Abstract
Endocyn is a root canal irrigant with a stable formulation of hypochlorous acid (HOCl), and should have significant antimicrobial effects. However, there are no available studies that evaluate these effects on different types of bacterial species. In this prospective in vitro study, bacterial species were grown with and without the addition of Endocyn to measure the effects on the Gram-positive bacteria Actinomyces naeslundii, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Streptococcus gordonii, and Streptococcus mutans, as well as the Gram-negative bacteria Porphyromonas gingivalis, Fusobacterium nucleatum, and Veillonella parvula. Turbidity was measured at 24 h, and the differences between the baseline and experimental treatments were measured using two-tailed Student’s t-tests and verified using ANOVA. Gram-positive bacteria were inhibited in the range of −8.2% to −35.5%, p = 0.14 to p = 0.004, while Gram-negative bacteria were inhibited in the range of −16.7% to −41.4%, p = 0.04 to p = 0.001, which were similar to the effects of 5% NaOCl (bleach). These data demonstrated that Gram-positive bacteria were somewhat resistant to Endocyn at lower levels but were inhibited at all higher concentrations, while Gram-negative bacteria were susceptible to Endocyn at all levels, and increased at higher concentrations. These results provide clinically relevant data regarding the efficacy of this disinfectant against common oral pathogens (and commensal bacteria), and are important as they provide evidence regarding public health and the environmental safety of clinical protocols regarding endodontic hygiene.
1. Introduction
Many endodontic procedures within the pediatric population may be performed on patients aged 12 years and older, with current evidence suggesting that as many as one in ten patients will experience the need for invasive dental treatment om one or more teeth by the age of 15 [1,2,3]. Additional studies have revealed that specific conditions and specialized providers may be able to facilitate these procedures in much younger patients, some as young as age six [4,5,6]. However, many studies now suggest that minimally invasive treatments that aim to retain vital pulp may result in healing in more than 80% of cases depending upon several factors, including the skill of the provider, the extent of the tooth structure injuries or trauma, and the selection of specific and effective non-toxic, antimicrobial dental irrigants [7,8,9].
Many of these procedures on the primary teeth of pediatric patients between the ages of 1 and 12 years may involve the treatment of a carious lesion with one or more disinfection or sterilization and tissue regeneration procedures, such as a pulpectomy or a pulpotomy [10,11,12]. In addition, an even larger percentage of general endodontic procedures and treatments may be experienced by adult patients with mature permanent teeth, which necessitates consistent and dedicated research into the use of bioactive materials for the disinfecting or sterilizing irrigation utilized during these common dental procedures [13,14,15]. Research into the development and implementation of effective intracanal irrigants to complement mechanical debridement, used to remove debris and disinfect the root canal system, is critically important for regenerative endodontic procedure success among both pediatric and adult populations undergoing these procedures to prevent secondary infections and improve treatment outcomes [16,17,18].
Canal irrigants and other functional agents that promote regeneration and repair or prevent pulp toxicity are specifically useful in these dental procedures and maintaining positive patient outcomes in routine clinical practice [19,20]. Thorough reviews of clinical procedures including the application of disinfectant irrigation, as well as intracanal medicament, have demonstrated more targeted research in the areas of clinical efficacy and reduced cellular toxicity to host tissues, and may provide direct and applied recommendations for improvements to clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction [21,22]. For example, sodium hypochlorite (bleach) is an effective antimicrobial agent used in many dental procedures and applications, but the use of this agent has been demonstrated to exhibit some toxicity to vital pulp tissue, which has driven research into the development of endodontic irrigants with antimicrobial properties that limit damage to dental pulp—one of the most important goals of endodontic biomaterials research [23,24].
Research regarding dental irrigants with antimicrobial properties has traditionally focused on the antimicrobial properties of chlorhexidine gluconate or sodium hypochlorite [25,26,27,28,29]. However, more recent studies have demonstrated that additional formulations, such as quaternary ammonium silane, may also be equally effective [30,31]. Furthermore, one recent addition to these potential agents is Endocyn, which is a novel formulation of pH-neutral combined hypochlorous acid and sodium hypochlorite for use as an endodontic irrigant [32].
Clinical research studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of the incorporation of hypochlorous acid formulations as an active component of mouthwashes and disinfectants, and as an endodontic irrigant [33,34,35]. However, much less is known about the effects of the specific formulation provided in this newly developed product known as Endocyn [36,37,38]. Due to the paucity of research regarding this specific agent and its unique formulation, the goal of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of Endocyn as an antimicrobial agent, as well as perform an analysis of any differential effects on a variety of oral microbes, including Gram-positive and Gram-negative oral bacterial species.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria commonly found in the oral cavity were provided by the American Type Culture Collection—ATCC (Manassas, VA, USA), as previously described [39]. Gram-positive organisms included Streptococcus mutans #25175 (Biosafety Level or BSL-1), Streptococcus gordonii #35105 (BSL-2), Lactobacillus acidophilus #4356 (BSL-1), and Actinomyces naeslundii #12104 (BSL-2). Gram-negative organisms included Porphyromonas gingivalis #33277 (BSL-2), Fusobacterium nucleatum #25586 (BSL-2), and Veillonella parvula #10790 (BSL-1). Culturing information was obtained and compiled in Table 1 from ATCC.com (https://www.atcc.org accessed on 24 January, 2025) as previously described [39]:

Table 1.
Bacterial culturing requirements.
2.2. Bacterial Culture
Trypticase Soy Broth (TSB) #B11768, defibrinated sheep’s blood #R54016, MRS (DeMan, Rogosa, and Sharpe) broth #OXCM0359B, and Brain–Heart Infusion (BHI) broth #CM1135B were all obtained from Fisher Scientific (Fair Lawn, NJ, USA) and autoclaved prior to use in the liquid cycle. Overnight, 250 mL of broth was inoculated and cultured in an anaerobic bacterial chamber with rotary shaking at 90 RPM and 37 °C, as previously described [39].
