Impact of Harvest Method on Development of European Sea Bass Skin Microbiome during Chilled Storage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Fish Sampling and Sample Collection
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Amplicon Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
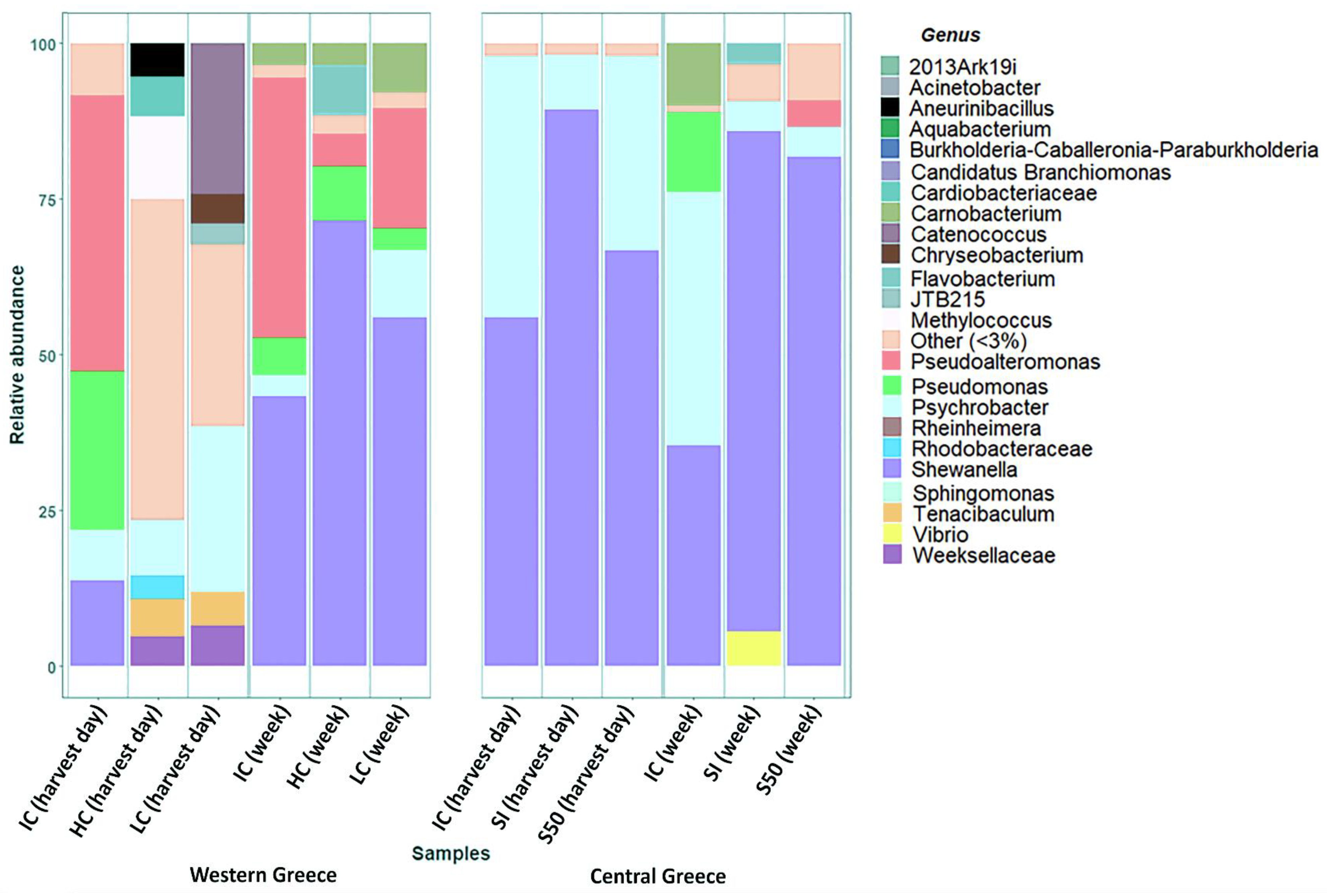
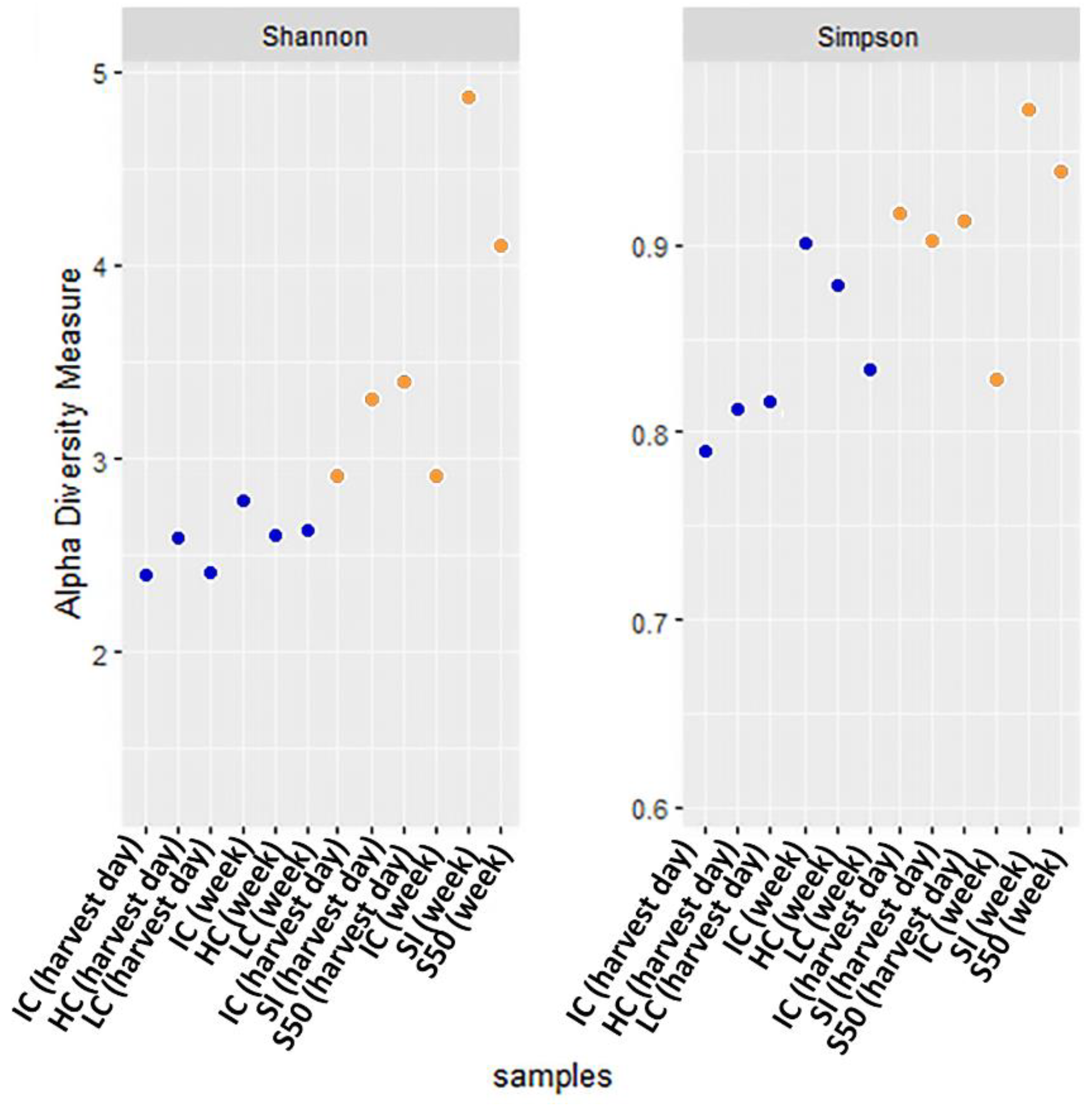
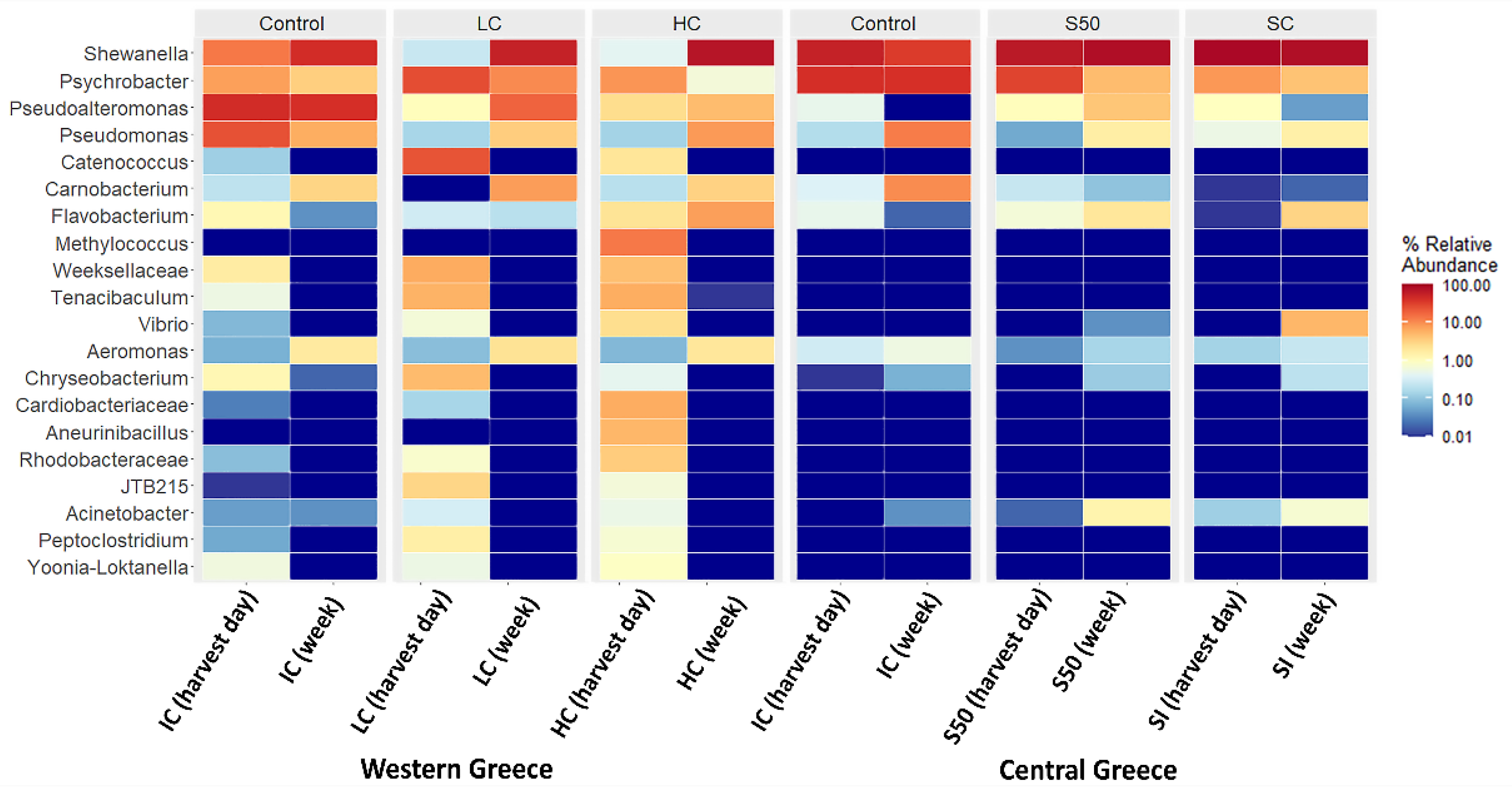
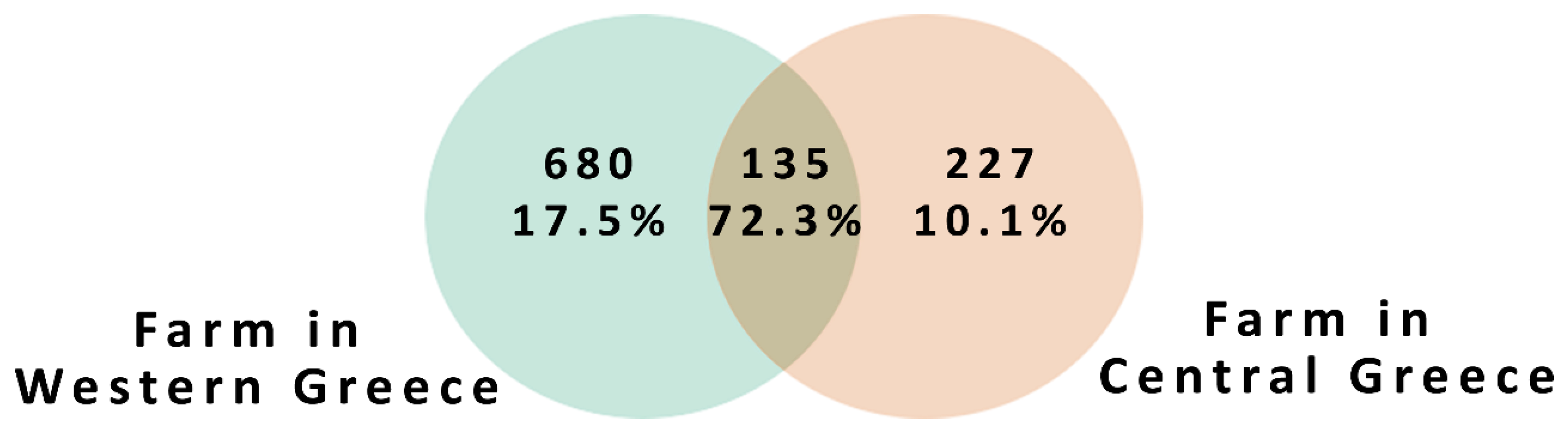
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2018—Meeting the Sustainable Development Goals; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- FAO; IFAD; UNICEF; WFP; WHO. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2023. In Urbanization, Agrifood Systems Transformation and Healthy Diets across the Rural–Urban Continuum; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinola, O.A.; Akinyemi, A.A.; Bolaji, B.O. Evaluation of Traditional and Solar Fish Drying Systems towards Enhancing Fish Storage and Preservation in Nigeria: Abeokuta Local Governments as Case Study. J. Fish. Int. 2006, 1, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Yalch, T.; Lofthouse, J.; Nordhagen, S. Creating Alliances and Fostering Innovations to Reduce Post- Harvest Food Loss: Experiences from GAIN’s Postharvest Loss Alliances for Nutrition; Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition Working Paper #9; Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntzimani, A.; Semenoglou, I.; Dermesonlouoglou, E.; Tsironi, T.; Taoukis, P. Surface Decontamination and Shelf-Life Extension of Gilthead Sea Bream by AlternativeWashing Treatments. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsironi, T.; Anjos, L.; Pinto, P.I.S.; Dimopoulos, G.; Santos, S.; Santa, C.; Manadas, B.; Canario, A.; Taoukis, P.; Power, D. High Pressure Processing of European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Fillets and Tools for Flesh Quality and Shelf Life Monitoring. J. Food Eng. 2019, 262, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, L.; Huss, H.H. Microbiological Spoilage of Fish and Fish Products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 33, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlapani, F.F.; Verdos, G.I.; Haroutounian, S.A.; Boziaris, I.S. The Dynamics of Pseudomonas and Volatilome during the Spoilage of Gutted Sea Bream Stored at 2 °C. Food Control 2015, 55, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivertsvik, M.; Jeksrud, W.K.; Rosnes, J.T. A Review of Modified Atmosphere Packaging of Fish and Fishery Products—Significance of Microbial Growth, Activities and Safety. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 37, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsironi, T.; Ntzimani, A.; Gogou, E.; Tsevdou, M.; Semenoglou, I.; Dermesonlouoglou, E.; Taoukis, P. Modeling the Effect of Active Modified Atmosphere Packaging on the Microbial Stability and Shelf Life of Gutted Sea Bass. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleologos, E.K.; Savvaidis, I.N.; Kontominas, M.G. Biogenic Amines Formation and Its Relation to Microbiological and Sensory Attributes in Ice-Stored Whole, Gutted and Filleted Mediterranean Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Food Microbiol. 2004, 21, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaharisis, L.; Tsironi, T.; Dimitroglou, A.; Taoukis, P.; Pavlidis, M. Stress Assessment, Quality Indicators and Shelf Life of Three Aquaculture Important Marine Fish, in Relation to Harvest Practices, Water Temperature and Slaughter Method. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 2608–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Ma, X.; Xie, J. Review on Natural Preservatives for Extending Fish Shelf Life. Foods 2019, 8, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlapani, F.F.; Mallouchos, A.; Haroutounian, S.A.; Boziaris, I.S. Microbiological Spoilage and Investigation of Volatile Profile during Storage of Sea Bream Fillets under Various Conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 189, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikš-Krajnik, M.; Yoon, Y.J.; Ukuku, D.O.; Yuk, H.G. Volatile Chemical Spoilage Indexes of Raw Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Stored under Aerobic Condition in Relation to Microbiological and Sensory Shelf Lives. Food Microbiol. 2016, 53, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalgaard, P.; Mejlholm, O.; Christiansen, T.J.; Huss, H.H. Importance of Photobacterium Phosphoreum in Relation to Spoilage of Modified Atmosphere-Packed Fish Products. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 24, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, L.; Dalgaard, P. Fish Spoilage Bacteria—Problems and Solutions. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokou, F.; Sasson, G.; Nitzan, T.; Doron-Faigenboim, A.; Harpaz, S.; Cnaani, A.; Mizrahi, I. Host Genetic Selection for Cold Tolerance Shapes Microbiome Composition and Modulates Its Response to Temperature. Elife 2018, 7, e36398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.; Coelho, F.J.R.C.; Cleary, D.F.R.; Pires, A.C.C.; Marques, B.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Quintino, V.; Gomes, N.C.M. Seasonal Patterns of Bacterioplankton Composition in a Semi-Intensive European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Aquaculture System. Aquaculture 2018, 490, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, L.N.; Coelho, F.J.R.C.; Cleary, D.F.R.; Bonifácio, D.; Martins, P.; Gomes, N.C.M. Bacterial and Microeukaryotic Plankton Communities in a Semi-Intensive Aquaculture System of Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax): A Seasonal Survey. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minich, J.J.; Petrus, S.; Michael, J.D.; Michael, T.P.; Knight, R.; Allen, E.E. Temporal, Environmental, and Biological Drivers of the Mucosal Microbiome in a Wild Marine Fish, Scomber Japonicus. mSphere 2020, 5, e00401-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, S.; Bernatchez, L.; Audet, C.; Derôme, N. Network Analysis Highlights Complex Interactions between Pathogen, Host and Commensal Microbiota. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, R.; Severino, R.; Silva, S.M. Signatures of Dysbiosis in Fish Microbiomes in the Context of Aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2024, 16, 706–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FEAP. European Aquaculture Production Report; FEAP: Brussels, Belgium, 2014; Available online: https://feap.info/ (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- HAPO. Annual Report: Aquaculture in Greece. 2023. Available online: https://fishfromgreece.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/HAPO_AR23_WEB-NEW.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Jobling, M.M.A. Pavlidis and C. C. Mylonas (Eds): Sparidae: Biology and Aquaculture of Gilthead Sea Bream and Other Species. Aquac. Int. 2011, 19, 809–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rosado, D.; Xavier, R.; Severino, R.; Tavares, F.; Cable, J.; Pérez-Losada, M. Effects of Disease, Antibiotic Treatment and Recovery Trajectory on the Microbiome of Farmed Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosado, D.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Severino, R.; Cable, J.; Xavier, R. Characterization of the Skin and Gill Microbiomes of the Farmed Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and Seabream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture 2019, 500, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafpour, B.; Pinto, P.I.S.; Sanz, E.C.; Martinez-Blanch, J.F.; Canario, A.V.M.; Moutou, K.A.; Power, D.M. Core Microbiome Profiles and Their Modification by Environmental, Biological, and Rearing Factors in Aquaculture Hatcheries. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 193, 115218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntzimani, A.; Angelakopoulos, R.; Semenoglou, I.; Dermesonlouoglou, E.; Tsironi, T.; Moutou, K.; Taoukis, P. Slurry Ice as an Alternative Cooling Medium for Fish Harvesting and Transportation: Study of the Effect on Seabass Flesh Quality and Shelf Life. Aquac. Fish. 2023, 8, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntzimani, A.; Angelakopoulos, R.; Stavropoulou, N.; Semenoglou, I.; Dermesonlouoglou, E.; Tsironi, T.; Moutou, K.; Taoukis, P. Seasonal Pattern of the Effect of Slurry Ice during Catching and Transportation on Quality and Shelf Life of Gilthead Sea Bream. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakopoulos, R.; Dimitroglou, A.; Papaharisis, L.; Moutou, K.A. Electrical Stunning Has the Potential to Delay Fillet Degradation Post-Harvest in Red Seabream (Pagrus major). Aquac. J. 2022, 2, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelino, M.; Eyre, S.; Moat, J.; Fox, G.; Martin, P.; Ho, P.; Upton, M.; Barton, A. Optimisation of Methods for Bacterial Skin Microbiome Investigation: Primer Selection and Comparison of the 454 versus MiSeq Platform. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of RRNA Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA and “All-Species Living Tree Project (LTP)” Taxonomic Frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D643–D648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R. RStudio; PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2020; Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 13 October 2024).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 13 October 2024).
