Time Integrated Metal Accumulation on Pellets in an Industrial Harbour “Durban Harbour”
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
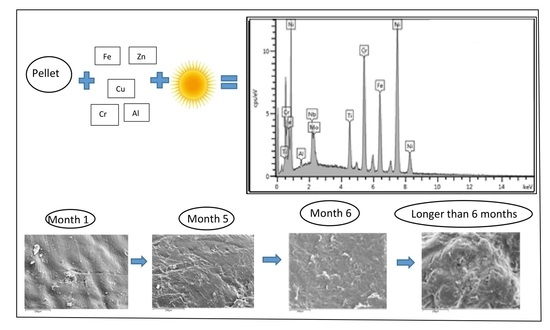
2.1. Experimental Methods
2.2. Metal Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moore, C.J. Synthetic polymers in the marine environment: A rapidly increasing, long-term threat. Environ. Res. 2008, 108, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, T.M.; Arneborg, L.; Broström, G.; Almroth, B.C.; Gipperth, L.; Hassellöv, M. The unaccountability case of plastic pellet pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, P.G. The effects of ingested plastic on seabirds: Correlations between plastic load and body condition. Environ. Pollut. 1987, 46, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, C.; Baker, J.; Bamford, H. In Proceedings of the International Research Workshop on the Occurrence, Effects, and Fate of Microplastic Marine Debris, Tacoma, WA, USA, 9–11 September 2009. Available online: http://marine.gov.scot/sma/content/proceedings-international-research-workshop-occurrence-effects-and-fate-microplastic-marine (accessed on 20 July 2021).
- Schuyler, Q.; Hardesty, B.D.; Wilcox, C.; Townsend, K. Global analysis of anthropogenic debris ingestion by sea turtles. Conserv. Biol. 2013, 28, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kershaw, P.J. (Ed.) Sources, Fate and Effects of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Global Assessment; International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Provencher, J.F.; Gaston, A.J.; Mallory, M.L. Evidence for increased ingestion of plastics by Northern Fulmars (Fulmarus glacialis) in the Canadian Arctic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1092–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.R.; Thompson, J.T. Deposit-and suspension-feeding sea cucumbers (Echinodermata) ingest plastic fragments. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 368, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, D.d.A.; de Carvalho-Souza, G.F. Are we eating plastic-ingesting fish? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 103, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, Y.; Isobe, T.; Takada, H.; Kanehiro, H.; Ohtake, C.; Kaminuma, T. Plastic resin pellets as a transport medium for toxic chemicals in the marine environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, S.; Takizawa, R.; Okuda, K.; Takada, H.; Chiba, K.; Kanehiro, H.; Ogi, H.; Yamashita, R.; Date, T. Concentration of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in beached resin pellets: Variability among individual particles and regional differences. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, K.; Holmes, L.; Turner, A. Association of metals with plastic production pellets in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, L.A.; Turner, A.; Thompson, R.C. Adsorption of trace metals to plastic resin pellets in the marine environment. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 160, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Bakir, A.; Burton, G.A.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastic as a vector for chemicals in the aquatic environment: Critical review and model-supported reinterpretation of empirical studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3315–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainbow, P.S.; Moore, P.G. Seasonal variation in copper and zinc concentrations in three talitrid amphipods (Crustacea). Hydrobiologia 1990, 196, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieboer, E.; Richardson, D.H.S. The replacement of the nondescript term ‘heavy metals’ by a biologically and chemically significant classification of metal ions. Environ. Pollut. Ser. B Chem. Phys. 1980, 1, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainbow, P.S. Biomonitoring of heavy metal availability in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1995, 31, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, L.; Taylor, J.H.; Davison, W.; Hewitt, C. Artefacts in sorption experiments with trace metals. Sci. Total Environ. 1994, 152, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobelo-Garcia, A.; Turner, A.; Millward, G.E.; Couceiro, F. Behaviour of palladium (II), platinum (IV), and rhodium (III) in artificial and natural waters: Influence of reactor surface and geochemistry on metal recovery. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 585, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Chang-Chien, G.-P.; Chiang, P.-C.; Chen, W.-H.; Lin, Y.-C. Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contaminations in seawater and sediments from a heavily industrialized harbor in Southern Taiwan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 76, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, T.; Glassom, D.; Smit, A.J. Plastic pollution in five urban estuaries of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumann, E.H.; MacKay, C.F.; Strydom, N.A. Nurdle drifters around South Africa as indicators of ocean structures and dispersion. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2019, 115, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asensio, R.C.; Moya, M.S.A.; de la Roja, J.M.; Gómez, M. Analytical characterization of polymers used in conservation and restoration by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 2081–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twyman, R. 2 Elemental Analysis: Wet Digestion. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Science, 2nd ed.; Worsfold, P., Townshend, A., Poole, C., Eds.; Elsevier Science: London, UK, 2005; pp. 146–153. [Google Scholar]
