely to emulate their peers than respond to adult authority, making them effective channels for behaviour change.
In Eswatini, research shows that cannabis production and alcohol abuse among adolescents are prevalent, with approximately 21.7% of youth reportedly addicted to drugs (Mhlongo, 2005). Peer culture and the easy availability of substances have contributed to early onset of use, leading to school failure and behavioural problems. In Lesotho, alcohol misuse is widespread and linked to poor academic performance, memory loss, vandalism, and risky sexual practices, including date rape and unprotected intercourse (Mofokeng, 2013). The Thaba-Bosiu Centre, established in 1989, plays a central role in prevention and rehabilitation through workshops, campaigns, and entrepreneurial training that discourage harmful practices such as home-brewing (Masihleho & Khalanyane, 2009; Ranotsi et al., 2012).
Across the SADC region, early detection of risky behaviours remains essential for prevention. Screening tools such as the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) have been successfully applied in youth populations to identify problems early and facilitate referrals for counselling and treatment (Kelly et al., 2019; Triolo et al., 2022). Such tools, when integrated into school health systems and community programmes, can prevent escalation to dependence. Collectively, the evidence demonstrates that substance abuse is a multidimensional challenge requiring integrated interventions that combine family support, community engagement, school-based prevention, and national policy measures.
This study contributes to the regional evidence base by synthesising interventions that address youth substance abuse in South Africa and other SADC countries. By highlighting the strengths and limitations of community, school, and policy-level strategies, the study underscores the need for holistic, youth-centred, and culturally sensitive approaches. Understanding what has worked in different contexts is critical for informing future interventions that can reduce the burden of substance misuse and foster positive youth development across Southern Africa.
While individual countries in the SADC region have implemented various policies and programmes to address youth substance abuse, there remains a lack of region-wide synthesis of youth development-oriented interventions. Previous research has largely focused on the prevalence and causes of substance use or on interventions within single countries, without systematically comparing approaches and effectiveness across multiple SADC states. This review addresses this gap by providing a cross-country examination of youth development measures, identifying common strengths, limitations, and opportunities for regional collaboration.
This study is guided by the following research questions.
- (i)
- What youth development intervention programmes are implemented by seven governments and non-governmental organisations to mitigate drug and alcohol abuse among youth in the SADC region?
- (ii)
- What effective youth development or youth work models can be used to address drug and alcohol abuse among youths in the SADC region?
2. Materials and Methods
This study adopted a scoping review to examine youth development interventions aimed at reducing alcohol and drug abuse in seven Southern African Development Community (SADC) countries. The objective was to explore the roles of these interventions and to advocate for sustainable, long-term mitigation strategies. A scoping review methodology was employed to analyse existing literature, policy frameworks, and youth development programmes relevant to substance abuse prevention. Arksey and O’Malley’s (2005) five-stage framework was used to guide the scoping review process of this study. Scoping review methods are vital where evidence is heterogeneous and plays an important part in providing direction to future development. The five-stage framework includes the following stages: (1) identifying the research question, (2) identifying relevant studies, (3) selecting relevant studies, (4) charting the data, and (5) collating, summarizing, and reporting the results. This scoping review adhered to the PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) guidelines (Tricco et al., 2018). Details of the steps involved in the policy and government document selection process are presented as Figure 1. The database search was conducted on platforms including a wide range of credible materials, including government policy documents, peer-reviewed journal articles, and organisational reports focused on youth development and substance abuse mitigation. In addition, database searches were also conducted across multiple databases and platforms, including Academic Search Complete, ERIC, MEDLINE, SocINDEX, Sage Journals Online, PubMed, and Google Scholar. The official websites of governments and non-profit organisations involved in youth development were also reviewed. These sources offered diverse and comprehensive insights into the implementation and effectiveness of youth-focused substance abuse interventions across the selected countries.
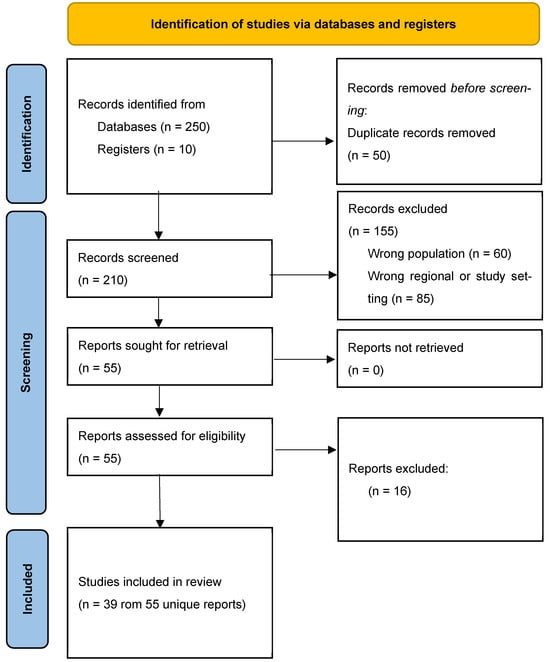
Figure 1.