2.3. DNA Isolation and Analysis
Aliquots of 500 µL were taken from each bacterial culture, and DNA was isolated using the FastDNA Fungal and Bacterial DNA Isolation Kit #MP119696300 from MP Biochemicals (Santa Ana, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s recommended protocol, as previously described [39,40]. DNA quantity and quality were confirmed using a NanoDrop 2000 Spectrophotometer from ThermoFisher Scientific (Fair Lawn, NJ, USA) and absorbance readings at A260 nm and A280 nm [39,40]. Confirmation of bacterial species was accomplished using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) performed using the PowerTrack SYBR Green Master Mix from Fisher Scientific (Fair Lawn, NJ, USA), according to the manufacturer’s recommended protocol, with the following validated qPCR primers (Table 2) synthesized by Eurofins MWG Operon (Huntsville, AL, USA) [39,40]:

Table 2.
Validated qPCR primer screening sets.
2.4. Experimental Reagents
Phosphate-buffered saline (1x PBS) #J61196-AP was obtained from Fisher Scientific (Fair Lawn, NJ, USA) and used as the negative control. Sterile sodium hypochlorite 5.0% (bleach) in aqueous solution #P005-03, also purchased from Fisher Scientific (Fair Lawn, NJ, USA), was used as the positive control. The experimental assays were performed with Endocyn obtained from New Line Medical (Breaux Bridge, LA, USA) and distributed by Sonoma pharmaceuticals (Woodstock, GA, USA).
2.5. Experimental Assays
Broth from each of the bacterial cultures was diluted to an optical density (OD) of 0.8 at an absorbance reading of 600 nm using a microplate reader from BioTek (Winooski, VT, USA), which corresponds to approximately 1 × 109 colony-forming units (CFUs) per mL for each experimental assay [40,41]. Negative (PBS) and positive (bleach) controls, as well as the experimental sample (Endocyn), were added to 96-well assay plates at concentrations of 0:100 (baseline), 1:100, 10:100, and 50:100 to a total volume of 100 µL and allowed to grow for 24 h (primary endpoint) prior to measurement, in line with other study protocols of endodontic irrigants assessing antimicrobial activity [42,43]. Turbidity was subsequently measured for each control and experimental condition at 600 nm. The bacterial counts from each assay were then quantified using 100 µL aliquots, which were analyzed using a TC20 Cell Counter from BioRad Laboratories (Hercules, CA, USA). Each assay was performed with n = 8 replicates per experimental condition and was repeated in three separate, independent experiments.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The minimum sample size or replicates for each group was determined to be n = 3 for this repeated measures study using the Prism Version 9 software package by Graph Pad (San Diego, California, USA) using a large effect size (0.8), a confidence level or alpha of 95%, and power or beta of 90% (beta = 1 − 0.1). Data from the turbidity and cell count assays were exported into Microsoft Excel (Redmond, WA, USA), and comparisons between the experimental and control conditions were analyzed using two-tailed Student’s t-tests and a significance level of alpha = 0.05, which are appropriate for continuous parametric data analysis. The normality of the data were confirmed using the Shapiro–Wilk test for parametric data, and the statistical findings were verified using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with a post hoc Tukey analysis using the online software package Prism, Version 9, from GraphPad (San Diego, CA, USA), as previously described [39,40]. Comparisons of the percentage changes in cell numbers between the different experimental reagents were conducted via an analysis of variance (difference), whereby we compared the change from baseline with the positive or negative control and the change from baseline with the experimental reagent (Endocyn) at the same concentration or dilution (1:100, 10:100, 50:100).
3. Results
The results of these experiments demonstrated that the data derived from the turbidity and cell counts were closely correlated (R2 = 0.998). The administration of the negative control (1x PBS) resulted in a reduction in both the turbidity and cell counts of the Gram-positive bacteria, which responded similarly and led to average reductions of −1.2% (1:100 PBS), −1.8% (10:100 PBS), and −22.4% (50:100 PBS), p = 0.688 to p = 0.022 (Figure 1). The administration of the positive control (5% NaOCl or bleach) also reduced the turbidity and cell counts among Gram-positive bacteria by averages of −6.6% (1:100 bleach), −21.6% (10:100 bleach), and −37.5% (50:100 bleach), p = 0.08 to p = 0.001. Finally, administration of the experimental reagent Endocyn also reduced the turbidity and cell counts among Gram-positive bacteria by averages of −8.2% (1:100 Endocyn), −29.6% (10:100 Endocyn), and −35.5% (50:100 Endocyn), p = 0.14 to p = 0.004.
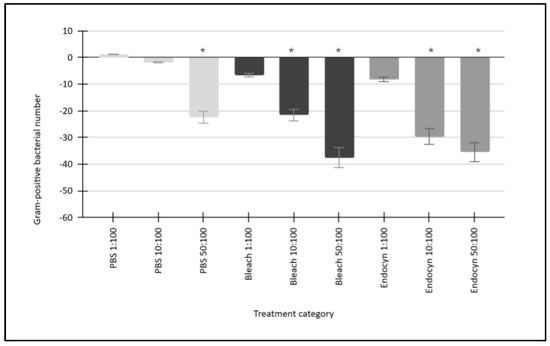
Figure 1.
Gram-positive bacterial responses to the administration of Endocyn and experimental controls. The negative control (1x PBS) reduced the turbidity and cell counts of the Gram-positive bacteria by between −1.2% and −22.4% (p = 0.688 to p = 0.022) on average over the concentration range tested compared with the baseline (0:100). The positive control (5% NaOCl or bleach) led to greater reductions ranging from −6.6% to −37.5% (p = 0.08 to p = 0.001), while Endocyn induced similar reductions of between −8.2% and −35.5% (p = 0.14 to p = 0.004) compared with the baseline. * Denotes the statistical significance of p-values less than alpha = 0.05.
The responses of Gram-negative bacterial species were also similar to each other (Figure 2). More specifically, the administration of the negative control (1x PBS) resulted in a reduction in both the turbidity and cell counts of the Gram-negative bacteria, which responded similarly and led to average reductions of −2.0% (1:100 PBS), −4.4% (10:100 PBS), and −18.6% (50:100 PBS), p = 0.712 to p = 0.024. Furthermore, the administration of the positive control (5% NaOCl or bleach) also reduced the turbidity and cell counts among Gram-negative bacteria by averages of −14.8% (1:100 bleach), −27.2% (10:100 bleach), and −46.9% (50:100 bleach), p = 0.041 to p = 0.001. In addition, the administration of Endocyn similarly reduced the turbidity and cell counts among Gram-negative bacteria by −16.7% (1:100 Endocyn), −40.7% (10:100 Endocyn), and −41.4% (50:100 Endocyn), p = 0.04 to p = 0.001.
