Cyclical Trends of Network Load Fluctuations in Traffic Jamming
Abstract
1. Introduction: Traffic of Information Packets on Complex Networks
2. Substrate Networks and Traffic Model Rules
2.1. Properties of Two Prototypal Networks
2.2. Traffic of Information Packets: Model Rules
- Posting: At each time step t, each node can create a new packet with the probability R; another randomly selected node sets the packet’s destination on the network’s connected component; the created packet is added to the top of the node’s queue;
- Queueing: If more than one packet is present at a node, they make a queue by order of arrival at that node, with a new arrival appearing at the top of the queue. The node’s queue length at the time t is , where H represents the maximum possible queue length of each node;
- Navigation: Each node with a nonempty queue tries to move the top packet in its queue, i.e., we apply LIFO (last-in-first-out) queueing rule. The node performs a next-neighbourhood search for the destination address of the packet; if the address is found in the searched depth, the packet is delivered to the neighbour along the shortest path to the destination, else it is transferred to a random neighbour. If the neighbour queues are full, the packet waits for the next transmission opportunity;
- Delivery: Upon arrival at its destination, the packet is removed from the traffic.
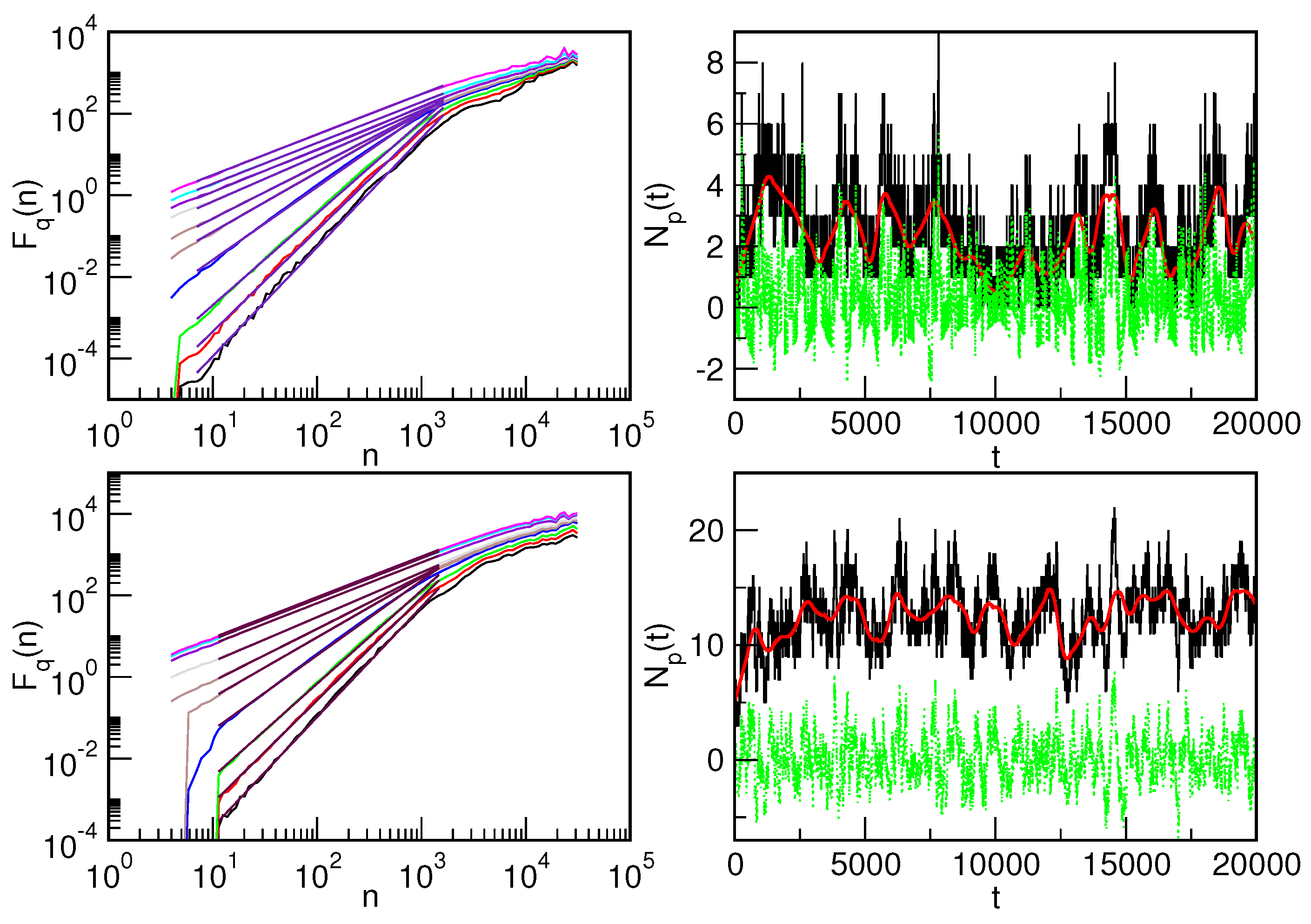
3. Traffic Cycles and the Power Spectra of Load Time Series on Webgraph and Statnet
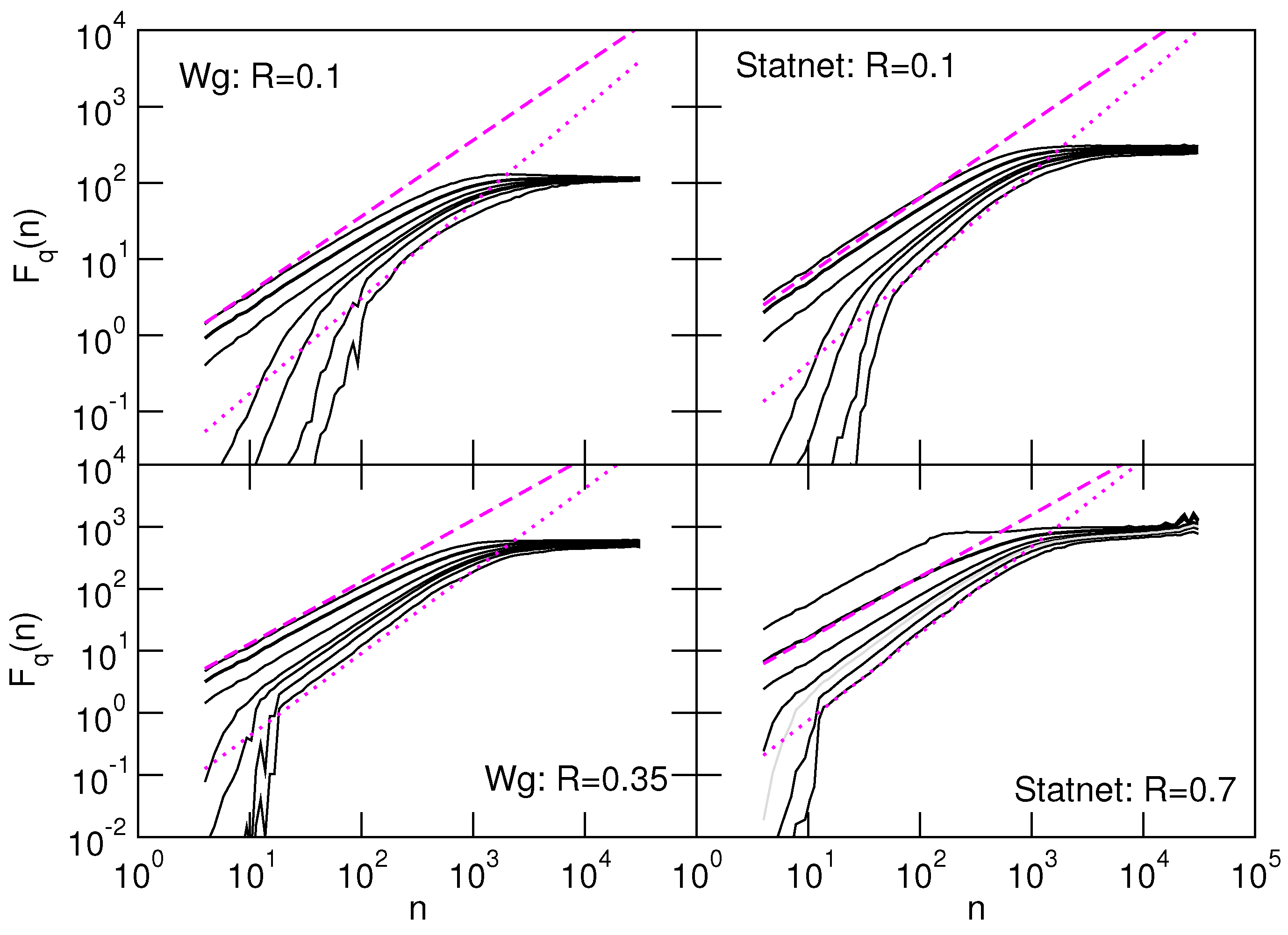
4. Mutifractality of the Traffic-Load Trends and Detrended Fluctuations
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tadić, B.; Rodgers, G.J.; Thurner, S. Transport on Complex Networks: Flow, Jamming and Optimization. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2007, 17, 2363–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupte, N.; Singh, B.K.; Janaki, T.M. Networks: Structure, function and optimisation. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2005, 346, 55–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, J.; Li, H.J. An efficient link closing strategy for improving traffic capacity on scale-free networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2022, 604, 127887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagatani, T. The physics of traffic jams. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2002, 65, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé-Ribalta, A.; Gómez, S.; Arenas, A. Decongestion of Urban Areas with Hotspot Pricing. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2018, 18, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isufaj, R.; Koca, T.; Piera, M.A. Spatiotemporal Graph Indicators for Air Traffic Complexity Analysis. Aerospace 2021, 8, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezaki, T.; Imura, N.; Nishinari, K. Towards understanding network topology and robustness of logistics systems. Commun. Transp. Res. 2022, 2, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.L.; Guo, Y.D.; Zhu, C.P.; Mitrovic, M.; Tadic, B. Congestion patterns of traffic studied on Nanjing city dual graph. In Proceedings of the 2009 16th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, Santorini, Greece, 5–7 July 2009; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezaki, T.; Nishinari, K. Potential global jamming transition in aviation networks. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 90, 022807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Dong, H.; Tse, C.K.; Ho, I.W.; Lau, F.C. Analysis of metro network performance from a complex network perspective. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2018, 492, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagatani, T. Chain reaction of traffic breakdowns in coupled-cycle networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2022, 587, 126549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daganzo, C.F.; Gayah, V.V.; Gonzales, E.J. Macroscopic relations of urban traffic variables: Bifurcations, multivaluedness and instability. Transp. Res. Part B: Methodol. 2011, 45, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, B.; Thurner, S. Information super-diffusion on structured networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2004, 332, 566–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, B.; Thurner, S.; Rodgers, G.J. Traffic on complex networks: Towards understanding global statistical properties from microscopic density fluctuations. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 036102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, D.; Dall’Asta, L.; Bianconi, G.; Marsili, M. Congestion phenomena on complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79, 015101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Wu, Z.X.; Jiang, R.; Chen, G.; Lai, Y.C. Abrupt transition to complete congestion on complex networks and control. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2009, 19, 033106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadić, B.; Rodgers, G.J. Packet Transport on Scale-free Networks. Adv. Complex Syst. 2002, 05, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, B. Guided Search and Distribution of Information Flow on Complex Graphs. In Computational Science—ICCS 2004, Proceedings of the 4th International Conference, Kraków, Poland, 6–9 June 2004; Bubak, M., van Albada, G.D., Sloot, P.M.A., Dongarra, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 1086–1093. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.H.; Yang, H.J. Traffic systems recovery from complete congestion by the targeted dropping of packets. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2019, 33, 1950096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, Q.Y.; Ling, X.; Zhang, L.J. The self-adaptive routing strategy to alleviate packet loss in finite buffer networks. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2021, 2021, 123402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Liu, Z.; Liang, X.; Hui, P.M. Self-adjusting routing schemes for time-varying traffic in scale-free networks. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 80, 026114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Zhou, T.; Hu, B.; Fu, Z.Q.; Wang, B.H. Efficient routing on complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 73, 046108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Cheng, D. Efficient path routing strategy for flows with multiple priorities on scale-free networks. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadi, A.A.; Abdulkader, O.A.; Al-Ardhi, S.; Thayananthan, V. Analytical Model of Enhancing Traffic Performance Based on Weighted Nodes. In Proceedings of the 2016 UKSim-AMSS 18th International Conference on Computer Modelling and Simulation (UKSim), Cambridge, UK, 6–8 April 2016; pp. 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, H.; Ren, H.; Xu, X.; Zhang, D.; Liu, G. Traffic dynamics on two-layer multiplex networks with limited queue resource. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2019, 33, 1950312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Qi, Z. Traffic dynamics on two-layer networks with community structure. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2021, 35, 2150272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; An, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, S. Traffic dynamics on homogeneous networks with community structure. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 2022, 33, 2250048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alweimine, A.O.B.; Bamaarouf, O.; Rachadi, A.; Ez-Zahraouy, H. Implementing beneficial prioritization of traffic flow in complex networks. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2018, 32, 1850273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.H.; Yang, H.J.; Pan, J.H. Efficient priority queueing routing strategy on networks of mobile agents. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 32, 1850137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, B.; Thurner, S. Search and topology aspects in transport on scale-free networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2005, 346, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andjelković, M.; Gupte, N.; Tadić, B. Hidden geometry of traffic jamming. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 91, 052817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, B. Dynamics of directed graphs: The world-wide Web. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2001, 293, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudo, S.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Sigarreta, J.M.; Vilaire, J.M. Gromov hyperbolic graphs. Discret. Math. 2013, 313, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, C. Hyperbolicity and chordality of a graph. Electron. J. Comb. 2011, 18, P43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krioukov, D.; Papadopoulos, F.; Kitsak, M.; Vahdat, A.; Boguñá, M. Hyperbolic geometry of complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 82, 036106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, O.; Saniee, I. Large-scale curvature of networks. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 84, 066108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nag Chowdhury, S.; Ray, A.; Dana, S.K.; Ghosh, D. Extreme events in dynamical systems and random walkers: A review. Phys. Rep. 2022, 966, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudo, S.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Rosario, O.; Sigarreta, J.M. Small values of the hyperbolicity constant in graphs. Discret. Math. 2016, 339, 3073–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, B.; Andjelković, M.; Melnik, R. Functional Geometry of Human Connectomes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, B.; Andjelković, M.; Boshkoska, B.M.; Levnajić, Z. Algebraic Topology of Multi-Brain Connectivity Networks Reveals Dissimilarity in Functional Patterns during Spoken Communications. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, R.; DasGupta, B.; Mobasheri, N. Topological implications of negative curvature for biological and social networks. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 89, 032811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani M, I.S. Materials inspired by mathematics. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2016, 17, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šuvakov, M.; Andjelković, M.; Tadić, B. Hidden geometries in networks arising from cooperative self-assembly. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, B. Self-organised criticality and emergent hyperbolic networks: Blueprint for complexity in social dynamics. Eur. J. Phys. 2019, 40, 024002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andjelković, M.; Tadić, B.; Maletić, S.; Rajković, M. Hierarchical sequencing of online social graphs. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2015, 436, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, W.S.; Saniee, I.; Narayan, O. On the hyperbolicity of large-scale networks and its estimation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Washington, DC, USA, 5–8 December 2016; pp. 3344–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballosa, W.; Pestana, D.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Sigarreta, J.M. Distortion of the hyperbolicity constant in minor graphs. Electron. Notes Discret. Math. 2014, 46, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, B. Modeling Traffic of Information Packets on Graphs with Complex Topology. In Computational Science—ICCS 2003, Proceedings of the International Conference Melbourne, Australia and St. Petersburg, Russia, 2–4 June 2003; Sloot, P.M.A., Abramson, D., Bogdanov, A.V., Dongarra, J.J., Zomaya, A.Y., Gorbachev, Y.E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Gao, J.; Wang, X. Multifractal analysis of sunspot time series: The effects of the 11-year cycle and Fourier truncation. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2009, 2009, P02066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šuvakov, M.; Mitrović, M.; Gligorijević, V.; Tadić, B. How the online social networks are used: Dialogues-based structure of MySpace. J. R. Soc. Interface 2012, 10, 20120819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijatović, S.; Graovac, S.; Spasojević, D.; Tadić, B. Tuneable hysteresis loop and multifractal oscillations of magnetisation in weakly disordered antiferromagnetic–ferromagnetic bilayers. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2022, 142, 115319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, A.; Anishchenko, V.S. Multifractal analysis of complex signals. Physics-Uspekhi 2007, 50, 819–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantelhardt, J.W.; Zschiegner, S.A.; Koscielny-Bunde, E.; Havlin, S.; Bunde, A.; Stanley, H. Multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis of nonstationary time series. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2002, 316, 87–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, B. Multifractal analysis of Barkhausen noise reveals the dynamic nature of criticality at hysteresis loop. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2016, 2016, 063305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Network | No. Triang | mod | D | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Webgraph | 3.439 | 0.175 | 192 | 3.196 | 0.497 | 9 | 2.0 |
| Statnet | 3.593 | 0.010 | 24 | 4.563 | 0.546 | 11 | 2.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tadić, B. Cyclical Trends of Network Load Fluctuations in Traffic Jamming. Dynamics 2022, 2, 449-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/dynamics2040026
Tadić B. Cyclical Trends of Network Load Fluctuations in Traffic Jamming. Dynamics. 2022; 2(4):449-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/dynamics2040026
Chicago/Turabian StyleTadić, Bosiljka. 2022. "Cyclical Trends of Network Load Fluctuations in Traffic Jamming" Dynamics 2, no. 4: 449-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/dynamics2040026
APA StyleTadić, B. (2022). Cyclical Trends of Network Load Fluctuations in Traffic Jamming. Dynamics, 2(4), 449-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/dynamics2040026