Abstract
Background: Gene fusions occur when two independent genes form a hybrid gene through genomic rearrangements, which often leads to abnormal expression and function of an encoded protein. In hematological and solid cancers, oncogenic fusions may be prognostic, diagnostic, or therapeutic biomarkers. Improved detection and understanding of the functional implications of such fusions may be beneficial for patient care. Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of our internal genomic database to identify known and novel gene fusions in different solid tumors seen in our community cancer center. We then investigated the clinical implications of the fusions we identified. Results: We identified 420 known oncogenic fusions and 25 unclassified gene fusions across twenty-six different cancer types. Of 420 fusion-positive tumors with known fusions, there were 366 unique gene fusions. Conclusions: About 10% of tumors investigated had oncogenic fusions, which supports the notion that comprehensive molecular profiling, including RNA sequencing, should be provided for patients with advanced cancers.
1. Introduction
Precision medicine programs seek to develop more targeted treatments with greater effectiveness and less toxicity to patients. Gene fusions occur when two independent genes form a hybrid gene through genomic rearrangements, which often leads to abnormal expression and function of their produced proteins. This is caused by genomic rearrangements including deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocation events []. Gene fusions may be identified in solid tumors or hematological malignancies and are therapeutic targets of interest. The most common genetic alteration in prostate cancer is the TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion, and about 90% of all lymphomas and over half of all leukemias have translocation-induced gene fusions. The expression of gene fusions also predicts cancer recurrence after surgery for some localized cancers as well as resistance or responsiveness to therapies [,]. Gene fusions affect many aspects of cancer cell biology, including self-renewal and differentiation as well as tumorigenicity []. Drugs targeting the oncogenic gain of function fusions have been proven to be effective in the case of NTRK1, NTRK2, NTRK3, ALK, RET, and FGFR fusions [,]. Gene fusions in oncogenes such as RAF, ALK, and FGFR have been reported in different epithelial tumors, and some tumor-specific gene fusions are defined as therapeutic, diagnostic, or prognostic biomarkers []. Thus, detecting gene fusion events and a better understanding of the potential oncogenic fusions are vital to the goal of precision medicine in developing drugs with higher efficacy. In addition to BRAF and EGFR mutations, ROS1 and ALK fusions have been reported in non-small cell lung cancers. ALK-EML4 fusions have been reported in 2–7% of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer []. ALK inhibitors are approved to treat these patients: crizotinib was the first approved targeted therapy, whereas lorlatinib, alectinib, brigatinib, ceritinib, and alectinib are the next generation of ALK inhibitors, and there are ongoing clinical trials to target these fusions and overcome resistance.
As mentioned, the molecular mechanisms of gene fusions include the following possible rearrangements: translocations, insertions, deletions, tandem duplications, or inversions []. Translocations are caused by exchanges of DNA sequences without the addition or subtraction of genetic information between two different chromosomes (balanced translocation), or a similar exchange where there is extra or missing genetic information (unbalanced translocation). Insertions are rearrangements caused by movement of DNA fragments from one region to another, either within the same chromosome (intrachromosomal insertion) or from one to another (nonreciprocal translocation). Deletions result in the fusion of two genes when regions between them are deleted. Tandem duplications are caused by the duplication of a genomic region, which results in a fusion with a gene within the original region. Last, inversions arise when chromosomal segments flip, resulting in the tail-to-tail or head-to-head fusion of genes.
Gene fusions can influence the biology of tumors through various mechanisms, including overexpression through promoter exchange or linking open reading frames to transcriptional control elements, such as in TMPRSS2 fusions, which we observed in our cohort in patients with prostate cancer. Other fusions can cause truncations, resulting in the loss of regulatory microRNA binding sites, which leads to the overexpression of its regulated proteins, as is the case in NFIB-MYB or FGFR3-TACC3 fusions, which we also observed in our cohort. Yet, a third mechanism by which gene fusions affect biological function is the interruption of intrinsic control mechanisms, which leads to the constitutive activation of proteins and downstream signaling pathways, such as in BCR-ABL1 (Supplemental Table S1) [].
Fusions in three tropomyosin receptor kinases (TRK) have been identified in different tumor types in pediatric and adult-onset tumors. Fusions in NTRK genes lead to TRK activation and oncogenic transformation. Previous studies have evaluated the safety and efficacy of loratrectenib, a selective TRK inhibitor, in fusion-positive tumors. The overall response rate was 75% (95% confidence interval, 61 to 85) []. A basket trial also showed the efficacy of treating all tumor types with NTRK fusions with larotrectinib []. Larotrectenib was approved by the FDA in November 2018 for all solid tumors harboring one NTRK gene fusion regardless of their tumor type. Entrectinib is another TRK inhibitor targeting NTRK gene fusions that has the capacity to penetrate the blood–brain barrier. The authors reported that 57% of patients showed an objective response (95% CI 43.2–70.8) []. Entrectinib was approved in August 2019 for pediatric and adult patients with NTRK gene fusions. The FDA also approved entrectinib for adult patients with tumors who harbor ROS1 fusions with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer.
