Comparative Analysis of the Culture of Pink Shrimp Farfantepenaeus brasiliensis and Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei in Biofloc System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Origin of Shrimps
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Biofloc Formation
2.5. Water Quality Management
2.6. Zootechnical Performance
2.7. Structure Analysis of the Maxillipeds
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
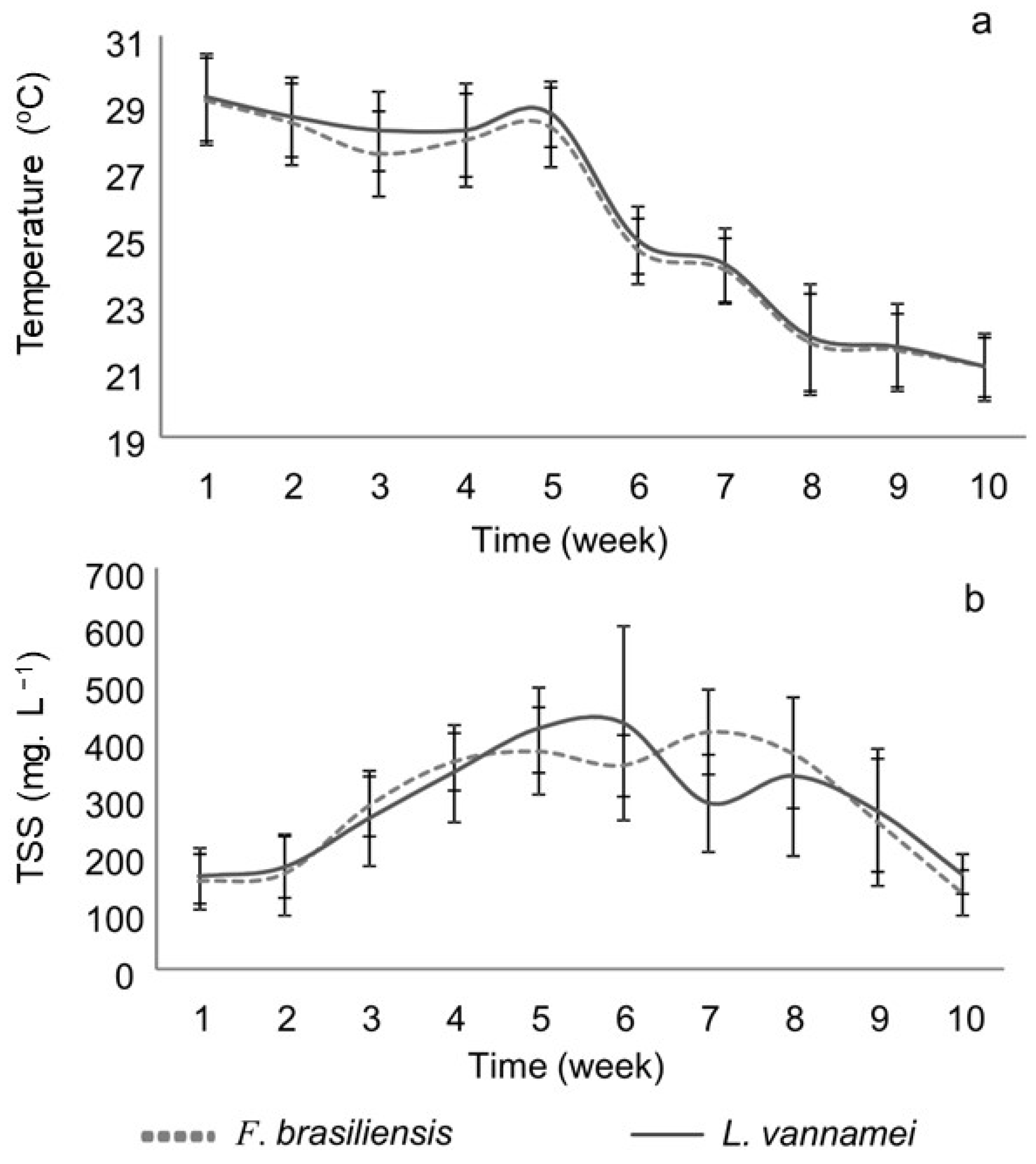
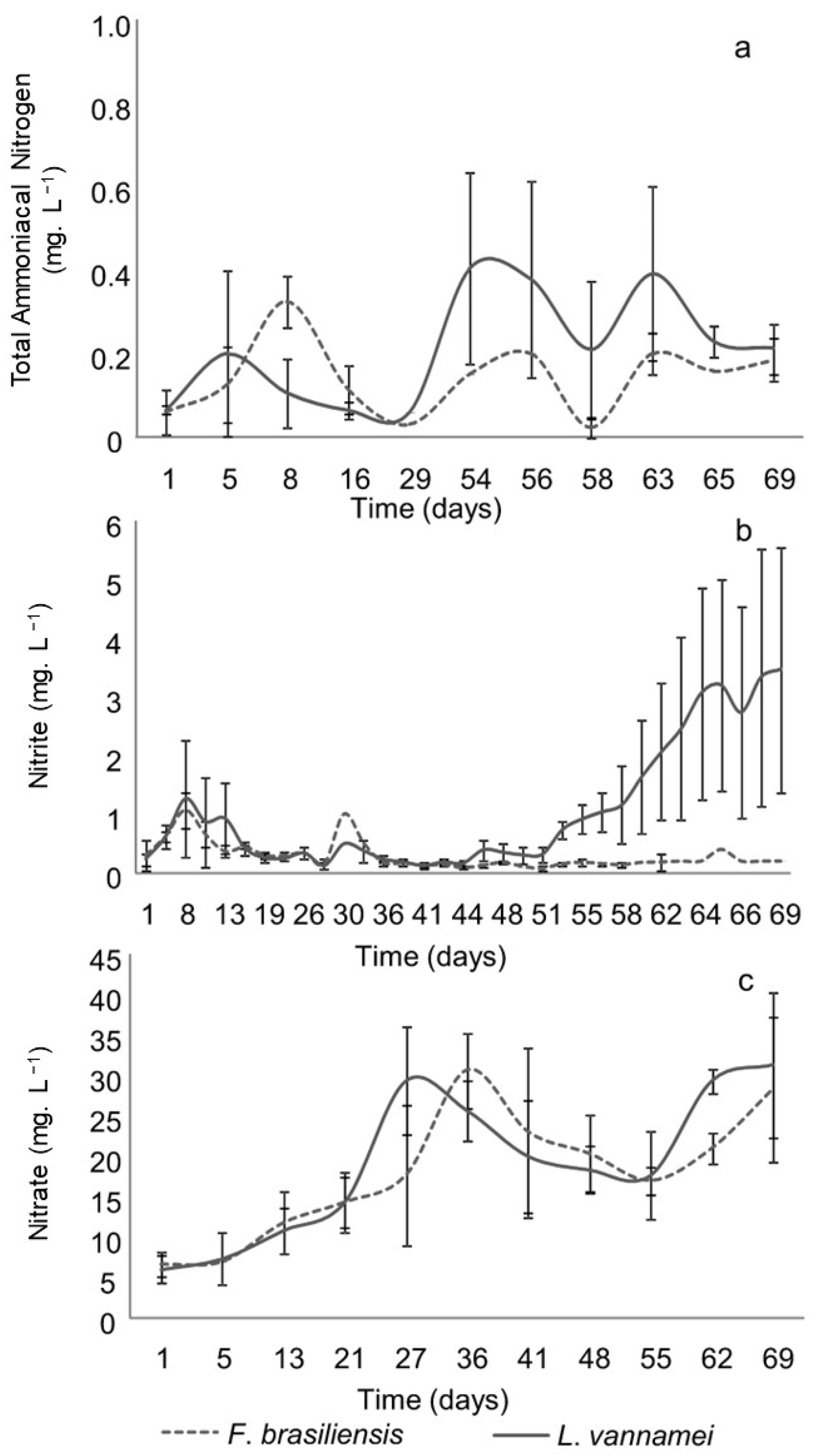
3.1. Water Quality
3.2. Structure Analysis of the Maxillipeds
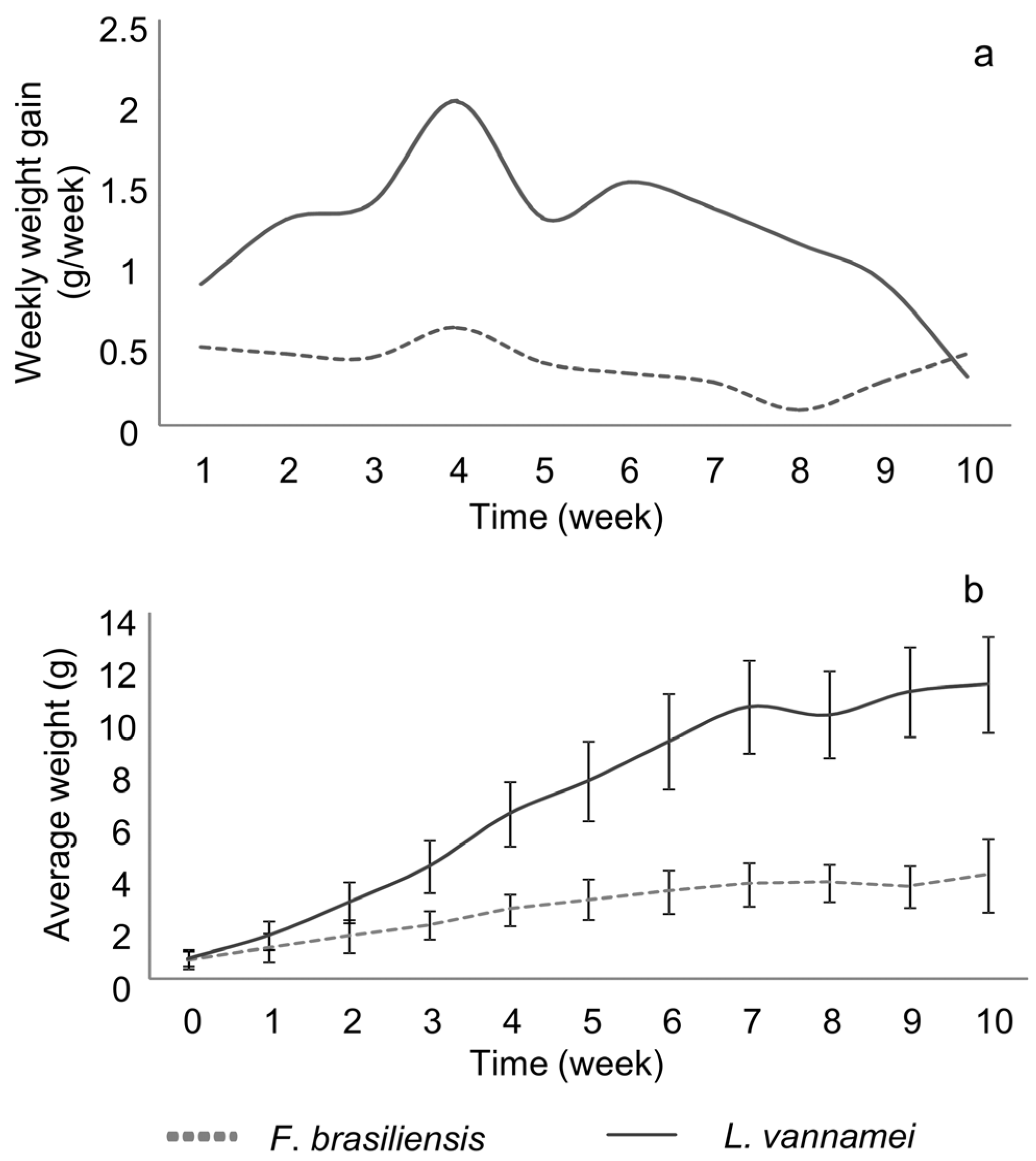
3.3. Zootechnical Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022—Towards Blue Transformation; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, R.C., Jr.; Neto, A.O. Camarões Marinhos: Reprodução, Maturação e Larvicultura; Aprenda Fácil: Viçosa, Brazil, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, I.C.; Chien, Y. The Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, in Asia: The World’s Most Widely Cultured Alien Crustacean. In The Wrong Place—Alien Marine Crustaceans: Distribution, Biology and Impacts, 1st ed.; Galil, B., Clark PC, J., Eds.; Invading Nature; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 489–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchiori, M.A. Guia Ilustrado de Maturação e Larvicultura do Camarão-Rosa Penaeus Paulensis Pérez-Farfante; Editora da FURG: Rio Grande, Brazil, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Roubach, R.; Correia, E.; Zaiden, S.; Martino, R.; Cavalli, R.O. Aquaculture in Brazil; World Aquaculture Society: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2003; Volume 34, pp. 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Worms Editorial Board. World Register of Marine Species. Worms Editorial Board. 2021. Available online: http://www.marinespecies.org (accessed on 14 October 2020).