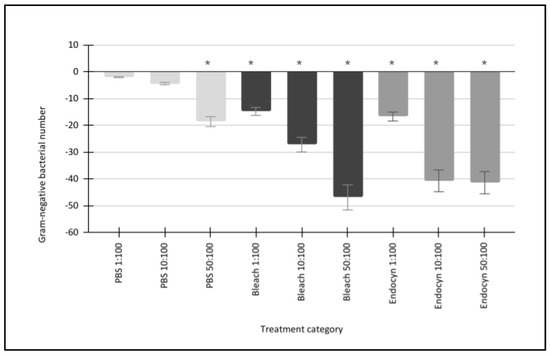
Figure 2.
Gram-negative bacterial responses to the administration of Endocyn and experimental controls. The negative control (1x PBS) reduced the turbidity and cell counts of the Gram-negative bacteria by between −2.0% and −18.6% (p = 0.712 to p = 0.024) on average over the concentration range tested compared with the baseline (0:100). The positive control (5% NaOCl or bleach) led to larger reductions ranging from −14.8% to −46.9% (p = 0.041 to p = 0.001), while Endocyn elicited similar reductions of between −16.7% and −41.4% (p = 0.04 to p = 0.001) compared with the baseline. * Denotes the statistical significance of p-values less than alpha = 0.05.
To more accurately analyze the effects of Endocyn, the differences between the effects on Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria were compared with the effects of the positive and negative controls directly (Figure 3). For example, the administration of Endocyn significantly reduced the turbidity and cell counts in both Gram-positive and -negative bacteria compared with the negative control (PBS) at 1:100 (−7% and −14.7%, respectively), 10:100 (−27.8% and −36.3%, respectively), and 50:100 (−13.1% and −22.8%, respectively), p < 0.05. However, some notable comparisons were found between the effects of Endocyn and the positive control (bleach). More specifically, there were no significant differences between the effects of Endocyn on Gram-positive and -negative bacteria compared with the positive control (bleach) at 1:100 (−1.6%, p = 0.711 and −1.9%, p = 0.68, respectively). However, more significant reductions were observed with Endocyn compared with the positive control among both Gram-positive and -negative bacteria at 10:100 (−8.0%, p = 0.49 and −13.5%, p = 0.41, respectively), although these differences were not observed with comparisons at the highest concentration of 50:100 (2%, p = 0.69 and 5.5%, p = 0.511, respectively).
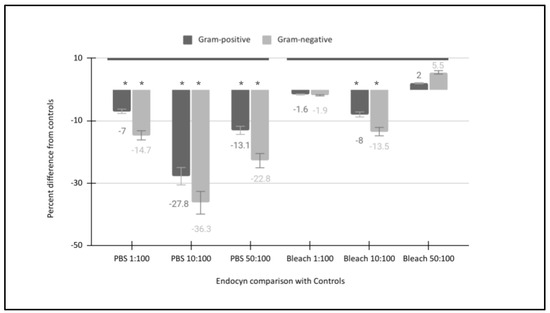
Figure 3.
Direct comparison of Endocyn’s effects with the positive and negative controls. Endocyn significantly reduced the turbidity and cell counts in both Gram-positive and -negative bacteria compared with the negative control (PBS) at 1:100 (−7% to −14.7%), 10:100 (−27.8% to −36.3%), and 50:100 (−13.1% to −22.8%), p < 0.05. However, no significant differences between Endocyn and the positive control (bleach) were found at 1:100 (−1.6% to −1.9%) or 50:100 (2% to 5.5%) p > 0.05, although more significant reductions were observed with Endocyn compared with the positive control at 10:100 (−8.0% to −13.5%, p = 0.41). * Denotes the statistical significance of p-values less than alpha = 0.05.
To provide more detailed information regarding the individual bacterial species responses to each of the independent (predictor) variables, all experimental trial data were compiled and summarized (Table 3). These data demonstrated that the turbidity and cell count averages were similar and the standard deviation (STD) or variation was low among the Gram-positive bacteria with the administration of the negative control (1x PBS) at 1:100 (average: 1.2%, STD ± 0.09), 10:100 (average: −1.8%, STD ± 0.09), or 50:100 (average: −22.4%, STD ± 0.75); this was also observed with the Gram-negative bacteria at 1:100 (average: −2.0%, STD ± 0.1), 10:100 (average: −4.4%, STD ± 0.1), and 50:100 (average: −18.6%, STD ± 0.55). In addition, the turbidity and cell count averages were consistent with low variation with the administration of the positive control (5% NaOCl) and the Gram-positive bacteria at 1:100 (average: −6.6%, STD ± 0.45), 10:100 (average: −21.6%, STD ± 1.65), and 50:100 (average: −37.5%, STD ± 0.66), similar to the observations of Gram-negative bacteria at 1:100 (average: −14.8%, STD ± 0.61), 10:100 (average: −27.2%, STD ± 1.17), and 50:100 (average: −46.9%, STD ± 0.67). Finally, the turbidity and cell averages were also uniform in the Endocyn administration experiments among the Gram-positive bacteria at 1:100 (average: −8.2%, STD ± 0.26), 10:100 (average: −29.6%, STD ± 1.30), and 50:100 (average −35.5%, STD± 1.26), similar to results observed with the Gram-negative bacteria at 1:100 (average: −16.7%, STD ± 1.46), 10:100 (average: −40.7%, STD ± 0.68), and 50:100 (average: −41.4%, STD ± 0.42).

Table 3.
Detailed summary data of experimental trials.
To confirm these analyses, aliquots from the bacterial suspensions used in the final experiments were processed to extract DNA for qPCR screening and analysis (Figure 4). These data demonstrated that each of the bacterial suspensions was found to express the positive control for bacterial presence (16S rRNA). In addition, each of the Gram-positive bacterial species was found to harbor DNA specific for that organism, as determined by validated screening primers (Actinomyces naeslundii, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus gordonii) without cross-contamination from the other cultured bacteria. Finally, each of the Gram-negative bacterial species was identified from each culture (Fusobacterium nucleatum, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Veillonella parvula), also without evidence of cross-contamination from the other concurrently cultured bacteria.