Selpercatinib is a small-molecule RET kinase inhibitor that was approved in September 2022 for adult patients with metastatic solid tumors whose tumors harbor RET fusions. Selpercatinib showed durable activity in patients with non-small lung cancer and an RET fusion with a 90% objective response rate among 39 patients (95% CI 75.8–97.1) []. In addition, patients with medullary thyroid cancer and RET mutations had a 62% objective response rate []. BCR-ABL fusions are present in more than 90% of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) []. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are the main therapy options for patients with CML, including imatinib, nilotinib, dasatinib, ponatinib, and bosutinib [].
Advancements in sequencing technologies have made it easier to detect structural anomalies in relevant cancer genes and for physicians to prescribe specific therapies to treat them []. An accompanied continuous development of centralized, open-access bioinformatic resources has also augmented the conduct of cancer research by allowing for the exploration, analysis, and visualization of cancer genomic datasets with relative ease [,]. For example, the cBio Cancer Genomics Portal provides large-scale clinical data and molecular profiles of patients in a user-friendly interface to support cancer researchers in managing the overwhelming influx of genomic data. In recent years, concerted efforts have also been made to facilitate the sharing of genomic and clinical data, such as the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) GENIE (Genomics, Evidence, Neoplasia, Information Exchange) project [], to accelerate the mission of precision oncology by encouraging cross-institutional collaboration. Since its initial release, Project GENIE has released clinical and genomic data from over 100,000 patients, promoting the dissemination of information that has impacted cancer patients’ treatment [].
Despite some movement toward centralization, most patients still primarily receive healthcare through community health centers, so community cancer centers maintain a crucial role in advancing precision oncology []. Herein, we retrospectively examine the prevalence of gene fusions reported in solid tumors in our internal genomics database and correlate fusion events with instances of tumor diagnoses to better understand the relationship between gene fusions and associated pathologies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Next-Generation Sequencing and Database Development
Our community cancer center in Orange County, CA provides care for a diverse population of patients and has built a private internal instance of the cBioPortal for Cancer Genomics database, made possible through a collaboration with a biomedical informatics company (The Hyve, The Netherlands), which facilitates rapid exploration of our patients’ DNA and RNA sequencing profiles. This includes data from whole-exome and transcriptome sequencing, which allows for the unbiased discovery of actionable gene alterations, such as gene fusion events [].
The present study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, the Belmont Report, and US Common Rule. In compliance with policy 45 CFR 46.101(b), this study was conducted using retrospective, de-identified clinical data, and patient consent was not required. We retrospectively analyzed our cBioPortal database for gene fusions identified by DNA and RNA next-generation sequencing (NGS) of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue samples derived from solid tumors through a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) and College of American Pathologists (CAP) commercial lab (Caris Life Sciences, Phoenix, AZ, USA) from 2016 to 2022. As described before [], for RNA sequencing, an RNA-based targeted capture panel of 52 genes with the ability to detect fusions and three variant transcripts was used until 2019, after which whole transcriptome sequencing was performed. FFPE specimens were closely reviewed by a pathologist to confirm the tumor size and content. The lab required a minimum of 20% tumor content to enable the extraction of tumor-specific RNA. A Qiagen RNA FFPE—a tissue extraction kit—was used for extraction, and the RNA quality and quantity were determined using the Agilent TapeStation. Additional biomarkers were evaluated using a DNA-based next-generation sequencing panel of 592 genes, including tumor mutational burden (TMB) and microsatellite instability (MSI), with a transition to whole-exome sequencing after 2019. Prior to molecular testing, tumor enrichment was achieved by harvesting targeted tissue using manual microdissection techniques.
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
In addition, again as before [], PD-L1 protein expression was evaluated by immunohistochemistry (IHC). IHC was performed on full formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) sections of glass slides. Slides were stained using the Agilent DAKO Link 48 (Santa Clara, CA, USA) automated platform and staining techniques, per the manufacturer’s instructions, and were optimized and validated per CLIA/CAP and ISO requirements. Staining was scored for intensity (0 = no staining; 1+ = weak staining; 2+ = moderate staining; 3+ = strong staining) and staining percentage (0–100%). PD-L1 antibody (SP142 or 28-8 clones) staining results were categorized as positive (≥1+ and ≥1% tumor cells) or negative (0 or 0%).
Tumor Mutational Burden (TMB) was measured by counting all non-synonymous missense, nonsense, in-frame insertion/deletion, and frameshift mutations found per tumor that had not been previously described as germline alterations in dbSNP151, Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD) databases, or benign variants identified by Caris’s geneticists.