- Sehnal, L.; Brammer-Robbins, E.; Wormington, A.M.; Blaha, L.; Bisesi, J.; Larkin, I.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Simonin, M.; Adamovsky, O. Microbiome Composition and Function in Aquatic Vertebrates: Small Organisms Making Big Impacts on Aquatic Animal Health. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 567408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parlapani, F.F. Microbial Diversity of Seafood. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 37, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itay, P.; Shemesh, E.; Ofek-Lalzar, M.; Davidovich, N.; Kroin, Y.; Zrihan, S.; Stern, N.; Diamant, A.; Wosnick, N.; Meron, D.; et al. An Insight into Gill Microbiome of Eastern Mediterranean Wild Fish by Applying next Generation Sequencing. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, L.; Melchiorsen, J. Interaction between Fish Spoilage Bacteria Pseudomonas Sp. and Shewanella Putrefaciens in Fish Extracts and on Fish Tissue. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1996, 80, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serda, M.; Becker, F.G.; Cleary, M.; Team, R.M.; Holtermann, H.; The, D.; Agenda, N.; Science, P.; Sk, S.K.; Hinnebusch, R.; et al. Isolation of Shewanella Putrefaciens from Cultured European Sea Bass, (Dicentrarchus labrax) In Turkey. Rev. Med. Vet. 2009, 160, 343–354. [Google Scholar]
- Tryfinopoulou, P.; Tsakalidou, E.; Vancanneyt, M.; Hoste, B.; Swings, J.; Nychas, G.J.E. Diversity of Shewanella Population in Fish Sparus Aurata Harvested in the Aegean Sea. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Syropoulou, F.; Anagnostopoulos, D.A.; Parlapani, F.F.; Karamani, E.; Stamatiou, A.; Tzokas, K.; Nychas, G.J.E.; Boziaris, I.S. Microbiota Succession of Whole and Filleted European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) during Storage under Aerobic and MAP Conditions via 16S RRNA Gene High-Throughput Sequencing Approach. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, D.A.; Syropoulou, F.; Parlapani, F.F.; Tsiartsafis, A.; Exadactylos, A.; Nychas, G.J.E.; Boziaris, I.S. Microbiota Profile of Filleted Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata) during Storage at Various Conditions by 16S RRNA Metabarcoding Analysis. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlapani, F.F.; Michailidou, S.; Pasentsis, K.; Argiriou, A.; Krey, G.; Boziaris, I.S. A Meta-Barcoding Approach to Assess and Compare the Storage Temperature-Dependent Bacterial Diversity of Gilt-Head Sea Bream (Sparus Aurata) Originating from Fish Farms from Two Geographically Distinct Areas of Greece. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 278, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosado, D.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Severino, R.; Xavier, R. Monitoring Infection and Antibiotic Treatment in the Skin Microbiota of Farmed European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Fingerlings. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 83, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas Baldi, S.C.; Parisi, G.; Bonelli, A.; Balieiro, J.C.C.; Lapa Guimarães, J.; Macedo Viegas, E.M. Effects of Different Stunning/Slaughter Methods on Frozen Fillets Quality of Cobia (Rachycentron canadum). Aquaculture 2018, 486, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverter, M.; Tapissier-Bontemps, N.; Lecchini, D.; Banaigs, B.; Sasal, P. Biological and Ecological Roles of External Fish Mucus: A Review. Fishes 2018, 3, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Nan, J.; Zu, Y.; Chen, F.; Liang, B.; Wang, A. Molecular Insights into the Response of Nonelectroactive Bacteria to Electro-Stimulation: Growth and Metabolism Regulation Mechanism. ACS ES T Eng. 2024, 4, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, A.; Erdemli, U.; Karakaya, M.; Yilmaz, M. Effects of Slaughter Methods on Physical, Biochemical and Microbiological Quality of Rainbow Trout Oncorhynchus Mykiss and Mirror Carp Cyprinus Carpio Filleted in Pre-, in- or Post-Rigor Periods. Fish. Sci. 2008, 74, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterniša, M.; Mraz, J.; Smole Možina, S. Microbiological Aspects of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) and Its Processing—Relevance for Final Product Quality: A Review. Aquac. Int. 2016, 24, 1569–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morzel, M.; Sohier, D.; Van De Vis, H. Evaluation of Slaughtering Methods for Turbot with Respect to Animal Welfare and Flesh Quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2003, 83, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Wang, L.; Sagada, G.; Tegomo, A.F.