The Genetic Basis of Future Pharmacological Strategies for the Management of Comorbid Obesity and Depression: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Review Process
3. Methodological Characteristics and Quality of the Included Studies
4. Genetic Associations Identified through the Review
4.1. Replicated Candidate-Gene Associations
4.2. Candidate-Gene Associations from Single Studies
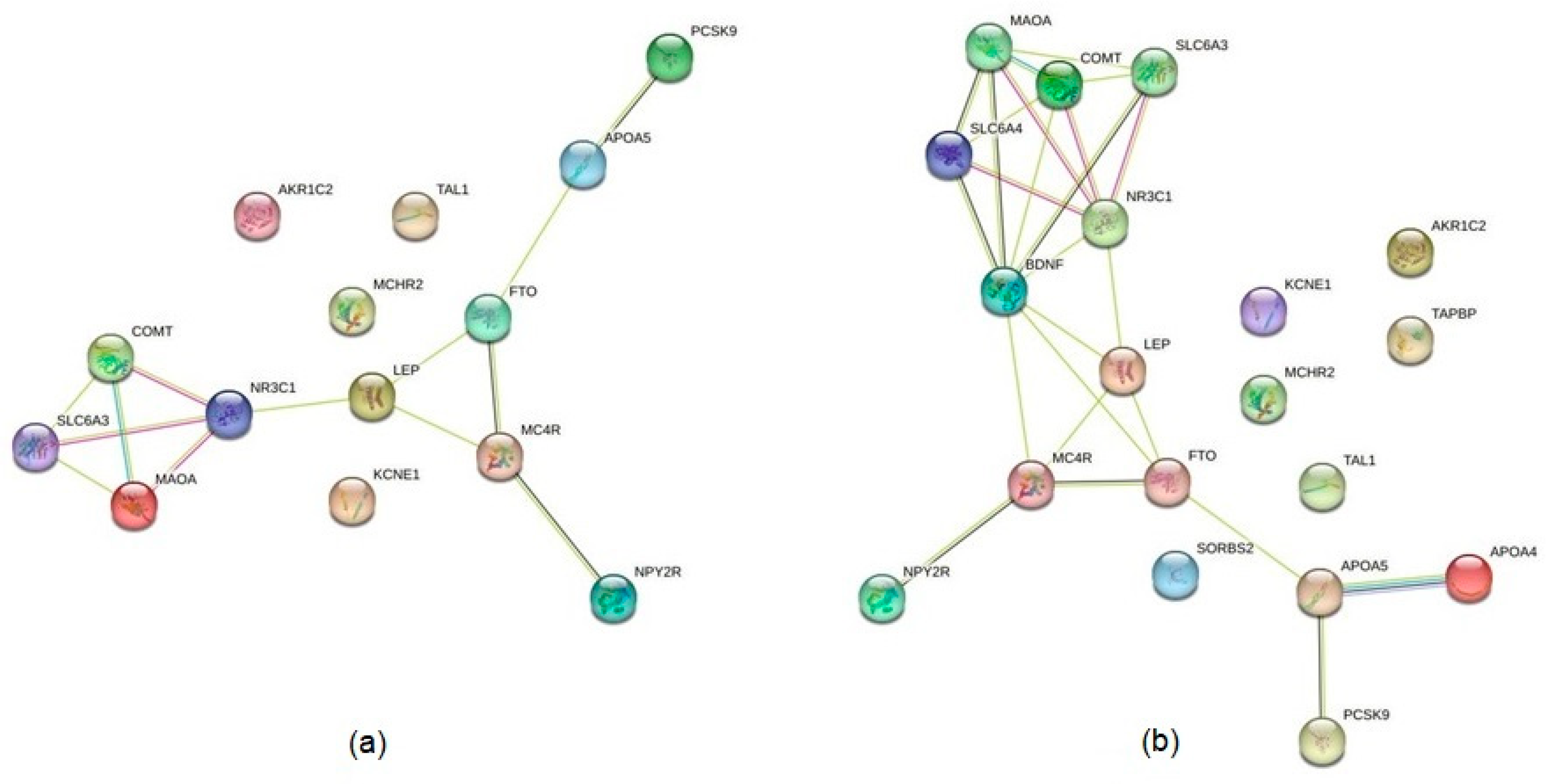
4.3. Identification of Interactions between the Products of Identified Genes
5. Discussion
5.1. Synthetic Pharmacological Therapies
5.2. Natural Compounds
5.3. Mapping Protein–Protein Interactions and Possible Molecular Hubs
5.4. Implications for Clinical Practice and Research
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Obesity Federation. Prevalence of Obesity. Available online: https://www.worldobesity.org/about/about-obesity/prevalence-of-obesity (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Wong, M.C.S.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Chan, P.S.F.; Lok, V.; Chen, X.; Leung, C.; Wang, H.H.X.; Lao, X.Q.; Zheng, Z.-J. Global, regional, and time-trend prevalence of central obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 13.2 million subjects. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 35, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, P.W.; Atabaki-Pasdar, N. Causal inference in obesity research. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 281, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppino, F.S.; de Wit, L.M.; Bouvy, P.F.; Stijnen, T.; Cuijpers, P.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Zitman, F.G. Overweight, obesity and depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutaria, S.; Devakumar, D.; Yasuda, S.S.; Das, S.; Saxena, S. Is obesity associated with depression in children? Systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2019, 104, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, P.; Antal, P.; Bolgar, B.; Bagdy, G.; Deakin, B.; Juhasz, G. Comorbidities in the diseasome are more apparent than real: What Bayesian filtering reveals about the comorbidities of depression. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtman, J.J.; Wurtman, R.J. Depression can beget obesity can beget depression. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2015, 76, e1619–e1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokela, M.; Hamer, M.; Singh-Manoux, A.; Batty, D.; Kivimaki, M. Association of metabolically healthy obesity with depressive symptoms: Pooled analysis of eight studies. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konttinen, H. Emotional eating and obesity in adults: The role of depression, sleep and genes. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2020, 79, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachter, J.; Martel, J.; Lin, C.-S.; Chang, C.-J.; Wu, T.-R.; Lu, C.-C.; Ko, Y.-F.; Lai, H.-C.; Ojcius, D.M.; Young, J.D. Effects of obesity on depression: A role for inflammation and the gut microbiota. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 69, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouakinin, S.R.S.; Barreira, D.P.; Gois, C.J. Depression and obesity: Integrating the role of stress, neuroendocrine dysfunction and inflammatory pathways. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, W.; Ambrosio, P.; Carizzone, F.; De Biasio, V.; Di Munzio, W.; Foia, M.G.; Capasso, A. Depression and obesity: Analysis of common biomarkers. Diseases 2020, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opel, N.; Thalamuthu, A.; Milaneschi, Y.; Grotegerd, D.; Flint, C.; Leenings, R.; Goltermann, J.; Richter, M.; Hahn, T.; Woditsch, G.; et al. Brain structural abnormalities in obesity: Relation to age, genetic risk, and common psychiatric disorders: Evidence through univariate and multivariate mega-analysis including 6420 participants from the ENIGMA MDD working group. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 4839–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Xu, J.; Li, R.; Teopiz, K.M.; McIntyre, R.S.; Chen, H. Interventions targeting comorbid depression and overweight/obesity: A systematic review. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 314, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Y.S.; Seo, H.-J.; McIntyre, R.S.; Bahk, W.-M. Obesity and its potential effects on antidepressant treatment outcomes in patients with depressive disorders: A literature review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigolon, R.B.; Trevisol, A.P.; Gerchman, F.; Bambokian, A.D.; Magee, T.; McIntyre, R.S.; Gomes, F.A.; Brietzke, E.; Mansur, R.B. Is obesity a determinant of success with pharmacological treatment for depression? A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 287, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabricatore, A.N.; Wadden, T.A.; Higginbotham, A.J.; Faulconbridge, L.F.; Nguyen, A.M.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Faith, M.S. Intentional weight loss and changes in symptoms of depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 1363–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabricatore, A.N.; Wadden, T.A.; Moore, R.H.; Butryn, M.L.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Nguyen, A.M. Predictors of attrition and weight loss success: Results from a randomized controlled trial. Behav. Res. Ther. 2009, 47, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.E.; Campbell, K.M. Past, present, and future of pharmacologic therapy in obesity. Prim. Care 2016, 43, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Paz-Filho, G.; Mastronardi, C.; Licinio, J.; Wong, M.-L. Is increased antidepressant exposure a contributory factor to the obesity pandemic? Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 15, e759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, A.; Michael, N.J. New horizons: Is obesity a disorder of neurotransmission? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e4872–e4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornhuber, J.; Gulbins, E. New molecular targets for antidepressant drugs. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afari, N.; Noonan, C.; Goldberg, J.; Roy-Byrne, P.; Schur, E.; Golnari, G.; Buchwald, D. Depression and obesity: Do shared genes explain the relationship? Depress. Anxiety 2010, 27, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jokela, M.; Berg, V.; Silventoinen, K.; Batty, G.D.; Singh-Manoux, A.; Kaprio, J.; Smith, G.D.; Kivimaki, M. Body mass index and depressive symptoms: Testing for adverse and protective associations in two twin cohort studies. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2016, 19, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Snieder, H.; Hartman, C.A. Familial co-aggregation and shared heritability between depression, anxiety, obesity and substance use. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speed, M.S.; Jefsen, O.H.; Borglum, A.D.; Speed, D.; Ostergaard, S.D. Investigating the association between body fat and depression via Mendelian randomization. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.-F.; Su, C.-Y.; Su, M.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lin, Y.-F.; Pan, Y.-J.; Hsiao, P.-C.; Chen, P.-C.; Huang, Y.-T.; et al. Association of polygenic risks, depression, and obesity-related traits in Taiwan Biobank. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 320, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.R.; Ruiz-Arenas, C.; Caceres, A.; Moran, I.; Lopez-Sanchez, M.; Alonso, L.; Guindo-Martinez, M.; Mercader, J.M.; Esko, T.; Torrents, D.; et al. Polymorphic inversions underlie the shared genetic susceptibility of obesity-related diseases. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 106, 846–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milaneschi, Y.; Lamers, F.; Peyrot, W.J.; Baune, B.T.; Breen, G.; Dehghan, A.; Forstner, A.J.; Grabe, H.J.; Homuth, G.; Kan, C.; et al. Genetic association of major depression with atypical features and obesity-related immunometabolic dysregulations. JAMA Psychiatry 2017, 74, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistis, G.; Milaneschi, Y.; Vandeleur, C.L.; Lasserre, A.M.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Lamers, F.; Boomsma, D.I.; Hottenga, J.-J.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Vollenweider, P.; et al. Obesity and atypical depression symptoms: Findings from Mendelian randomization in two European cohorts. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amare, A.T.; Schubert, K.O.; Tekola-Ayele, F.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Sangkuhl, K.; Jenkins, G.; Whaley, R.M.; Barman, P.; Batzler, A.; Altman, R.B.; et al. The association of obesity and coronary artery disease genes with response to SSRIs treatment in major depression. J. Neural Transm. 2019, 126, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, F.P.; Bowden, J.; de Mola, C.L.; Tovo-Rodrigues, L.; Smith, G.D.; Horta, B.L. Body mass index and psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docherty, A.R. Leveraging psychiatric and medical genetics to understand comorbid depression and obesity. Br. J. Psychiatry 2017, 211, 61–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharipour, M.; Barekatain, M.; Sung, J.; Emami, N.; Sadeghian, L.; Dianatkhah, M.; Sarrafzadegan, N.; Jahanfar, S. The epigenetic overlap between obesity and mood disorders: A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohani, Z.N.; Meyre, D.; de Souza, R.J.; Joseph, P.G.; Gandhi, M.; Dennis, B.B.; Norman, G.; Anand, S.S. Assessing the quality of published genetic association studies in meta-analyses: The quality of genetic studies (Q-Genie) tool. BMC Genet. 2015, 16, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comings, D.E.; Comings, B.G.; Muhleman, D.; Dietz, G.; Shahbahrami, B.; Tast, D.; Knell, E.; Kocsis, P.; Baumgarten, R.; Kovacs, B.W. The dopamine D2 receptor locus as a modifying gene in neuropsychiatric disorders. JAMA 1991, 266, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comings, D.E.; Gade, R.; MacMurray, J.P.; Muhleman, D.; Peters, W.R. Genetic variants of the human obesity (OB) gene: Association with body mass index in young women, psychiatric symptoms, and interaction with the dopamine D2 receptor (DRD2) gene. Mol. Psychiatry 1996, 1, 325–335. [Google Scholar]
- Ejchel, T.F.; Araujo, L.M.Q.; Ramos, L.R.; Cendoroglo, M.S.; de Smith, M.A.C. Association of the apolipoprotein A-IV: 360 Gln/His polymorphism with cerebrovascular disease, obesity, and depression in a Brazilian elderly population. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2005, 135B, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.S.; Cendoroglo, M.S.; Ramos, L.R.; Araujo, L.M.Q.; Carvalheira, G.M.G.; de Labio, R.W.; Burbano, R.R.; Payao, S.L.M.; de Smith, M.A.C. APO A-V -113T→C polymorphism frequency and its association with morbidity in a Brazilian elderly population. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2006, 44, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, P.; Romagni, P.; Torvik, S.; Gold, P.W.; Charney, D.S.; Detera-Wadleigh, S.; Cizza, G.; P.O.W.E.R. Study Group. Glucocorticoid receptor gene polymorphisms in premenopausal women with major depression. Comparative Study Horm. Metab. Res. 2008, 40, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalova, J.; Zamrazilova, H.; Vcelak, J.; Vankova, M.; Lukasova, P.; Hill, M.; Hlatava, K.; Sramkova, P.; Fried, M.; Aldhoon, B.; et al. Neuromedin beta: P73T polymorphism in overweight and obese subjects. Physiol. Res. 2008, 57, S39–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuemmeler, B.F.; Agurs-Collins, T.; McClermon, F.J.; Kollins, S.H.; Garrett, M.E.; Ashley-Koch, A.E. Interactions between genotype and depressive symptoms on obesity. Behav. Genet. 2009, 39, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivimaki, M.; Jokela, M.; Hamer, M.; Geddes, J.; Ebmeier, K.; Kumari, M.; Singh-Manoux, A.; Hingorani, A.; Batty, D.G. Examining overweight and obesity as risk factors for common mental disorders using fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) genotype-instrumented analysis: The Whitehall II study, 1985-2004. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 173, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, M.; Cohen-Woods, S.; Kapur, K.; Breen, G.; Ng, M.Y.; Butler, A.W.; Craddock, N.; Gill, M.; Korszun, A.; Maier, W.; et al. Depressive disorder moderates the effect of the FTO gene on body mass index. Mol. Psychiatry 2012, 17, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaan, Z.; Anand, S.; Zhang, X.; Desai, D.; Rivera, M.; Pare, G.; Thabane, L.; Xie, C.; Gerstein, H.; Engert, J.C.; et al. The protective effect of the obesity-associated rs9939609 A variant in fat mass- and obesity-associated gene on depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beydoun, M.A.; Nalls, M.A.; Canas, J.A.; Evans, M.K.; Zonderman, A.B. Gene polymorphisms and gene scores linked to low serum carotenoid status and their associations with metabolic disturbance and depressive symptoms in African-American adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbron, J.; van der Merwe, L.; Zaahl, M.G.; Kotze, M.J.; Senekal, M. Fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) gene polymorphisms are associated with physical activity, food intake, eating behaviors, psychological health, and modeled change in body mass index in overweight / obese Caucasian adults. Nutrients 2014, 6, 3130–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielinski, M.; Tomaszewska, M.; Jaracz, M.; Pulkowska-Ulfig, J.; Dlugosz, D.; Sikora, M.; Tretyn, A.; Kaminska, A.; Junik, R.; Borkowska, A. The polymorphisms in serotonin-related genes (5-HT2A and SERT) and the prevalence of depressive symptoms in obese patients. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 586, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkowska, A.; Bielinski, M.; Szczesny, W.; Szwed, K.; Tomaszewska, M.; Kalwa, A.; Lesiewska, N.; Junik, R.; Golebiewski, M.; Sikora, M.; et al. Effect of the 5-HTTLPR polymorphism on affective temperament, depression and body mass index in obesity. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 184, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delacretaz, A.; Preisig, M.; Vandenberghe, F.; Morgui, N.S.; Quteineh, L.; Choong, E.; Gholam-Rezaee, M.; Kutalik, Z.; Magistretti, P.; Aubry, J.-M.; et al. Influence of MCHR2 and MCHR2-AS1 genetic polymorphisms on body mass index in psychiatric patients and in population-based subjects with present or past atypical depression. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaffery, J.M.; Papandonatos, G.D.; Faulconbridge, L.F.; Erar, B.; Peter, I.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Pajewski, N.M.; Anderson, A.; Wadden, T.A.; Wing, R.R. Look AHEAD Research Group. Genetic predictors of depressive symptoms in the Look AHEAD trial. Psychosom. Med. 2015, 77, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaan, Z.; Lee, Y.K.; Gerstein, H.C.; Engert, J.C.; Bosch, J.; Mohan, V.; Diaz, R.; Yusuf, S.; Anand, S.S.; Meyre, D.; et al. Obesity genes and risk of major depressive disorder in a multiethnic population: A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2015, 76, e1611–e1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, Z.; Davis, C.; Loxton, N.J.; Kaplan, A.S.; Levitan, R.D.; Carter, J.C.; Kennedy, J.L. Association between MC4R rs17782313 polymorphism and overeating behaviours. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quteineh, L.; Preisig, M.; Rivera, M.; Milaneschi, Y.; Castelao, E.; Gholam-Razee, M.; Vandenberghe, F.; Saigi-Morgui, N.; Delacretaz, A.; Cardinaux, J.-R.; et al. Association of CRTC1 polymorphisms with obesity markers in subjects from the general population with lifetime depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 198, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielinski, M.; Jaracz, M.; Lesiewska, N.; Tomaszewska, M.; Sikora, M.; Junik, R.; Kaminska, A.; Tretyn, A.; Borkowska, A. Association between COMT Val158Met and DAT1 polymorphisms and depressive symptoms in the obese population. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, 13, 2221–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellgren, C.; Comasco, E.; Skalkidou, A.; Sundstrom-Poromaa, I. Allopregnanolone levels and depressive symptoms during pregnancy in relation to single nucleotide polymorphisms in the allopregnanolone synthetic pathway. Horm. Behav. 2017, 94, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, M.; Locke, A.E.; Corre, T.; Czamara, D.; Wolf, C.; Ching-Lopez, A.; Milaneschi, Y.; Kloiber, S.; Cohen-Woods, S.; Rucker, J.; et al. Interaction between the FTO gene, body mass index and depression: Meta-analysis of 13701 individuals. Br. J. Psychiatry 2017, 211, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepers, R.; and Markus, C.R. The interaction between 5-HTTLPR genotype and ruminative thinking on BMI. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 118, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treutlein, J.; Strohmaier, J.; Frank, J.; Witt, S.H.; Rietschel, L.; Forstner, A.J.; Lang, M.; Degenhardt, F.; Dukal, H.; Herms, S.; et al. Association between neuropeptide Y receptor Y2 promoter variant rs6857715 and major depressive disorder. Psychiatr. Genet. 2017, 27, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummett, B.H.; Babyak, M.A.; Singh, A.; Hauser, E.R.; Jiang, R.; Huffman, K.M.; Kraus, W.E.; Shah, S.H.; Siegler, I.C.; Williams, R.B. Lack of association of a functional polymorphism in the serotonin receptor gene with body mass index and depressive symptoms in a large meta-analysis of population based studies. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, R.; Cullen, B.; Graham, N.; Lyall, D.M.; Aman, A.; Pell, J.P.; Ward, J.; Smith, D.J.; Strawbridge, R.J. Genetic analysis of the PCSK9 locus in psychological, psychiatric, metabolic and cardiovascular traits in UK Biobank. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 30, 1380–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Brouwers, B.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Lawler, K.; de Oliveira, E.M.; Lee, D.-K.; Yang, Y.; Cox, A.R.; Keogh, J.M.; et al. Human loss-of-function variants in the serotonin 2C receptor associated with obesity and maladaptive behavior. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2537–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahati, S.; Qorbani, M.; Naghavi, A.; Pishva, H. Association and interaction of the MC4R rs17782313 polymorphism with plasma ghrelin, GLP-1, cortisol, food intake and eating behaviors in overweight/obese Iranian adults. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerken, T.; Girard, C.A.; Tung, Y.-C.L.; Webby, C.J.; Saudek, V.; Hewitson, K.S.; Yeo, G.S.H.; McDonough, M.A.; Cunliffe, S.; McNeill, L.A.; et al. The obesity-associated FTO gene encodes a 2-oxoglutarate-dependent nucleic acid demethylase. Science 2007, 318, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speakman, J.R. The ‘fat mass and obesity related’ (FTO) gene: Mechanisms of impact on obesity and energy balance. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2015, 4, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainer, V.; Hainerova, I.A.; Kunesova, M.; Braunerova, R.T.; Zamrazilova, H.; Bendlova, B. Melanocortin pathways: Suppressed and stimulated melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R). Physiol. Res. 2020, 69, S245–S254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shende, P.; Desai, D. Physiological and therapeutic roles of neuropeptide Y on biological functions. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1237, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, G.B.; Bittencourt, J.G. The melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) system: A tale of two peptides. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Yan, H.; Wen, Y.; Lai, C.; Shi, L. Association between NR3C1 rs41423247 polymorphism and depression: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e12541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yuan, L.-H.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, M.-Y.; Zhang, L.-J.; Wang, Y. Association of leptin gene -2548 G/A polymorphism with obesity: A meta-analysis. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 64, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-F.; Breen, G.; Czamara, D.; Corre, T.; Wolf, C.; Kloiber, S.; Bergmann, S.; Craddock, N.; Gill, M.; Holsboer, F.; et al. A genetic risk score combining 32 SNPs is associated with body mass index and improves obesity prediction in people with major depressive disorder. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguita-Ruiz, A.; Zarza-Rebollo, J.A.; Perez-Gutierrez, A.M.; Molina, E.; Guiterrez, B.; Bellon, J.A.; Moreno-Peral, P.; Conejo-Ceron, S.; Aiarzaguena, J.M.; Ballesta-Rodriguez, M.I.; et al. Body mass index interacts with a genetic risk score for depression increasing the risk of the disease in high-susceptibility individuals. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jokela, M.; Elovainio, M.; Keltikangas-Jarvinen, L.; Batty, G.D.; Hintsanen, M.; Seppala, I.; Kahonen, M.; Viikari, J.S.; Raitakari, O.T.; Lehtimaki, T.; et al. Body mass index and depressive symptoms: Instrumental-variables regression with genetic risk score. Genes Brain Behav. 2012, 11, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulugeta, A.; Vimaleswaran, K.S.; Dickson, C.; Hypponen, E. Depression increases the genetic susceptibility to high body mass index: Evidence from UK Biobank. Depress. Anxiety 2019, 36, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avinun, R.; Hariri, A.R. A polygenic score for body mass index is associated with depressive symptoms via early life stress: Evidence for gene-environment correlation. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2019, 118, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khera, R.; Murad, M.H.; Chandar, A.K.; Dulai, P.S.; Wang, Z.; Prokop, L.J.; Loomba, R.; Camilleri, M.; Singh, S. Association of pharmacological treatments for obesity with weight loss and adverse events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2016, 315, 2424–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serretti, A.; Mandelli, L. Antidepressants and body weight: A comprehensive review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2010, 71, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.-L.; Xu, H.; Huang, Y.; Yang, C.-G. Targeting the RNA demethylase FTO for cancer therapy. RSC Chem. Biol. 2021, 2, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, S.; Kummetha, I.R.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Bray, W.; Yin, J.; Kelley, V.; Wang, Y.; Rana, T.M. Rational design and optimization of m6A-RNA demethylase FTO inhibitors as anticancer agents. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 10920–10937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spana, C.; Jordan, R.; Fischkoff, S. Effect of bremelanotide on body weight of obese women: Data from two phase 1 randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressley, H.; Cornelio, C.K.; Adams, E.N. Setmelanotide: A novel targeted treatment for monogenic obesity. J. Pharm. Technol. 2022, 38, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haqq, A.M.; Chung, W.K.; Dollfus, H.; Haws, R.M.; Martos-Moreno, G.A.; Poitou, C.; Yanovski, J.A.; Mittleman, R.S.; Yuan, G.; Forsythe, E.; et al. Efficacy and safety of setmelanotide, a melanocortin-4 receptor agonist, in patients with Bardet-Biedl syndrome and Alstrom syndrome: A multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial with an open label period. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serova, L.I.; Laukova, M.; Alaluf, L.G.; Sabban, E.L. Intranasal infusion of melanocortin receptor four (MC4R) antagonist to rats ameliorates development of depression and anxiety related symptoms induced by single prolonged stress. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 250, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabban, E.L.; Serova, L.I.; Alaluf, L.G.; Laukova, M.; Peddu, C. Comparative effects of intranasal neuropeptide Y and HS014 in preventing anxiety and depressive-like behavior elicited by single prolonged stress. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 295, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, N.; Kleinau, G.; Heyder, N.; Clark, T.; Hildebrand, P.W.; Scheerer, P. Binding, thermodynamics, and selectivity of a non-peptide antagonist to the melanocortin-4 receptor. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehlert, D.R.; Rasmussen, K.; Shaw, J.; Li, X.; Aradyfio, P.; Craft, L.; Coskun, T.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, Y.; Witkin, J.M. Preclinical evaluation of melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 antagonism for the treatment of obesity and depression. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 329, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mihalic, J.; Fan, P.; Liang, L.; Lindstrom, M.; Wong, S.; Ye, Q.; Fu, Y.; Jaen, J.; Chen, J.-L.; et al. Discovery and characterization of a potent and selective antagonist of melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 2. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domin, H. Neuropeptide Y Y2 and Y5 receptors as potential targets for neuroprotective and antidepressant therapies: Evidence from preclinical studies. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 111, 110349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, R.; Moreno, A.; Zhang, Y.; Herman, R.; Ben Nathan, J.; Zeb, S.; Rahematpura, S.; Stecyk, K.; Milliken, B.T.; Hayes, M.R.; et al. A novel approach to treating opioid use disorders: Dual agonists of glucagon-like peptide receptors and neuropeptide Y2 receptors. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 131, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anam, M.; Maharjan, S.; Amjad, Z.; Abaza, A.; Vasavada, A.M.; Sadhu, A.; Valencia, C.; Fatima, H.; Nwankwo, I. Efficacy of semaglutide in treating obesity: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Cureus 2022, 14, e32610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.D. Glucocorticoid receptor antagonists. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 813–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morice, C.; Baker, D.G.; Patel, M.M.; Nolen, T.L.; Nowak, K.; Hirsch, S.; Kosten, T.R.; Verrico, C.D. A randomized trial of safety and pharmacodynamic interactions between a selective glucocorticoid receptor antagonist, PT150, and ethanol in healthy volunteers. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon, J.; Koorneef, L.L.; van den Heuvel, J.K.; Verzijl, C.R.C.; van de Velde, N.M.; Mol, I.M.; Sips, H.C.M.; Hunt, H.; Rensen, P.C.N.; Meijer, O.C. Selective glucocorticoid receptor antagonist CORT125281 activates brown adipose tissue and alters lipid distribution in male mice. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, J.B.; Aftab, A.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Widge, A.; Rodriguez, C.I.; Carpenter, L.L.; Nemeroff, C.B.; McDonald, W.M.; Kalin, N.H.; APA Council of Research Task Force on Novel Biomarkers and Treatments. Hormonal treatments for major depressive disorder: State of the art. Am. J. Psychiatry 2020, 177, 686–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Suo, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Q.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y. Effect of PCSK9 inhibitor on blood lipid levels in patients with high and very-high CVD risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2022, 2022, 8729003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshycka, R.; Sudaryo, V.; Huang, N.-J.; Xie, Y.; Smeding, L.Y.; Choi, M.K.; Ploegh, H.L.; Lodish, H.F.; Pishesha, N. Engineered red blood cells carrying PCSK9 inhibitors persistently lower LDL and prevent obesity. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, J.; Matou-Nasri, S.; Alghamdi, F.; Alghamdi, S.; Alfadhel, M.; Padmanabham, S. Risk of neuropsychiatric adverse effects of lipid-lowering drugs: A Mendelian randomization study. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 21, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kljun, J.; Pavlic, R.; Hafner, E.; Lipec, T.; Moreno-Da Silva, S.; Tic, P.; Turel, I.; Budefeld, T.; Stojan, J.; Rizner, T.L. Ruthenium complexes show potent inhibition of AKR1C1, AKR1C2, and AKR1C3 enzymes and anti-proliferative action against chemoresistant ovarian cancer cell line. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 920379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, F.Q.; Chan, A.S.-Y.; Yokomori, R.; Huang, X.Z.; Theardy, M.S.; Yeoh, A.E.J.; Tan, S.H.; Sanda, T. Targeting dual oncogenic machineries driven by TAL1 and PI3K-AKT pathways in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2023, 108, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Zhang, H.; Duan, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Niu, L. Anti-obesity effect of radix Angelica sinensis and candidate causative genes in transcriptome analyses of adipose tissues in high-fat diet-induced mice. Gene 2017, 599, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Mi, X.; Li, Q.; Gao, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, J.; Liu, X.-M. The phytochemical rhein mediates M6A-independent suppression of adipocyte differentiation. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 756803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, S.M.; El Bishbishy, M.H.; Aborehab, N.M.; Salama, M.M.; Hasheesh, A.; Motaal, A.A.; Rashad, H.; Metwally, F.M. Upregulation of MC4R and PPAR-α expression mediates the anti-obesity activity of Moringa oleifera Lam. in high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 251, 112541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, S.; Sakamaki, A.; Koyama, K.; Shibata, O.; Owaki, T.; Oda, C.; Kimura, A.; Nakaya, T.; Ohbuchi, K.; Nahata, M.; et al. Daisaikoto improves fatty liver and obesity in melanocortin-4 receptor gene-deficient mice via the activation of brown adipose tissue. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.-H.; Cui, X.-Y.; Wang, D.; Jin, Y.; Guan, Y.-X. Anti-obesity effect of escin: A study on high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 7797–7812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Pan, W.; Shi, H.; Qi, F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, T.; Si, H.; Si, G. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on the mechanism of Baihe Zhimu decoction in the treatment of postpartum depression. Medicine 2022, 101, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; He, L.-J.; Tian, D.-F.; Gao, Q.; Ling, J.-F.; Wang, Y.-C.; Han, Z.-Y.; Guo, R.-J. Therapeutic targets and mechanism of Xingpi Jieyu decoction in depression: A network pharmacology study. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 5516525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Kim, M.-S. The protective effects of curcumin on depression: Genes, transcription factors, and microRNAs involved. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 319, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, H.M.; Jang, D.; Trinh, T.A.; Lee, D.; Nguyen, Q.N.; Kim, C.-E.; Kang, K.S. Regulation of appetite-related neuropeptides by Panax ginseng: A novel approach for obesity treatment. J. Ginseng Res. 2022, 46, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashmawy, A.I.; El-Abhar, H.S.; Abdallah, D.M.; Ali, M.A. Chloroquine modulates the sulforaphane anti-obesity mechanisms in a high-fat diet model: Role of JAK-2/STAT-3/SOCS-3 pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 927, 175066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Kim, J.; Park, H.J.; Kim, H. Anti-obesity effects of a Prunus persica and Nelumbo nucifera mixture in mice fed a high-fat diet. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orabi, S.H.; Al-Sabbagh, E.S.; Khalifa, H.K.; Mohamed, M.A.E.; Elhamouly, M.; Gad-Allah, S.M.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Abd Eldaim, M.A. Commiphora myrrha resin alcoholic extract ameliorates high fat diet induced obesity via regulation of UCP1 and adiponectin proteins expression in rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, X.; Luo, P.; Liu, H. Analysis of asthaxanthin molecular targets based on network pharmacological strategies. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.-F.; Song, Z.-Y.; Xu-Shao, L.-Y.; Huang, J.-G.; Zhao, T.; Yang, Z. The mechanism of Bai He Gu Jin Tiang against non-small cell lung cancer revealed by network pharmacology and molecular docking. Medicine 2022, 101, e32555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pel, P.; Kim, Y.-M.; Kim, H.J.; Nhoek, P.; An, C.-Y.; Son, M.-G.; Won, H.; Lee, S.E.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.W.; et al. Isocoumarins and benzoquinones with their proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 expression inhibitory activities from dried roots of Lysimachia vulgaris. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 47296–47305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannino, G.; Iovino, P.; Lauria, A.; Genova, T.; Asteggiano, A.; Notarbartolo, M.; Porcu, A.; Serio, G.; Chinigo, G.; Occhipinti, A.; et al. Bioactive triterpenes of Protium heptaphyllum gum resin extract display cholesterol-lowering potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhoek, P.; Chae, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-M.; Pel, P.; Huh, J.; Kim, H.