Interleukin-6: A Central Biomarker in Adult and Pediatric Cancer and Infectious Disease
Abstract
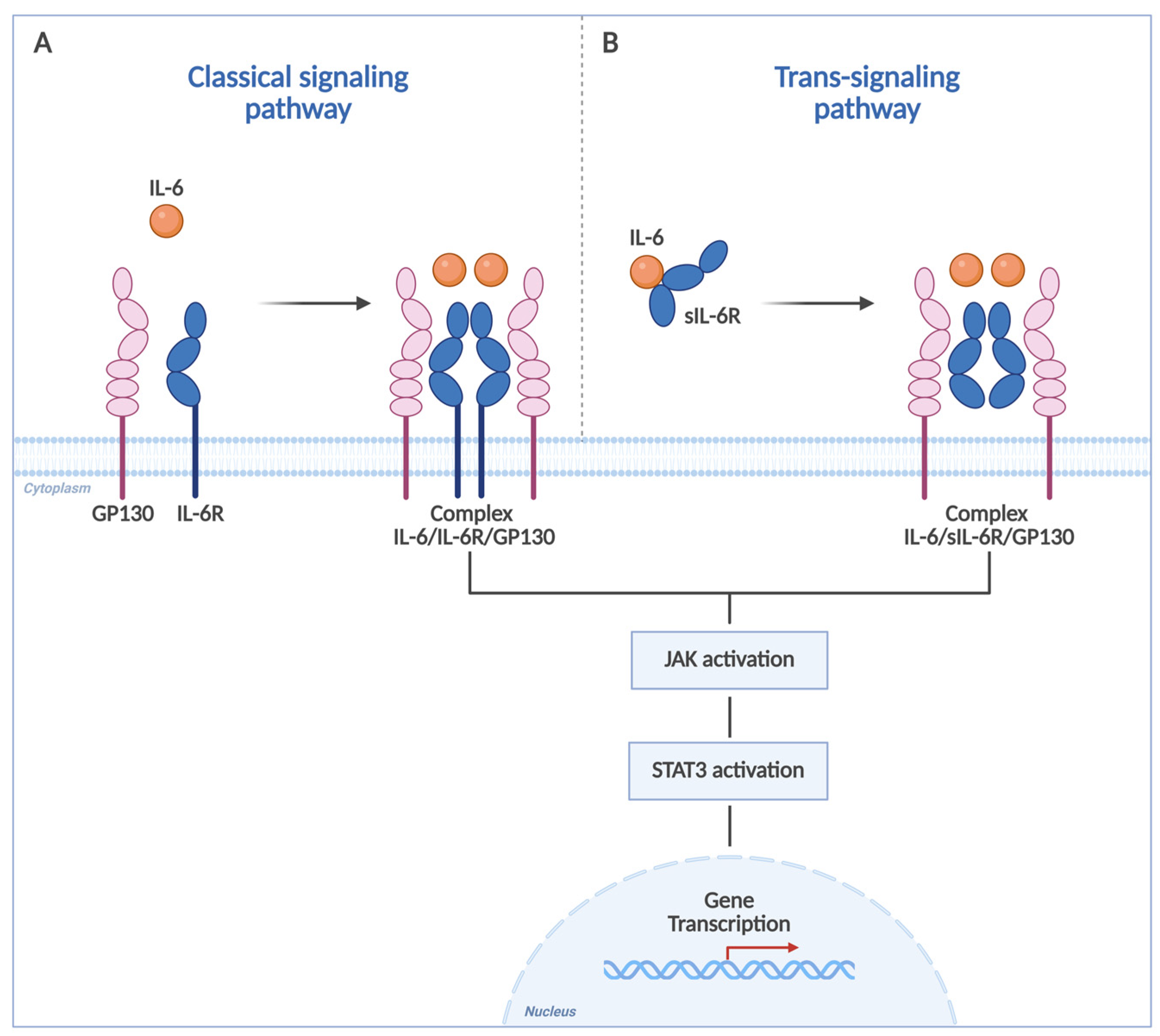
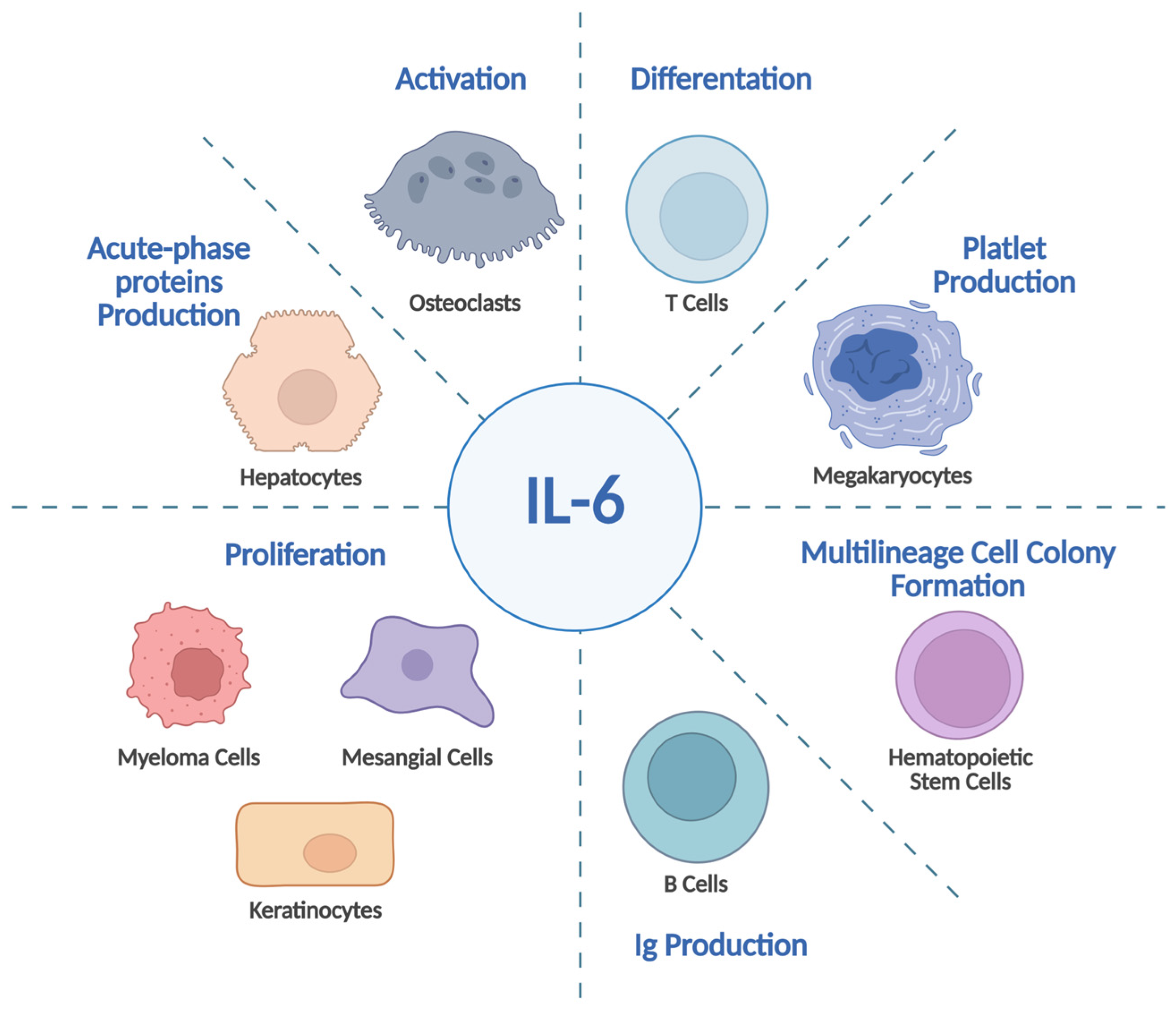
1. Introduction
2. IL-6 as a Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Cancer
| Cancer Type | Role of IL-6 | IL-6 Levels (pg/mL) | Assay Method | Clinical Implications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorectal cancer | Inflammation-driven progression | 0.7–68.0 pg/mL in patients (mean ~6.6 pg/mL); controls ~2.6 pg/mL; cutoff 6.3 pg/mL | ELISA | Poor prognosis; recurrence risk | [28] |
| Prostate cancer | STAT3 activation, chemoresistance | 36.7 ± 20.8 pg/mL (non-responders) vs. 10.8 ± 9.5 pg/mL (responders) | ELISA | Predictor of docetaxel resistance | [29] |
| Breast cancer | Tumor progression, EMT, immune evasion, therapy resistance | >25.3 pg/mL in metastatic disease; 5.6–39.8 pg/mL by stage; >15.5 pg/mL associated with higher metastasis risk | ELISA | Prognostic biomarker; predictor of metastasis; marker of treatment resistance | [30,31] |
| NSCLC | Tumor progression, immunotherapy resistance | 3.7 pg/mL (IQR 2.3–7.2) in patients vs. 2.1 pg/mL (IQR 1.4–3.8) in healthy controls | Electro- chemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLIA) | Prognostic and predictive biomarker for ICI response | [32] |
| Various solid and hematologic tumors | TME remodeling, immune suppression | Variable | ELISA/multiplex | Pan-cancer prognostic biomarker | [33,34,35] |
Challenges and Clinical Relevance of IL-6 as a Biomarker in Pediatric Cancers
3. IL-6 as a Biomarker for Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Infections
IL-6 as a Biomarker for Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Infections in Pediatric Oncologic Populations
4. IL-6 as a Potential Biomarker for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Viral Infections
IL-6 as a Potential Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Viral Infections in Pediatric Populations
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
5.1. Limitations and Clinical Challenges
5.2. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANC | Absolute Neutrophil Count |
| ADAM10 | A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase 10 |
| ADAM17 | A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase 17 |
| ALL | Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia |
| AML | Acute Myeloid Leukemia |
| ARDS | Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| B-ALL | B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia |
| CAR | Chimeric Antigen Receptor |
| CBA | Cytometric Bead Array |
| CD126 | Interleukin-6 Receptor α |
| CD130 | Glycoprotein 130 |
| CDK4/6 | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4 and 6 |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| CRS | Cytokine Release Syndrome |
| ECLIA | Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| EMT | Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition |
| EFS | Event-Free Survival |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FluA | Influenza A |
| GN | Gram-Negative |
| GP | Gram-Positive |
| HSCs | Hematopoietic Stem Cells |
| IL-1 | Interleukin-1 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-6R | Interleukin-6 Receptor |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| MDI | Microbiologically Proven Infection |
| mTOR | Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin |
| NSCLC | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer |
| PD-1 | Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed Death-Ligand 1 |
| PCT | Procalcitonin |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase |
| RAS | Rat Sarcoma Virus Oncogene |
| RIA | Radioimmunoassay |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| RR | Relative Risk |
| RSV | Respiratory Syncytial Virus |
| sIL-6R | Soluble Interleukin-6 Receptor |
| STAT3 | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 |
| TAMs | Tumor-Associated Macrophages |