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, L.; Ullah, S.; et al. Evaluation of Methanotroph (Methylococcus capsulatus, Bath) Bacteria Meal (FeedKind®) as an Alternative Protein Source for Juvenile Black Sea Bream, Acanthopagrus Schlegelii. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 778301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlapani, F.F.; Boziaris, I.S.; Meziti, A.; Michailidou, S.; Haroutounian, S.A.; Argiriou, A.; Karapanagiotidis, I.T. Microbiological Status Based on 454-Pyrosequencing and Volatilome Analysis of Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata) Fed on Diets with Hydrolyzed Feather Meal and Poultry by-Product Meal as Fishmeal Replacers. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1409–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boziaris, I.S.; Parlapani, F.F. Specific Spoilage Organisms (SSOs) in Fish. In The Microbiological Quality of Food: Foodborne Spoilers; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; pp. 61–98. [Google Scholar]
- Parlapani, F.F.; Michailidou, S.; Anagnostopoulos, D.A.; Koromilas, S.; Kios, K.; Pasentsis, K.; Psomopoulos, F.; Argiriou, A.; Haroutounian, S.A.; Boziaris, I.S. Bacterial Communities and Potential Spoilage Markers of Whole Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus) Stored under Commercial Simulated Conditions. Food Microbiol. 2019, 82, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuuliala, L.; Al Hage, Y.; Ioannidis, A.G.; Sader, M.; Kerckhof, F.M.; Vanderroost, M.; Boon, N.; De Baets, B.; De Meulenaer, B.; Ragaert, P.; et al. Microbiological, Chemical and Sensory Spoilage Analysis of Raw Atlantic Cod (Gadus morhua) Stored under Modified Atmospheres. Food Microbiol. 2018, 70, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Geography | Day | Harvest Method | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | Read Utilization Ratio (%) | Reads Used for the Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Western Greece | Harvest day | IC | 176,766 | 168,490 | 95.32 | 142,586 |
| Harvest day | HC | 175,402 | 166,942 | 95.18 | 139,064 | |
| Harvest day | LC | 173,644 | 166,446 | 95.85 | 141,201 | |
| One week post-harvest | IC | 173,172 | 165,802 | 95.74 | 143,016 | |
| One week post-harvest | HC | 174,944 | 166,382 | 95.11 | 151,340 | |
| One week post-harvest | LC | 172,094 | 164,598 | 95.64 | 149,879 | |
| Central Greece | Harvest day | IC | 170,766 | 164,996 | 96.62 | 138,704 |
| Harvest day | SI | 171,372 | 165,294 | 96.45 | 150,699 | |
| Harvest day | S50 | 170,882 | 165,224 | 96.69 | 145,253 | |
| One week post-harvest | IC | 171,926 | 166,166 | 96.65 | 148,649 | |
| One week post-harvest | SI | 173,442 | 166,488 | 95.99 | 145,874 | |
| One week post-harvest | S50 | 173,162 | 166,780 | 96.31 | 144,691 |
| Genus | Western Greece | Central Greece | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harvest Day | One Week Post-Harvest | Harvest Day | One Week Post-Harvest | |||||||||
| IC | HC | LC | IC | HC | LC | IC | SI | S50 | IC | SI | S50 | |
| Shewanella | 13.73% | 0.44% | 0.26% | 43.63% | 72.61% | 56.44% | 55.81% | 89.48% | 67.13% | 34.89% | 81.27% | 82.03% |
| Psychrobacter | 7.82% | 9.07% | 26.64% | 3.47% | 0.66% | 10.62% | 42.15% | 8.69% | 30.60% | 40.73% | 4.33% | 4.89% |
| Pseudomonas | 25.05% | 0.14% | 0.15% | 6.32% | 8.48% | 3.58% | 0.18% | 0.54% | 0.06% | 12.93% | 1.57% | 1.67% |
| Flavobacterium | 1.24% | 2.25% | 0.30% | 0.04% | 7.84% | 0.20% | 0.49% | 0.01% | 0.67% | 0.02% | 3.13% | 2.04% |
