Abstract
The recommendations for the wear and hygiene of ocular prostheses can vary among practitioners, and it is still a controversial theme in the literature. This clinical trial evaluated the microbial load, tissue health of the socket, and the participants’ opinions before and after the use of two hygiene protocols. Thirty ocular prosthesis wearers used either a Daily Protocol (DPt: hygiene once a day) or Weekly Protocol (WPt: hygiene once a week) for 5 weeks with a washout of 7 days. The microbial load was quantified by the colony-forming unit count of the aerobic bacteria, Candida spp., Staphylococcus spp., and Gram-negative bacteria. The tissue health of the socket was evaluated by scores, and patients’ opinion of the protocols was evaluated using the analogic visual scale (VAS). Data were analyzed by ANOVA Repeated Measures, Friedman, Cochran’s Q Test, Wilcoxon, Fisher, and Pearson’s chi-square tests considering p < 0.05. There was no difference in the microbial load of the microorganisms (p > 0.05). Both protocols improved socket inflammation (p = 0.005) and discharge (p < 0.001); DPt improved edema (p = 0.021) and crusting (p = 0.020). There was no difference in patients’ rating responses (VAS) for all the questions of patients’ opinion (Q1: p = 1.0; Q2: p = 1.0; Q3: p = 1.0; Q4: p = 1.0; Q5: p = 1.0; Q6: p = 0.317; Q7: p = 1.0; Q8: p = 0.159). There was a correlation between eye drops/edema (p = 0.030), eye drops/pain (p = 0.016), microbial load with discharge, inflammation, eyelid edema, and pain. Inflammation was correlated with edema at baseline (p < 0.001) and after DPt (p = 0.018), and with crusting at baseline (p = 0.003); edema was correlated with crusting at baseline (p < 0.001); crusting was correlated with discharge after WPt (p < 0.001). The protocols showed no effects on the microbial load of the anophthalmic socket and ocular prosthesis. However, better tissue health and patient acceptance were observed after both regimens.
1. Introduction
The rehabilitation with an ocular prosthesis positively impacts quality of life by restoring appearance and social functioning [1]. However, some complications related to rehabilitation can occur while using an ocular prosthesis. Ocular prosthesis wearers may experience socket discomfort, including discharge, crusty eyelashes, inflammation, eyelid edema, dryness, and pain. The causes of discomfort can be related to infections or inflammation of the socket, tear film impairment, alterations in lacrimal drainage, surgical complications, phantom eye pain, environment changes, poor fitting, and frequent or inappropriate cleaning of the prosthesis [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. The association between cleaning and socket discomfort may be related to a dysbiosis of the microenvironment of the anophthalmic socket caused by the introduction of pathogenic microorganisms from hands or by the removal of the lacrimal proteins that coat and lubricate the ocular prosthesis [2,3,16,17,18,19,20].
The ocular prosthesis cleaning regimen is still controversial in the literature [2,21,22,23,24,25]. Studies found no association between cytological alterations of the anophthalmic socket conjunctiva and prosthesis care [21], and between the discharge and irritation of the socket with care and wear routine [24]. However, regular cleaning of the ocular prosthesis may be important to prevent the anophthalmic socket from contracting infections [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32].
Studies have found that the microorganisms that colonize the ocular prosthesis are similar to those that colonize the anophthalmic socket [29,30,33] and found 38 different species of microorganisms colonizing both anophthalmic socket and ocular prosthesis, with a higher percentage of Gram-negative and of Staphylococcus aureus [30,33,34]. Care with the hygiene of the ocular prosthesis should consider the individual needs of the patients, but the establishment of guiding protocols can be of great help for decision making and for the adequate orientation of the patient [2]. Currently, randomized controlled clinical trials to evaluate the effect of the standardized prosthetic ocular hygiene protocols on the microbial load and the tissue health of the anophthalmic socket are scarce [29].
Thus, this cross-over randomized controlled clinical trial evaluated the microbial load present in the socket and on the ocular prosthesis, tissue health of the anophthalmic socket, and the opinion of the ocular prosthesis wearers before and after the use of two hygiene protocols, as well as the relationship among these variables. The null hypothesis considered there are no differences between the Daily Protocol (DPt) and Weekly Protocol (WPt) regarding the effect on microbial load, tissue health of the anophthalmic socket, and patients’ opinions.