- Lopes, D.L.d.A.; Ballester, E.L.C.; Wasielesky, W., Jr.; Peixoto, S.R.M. Avaliação da performance Reprodutiva de Fêmeas Selvagens do Camarão-Rosa Farfantepenaeus brasiliensis (Crustácea: Decapoda) em Laboratório. Atlântica 2010, 32, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poersch, L.; Cavalli, R.O.; Wasielesky, W.; Castello, J.P.; Peixoto, S.R.M. Perspectivas para o desenvolvimento dos cultivos de camarões marinhos no estuário da Lagoa dos Patos, RS. Cienc. Rural. 2006, 36, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Incao, F. Subordem Dendrobranchiata (camarões marinhos). In Crustaceos do Rio Grande do Sul, 1st ed.; Buckup, L., Bond-Buckup, G., Eds.; Editora da FURG: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 1999; pp. 229–275. [Google Scholar]
- Dias-Neto, J.; Dias J de, F.O. O Uso da Biodiversidade Aquática no Brasil: Uma Avaliação Com Foco na Pesca; IBAMA: Brasilia, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, D.L.d.A.; Wasielesky, W., Jr.; Ballester, E.L.C.; Peixoto, S.R.M. Análise comparativa da criação dos camarões-rosa Farfantepenaeus brasiliensis e Farfantepenaeus paulensis criados em gaiolas em ambiente estuarino. Ciência Rural 2009, 39, 1540–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, M.; Thirumurthy, S.; Muralidhar, M.; Ravichandran, P. Impact of shrimp aquaculture development on important ecosystems in India. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2018, 52, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslun, J.; Correia, E.S.; Strychar, K.; Morris, T.C.; Samocha, T.M. Characterization of Bioflocs in a No Water Exchange Super-intensive System for production of Food Size Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Int. J. Aquac. 2012, 2, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Avnimelech, Y. Carbon/nitrogen ratio as a control element in aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 1999, 176, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnimelech, Y. Biofloc Technology: A Practical Guide Book; The World Aquaculture Society: Sorrento, LA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Brandão, H.; Xavier, Í.V.; Santana, G.K.K.; Santana, H.J.K.; Krummenauer, D.; Wasielesky, W. Heterotrophic versus mixed BFT system: Impacts on water use, suspended solids production and growth performance of Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Eng. 2021, 95, 102194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, W.G.; Wasielesky, W.; Abreu, P.C.; Brandão, H.; Krummenauer, D. Rearing of the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) in BFT system with different photoperiods: Effects on the microbial community, water quality, and zootechnical performance. Aquaculture 2019, 508, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.J.; Pan, L.Q. Effects of bioflocs on growth performance, digestive enzyme activity and body composition of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei in zero-water exchange tanks manipulating C/N ratio in feed. Aquaculture 2012, 356–357, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, M.A.; Thompson, P.J.; Mcintosh, R.P.; Bauman, R.H.; Pearson, D.C. The contribution of flocculated material to shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) nutrition in a high-intensity, zero-exchange system. Aquaculture 2004, 232, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasielesky, W.; Atwood, H.; Stokes, A.; Browdy, C.L. Effect of Natural Production in a Zero Exchange Suspended Microbial Floc-Based Super-Intensive Culture System for White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krummenauer, D.; Abreu, P.C.; Poersch, L.; Reis, P.A.C.P.; Suita, S.M.; dos Reis, W.G.; Wasielesky, W. The relationship between shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) size and biofloc consumption determined by the stable isotope technique. Aquaculture 2020, 529, 735635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, F.L.; Abreu, P.C.; Cavalli, R.O. The use of microorganisms as a food source for Penaeus paulensis larvae. Aquaculture 1999, 174, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, C.K.; Wasielesky, W., Jr.; Abreu, P.C. The use of protozoan, rotifers and nematodes as live food for shrimp raised in BFT system. Atlântica 2012, 34, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Cordova, L.R.; Emerenciano, M.; Miranda-Baeza, A.; Martínez-Porchas, M. Microbial-based Systems for Aquaculture of Fish and Shrimp: An Updated Review. Rev. Aquac. 2014, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaña-Gallegos, E.; González-Zúñiga, R.; Cuzon, G.; Arevalo, M.; Pacheco, E.; Valenzuela, M.A.J.; Gaxiola, G.; Chan-Vivas, E.; López-Aguiar, K.; Noreña-Barroso, E. Nutritional Contribution of Biofloc within the Diet of Growout and Broodstock of Litopenaeus vannamei, Determined by Stable Isotopes and Fatty Acids. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2018, 49, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suita, S.M.; Braga, A.; Ballester, E.; Cardozo, A.; Abreu, P.C.; Wasielesky, W., Jr. Contribution of bioflocs to the culture of Litopenaeus vannamei post-larvae determined using stable isotopes. Aquac. Int. 2016, 24, 1473–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerenciano, M.; Ballester, E.L.C.; Cavalli, R.O.; Wasielesky, W. Biofloc technology application as a food source in a limited water exchange nursery system for pink shrimp Farfantepenaeus brasiliensis (Latreille, 1817). Aquac. Res. 2012, 43, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostins, B.; Braga, A.; Lopes, D.L.A.; Wasielesky, W.; Poersch, L.H. Effect of temperature on nursery and compensatory growth of pink shrimp Farfantepenaeus brasiliensis reared in a super-intensive biofloc system. Aquac. Eng. 2015, 66, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, D.L.d.A.; Suita, S.M.; Bueno, C.; Wasielesky, W., Jr.; Poersch, L. Determinação da densidade de estocagem ótima do camarão rosa Farfantepenaeus brasiliensis produzido em tecnologia de bioflocos durante a fase de berçário. Atlântica 2012, 34, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jory, D.E.; Cabrera, T.R.; Dugger, D.M.; Fegan, D.; Lee, P.G.; Lawrence, A.L.; Jackson, R.P.; McIntosh, R.P.; Castaneda, J. A global review of shrimp feed management: Status and perspectives. In The New Wave: Proceedings of the Special Session on Sustainable Shrimp Culture, Aquaculture; Browdy, C.L., Jory, D.E., Eds.; The World Aquaculture Society: Sorrento, LA, USA, 2001; pp. 104–152. [Google Scholar]
- Krummenauer, D.; Samocha, T.; Poersch, L.; Lara, G.; Wasielesky, W. The reuse of water on the culture of Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, in BFT system. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2014, 45, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeling, J.M.; Timmons, M.B.; Bisogni, J.J. Engineering analysis of the stoichiometry of photoautotrophic, autotrophic, and heterotrophic removal of ammonia-nitrogen in aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 2006, 257, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wyk, P.; Scarpa, J. Water Quality Requirements and Management. In Farming Marine Shrimp in Recirculating Fresh Water Systems; Van Wyk, P., Hodgkins-Davis, M., Laramore, R., Main, K.L., Mountain, J., Scarpa, J., Eds.; Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institution: Fort Pierce, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Furtado, P.S.; Gaona CA, P.; Poersch, L.H.; Wasielesky, W., Jr. Application of Different Doses of Calcium Hydroxide in the Farming Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei with the Biofloc Technology (BFT). Aquac. Int. 2014, 22, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, J.D.H.; Parsons, T.R. A Practical Handbook of Seawater Analysis. In Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Supply and Services Canada, 1st ed.; Fisheries Research Board of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminot, A.E.; Chaussepied, M. Manuel des Analyses Chimiques en Milieu Marin; CNEXO: Brest, France; Paris, France, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- APHA American Public Health Association; AWWA American Water Works Association; WEF Water Enviroment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gaona, C.A.P.; Almeida, M.S.; De Viau, V.; Poersch, L.; Wasielesky, W., Jr. Effect of different total suspended solids levels on a Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) BFT culture system during biofloc formation. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 1070–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.; Chen, S. Performance evaluation of radial/vertical flow clarification applied to recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 34, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaona, C.A.P.; Poersch, L.H.; Krummenauer, D.; Foes, G.K.; Wasielesky, W., Jr. The Effect of Solids Removal on Water Quality, Growth and Survival of Litopenaeus vannamei in a Biofloc Technology Culture System. Int. J. Recirc. Aquac. 2011, 12, 54–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, A.; Cleserci, L.; Greeberg, A. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste Water, 10th ed.; Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- de Castro, L.A.S. Processamento de Amostras para Microscopia Eletrônica de Varredura; Embrapa Clima Temperado: Pelotas, Brazil, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zar, J. Biostatistical Analysis, 5th ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.N.; Wang, A.L.; Liu, Y.; Xiu, J.; Liu, Z.B.; Sun, R.Y. Effects of temperature on growth, adenosine phosphates, ATPase and cellular defense response of juvenile shrimp Macrobrachium nipponense. Aquaculture 2006, 256, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.J.; Neill, W.H.; Lawrence, A.L.; Gatlin, D.M. Effects of temperature and starvation on ecophysiological performance of the Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquaculture 2011, 319, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuñiga, O.; Ramos, R.; Wilson, P.; Lión, M. Introducción, aclimatación y crecimiento de los camarones Penaeus vannamei e Penaeus stylirostris en el norte de Chile. Estud. Ocean. 