| Other | 52.09% | 88.02% | 72.56% | 44.70% | 8.40% | 26.89% | 1.07% | 1.14% | 1.50% | 10.86% | 9.45% | 9.22% |
| Phylum | Western Greece | Central Greece | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harvest Day | One Week Post-Harvest | Harvest Day | One Week Post-Harvest | |||||||||
| IC | HC | LC | IC | HC | LC | IC | SI | S50 | IC | SI | S50 | |
| Proteobacteria | 96.73% | 88.63% | 91.68% | 98.93% | 99.97% | 98.90% | 89.18% | 95.19% | 95.83% | 92.81% | 63.70% | 65.11% |
| Bacteroidota | 0.06% | 7.85% | 0.20% | 0.50% | 0.01% | 0.67% | 0.09% | 3.43% | 2.24% | 5.23% | 19.97% | 23.73% |
| Firmicutes | 3.18% | 3.46% | 8.11% | 0.57% | 0.01% | 0.43% | 10.68% | 0.84% | 1.41% | 0.91% | 9.67% | 7.38% |
| Other | 0.03% | 0.06% | 0.01% | 0.00% | 0.01% | 0.00% | 0.05% | 0.54% | 0.52% | 1.05% | 6.66% | 3.78% |
| Genus | Harvest Day | |
|---|---|---|
| IC | ||
| Western Greece | Central Greece | |
| Shewanella | 13.73% | 55.81% |
| Psychrobacter | 7.82% | 42.15% |
| Pseudoalteromonas | 44.46% | 0.49% |
| Pseudomonas | 25.05% | 0.18% |
| Aeromonas | 8.94% | 1.37% |
| Genus | Central Greece | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC | SI | S50 | ||||
| Harvest Day | One Week Post-Harvest | Harvest Day | One Week Post-Harvest | Harvest Day | One Week Post-Harvest | |
| Shewanella | 55.81% | 34.89% | 89.48% | 81.27% | 67.13% | 82.03% |
| Psychrobacter | 42.15% | 40.73% | 8.69% | 4.33% | 30.60% | 4.89% |
| Pseudoalteromonas | 0.49% | 0.00% | 0.99% | 0.05% | 1.05% | 4.05% |
| Pseudomonas | 0.18% | 12.93% | 0.54% | 1.57% | 0.06% | 1.67% |
| Carnobacterium | 0.38% | 10.45% | 0.01% | 0.02% | 0.25% | 0.10% |
| Flavobacterium | 0.49% | 0.02% | 0.01% | 3.13% | 0.67% | 2.04% |
| Vibrio | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 5.34% | 0.00% | 0.04% |
| Other | 0.50% | 0.98% | 0.28% | 4.29% | 0.24% | 5.18% |
| Genus | Western Greece | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC | LC | HC | ||||
| Harvest Day | One Week Post-Harvest | Harvest Day | One Week Post-Harvest | Harvest Day | One Week Post-Harvest | |
| Shewanella | 13.73% | 43.63% | 0.26% | 56.44% | 0.44% | 72.61% |
| Psychrobacter | 7.82% | 3.47% | 26.64% | 10.62% | 9.07% | 0.66% |
| Pseudoalteromonas | 44.46% | 41.41% | 1.07% | 18.72% | 2.62% | 4.85% |
| Pseudomonas | 25.05% | 6.32% | 0.15% | 3.58% | 0.14% | 8.48% |
| Catenococcus | 0.13% | 0.00% | 23.96% | 0.00% | 2.09% | 0.00% |
| Carnobacterium | 0.22% | 3.08% | 0.00% | 8.10% | 0.20% | 3.26% |
| Flavobacterium | 1.24% | 0.04% | 0.30% | 0.20% | 2.25% | 7.84% |
| Methylococcus | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 13.64% | 0.00% |
| Weeksellaceae | 1.73% | 0.00% | 6.47% | 0.00% | 4.62% | 0.00% |
| Tenacibaculum | 0.56% | 0.00% | 5.73% | 0.00% | 6.29% | 0.01% |
| Vibrio | 0.08% | 0.00% | 0.67% | 0.00% | 2.55% | 0.00% |
| Aeromonas | 0.07% | 1.84% | 0.09% | 2.27% | 0.08% | 2.01% |
| Other | 4.91% | 0.21% | 34.66% | 0.07% | 56.01% | 0.28% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angelakopoulos, R.; Tsipourlianos, A.; Fytsili, A.E.; Giannoulis, T.; Moutou, K.A. Impact of Harvest Method on Development of European Sea Bass Skin Microbiome during Chilled Storage. Aquac. J. 2024, 4, 270-282. https://doi.org/10.3390/aquacj4040020
Angelakopoulos R, Tsipourlianos A, Fytsili AE, Giannoulis T, Moutou KA. Impact of Harvest Method on Development of European Sea Bass Skin Microbiome during Chilled Storage. Aquaculture Journal. 2024; 4(4):270-282. https://doi.org/10.3390/aquacj4040020
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngelakopoulos, Rafael, Andreas Tsipourlianos, Alexia E. Fytsili, Themistoklis Giannoulis, and Katerina A. Moutou. 2024. "Impact of Harvest Method on Development of European Sea Bass Skin Microbiome during Chilled Storage" Aquaculture Journal 4, no. 4: 270-282. https://doi.org/10.3390/aquacj4040020
APA StyleAngelakopoulos, R., Tsipourlianos, A., Fytsili, A. E., Giannoulis, T., & Moutou, K. A. (2024). Impact of Harvest Method on Development of European Sea Bass Skin Microbiome during Chilled Storage. Aquaculture Journal, 4(4), 270-282. https://doi.org/10.3390/aquacj4040020