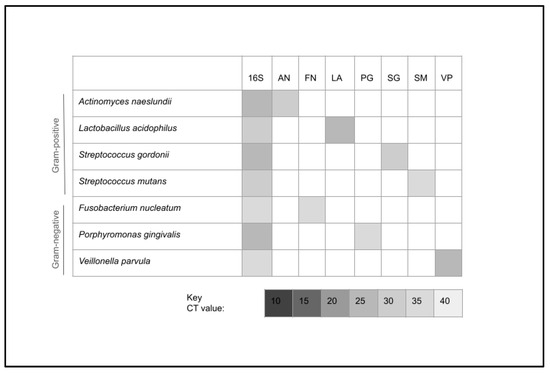
Figure 4.
DNA screening using qPCR screening and analysis. All experimental cultures expressed bacterial DNA (16S rRNA). In addition, all Gram-positive (Actinomyces naeslundii, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus gordonii) and Gram-negative (Fusobacterium nucleatum, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Veillonella parvula) bacterial species were screened and validated without evidence of cross contamination from the other concurrently cultured bacteria. CT = qPCR cycle threshold value.
4. Discussion
The primary objective of this study was to conduct an evaluation of the effectiveness of Endocyn as an antimicrobial agent, as well as an analysis of any differential effects on oral microbes, including Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The analysis of these data and the results strongly suggests that Endocyn is a much more effective antimicrobial agent than the negative control (sterile phosphate-buffered saline), which supports previous comparative studies and observational evidence [42,43,44]. However, the current study sought to provide more information regarding the efficacy of this specific formulation of Endocyn, a pH-neutral combined hypochlorous acid and hypochlorite endodontic irrigant, compared with a more rigorous positive control [45,46,47].
For example, the efficacy of chlorhexidine compared with sodium hypochlorite or bleach (NaOCl) has been demonstrated for the disinfection of root canals in several systematic reviews and meta analyses [48,49,50]. Although the mechanisms of action may be different and distinct for these disinfection methods and agents, the outcomes and bactericidal effects have been demonstrated to be comparable [51,52]. This study may therefore provide the first comprehensive analysis of and evidence for the antimicrobial effects of the Endocyn formulation compared with a known and validated standard—independently of its effects and activity on cells and tissues of the dental pulp [32].
This study demonstrated that the antimicrobial activity of Endocyn (with the proprietary mix of hypochlorous acid) against Gram-positive bacteria was similar to the effects of 5% sodium hypochlorite or bleach (NaOCl), which has been validated in numerous studies included in multiple systematic reviews and meta analyses [53,54,55,56]. In addition, these data revealed stronger and more robust antimicrobial effects of Endocyn against Gram-negative bacteria, which have also developed strong and robust adaptive responses to chlorine stress [57,58]. In fact, many of these organisms have presented significant challenges to many types of antimicrobial disinfection, including sodium hypochlorite, which suggests that the inhibition of Gram-negative bacteria at levels similar to or higher than those observed within the current study are significant findings of particular importance and clinical relevance to dental and oral healthcare providers [59,60,61].
In addition, these findings also represent a significant contribution to the range of organisms tested for individual susceptibility to this disinfectant and root canal irrigant. For example, recent studies of in vitro cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity involving hypochlorous acid (HOCl) have typically evaluated no more than two Gram-negative and two Gram-positive species, such as Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Streptococcus mutans, and Streptococcus sanguinis or even single bacterial species, such as Stenotrophomonas maltophilia [62,63]. This study included a detailed and specific analysis of seven bacterial species, including four Gram-positive organisms (Actinomyces naeslundii, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus gordonii) and three Gram-negative bacteria (Fusobacterium nucleatum, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Veillonella parvula) often found in complex dental infections and endodontic lesions [64,65,66].
Although this study provides novel information regarding the antimicrobial effectiveness of Endocyn against several clinically important species of oral bacteria, there are some limitations associated with this type of in vitro study that should be carefully considered. First, and most importantly, this study was performed using commercially available bacterial cells and species, which may not represent the full breadth and depth of bacterial species that may be present in complex endodontic infections [67,68]. Although proof of concept may be required prior to the initiation of clinical studies, ex vivo research studies may be an important next step in this research, as these types of data may be combined with in vitro data to provide a more thorough understanding of how a potential disinfectant and irrigant, such as Endocyn, may function in clinical applications [69,70,71].
In addition, the limited time course and in vitro design of this study (and other similar studies) does not allow for the evaluation of whether exposure to these disinfectants and irrigants may sufficiently impede bacterial growth to allow other mechanisms of the host immune response to overcome any residual bacterial presence within the root canal space, although this could be the subject of future clinical studies involving potential secondary infections that develop following the use of any endodontic irrigant—including Endocyn [72,73,74]. For example, several recent studies have suggested that long-term follow-up among patients on whom these various endodontic irrigants have been used in clinical trials may reveal additional information about patient outcomes and the incidence or prevalence of endodontic retreatments, which may provide new information or insights into the efficacy and reliability of these different clinical treatment options [75,76,77]. Moreover, research into the volumes and techniques associated with endodontic irrigation has demonstrated that clinical patient outcomes may differ not only according to the endodontic irrigation used, but also according to the technical procedures applied during the clinical treatment [78,79]. However, the lack of clinical trials in this area should be addressed by clinical and oral health researchers in future studies.
For example, due to the targeted nature of this study, it was not possible to investigate the effects of Endocyn on host tissues and cells, although this may be among the most important considerations for any clinical treatment [80,81]. Future clinical studies could evaluate Endocyn not only against other traditional dental irrigants, but also with other recently introduced adjunctive treatments such as Ozone, which may improve antimicrobial effects without significantly altering the survival of pulp tissues [82,83,84]. In addition, future clinical studies could also evaluate other alternative techniques and methods, such as erbium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Er:YAG) lasers, which have been proven to be clinically effective as bur preparations but may yield slightly different outcomes that could be dependent upon the endodontic irrigant used [85,86,87].
The only previous evaluation of Endocyn demonstrated lower levels of toxicity and higher levels of survival compared with 6% sodium hypochlorite and 2% chlorhexidine among human periodontal ligament (PDL) fibroblasts and stem cells of the apical papilla (SCAPs) [32]. In addition, several studies and reviews have already evaluated the comparative benefit to cell survival using hypochlorous acid compared with sodium hypochlorite, although not all studies evaluated the full range of cell types that may be affected by these treatments [88,89,90]. However, more recent work analyzing the effects of Endocyn revealed similar effects on DPSC growth as the positive control (sodium hypochlorite) but with less toxic effects on cellular viability—an important consideration for vital pulp treatment and therapy and improvements in patient outcomes [91].