2.3. Data Analysis and Curation
Raw data were demultiplexed using the Illumina DRAGEN FFPE accelerator. FASTQ files were aligned with STAR aligner (Alex Dobin, release 2.7.4a GitHub). A full 22,948-gene dataset of expression data was produced by Salmon, as previously described [,]. Unclassified gene fusions refer to those not previously reported during the literature review, due to the lack of standardized classification guidelines. Tumor samples were queried for the presence of gene fusions, from which we divided the identified fusion-positive samples into two groups based on the presence or absence of annotations on a precision oncology knowledge base, OncoKB []: (1) known oncogenic fusions and (2) unclassified gene fusions, respectively. Annotations are based on biological consequences and clinical implications, including Diagnostic, Prognostic, Therapeutic, and Resistance to Treatment. Known oncogenic fusions were verified by cross-referencing to an NCI-supported database of chromosome aberrations and gene fusions in cancer [].
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Gene Fusion Events across Cancer Types
We retrospectively analyzed 4415 tumor samples from which we identified 420 known oncogenic fusions (Supplemental Table S1). Twenty-six different cancer types had reported oncogenic fusions, which occurred most often in ovarian adenocarcinoma (N = 62/420; 14.8%), followed by non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (N = 55/420; 13.1%), prostate cancer (N = 48/420; 11.4%), breast cancer (N = 46/420; 10.9%), glioblastoma (N = 35/420; 8.3%), and colorectal cancer (N = 22/420; 5.2%) (Figure 1). We identified EML4-ALK fusions in 13 tumor samples and KIF5B-RET fusions in 9 tumor samples, all in NSCLC. We identified 18 fusions in soft tissue sarcomas, including those that are the hallmark of synovial sarcomas, such as SS18-SSX1 and SS18-SSX2. The most common fusions identified were TMPRSS2-ERG in prostatic tumor samples (N = 18/89, 20.2% prevalence), which has been previously reported as a common oncogenic fusion in prostate cancer [].
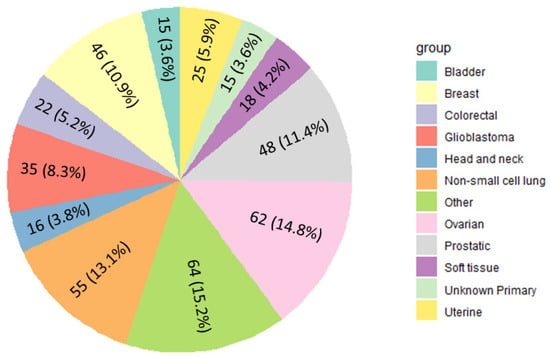
Figure 1.
Distribution of reported classified fusions by cancer type. Cancer groups with fewer than 11 reported fusions were categorized as “Other” (including esophageal, melanoma, cholangiocarcinoma, pancreatic, thyroid, neuroendocrine, cervical, salivary gland, kidney, hepatocellular, small cell lung, thymic, gastric, low-grade glioma, and gastrointestinal). Fusion prevalence by tumor site is available in Supplementary Table S1.
Of 420 fusion-positive tumors with known fusions, 55 of them had gene fusions that reoccurred across multiple patients (for example, 18 instances of TMPRSS-ERG2, 13 of EML4-ALK, 9 of KIF5B-RET, 4 of YAF2-RYBP, 3 of FGFR3-TACC3, 2 of EPC1-EED, 2 of SS18-SSX2, 2 of ESR1-CCDC170, 2 of FUBP1-USP33) and 365 were only observed once each within our cohort. Of these fusions, 71 (19.45%) had clinical implications. Four of those (1.09%) had diagnostic, six (1.64%) had prognostic, fifty-six (15.3%) had therapeutic implications, and five (1.37%) were resistant to treatment.
In addition, we identified 25 unclassified gene fusions, most of which were identified in breast and prostate and the least of which were identified in salivary and head and neck tumor samples (Table 1). Twelve patients showed recurrent unclassified gene fusions, which were selected for further investigation of their clinical implications (Supplemental Table S2). The gene breakpoints, junction reads, and fusion topology were explored and compared to known gene functions and associations with oncologic or other diseases. Two in-frame fusions were discovered in clinically relevant genes, both in breast cancers: BMPR1B-PDLIM5, involving exon 10 of BMPR1B with exon 4 of PDLIM5, which likely arises from a deletion event. We suspect this is the case because the region of the gene fusion is on the same chromosome and both are plus strands, which would result when regions between the two were deleted. NIPBL-PIEZO1 involving exon 10 of NIPBL with exon 23 of PIEZO1 likely arises from a translocation event, since the fusion break points were on the plus strand of Chromosome 5 and minus strand of Chromosome 16, respectively, resulting in an in-frame fusion transcript. It is highly likely to be a translocation event considering that the break points were on different chromosomes, so the two genes would otherwise not have fused, since they would not be adjacent without a chromosomal translocation.

Table 1.
Unclassified gene fusions identified in our cohort (number per total unclassified gene fusions).
