The Raman Spectroscopy Approach to Different Freshwater Microplastics and Quantitative Characterization of Polyethylene Aged in the Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
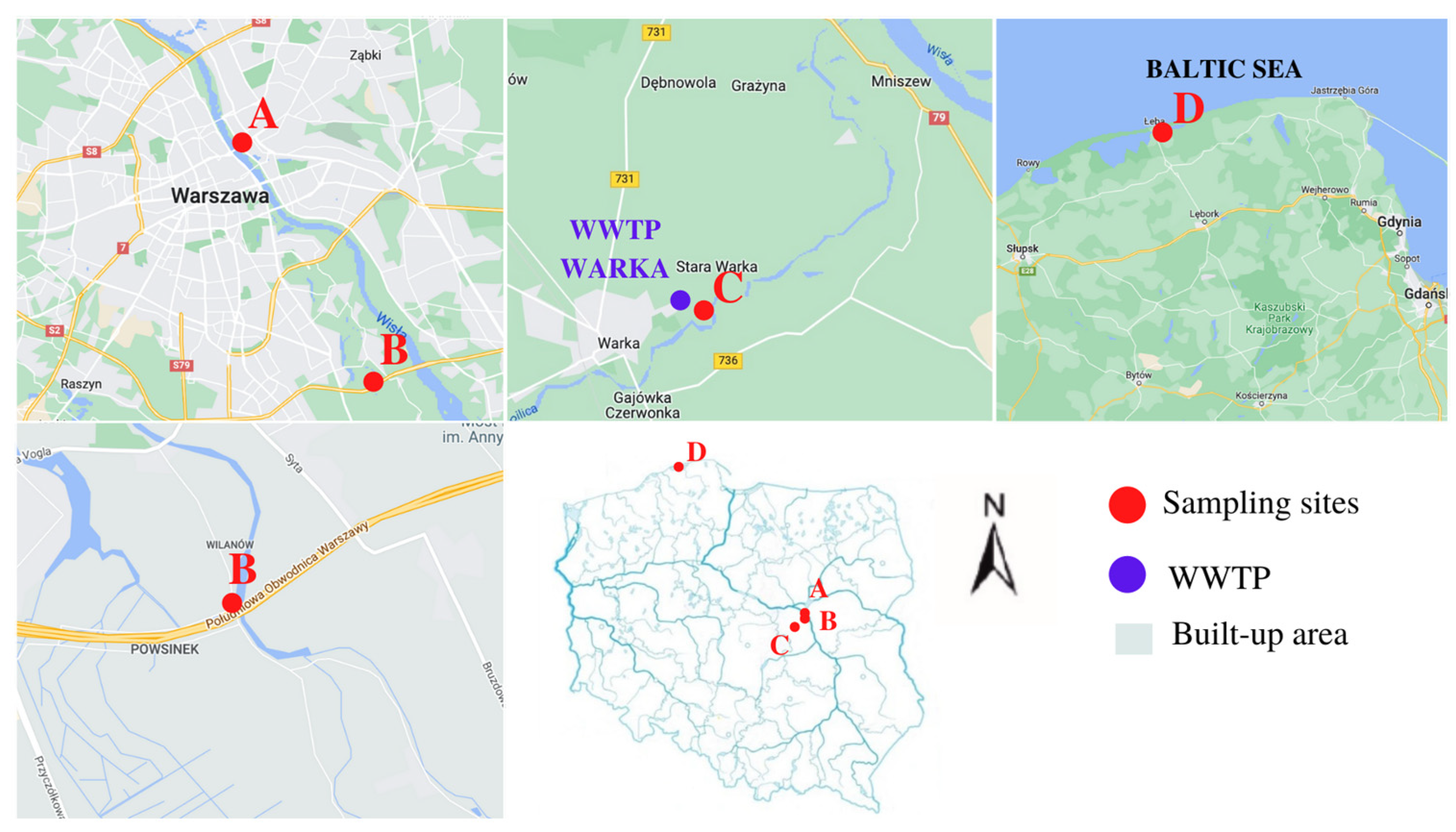
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Identification by Raman Spectroscopy
2.3. Quantitative Signal Analyses
- ▪
- OMNIC standard;
- ▪
- Adaptive iteratively reweighted penalized least squares (AIRPLS, named A);
- ▪
- Asymmetrically reweighted penalized least squares (ARPLS, named B);
- ▪
- Asymmetric least squares smoothing (ALSS, named C) and its updates.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Qualitative Characterization of MP by Raman Spectroscopy
3.2. Characteristics of the Morphology
3.3. Quantitative Characterization of Polyethylene MP by Raman Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frias, J.P.G.L.; Nash, R. Microplastics: Finding a consensus on the definition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattsson, K.; Ekvall, M.T.; Hansson, L.-A.; Linse, S.; Malmendal, A.; Cedervall, T. Altered Behavior, Physiology, and Metabolism in Fish Exposed to Polystyrene Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Review of the Methods Used for Identification and Quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldschläger, K.; Lechthaler, S.; Stauch, G.; Schüttrumpf, H. The way of microplastic through the environment—Application of the source-pathway-receptor model (review). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Paul Chen, J. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review on occurrence, environmental effects, and methods for microplastics detection. Water Res. 2018, 137, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Busquets, R.; Campos, L.C. Assessment of microplastics in freshwater systems: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Foekema, E.M. Leaching of