2. Materials and Methods
This randomized, controlled, blinded, and cross-over clinical trial followed the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials statement, CONSORT. Research Ethics Committees of the University of São Paulo at Ribeirão Preto School of Dentistry (CAAE: 71783917.6.0000.5419) approved the study, and the trial was registered at http://www.ensaiosclinicos.gov.br/rg/view/6866/(TRIAL: RBR-8VZWDG) URL accessed on 24 September 2018. Participants were enrolled in the study after an informed consent form was signed.
Participants were recruited from the Ribeirão Preto School of Dentistry. The inclusion criteria were age ≥ 18 years, good general health conditions, and wearing ocular prostheses for at least 3 months with satisfactory retention, adaptation, and finished surface. The exclusion criteria were inflammatory and/or local infectious diseases, neoplasms, or other diagnosed and untreated deformities; the presence of orbital prosthesis; the use of antibiotics, steroids, or antifungal agents at least 3 months before the study or during follow-up; alcoholism; serious illnesses; the need for frequent hospitalization; and the inability to attend the return visits for evaluation.
The sample size was determined by Open-Source Epidemiologic Statistics (openepi.com) [35], and an estimation was based on the colony-forming unit (CFULog10) counts. The parameters showing a minimally significant difference of 1 log and a standard deviation of 1.30 led to a total sample size of 23 participants to ensure a power of 80% (α = 0.050; β = 0.200) and to reject the null hypothesis, considering results found in the literature [26].
The sociodemographic and baseline data were assessed, and the participants were randomly assigned following computer-generated randomization (Excel 2010; Microsoft Corp, Redmond, WA, USA) into two groups: one group following the DPt, which consisted of cleaning the ocular prosthesis with neutral soap (Pleasant; Perol, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil) once a day, and another group following the WPt, which consisted of cleaning the ocular prosthesis with neutral soap (Pleasant; Perol) once a week. These protocols were applied following two interventions, according to a cross-over design for 5 weeks with a washout period of 7 days. During the washout, the patients were oriented to maintain the routine care they usually performed before the research.
Participants received a dosed bottle with neutral soap and another with saline solution. They were instructed to wash their hands with the neutral soap and in the morning, upon waking up, the prosthesis should be removed from the cavity, rubbed on all surfaces with the fingertips with a drop of soap for one minute, and rinsed thoroughly under running water. The face should also be washed with the same soap, and the anophthalmic socket should be washed with plenty of water. To avoid rubbing and the manipulation of the prosthesis during the day, the participants were instructed to drip saline solution (Saline Solution; Arboretum) into the cavity, without removing the prosthesis. The use of eye drops or any other product for cleaning during the experiment was suspended. Response variables were measured in baseline (B) and after each period of the protocol used.
Researchers were blinded to the protocols. A researcher (V.C.O.) generated the randomization list, and another researcher (L.R.M.) instructed participants on the hygiene protocols. L.S.E. and C.M.A.P.M. performed the biofilm collection and laboratory processing, the evaluation of the clinical characteristics was performed by C.H.S.-L., and data tabulation and analysis were performed by C.H.S.-L. and A.P.M. The participants were not “blinded” once they needed the instructions to perform the instituted protocol.
The primary outcome was the quantification of the microbial load of the specific microorganism. Biofilm was collected from all surfaces of the ocular prostheses and the lower, upper tarsal, and bulbar conjunctivas with two sterile micro brushes (Micro brush; Shanghai Even Medical Instruments Co., Shangai, China) for each site [24]. The two active tips of each site were inserted into micro tubes containing 250 µL of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), which were immediately vortexed for 1 min. Then, 25 µL this solution was diluted from 100 to 10−3, sown in Petri dishes in a specific culture medium, and incubated at 37 °C for 48 h for the growth of total aerobic bacteria, Candida spp., Staphylococcus spp., and Gram-negative bacteria. The anticandidal effects were determined by microbial load using the formula CFU/mL = number of colonies × 10 n/q, where n is the absolute value of dilution (0, 1, 2, or 3, considering dilution that CFUs count ranged from 0 to 300 colonies), and q is the quantity pipetted for each dilution at inoculation (0.025 mL). The data were Log10-transformed.