1988, 7, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Ponce-Palafox, J.; Martinez-Palacios, C.A.; Ross, L.G. The Effects of Salinity and Temperature on the Growth and Survival Rates of Juvenile White Shrimp, Penaeus vannamei, (Boone, 1931). Aquaculture 1997, 157, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasielesky, W., Jr.; Jensen, L.; Cavalli, R.O.; Peixoto SR, M.; Santos MH, S.; Poersch, L.H. A qualidade da água em um cultivo de Farfantepenaeus paulensis em cercado no estuário da Lagoa dos Patos. In Cultiivo de Camarões em Gaiolas e Cercados No Estuário Da Lagoa Dos Patos; Wasielesky, W., Jr., Poersch, L.H., Eds.; Editora da FURG: Rio Grande, Brazil, 2016; pp. 349–360. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Huang, G. The effects of body weight, temperature, salinity, pH, light intensity, and feeding condition on lethal DO levels of whiteleg shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931). Aquaculture 2006, 256, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durai, V.; Alagappan, M.; Yuvarajan, P. Importance of Water Quality in Whiteleg Shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) Farming. AgriCos e-Newsl. 2021, 2, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.M.; Samocha, T.M.; Fox, J.M.; Gandy, R.L.; Lawrence, A.L. Characterization of water quality factors during intensive raceway production of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei using limited discharge and biosecure management tools. Aquac. Eng. 2005, 32, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schryver, P.; Crab, R.; Defoirdt, T.; Boon, N.; Verstraete, W. The basics of bio-flocs technology: The added value for aquaculture. Aquaculture 2008, 277, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, J.A. Biofloc Production Systems for Aquaculture. In Biofloc Technology: A Practical Guidebook, 3rd ed.; Avnimelech, Y., Rakocy, J., Brune, D., Ebeling, J., Browdy, C., Leffler, J., Ray, A., Samocha, T., Taw, N., Ernst, D., et al., Eds.; Southern Regional Aquaculture Center: Stoneville, MS, USA, 2013; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Samocha, T.M.; Patnaik, S.; Speed, M.; Ali, A.; Burger, J.M.; Almeida, R.V.; Ayub, Z.; Harisanto, M.; Horowitz, A.; Brock, D.L.; et al. Use of molasses as a carbon source in limited discharge nursery and grow-out systems for Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Eng. 2007, 36, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schveitzer, R.; Arantes, R.; Costodio, P.; Espírito, C.M.; Vinatea, L.; Seiffert, W.Q.; Andreatta, E. Effect of different biofloc levels on microbial activity, water quality, and performance of Litopenaeus vannamei in a tank system operated with no water exchange. Aquac. Eng. 2013, 56, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, D.M.; Suita, S.M.; Leite, F.P.L.; Romano, L.A.; Wasielesky, W.; Ballester, E.L.C. The use of probiotics during the nursery rearing of the pink shrimp Farfantepenaeus brasiliensis (Latreille, 1817) in a zero exchange system. Aquac. Res. 2011, 43, 1828–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemor, J.; Wasielesky, W.; Fóes, G.; Poersch, L. The use of clarifiers to remove and control the total suspended solids in large-scale ponds for production of Litopenaeus vannamei in a biofloc system. Aquac. Eng. 2019, 85, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinatea, L.; Gálvez, A.O.; Browdy, C.L.; Stokes, A.; Venero, J.; Haveman, J.; Lewis, B.L.; Lawson, A.; Shuler, A.; Leffler, J.W. Photosynthesis, water respiration, and growth performance of Litopenaeus vannamei in a super-intensive raceway culture with zero water exchange: Interaction of water quality variables. Aquac. Eng. 2010, 42, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnault, M. Nitrogen Excretion in marine and freshwater crustacea. Biol. Rev. 1987, 62, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtado, P.; Campos, B.R.; Serra, F.P.; Klosterhoff, M.; Romano, L.A. Effects of nitrate toxicity in the Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, reared with biofloc technology (BFT). Aquac. Int. 2015, 23, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chen, J.C. Acute toxicity of ammonia on Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) juveniles at different salinity levels. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2001, 259, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, J. Acute toxicity of nitrite on Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) juveniles at different salinity levels. Aquaculture 2003, 224, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, B.R.; Furtado, P.S.; D’Incao, F.; Poersch, L.; Wasielesky, W. The chronic toxicity of ammonia, nitrite and nitrate on juvenile Farfantepenaeus brasiliensis (crustacea: Decapoda). Bol. Inst. Pesca 2015, 41, 261–269. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, A.J.; Seaborn, G.; Leffler, J.W.; Wilde, S.B.; Lawson, A.; Browdy, C.L. Characterization of microbial communities in minimal-exchange, intensive aquaculture systems and the effects of suspended solids management. Aquaculture 2010, 310, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barak, Y.; Cytryn, E.; Gelfand, I.; Krom, M.; Van Rijn, J. Phosphorus removal in a marine prototype, recirculating aquaculture system. Aquaculture 2003, 220, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samocha, T.M.; Prangnell, D.I.; Hanson, T.R.; Treece, G.D.; Morris, T.C.; Castro, L.F.; Staresinic, N. Design and Operation of Super-Intensive, Biofloc-Dominated Systems for Indoor Production of the Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei—The Texas A & M Agrilife Research Experience; The World Aquaculture Society: Sorrento, LA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Brol, J.; Müller, L.; Prates, E.C.A.; de Farias, B.S.; Pedrosa, V.F.; Pinto, L.A.d.A.; Cadaval, T.R.S.; Tesser, M.B.; Wasielesky, W.; Ventura-Lima, J. Dietary chitosan supplementation in Litopenaeus vannamei reared in a biofloc system: Effect on antioxidant status facing saline stress. Aquaculture 2021, 544, 737034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, S.; Wasielesky, W.; Louzada, L. Comparative analysis of pink shrimp, Farfantepenaeus paulensis, and Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, culture in extreme Southern Brazil. J. Appl. Aquac. 2003, 14, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandifer, P.A.; Hopkins, J.S.; Stokes, A.D.; Browdy, C.L. Preliminary Comparisons of the Native Penaeus setiferus and Pacific Penaeus vannamei White Shrimp for Pond Culture in South Carolina, USA. J. World Aquac. Soc. 1993, 24, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silveira, L.G.P.; Krummenauer, D.; Poersch, L.H.; Rosas, V.T.; Wasielesky, W. Hyperintensive stocking densities for Litopenaeus vannamei grow-out in biofloc technology culture system. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2020, 51, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krummenauer, D.; Peixoto, S.; Cavalli, R.O.; Poersch, L.H.; Wasielesky, W. Superintensive Culture of White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, in a Biofloc Technology System in Southern Brazil at Different Stocking Densities. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2011, 42, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krummenauer, D.; Wasielesky, W.; Cavalli, R.O.; Peixoto, S.; Zogbi, P.R. Viabilidade do cultivo do camarão-rosa Farfantepenaeus paulensis (Crustácea, Decapoda) em gaiolas sob diferentes densidades durante o outono no sul do Brasil. Ciência Rural 2006, 36, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, E.A.; Palafox, J.P.; Santos, R.C.D.L.; Noriega, E.A.; Dominguez, G.R.; Vargasmachuca, S.C. Influence of Stocking Density on Production and Water Quality of a Photoheterotrophic Intensive System of White Shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) in Circular Lined Grow-Out Ponds, with Minimal Water Replacement. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2019, 47, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silveira, L.G.P.; Rosas, V.T.; Krummenauer, D.; Fróes, C.; Silva, A.; Poersch, L.H.; Fóes, G.; Wasielesky, W. Establishing the Most Productive Stocking Densities for Each Stage of a Multi-phase Shrimp Culture in BFT System. Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 1889–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, W.G.; Wasielesky, W., Jr.; Abreu, P.C.; Brandão, H.; Krummenauer, D. The Influence of Different Light Wavelengths in the Culture of the Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Reared in BFT Using LED Lights. Aquaculture 2023, 563, 738924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.F.; Lara, G.R.; Ballester, E.C.; Krumennauer, D.; Abreu, P.C.; Wasielesky, W., Jr. Efeito das altas densidades de estocagem no crescimento e sobrevivência de Litopenaeus vannamei na fase final de engorda, cultivados em sistemas de bioflocos (BFT). Ciência Anim. Bras. 2013, 14, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, M.; Júnior, W.W.; Hostins, B.; Bequé, E.; Krummenauer, D. The Use of a Flocculant Additive and Its Effect on Biofloc Formation, Nitrification, and Zootechnical Performance During the Culture of Pacific White Shrimp (Penaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931)) in a BFT System. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2022, 50, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rego, M.A.S.; Sabbag, O.J.; Soares, R.; Peixoto, S. Financial Viability of Inserting the Biofloc Technology in a Marine Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Farm: A Case Study in the State of Pernambuco, Brazil. Aquac. Int. 2016, 25, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayisi, C.L.; Hua, X.; Apraku, A.; Afriyie, G.; Kyei, B.A. Recent Studies Toward the Development of Practical Diets for Shrimp and Their Nutritional Requirements. HAYATI J. Biosci. 2017, 24, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Suárez, L.E.; Tapia-Salazar, M.; Villarreal-Cavazos, D.; Beltran-Rocha, J.; Nieto-López, M.G.; Lemme, A.; Ricque-Marie, D. Apparent dry matter, energy, protein and amino acid digestibility of four soybean ingredients in white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei juveniles. Aquaculture 2009, 292, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.G.; Lawrence, A.L. Digestibility. In Crustacean Nutrition: Advances in World Aquaculture; D’Abramo, L.R., Conklin, D.E., Eds.; World Aquaculture Society: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1997; pp. 194–260. [Google Scholar]