3.2. Detection of Co-Mutations Associated with Unclassified Gene Fusions
Co-occurring genomic alterations, especially in tumor suppressor genes like TP53, contribute to the molecular heterogeneity of oncogene-driven cancers [,]. To explore the heterogeneity of tumor samples with unclassified gene fusions, we searched for genomic co-alterations and observed them in 16 of the 25 (64%) samples. Co-occurring mutations in two or more genes per tumor were identified in 9 of 25 (36%) samples.
Though some samples showed high tumor mutational burdens (TMB-H) and positive PD-L1 expression (PD-L1+), they were observed concurrently in only one sample (Figure 2). All tumor samples had microsatellite stability and proficient mismatch repair status.
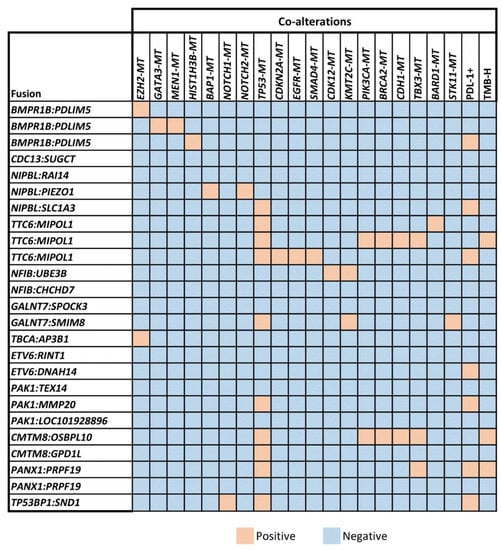
Figure 2.
Co-occurring genomic mutations (MT denotes mutations in columns) were identified in unclassified gene-fusion-positive samples. TP53 mutations are the most common co-occurring mutations, with all samples showing microsatellite stability and proficient mismatch repair status (Supplemental Data).
4. Discussion
As commercial labs now offer whole-exome and transcriptome somatic sequencing, previously unreported fusions are identified. Consequently, we concluded that it would be important to examine the utility of molecular profiling in identifying known oncogenic and novel gene fusions in solid tumors across many cancer types from a large, real-world cohort. The identification of oncogenic fusions, particularly unclassified gene fusions, is essential in developing novel therapies and maximizing the efficacy of existing treatments. The cost of DNA sequencing had proven to be a barrier for its combined utility with RNA sequencing in the past, but using them in tandem is necessary for discovering unclassified gene fusions and is now feasible due to its exponential decrease in cost over the past two decades. With DNA sequencing, we are able to identify the genomic breakpoints (Supplemental Table S2), and then corroborate these variants at the transcriptomic level with RNA sequencing, where we are able to see expression or loss of expression for any given variant [].
Unclassified gene fusion events were identified in a small subset of tumor samples, occurring in 25 of 4415 (0.57%) of our samples, while known oncogenic fusions were more common at a prevalence of 9.5%. Though the fusions we identified are generally of low frequency within these samples, other low-frequency fusions have been reported to have significant functional effects on cancer predisposition, tumor growth, and drug sensitivity []. Further, this highlights how including a wide variety of tumor types, with some types having vastly greater numbers of samples than others, might skew the prevalence of fusions. This is one limitation of our present study, as the true prevalence might be different if all tumor types had equal representation in their sample size. For example, in the case of NTRK fusions, some pediatric cancer types have a high prevalence (>90%), such as in infantile fibrosarcoma, congenital mesoblastic nephroma, and secretory carcinoma, while others have a much lower prevalence (5–26%), such as in pediatric papillary thyroid carcinomas and in a subset of pediatric gliomas []. Other possible limitations of our study include a lack of specific demographic information (such as race and ethnicity), information on treatment outcomes in response to targeted therapies, and detailed clinical history and staging. In addition, we have two different sequencing methodologies in the detection of gene fusions due to the length of the study and the advancement of the technology. This could lead to an underestimation of the prevalence of the fusions as the primary set of data was based on an RNA gene panel and not whole-exome sequencing.
Two novel fusions that may have clinical implications are reported here. The first, BMPR1B-PDLIM5, appears to be generated from a deletion event involving BMPR1 and PDLIM5 genes. BMPR1B is part of the TGF-Beta superfamily of receptors and has several inherited conditions arising from the loss of function (MIM number 603248) []. While TGF-Beta and other BMP factors, such as BMPR1A, have known roles in oncogenesis [], the role of BMPR1B gene fusions and their protein products in cancer biology is largely unknown. Further, while gain-of-function gene fusions such as NTRK fusions benefit from existing guidelines or recommendations for their detection and reporting [,], similar standardized methods do not exist to date for loss-of-function gene fusions. There are expert panel working groups currently working on guidelines in the classification of oncogenic gene fusions that lead to gain of function. The NTRK fusion standardized classification guidelines take into account the 3′ fusion partner if the fusion is in frame, and if the kinase domain is intact []. Similar work is underway for other oncogenic fusions by expert panels. However, in the meantime, the classification of the suspected oncogenic fusions is based on laboratory-developed test internal guidelines []. Both gain-of-function and loss-of-function gene fusion events are in dire need for standardized guidelines published by expert groups. Although it would be out of the scope of this report, future plans include suggesting standardized methods for the detection and reporting of loss-of-function gene fusions, such as the reported BMPR1B-PDLIM5 fusion.