| TME | Tumor Microenvironment |
| Tfh | T Follicular Helper Cells |
| Th17 | T Helper 17 Cells |
| Treg | Regulatory T Cells |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| JAK | Janus Kinase |
| AKT | Protein Kinase B |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
References
- Hirano, T.; Yasukawa, K.; Harada, H.; Taga, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Matsuda, T.; Kashiwamura, S.; Nakajima, K.; Koyama, K.; Iwamatsu, A. Complementary DNA for a novel human interleukin (BSF-2) that induces B lymphocytes to produce immunoglobulin. Nature 1986, 324, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, T. Interleukin-6: Discovery of a pleiotropic cytokine. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grebenciucova, E.; VanHaerents, S. Interleukin 6: At the interface of human health and disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1255533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. Targeting Interleukin-6 Signaling in Clinic. Immunity 2019, 50, 1007–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J.; Elson, G.; Jones, S.A. Interleukin-6 biology is coordinated by membrane-bound and soluble receptors: Role in inflammation and cancer. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 80, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. Endosomes as Signaling Platforms for IL-6 Family Cytokine Receptors. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 688314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose-John, S.; Jenkins, B.J.; Garbers, C.; Moll, J.M.; Scheller, J. Targeting IL-6 trans-signalling: Past, present and future prospects. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose-John, S. IL-6 trans-signaling via the soluble IL-6 receptor: Importance for the pro-inflammatory activities of IL-6. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ara, T.; Declerck, Y.A. Interleukin-6 in bone metastasis and cancer progression. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S. IL-6-regulated transcription factors. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 29, 1401–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuya, W.L.; Cao, Y.; Ho, P.C.; Wong, A.L.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J.; Nicot, C.; Goh, B.C. Insights into IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signaling in the tumor microenvironment: Implications for cancer therapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2025, 85, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, C.A.; Jones, S.A. IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Haan, S.; Hermanns, H.M.; Müller-Newen, G.; Schaper, F. Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem. J. 2003, 374, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Wei, W.; Zeng, F.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Cai, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, H. IL-6 Up-Regulates Expression of LIM-Domain Only Protein 4 in Psoriatic Keratinocytes through Activation of the MEK/ERK/NF-κB Pathway. Am. J. Pathol. 2024, 194, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, T.; Yao, F.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Zhu, X.; Yao, Y. Megakaryocyte in sepsis: The trinity of coagulation, inflammation and immunity. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.; Thatavarty, A.; King, K.Y. Forged in the fire: Lasting impacts of inflammation on hematopoietic progenitors. Exp. Hematol. 2024, 134, 104215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, L.; Shi, W.; Xu, K.; Shen, Y.; Dai, B. Oxidative stress and inflammation: Roles in osteoporosis. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1611932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korn, T.; Mitsdoerffer, M.; Croxford, A.L.; Awasthi, A.; Dardalhon, V.A.; Galileos, G.; Vollmar, P.; Stritesky, G.L.; Kaplan, M.H.; Waisman, A.; et al. IL-6 controls Th17 immunity in vivo by inhibiting the conversion of conventional T cells into Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18460–18465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, T.P.; Wiemels, J.L.; Zhou, M.; Kang, A.Y.; McCoy, L.S.; Wang, R.; Fitch, B.; Petrick, L.M.; Yano, Y.; Imani, P.; et al. Cytokine Levels at Birth in Children Who Developed Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2021, 30, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, A.M.; Miller, J.M.; Munoz, J.O.; Gaikwad, A.S.; Redell, M.S. Interleukin-6 levels predict event-free survival in pediatric AML and suggest a mechanism of chemotherapy resistance. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Song, X.; Yuan, M.; Li, Y. The Diverse Function of IL-6 in Biological Processes and the Advancement of Cancer. Immune Netw. 2025, 25, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.H.; Ahmed, A.T.; Al Abdulmonem, W.; Bokov, D.O.; Shafie, A.; Al-Hetty, H.R.A.K.; Hsu, C.Y.; Alissa, M.; Nazir, S.; Jamali, M.C.; et al. Interleukin-6 serves as a critical factor in various cancer progression and therapy. Med. Oncol. 2024, 41, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Shao, Y.; Gu, W. Role of interleukin-6 in resistance to tumor therapy. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhou, X.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J. CAA-derived IL-6 promoted the PD-L1 expression of breast cancer via STAT3/miR-497a-5p signaling. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 151, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopresti, L.; Tatangelo, V.; Baldari, C.T.; Patrussi, L. Rewiring the T cell-suppressive cytokine landscape of the tumor microenvironment: A new frontier for precision anti-cancer therapy. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1418527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Wei, L.; Ruan, G.; Zhang, H.; Shi, H. Interleukin-6 as a Pan-Cancer Prognostic Inflammatory Biomarker: A Population-Based Study and Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2025, 18, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiga, K.; Hara, M.; Nagasaki, T.; Sato, T.; Takahashi, H.; Sato, M.; Takeyama, H. Preoperative Serum Interleukin-6 Is a Potential Prognostic Factor for Colorectal Cancer, including Stage II Patients. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2016, 2016, 9701574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo-Domenech, J.; Oliva, C.; Rovira, A.; Codony-Servat, J.; Bosch, M.; Filella, X.; Montagut, C.; Tapia, M.; Campás, C.; Dang, L.; et al. Interleukin 6, a nuclear factor-kappaB target, predicts resistance to docetaxel in hormone-independent prostate cancer and nuclear factor-kappaB inhibition by PS-1145 enhances docetaxel antitumor activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5578–5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhiatma, D.; Ali, I.; Ghoib, H. Interleukin-6 serum levels in metastatic breast cancer and non-metastatic breast cancer. Int. J. Health Sci. 2022, 6, 3512–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettner, N.M.; Bui, T.N.; Navarro-Yepes, J.; Ghotbaldini, S.; Quintela, B.; Luo, C.K.; Lam, N.; Rao, X.; Raghavendra, A.S.; Wang, Y.; et al. IL-6 predicts CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance, identifying STAT3 as a target in HR + /HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2025, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pine, S.R.; Mechanic, L.E.; Enewold, L.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Katki, H.A.; Zheng, Y.L.; Bowman, E.D.; Engels, E.A.; Caporaso, N.E.; Harris, C.C. Increased levels of circulating interleukin 6, interleukin 8, C-reactive protein, and risk of lung cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Jin, T.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; He, F.; Hu, J.; Yang, K. Association between IL-6 and prognosis of gastric cancer: A retrospective study. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2023, 16, 17562848231211543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, S.U.; Pickl, C.; Haas, M.; Kasparbauer, F.; Rinderknecht, E.; Kälble, S.; van Rhijn, B.W.G.; Siska, P.J.; Decking, S.M.; Renner, K.; et al. Prognostic Role of Serum IL-6 Levels in Bladder Cancer Patients and Hints of its Origin. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2025, 23, 102378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, K.H.; Jung, H.W.; Jeong, E.O.; Lee, H.J.; Kwon, J.; Kwon, H.J.; Choi, S.W.; Koh, H.S.; Kim, S.H. Elevated Serum IL-6 as a Negative Prognostic Biomarker in Glioblastoma: Integrating Bioinformatics and Clinical Validation. J. Cancer 2025, 16, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, P.S.Y.; Chng, W.J.; de Mel, S. STAT3: A Promising Therapeutic Target in Multiple Myeloma. Cancers 2019, 11, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knüpfer, H.; Preiss, R. Serum interleukin-6 levels in colorectal cancer patients—A summary of published results. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2010, 25, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Tsunedomi, R.; Nakajima, M.; Suzuki, N.; Yoshida, S.; Tomochika, S.; Xu, M.; Nakagami, Y.; Matsui, H.; Tokumitsu, Y.; et al. IL-6 Levels Correlate with Prognosis and Immunosuppressive Stromal Cells in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 30, 5267–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, E.; Shi, Q.; Shields, A.F.; Nixon, A.B.; Shergill, A.P.; Ma, C.; Guthrie, K.A.; Couture, F.; Kuebler, P.; Kumar, P.; et al. Association of Inflammatory Biomarkers With Survival Among Patients With Stage III Colon Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennel, K.A.F.; Kurniawan, A.; Samir Foad Al-Badran, S.; Schubert Santana, L.; Quinn, J.; Nixon, C.; Hatthakarnkul, P.; Maka, N.; Roxburgh, C.; McMillan, D.; et al. IL6 and IL6R as Prognostic Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, M.; Abbaszadeh, S.; Rashidi, M.; Amini, N.; Talebi Anaraki, K.; Motahhary, M.; Khalilipouya, E.; Harif Nashtifani, A.; Shafiei, S.; Ramezani Farani, M.; et al. STAT3 as a newly emerging target in colorectal cancer therapy: Tumorigenesis, therapy response, and pharmacological/nanoplatform strategies. Environ. Res. 2023, 233, 116458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, W.; Wu, K.; Long, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhong, C.; Wang, S.; Lai, H.; Guo, Y.; Lv, D.; Lu, J.; et al. Gut dysbiosis promotes prostate cancer progression and docetaxel resistance via activating NF-κB-IL6-STAT3 axis. Microbiome 2022, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Cruz-Vargas, J.A.; Gómez, H.; Talavera, J.E.; Gonzales-Rospigliosi, C.; Córdova Salazar, A.A.; Pichardo-Rodriguez, R. Prognostic Relevance of Inflammatory Cytokines Il-6 and TNF-Alpha in Patients with Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.Z.; Al Fikky, A.; Abdel Bar, I.; Attia, O. Serum IL-6 and IL-12 levels in breast cancer patients. Egypt. J. Immunol. 2004, 11, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Ravishankaran, P.; Karunanithi, R. Clinical significance of preoperative serum interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein level in breast cancer patients. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, O.I.; Adel, A.M.; Diab, D.R.; Gobran, N.S. Prognostic value of serum level of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 in metastatic breast cancer patients. Egypt. J. Immunol. 2006, 13, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Benoy, I.; Salgado, R.; Colpaert, C.; Weytjens, R.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Dirix, L.Y. Serum interleukin 6, plasma VEGF, serum VEGF, and VEGF platelet load in breast cancer patients. Clin. Breast Cancer 2002, 2, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Differences of Interleukin-6 Serum Levels in Lung Cancer Patients and Healthy Individuals in Medan. J. Respirol. Indones. 