-W.; Choi, Y.H.; Lee, K.; Chin, Y.-W. Sesquiterpenoids from the aerial parts of Salvia plebeia with inhibitory activities on proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 expression. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matschke, V.; Piccini, I.; Schubert, J.; Wrobel, E.; Lang, F.; Matschke, J.; Amedonu, E.; Meuth, S.G.; Strunker, T.; Strutz-Seebohm, N.; et al. The natural plant product rottlerin activates KV7.1/KCNE1 channels. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 40, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manville, R.M.; Abbott, G.W. Cilantro leaf harbors a potent potassium channel-activating anticonvulsant. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 11349–11363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.-H.; Lee, B.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; Jung, S.-W.; Kim, H.-S.; Shin, H.-C.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, H.-C.; Rhim, H.; Hwang, S.-H.; et al. Ginseng gintonin activates the human cardiac delayed rectifier K+ channel: Involvement of Ca2+/calmodulin binding sites. Mol. Cells 2014, 37, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koochakpoor, G.; Hosseini-Esfahani, F.; Daneshpour, M.S.; Hosseini, S.A.; Mirmiran, P. Effect of interactions of polymorphisms in the melanocortin-4 receptor gene with dietary factors on the risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. Diabet. Med. 2016, 33, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normann, C.; Buttenschon, H.N. Gene-environment interactions between HPA-axis genes and childhood maltreatment in depression: A systematic review. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2020, 32, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Muniesa, P.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.-A.; Hu, F.B.; Despres, J.-P.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Loos, R.J.F.; Moreno, L.A.; Bray, G.A.; Martinez, J.A. Obesity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.; Nemeroff, C.B. Precision psychiatry: Biomarker-guided tailored therapy for effective treatment and prevention in major depression. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1305, 535–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konuma, T.; Okada, Y. Statistical genetics and polygenic risk score for precision medicine. Inflamm. Regen. 2021, 41, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, T.; Nakata, Y.; Hotta, K.; Tanaka, K. The FTO genotype as a useful predictor of body weight maintenance: Initial data from a 5-year follow-up study. Metabolism 2014, 63, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vincentis, A.; Pedone, C.; Vespasiani-Gentilucci, U.; Picardi, A.; Derosa, G.; Maffioli, P.; Sahebkar, A. Effect of sibutramine on plasma C-reactive protein, leptin and adiponectin concentrations: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Xiu, J.; Zhu, C.; Meng, K.; Li, C.; Han, R.; Du, T.; Li, L.; Xu, L.; Liu, R.; et al. Fat mass and obesity-associated protein regulates RNA methylation associated with depression-like behavior in mice. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Niu, X.; Wang, C.; Qin, D.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, J.; et al. Inflammation-activated C/EPBβ mediates high-fat diet-induced depression-like behaviors in mice. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1068164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, A.; Joo, Y.; Cheon, Y.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, S. Neuronal growth regulator 1 promotes adipocyte lipid trafficking via interaction with CD36. J. Lipid Res. 2022, 63, 100221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, I.; Cussotto, S.; Anesi, A.; Dexpert, S.; Aubert, A.; Aouizerate, B.; Beau, C.; Forestier, D.; Ledaguenel, P.; Magne, E.; et al. Association between the indole pathway of tryptophan metabolism and subclinical depressive symptoms in obesity: A preliminary study. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek, A.; Glombik, K.; Detka, J.; Basta-Kaim, A.; Kubera, M.; Lason, W.; Budziszewska, B. Regulators of glucocorticoid receptor function in an animal model of depression and obesity. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2018, 30, e12591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glombik, K.; Detka, J.; Goralska, J.; Kurek, A.; Solnica, B.; Budziszewska, B. Brain metabolic alterations in rats showing depression-like and obesity phenotypes. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 37, 406–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielmans, G.I.; Spence-Sing, T.; Parry, P. Duty to warn: Antidepressant black box suicidality warning is empirically justified. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mead, E.; Atkinson, G.; Richter, B.; Metzendorf, M.-I.; Baur, L.; Finer, N.; Corpeleijn, E.; O’Malley, C.; Ells, L.J. Drug interventions for the treatment of obesity in children and adolescents. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 11, CD012436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.M.; Dahlin, J.L.; Bisson, J.; Graham, J.; Pauli, G.F.; Walters, M.A. Curcumin may (not) defy science. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study and Year of Publication | Candidate Gene(s) and Polymorphisms Studied | Study Design | Study Population and Sample Size | Results | Study Quality (Q-Genie Quality Score) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comings et al., 1991 [37] | DRD2 (Taq1 SNP) | Single-gene association | Patients seeking psychiatric care, Caucasian (n = 314) | DRD2 Taq1 A1 allele not significantly associated with depression or obesity | Poor (31) |
| Comings et al., 1996 [38] | Ob (D7S1875 repeat polymorphism) | Single-gene association | Young adults (age 26–30), Caucasian (n = 208) | Ob D7S1875 < 208 bp repeat polymorphism significantly associated with BMI and depressive symptoms, but only in women | Moderate (42) |
| Ejchel et al., 2005 [39] | APOA4 (360 Gln/His SNP) | Single-gene association | Elderly adults (age ≥ 60) (n = 383) | APOA4 360 His allele associated with both obesity and depression | Moderate (39) |
| Chen et al., 2006 [40] | APOA5 (−1131T→C SNP) | Single-gene association | Elderly adults (age 66–97) (n = 371) | APOA5-1131 C allele associated with obesity in the presence of depression | Moderate (37) |