plastic additives to marine organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 187, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windsor, F.M.; Durance, I.; Horton, A.A.; Thompson, R.C.; Tyler, C.R.; Ormerod, S.J. A catchment-scale perspective of plastic pollution. Glob Chang. Biol 2019, 25, 1207–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Triebskorn, R.; Braunbeck, T.; Grummt, T.; Hanslik, L.; Huppertsberg, S.; Jekel, M.; Knepper, T.P.; Krais, S.; Müller, Y.K.; Pittroff, M.; et al. Relevance of nano- and microplastics for freshwater ecosystems: A critical review. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Klöckner, P.; Stier, B.; Römer, M.; Seiwert, B.; Reemtsma, T.; Schmidt, C. Relationship between Discharge and River Plastic Concentrations in a Rural and an Urban Catchment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10082–10091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.; Worch, E.; Knepper, T.P. Occurrence and Spatial Distribution of Microplastics in River Shore Sediments of the Rhine-Main Area in Germany. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6070–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, T.; Hauk, A.; Walter, U.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Microplastics profile along the Rhine River OPEN. Nat. Publ. Gr. 2015, 5, 17988. [Google Scholar]
- Abuwatfa, W.H.; Al-Muqbel, D.; Al-Othman, A.; Halalsheh, N.; Tawalbeh, M. Insights into the removal of microplastics from water using biochar in the era of COVID-19: A mini review. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2021, 4, 100151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekudewicz, I.; Dąbrowska, A.M.; Syczewski, M.D. Microplastic pollution in surface water and sediments in the urban section of the Vistula River (Poland). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 763, 143111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony Browne, M.