- D’Abramo, L.R.; Conklin, D.E.; Akiyama, D.M. Crustacean Nutrition; World Aquaculture Society: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Eap, D.; Correa, S.; Ngo-Vu, H.; Derby, C.D. Chemosensory basis of feeding behavior in Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Biol. Bull. 2020, 239, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garm, A. Mechanical functions of setae from the mouth apparatus of seven species of decapod crustaceans. J. Morphol. 2004, 260, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, C.G.; Hindley JP, R.; Jones, S.G. Structure and function of the third maxillipeds of the banana prawn Penaeus merguiensis. Mar. Biol. 1980, 58, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Flores, A.; Ponce-Palafox, J.; Spanopoulos-Hernández, M.; Martinez-Cardenas, L. Feeding behavior and ingestion rate of juvenile shrimp of the genus Penaeus (Crustacea: Decapoda). Med. Crave 2019, 3, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertoni, E.F.; Palma-Silva, C.; Esteves, F.S. Natural Diet of Three Species of Shrimp in a Tropical Coastal Lagoon. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2003, 46, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.; Keunecke, K.A.; Lavrado, H.P. Differences in feeding ecology of the pink shrimps Penaeus brasiliensis and P. paulensis (Decapoda: Penaeidae) in Brazilian tropical ecosystems. Aquat. Ecol. 2023, 57, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Guo, Q.; Jang, I.-K. Effect of Biofloc on the Survival and Growth of the Postlarvae of Three Penaeids (Litopenaeus vannamei, Fenneropenaeus chinensis, and Marsupenaeus japonicus) and Their Biofloc Feeding Efficiencies, as Related to the Morphological Structure of the Third Maxilliped. J. Crustac. Biol. 2015, 35, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatments | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameters | F. brasiliensis | L. vannamei |
| Temperature (°C) | 25.4 ± 3.1 | 25.7 ± 3.2 |
| Dissolved oxygen (mg L−1) | 6.6 ± 0.5 | 6.5 ± 0.4 |
| pH | 8.1 ± 0.2 | 8.0 ± 0.2 |
| Salinity | 32.8 ± 0.7 | 33.12 ± 0.8 |
| Alkalinity (mg of CaCO3 L−1) | 157.7 ± 23.3 | 143.56 ± 22.1 |
| Total suspended solids (mg L−1) | 298.5 ± 119.7 | 299.7 ± 128.4 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 105.0 ± 83.9 | 110.8 ± 90.2 |
| TA-N (mg L−1) | 0.15 ± 0.11 | 0.20 ± 0.18 |
| NO2− N (mg L−1) | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 1.30 |
| NO3− N (mg L−1) | 17.9 ± 8.8 | 19.1 ± 9.6 |
| PO34− P (mg L−1) | 1.43 ± 0.93 | 1.30 ± 1.0 |
| Treataments | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameters | F. brasiliensis | L. vannamei |
| Initial weight (g) | 0.72 ± 0.37 a | 0.78 ± 0.29 a |
| Final weight (g) | 3.96 ± 1.40 a | 11.28 ± 1.89 b |
| Weekly growth (g week−1) | 0.32 ± 0.20 a | 1.05 ± 0.62 b |
| Final biomass (kg) | 9.34 ± 1.68 a | 40.49 ± 2.55 b |
| Survival (%) | 64.50 ± 9.68 a | 98.12 ± 6.12 b |
| Productivity (kg m−2) | 0.26 ± 0.05 a | 1.12 ± 0.07 b |
| Feed conversion ratio | 5.45 ± 1.34 a | 1.43 ± 0.06 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krummenauer, D.; da Silva, A.F.; Xavier, M.; Foes, G.K.; Poersch, L.H.; Cardozo, A.; Wasielesky, W. Comparative Analysis of the Culture of Pink Shrimp Farfantepenaeus brasiliensis and Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei in Biofloc System. Aquac. J. 2024, 4, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/aquacj4010001
Krummenauer D, da Silva AF, Xavier M, Foes GK, Poersch LH, Cardozo A, Wasielesky W. Comparative Analysis of the Culture of Pink Shrimp Farfantepenaeus brasiliensis and Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei in Biofloc System. Aquaculture Journal. 2024; 4(1):1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/aquacj4010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrummenauer, Dariano, André Freitas da Silva, Missileny Xavier, Geraldo Kipper Foes, Luís H. Poersch, Alessandro Cardozo, and Wilson Wasielesky. 2024. "Comparative Analysis of the Culture of Pink Shrimp Farfantepenaeus brasiliensis and Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei in Biofloc System" Aquaculture Journal 4, no. 1: 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/aquacj4010001
APA StyleKrummenauer, D., da Silva, A. F., Xavier, M., Foes, G. K., Poersch, L. H., Cardozo, A., & Wasielesky, W. (2024). Comparative Analysis of the Culture of Pink Shrimp Farfantepenaeus brasiliensis and Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei in Biofloc System. Aquaculture Journal, 4(1), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/aquacj4010001