PRISMA-ScR flow chart. Note: ScR = Scoping Review.
The search strategy combined keywords and Boolean operators tailored to each database, for example: (“youth” OR “young people” OR “adolescents”) AND (“substance abuse” OR “drug use” OR “alcohol use”) AND (“Southern African Development Community” OR “SADC” OR “Botswana” OR “Zimbabwe” OR “Namibia” OR “Zambia” OR “Eswatini” OR “Lesotho” OR “South Africa”).
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
The following inclusion criteria were used in this review:
- (i)
- Study designs: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-methods research; policy analyses; programme evaluations.
- (ii)
- Participants: young people aged 14–35 years in any of the seven selected SADC countries; interventions involving youth workers, teachers, social workers, health practitioners, or NGOs.
- (iii)
- Publication type: peer-reviewed journal articles, government reports, organisational policy documents, and grey literature.
- (iv)
- Language: English.
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
We excluded the following:
- (i)
- Studies not focused on youth-specific substance abuse interventions.
- (ii)
- Studies conducted outside the seven target countries.
- (iii)
- Opinion pieces or commentaries without intervention description.
- (iv)
- Studies in other languages than English
From the database search, a total of 200 articles, 20 government policies, and 30 government documents were identified. Following this identification, title and abstract screening was conducted. The selection of articles, government policies, and government documents was performed manually by the researchers, who assessed the suitability of each identified source for inclusion or exclusion in the study.
Data from this scoping review were analysed using a thematic analysis framework. The process involved several iterative stages: Familiarisation: We became familiar with the content of policy documents, programme reports, and articles. Systematic Coding: Relevant information concerning intervention strategies, outcomes, and contextual factors was systematically coded. Theme Development: We identified and refined recurring patterns and concepts to develop key themes. Final Categorization: Key themes emerging from the data were categorized and defined. This analytical approach allowed for a nuanced understanding of the effectiveness, commonalities, and contextual variations in youth development initiatives addressing alcohol and drug abuse in the SADC region. While this scoping review was conducted manually without the use of software, researchers carefully assessed sources against the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Inclusion criteria, we specifically looked for government policies and documents detailing intervention strategies aimed at addressing alcohol and drug use among young people aged 14–35 years old in the SADC region. For published articles, we focused on those discussing strategies to reduce alcohol and drug use among young people in the SADC region, particularly if they involved young people, youth workers, teachers, social workers, or psychologists as participants. Exclusion criteria: Conversely, we excluded all government policies, documents, programmes, and articles that discussed alcohol and drug abuse generally but did not specifically focus on youth development interventions.
Since this scoping review was solely based on secondary data from previous published work, government policies and documents, it was not necessary to obtain ethical approval from the university.
3. Results and Discussion
This scoping review aimed to examine and identify youth development measures to mitigate drug and alcohol abuse. A total of 55 sources, including articles, government policy, and government documents, were included in the final analysis. The publication based on the methods used are shown in Figure 2.
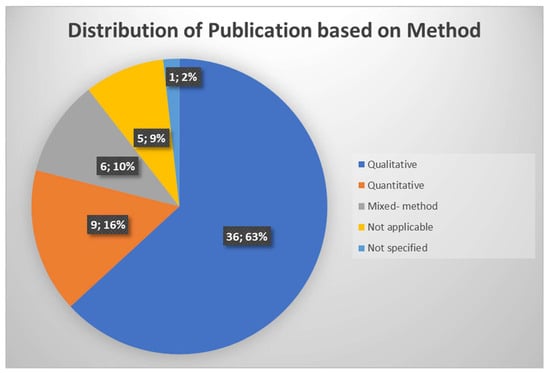
Figure 2.
Publications based on the methods used.