The secondary outcomes were clinical characteristics of the anophthalmic cavity and participants’ opinions about the two protocols. An experienced professional evaluated the clinical characteristics during the clinical examination associated with analyses of the images obtained of the anophthalmic socket, without their ocular prosthesis. The photographs (Canon EOS Digital Rebel EF-S 18–55; Canon Inc., Tokyo, Japan) were performed with standardized camera-to-object distance and exposure time, and transferred to a computer to obtain the scores, as follows: inflammation of the socket (absent = score 0; present: score 1); eyelid edema (absent = score 0; present: score 1); discharge (absent = score 0; present = score 1; abundant = score 2); and crusting (absent = score 0; present = score 1) [36]. Based on the patient’s report, the pain was scored as absent = 0 or present = 1. The results were analyzed based on the frequency of the participants with the improvement or worsening of clinical characteristics before and after using the protocols.
Information about the participants’ opinions and adherence to one of the two protocols was obtained by a form (Table 1). The questions were answered on a 0–10 scale (Analogic Visual Scale–AVS), in which “0” was the worst possible (most negative) answer and “10” was the best possible (most positive) answer.

Table 1.
Questionnaire to assess participants’ satisfaction with hygiene protocols.
As complementary analyses were verified the correlation between clinical characteristics with sociodemographic data, clinical characteristics between them, and clinical characteristics with microbial load.
The protocols were compared to the capacity of the microbial load reduction and the ability to maintain or obtain healthy tissues. Shapiro–Wilk and Levene tests were used to verify the normality and homoscedasticity of the data, respectively. The ANOVA Repeated Measures Test and the Friedman Test were used for comparison of the microbial load. The Friedman Test was used to compare discharge, and the Q Test of Cochran was used to compare eyelid conjunctiva inflammation, eyelid edema, crusted eyelashes, and pain. The Wilcoxon Test was used for the analysis of the items of the questionnaire. Fisher’s exact test and Pearson’s chi-square test were used to analyze the correlation between variables. Differences were considered significant when p < 0.05 and all tests were performed by using a statistical software program (SPSS Statistics 21.0; IBM, Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Results
A total of 51 individuals were assessed. The final sample consisted of 30 participants (Figure 1).
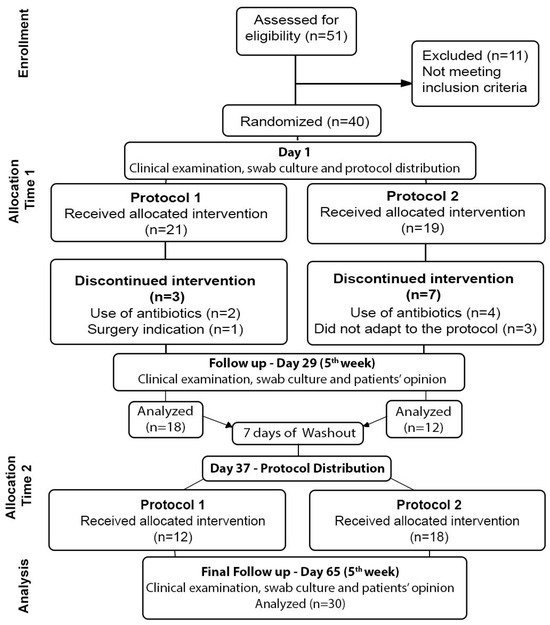
Figure 1.
CONSORT 2010 Flow Diagram.
The characteristics of the sample are summarized in Table 2. There was no significant difference between the microbial load of the analyzed microorganisms in the baseline and after the use of the protocols (Table 3).

Table 2.
Sociodemographic and clinical information of the participants in absolute number and percentage (%).

Table 3.
Microbial load (CFULog10) of the microorganisms in baseline and after the use of the daily (DPt) and weekly (WPt) hygiene protocols.
The frequency of the participants with inflammation of the mucosa and discharge was significantly lower after the use of both protocols when compared to the Baseline. After the use of the DPt, there was a decrease in the frequency of individuals with eyelid edema and crusting followed by WPt and Baseline. The protocols did not influence the pain complaints (Table 4).

