Pathophysiology of Placenta in Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Epidemiology
4. Prognosis, Mortality, and Morbidity
5. Perinatal Morbidity and Mortality
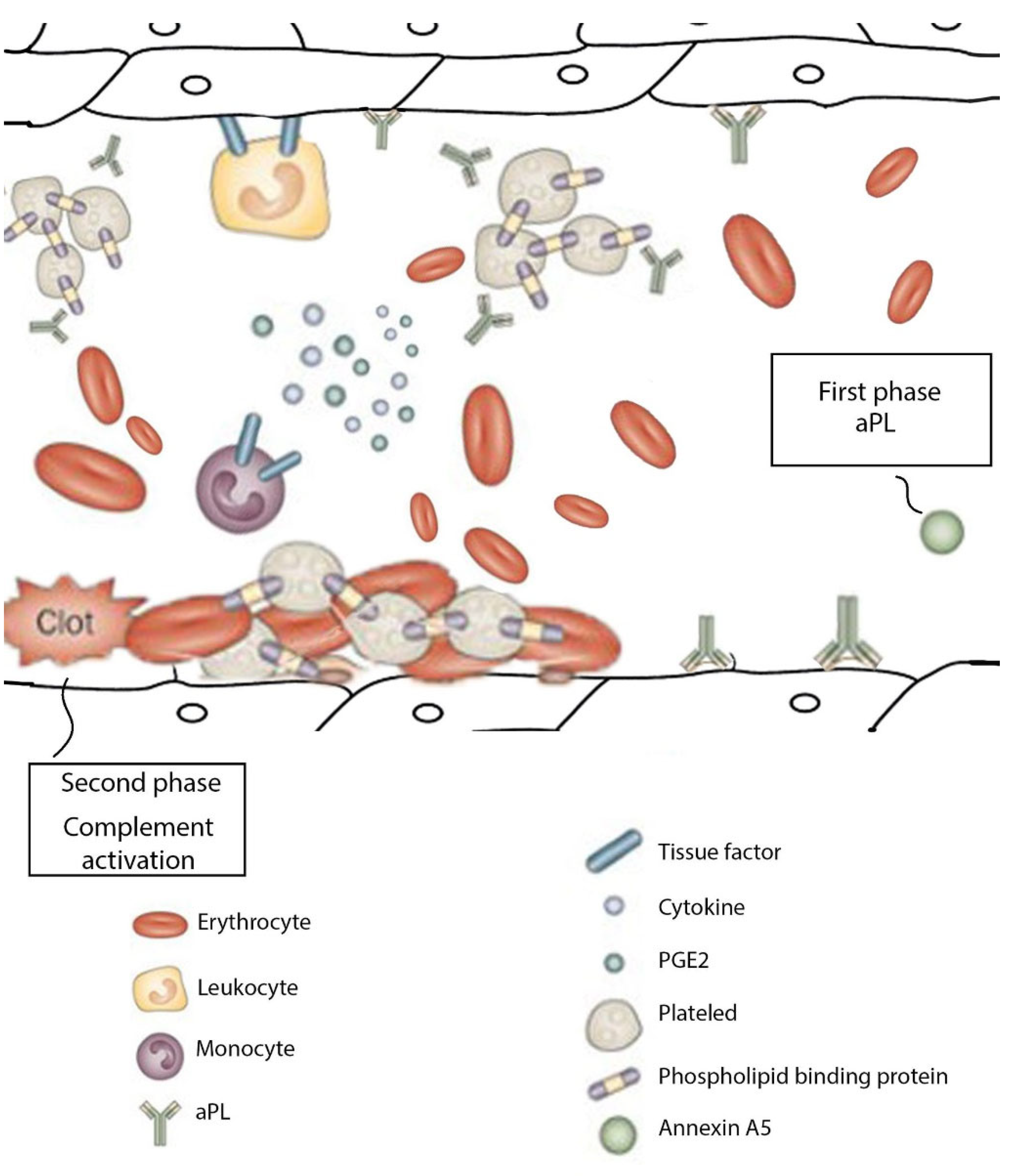
6. Pathophysiology
7. History
- Miscarriage (especially in the third trimester or recurrent) or premature birth;
- History of cardiac murmur or heart valve vegetations;
- History of hematologic abnormalities, such as thrombocytopenia or hemolytic anemia;
- History of nephropathy;
- Non-thrombotic neurological symptoms—headaches, chorea, seizures, transverse myelitis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, or dementia (rare);
- Adrenal insufficiency with unknown cause;
- Avascular osteonecrosis in the absence of other risk factors;
- Pulmonary hypertension;
- Thrombosis-myocardial infarction, transient ischemic attack, or stroke, especially if recurrent, at an earlier age, or if there are no risk factors.