An analysis of the research design used in this scoping review of youth development measures to mitigate drug and alcohol abuse among young people in the Southern African Development Community (SADC) region revealed that qualitative methods were the most prevalent, appearing in 36 out of 57 studies (63%). This dominance highlights a strong focus on exploring the lived experiences, perceptions, and contextual factors influencing substance use among youth. Such studies often delve into social, cultural, and environmental determinants, providing rich, narrative insights into the drivers of substance abuse and the effectiveness of various interventions. Quantitative methods were employed in only nine studies (16%), indicating a limited emphasis on statistical measurement and generalisable findings. Mixed methods, combining both qualitative and quantitative approaches, appeared in six studies (11%), suggesting a growing interest in integrative methodologies that capture both depth and breadth.
Additionally, five studies (9%) were categorised as “not applicable,” referring to conceptual and policy-based documents, while one study (1%) did not specify its methodological approach. The qualitative dominance suggests the field is currently more focused on exploration, theory building, and understanding processes (“how” and “why”) rather than definitively establishing causal outcomes (“how much” or “what works best”).
This methodological imbalance has profound implications. The lack of strong quantitative evidence, particularly from controlled trials or large-scale outcome evaluations, severely hinders the ability to attribute reductions in substance abuse directly to specific youth development programmes or to compare their relative effectiveness and cost-efficiency. Consequently, policymakers and funders face significant challenges in identifying which interventions merit broader replication or scaling, as the existing evidence base, while rich in contextual understanding, offers limited proof of measurable impact at scale.
An Overview of Youth Development Measures in the SADC Region
According to SADC’s 2013–2016 Regional Programme, the prevention of drug and alcohol addiction among young people is a top priority in their youth development strategy and policy. This programme includes the establishment of a regional surveillance network called the SADC Epidemiology Network on Drug Use (SENDU). SENDU’s goal is to establish a sentinel surveillance system targeting substance misuse in all member states (United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime [UNODC], 2013). To deal with the growing problem of drug and alcohol abuse among youth, many member states have developed national youth policies and strategic plans. In South Africa, for example, the government has created a National Drug Master Plan, adopting a multi-sectoral approach to combat drug misuse as a prominent health concern in many communities (Department of Social Development, 2019). Non-governmental organisations recognise the fact that adolescents play an important role in preventing drug and alcohol consumption among young people despite minimal resources and no official funding. Their primary job is community outreach to inform young people of the services they provide such as home visiting programmes to help young individuals battling with substance misuse to get back on track (Machethe et al., 2022).
Table 1 summarises the evidence on youth drug and alcohol abuse across seven SADC countries, highlighting both the methods used and the main issues identified. In South Africa (16 studies), the research relies heavily on qualitative and mixed-method designs, pointing to boredom, poverty, and corruption as key drivers of substance misuse among young people. Community- and faith-based interventions, family empowerment, and recreational activities, such as chess and ecological initiatives, have been promoted as preventive strategies (Mulaudzi, 2018; Setlalentoa et al., 2015; Van ZuI, 2013).

Table 1.
Summary of Included Studies and Country Context.
In Botswana (four studies), both quantitative and qualitative approaches were used to explore adolescent drug and alcohol use, with a strong policy focus. National measures, such as the presidential alcohol levy and sales restrictions, have complemented educational campaigns that seek to reshape knowledge, attitudes, and behaviours toward alcohol (Pitso & Obot, 2011; Letamo et al., 2016). The evidence from Zimbabwe (20 studies) shows a sharp rise in substance abuse in urban areas, driven by socio-economic hardship, unemployment, trauma, and depression. Studies also document community responses, including the role of churches, NGOs, and the government’s National Drug Master Plan (Nhapi, 2019; Maraire et al., 2020).
The research from Namibia (two studies) is largely quantitative, highlighting alarmingly high alcohol consumption rates among adolescents, with over 53% of youth aged 13–30 reporting use. The consequences range from risky sexual behaviour to school dropout and legal troubles, with interventions by the Drug Action Group and Horizon Project providing some limited support (Strijdom, 1992; Netope et al., 2023). In Zambia (10 studies), primarily qualitative studies document widespread substance abuse among secondary school learners, linking it to poor academic performance, absenteeism, and dropout. Peer education and counselling appear particularly promising, as peer influence carries more weight among youth than adult authority (Masiye & Ndhlovu, 2015; Zemba, 2022).
The evidence from Eswatini (one study) remains limited but points to the influence of peer culture and cannabis availability in fuelling adolescent drug use (Mhlongo, 2005). Finally, Lesotho (three studies) highlights alcohol abuse as a dominant concern, linked to poor academic outcomes, health challenges, and risky sexual behaviours. The Thaba-Bosiu Centre has emerged as a central institution in addressing these challenges through community workshops and vocational skills programmes (Mofokeng, 2013; Masihleho & Khalanyane, 2009).