- LRios, M.; Moore, C.; Jones, P.R. Persistent organic pollutants carried by synthetic polymers in the ocean environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Schwertmann, U.; Taylor, R.M. Iron Oxides. In Minerals in Soil Environments, 2nd ed.; Dixon, J.B., Weed, S.B., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1989; Volume 1, pp. 379–438. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Lu, H.; Ruffine, L. Geochemical characteristics of iron in sediments from the Sea of Marmara. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2018, 153, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, A.; Holmes, L.A. Adsorption of trace metals by microplastic pellets in fresh water. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öz, N.; Kadizade, G.; Yurtsever, M. Investigation of heavy metal adsorption on microplastics. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 7301–7310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munier, B.; Bendell, L. Macro and micro plastics sorb and desorb metals and act as a point source of trace metals to coastal ecosystems. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hentschel, B.T.; Teh, S.J. Long-term sorption of metals is similar among plastic types: Implications for plastic debris in aquatic environments. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teuten, E.L.; Rowland, S.J.; Galloway, T.S.; Thompson, R.C. Potential for plastics to transport hydrophobic contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7759–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennecke, D.; Duarte, B.; Paiva, F.; Caçador, I.; Canning-Clode, J. Microplastics as vector for heavy metal contamination from the marine environment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 178, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.-H.; Chang, S.; Hong, S.H.; Shim, W.J. Microplastics as a vector of hydrophobic contaminants: Importance of hydrophobic additives. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedolin, M.C.; Teophilo, C.Y.S.; Turra, A.; Figueira, R.C.L. Spatial variability in the concentrations of metals in beached microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, M.; Smith, J.; Mayfield, A., III; Minno, M.; Shin, K. First report of laurel wilt disease caused by Raffaelea lauricola on pondspice in Florida. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montecchio, L.; Faccoli, M. First record of thousand cankers disease Geosmithia morbida and walnut twig beetle Pityophthorus juglandis on Juglans nigra in Europe. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Polymers | Absorption Bands (cm−1) Used for Identification | Assignment |
|---|---|---|
| High-density polyethylene HDPE | 2915, 2845 | CH stretch |
| 1472, 1462 | CH2 bend | |
| 730, 717 | CH2 rock |
| Al | Cr | Cu | Fe | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | 4.67 ± 0.17 | 0.046 ± 0.00 | 0.84 ± 0.78 | 4.23 ± 0.15 | 2.23 ± 0.13 |
| Oct | 1.63 ± 0.07 | 0.051 ± 0.00 | 0.681 ± 0.81 | 2.27 ± 0.07 | 1.88 ± 0.08 |
| Nov | 1.40 ± 0.47 | 0.186 ± 0.01 | 2.516 ± 1.01 | 1.70 ± 0.45 | 1.41 ± 0.40 |
| Dec | 0.99 ± 0.002 | 0.038 ± 0.01 | 1.30 ± 0.56 | 1.48 ± 0.16 | 1.03 ± 0.43 |
| Jan | 0.67 ± 0.05 | 0.033 ± 0.1 | 0.59 ± 0.31 | 0.79 ± 0.02 | 0.46 ± 0.09 |
| Feb | 0.54 ± 0.42 | * 0.00 ± 0.1 | 0.49 ± 0.30 | 0.78 ± 0.00 | 0.17 ± 0.001 |
| March | 1.02 ± 0.83 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.55 ± 0.57 | 0.70 ± 0.11 | 0.38 ± 0.05 |
| Al | Cr | Cu | Fe | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| During spill | 0.58 ± 0.1 | 0.060 ± 0.01 | 0.37 ± 0.01 | 1.27 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.01 |
| Four months after spill | 0.70 ± 0.01 | 0 | 0.68 ± 0.01 | 2.7 ± 156 | 0.16 ± 0.01 |
| Six months after spill | 0.68 ± 0.24 | 0 | 0.2 ± 0.01 | 0.86 ± 0.01 | 0.6 ± 0.01 |
| Cr | Cu | Fe | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | 0.10 | 2.82 | 0.41 | 4.62 |
| 10 October 2017 | * | 0.43 | 0.36 | 1.31 |
| Nov | * | 1.84 | 0.31 | 4.41 |
| Dec | * | 1.35 | 0.39 | 4.56 |
| Jan | * | 0.91 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| Feb | * | 1.67 | 0.66 | 3.29 |
| March | * | 1.01 | 0.18 | 3.60 |
| Df | Sum | Mean | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 7 | 1.43 | 0.22 | 0.82 |
| Df | Sum | Mean | F | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | 6 | 11.2 | 1.87 | 34.45 | 1.3 × 10−7 |
| Cu | 6 | 8.9 | 1.4 | 9.6 | 0.0002 |
| Fe | 6 | 26.9 | 4.45 | 117.4 | 3.7 × 10−11 |
| Cr | 6 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 293.9 | 6.6 × 10−7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mofokeng, R.P.; Glassom, D. Time Integrated Metal Accumulation on Pellets in an Industrial Harbour “Durban Harbour”. Microplastics 2022, 1, 3-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1010002
Mofokeng RP, Glassom D. Time Integrated Metal Accumulation on Pellets in an Industrial Harbour “Durban Harbour”. Microplastics. 2022; 1(1):3-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleMofokeng, Refilwe Precious, and David Glassom. 2022. "Time Integrated Metal Accumulation on Pellets in an Industrial Harbour “Durban Harbour”" Microplastics 1, no. 1: 3-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1010002
APA StyleMofokeng, R. P., & Glassom, D. (2022). Time Integrated Metal Accumulation on Pellets in an Industrial Harbour “Durban Harbour”. Microplastics, 1(1), 3-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1010002