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.J.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Accumulation of Microplastic on Shorelines Woldwide: Sources and Sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eerkes-Medrano, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Aldridge, D.C. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review of the emerging threats, identification of knowledge gaps and prioritisation of research needs. Water Res. 2015, 75, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, V.; Martín-Lara, M.A.; Calero, M.; Blázquez, G. Physical-chemical characterization of microplastics present in some exfoliating products from Spain. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 139, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveena, S.M.; Shaifuddin, S.N.M.; Akizuki, S. Exploration of microplastics from personal care and cosmetic products and its estimated emissions to marine environment: An evidence from Malaysia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 136, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, A.; Hoellein, T.J.; Mason, S.A.; Schluep, J.; Kelly, J.J. Microplastic is an Abundant and Distinct Microbial Habitat in an Urban River. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11863–11871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbetts, J.; Krause, S.; Lynch, I.; Smith, G.H.S. Abundance, Distribution, and Drivers of Microplastic Contamination in Urban River Environments. Water 2018, 10, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graca, B.; Szewc, K.; Zakrzewska, D.; Dołęga, A.; Szczerbowska-Boruchowska, M. Sources and fate of microplastics in marine and beach sediments of the Southern Baltic Sea—A preliminary study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 7650–7661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Su, L.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Lan, W. The distribution of microplastics in water, sediment, and fish of the Dafeng River, a remote river in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 228, 113009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shruti, V.C.; Jonathan, M.P.; Rodriguez-Espinosa, P.F.; Rodríguez-González, F. Microplastics in freshwater sediments of Atoyac River basin, Puebla City, Mexico. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.O.; Abrantes, N.; Gonçalves, F.J.M.; Nogueira, H.; Marques, J.C.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Spatial and temporal distribution of microplastics in water and sediments of a freshwater system (Antuã River, Portugal). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, N.; Reichardt, A.M.; Waniek, J.J. Sinking rates of microplastics and potential implications of their alteration by physical, biological, and chemical factors. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbyszewski, M.; Corcoran, P.L.; Hockin, A. Comparison of the distribution and degradation of plastic debris along shorelines of the Great Lakes, North America. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xiong, X.; Jiang, X.; Shi, H.; Wu, C. Sinking of floating plastic debris caused by biofilm development in a freshwater lake. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, H.A.; Dalu, T.; Wasserman, R.J. Sinks and sources: Assessing microplastic abundance in river sediment and deposit feeders in an Austral temperate urban river system. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, T.; Ostrowski, P.; Siwicki, P.; Brach, M. Channel morphology changes and their relationship to valley bottom geology and human interventions; a case study from the Vistula Valley in Warsaw, Poland. Geomorphology 2017, 297, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zuo, L.Z.; Peng, J.P.; Cai, L.Q.; Fok, L.; Yan, Y.; Li, H.X.; Xu, X.R. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in an urban river: A case study in the Pearl River along Guangzhou City, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.L.; Thomas, K.V.; Luo, Z.; Gowen, A.A. FTIR and Raman imaging for microplastics analysis: State of the art, challenges and prospects. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, G.; Schmidt, T.C.; Schram, J. Automated rapid & intelligent microplastics mapping by FTIR microscopy: A Python–based workflow. MethodsX 2020, 7, 100742. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Renner, G.; Nellessen, A.; Schwiers, A.; Wenzel, M.; Schmidt, T.C.; Schram, J. Data preprocessing & evaluation used in the microplastics identification process: A critical review & practical guide. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 111, 229–238. [Google Scholar]
- Cowger, W.; Gray, A.; Christiansen, S.H.; DeFrond, H.; Deshpande, A.D.; Hemabessiere, L.; Lee, E.; Mill, L.; Munno, K.; Ossmann, B.E.; et al. Critical Review of Processing and Classification Techniques for Images and Spectra in Microplastic Research. Appl. Spectrosc. 2020, 74, 989–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Yang, X.; Chen, F.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, Y.; Ruan, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y. Fate and transport of nanoplastics in complex natural aquifer media: Effect of particle size and surface functionalization. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiejima, Y.; Kida, T.; Takeda, K.; Igarashi, T.; Nitta, K.H. Microscopic structural changes during photodegradation of low-density polyethylene detected by Raman spectroscopy. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 150, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerer, C.; Matulaitiene, I.; Niaura, G.; Reuter, U.; Janke, A.; Boldt, R.; Sablinskas, V.; Steiner, G. Nondestructive characterization of the polycarbonate-octadecylamine interface by surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Polym. Test. 2019, 73, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Cossar, M.; Dang, V.; Teh, J. The application of Raman spectroscopy to three-phase characterization of polyethylene crystallinity. Polym. Test. 2007, 26, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, M.J.; Hendra, P.J.; Peacock, C.J.; Cudby, M.E.A.; Willis, H.A. Laser-Raman spectrum of polyethylene: Part 1. Structure and analysis of the polymer. Polymer 1972, 13, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, M.J.; Hendra, P.J.; Peacock, O.J.; Cudby, M.E.A.; Willis, H.A. The laser-Raman spectrum of polyethylene. The assignment of the spectrum to fundamental modes of vibration. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Spectrosc. 1972, 28, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, R.G. Interpretation of the Raman spectrum of polyethylene and deuteropolyethylene. J. Mol. Spectrosc. 1970, 36, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-M.; Chen, S.; Liang, Y.Z. Baseline correction using adaptive iteratively reweighted penalized least squares. Analyst 2010, 135, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.J.; Park, A.; Ahna, Y.J.; Choo, J. Baseline correction using asymmetrically reweighted penalized least squares smoothing. Analyst 2015, 140, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boelens, H.F.; Eilers, P.H.; Hankemeier, T. Sign Constraints Improve the Detection of Differences between Complex Spectral Data Sets: LC−IR As an Example. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 7998–8007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y.; He, J.; Xie, W.; Wu, P.; Du, C. Baseline Correction for Raman Spectra Using Improved Asymmetric Least Squares. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 4402–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