Overall, Table 1 reveals that South Africa and Zimbabwe provide the richest qualitative insights, while Botswana and Namibia contribute stronger quantitative prevalence data. Zambia stands out for its innovative peer-led strategies, whereas Eswatini and Lesotho demonstrate significant research gaps. Collectively, the evidence underscores that youth substance abuse in the SADC region is shaped by structural, cultural, and social factors, requiring multi-layered interventions at community, policy, and school levels.
The evidence in Table 2 demonstrates that countries within the SADC have adopted diverse intervention strategies to curb drug and alcohol abuse among young people. In South Africa, interventions have largely been community-oriented, focusing on providing alternatives to boredom, which has been strongly linked with substance misuse in low socio-economic areas. Recreational activities, such as chess, reading, dancing, and ecological recovery initiatives, have been promoted to redirect youth energy into constructive outlets (Van ZuI, 2013). Beyond recreational programmes, religious-based organisations and civil society partnerships have been mobilised to combat substance misuse, highlighting the importance of collective social responsibility in drug prevention (Ndawonde, 2020). Family empowerment programmes, which train parents to nurture children with resilience and self-esteem, further illustrate the recognition that prevention begins within the household (Mudavanhu & Schenck, 2014). Non-governmental organisations (NGOs) also play a central role, particularly in discouraging the sale of alcohol and drugs to underage youth while simultaneously providing youth with life skills through recreational facilities (Department of Social Development, 2013; Ngcobo, 2018).

Table 2.
Summary of Intervention Strategies addressing drug and alcohol abuse in the seven countries.
Botswana’s interventions take a more policy-oriented approach, with the government introducing measures such as the presidential alcohol levy, restrictions on sales, and minimum purchase age requirements. These measures are complemented by extensive informational programmes aimed at reshaping attitudes and knowledge about the risks of alcohol and drug use (Pitso & Obot, 2011; Letamo et al., 2016). In Zimbabwe, strategies have centred on state-led initiatives such as the National Drug Master Plan (2020–2025), supported by law enforcement awareness campaigns in schools and communities (Nhapi, 2019; Maraire et al., 2020). Namibia has relied on a mixture of government and civil society campaigns, including the Drug Action Group (DAG) and Christelike Alkoholiste Diens (CAD), as well as the Horizon Project, run in collaboration with the University of Namibia and the Ministry of Health (Strijdom, 1992).
In Zambia, peer-based strategies have been at the forefront, with peer educators and counsellors being trained to influence their peers positively and delay the onset of drug use (Masiye & Ndhlovu, 2015; Mertens & Wilson, 2012). The Kingdom of Eswatini, meanwhile, has focused on national-level coordination supported by international partners such as the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), while Lesotho has relied on the Thaba-Bosiu Centre, which runs both prevention and treatment programmes, alongside workshops and campaigns that raise awareness of the dangers of substance misuse (Masihleho & Khalanyane, 2009). Collectively, these strategies illustrate a spectrum of approaches, ranging from community-based and peer-led interventions to policy-driven and institutional measures, which demonstrates that no single intervention can be relied upon; rather, a multi-layered strategy is necessary across the region.
The evidence presented in Table 3 shows that, while these interventions have had promising outcomes, their effectiveness has been uneven across the region. In South Africa, community-based programmes that combine recreational opportunities with faith-based and civil society collaboration have shown potential in reducing youth substance misuse, particularly in township contexts where structural disadvantage fuels high rates of abuse (Nyashanu & Visser, 2022; Muthelo et al., 2023). Botswana’s mix of policy restrictions, alcohol levies, and educational campaigns has been relatively successful in shifting knowledge and attitudes around substance use. Letamo et al. (2016) found that these approaches not only improved citizens’ awareness of drug risks but also helped reduce risky alcohol consumption patterns among adolescents.

Table 3.
Summary of Reported Effectiveness of Intervention Strategies used in addressing drug and alcohol abuse in the seven countries.
Zimbabwe’s National Drug Master Plan has also achieved some success, particularly in leveraging law enforcement to deter drug use. Fear of prosecution has dissuaded some youth from substance abuse; however, as Nhapi (2019) and Maraire et al. (2020) point out, relapse remains common after legal sentences are served, reflecting the limits of punitive approaches without sufficient rehabilitative support. In Namibia, targeted interventions by groups such as DAG and the Horizon Project have shown effectiveness in specific areas, but their limited coverage means that broader national impact remains constrained (Netope et al., 2023).