8. Management of APS
8.1. Obstetric Care
8.2. Anticoagulation Therapy
9. Antiphospholipid Antibodies
10. Abnormal Placental Development in APS
11. Mechanisms of Obstetric APS
12. Placental Pathogenesis Related to APS
12.1. Thrombosis
12.2. Pathogenicity of aPL
12.3. Inflammatory Responses
Defective Placentation
13. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bobirca, A.; Alexandru, C. Antiphospholipid syndrome and pregnancy. In Managment of Rheumatic Diseases in Pregnancy; Printech: Bucharest, Romania, 2021; pp. 76–89. [Google Scholar]
- Sammaritano, L.R. Antiphospholipid syndrome. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 34, 101463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tektonidou, M.G.; Andreoli, L.; Limper, M.; Amoura, Z.; Cervera, R.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Cuadrado, M.J.; Dörner, T.; Ferrer-Oliveras, R.; Hambly, K.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of antiphospholipid syndrome in adults. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durcan, L.; Petri, M. Epidemiology of the Antiphospholipid Syndrome. In Handbook of Systemic Autoimmune Diseases; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoli, L.; Chighizola, C.B.; Banzato, A.; Pons-Estel, G.J.; de Jesus, G.R.; Erkan, D.; Action, O.B.O.A. Estimated Frequency of Antiphospholipid Antibodies in Patients With Pregnancy Morbidity, Stroke, Myocardial Infarction, and Deep Vein Thrombosis: A Critical Review of the Literature. Arthritis Care Res. 2013, 65, 1869–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, K.; Sciascia, S.; De Groot, P.G.; Devreese, K.; Jacobsen, S.; Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Salmon, J.E.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Shovman, O.; Hunt, B.J. Antiphospholipid syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 17103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammaritano, L.R.; Bermas, B.L.; Chakravarty, E.E.; Chambers, C.; Clowse, M.E.B.; Lockshin, M.D.; Marder, W.; Guyatt, G.; Branch, D.W.; Buyon, J.; et al. 2020 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Management of Reproductive Health in Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases. Arthritis Care Res. 2020, 72, 461–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.M.; Balcázar, N.; Martín, S.S.; Markert, U.R.; Cadavid, A.P. Modulation of antiphospholipid antibodies-induced trophoblast damage by different drugs used to prevent pregnancy morbidity associated with antiphospholipid syndrome. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2017, 77, e12634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijotas-Reig, J.; Ferrer-Oliveras, R.; Ruffatti, A.; Tincani, A.; Lefkou, E.; Bertero, M.T.; Coloma-Bazan, E.; de Carolis, S.; Espinosa, G.; Rovere-Querini, P.; et al. The European Registry on Obstetric Antiphospholipid Syndrome (EUROAPS): A survey of 247 consecutive cases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvier, S.; Cochery-Nouvellon, E.; Lavigne-Lissalde, G.; Mercier, E.; Marchetti, T.; Balducchi, J.-P.; Marès, P.; Gris, J.-C. Comparative incidence of pregnancy outcomes in treated obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome: The NOH-APS observational study. Blood 2014, 123, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, K.; Ozawa, N.; Murashima, A. Obstetric anti-phospholipid syndrome: From pathogenesis to treatment. Immunol. Med. 2021, 45, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, L.H.; McLean, W.T. Management of Landry-Guillain-Barré syndrome in pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 1985, 65, 25S–29S. [Google Scholar]
- Bitsadze, V.; Nalli, C.; Khizroeva, J.; Lini, D.; Andreoli, L.; Lojacono, A.; Fazzi, E.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Tincani, A.; Makatsariya, A. “APS pregnancy—The offspring”. Lupus 2020, 29, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, K.; Radin, M.; Sciascia, S. Current insights in obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 29, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tektonidou, M.G.; Andreoli, L.; Limper, M.; Tincani, A.; Ward, M.M. Management of thrombotic and obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome: A systematic literature review informing the EULAR recommendations for the management of antiphospholipid syndrome in adults. RMD Open 2019, 5, e000924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viall, C.A.; Chamley, L.W. Histopathology in the placentae of women with antiphospholipid antibodies: A systematic review of the literature. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 446–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Crowther, M.; Branch, W.; Khamashta, M.A. Antiphospholipid syndrome. Lancet 2010, 376, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, K.J.; Müller-Calleja, N.; Lackner, K.J.; Müller-Calleja, N. Pathogenesis of antiphospholipid syndrome: Recent insights and emerging concepts. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 15, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelusa, H.F.; Pezzarini, E.; Basiglio, C.L.; Musuruana, J.; Bearzotti, M.; Svetaz, M.J.; Daniele, S.M.; Bottai, H.; Arriaga, S.M.M. Antiphospholipid and antioangiogenic activity in females with recurrent miscarriage and antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann. Clin. Biochem. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Lin, X.; Jia, C.; Yu, X. Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry based serum metabolomics study on recurrent abortion women with antiphospholipid syndrome. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chighizola, C.B.; Lonati, P.A.; Trespidi, L.; Meroni, P.L.; Tedesco, F. The Complement System in the Pathophysiology of Pregnancy and in Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases During Pregnancy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arreola-Diaz, R.; Majluf-Cruz, A.; Sanchez-Torres, L.; Hernandez-Juarez, J. The Pathophysiology of The Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Perspective from The Blood Coagulation System. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2022, 28, 107602962210885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyakis, S.; Lockshin, M.D.; Atsumi, T.; Branch, D.W.; Brey, R.L.; Cervera, R.; Derksen, R.H.W.M.; De Groot, P.G.; Koike, T.; Meroni, P.L.; et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D′Ippolito, S.; Meroni, P.L.; Koike, T.; Veglia, M.; Scambia, G.; Di Simone, N. Obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome: A recent classification for an old defined disorder. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Jang, S.; Park, C.-J.; Chi, H.-S. Clinical Application of Revised Laboratory Classification Criteria for Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome: Is the Follow-Up Interval of 12 Weeks Instead of 6 Weeks Significantly Useful? BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, S.; McCrae, K.R. Diagnosis and management of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Blood Rev. 2017, 31, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoli, L.; Bertsias, G.K.; Agmon-Levin, N.; Brown, S.; Cervera, R.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Doria, A.; Fischer-Betz, R.; Forger, F.; Moraes-Fontes, M.F.; et al. EULAR recommendations for women’s health and the management of family planning, assisted reproduction, pregnancy and menopause in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and/or antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekinian, A.; Loire-Berson, P.; Nicaise-Roland, P.; Lachassinne, E.; Stirnemann, J.; Boffa, M.-C.; Chollet-Martin, S.; Carbillon, L.; Fain, O. Outcomes and treatment of obstetrical antiphospholipid syndrome in women with low antiphospholipid antibody levels. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2012, 94, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chighizola, C.B.; Andreoli, L.; Gerosa, M.; Tincani, A.; Ruffatti, A.; Meroni, P.L. The treatment of anti-phospholipid syndrome: A comprehensive clinical approach. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 90, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Cuadrado, M.J.; Ruiz-Arruza, I.; Brey, R.; Crowther, M.; Derksen, R.; Erkan, D.; Krilis, S.; Machin, S.; Pengo, V.; et al. Evidence-based recommendations for the prevention and long-term management of thrombosis in antiphospholipid antibody-positive patients: Report of a Task Force at the 13th International Congress on Antiphospholipid Antibodies. Lupus 2011, 20, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekinian, A.; Vicaut, E.; Cohen, J.; Bornes, M.; Kayem, G.; Fain, O. Évaluation du bénéfice de l’utilisation d’hydroxychloroquine pour l’obtention d’une grossesse à terme non compliquée en cas de syndrome des antiphospholipides primaire: Étude de phase II multicentrique randomisée en double insu versus placebo, HYDROSAPL. Gynécologie Obs. Fertil. Sénologie 2018, 46, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefkou, E.; Varoudi, K.; Pombo, J.; Jurisic, A.; Jurisic, Z.; Contento, G.; Girardi, G. Triple therapy with pravastatin, low molecular weight heparin and low dose aspirin improves placental haemodynamics and pregnancy outcomes in obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome in mice and women through a nitric oxide-dependent mechanism. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 182, 114217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Tian, Y.; Wan, S.; Hu, M.; Song, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Q.; Xia, Y.; Wang, X. Protection by hydroxychloroquine prevents placental injury in obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derksen, R.H.W.M.; Khamashta, M.A.; Branch, D.W. Management of the obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome. Arthritis Care Res. 2004, 50, 1028–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaud, L.; Mathian, A.; Ruffatti, A.; Erkan, D.; Tektonidou, M.; Cervera, R.; Forastiero, R.; Pengo, V.; Lambert, M.; Martinez-Zamora, M.A.; et al. Efficacy of aspirin for the primary prevention of thrombosis in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies: An international and collaborative meta-analysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 13, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkan, D.; Harrison, M.J.; Levy, R.A.; Peterson, M.; Petri, M.; Sammaritano, L.; Unalp-Arida, A.; Vilela, V.; Yazici, Y.; Lockshin, M.D. Aspirin for primary thrombosis prevention in the antiphospholipid syndrome: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in asymptomatic antiphospholipid antibody–positive individuals. Arthritis Care Res. 2007, 56, 2382–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, P.; Falach-Vaknin, E.; Sredni, B.; Meroni, P.L.; Rudniki, C.; Shoenfeld, Y. Aspirin modulates interleukin-3 produc-tion: Additional explanation for the preventive effects of aspirin in antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. J. Rheumatol. 1995, 22, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar]
- D’Cruz, D.P. Antiphospholipid (Hughes) Syndrome: An Overview. In Hughes Syndrome; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynaud, Q.; Lega, J.-C.; Mismetti, P.; Chapelle, C.; Wahl, D.; Cathébras, P.; Laporte, S. Risk of venous and arterial thrombosis according to type of antiphospholipid antibodies in adults without systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, M. Epidemiology of Antiphospholipid Syndrome. In Hughes Syndrome; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeith, L.; Abou-Nassar, K.E.; Walker, M.; Ramsay, T.; Booth, R.; Wen, S.W.; Smith, G.N.; Rodger, M.A. Are Anti-β2 Glycoprotein 1 Antibodies Associated with Placenta-Mediated Pregnancy Complications? A Nested Case–Control Study. Am. J. Perinatol. 2018, 35, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, V.; Nuccetelli, M.; Ticconi, C.; Bruno, A.; Martelli, F.; Capogna, M.V.; Bernardini, S.; Piccione, E.; Pietropolli, A. Amniotic fluid antiphospholipid antibodies: Potential role in antiphospholipid syndrome-independent aberrant implantation process. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2019, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benirschke, K.; Kaufmann, P. Pathology of the Human Placenta; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppertz, B.; Frank, H.-G.; Kingdom, J.C.P.; Reister, F.; Kaufmann, P. Villous cytotrophoblast regulation of the syncytial apoptotic cascade in the human placenta. Histochem. Cell Biol. 1998, 110, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhew, T.; Leach, L.; McGee, R.; Ismail, W.W.; Myklebust, R.; Lammiman, M. Proliferation, Differentiation and Apoptosis in Villous Trophoblast at 13–41 Weeks of Gestation (Including Observations on Annulate Lamellae and Nuclear Pore Complexes). Placenta 1999, 20, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benirschke, K.; Burton, G.J.; Baergen, R.N. Pathology of the Human Placenta, 6th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askelund, K.; Chamley, L. Trophoblast deportation part I: Review of the evidence demonstrating trophoblast shedding and deportation during human pregnancy. Placenta 2011, 32, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantham, P.; Askelund, K.; Chamley, L. Trophoblast deportation part II: A review of the maternal consequences of trophoblast deportation. Placenta 2011, 32, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerardi, M.C.; Fernandes, M.A.; Tincani, A.; Andreoli, L. Obstetric Anti-phospholipid Syndrome: State of the Art. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2018, 20, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, G.; Woods, A.; Jauniaux, E.; Kingdom, J. Rheological and Physiological Consequences of Conversion of the Maternal Spiral Arteries for Uteroplacental Blood Flow during Human Pregnancy. Placenta 2009, 30, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quao, Z.C.; Tong, M.; Bryce, E.; Guller, S.; Chamley, L.W.; Abrahams, V.M. Low molecular weight heparin and aspirin exacerbate human endometrial endothelial cell responses to antiphospholipid antibodies. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2017, 79, e12785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powe, C.E.; Levine, R.J.; Karumanchi, S.A. Preeclampsia, a Disease of the Maternal Endothelium. Circulation 2011, 123, 2856–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.; Hubel, C. The Two Stage Model of Preeclampsia: Variations on the Theme. Placenta 2009, 30, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, R.J.; Lam, C.; Qian, C.; Yu, K.F.; Maynard, S.E.; Sachs, B.P.; Sibai, B.M.; Epstein, F.H.; Romero, R.; Thadhani, R.; et al. Soluble Endoglin and Other Circulating Antiangiogenic Factors in Preeclampsia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 992–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, M.; Donald, A.E.; Angelakopoulou, A.; Hingorani, A.; Williams, D. Prospective Study of Placental Angiogenic Factors and Maternal Vascular Function Before and After Preeclampsia and Gestational Hypertension. Circulation 2010, 122, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochery-Nouvellon, É.; Mercier, É.; Bouvier, S.; Balducchi, J.-P.; Quéré, I.; Perez-Martin, A.; Mousty, E.; Letouzey, V.; Gris, J.-C. Obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome: Early variations of angiogenic factors are associated with adverse outcomes. Haematologica 2017, 102, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer-Pickel, K.; Stern, C.; Eberhard, K.; Lang, U.; Obermayer-Pietsch, B.; Cervar-Zivkovic, M. Angiogenic factors in pregnancies of women with antiphospholipid syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2018, 127, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Almaraz, M.; Herraiz, I.; Gómez-Arriaga, P.; Vallejo, P.; Gonzalo-Gil, E.; Usategui, A.; López-Jiménez, E.; Galindo, A. The role of angiogenic biomarkers and uterine artery Doppler in pregnant women with systemic lupus erythematosus or antiphospholipid syndrome. Pregnancy Hypertens. Int. J. Women′s Cardiovasc. Health 2018, 11, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitsadze, V.; Bouvier, S.; Khizroeva, J.; Cochery-Nouvellon, É.; Mercier, É.; Perez-Martin, A.; Makatsariya, A.; Gris, J.-C. Early ADAMTS13 testing associates with pre-eclampsia occurrence in antiphospholipid syndrome. Thromb. Res. 2021, 203, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, H.; Cuadrado, M.J.; Erkan, D.; Duarte-Garcia, A.; Isenberg, D.A.; Knight, J.S.; Ortel, T.L.; Rahman, A.; Salmon, J.E.; Tektonidou, M.G.; et al. 16th International Congress on Antiphospholipid Antibodies Task Force Report on Antiphospholipid Syndrome Treatment Trends. Lupus 2020, 29, 1571–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meroni, P.L.; Borghi, M.O.; Grossi, C.; Chighizola, C.B.; Durigutto, P.; Tedesco, F. Obstetric and vascular antiphospholipid syndrome: Same antibodies but different diseases? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrai, C.E.; Rand, J.H.; Baergen, R.N. Absence of Distinct Immunohistochemical Distribution of Annexin A5, C3b, C4d, and C5b-9 in Placentas From Patients With Antiphospholipid Antibodies, Preeclampsia, and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2019, 22, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, V.M.; Chamley, L.W.; Salmon, J.E. Emerging Treatment Models in Rheumatology: Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Pregnancy: Pathogenesis to Translation. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1710–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chighizola, C.B.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Meroni, P.L. Therapy for antiphospholipid miscarriages: Throwing the baby out with the bathwater? Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2017, 79, e12792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardi, G.; Yarilin, D.; Thurman, J.M.; Holers, V.M.; Salmon, J.E. Complement activation induces dysregulation of angiogenic factors and causes fetal rejection and growth restriction. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2165–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, J.; Girardi, G.; Salmon, J.E. TNF-α Is a Critical Effector and a Target for Therapy in Antiphospholipid Antibody-Induced Pregnancy Loss. J. Immunol. 2004, 174, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacharidou, A.; Shaul, P.W.; Mineo, C. New Insights in the Pathophysiology of Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2017, 44, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, J.; Wu, X.-X.; Quinn, A.; Taatjes, D. The annexin A5-mediated pathogenic mechanism in the antiphospholipid syndrome: Role in pregnancy losses and thrombosis. Lupus 2010, 19, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Lian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Shen, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lu, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Platelet-derived microparticles from recurrent miscarriage associated with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome influence behaviours of trophoblast and endothelial cells. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2019, 25, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chighizola, C.B.; Raschi, E.; Borghi, M.O.; Meroni, P.L. Mechanisms of Action of the Antiphospholipid Antibodies. In Handbook of Systemic Autoimmune Diseases; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 12, pp. 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinillo, A.; Bellingeri, C.; Cavagnoli, C.; De Maggio, I.; Riceputi, G.; Ruspini, B.; Cesari, S.; Beneventi, F. Maternal and foetal placental vascular malperfusion in pregnancies with anti-phospholipid antibodies. Rheumatology 2020, 60, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canti, V.; Del Rosso, S.; Tonello, M.; Lucianò, R.; Hoxha, A.; Coletto, L.A.; Tessitore, I.V.; Rosa, S.; Manfredi, A.A.; Castiglioni, M.T.; et al. Antiphosphatidylserine/prothrombin Antibodies in Antiphospholipid Syndrome with Intrauterine Growth Restriction and Preeclampsia. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 45, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulla, M.J.; Pasternak, M.C.; Salmon, J.E.; Chamley, L.W.; Abrahams, V.M. Role of NOD2 in antiphospholipid antibody-induced and bacterial MDP amplification of trophoblast inflammation. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 98, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon-Martinez, D.; Mulla, M.J.; Han, C.S.; Chamley, L.W.; Abrahams, V.M. Modulation of trophoblast function by concurrent hyperglycemia and antiphospholipid antibodies is in part TLR4-dependent. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2018, 80, e13045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonati, P.A.; Scavone, M.; Gerosa, M.; Borghi, M.O.; Pregnolato, F.; Curreli, D.; Podda, G.; Femia, E.A.; Barcellini, W.; Cattaneo, M.; et al. Blood Cell-Bound C4d as a Marker of Complement Activation in Patients With the Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scambi, C.; Ugolini, S.; Tonello, M.; Bortolami, O.; De Franceschi, L.; Castagna, A.; Lotti, V.; Corbella, M.; Raffaelli, R.; Caramaschi, P.; et al. Complement activation in the plasma and placentas of women with different subsets of antiphospholipid syndrome. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2019, 82, e13185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Torre, Y.M.; Buracchi, C.; Borroni, E.M.; Dupor, J.; Bonecchi, R.; Nebuloni, M.; Pasqualini, F.; Doni, A.; Lauri, E.; Agostinis, C.; et al. Protection against inflammation- and autoantibody-caused fetal loss by the chemokine decoy receptor D6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2319–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samudra, A.N.; Dwyer, K.M.; Selan, C.; Freddi, S.; Murray-Segal, L.; Nikpour, M.; Hickey, M.J.; Peter, K.; Robson, S.C.; Sashindranath, M.; et al. CD39 and CD73 activity are protective in a mouse model of antiphospholipid antibody-induced miscarriages. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 88, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krivokuća, M.J.; Abu Rabi, T.; Stefanoska, I.; Vrzić-Petronijević, S.; Petronijević, M.; Vićovac, L. Immunoglobulins from sera of APS patients bind HTR-8/SVneo trophoblast cell line and reduce additional mediators of cell invasion. Reprod. Biol. 2017, 17, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, D.; Wang, X.; Ge, R.; Zhang, M.; Xia, Y.; Wang, X. Antiphospholipid antibody-activated NETs exacerbate trophoblast and endothelial cell injury in obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 6690–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.; Sacharidou, A.; Nguyen, A.; Li, C.; Chambliss, K.L.; Salmon, J.E.; Shen, Y.-M.P.; Lo, J.; Leone, G.W.; Herz, J.; et al. Protein Phosphatase 2A Activation Via ApoER2 in Trophoblasts Drives Preeclampsia in a Mouse Model of the Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Circ. Res. 2021, 129, 735–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.Y.; Guerra, M.M.; Kaplowitz, E.; Laskin, C.A.; Petri, M.; Branch, D.W.; Lockshin, M.D.; Sammaritano, L.R.; Merrill, J.T.; Porter, T.F.; et al. Complement activation predicts adverse pregnancy outcome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and/or antiphospholipid antibodies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DI Simone, N.; Raschi, E.; Testoni, C.; Castellani, R.; D’Asta, M.; Shi, T.; Krilis, S.A.; Caruso, A.; Meroni, P.L. Pathogenic role of anti- 2-glycoprotein I antibodies in antiphospholipid associated fetal loss: Characterisation of 2-glycoprotein I binding to trophoblast cells and functional effects of anti- 2-glycoprotein I antibodies in vitro. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004, 64, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, T.; Artim-Esen, B.; Wincup, C.; Ripoll, V.M.; Isenberg, D.; Giles, I.P.; Rahman, A.; Pericleous, C. Antiphospholipid Antibodies to Domain I of Beta-2-Glycoprotein I Show Different Subclass Predominance in Comparison to Antibodies to Whole Beta-2-glycoprotein I. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Simone, N.; D’Ippolito, S.; Marana, R.; Di Nicuolo, F.; Castellani, R.; Pierangeli, S.S.; Chen, P.; Tersigni, C.; Scambia, G.; Meroni, P.L. Antiphospholipid Antibodies Affect Human Endometrial Angiogenesis: Protective Effect of a Synthetic Peptide (TIFI) Mimicking the Phospholipid Binding Site of β2glycoprotein I. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2013, 70, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, P.; Tedesco, F.; Locati, M.; Vecchi, A.; Di Simone, N.; Acaia, B.; Pierangeli, S.; Borghi, M. Anti-phospholipid antibody mediated fetal loss: Still an open question from a pathogenic point of view. Lupus 2010, 19, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijotas-Reig, J.; Esteve-Valverde, E.; Ferrer-Oliveras, R.; Llurba, E.; Gris, J.M. Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha and Pregnancy: Focus on Biologics. An Updated and Comprehensive Review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 53, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, S. Mitigating placental injuries through up-regulating DAF in experimental APS mice: New mechanism of progesterone. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 197, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabacco, S.; Giannini, A.; Garufi, C.; Botta, A.; Salvi, S.; Del Sordo, G.; Panici, P.B.; Lanzone, A.; De Carolis, S. Complementemia in pregnancies with antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus 2019, 28, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bobircă, A.; Dumitrache, A.; Alexandru, C.; Florescu, A.; Ciobotaru, G.; Bobircă, F.; Sima, R.-M.; Poalelungi, C.; Bojincă, M.; Ancuța, I. Pathophysiology of Placenta in Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Physiologia 2022, 2, 66-79. https://doi.org/10.3390/physiologia2030007
Bobircă A, Dumitrache A, Alexandru C, Florescu A, Ciobotaru G, Bobircă F, Sima R-M, Poalelungi C, Bojincă M, Ancuța I. Pathophysiology of Placenta in Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Physiologia. 2022; 2(3):66-79. https://doi.org/10.3390/physiologia2030007
Chicago/Turabian StyleBobircă, Anca, Ana Dumitrache, Cristina Alexandru, Anca Florescu, George Ciobotaru, Florin Bobircă, Romina-Marina Sima, Cristian Poalelungi, Mihai Bojincă, and Ioan Ancuța. 2022. "Pathophysiology of Placenta in Antiphospholipid Syndrome" Physiologia 2, no. 3: 66-79. https://doi.org/10.3390/physiologia2030007
APA StyleBobircă, A., Dumitrache, A., Alexandru, C., Florescu, A., Ciobotaru, G., Bobircă, F., Sima, R.-M., Poalelungi, C., Bojincă, M., & Ancuța, I. (2022). Pathophysiology of Placenta in Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Physiologia, 2(3), 66-79. https://doi.org/10.3390/physiologia2030007