The second fusion of interest involves an in-frame NIPBL-PIEZO1 fusion, likely arising from a translocation event. The NIPBL gene encodes for the Nipped-B-like protein, which is a known essential regulator of the cohesin complex function (MIM number 608667). NIPBL germline loss-of-function mutations are the most common alterations associated with the Cornelia de Lange developmental syndrome, a devastating germline genetic multisystem malformation syndrome []. Recent studies have implicated NIPBL in tumorigenesis, with evidence suggesting that loss-of-function mutations and possibly overexpression of NIPBL may promote cancer cell growth and survival. In addition to disease model studies, a unique “cholangioblastic” variant of cholangiocarcinoma is characterized by a similar in-frame NIPBL-NACC1 fusion involving exon 8 of NIPBL [,,]. Other studies show high rates of overexpression of NIPBL mRNA in up to 31% of non-small cell lung cancers []. However, the potential of NIPBL as a therapeutic target in cancer has not been thoroughly explored. It is uncertain if NIPBL functions as an oncogene or tumor suppressor or perhaps has pleiotropic effects depending on tumor and mutational contexts. Interestingly, other components of the cohesin complex, mainly STAG2, are being evaluated as potential therapeutic targets and biomarkers in cancers due to demonstrated associations with aggressive clinical behaviors and resistance to chemotherapy. Furthermore, cohesin complexes have been shown to regulate the expression of components important for immune responses, such as IFN-Gamma. Most recently, a deficiency of NIPBL has been shown to cause the upregulation of endogenous retroviruses and lead to the stimulation of PD-L1 expression and thus presents a potential mechanism for cancer immune evasion []. Further investigation of the role of NIPBL in cancer is warranted to understand and validate its potential as a therapeutic target. In addition, it will be important to assess expression levels of NIPBL and patterns of mutations across various cancer types.
Over 60% of unclassified gene fusions we observed had co-occurring mutations in other genes separate from their fusions, including mutated BRCA2, PIK3CA, and CDH1 genes. Co-occurring mutations, especially in tumor suppressor genes such as TP53 and STK11, have been reported as key characteristics of oncogene-driven cancers, such as non-small cell lung cancer []. In our own cohort, we observe one non-small cell lung tumor with an unclassified gene fusion (GALNT7-SMIM8), which also harbors co-occurring mutations in TP53 and STK11. One possible explanation for the co-occurrence of mutations in other genes in combination with gene fusions is the co-selection of oncogenic alterations, where one early event influences the genetic trajectory and results in subsequent alterations. This is supported by the existence of distinct patterns of co-occurring alterations, which depend on specific oncogenic drivers [,]. Another explanation for the co-occurrence of mutations is the compounding nature of the effects of oncogenic mutations. That is, the simultaneous occurrence of specific mutations could have a stronger impact than the single mutations alone. This compounding effect can be seen in TP53 and KRAS mutations in pancreatic adenocarcinoma, where the disease-specific survival is significantly affected when both are mutated as compared to either one on its own []. When mutations emerge concurrently in the same tumor, the cooperative effects have the potential to change the immune microenvironment, resistance or responsiveness to therapies, and tumor metastasis []. Though not all fusion-positive tumor samples had co-occurring mutations, those that did often had multiple co-occurring mutations, which affirms this compounding effect. Thus, the identification of co-occurring mutations can provide additional insight into the personalized treatment of various cancer types. In addition, we observed PD-L1 overexpression in 7 of 25 (28%) of our unclassified gene fusion samples, which is consistent with previous reports across certain cancer types [,].
Gene fusions represent promising targets that can be useful for identifying patients who qualify for FDA-approved therapies or enrollment in clinical trials, which could be beneficial for patients with cancer. Despite the progress in recent years in their identification and development as informative biomarkers, however, there remain some disadvantages to their use in clinical practice. One of the major obstacles remaining is the need for the standardization in their discovery and validation, particularly for novel gene fusions. Establishing a standardized procedure for target validation would help clarify any ambiguity on whether or not their molecular targeting would be helpful for patients. Though future functional validation of all structural variants identified is required and beyond the scope of this study, the number of fusions identified within our patient population indicates that oncogenic fusions are not as rare as previously thought and may be more important in pathogenesis than expected. The low number of fusion events with clinical implications in available knowledge bases supports the notion that actionable targets are rare. Furthermore, this also suggests that there could be potential to explore how novel fusions might be leveraged to improve patient care and the design of future clinical trials.