5. Conclusions
This study represents the first extensive analysis and evaluation of the antimicrobial effects of Endocyn, a commercially available disinfectant and irrigant available for use in endodontic procedures, including root canals, pulpotomies, and pulpectomies. These data demonstrated clinically relevant levels of antimicrobial activity similar to those exhibited by other disinfectants and sterilants (including sodium hypochlorite or bleach), with more robust inhibition and other differences observed against some of the Gram-negative bacterial species tested across concentration ranges that may be important in clinical settings and dental procedures. These data strongly suggest that Endocyn may exhibit antimicrobial properties against Gram-positive and Gram-negative oral bacterial species of medical importance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.K. and V.S.; methodology, K.K.; formal analysis, S.S., L.M. and M.P.; investigation, S.S., L.M. and M.P.; resources, K.K. and V.S.; data curation, K.K. and M.P.; writing—original draft preparation, K.K., V.S. and M.P.; writing—review and editing, V.S., M.P. and K.K.; supervision, V.S. and K.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable, as this study does not involve humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data utilized in this study are presented in full. The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would also like to thank the Department of Advanced Education in Pediatric Dentistry for their assistance with this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| HOCl | Hypochlorous acid |
| pH | Potential of hydrogen |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| BSL | Biosafety Level |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| TSB | Trypticase Soy Broth |
| MRS | DeMan, Rogosa, and Sharpe |
| BHI | Brain–Heart Infusion |
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| CFR | Colony-forming unit |
References
- Boutsiouki, C.; Frankenberger, R.; Krämer, N. Clinical and radiographic success of (partial) pulpotomy and pulpectomy in primary teeth: A systematic review. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2021, 22, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.J.; Seremidi, K.; Stratigaki, E.; Kloukos, D.; Duggal, M.; Gizani, S. Deep dentine caries management of immature permanent posterior teeth with vital pulp: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dent. 2022, 124, 104214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matoug-Elwerfelli, M.; ElSheshtawy, A.S.; Duggal, M.; Tong, H.J.; Nazzal, H. Vital pulp treatment for traumatized permanent teeth: A systematic review. Int. Endod. J. 2022, 55, 613–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, J.A.; Dhar, V.; Chen, C.Y.; Crystal, Y.O.; Guelmann, M.; Marghalani, A.A.; AlShamali, S.; Xu, Z.; Glickman, G.N.; Wedeward, R. Use of Vital Pulp Therapies in Primary Teeth 2024. Pediatr. Dent. 2024, 46, 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- Urquhart, O.; Tampi, M.P.; Pilcher, L.; Slayton, R.L.; Araujo, M.W.B.; Fontana, M.; Guzmán-Armstrong, S.; Nascimento, M.M.; Nový, B.B.; Tinanoff, N.; et al. Nonrestorative Treatments for Caries: Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. J. Dent. Res. 2019, 98, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, J.A.; Seale, N.S.; Vargas, K.; Marghalani, A.A.; Al Shamali, S.; Graham, L. Primary Tooth Vital Pulp Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Pediatr. Dent. 2017, 39, 16–123. [Google Scholar]
- Schwendicke, F.; Walsh, T.; Lamont, T.; Al-Yaseen, W.; Bjørndal, L.; Clarkson, J.E.; Fontana, M.; Gomez Rossi, J.; Göstemeyer, G.; Levey, C.; et al. Interventions for treating cavitated or dentine carious lesions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 7, CD013039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, J.A.; Dhar, V.; Chen, C.Y.; Crystal, Y.O.; Guelmann, M.; Marghalani, A.A.; AlShamali, S.; Xu, Z.; Glickman, G.; Wedeward, R. Primary Tooth Vital Pulp Treatment Interventions: Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses. Pediatr. Dent. 2023, 45, 474–546. [Google Scholar]
- Chouchene, F.; Oueslati, A.; Masmoudi, F.; Baaziz, A.; Maatouk, F.; Ghedira, H. Efficacy of non-instrumental Endodontic treatment in primary teeth: A systematic review of clinical randomized trials. Syst. Rev. 2024, 13, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhamouly, Y.; Adham, M.M.; Dowidar, K.M.L.; El Backly, R.M. Outcome assessment methods of bioactive and biodegradable materials as pulpotomy agents in primary and permanent teeth: A scoping review. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringhini Junior, E.; Vitcel, M.E.; Oliveira, L.B. Evidence of pulpotomy in primary teeth comparing MTA, calcium hydroxide, ferric sulphate, and electrosurgery with formocresol. Eur. Arch. Paediatr. Dent. 2015, 16, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzanetakis, G.N.; Tsiouma, O.; Mougiou, E.; Koletsi, D. Factors Related to Pulp Survival After Complicated Crown Fracture Following Vital Pulp Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Endod. 2022, 48, 457–478.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Zeng, Q.; Tang, M.; Massey, J.; Bergeron, B.E.; Gu, L.; Tay, F.R. Efficacy of pulpotomy in managing irreversible pulpitis in mature permanent teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dent. 2024, 144, 104923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrashtehfar, K.I.; Jurado, C.A.; Al-Hadi, D.; Shetty, K.P. Pulpotomy versus root canal treatment in permanent teeth with spontaneous pain: Comparable clinical and patient outcomes, but insufficient evidence. Evid. Based Dent. 2023, 24, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.D.; Vernazza, C.R.; Abdulmohsen, B. Success of endodontic management of compromised first permanent molars in children: A systematic review. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2020, 30, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, L.B.; Neves, J.A.; Botelho, J.; Machado, V.; Mendes, J.J. Regenerative Endodontic Procedures: An Umbrella Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Deng, J.; Zou, J.; Wang, Y. Materials for pulpotomy in immature permanent teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snigdha, N.T.; Karobari, M.I.; Kamarudin, A.; Samsudin, N.A.; Baharin, F.; Dziaruddin, N.; Assiry, A.A.; Luke, A.M.; Scardina, G.A. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Regenerative Pulpotomy in the Treatment of Vital Primary Teeth. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2024, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoud, T.M.A.; Ricucci, D.; Lin, L.M.; Gaengler, P. Regeneration and Repair in Endodontics-A Special Issue of the Regenerative Endodontics-A New Era in Clinical Endodontics. Dent. J. 2016, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Malek, M.; Sigurdsson, A.; Lin, L.M.; Kahler, B. Regenerative endodontics: A comprehensive review. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 1367–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galler, K.M. Clinical procedures for revitalization: Current knowledge and considerations. Int. Endod. J. 2016, 49, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; De Deus, G.; Kristoffersen, I.M.; Wiig, E.; Reseland, J.E.; Johnsen, G.F.; Silva, E.J.N.L.; Haugen, H.J. Regenerative Endodontics by Cell Homing: A Review of Recent Clinical trials. J. Endod. 2023, 49, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, M.L.; Pires, P.M.; Ferreira, D.M.; Pintor, A.V.B.; de Almeida Neves, A.; Maia, L.C.; Primo, L.G. Is there evidence for the use of lesion sterilization and tissue repair therapy in the endodontic treatment of primary teeth? A systematic review and meta-analyses. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 2959–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozos-Guillen, A.; Garcia-Flores, A.; Esparza-Villalpando, V.; Garrocho-Rangel, A. Intracanal irrigants for pulpectomy in primary teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2016, 26, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasan, P.K.; Haraszthy, V.I. Chlorhexidine Improves Hygiene Reducing Oral Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes with Antimicrobial Effects at Distinct Microenvironments amongst Subjects Stratified by Health Status. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruksakiet, K.; Hanák, L.; Farkas, N.; Hegyi, P.; Sadaeng, W.; Czumbel, L.M.; Sang-Ngoen, T.; Garami, A.; Mikó, A.; Varga, G.; et al. Antimicrobial Efficacy of Chlorhexidine and Sodium Hypochlorite in Root Canal Disinfection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 1032–1041.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikström, A.; Romani Vestman, N.; Rakhimova, O.; Lazaro Gimeno, D.; Tsilingaridis, G.; Brundin, M. Microbiological assessment of success and failure in pulp revitalization: A randomized clinical trial using calcium hydroxide and chlorhexidine gluconate in traumatized immature necrotic teeth. J. Oral Microbiol. 2024, 16, 2343518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogales, C.G.; Cazares, R.X.R.; Nardello, L.C.L.; Mayer, M.P.A.; Gavini, G.; Zehnder, M.; Pinheiro, E.T. Evaluating the Impact of Ultrasonic Irrigation on Bacterial Levels and Activity Following Chemomechanical Procedures. J. Endod. 2025, 51, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirali, R.E.; Bodur, H.; Ece, G. In vitro antimicrobial activity of sodium hypochlorite, chlorhexidine gluconate and octenidine dihydrochloride in elimination of microorganisms within dentinal tubules of primary and permanent teeth. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2012, 17, e517–e522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daood, U.; Parolia, A.; Matinlinna, J.; Yiu, C.; Ahmed, H.M.A.; Fawzy, A. Properties of a modified quaternary ammonium silane formulation as a potential root canal irrigant in endodontics. Dent. Mater. 2020, 36, e386–e402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daood, U.; Parolia, A.; Elkezza, A.; Yiu, C.K.; Abbott, P.; Matinlinna, J.P.; Fawzy, A.S. An in vitro study of a novel quaternary ammonium silane endodontic irrigant. Dent. Mater. 2019, 35, 1264–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott MB 2nd Zilinski, G.S.; Kirkpatrick, T.C.; Himel, V.T.; Sabey, K.A.; Lallier, T.E. The Effects of Irrigants on the Survival of Human Stem Cells of the Apical Papilla, Including Endocyn. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Tsai, C.F.; Huang, H.L. Effects of hypochlorous acid mouthwash on salivary bacteria including Staphylococcus aureus in patients with periodontal disease: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lineback, C.B.; Nkemngong, C.A.; Wu, S.T.; Li, X.; Teska, P.J.; Oliver, H.F. Hydrogen peroxide and sodium hypochlorite disinfectants are more effective against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms than quaternary ammonium compounds. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyski, S.; Bocian, E.; Laudy, A.E. Application of normative documents for determination of biocidal activity of disinfectants and antiseptics dedicated to the medical area: A narrative review. J. Hosp. Infect. 2022, 125, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rôças, I.N.; Provenzano, J.C.; Neves, M.A.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr. Disinfecting Effects of Rotary Instrumentation with Either 2.5% Sodium Hypochlorite or 2% Chlorhexidine as the Main Irrigant: A Randomized Clinical Study. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, L.S.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Andrade Junior, C.V.; Soares, R.G.; Vettore, M.V. The Effect of Sodium Hypochlorite and Chlorhexidine as Irrigant Solutions for Root Canal Disinfection: A Systematic Review of Clinical Trials. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafaurie, G.I.; Zaror, C.; Díaz-Báez, D.; Castillo, D.M.; De Ávila, J.; Trujillo, T.G.; Calderón-Mendoza, J. Evaluation of substantivity of hypochlorous acid as an antiplaque agent: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2018, 16, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.; Swanbeck, S.; Banning, G.; Alhwayek, T.; Sullivan, V.; Howard, K.M.; Kingsley, K. Assessment of Sodium Diamine Fluoride (SDF) with Light Curing Technique: A Pilot Study of Antimicrobial Effects. Methods Protoc. 2022, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emett, J.; David, R.; McDaniel, J.; McDaniel, S.; Kingsley, K. Comparison of DNA Extracted from Pediatric Saliva, Gingival Crevicular Fluid and Site-Specific Biofilm Samples. Methods Protoc. 2020, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, S.H.; Hu, S.W.; Yang, J.J.; Yan, M.; Lin, Y.Y. Potential Oral Health Care Agent from Coffee Against Virulence Factor of Periodontitis. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, R.K.; Jain, N.; Singh, A.; Jain, A.; Jindal, A.; Kumawat, M.K.; Paiwal, K. Comparative Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Efficacy of Chemical and Phytomedicinal Agents When Used As Intracanal Irrigants: An In Vitro Study. Cureus 2023, 15, e48754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botu, R.K.; Rachuri, P.; Martha, S.; Raparla, M.; Matilda, S.; Yemparla, S. Comparative Evaluation of the Efficacy of Chlorhexidine, Diode Laser, and Saline in Reducing the Microbial Count in Primary Teeth Root Canals: An In Vivo Study. Int. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2023, 16, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.; Kumar, G.; Goswami, M.; Johar, S.; Sharma, A. Antimicrobial efficacy of sodium hypochlorite, saline, and Er, Cr:YSGG laser-assisted disinfection in root canal treatment of primary molars: An in vivo study. J. Indian. Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2023, 41, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.S.; Ankola, A.; Peerzade, M.; Sankeshwari, R.; Hampiholi, V.; Pai Khot, A.; Shah, M.A. Comparative Efficacy of Different Irrigant Activation Techniques for Irrigant Delivery Up to the Working Length of Mature Permanent Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. Endod. J. 2023, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teja, K.V.; Janani, K.; Srivastava, K.C.; Shrivastava, D.; Jose, J.; Marya, A.; Karobari, M.I. Comparison of Herbal Agents with Sodium Hypochlorite as Root Canal Irrigant: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 8967219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, G.G.; Rabello, D.G.D.; Corazza, B.J.M.; Gomes, A.P.M.; Silva, E.G.; Martinho, F.C. Comparison of the effectiveness of single- and multiple-sessions disinfection protocols against endotoxins in root canal infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi, H.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Kristoffersen, A.K.; Enersen, M.; Mdala, I.; Ørstavik, D.; Rôças, I.N.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr. Antibacterial Effectiveness of 2 Root Canal Irrigants in Root-filled Teeth with Infection: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonini, R.; Salvadori, M.; Audino, E.; Sauro, S.; Garo, M.L.; Salgarello, S. Irrigating Solutions and Activation Methods Used in Clinical Endodontics: A Systematic Review. Front. Oral Health 2022, 3, 838043, Erratum in Front. Oral Health 2022, 3, 876265. https://doi.org/10.3389/froh.2022.876265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharchi, A.S.; Tagiyeva-Milne, N.; Kanagasingam, S. Regenerative Endodontic Procedures, Disinfectants and Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Prim. Dent. J. 2020, 9, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada, I.; Micó-Muñoz, P.; Giner-Lluesma, T.; Micó-Martínez, P.; Collado-Castellano, N.; Manzano-Saiz, A. Influence of microbiology on endodontic failure. Literature review. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2019, 24, e364–e372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swimberghe, R.C.D.; Coenye, T.; De Moor, R.J.G.; Meire, M.A. Biofilm model systems for root canal disinfection: A literature review. Int. Endod. J. 2019, 52, 604–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparelli, C.H.C.; Marceliano-Alves, M.F.V.; Bastos, L.F.; Lopes, R.T.; Limoeiro, A.G.D.S.; Nascimento, W.M.; Dos Santos, L.M.H.; Boukpessi, T.; Soares, A.J.; Frozoni, M. Analysis of the penetration of NaOCl 5.25% into dentinal tubules using different irrigation protocols: An ex vivo study. Aust. Endod. J. 2024, 50, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabino-Silva, R.; Cardoso, I.V.; Vitali, F.C.; Alves, A.M.H.; Souza, B.D.M.; Bortoluzzi, E.A.; da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, L.; da Silveira Teixeira, C. Prevalence of postoperative pain after endodontic treatment using low and high concentrations of sodium hypochlorite: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2023, 27, 4157–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, E.A.; Toner, R.; Kilgariff, J.K. Evidence-based Standard Operating Procedures FoR the Prevention and Management of Sodium Hypochlorite Accidents in Dentistry. Prim. Dent. J. 2023, 12, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruwa, A.O.; Martins, J.N.R.; Maravic, T.; Mazzitelli, C.; Mazzoni, A.; Ginjeira, A. Effect of Endodontic Irrigating Solutions on Radicular Dentine Structure and Matrix Metalloproteinases-A Comprehensive Review. Dent. J. 2022, 10, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cruz Nizer, W.S.; Inkovskiy, V.; Overhage, J. Surviving Reactive Chlorine Stress: Responses of Gram-Negative Bacteria to Hypochlorous Acid. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampf, G. Biocidal Agents Used for Disinfection Can Enhance Antibiotic Resistance in Gram-Negative Species. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Septimus, E.J.; Schweizer, M.L. Decolonization in Prevention of Health Care-Associated Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 29, 201–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, J.M. Hand and environmental hygiene: Respective roles for MRSA, multi-resistant gram negatives, Clostridioides difficile, and Candida spp. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2024, 13, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampf, G. Antibiotic ResistanceCan Be Enhanced in Gram-Positive Species by Some Biocidal Agents Used for Disinfection. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.F.; Chung, J.J.; Ding, S.J.; Chen, C.C. In vitro cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity of hypochlorous acid antimicrobial agent. J. Dent. Sci. 2024, 19, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anari, R.K.; Nikkhahi, F.; Javadi, A.; Bakht, M.; Rostamani, M.; Kelishomi, F.Z.; Alizadeh, S.A. Evaluation of antibacterial activity of five biocides and the synergistic effect of biocide/EDTA combinations on biofilm-producing and non-producing Stenotrophomonas maltophilia strains isolated from clinical specimens in Iran. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadainy, H.A.; Abdel-Karim, A.H.; Fouad, A.F. Prevalence of Fusobacterium Species in Endodontic Infections Detected With Molecular Methods: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Endod. 2023, 49, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Gonzalez, M.V.; Mungarro-Cornejo, G.A.; Espinosa-Cristóbal, L.F.; Donohue-Cornejo, A.; Tovar Carrillo, K.L.; Saucedo Acuña, R.A.; García Calderón, A.G.; Guzmán Gastelum, D.A.; Zambrano-Galván, G.; Cuevas-Gonzalez, J.C. Antimicrobial resistance in odontogenic infections: A protocol for systematic review. Medicine 2022, 101, e31345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardila, C.M.; Bedoya-García, J.A.; González-Arroyave, D. Antimicrobial resistance in patients with endodontic infections: A systematic scoping review of observational studies. Aust. Endod. J. 2023, 49, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronzato, J.D.; Bomfim, R.A.; Hayasida, G.Z.P.; Cúri, M.; Estrela, C.; Paster, B.J.; Gomes, B.P.F.A. Analysis of microorganisms in periapical lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 124, 105055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ahmad, A.; Elamin, F.; Gärttner, R.; Anderson, A.; Wittmer, A.; Mirghani, Y.; Hellwig, E. New Bacterial Combinations in Secondary Endodontic Infections of Patients with a Recent Systematic Antibiotic Therapy. Monogr. Oral Sci. 2021, 29, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brave, D.R.; Langaliya, A.K.; Rai, J.S.; Buch, A.; Mahendra, M.; Patel, S. The Impact of Chlorhexidine as an Endodontic Irrigant/Medicament on Post-Obturation Pain in Patients Following Endodontic Therapy: A Preliminary Bayesian Meta-Analysis. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2024, 16 (Suppl. S3), S2935–S2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi Mazreah, S.; Shirvani, A.; Azizi Mazreah, H.; Dianat, O. Evaluation of irrigant extrusion following the use of different root canal irrigation techniques: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aust. Endod. J. 2023, 49, 396–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendell-Wall, R.; Nguyen, J.T.; Salleras, F.; Kamboj, A.S.; Diwen Tan, S.A.; Manish Trivedi, V.; de Mello-Neto, J.M.; Rodrigues Amaral, R. Antimicrobial efficacy of Odontopaste in endodontics: A systematic review. Evid. Based Dent. 2024, 25, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duggal, M.; Tong, H.J.; Al-Ansary, M.; Twati, W.; Day, P.F.; Nazzal, H. Interventions for the endodontic management of non-vital traumatised immature permanent anterior teeth in children and adolescents: A systematic review of the evidence and guidelines of the European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry. Eur. Arch. Paediatr. Dent. 2017, 18, 139–151, Erratum in Eur. Arch. Paediatr. Dent. 2017, 18, 153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-017-0292-x. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malu, K.; Khubchandani, M. Triple Antibiotic Paste: A Suitable Medicament for Intracanal Disinfection. Cureus. 2022, 14, e29186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchal, K.G.; Virani, K.; Patel, V.; Ali Khan, A.; Pettiwala, A.; Puranik, S.S.; Joshi, S. Triple Antibiotic Paste: A Game Changer in Endodontics. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2024, 16 (Suppl. S3), S1913–S1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutsioukis, C.; Arias-Moliz, M.T. Present status and future directions—Irrigants and irrigation methods. Int. Endod. J. 2022, 55 (Suppl. S3), 588–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, B.P.F.A.; Aveiro, E.; Kishen, A. Irrigants and irrigation activation systems in Endodontics. Braz. Dent. J. 2023, 34, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, Y.; Anil, C.K.; Kumar, N.S.; Batra, D.; Kapur, I.; Chaturvedi, M.; Mustafa, M. Exploring Efficacy and Safety: Comparative Evaluation of Different Irrigation Solutions in Root Canal Therapy at a Tertiary Care Setting. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2024, 16 (Suppl. S3), S2546–S2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arul, B.; Suresh, N.; Sivarajan, R.; Natanasabapathy, V. Influence of volume of endodontic irrigants used in different irrigation techniques on root canal dentin microhardness. Indian. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 32, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixão, S.; Rodrigues, C.; Grenho, L.; Fernandes, M.H. Efficacy of sonic and ultrasonic activation during endodontic treatment: A Meta-analysis of in vitro studies. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2022, 80, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaïl-Faugeron, V.; Glenny, A.M.; Courson, F.; Durieux, P.; Muller-Bolla, M.; Fron Chabouis, H. Pulp treatment for extensive decay in primary teeth. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 5, CD003220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, N.; Goel, S.; Mathur, V.P.; O’Connell, A.C.; Johnson, R.M.; Rahul, M.; Sultan, F.; Goswami, M.; Srivastav, S.; Ritwik, P. Success of medicaments and techniques for pulpotomy of primary teeth: An overview of systematic reviews. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2022, 32, 828–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Gallo, S.; Garofoli, A.; Poggio, C.; Arciola, C.R.; Scribante, A. Ozone Gel in Chronic Periodontal Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial on the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Ozone Application. Biology 2021, 10, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, P.; Sharma, K.; Maiti, N.; Yadav, S.; Verma, V.; Puthenkandathil, R. Ozone: An Adjunct in Dental Treatment. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2024, 16 (Suppl. S1), S2–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.J.N.L.; Prado, M.C.; Soares, D.N.; Hecksher, F.; Martins, J.N.R.; Fidalgo, T.K.S. The effect of ozone therapy in root canal disinfection: A systematic review. Int. Endod. J. 2020, 53, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Ren, C.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, J.; Wu, M. Clinical application of Er:YAG laser and traditional dental turbine in caries removal in children. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2024, 48, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valério, R.A.; Borsatto, M.C.; Serra, M.C.; Polizeli, S.A.; Nemezio, M.A.; Galo, R.; Aires, C.P.; Dos Santos, A.C.; Corona, S.A. Caries removal in deciduous teeth using an Er:YAG laser: A randomized split-mouth clinical trial. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 20, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenyan, H.; Pujue, Z.; Yuhang, H.; Zhenni, L.; Yuejun, W.; Wenbin, W.; Ziling, L.; Pathak, J.L.; Sujuan, Z. The impact of Er:YAG laser combined with fluoride treatment on the supragingival plaque microbiome in children with multiple caries: A dynamic study. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susila, A.V.; Sai, S.; Sharma, N.; Balasubramaniam, A.; Veronica, A.K.; Nivedhitha, S. Can natural irrigants replace sodium hypochlorite? A systematic review. Clin. Oral Investig. 2023, 27, 1831–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrel, S.I.; Matichescu, A.; Dinu, S.; Buzatu, R.; Popovici, R.; Dinu, D.C.; Bratu, D.C. New Insights Regarding the Use of Relevant Synthetic Compounds in Dentistry. Molecules 2024, 29, 3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coaguila-Llerena, H.; Raphael da Silva, L.; Faria, G. Research methods assessing sodium hypochlorite cytotoxicity: A scoping review. Heliyon 2023, 10, e23060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Truman, B.; Ma, L.; Stewart, S.; Kingsley, K.; Sullivan, V. Assessment of Endocyn on Dental Pulp Stem Cells (DPSCs): A Pilot Study of Endodontic Irrigant Effects. Methods Protoc. 2025, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).