2021, 41, 28–32. [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.H.; Park, C.K.; Chung, C.; Oh, I.J.; Kim, Y.C.; Park, D.; Kim, J.; Kwon, G.C.; Kwon, I.; Sun, P.; et al. Baseline Serum Interleukin-6 Levels Predict the Response of Patients with Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer to PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors. Immune Netw. 2020, 20, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, H.; Chu, T.; Zhong, R.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; Han, B. Prognostic role of serum cytokines level in non-small cell lung cancer patients with anti-PD-1 and chemotherapy combined treatment. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1430301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Shaibu, Z.; Xu, A.; Yang, F.; Cao, R.; Yang, F. Predictive value of serum cytokines in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer receiving anti-PD-1 blockade therapy: A meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2025, 25, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Z.; Lu, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Lin, C.; Tang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Han, R.; et al. Ibrutinib reverses IL-6-induced osimertinib resistance through inhibition of Laminin α5/FAK signaling. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, H.; Sato, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Okuda, Y.; Takeda, M.; Akamine, Y.; Nakayama, K.; Miura, M. Influence of interleukin-6 on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of osimertinib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2025, 95, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pektaş, G.; Gönül, E.; Öncü, Ş.; Becit Kızılkaya, M.; Sadi, G.; Pektaş, M.B. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Investigation of Survival and Prognostic Factors with Drug-Related Remission. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; Zheng, X.; Cai, D.; You, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Liao, X.; Tan, M.; Lin, L.; Wang, J.; et al. Interleukin-6 Facilitates Acute Myeloid Leukemia Chemoresistance via Mitofusin 1-Mediated Mitochondrial Fusion. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2023, 21, 1366–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchia, D.; Bîcă, O.D.; Sârbu, I.; Savu, B.; Farcaș, D.; Miron, I.; Postolache, A.L.; Cojocaru, E.; Abbo, O.; Ciongradi, C.I. Targeting Pathways in Neuroblastoma: Advances in Treatment Strategies and Clinical Outcomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Liu, W.; Sun, Q.; Shi, Y. Predictive and prognostic value of inflammatory factors (IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α) in saliva for radiotherapy response in patients with HPV-associated oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egler, R.A.; Burlingame, S.M.; Nuchtern, J.G.; Russell, H.V. Interleukin-6 and soluble interleukin-6 receptor levels as markers of disease extent and prognosis in neuroblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 7028–7034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinecke, J.B.; Jimenez Garcia, L.; Saraf, A.J.; Hinckley, J.; Gross, A.C.; Le Pommellet, H.; Gutpell, K.M.; Cam, M.; Cannon, M.V.; Gust, M.J.; et al. Metastasis-Initiating Osteosarcoma Subpopulations Establish Paracrine Interactions with Lung and Tumor Cells to Create a Metastatic Niche. Cancer Res. 2025; advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Guerrero, S.S.; Ramírez-Pacheco, A.; Rocha-Ramírez, L.M.; Hernández-Pliego, G.; Eguía-Aguilar, P.; Escobar-Sánchez, M.A.; Reyes-López, A.; Juárez-Villegas, L.E.; Sienra-Monge, J.J.L. Association of Genetic Polymorphisms and Serum Levels of IL-6 and IL-8 with the Prognosis in Children with Neuroblastoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, E.C.; Singh, A.; Harden, A.M.; Soanes, K.; Habash, H.; Toracchio, L.; Carrabotta, M.; Schreck, C.; Shah, K.M.; Riestra, P.V.; et al. Targeting metastasis in paediatric bone sarcomas. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.N.; Fry, T.J. Mechanisms of resistance to CAR T cell therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadauke, S.; Myers, R.M.; Li, Y.; Aplenc, R.; Baniewicz, D.; Barrett, D.M.; Barz Leahy, A.; Callahan, C.; Dolan, J.G.; Fitzgerald, J.C.; et al. Risk-Adapted Preemptive Tocilizumab to Prevent Severe Cytokine Release Syndrome After CTL019 for Pediatric B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Prospective Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.Y.; Nam, E.; Shih, R.M.; Shafer, A.; Bouren, A.; Ayala Ceja, M.; Harris, C.; Khericha, M.; Vo, K.H.; Kim, M.; et al. Self-regulating CAR-T cells modulate cytokine release syndrome in adoptive T-cell therapy. J. Exp. Med. 2024, 221, e20221988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.J.; Zhang, H.L.; Chen, F.; Guo, X.J.; Liu, Q.G.; Hou, J. The double-edged effects of IL-6 in liver regeneration, aging, iflammation, and diseases. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, A.; Evans, L.E.; Alhazzani, W.; Levy, M.M.; Antonelli, M.; Ferrer, R.; Kumar, A.; Sevransky, J.E.; Sprung, C.L.; Nunnally, M.E.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 304–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, Q.; Wu, Q.; Lu, H.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, X.; et al. IL-6 and IL-10 Closely Correlate with Bacterial Bloodstream Infection. Iran. J. Immunol. 2020, 17, 185–203. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zeng, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Q.; Bai, T.; Xu, Y. PCT, IL-6, and IL-10 facilitate early diagnosis and pathogen classifications in bloodstream infection. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2023, 22, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bal, W.; Piasecka, Z.; Szuler, K.; Chaber, R. Infection Biomarkers in Children with Chemotherapy-Induced Severe Neutropenia. Cancers 2025, 17, 2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soker, M.; Colpan, L.; Ece, A.; Devecioğlu, C.; Haspolat, K. Serum levels of IL-1 beta, sIL-2R, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-alpha in febrile children with cancer and neutropenia. Med. Oncol. 2001, 18, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.J.; Luo, Z.B.; Xia, T.; Song, H.; Yang, S.L.; Xu, W.Q.; Ni, Y.R.; Zhao, N.; Tang, Y.M. Comparison of interleukin-6, interleukin-10, procalcitonin and C-reactive protein in identifying high-risk febrile illness in pediatric cancer patients: A prospective observational study. Cytokine 2019, 116, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Kini, P.G.; Bhat, Y.R.; Aroor, S. Interleukin 6 versus C reactive Protein as Markers for Early Detection of Bacteremia in Febrile Neutropenia in Pediatric Population. Indian J. Med. Paediatr. Oncol. 2021, 41, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nair, H. Trends in the global burden of lower respiratory infections: The knowns and the unknowns. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1523–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkhoo, B.; Mohammadi, M.; Hasani, S.; Sigari, N.; Borhani, A.; Ramezani, C.; Charajoo, A.; Badri, S.; Rostami, F.; Etemadi, M.; et al. Elevated interleukin (IL)-6 as a predictor of disease severity among COVID-19 patients: A prospective cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iftimie, S.; Gabaldó-Barrios, X.; Penadés-Nadal, J.; Canela-Capdevila, M.; Piñana, R.; Jiménez-Franco, A.; López-Azcona, A.F.; Castañé, H.; Cárcel, M.; Camps, J.; et al. Serum Levels of Arachidonic Acid, Interleukin-6, and C-Reactive Protein as Potential Indicators of Pulmonary Viral Infections: Comparative Analysis of Influenza A, Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection, and COVID-19. Viruses 2024, 16, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Mani, R.S.; Philip, M.; Adhikary, R.; Joshi, S.; Revadi, S.S.; Buggi, S.; Desai, A.; Vasanthapuram, R. Proinflammatory chemokines are major mediators of exuberant immune response associated with Influenza A (H1N1) pdm09 virus infection. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagarasu, K.; Kaushal, H.; Shinde, P.; Kakade, M.; Chaudhary, U.; Padbidri, V.; Sangle, S.A.; Salvi, S.; Bavdekar, A.R.; D’costa, P.; et al. TNFA and IL10 Polymorphisms and IL-6 and IL-10 Levels Influence Disease Severity in Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 Virus Infected Patients. Genes 2021, 12, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, B.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Teng, Z.; Shao, J.; Shen, J.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, Z.; et al. Intensive cytokine induction in pandemic H1N1 influenza virus infection accompanied by robust production of IL-10 and IL-6. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaretti, A.; Pulitanò, S.; Barone, G.; Ferrara, P.; Romano, V.; Capozzi, D.; Riccardi, R. IL-1 β and IL-6 upregulation in children with H1N1 influenza virus infection. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 495848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Chen, M.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Sun, R.; Jia, W.; Fu, S.; Cui, J.; Song, C. Clinical characteristics of severe influenza as a risk factor for febrile seizures in children: A retrospective analysis. Front. Pediatr. 2024, 12, 1418499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Morozumi, M.; Ubukata, K.; Takahashi, T.; Inamo, Y. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum complicating pneumonia in children infected with the 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) virus. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhung, M.A.; Swerdlow, D.; Olsen, S.J.; Jernigan, D.; Biggerstaff, M.; Kamimoto, L.; Kniss, K.; Reed, C.; Fry, A.; Brammer, L.; et al. Epidemiology of 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, S13–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Rubio, G.; Ponce-Gallegos, M.A.; Domínguez-Mazzocco, B.A.; Ponce-Gallegos, J.; García-Ramírez, R.A.; Falfán-Valencia, R. Role of the Host Genetic Susceptibility to 2009 Pandemic Influenza A H1N1. Viruses 2021, 13, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.J.; Xu, S.S.; Li, X.J.; Liu, J.L.; Wu, X.L.; Xu, X.F. Low birth weight contributed to increased serum IL-6 levels in infantile respiratory syncytial virus infection. BMC Pediatr. 2017, 17, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Pediatric Cancer | Role of IL-6 | IL-6 Levels (pg/mL) | Assay Method | Clinical Implications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neuroblastoma | Marker of high-risk disease and poor prognosis | Peripheral blood: High-risk: ~23.9; low/intermediate: ~4.3; controls: ~3.3 Bone marrow: High-risk: ~15 pg/mL, undetectable in low/intermediate | ELISA | Prognostic marker of high-risk disease | [58] |
| Osteosarcoma | Tumor progression and metastasis | Elevated vs. controls | ELISA | Associated with lung metastasis and poor survival | [59] |
| Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) | Modulates immune signaling; context-dependent | Variable (neonatal samples) | Multiplex immunoassay | Potential early-life biomarker; may indicate increased ALL risk | [20] |
| Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) | Microenvironment-mediated chemoresistance | Elevated at diagnosis in poor EFS | Multiplex bead-based assay | Prognostic marker; relapse risk | [21] |
| Patient Group | Clinical Context | Role of IL-6 | IL-6 Levels (pg/mL) | Clinical Implications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult patients | Bloodstream infection (BSI) | Marker of systemic inflammation and septic shock | <534.7 excludes septic shock; >1000 associated with septic shock and mortality | Risk stratification and early identification of septic shock | [67] |
| Bloodstream infection (BSI) | Differentiation between Gram-negative (GN) and Gram-positive infections (GP) | GN-BSI: 4–31-fold higher than GP-BSI | May guide early pathogen-oriented antimicrobial therapy | [67] | |