Zambia’s peer education model has been particularly effective in delaying initiation into drug use, as peer role models resonate strongly with young people (Midford et al., 2000; Masiye & Ndhlovu, 2015). Nevertheless, inconsistent coverage and insufficient institutional support hinder the scaling up of this promising intervention. In Eswatini and Lesotho, national and NGO-led programmes have proven valuable in creating awareness and offering treatment opportunities. For example, the Thaba-Bosiu Centre’s alternative livelihood programmes in Lesotho have improved both community awareness and socioeconomic wellbeing among participants (Masihleho & Khalanyane, 2009). Yet, in both countries, the effectiveness of such interventions has been limited by financial constraints and a lack of resources, which restrict expansion and sustainability.
Taken together, the findings in Table 3 underscore that interventions across the SADC region have produced important short-term gains, particularly in raising awareness and reducing initiation into drug use; however, structural challenges such as poverty, unemployment, limited coverage, and weak monitoring frameworks undermine long-term success. These lessons suggest that, while policy restrictions and law enforcement can yield immediate behavioural changes, sustainable reductions in youth substance abuse require stronger investment in community-based programmes, family support systems, peer-led initiatives, and adequate funding to ensure scalability and continuity.
4. Limitation
This review is limited by reliance on secondary sources, which vary in methodological quality and depth of reporting. The exclusion of non-English publications may have omitted relevant local interventions. Additionally, variations in study design and reporting made it difficult to compare intervention effectiveness across countries. A key limitation identified across the included studies is the frequent absence of rigorous outcome evaluation. Many interventions are described in terms of activities and intended goals, without clear measurement of behavioural change, reduction in substance use, or long-term impact. This limits the ability to draw firm conclusions about intervention effectiveness and highlights the need for future research to incorporate robust monitoring and evaluation frameworks.
5. Conclusions
This review demonstrates that all seven Southern African Development Community (SADC) countries examined—South Africa, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Namibia, Zambia, Eswatini, and Lesotho—have implemented a mix of government-led, community-based, and non-governmental youth development interventions to curb substance abuse. While these interventions vary in scope and focus, commonalities include the use of peer education, community outreach, law enforcement partnerships, faith-based support, and recreational programmes. However, effectiveness is often limited by inadequate funding, insufficient trained personnel, and a lack of rigorous outcome evaluation. Strengthening regional cooperation and sharing best practices can enhance the impact of interventions across the SADC region.
The abuse of drugs and alcohol among young people should be prioritised in the SADC to improve youth health and economic development. In order to promote good relationships in families, schools, and youth-focused organisations, a SADC Positive Youth Development (PYD) model is proposed. It must emphasise the importance of early interventions to reduce the risk factors of substance misuse. The PYD model highlights the necessity of long-term youth development strategies to rapidly reduce drug and alcohol usage among young people. Many young people in the SADC region have to deal with unemployment, which drives them to misuse substances as a means of coping. This emphasises the need for the establishment of youth clinics where social workers, psychologists, and youth workers provide mental care in the early phases of substance abuse.
A SADC Youth Service Programme with similar strategies is required to assign unemployed young people to various state-funded non-governmental groups. Its objective must be to raise awareness of the dangers of drug and alcohol abuse. This programme must empower unemployed young people economically by allowing them to earn income through voluntary activities. Finally, these young people must act as ambassadors, persuading their peers to avoid the snare of alcohol and drugs. In this study, we advocate for the establishment of a Drug Youth Café Centre (DYCC) within the SADC region, encompassing the seven countries under discussion in this study. The envisioned DYCC would serve as a dedicated facility where young people can converge to avail themselves of a comprehensive suite of drug education services and emotional support mechanisms facilitated by trained professionals, including youth workers, psychologists, and social workers. This envisioned space is conceived as a platform offering a safe haven for youths grappling with substance misuse, wherein they can not only access vital information but also engage in peer-supported dialogue concerning their personal experiences and the multifaceted challenges encountered in their lives. In the proposed initiative of the DYCC, it is recommended that a comprehensive curriculum be developed to equip young people with essential life skills, including, but not limited to, anger management techniques, strategies for coping with stress, and emotional regulation strategies. By integrating these pivotal components into the educational framework, this initiative aims to mitigate the likelihood of young people resorting to substance abuse, particularly alcohol and illicit drugs, amidst the various challenges they encounter during their formative years.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.A.C. and methodology T.A.C.; software, T.A.C.; validation, N.D.N. and formal analysis N.D.N. and T.A.C.; investigation, N.D.N.; resources, N.D.N.; data curation, T.A.C.; writing—original draft preparation, T.A.C. and N.D.N.; writing—review and editing, T.A.C. and N.D.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the UNISA Language Editing Team for editing our work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Arksey, H., & O’Malley, L. (2005). Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 8(1), 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, K., & Hubbard, D. (2009). Alcohol and youths: Suggestions for law reform. Legal Assistance Centre. [Google Scholar]