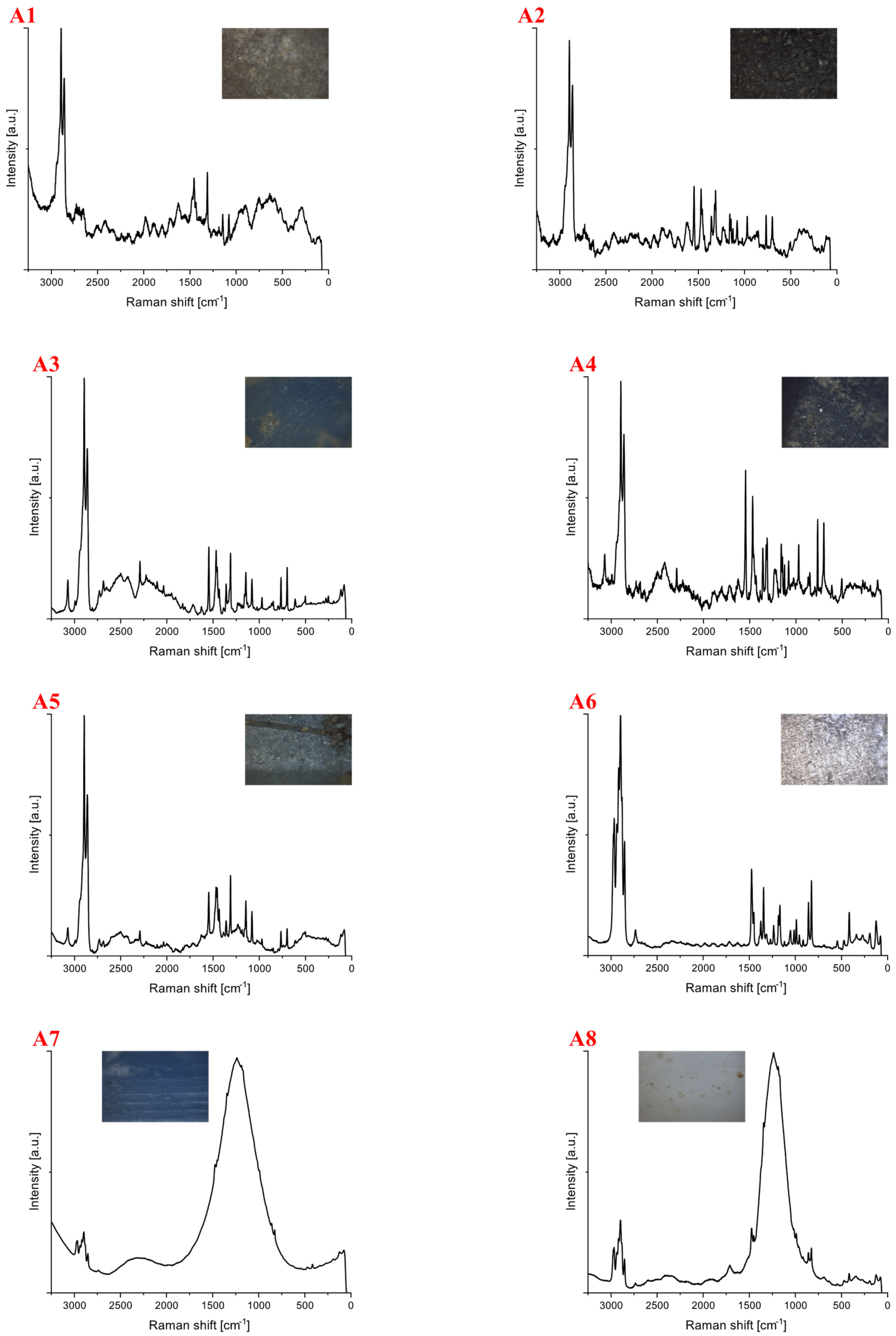
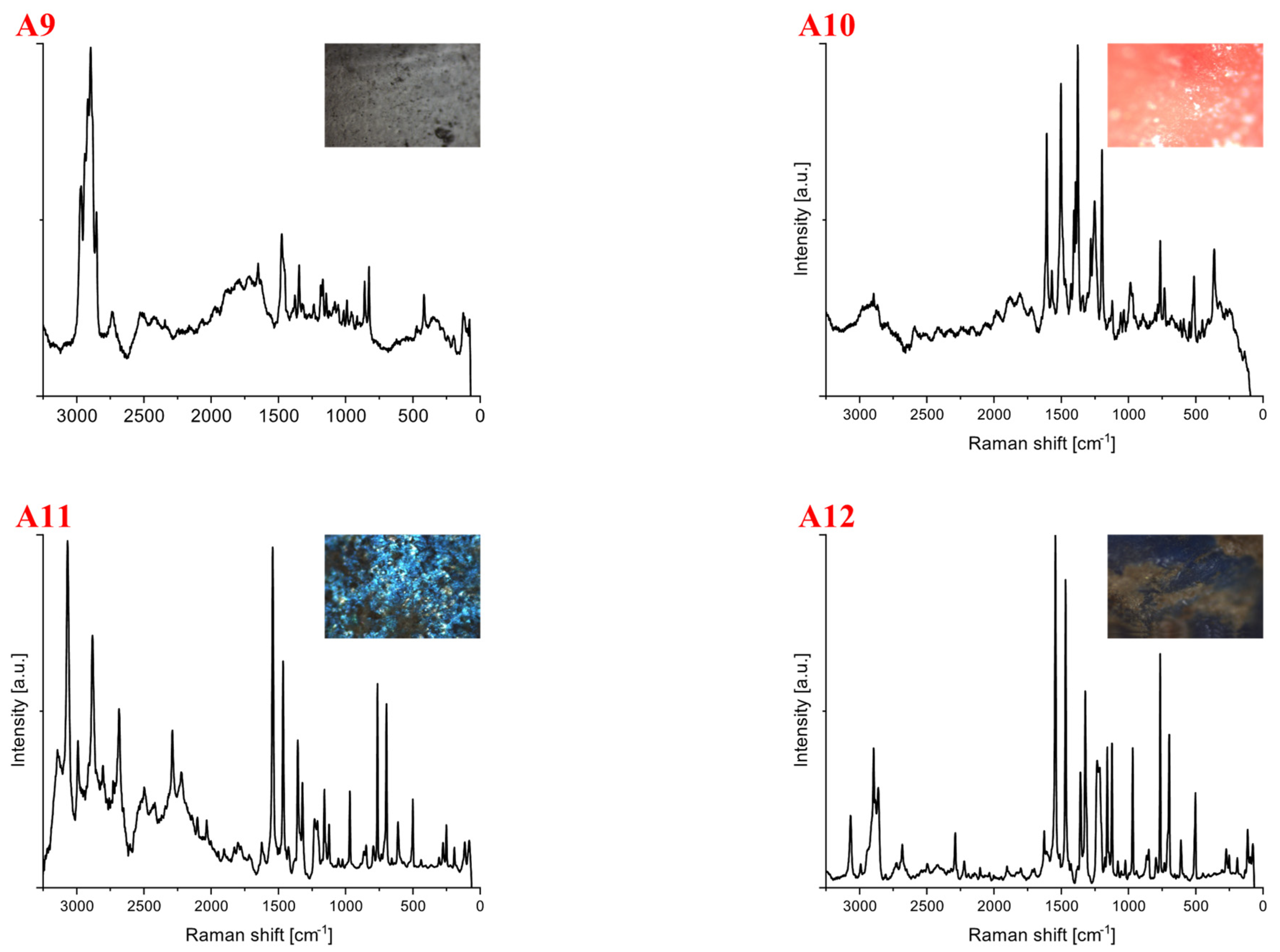
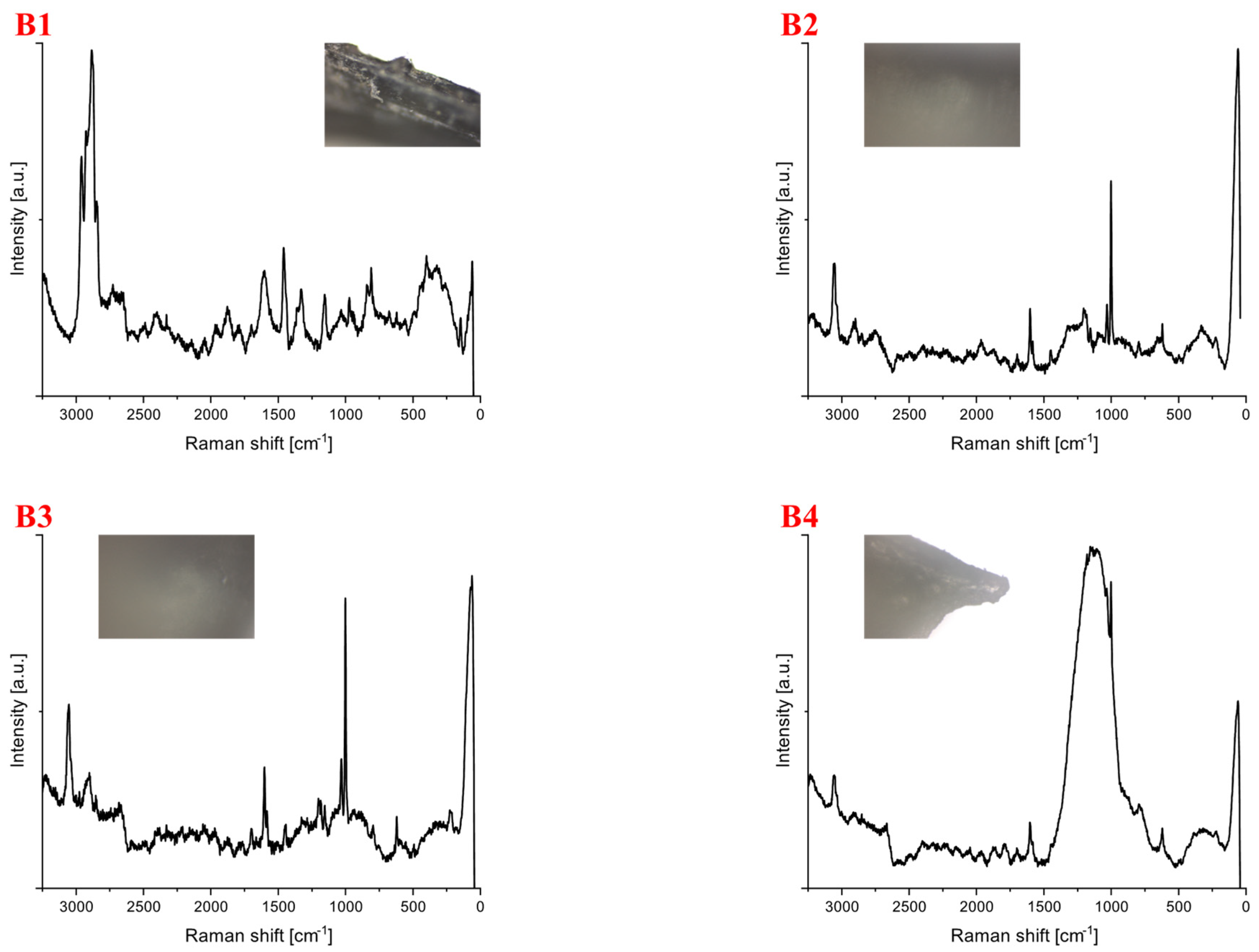
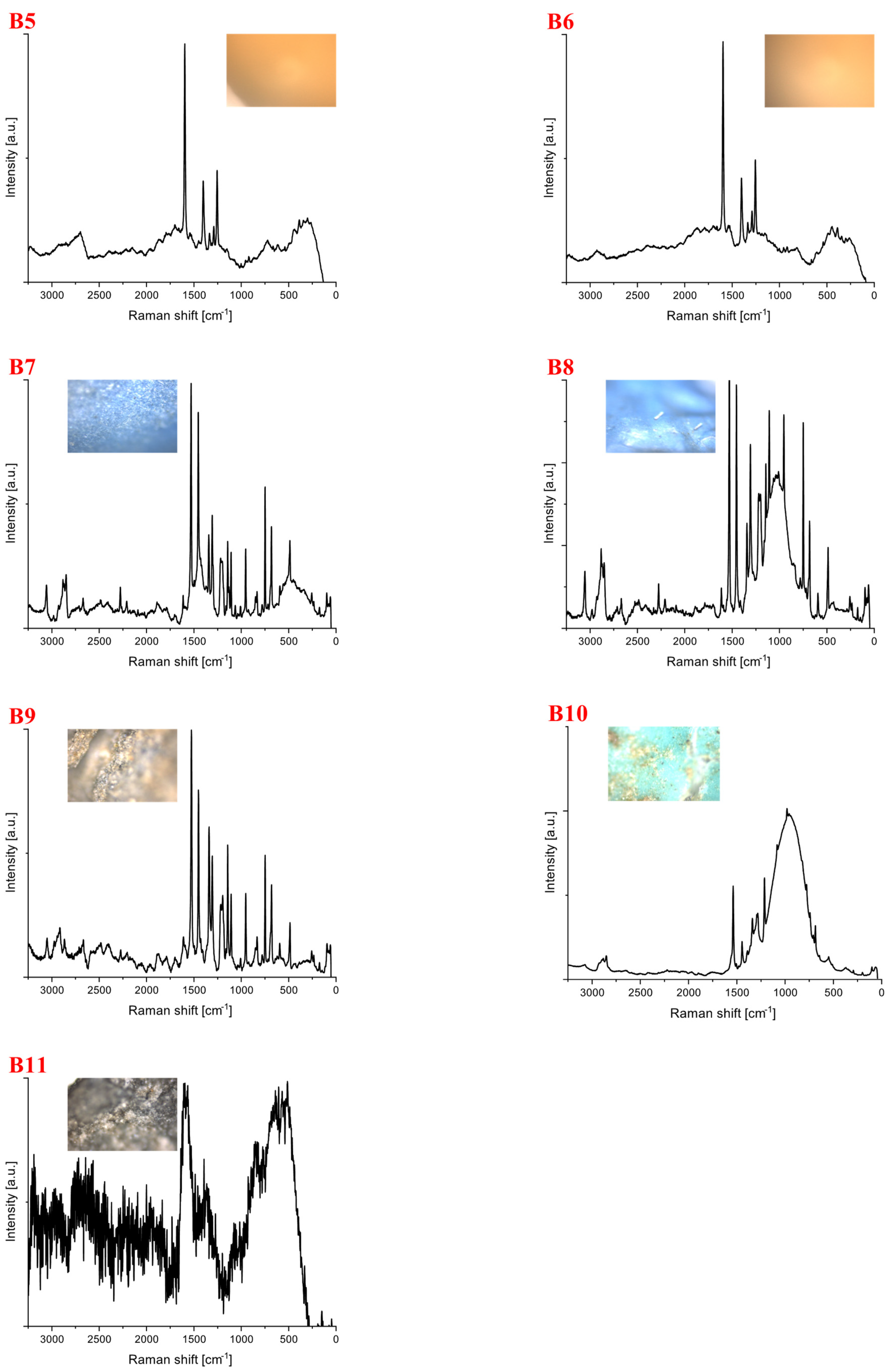
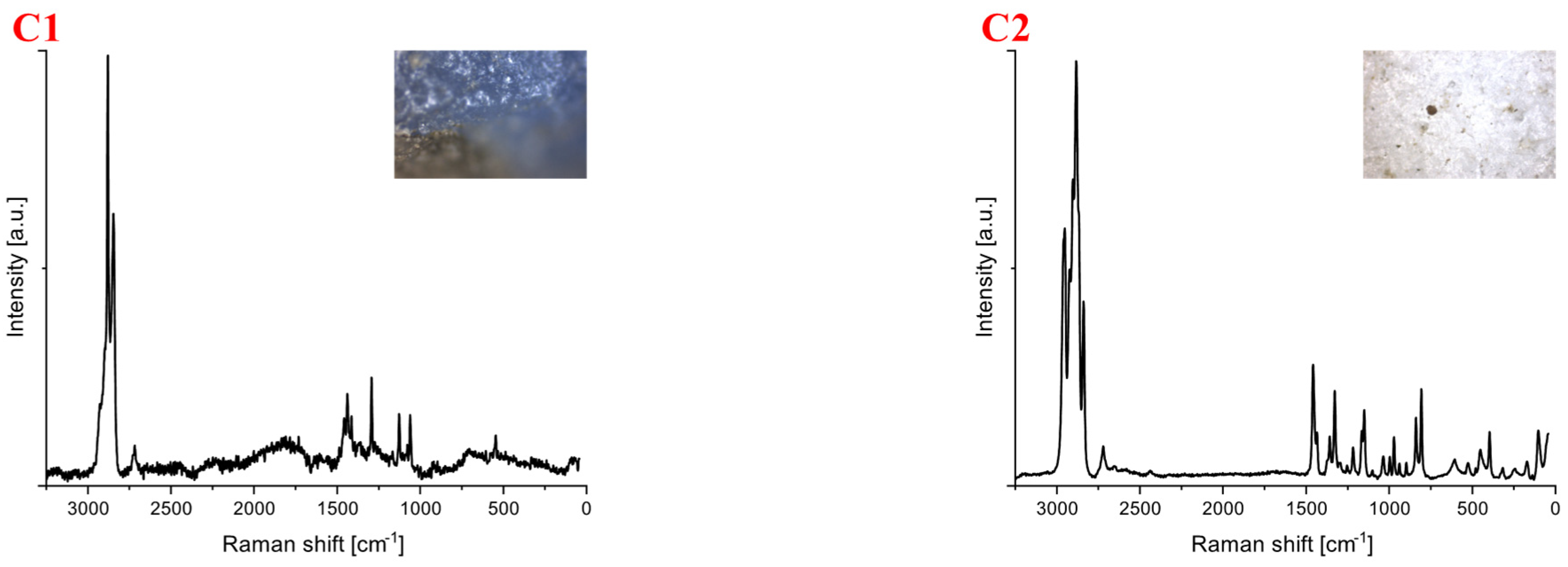
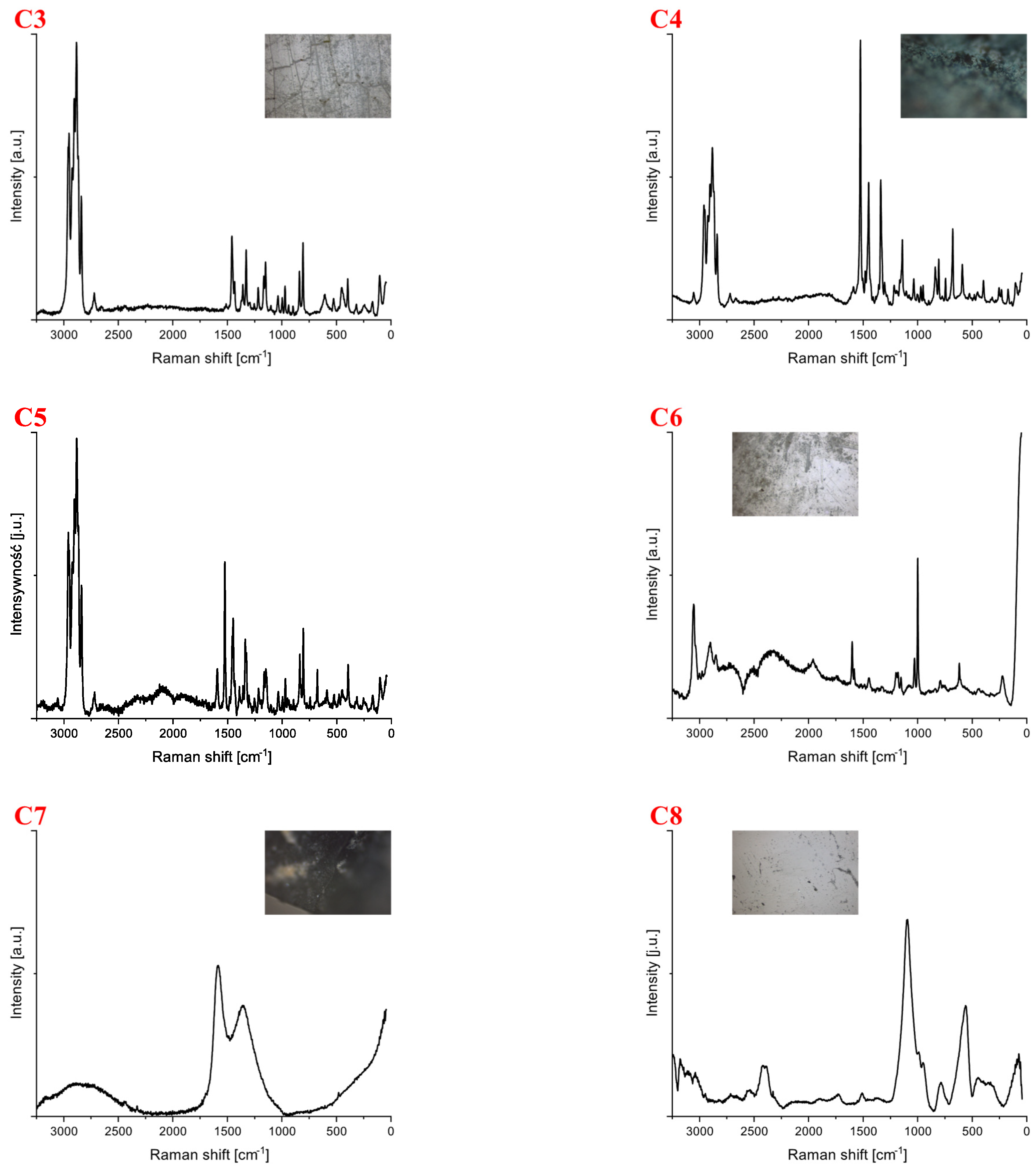
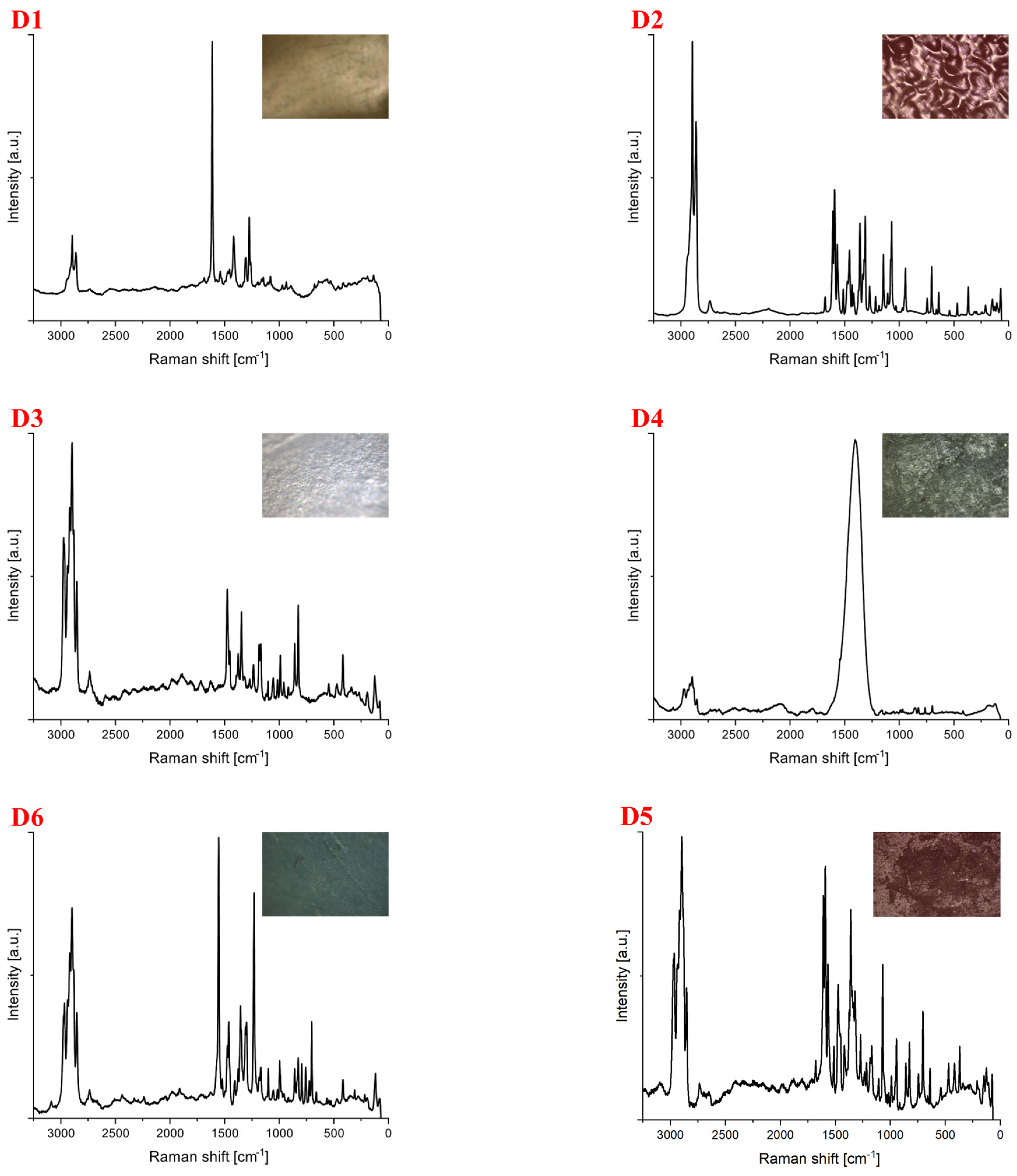
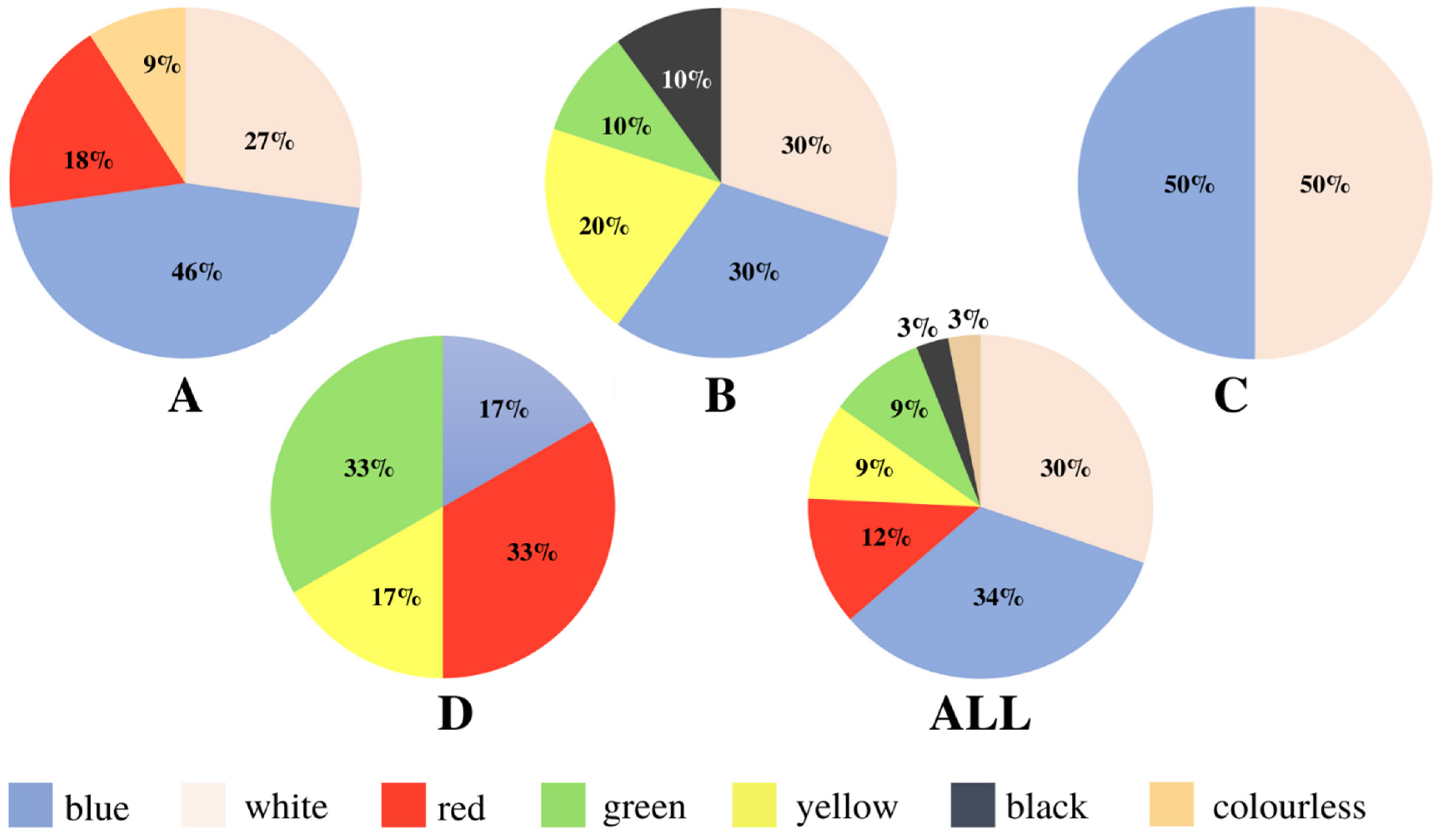

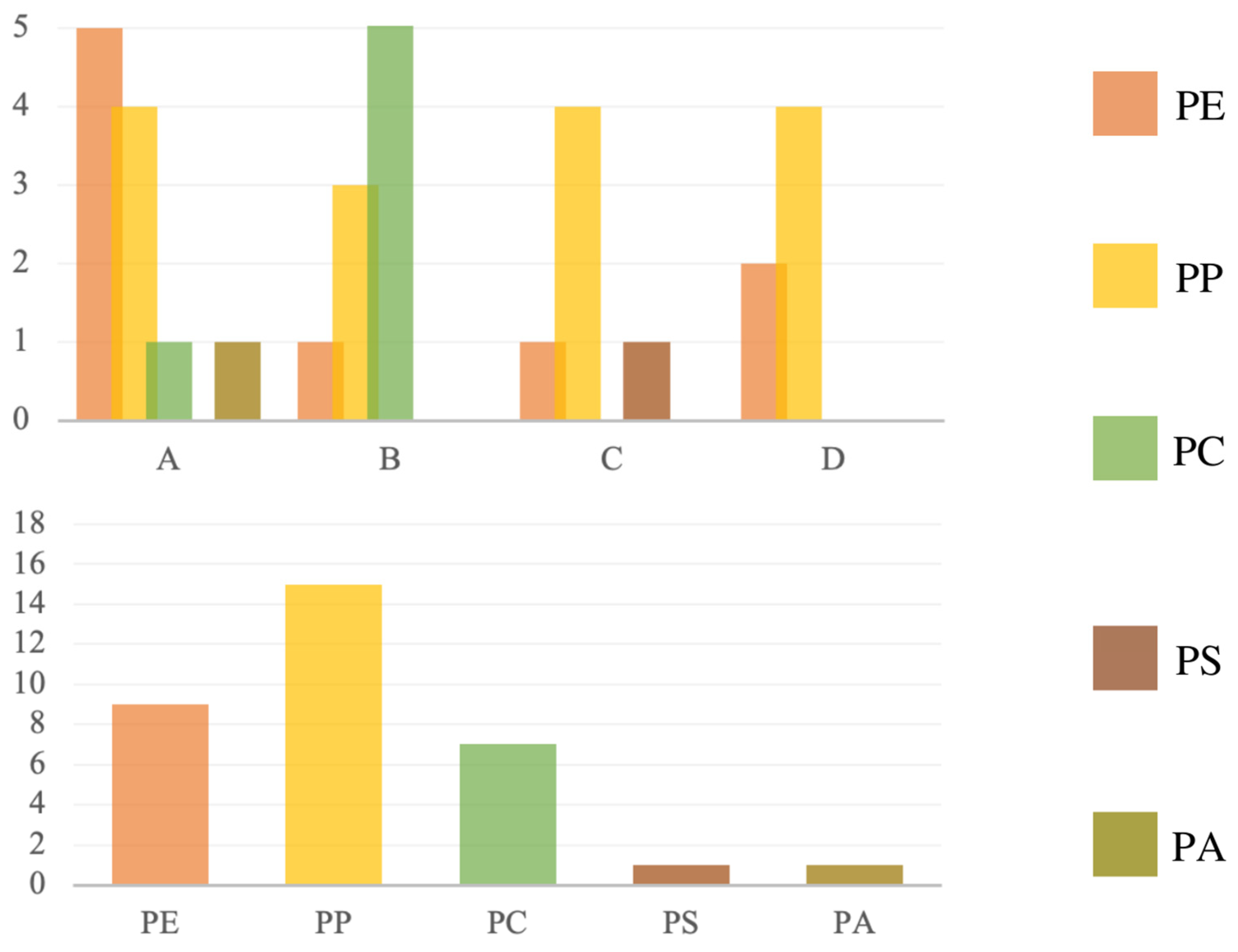

| Polymer Type | Signature | Color | Shape | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene | A1 | White | foil | upper limit |
| A2 | Blue | fragment (rectangular) | upper limit | |
| A3 | Red | fragment (irregular) | upper limit | |
| A4 | Blue | fragment (irregular) | 5 mm × 2 mm | |
| A5 | blue | fragment (irregular) | 2 mm × 1 mm | |
| Polypropylene | A6 | white | fragment (rectangular) | upper limit |
| A7 | white | cylindric, lollipop stick-like | upper limit | |
| A8 | blue | cylindric, lollipop stick-like | upper limit | |
| A9 | colorless | foil | upper limit | |
| Polyamide | A10 | red | foil | upper limit |
| Polycarbonate | A11 | blue | foil | 3 mm × 2 mm |
| Polymer Type | Signature | Color | Shape | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene | B1 | black | Foil | upper limit |
| Polypropylene | B2 | white | fragment (fibrous) | upper limit |
| B3 | white | fragment (irregular) | 5 mm × 4 mm | |
| B4 | white | fragment (irregular) | upper limit | |
| Polycarbonate | B5 | yellow | fragment (irregular) | 4 mm × 2 mm |
| B6 | yellow | fragment (irregular) | 4 mm × 3 mm | |
| B7 | blue | foil | upper limit | |
| B8 | blue | foil | 4 mm × 1 mm | |
| B9 | blue | foil | upper limit | |
| B10 | green | foil | upper limit |
| Polymer Type | Signature | Color | Shape | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene | C1 | blue | fragment (irregular) | 4 mm × 3 mm |
| Polypropylene | C2 | white | fragment (irregular) | upper limit |