5. Conclusions
In our cohort, 9.5% of analyzed tumors had oncogenic gene fusion events that may be of clinical relevance. This suggests that patients with advanced cancers would benefit from comprehensive molecular profiling, including RNA sequencing. Additional studies are needed to determine the functional consequences of the identified unclassified gene fusions to assess potential clinical significance. Due to the lack of standardized fusion gene classification guidelines, further research collaboration is needed to establish classification guidelines to better understand their function and role in cancer development. Once the guidelines are established, these events could be reported with more confidence.
Our study further highlights the relationship between co-occurring gene mutations and gene fusion events in specific types of cancer in a private community cancer center in Southern California. The data should assist clinicians in making decisions regarding patient treatment and inclusion in clinical trials. Further, we identified unclassified fusion events that have the potential for additional translational research studies and further clinical application. The FDA has approved drugs targeting oncogenic fusions for pan-tumor indications, and additional clinical trials are underway to investigate the targetability of other fusions in various cancers. Future clinical trials should consider the inclusion of tumor profiling by whole-transcriptome and whole-exome sequencing to identify gene fusion events that targeted sequencing panels may not detect. This could direct the treatment of patients with targeted therapies by identifying known fusions in novel tumor histologies or novel fusion events altogether, in addition to identifying patients with fusion-positive cancers who would qualify for those future clinical trials [,,,].
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biologics3030011/s1; Table S1: List of classified fusions along with prevalence reported by tumor site; Table S2: Breakpoints and topology of recurrent unclassified fusions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, supervision, manuscript writing and editing: S.D. and M.J.D.; methodology, validation, formal analysis, manuscript writing and editing: C.E.Z., S.D., D.R.B., B.L.E. and M.J.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, Belmont report, and U.S. Common rule. In keeping with 45 CFR 46.101(b)(4), this study was performed utilizing retrospective, deidentified clinical data. Therefore, this study is considered IRB-exempt and no patient consent was necessary.
Informed Consent Statement
This study is considered IRB-exempt and no patient consent was necessary from the subject.
Data Availability Statement
The data generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Hoag Hospital Foundation, the William H. Hurt Foundation, and the Otis Healy Family Endowment.
Conflicts of Interest
Sourat Darabi: Consulting and advisory work: Oncolens, Bayer, BostonGene; David R Braxton: Consulting and advisory work: Amgen, Eosin microscopic intelligence; Carlos E. Zuazo: no relevant COI. Burton L. Eisenberg: no relevant COI. Michael J Demeure: Consulting or Advisory Role: Loxo/Lilly, Aadi, Orphagen Pharmaceuticals, Bayer, TD2, Theralink, OnCusp Therapeutics, Pfizer, Aadi; Boehringer Ingelheim Uncompensated Relationships: TransMed7.
References
- Quan, V.L.; Panah, E.; Zhang, B.; Shi, K.; Mohan, L.S.; Gerami, P. The role of gene fusions in melanocytic neoplasms. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2019, 46, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobato, M.N.; Metzler, M.; Drynan, L.; Forster, A.; Pannell, R.; Rabbitts, T.H. Modeling chromosomal translocations using conditional alleles to recapitulate initiating events in human leukemias. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 2008, 2008, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, R.; Sugar, L.; Yang, W.; Srivastava, S.; Klotz, L.; Yang, L.; Stanimirovic, A.; Encioiu, E.; Neill, M.; Loblaw, D. Expression of the TMPRSS2: ERG fusion gene predicts cancer recurrence after surgery for localised prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 1690–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panicker, S.; Venkatabalasubramanian, S.; Pathak, S.; Ramalingam, S. The impact of fusion genes on cancer stem cells and drug resistance. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 3771–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabi, S.; Elliott, A.; Braxton, D.R.; Zeng, J.; Hodges, K.; Poorman, K.; Swensen, J.; Shanthappa, B.U.; Hinton, J.P.; Gibney, G.T. Transcriptional Profiling of Malignant Melanoma Reveals Novel and Potentially Targetable Gene Fusions. Cancers 2022, 14, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikanjam, M.; Okamura, R.; Barkauskas, D.A.; Kurzrock, R. Targeting fusions for improved outcomes in oncology treatment. Cancer 2020, 126, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar-Sinha, C.; Kalyana-Sundaram, S.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. Landscape of gene fusions in epithelial cancers: Seq and ye shall find. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Manochakian, R.; James, L.; Azzouqa, A.-G.; Shi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, K.; Lou, Y. Emerging therapeutic agents for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuna, M.; Amos, C.I.; Mills, G.B. Molecular mechanisms and pathobiology of oncogenic fusion transcripts in epithelial tumors. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Laetsch, T.W.; Kummar, S.; DuBois, S.G.; Lassen, U.N.; Demetri, G.D.; Nathenson, M.; Doebele, R.C.; Farago, A.F.; Pappo, A.S. Efficacy of larotrectinib in TRK fusion–positive cancers in adults and children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chi, P. Basket trial of TRK inhibitors demonstrates efficacy in TRK fusion-positive cancers. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doebele, R.C.; Drilon, A.; Paz-Ares, L.; Siena, S.; Shaw, A.T.; Farago, A.F.; Blakely, C.M.; Seto, T.; Cho, B.C.; Tosi, D. Entrectinib in patients with advanced or metastatic NTRK fusion-positive solid tumours: Integrated analysis of three phase 1–2 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, K.; Oxnard, G.R.; Tan, D.S.-W.; Loong, H.H.; Bauer, T.M.; Gainor, J.F.; McCoach, C.E.; Gautschi, O.; Besse, B.; Cho, B.C. Selpercatinib (LOXO-292) in patients with RET-fusion+ non-small cell lung cancer. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.H.; Sherman, E.J.; Robinson, B.; Solomon, B.J.; Kang, H.; Lorch, J.H.; Worden, F.P.; Brose, M.S.; Leboulleux, S.; Godbert, Y. Selpercatinib (LOXO-292) in patients with RET-mutant medullary thyroid cancer. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 4, PO.20.00096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Tiwari, A.K.; Sun, Y.; Ding, P.-R.; Ashby Jr, C.R.; Chen, Z.-S. BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia: A review. Leuk. Res. 2010, 34, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuellar, S.; Vozniak, M.; Rhodes, J.; Forcello, N.; Olszta, D. BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2018, 24, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Lage, M.; Torres-Ruiz, R.; Puig-Serra, P.; Moreno-Gaona, P.; Martin, M.; Moya, F.; Quintana-Bustamante, O.; Garcia-Silva, S.; Carcaboso, A.; Petazzi, P. In vivo CRISPR/Cas9 targeting of fusion oncogenes for selective elimination of cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consortium, A.P.G.; Consortium, A.P.G.; André, F.; Arnedos, M.; Baras, A.S.; Baselga, J.; Bedard, P.L.; Berger, M.F.; Bierkens, M.; Calvo, F. AACR Project GENIE: Powering precision medicine through an international consortium. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 818–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, T.J.; Bell, J.L.; Bruce, J.P.; Doherty, G.J.; Galvin, M.; Green, M.F.; Hunter-Zinck, H.; Kumari, P.; Lenoue-Newton, M.L.; Li, M.M. AACR Project GENIE: 100,000 cases and beyond. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 2044–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melas, M.; Subbiah, S.; Saadat, S.; Rajurkar, S.; McDonnell, K.J. The community oncology and academic medical center alliance in the age of precision medicine: Cancer genetics and genomics considerations. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabi, S.; Braxton, D.; Homer, J.; Brodie, T.; Holnagel, D.; Eisenberg, B.; Demeure, M.J. Programmatic Efforts Increase Adoption of Genomic Precision Medicine in Cancer Care in a Community Cancer Center. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, e2200090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarty, D.; Gao, J.; Phillips, S.; Kundra, R.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Rudolph, J.E.; Yaeger, R.; Soumerai, T.; Nissan, M.H. OncoKB: A precision oncology knowledge base. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2017, 2017, PO.17.00011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitelman, F.; Johansson, B.; Mertens, F. Mitelman Database of Chromosome Aberrations and Gene Fusions in Cancer. 2022. Available online: https://mitelmandatabase.isb-cgc.org/ (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Q.; Zhi, F.; Zhang, S.; Mao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, H. Significance of the TMPRSS2: ERG gene fusion in prostate cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 5450–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adashek, J.J.; Desai, A.P.; Andreev-Drakhlin, A.Y.; Roszik, J.; Cote, G.J.; Subbiah, V. Hallmarks of RET and Co-occuring Genomic Alterations in RET-aberrant Cancers. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 1769–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoulidis, F.; Heymach, J.V. Co-occurring genomic alterations in non-small-cell lung cancer biology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeser, J.W.; Martin, D.; Miya, J.; Kautto, E.A.; Lyon, E.; Zhu, E.; Wing, M.R.; Smith, A.; Reeder, M.; Samorodnitsky, E. Validation of a targeted RNA sequencing assay for kinase fusion detection in solid tumors. J. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 19, 682–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, H.; Ng, P.K.-S.; Pantazi, A.; Ip, C.K.M.; Jeong, K.J.; Amador, B.; Tran, R.; Tsang, Y.H.; Yang, L. A functional genomic approach to actionable gene fusions for precision oncology. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Kotch, C.; Fox, E.; Surrey, L.F.; Wertheim, G.B.; Baloch, Z.W.; Lin, F.; Pillai, V.; Luo, M.; Kreiger, P.A. NTRK fusions identified in pediatric tumors: The frequency, fusion partners, and clinical outcome. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2021, 1, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamosh, A.; Scott, A.F.; Amberger, J.; Valle, D.; McKusick, V.A. Online Mendelian inheritance in man (OMIM). Hum. Mutat. 2000, 15, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, D.-H.; Park, H.J.; Lee, S.K. The dual role of bone morphogenetic proteins in cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchiò, C.; Scaltriti, M.; Ladanyi, M.; Iafrate, A.; Bibeau, F.; Dietel, M.; Hechtman, J.; Troiani, T.; López-Rios, F.; Douillard, J.-Y. ESMO recommendations on the standard methods to detect NTRK fusions in daily practice and clinical research. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, J.; Church, A.J.; Rao, S.; Danos, A.; Furtado, L.V.; Laetsch, T.; Zhang, L.; Nardi, V.; Lin, W.-H.; Ritter, D.I. Standardized evidence-based approach for assessment of oncogenic and clinical significance of NTRK fusions. Cancer Genet. 2022, 264, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gene Fusion Curation. Available online: https://cancervariants.org/projects/fusions/ (accessed on 25 June 2023).