- Chauke, T. A. (2023). Responsive measures for youth development to prevent delinquent behaviour among youths not in education, employment or training. Southern African Journal of Social Work and Social Development, 35(2), 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikwanah, E. (2019). Zimbabwe church trains youth leaders to avoid drugs. UM News. Available online: https://www.umnews.org (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Cupido, X. (2017). An exploration of school-based substance-abuse prevention programmes in the Cape metropolitan region [Unpublished master’s thesis, University of the Western Cape]. [Google Scholar]
- Das, J. K., Salam, R. A., Arshad, A., Finkelstein, Y., & Bhutta, Z. A. (2016). Interventions for adolescent substance abuse: An overview of systematic reviews. The Journal of Adolescent Health, 59(4S), 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Department of Social Development. (2013). Substance use, misuse and abuse amongst the youth in Limpopo Province. Department of Social Development. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Social Development. (2019). National drug master plan: 2019 to 2024 South Africa free of substance abuse. Department of Social Development. [Google Scholar]
- Diraditsile, K., & Rasesigo, K. (2018). Substance abuse and mental health effects among the youth in Botswana: Implications for Social Research. Journal of Education, Society and Behavioural Science, 24(2), 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzinamarira, T. R., Mutevere, M., Nyoka, S., Moyo, E., Mkwapatira, M., Murewanhema, G., & Dzinamarira, T. (2023). Illicit substance use among adolescents and youths in Zimbabwe: A stakeholder’s perspective on the enabling factors and potential strategies to address this scourge. International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health, 10(8), 2913–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekpenyong, S. N. (2012). Drug abuse in Nigerian schools: A study of selected secondary institutions in Bayelsa State, South-South, Nigeria. International Journal of Scientific Research in Education, 5(3), 260–268. [Google Scholar]
- Grim, B. J., & Grim, M. E. (2019). Belief, behavior, and belonging: How faith is indispensable in preventing and recovering from substance abuse. Journal of Religion and Health, 58(5), 1713–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, Y., Zilanawala, A., Booker, C., & Sacker, A. (2019). Social media use and adolescent mental health: Findings from the UK Millennium Cohort Study. EClinicalMedicine, 6, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, H. G. (2012). Religion, spirituality, and health: The research and clinical implications. ISRN Psychiatry, 2012, 278730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumuterera, C. (2019, November 6). Church continues to support cyclone Idai victims. UM News. Available online: www.umnews.org (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Letamo, G., Bowelo, M., & Majelantle, R. (2016). Prevalence of substance use, and correlates of multiple substance use among school going adolescents in Botswana. African Journal of Drug and Alcohol Studies, 15(2), 76–89. [Google Scholar]
- Macheka, T., & Masuku, S. (2019). Youth participation structures in Zimbabwe: A lens into the experiences of rural youth within WADCOs and VIDCOs. Centre for Social Science Research, UCT. [Google Scholar]
- Machethe, P., Obioha, E., & Mofokeng, J. (2022). Community-based initiatives in preventing and combatting drug abuse in a South African township. International Journal of Research in Business and Social Science, 11(1), 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaya, E. (2017). An assessment of the impact of e-government on service delivery in Zimbabwe’s public sector. The case of Home Affairs: Department of the Zimbabwe Republic Police from period 2005–2015. Afribary. [Google Scholar]
- Mahiya, I. T. (2016). Urban youth unemployment in the context of a dollarised economy in Zimbabwe. Commonwealth Youth and Development, 14(1), 97–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makande, N. A. (2017). The effectiveness of the Zimbabwe Republic Police Criminal Investigation Department in curbing drug abuse among youths in Zimbabwe: A case of Mbare [Unpublished master’s thesis, Midlands States University]. [Google Scholar]
- Makwanise, N. (2023). The challenges of fighting drug abuse among the youth in Zimbabwe. GNOSI: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Human Theory and Praxis, 6(2), 52–62. [Google Scholar]
- Maraire, T., Chethiyar, S. D. M., & Jasni, M. A. B. (2020). A general review of Zimbabwe’s response to drug and substance abuse among the youth. PEOPLE: International Journal of Social Sciences, 6(2), 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraire, T., Ismail, S. B., & Jasni, M. A. B. (2022). A Christian based drug abuse intervention among Zimbabwean youths: An empirical investigation. Journal of Positive School Psychology, 6(6), 10099–10113. [Google Scholar]
- Masihleho, M. J., & Khalanyane, T. (2009). The impact of Thaba-Bosiu Centre alternative livelihoods programme on alcohol problems: A case study of Ha Mothae. African Journal of Drug and Alcohol Studies, 8(2), 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Masiye, I., & Ndhlovu, D. (2015). Drug and alcohol abuse prevention education in Zambia’s secondary schools: Literature survey. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Development, 2(10), 513–517. Available online: https://www.allsubjectjournal.com/assets/archives/2015/vol2issue10/2-10-69.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2024).[Green Version]
- Matunhu, J., & Matunhu, V. (2016). Drugs and drug control in Zimbabwe. In A. Kalunta-Crumpton (Ed.), Pan-African issues in drugs and drug control (pp. 155–178). Routledge. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matutu, V., & Mususa, D. (2019). Drug and alcohol abuse among young people in zimbabwe: A crisis of morality or public health problem. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3489954 (accessed on 13 July 2024).