| C3 | white | fragment (irregular) | 3 mm × 2 mm | |
| C4 | blue | Foil | 5 mm × 4 mm | |
| C5 | blue | Foil | 4 mm × 2 mm | |
| Polystyrene | C6 | white | fragment (irregular) | 5 mm × 4 mm |
| Carbone | C7 | black | fragment (irregular) | upper limit |
| Cellulose | C8 | white | fragment (irregular) | 4 mm × 3 mm |
| Polymer Type | Signature | Color | Shape | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene | D1 | yellow | foil | upper limit |
| D2 | Red | spherical, cap-like | upper limit | |
| Polypropylene | D3 | white | foil | upper limit |
| D4 | green | fragment (irregular) | upper limit | |
| D5 | Red | fragment (rectangular) | upper limit | |
| D6 | green | fragment (cylindric) | upper limit |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rytelewska, S.; Dąbrowska, A. The Raman Spectroscopy Approach to Different Freshwater Microplastics and Quantitative Characterization of Polyethylene Aged in the Environment. Microplastics 2022, 1, 263-281. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1020019
Rytelewska S, Dąbrowska A. The Raman Spectroscopy Approach to Different Freshwater Microplastics and Quantitative Characterization of Polyethylene Aged in the Environment. Microplastics. 2022; 1(2):263-281. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleRytelewska, Sylwia, and Agnieszka Dąbrowska. 2022. "The Raman Spectroscopy Approach to Different Freshwater Microplastics and Quantitative Characterization of Polyethylene Aged in the Environment" Microplastics 1, no. 2: 263-281. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1020019
APA StyleRytelewska, S., & Dąbrowska, A. (2022). The Raman Spectroscopy Approach to Different Freshwater Microplastics and Quantitative Characterization of Polyethylene Aged in the Environment. Microplastics, 1(2), 263-281. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1020019