Table 4.
Comparison of the participant’s frequency (absolute number (%)) with or without alterations in the clinical characteristics assessed at Baseline (B) and after the use of the daily (DPt) and weekly (WPt) hygiene protocols.
The analysis did not show significant difference between the participants’ opinions with DPt and WPt (Q1: p = 1.0; Q2: p = 1.0; Q3: p = 1.0; Q4: p = 1.0; Q5: p = 1.0; Q6: p = 0.317; Q7: p = 1.0; and Q8: p = 0.159). Regarding the correlation between sociodemographic data with clinical characteristics (Table 5), there was a significant correlation between the use of eye drops with eyelid edema (p = 0.030) and the use of eye drops with pain (p = 0.016).

Table 5.
Correlation between sociodemographic data with clinical characteristics.
The correlation analyses between clinical characteristics at baseline and after the use of the hygiene protocols showed a correlation between socket inflammation with eyelid edema at baseline (p < 0.001) and after the DPt (p = 0.018); socket inflammation with crusting (p = 0.003) and eyelid edema with crusting (p < 0.001) at baseline; and crusting with discharge (p < 0.001) after the WPt (Table 6).

Table 6.
Correlation (p) between clinical characteristics at baseline (B), and after the use of the daily (DPt) and weekly (WPt) hygiene protocols.
The correlation between all microorganisms with signs of inflammation at different times of collection shows some correlation between microorganisms and eyelid edema, discharge, and pain was also identified (Table 7).

Table 7.
Correlation between clinical characteristics and microbial load of the prosthesis and socket at Baseline(B) and after the use of the daily (DPt) and weekly (WPt) hygiene protocols.
4. Discussion
Anophthalmic socket discomfort and discharge are the main complaints of the ocular prosthesis wearers [3,4,5,12,14,20,29]. Studies investigating the factors related to the clinical signs and symptoms of these population demonstrates conflicting observations, which are mainly associated with the frequency of cleaning habits and the presence of pathogenic microorganisms [2,3,8,12,16,17,21,24,25,26,28,29,30,31,33]. Since ocular prosthesis wearers have a relative risk of developing ocular infections once the anophthalmic socket has more microorganisms than the fellow eye and carries potential pathogenic bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, S. epidermidis, and Gram-negative species [25,26,27,28,29,30], the investigation of the influence of microorganisms and the relationship with clinical signs and discomfort has been of great interest.
Thus, our study aimed to establish a protocol for prosthetic ocular wearers, assessing the effect of two protocols of prosthesis hygiene on the microbial load of the anophthalmic socket and ocular prosthesis, to assess the influence of the protocols on the tissue health of the anophthalmic socket and to collect the patient’s opinion of the established protocols. The null hypothesis of this study was partially accepted. No differences were found regarding the effect of the protocols on microbial load and patients’ opinions, but there were differences between the baseline and the protocols on tissue health (clinical signs of inflammation).
Although no difference was found in the microbial load before and after the protocols the colony-forming units count in all observations was higher than 1Log for total aerobic, Gram-negatives, and Staphylococcus spp., and this is considered a high value [37]. This result corroborates in part with an observational study of Toribio et al. (2017) who found a high microbiological density and the presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the anophthalmic socket [29] and is in contrast with a clinical trial of Paranhos et al. (2008), who found a decrease in microorganisms before and after the use of cleaning agents, such as liquid soap [26]. This difference could be associated with differences in the methodology of the studies.
The signs of inflammation and discharge on the anophthalmic socket can be caused by many factors, including poor fitting and finishing of the ocular prosthesis [8,16,17,21,38]; biofilm adhesion [26,27,32,33]; bacterial or viral infections [4,5]; the frequent removal of the prosthesis [2,3,16]; surgical complications, such as implant exposure or pyogenic granuloma [4,5,9]; alterations in meibomian glands and poor lubrication of the socket [4,5,13,15,20]; and exposure to adverse environmental conditions, like dry weather and air conditioner [20,38,39].