| Krishnamurthy et al., 2008 [41] | NR3C1 (Bcl1, N363S, rs33388 and rs33389 SNPs) | Single-gene association | Premenopausal women (age 21–45) with (n = 52) and without (n = 29) depression | NR3C1 Bcl1 G/G genotype associated with greater abdominal obesity in women with depression; no significant association for other SNPs | Moderate (39) |
| Spalova et al., 2008 [42] | NMB (P73T SNP) | Single-gene association | Adults with (n = 292) and without (n = 155) obesity or overweight, Caucasian | No significant effect of NMB P73T on weight loss or depressive symptoms when followed up over 2.5 years after a weight-reduction programme | Moderate (42) |
| Fuemmeler et al., 2009 [43] | MAOA (30 bp VNTR) and SLC6A4 (5-HTTLPR 44bp Ins/Del) | Multiple-gene association, gene x depression interaction | Adolescents (n = 1584) | MAOA high-activity variant associated with lower risk of obesity in the presence of depression in male but not female adolescents | Moderate (45) |
| Kivimaki et al., 2011 [44] | FTO (rs1421085 SNP) | Single-gene association | Adults (age 35–55) (n = 4145) | FTO rs1421085 C allele associated with depression and obesity in men, but not in women; link between risk allele and depression in men apparently independent of obesity | Good (48) |
| Rivera et al., 2012 [45] | FTO (10 SNPs) | Single-gene association; gene x depression interaction | Two independent samples of adults with (n = 3734) and without (n = 2499) major depression | Significant associations between 5 SNPs of FTO and BMI in adults with depression, but not in controls | Good (55) |
| Samaan et al., 2013 [46] | FTO (rs9939609 SNP) | Single-gene association | Pooled data from 4 samples of adults with (n = 6561) and without (n = 21932) depression | FTO rs993609 A variant associated with increased BMI but lower risk of depression | Good (53) |
| Beydoun et al., 2014 [47] | 21 SNPs across 10 genes (ABCG5, APOB, APOA4, APOE, BCMO1, CD36, LIPC, FABP2, LPL, SCARB1) associated with serum-carotenoid levels | Multiple-gene association study | Adults (age 30–64), African-American (n = 873) | No specific association between any individual SNP and either obesity or depression | Good (49) |
| Harbron et al., 2014 [48] | FTO (rs1421085 and rs17817449 SNPs and haplotype) | Single-gene association; gene x depression interaction | Adults with obesity, Caucasian (n = 133) | FTO rs17817449 GG genotype associated with more severe depressive symptoms; rs1421085 C allele mediates relationship between depressive symptoms and BMI | Moderate (41) |
| Bielinski et al., 2015 [49] | SLC6A4 (44-bp Ins/Del) and HTR2A (1438G/A SNP) | Multiple-gene association | Adults (age 18–73) with obesity, Caucasian (n = 180) | No significant association between either variant and depressive symptoms | Moderate (43) |
| Borkowska et al., 2015 [50] | SLC6A4 (5-HTTLPR repeat polymorphism) | Single-gene association | Adults with obesity, Caucasian (n = 390) | 5-HTTLPR L/L genotype associated with higher BMI and more severe depressive symptoms | Good (47) |
| Delacretaz et al., 2015 [51] | MCHR2 (8 SNPs) and MCHR2-AS1 (4 SNPs) | Multiple-gene association | Independent analyses of Caucasian adults with psychiatric disorders (n = 816) and in the general population (n = 119,218) | MCHR2 rs7754794 TT genotype associated with lower BMI in patients with depression; similar but weaker association observed in the general population | Good (57) |
| McCaffery et al., 2015 [52] | 8 SNPs at 6 loci previously associated with depressive symptoms | Multiple-gene association | Adults with obesity or overweight, multi-ethnic (n = 2118) | KCNE1 rs1543654 associated with depressive symptoms; no significant associations for other SNPs | Good (46) |
| Samaan et al., 2015 [53] | 21 SNPs previously associated with obesity | Multiple-gene association | Multi-ethnic adults with (n = 3209) and without (n = 14,195) depression | TAL1 rs2984618 SNP significantly associated with both BMI and major depression | Good (53) |
| Yilmaz et al., 2015 [54] | MC4R (rs571312, rs17782313, rs489693, rs11872992 and rs8087522 SNPs) | Single-gene association | Adults (age 24–50), Caucasian (n = 328) | MC4R rs17782313 C allele associated with higher depressive symptoms and higher BMI, but the latter was not significant after correction | Good (51) |
| Quteineh et al., 2016 [55] | CRTC1 (rs3746266 and rs6510997 SNPs) | Single-gene association | Pooled data from 3 samples of adults with (n = 5344) and without (n = 5515) major depression | No overall association between CRTC1 polymorphisms and depression; CRTC1 rs3746266 G allele and rs6510997 C allele associated with BMI in one of the samples | Moderate (43) |
| Bielinski et al., 2017 [56] | COMT (Val158Met) and DAT1 (VNTR polymorphism) | Multiple-gene association | Adults (age 39–69) with obesity, Caucasian (n = 364) | DAT1 9-repeat allele associated with higher BMI and depressive symptoms; COMT Met/Met genotype associated with depressive symptoms | Moderate (42) |
| Hellgren et al., 2017 [57] | 38 SNPs of four genes (AKR1C2, AKR1C4, SRD5A1 and SRD5A2) involved in allopregnanolone synthesis | Multiple-gene association | Pregnant women, Caucasian (n = 1351) | AKR1C2 rs28488494 SNP associated with BMI; AKR1C2 rs1937863 SNP associated with postnatal depressive symptoms | Good (50) |
| Rivera et al., 2017 [58] | FTO (rs9939609 SNP) | Single-gene association; gene x depression interaction | Pooled data from 5 samples of adults with (n = 6902) and without (n = 6799) depression | FTO rs9939609 A variant associated with higher BMI in patients with depression but not in controls | Good (54) |
| Schepers and Markus, 2017 [59] | SLC6A4 (5-HTTLPR repeat polymorphism) | Single-gene association | Healthy young adults (mean age 21.3) (n = 827) | 5-HTTLPR S allele associated with higher BMI and depressive symptoms | Moderate (45) |
| Treutlein et al., 2017 [60] | NPY2R (rs6857715 SNP) | Single-gene association; gene x weight interaction | Adults with depression (n = 595) and general population controls (n = 1295) | NPY2R rs6857715 T allele associated with depression independent of increased weight; trend towards an association between T allele weight gain in depressed patients | Good (51) |
| Brummett et al., 2018 [61] | HTR2C (rs6318 SNP) | Single-gene association | Pooled data from 10 adult samples, Caucasian and African-American (n = 27,161) | No association between HTR2C rs6318 and either depressive symptoms or BMI | Good (54) |
| Hay et al., 2022 [62] | PCSK9 and surrounding locus (7 lead SNPs identified through sequential analysis of biobank data) | Single-locus association | Data from adult Biobank samples, mixed ethnicity (n = 73,627) | PCSK9 rs2647282 associated with BMI; no association between any PCSK9 SNP and major depression | Good (49) |