- Liu, J.; Krantz, I. Cornelia de Lange syndrome, cohesin, and beyond. Clin. Genet. 2009, 76, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argani, P.; Palsgrove, D.N.; Anders, R.A.; Smith, S.C.; Saoud, C.; Kwon, R.; Voltaggio, L.; Assarzadegan, N.; Oshima, K.; Rooper, L. A novel NIPBL-NACC1 gene fusion is characteristic of the cholangioblastic variant of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2021, 45, 1550–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braxton, D.R.; Saxe, D.; Damjanov, N.; Stashek, K.; Shroff, S.; Morrissette, J.D.; Tondon, R.; Furth, E.E. Molecular and cytogenomic profiling of hepatic adenocarcinoma expressing inhibinA, a mimicker of neuroendocrine tumors: Proposal to reclassify as “cholangioblastic variant of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma”. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 62, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Howard, L.N.; Alonsozana, E.; Sill, D.; Bose, D.; Lai, J. Molecular Characteristics and Immunogenomic Profiling of Cholangioblastic Variant of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma in a 68-year-old Patient. Anticancer Res. 2022, 42, 5475–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ying, Y.; Shan, L.; Feng, J.; Zhang, S.; Gao, Y.; Xu, X.; Yao, Y.; Zhu, C.; Mao, W. Enhanced expression of cohesin loading factor NIPBL confers poor prognosis and chemotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Han, Y.; Peng, F.; Chang, Y.; Liu, T.; Shen, J.; Chen, Z.; Dong, Q.; Zhou, P.; Jiang, F.; Xiang, H. Cohesin mutation sensitizes cancer cells to anti-PD-1 therapy through endogenous retrovirus-mediated PD-L1 upregulation. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zehir, A.; Benayed, R.; Shah, R.H.; Syed, A.; Middha, S.; Kim, H.R.; Srinivasan, P.; Gao, J.; Chakravarty, D.; Devlin, S.M. Mutational landscape of metastatic cancer revealed from prospective clinical sequencing of 10,000 patients. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imielinski, M.; Berger, A.H.; Hammerman, P.S.; Hernandez, B.; Pugh, T.J.; Hodis, E.; Cho, J.; Suh, J.; Capelletti, M.; Sivachenko, A. Mapping the hallmarks of lung adenocarcinoma with massively parallel sequencing. Cell 2012, 150, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yu, H.; Ness, S.; Mao, P.; Guo, F.; Tang, J.; Guo, Y. Comprehensive analysis of co-mutations identifies cooperating mechanisms of tumorigenesis. Cancers 2022, 14, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Boyle, T.A.; Zhou, C.; Rimm, D.L.; Hirsch, F.R. PD-L1 expression in lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, V.K.; Overman, M.J.; Lam, M.; Parseghian, C.M.; Johnson, B.; Dasari, A.; Raghav, K.; Kee, B.K.; Huey, R.; Wolff, R.A. Bintrafusp Alfa, an Anti-PD-L1: TGFβ Trap Fusion Protein, in Patients with ctDNA-positive, Liver-limited Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. Commun. 2022, 2, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyer, E.E.; Deveson, I.W.; Wooi, D.; Selinger, C.I.; Lyons, R.J.; Hayes, V.M.; O’Toole, S.A.; Ballinger, M.L.; Gill, D.; Thomas, D.M. Diagnosis of fusion genes using targeted RNA sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, E.S.; Grisdale, C.J.; Pleasance, E.; Topham, J.T.; Mungall, K.; Reisle, C.; Choo, C.; Carreira, M.; Bowlby, R.; Karasinska, J.M. Uncovering Clinically Relevant Gene Fusions with Integrated Genomic and Transcriptomic Profiling of Metastatic CancersLandscape of Genomic Fusions. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.; Ju, Y.S. Patterns and mechanisms of structural variations in human cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, K.; Wang, Q.; Torres-Garcia, W.; Zheng, S.; Vegesna, R.; Kim, H.; Verhaak, R.G. The landscape and therapeutic relevance of cancer-associated transcript fusions. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4845–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).