- Mertens, D. M., & Wilson, A. T. (2012). Program evaluation theory and practice: Acomprehensive guide. Guilford Press. [Google Scholar]
- Mhlongo, T. (2005). Drug abuse in adolescents in Swaziland [Unpublished dissertation, University of South Africa]. [Google Scholar]
- Midford, R., Lenton, S., & Hancock, L. (2000). A critical review and analysis: Cannabis education in schools. NSW Department of Cutin University of Technology. [Google Scholar]
- Mofokeng, M. (2013, October 7–9). Effects on the family: Destruction behind quenching the thirst [Paper presentation]. Global Alcohol Policy Conference 2013 (GAPC 2013), Seoul, Republic of Korea. [Google Scholar]
- Mphande, F., Kalimaposo, K., Mubita, K., Milupi, I., Mundende, K., Phiri, C., & Daka, H. (2023). Voices of teachers and pupils on school-based alcohol abuse preventive strategies in selected schools of Lusaka, Zambia. Research Studies, 3(5), 932–940. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Mudavanhu, N., & Schenck, R. (2014). Substance abuse amongst the youth in Grabouw Wester Cape: Voices from the Community. Social Work, 50(3), 370–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukwenha, S., Murewanhema, G., Madziva, R., Dzinamarira, T., Herrera, H., & Musuka, G. (2022). Increased illicit substance use among Zimbabwean adolescents and youths during the COVID-19 era: An impending public health disaster. Addiction, 117(4), 1177–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulaudzi, H. (2018). Factors contributing to substance abuse among youth in Atteridgeville, Tshwane Metropolitan, South Africa [Unpublished master’s thesis, University of Venda]. [Google Scholar]
- Muthelo, L., Mbombi, M. O., Mphekgwana, P., Mabila, L. N., Dhau, I., Tlouyamma, J., Nemuramba, R., Mashaba, R. G., Mothapo, K., Ntimana, C. B., & Maimela, E. (2023). Exploring roles of stakeholders in combating substance abuse in the DIMAMO Surveillance Site, South Africa. Substance Abuse: Research and Treatment, 17, 11782218221147498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidoo, P., Mangoma-Chaurura, J., Khan, G., Canham, B., & Malope-Rwodzi, N. (2016). Using sport as an intervention for substance abuse reduction among adolescents and young adults in three selected communities in South Africa: An exploratory study. Human Sciences Research Council. [Google Scholar]
- National Youth Policy. (2021). A decade to accelerate positive youth development. The Presidency of Republic of South Africa. [Google Scholar]
- Ndawonde, S. (2020). Examining substance abuse prevention strategies to combat school violence in Inanda, KZN, South Africa [Unpublished masters’ thesis, University of Kwazulu-Natal]. [Google Scholar]
- Netope, R. N., Nghitanwa, E. M., & Endjala, T. (2023). Investigation of the determinants of alcohol use among women in Oshikoto region, Namibia. Journal of Public Health in Africa, 14(3), 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngcobo, P. (2018). An examination of substance abuse prevention programmes and their impact on minors who are prone to substance abuse in South Africa [Unpublished master’s thesis, University of KwaZulu Natal]. [Google Scholar]
- Nhapi, T. (2019). Drug addiction among youths in Zimbabwe: Social work perspective. In Y. Ndasauka, & G. M. Kayange (Eds.), Addiction in South and East Africa (pp. 241–259). Palgrave Macmillan. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhapi, T., & Mathende, T. (2016). Drug abuse: An out of school adolescent’s survival mechanism in the context of a turbulent economic landscape–some Zimbabwean perspectives. Acta Criminologica, 29(3), 126–139. [Google Scholar]
- Nyashanu, T., & Visser, M. (2022). Treatment barriers among young adults living with a substance use disorder in Tshwane, South Africa. Substance Abuse and Treatment, Prevention, and Policy, 17, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyimbili, F., Mainza, R., Mumba, L., & Kutunansa, B. (2019). Teacher and parental involvement in providing comprehensive sexuality education in selected primary schools of Kalomo district of Zambia. Journal of Adult Education, 1(2), 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, M. J. (2016). Cognitive behavioural therapy for Christian clients with depression: A practical tool-based primer. Templeton Press. [Google Scholar]