| He et al., 2022 [63] | HTR2C (13 rare variants identified in a prior sample) | Single-gene association | Data from adult Biobank samples, Caucasian (n = 153,352) | HTR2C V61I variant associated with depression and obesity, but not significant after correction | Moderate (44) |
| Rahati et al., 2022 [64] | MC4R (rs17782313 SNP) | Single-gene association | Adults (age 20–50) with obesity or overweight, Iranian (n = 403) | MC4R rs17782313 C allele associated with higher depressive symptoms; CC genotype associated with higher body weight | Moderate (45) |
| Genetic Locus | Physiological Effects of Gene Product | Impact on Obesity and Depression |
|---|---|---|
| Genes with replicated associations | ||
| FTO (5 studies) | DNA/RNA demethylase enzyme that influences food intake, adiposity, and energy expenditure | Multiple SNPs associated with elevated BMI in depression but not in general samples [45] rs9939609 A allele associated with higher BMI both in general samples and in patients with depression; also associated with lower depressive symptoms in general samples [46,58] rs17817749 GG genotype associated with elevated depressive symptoms in adults with obesity [48] rs1421085 C allele interacts with depressive symptoms to influence higher BMI [44] |
| MC4R (2 studies) | G-protein-coupled, membrane-bound receptor for α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone | rs17782313 C allele associated with increased depressive symptoms in adults both with and without obesity [54] CC genotype associated with increased body weight in adults with obesity [64] |
| Genes with positive findings in single studies | ||
| AKR1C2 | Reduction of 5α-dihydroprogesterone to allopregnanolone; one of two isoforms expressed in the brain | rs28488494 associated with BMI and rs1937863 associated with post-partum depressive symptoms in pregnant women [57] |
| APOA5 | Component of high-density lipoprotein (HDL); involved in regulation of plasma-triglyceride levels | −1131 C allele associated with obesity in elderly adults with depression [40] |
| COMT | O-methylation and inactivation of catecholamine neurotransmitters—dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine | rs4680 Met/Met genotype associated with depressive symptoms in adults with obesity [56] |
| DAT1 | Reputake of dopamine into presynaptic neurons | 9-repeat allele associated with higher BMI and elevated depressive symptoms [56] |
| KCNE1 | Regulation of voltage-gated potassium channel activity in cardiac muscle, inner ear, and brain | rs1543654 associated with depressive symptoms in adults with obesity [52] |
| MAOA | Catabolism of monoamine neurotransmitters—dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine | High-activity variant associated with reduced obesity in adolescent girls with depression [43] |
| MCHR2 | G-protein-coupled, membrane-bound receptor for melanin-concentrating hormone | rs7754794 TT genotype associated with lower BMI in patients with depression [51] |
| NPY2R | Receptor for neuropeptide Y, which is involved in the stress response, eating behaviour, cognition, and pain perception | rs6857715 T allele associated with depression independent of BMI [60] Trend towards an association between this allele and increased BMI in patients with depression [60] |
| NR3C1 | Nuclear receptor for cortisol and other glucocorticoid hormones; involved in regulation of carbohydrate metabolism, immune-inflammatory activity, and the stress response | Bcl1 G/G genotype associated with greater obesity in women with depression [41] |
| Ob (Leptin) | Centrally active hormone secreted by adipose cells; regulates satiety and energy expenditure | D7S1875 < 208 bp variant associated with depressive symptoms and higher BMI in women [38] |
| PCSK9 | Proprotein convertase enzyme; regulates serum cholesterol levels by modulating the number of low-density lipoprotein receptors (LDL) | rs2647282 associated with BMI in adults; no association with depression [62] |
| TAL1 | Transcription factor involved in differentiation of erythroid and myeloid cells | rs2984618 associated with higher BMI and risk of major depression in adults [53] |
| Genes with mixed positive and negative findings | ||
| SLC6A4 a | Reputake of serotonin into presynaptic neurons | 5-HTTLPR s allele associated with higher BMI and depressive symptoms in young adults [59] 5-HTTLPR l/l genotype associated with higher BMI and more severe depressive symptoms in adults with obesity [50] |
| APOA4 b | Component of very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and chylomicrons; activator of enzymes involved in lipid metabolism; involved in regulation of serum cholesterol levels | 360 Gln/His associated with obesity and depression in elderly adults [39] |
| Target Gene | Synthetic Agents | Natural Agents |
|---|---|---|
| FTO | Selective inhibitors of FTO demethylase a | Angelica sinensis ext. Rhein |
| MC4R | Bremelanotide b Setmelanotide b | Moringa oleifera ext. Daisaikoto |
| AKR1C2 | Selective ARK1C2 inhibitors a | Astaxanthin Bai He Gun Jin Tiang |
| KCNE1 | - | Coriandrum sativum ext. Gintoin Rottlerin |
| MCHR2 | GW803430 a | - |
| NPY2R | Neuropeptide Y, intranasal a Combined NPY2R and GLP-1 agonists a | Panax ginseng ext. |
| NR3C1 | CORT125281 a PT150 c | Aesculus turbinata ext. Curcumin Baihe Zhimu Xingpi Jieyu |
| Ob | - | Commiphora myrrha ext. Nelumbo nucifera ext. Prunus persica ext. |
| PCSK9 | Alirocumab b Evolocumab b | Lysimacha vulgaris ext. Protium heptaphyllum ext. Salvia plebeia ext. |
| TAL1 | PIK-75 a | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajkumar, R.P. The Genetic Basis of Future Pharmacological Strategies for the Management of Comorbid Obesity and Depression: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 3, 160-182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm3010012
Rajkumar RP. The Genetic Basis of Future Pharmacological Strategies for the Management of Comorbid Obesity and Depression: A Scoping Review. International Journal of Translational Medicine. 2023; 3(1):160-182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm3010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajkumar, Ravi Philip. 2023. "The Genetic Basis of Future Pharmacological Strategies for the Management of Comorbid Obesity and Depression: A Scoping Review" International Journal of Translational Medicine 3, no. 1: 160-182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm3010012
APA StyleRajkumar, R. P. (2023). The Genetic Basis of Future Pharmacological Strategies for the Management of Comorbid Obesity and Depression: A Scoping Review. International Journal of Translational Medicine, 3(1), 160-182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm3010012