Recommendations for the use, removal, and cleaning of the ocular prosthesis may vary between professionals [22]. This fact can also be observed by the heterogenous habits of our sample at baseline. Studies have demonstrated an association between the frequent removal or cleaning of the prosthesis and socket discomfort, inflammation, discharge, and lid abnormalities [3,12,16]. However, these observations are in contrast with other studies that showed that patients who performed daily hygiene had fewer problems with the anophthalmic socket [25], and symptoms of discomfort were not correlated with hygiene habits but with the presence of pathogenic microorganisms [24]. The relationship direction between the frequency of cleaning and eyelid abnormalities or discharge, for example, is still not clear, since both problems have multifactorial causes. Lid abnormalities can be associated with many other variables, such as aging, surgical complications, inadequate implant size, and heavy ocular prosthesis [40], and their appearance can be a clinical course of those complications. Discharge can be associated with tear film impairment or morphological alterations of the lacrimal apparatus [21,24]. So, there is a clear importance of the development of longitudinal studies and clinical trials to effectively assess the relationship between prosthesis insertion, hygiene regimen, and signs and symptoms of anophthalmic socket. Also, there is the importance of a protocol establishment, with regular care, to avoid the inadequate care of the patients (such as an excess or a lack of hygiene) and a protocol that considers the exposure to external environmental factors [20].
Although the results of the present study do not demonstrate a decrease in the microbial load, they also show that there was no increase. Thus, through this controlled clinical trial, it can be stated that frequent manipulation for the hygiene of the prostheses did not influence the microbial load. This observation and the conflicting result in the literature highlight that cleaning habits and microbiological aspects may not be the main causes of signs and symptoms of anophthalmic socket and other factors must be investigated.
Although the protocols did not influence microbiological control, the clinical signs showed an improvement after the institution of the protocols. As previously mentioned, inflammation and discharge can occur for several reasons. A transitory irritation due to environmental conditions could be present during one of the periods of examination, or the institution of the protocols could have improved the tissue health (inflammation, edema, discharge, and crusting) via the daily and weekly hygiene protocols because of the patient’s adherence to instructions regarding the need to wash their prosthesis, as well as their hands and face.
A guideline proposed for contact lens wearers demonstrates the importance of avoiding the manipulation of the eyelids or the face when the hands are not properly cleaned [19]. The establishment of a step-by-step hand and face washing routine may avoid the introduction of pathogenic microorganisms inside the socket and remove the residuals from the eyelashes [20,26,28,41,42]. Moreover, the adequate hygiene of the eyelids can benefit the functioning of the meibomian glands.
Another factor that must be cited is the formation of deposits. The coverage of the deposits over the ocular prosthesis surface may increase after a long period of wear and break the equilibrium of the anophthalmic socket. The duration of the equilibrium may vary between individuals. Environmental conditions or the quality of the surface [8,38] of the prosthesis may be important in deciding the duration of the socket homeostasis and the adequate intervals of removal, cleaning, and re-polishing of the prosthesis [2].
Despite the reduction in individuals with inflammation and discharge, the WPt could not reduce the frequency of edema and crusting after the DPt. Probably, daily cleaning allowed for the complete removal of discharge that may be retained inside the socket. In this way, with the WPt, the patients were subjected to long periods with discharge, which may favored the crusting formation. Crusting can be tacky and irritates the eyelids during blinking [16], causing the appearance of edema.
The combination of some precautions can make the proposed protocols more effective in terms of socket comfort, and further investigations should consider specific orientations about eyelid scrubs for crust removal [41,42]. A hand hygiene protocol should be considered too so that the patients can be reinforced to wash their hands, but they were not instructed in how to perform this. Poor hand hygiene and frequent handling of the prostheses seem to be related to socket symptoms [10,20].
The correlation results between clinical information of the participant’s data and clinical characteristics indicated a relationship between the use of eye drops with edema and pain. In accordance with the literature, this result suggests that the deficient lubrication of the anophthalmic socket may cause, as a consequence, pain and edema due to the friction of eyelids over the dry surface of the prosthesis [8,11,13,14,16].
There was a significant reduction in the frequency of individuals with inflammation and edema after DPt, but for the individuals who continued to experience with inflammation and edema, the results indicated a positive correlation between them. A positive relationship was found between discharge and crusting eyelashes when the WPt was used. These results were expected since clinical observation suggested that the weekly removal of the prosthesis favors the accumulation of discharge and crusting formation. However, these observations are in disagreement with the literature since some authors do not recommend the frequent removal of the prosthesis due to the risks of irritation [3,16,20].