- Pitso, J. M. N., & Obot, I. S. (2011). Botswana alcohol policy and the presidential levy controversy. Addiction, 106(5), 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pufall, E. L., Eaton, J. W., Robertson, L., Mushati, P., Nyamukapa, C., & Gregson, S. (2017). Education, substance use, and HIV risk among orphaned adolescents in Eastern Zimbabwe. Vulnerable Children and Youth Studies, 12(4), 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranotsi, A., Makatjane, T., & Aiyuk, S. (2012). The extent of drug abuse in Lesotho: The case of Mapoteng community. Lesotho Medical Association Journal, 10(1), 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Riva, K., Allen-Taylor, L., Schupmann, W. D., Mphele, S., Moshashane, N., & Lowenthal, E. D. (2018). Prevalence and predictors of alcohol and drug use among secondary school students in Botswana: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health, 18(1), 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, O. A., Weir, C., & Aceves-Martins, M. (2021). Substance use prevention interventions for children and young people in Sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review. The International Journal on Drug Policy, 94, 103251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setlalentoa, M., Ryke, E., & Strydom, H. (2015). Intervention strategies used to address alcohol abuse in the North-West province, South Africa. Social Work, 51(1), 80–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibalika, M., & Chileshe, B. (2022). Perceptions of stakeholders on the causes of drug abuse among primary school learners in Shibuyunji District, Zambia. Multidisciplinary Journal of Language and Social Sciences Education, 5(1), 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Strijdom, J. L. (1992). A drug policy and strategy for Namibia [Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University of Bophuthatswana]. [Google Scholar]
- Tomokawa, S., Miyake, K., Akiyama, T., Makino, Y., Nishio, A., Kobayashi, J., Jimba, M., Ayi, I., Njenga, S. M., & Asakura, T. (2020). Effective school-based preventive interventions for alcohol use in Africa: A systematic review. African Health Sciences, 20(3), 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricco, A. C., Lillie, E., Zarin, W., O’Brien, K. K., Colquhoun, H., Levac, D., Moher, D., Peters, M. D. J., Horsley, T., Weeks, L., Hempel, S., Akl, E. A., Chang, C., McGowan, J., Stewart, L., Hartling, L., Aldcroft, A., Wilson, M. G., Garritty, C., Lewin, S., … Straus, S. E. (2018). PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Annals of Internal Medicine, 169(7), 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triolo, M., Bhattacharya, D., & Hood, D. A. (2022). Denervation induces mitochondrial decline and exacerbates lysosome dysfunction in middle-aged mice. Aging, 14(22), 8758–8773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime [UNODC]. (2013). Making the Southern African Development Community (SADC) region safer from crime and drugs regional programme: 2013–2016. United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime [UNODC]. (2018). Drugs and age. Drugs and associated issues among young people and older people. United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime [UNODC]. (2020). Conducting effective substance abuse prevention work among the youth in South Africa. United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. [Google Scholar]
- Van ZuI, A. E. (2013). Drug use amongst South African youths: Reasons and solutions. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 4(14), 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D., Mhlaba, M., Molelekeng, M., Chauke, T. A., Simao, S. C., Jenner, S., Ware, L. J., & Barker, M. (2023). How do we best engage young people in decision-making about their health? A scoping review of deliberative priority setting methods. International Journal for Equity Health, 22(1), 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation (WHO). (2014). World drug report 2014. World Health Organisation. [Google Scholar]
- Zemba, M. (2022). The causes and effects of drug abuse on pupils’ academic performance: A case study of Mindolo secondary school in Kitwe, Zambia. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Analysis, 5(08), 2253–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimonyo, T. (2020). Zimbabwe: Drug abuse-Soul Jah love seeks help. The Herald P1. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).