| Bloodstream infection (BSI) | Discrimination between Gram-negative and Gram-positive infections | GN-BSI: median 397.4 (IQR 125.1–1447.0); GP-BSI: 172.4 (IQR 84.81–216.1) | Diagnostic aid for Gram-negative infection and severity assessment | [68] | |
| Pediatric cancer patients | Febrile neutropenia | Early marker of Gram-negative infection | Gram-negative bacteremia: median 166 (21–1780); Gram-positive bacteremia: 26 (16–33) | Early identification of fever infectious vs. non-infectious febrile episodes | [70] |
| Febrile neutropenia | Predictor of Gram-negative bacteremia | GN infection: median 169 (IQR 124–2600); sterile: 52; Gram-positive infection: 17.5 | Guides early escalation of antimicrobial therapy | [72] | |
| Febrile neutropenia | Independent predictor of Gram-negative bacteremia | ≥185 predictive of GN-BSI (AUC 0.77) | Risk stratification and early clinical decision-making | [71] |
| Infection Context | Role of IL-6 | IL-6 Levels | Clinical Implications | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viral infections (Influenza A, RSV, COVID-19) in adults | Reflects systemic inflammation and immune activation. | Elevated level of IL-6 in all viral infections (AUC > 0.85); Elevated levels of IL-6 in FluA non-survivors (AUC = 0.80) compared to FluA survivors. | Diagnostic biomarker to identify viral infections; elevated levels associated with worse outcomes, complications, prolonged hospitalization and higher risk of mortality. | [75] |
| Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 infection in adults | Indicator of hyperinflammatory response and predictor of mortality and disease severity. | Higher levels of IL-6 in early stage of lethal cases (mean ± SE, 812 pg/mL ± 451.3, p < 0.001) and in surviving critically ill patients (mean ± SE, 112.6 pg/mL ± 53, p < 0.05) compared to healthy individuals (mean ± SE, 5.039 pg/mL ± 1.69) and non-severe recovered cases (mean ± SE, 6.11 pg/mL ± 3.57). | Predictive biomarker for identifying patients at higher risk of fatal outcomes. | [77] |
| H1N1 influenza in children | IL-6 contributes to airway inflammation, respiratory dysfunction and disease severity. | Significantly elevated IL-6 levels (108.1 ± 22.8 pg/mL) in H1N1-infected children. | Biomarker for early detection of severe airway inflammation in pediatric H1N1 infection. | [79] |
| Severe influenza with febrile seizures in children | Serves as a risk factor for febrile seizures, reflecting systemic and neuronal inflammation. | IL-6 ≥ 9.84 pg/mL associated with higher risk of developing febrile seizures. | IL-6 levels can help identify children at risk of febrile convulsions, guiding early clinical monitoring and treatment optimization. | [80] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Benedetto, G.D.; Sorice, C.; Cantiello, I.; Savarese, M.; Leone, O.; Capozza, M.A.; Alfieri, M. Interleukin-6: A Central Biomarker in Adult and Pediatric Cancer and Infectious Disease. Biologics 2026, 6, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics6010005
Benedetto GD, Sorice C, Cantiello I, Savarese M, Leone O, Capozza MA, Alfieri M. Interleukin-6: A Central Biomarker in Adult and Pediatric Cancer and Infectious Disease. Biologics. 2026; 6(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics6010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenedetto, Giorgia Di, Carmen Sorice, Immacolata Cantiello, Maria Savarese, Ornella Leone, Michele Antonio Capozza, and Mariaevelina Alfieri. 2026. "Interleukin-6: A Central Biomarker in Adult and Pediatric Cancer and Infectious Disease" Biologics 6, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics6010005
APA StyleBenedetto, G. D., Sorice, C., Cantiello, I., Savarese, M., Leone, O., Capozza, M. A., & Alfieri, M. (2026). Interleukin-6: A Central Biomarker in Adult and Pediatric Cancer and Infectious Disease. Biologics, 6(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics6010005