The results of the weak correlation between clinical characteristics and the presence of the microorganisms assessed explain the microbiological results and the isolated clinical characteristics. Although the protocols has not influenced the CFU count, the participants showed an improvement in the clinical characteristics assessed. Thus, the adequate management of the prosthesis and anophthalmic socket may control the clinical signs of inflammation. These results corroborate other studies, which affirm that the appearance of inflammation may be not necessarily associated with the growth of biofilm on the surface of the prosthesis [31,32].
Regarding patients’ opinions, both protocols were well accepted by patients who finalized the study. However, three individuals allocated in the WPt group withdrew because they had not adapted to the weekly removal of the prostheses. It is likely that the occupation of the patient influenced the cleaning habits of the prosthesis due to patients who work having daily cleaning habits for their prostheses, while retired patients had weekly cleaning habits [25] possibly due to greater exposure to environmental factors. So, it is important to understand that some patients may have a personal preference due to specificities, like professional occupation and daily habits. The professionals must be able to adapt their protocols in these situations without losing their effectiveness. The results of this study suggest that frequent hygiene might be involved in socket discomfort if performed improperly. Poor care with hand or face hygiene during prosthesis handling and the place where it is stored may be related to discomfort more than the frequent manipulation itself. Also, physiological, environmental, and emotional conditions might play an important role in the motivations of the patient to perform a correct frequent manipulation of the prosthesis [2,5]. Without a standardized protocol of care, ocular prosthesis wearers may develop poor habits with their prosthesis.
The limitations considered in this study were regarding sample size, there was a loss of 25% of the participants, the non-diagnostic lubrication deficiency of the anophthalmic socket, the short period of follow-up, the use of a limited number of target microorganisms, and the assessment of the patient’s opinion without a standardized questionnaire. In addition, disinfectant solutions, such as chlorhexidine and contact lens multiuse solution [26], were not used because care must be taken during the period of disinfection and storage of the prosthesis because of color alteration of the iris [43]. Therefore, further investigations must be considered as research aimed at complementing the findings and limitations of the present study. It should be noted, however, that the results are consistent since the study followed a model of controlled clinical research, randomized and blinded to the researchers.
5. Conclusions
Regardless of the daily or weekly hygiene, neither protocol showed an influence on the microbial load, on the prostheses, and on the socket, but they improved the tissue health of the anophthalmic socket, specifically on inflammation signs and discharge production. In addition, the patients manifested satisfactory opinions about both protocols tested.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: C.H.S.-L. and E.W.; methodology: L.R.M., A.B.R., L.d.S.E., and V.d.C.O.; investigation: L.R.M., A.B.R., L.d.S.E., and V.d.C.O.; formal analysis: A.P.M. and C.H.S.-L.; data curation: A.P.M. and C.H.S.-L.; writing preparation: L.R.M. and C.H.S.-L.; writing review and editing: L.R.M., A.B.R., L.d.S.E., V.d.C.O., A.P.M., E.W., and C.H.S.-L.; project administration: C.H.S.-L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior–Brazil (CAPES)–Finance Code 001.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted following the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Ribeirão Preto School of Dentistry (Protocol Code 71783917.6.0000.5419 approved on 29 August 2017).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The scientific data produced will be made available in open access on the platform of the University of São Paulo (AGUIA–Academic Information Management Agency of the University of São Paulo).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Amornvit, P.; Rokaya, D.; Shrestha, B.; Srithavaj, T. Prosthetic rehabilitation of an ocular defect with post-enucleation socket syndrome: A case report. Saudi Dent. J. 2014, 26, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pine, K.R.; Sloan, B.H.; Jacobs, R.J. A proposed model of the response of the anophthalmic socket to prosthetic eye wear and its application to the management of mucoid discharge. Med. Hypotheses 2013, 81, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pine, K.; Sloan, B.; Stewart, J.; Jacobs, R. The response of the anophthalmic socket to prosthetic eye wear. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2013, 96, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohman, E.; Roed Rassmusen, M.L.; Kopp, E.D. Pain and discomfort in the anophthalmic socket. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2014, 25, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokohl, A.C.; Trester, M.; Guo, Y.; Kopecky, A.; Lin, M.; Kratky, V.; Heindl, L.M. Socket discomfort in anophthalmic patients—Reasons and therapy options. Ann. Eye Sci. 2020, 5, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizada, K.; Rani, D. Ocular prosthesis. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2007, 30, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Allen, D.; Morley, A.; Frcophth, R. Features and management of an acute allergic response to acrylic ocular prostheses. Orbit 2009, 28, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwin, A.S.; Worrell, E.; Roos, J.C.P.; Edwards, B.; Malhotra, R. Can we improve the tolerance of an ocular prosthesis by enhancing its surface finish? Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 34, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baino, F.; Perero, S.; Ferraris, S.; Miola, M.; Balagna, C.; Verné, E.; Vitale-Brovarone, C.; Coggiola, A.; Dolcino, D.; Ferraris, M. Biomaterials for orbital implants and ocular prostheses: Overview and future prospects. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1064–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, B.; Jakobiec, F.; Iwamoto, T.; DeVoe, A. Giant papillary conjunctivitis with ocular prostheses. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1979, 97, 892–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashkouli, M.B.; Zolfaghari, R.; Es’haghi, A.; Amirsardari, A.; Abtahi, M.B.; Karimi, N.; Alemzadeh, A.; Aghamirsalim, M. Tear film lacrimal drainage system, and eyelid findings in subjects with anophthalmic socket discharge. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 165, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pine, N.S.; de Terte, I.; Pine, K.R. An investigation into discharge, visual perception, and appearance concerns of prosthetic eye wearers. Orbit 2017, 36, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokohl, A.; Trester, M.; Naderi, P.; Loreck, N.; Zwingelberg, S.; Bucher, F.; Pine, K.R.; Heindl, L.M. Dry anophthalmic socket syndrome—Morphological alterations in meibomian glands. Eye 2021, 35, 3358–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapira, Y.; Worrell, E.; Ullrich, K.; Litwin, A.; Malhotra, R. UK National Artificial Eye Questionnaire study: Comparisons between cosmetic shell and artificial eye users. Part 1: Demographics, comfort and satisfaction. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 105, 1346–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, G.; De Piano, M.; Mazzone, G.; Micera, A.; Bonini, S.; Modugno, A.C. Should we care about the ocular surface in the anophthalmic patient? Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 32, 1924–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pine, K.; Sloan, B.; Jacobs, R.J. Deposit buildup on prosthetic eyes and implications for conjunctival inflammation and mucoid discharge. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2012, 6, 1755–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pine, K.R.; Sloan, B.; Han, K.Y.; Swift, S.; Jacobs, R.J. Deposit buildup on prosthetic eye material (in vitro) and its effect on surface wettability. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2013, 7, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, G.R.; Goldman, B.M.; Rahn, A.O. Post insertion care of the ocular prosthesis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1983, 49, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMonnies, C.W. Hand hygiene prior to contact lens handling is problematical. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2012, 35, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokohl, A.C.; Adler, W.; Koch, K.R.; Mor, J.M.; Jia, R.; Trester, M.; Pine, N.S.; Pine, K.R.; Heindl, L.M. Cryolite glass prosthetic eyes-the response of the anophthalmic socket. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2019, 257, 2015–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.J.; Choung, H.K.; Kim, N.J.; Hwang, S.W.; Sung, M.S.; Khwarg, S.I. Conjunctival cytologic features in anophthalmic patients wearing an ocular prosthesis. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 24, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborn, K.L.; Hetller, D. A survey of recommendations on the care of ocular prostheses. Optometry 2010, 81, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaque-González, S.; Amigó, A.; Rodríguez-Luna, C. Recommendations for post-adaption care of an ocular prosthesis: A review. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2015, 38, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourits, D.; Hartong, D.; Buddin, A.E.; Bosscha, M.I.; Tan, H.S.; Moll, A.C. Discharge and infection in retinoblastoma post-enucleation sockets. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2017, 11, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatamleh, M.; Abbariki, M.; Alqudah, N.; Cook, A. Survey of ocular prosthetics rehabilitation in the United Kingdom, part 1: Anophthalmic patients’ aetiology, opinions, and attitudes. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2017, 28, 1293–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranhos, R.M.Z.F.; Batalhão, C.H.; Semprini, M.; Regalo, S.C.H.; Ito, I.Y.; Mattos, M.G.C. Evaluation of ocular prosthesis biofilm and anophthalmic cavity contamination after use of three cleansing solutions. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2007, 15, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behlau, I.; Gilmore, M.S. Microbial biofilms in ophthalmology and infectious disease. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2008, 126, 1572–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penitente, P.A.; Da Silva, E.V.F.; Goiato, M.C.; Maniçoba, L.L.P.; Brito, V.G.B.; Túrcio, K.H.L.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Nagay, B.E.; Dos Santos, D.M. The Inflammation Level and a Microbiological Analysis of the Anophthalmic Cavities of Unilateral Ocular Prosthesis Users: A Blind, Randomized Observational Study. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toribio, A.; Marrodán, T.; Fernández-Natal, I.; Martínez-Blanco, H.; Rodríguez-Aparicio, L.; Ferrero, M.A. Study of conjunctival flora in anophthalmic patients: Influence on the comfort of the socket. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2017, 255, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiotti, A.M.; Da Silva, E.V.F.; Catanoze, I.; De Carvalho, K.; Malavazi, E.M.; Goiato, M.C.; Dos Santos, D.M.; De Almeida, M.T. Microbiological analysis of conjunctival secretion in anophthalmic cavity, contralateral eye and ocular prosthesis of patients with maxillofacial abnormalities. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 66, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, R.J.; Linberg, J.V. The anophthalmic socket and the prosthetic eye. A clinical and bacteriologic study. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1989, 5, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.T.; Pirbhai, A.; Franzco, D.S. Bacterial biofilms associated with ocular prostheses. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2015, 43, 602–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, J.; Vomero, M.; do Nascimento, C.; Watanabe, E.; Paranhos, H.F.O.; Coto, N.P.; Dias, R.B.; Oliveira, V.C.D.; Silva-Lovato, C.H. Genomic identification of microbial species adhering to maxillofacial prostheses and susceptibility to different hygiene protocols. Biofouling 2018, 34, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, A.L.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A. The human skin microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, K.M.; Dean, A.; Soe, M.M. OpenEpi: A web-based epidemiologic and statistical calculator for public health. Public Health Rep. 2009, 124, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pine, K.; Sloan, B.; Jacobs, R. The development of measurement tools for prosthetic eye research. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2013, 96, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agência Nacional de Vigilância do Brasil. Farmacopeia Brasileira, 5th ed.; Fiocruz: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2010; Volume 1, pp. 273–275. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhaldi, S.A.; Allam, K.H.; Radwan, M.A.; Sweeney, L.E.; Alshammeri, S. Estimates of dry eye disease in Saudi Arabia based on a short questionnaire of prevalence, symptoms and risk factors: The Twaiq Mountain Eye Study I. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2023, 46, 101770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meduri, A.; Frisina, R.; Rechichi, M.; Oliverio, G.W. Prevalence of Meibomian Gland Dysfunction and Its Effect on Quality of Life and Ocular Discomfort in Patients with Prosthetic Eyes. Prosthesis 2020, 2, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pine, K.R.; Sloan, B.H.; Jacobs, R.J. Socket Complications: Complications of Prosthesis Retention. In Clinical Ocular Prosthetics; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 180–186. [Google Scholar]
- Aryasit, O.; Uthairat, Y.; Singha, P.; Horatanaruang, O. Efficacy of baby shampoo and commercial eyelid cleanser in patients with meibomian gland dysfunction. Medicine 2020, 99, e20155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.S.; Seo, Y.; Chae, M.K.; Jang, S.Y.; Yoon, J.S. Effect of topical loteprednol etabonate with lid hygiene on tear cytokines and meibomian gland dysfunction in prosthetic eye wearers. Eye 2018, 32, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, A.; Goiato, M.C.; dos Santos, D.M.; Haddad, M.F.; Pesqueira, A.A.; Bannwart, L.C. Influence of different disinfecting solutions on the color change of artificial irises used in ocular prostheses. Color Res. Appl. 2014, 39, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).